The Legacy of AAZTA—Synthesis and Coordination Chemistry of Two AAZTA Structural Analogs
Abstract
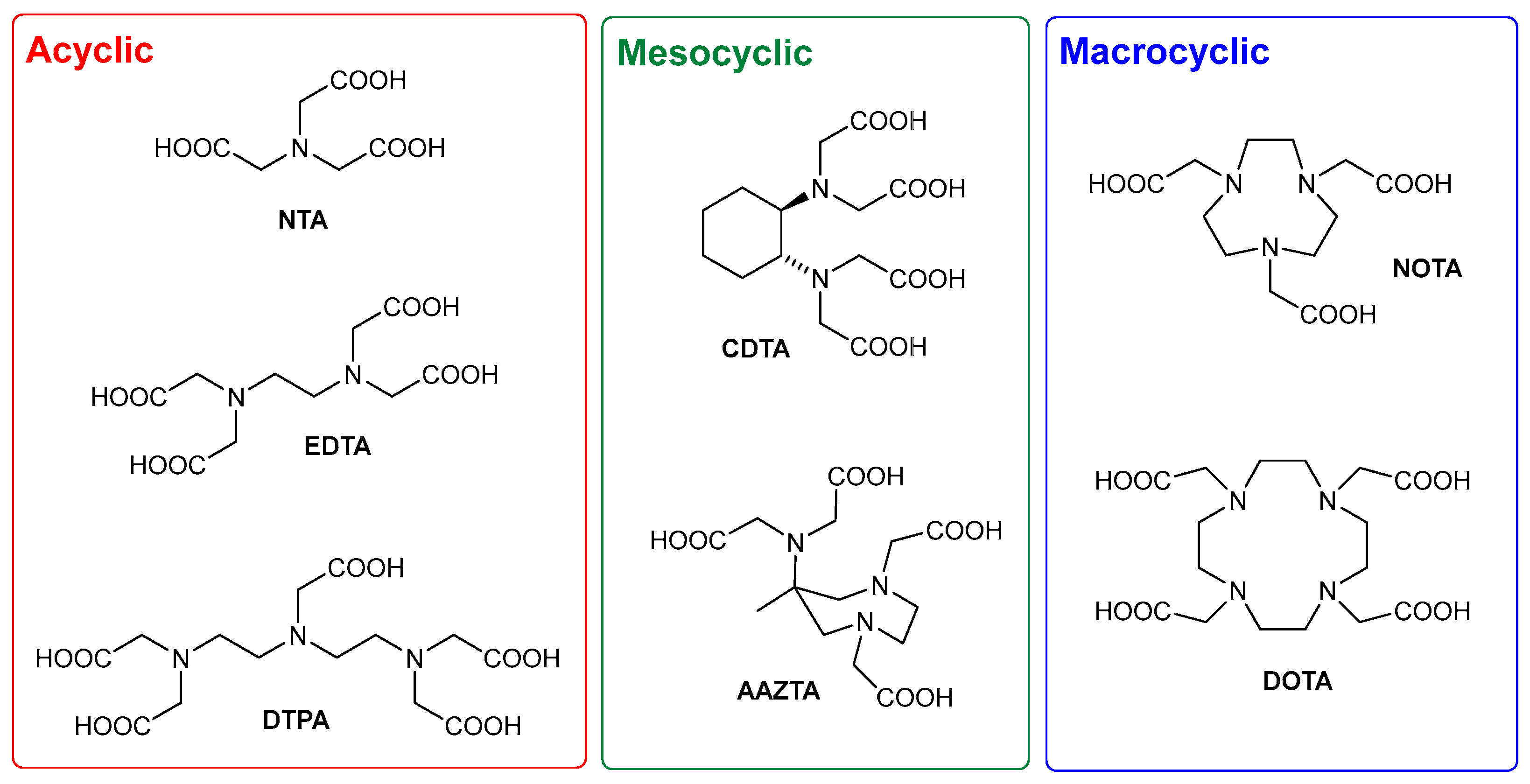
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
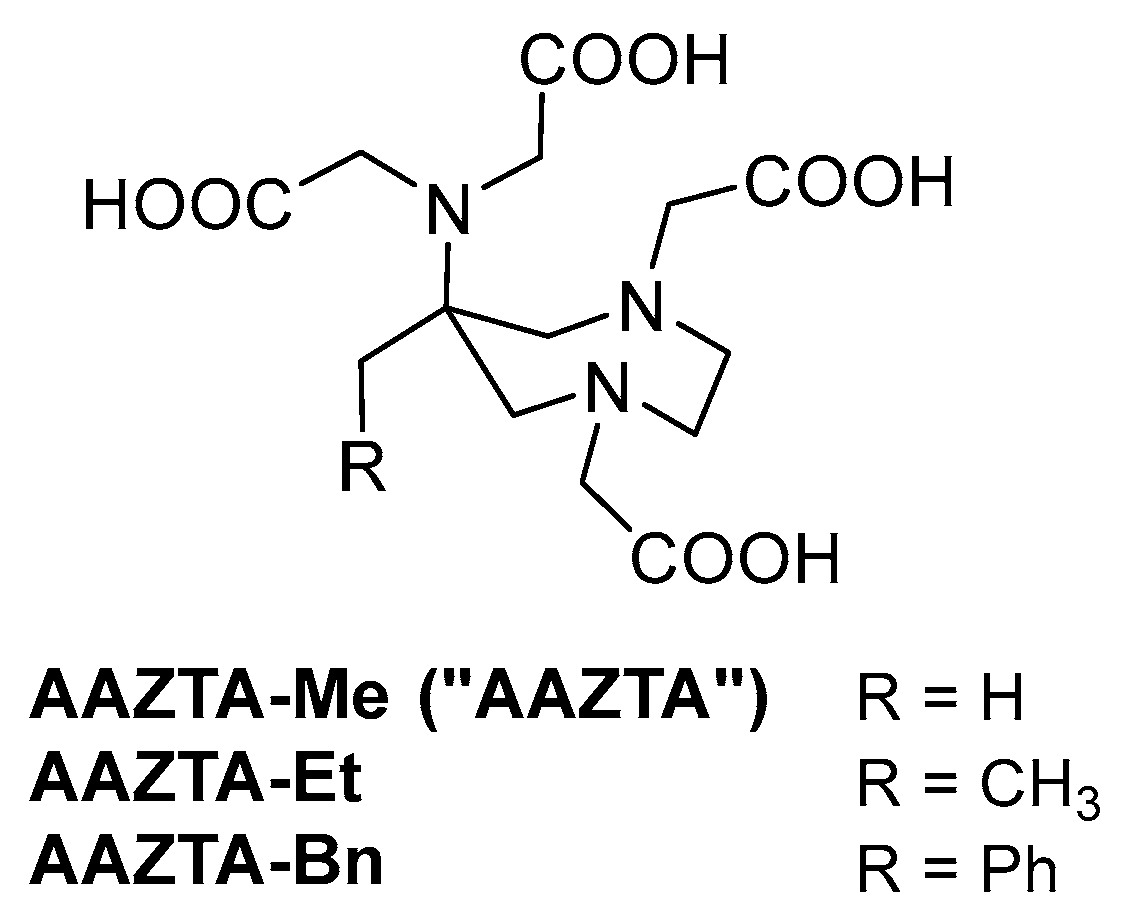
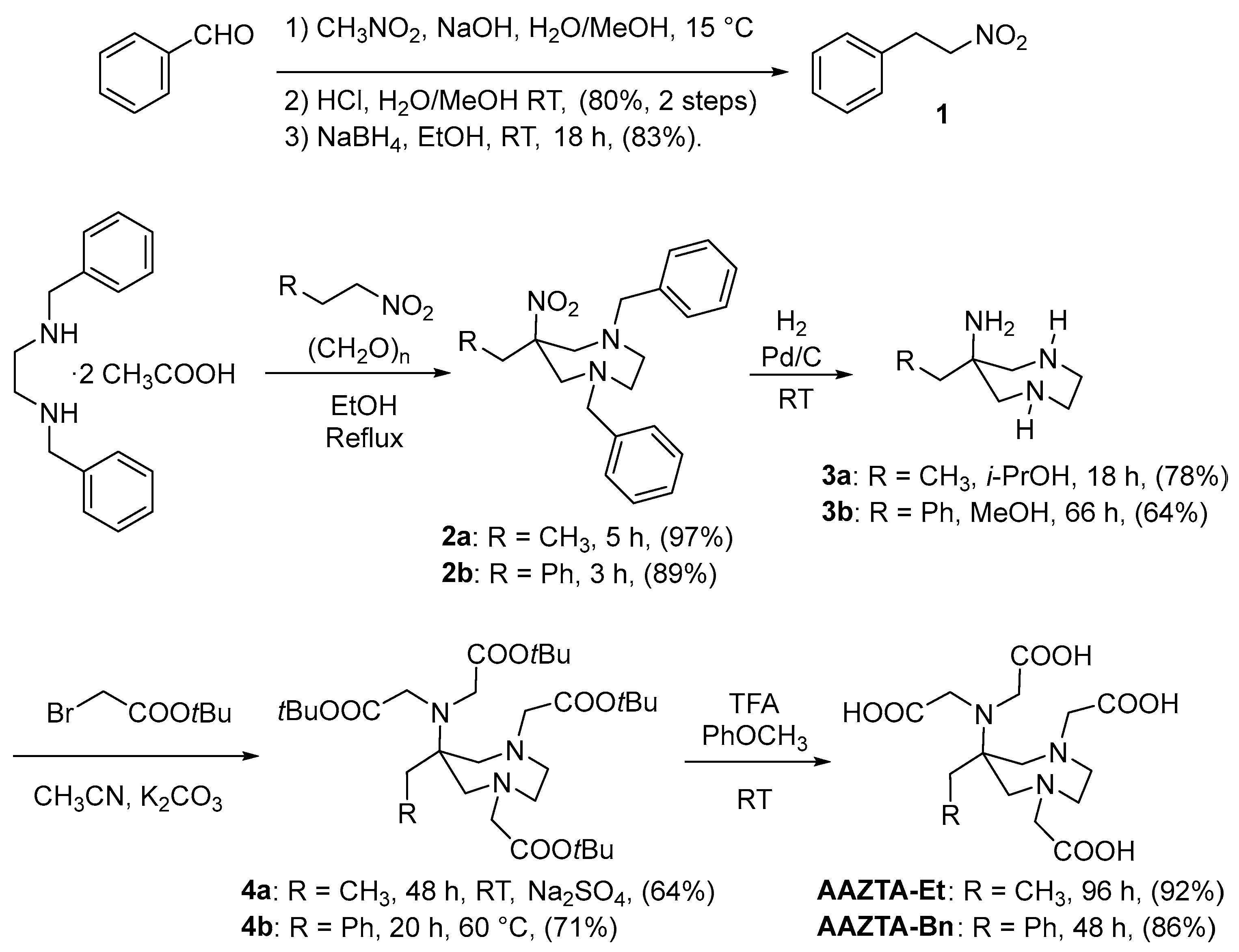
2.1. Design and Synthesis of AAZTA Derivatives
2.2. Acid–Base Properties of AAZTA-Et and AAZTA-Bn Ligands
2.3. Complexation Properties of AAZTA-Et and AAZTA-Bn Ligands with M2+/3+ Cations
2.4. Kinetic Inertness of [Gd(AAZTA-Et)]− and [Gd(AAZTA-Bn)]− Complexes
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis—General Information
3.1.1. 1,4-Dibenzyl-6-ethyl-6-nitro-1,4-diazepane (2a)
3.1.2. 6-Ethyl-1,4-diazepan-6-amine (3a)
3.1.3. Di-tert-butyl 2,2′-((1,4-Bis(2-(tert-butoxy)-2-oxoethyl)-6-ethyl-1,4-diazepan-6-yl)azanediyl)diacetate (4a)
3.1.4. 2,2′-((1,4-Bis(carboxymethyl)-6-ethyl-1,4-diazepan-6-yl)azanediyl)diacetic Acid (AAZTA-Et)
3.1.5. 2-Nitroethylbenzene (1) [29]
3.1.6. 1,4-Dibenzyl-6-benzyl-6-nitro-1,4-diazepane (2b) [29]
3.1.7. 6-Benzyl-1,4-diazepan-6-ylamine (3b) [29]
3.1.8. Di-tert-butyl 2,2′-((6-Benzyl-1,4-bis(2-(tert-butoxy)-2-oxoethyl)-1,4-diazepan-6-yl)azanediyl)diacetate (4b) [29]
3.1.9. [6-Bis(carboxymethylamino)-4-carboxymethyl-6-benzyl-1,4-diazepan-1-yl]acetic Acid (AAZTA-Bn) [29]
3.2. Equilibrium Properties—General Information
3.2.1. Materials
3.2.2. pH Potentiometry
3.2.3. Spectrophotometry
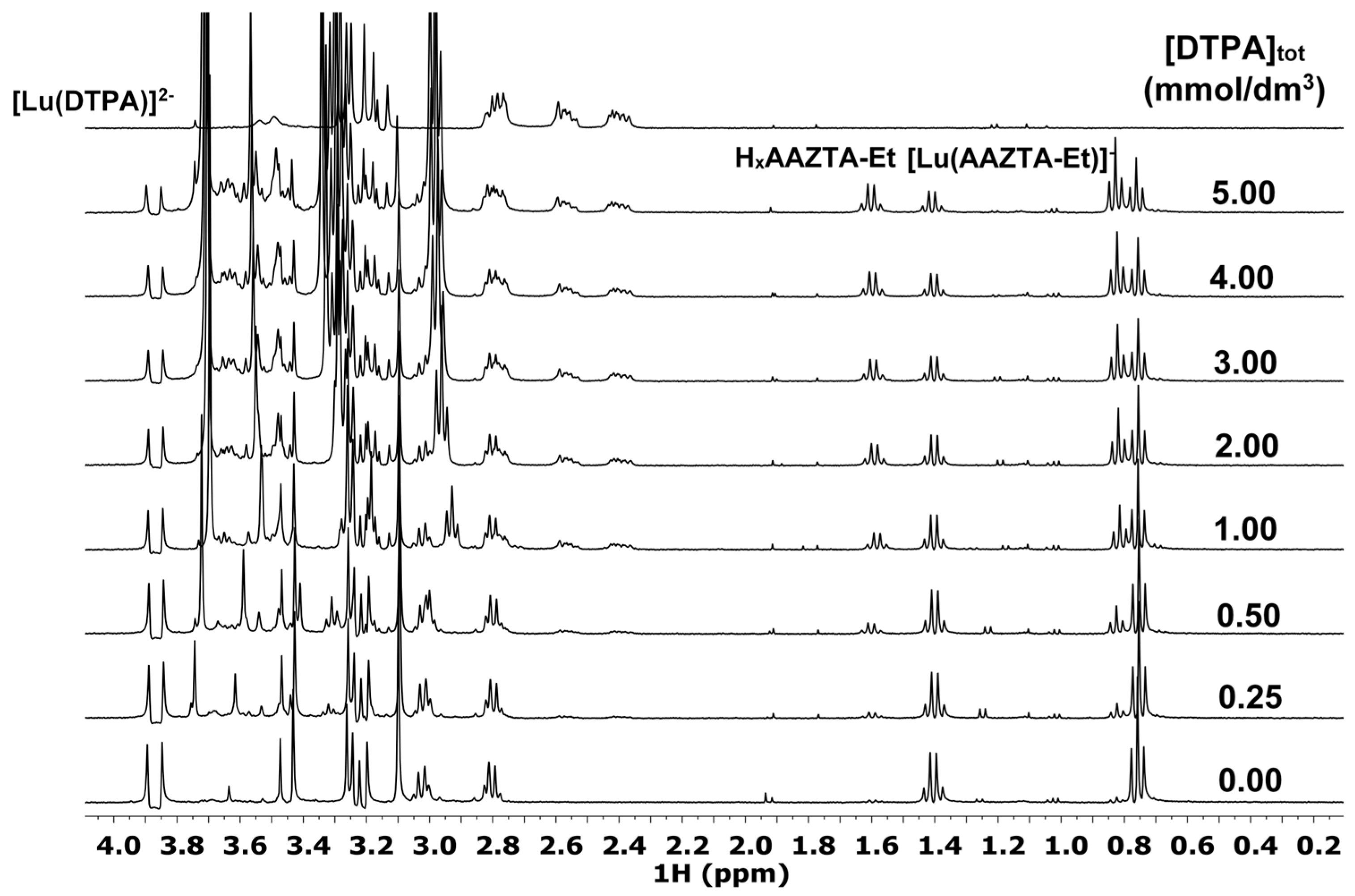
3.2.4. 1H NMR Relaxometry
3.2.5. NMR Experiments
3.2.6. Kinetics—Transmetallation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mjos, K.D.; Orvig, C. Metallodrugs in Medicinal Inorganic Chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 4540–4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaynor, D.; Griffith, D.M. The Prevalence of Metal-Based Drugs as Therapeutic or Diagnostic Agents: Beyond Platinum. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 13239–13257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessio, E. (Ed.) Bioinorganic Medicinal Chemistry, 1st ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2011; ISBN 978-3-527-32631-0. [Google Scholar]
- Hart, J.R. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid and Related Chelating Agents. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; ISBN 978-3-527-30673-2. [Google Scholar]
- Lattuada, L.; Barge, A.; Cravotto, G.; Giovenzana, G.B.; Tei, L. The Synthesis and Application of Polyamino Polycarboxylic Bifunctional Chelating Agents. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 3019–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahsner, J.; Gale, E.M.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, A.; Caravan, P. Chemistry of MRI Contrast Agents: Current Challenges and New Frontiers. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 957–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merbach, A.S.; Helm, L.; Tóth, É. The Chemistry of Contrast Agents in Medical Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1-119-99176-2. [Google Scholar]
- Herrero Álvarez, N.; Bauer, D.; Hernández-Gil, J.; Lewis, J.S. Recent Advances in Radiometals for Combined Imaging and Therapy in Cancer. ChemMedChem 2021, 16, 2909–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, E.W.; Orvig, C. Matching Chelators to Radiometals for Radiopharmaceuticals. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 260–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramogida, C.F.; Orvig, C. Tumour Targeting with Radiometals for Diagnosis and Therapy. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 4720–4739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aime, S.; Calabi, L.; Cavallotti, C.; Gianolio, E.; Giovenzana, G.B.; Losi, P.; Maiocchi, A.; Palmisano, G.; Sisti, M. [Gd-AAZTA]−: A New Structural Entry for an Improved Generation of MRI Contrast Agents. Inorg. Chem. 2004, 43, 7588–7590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranyai, Z.; Uggeri, F.; Giovenzana, G.B.; Bényei, A.; Brücher, E.; Aime, S. Equilibrium and Kinetic Properties of the Lanthanoids(III) and Various Divalent Metal Complexes of the Heptadentate Ligand AAZTA. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 1696–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianolio, E.; Giovenzana, G.B.; Longo, D.; Longo, I.; Menegotto, I.; Aime, S. Relaxometric and Modelling Studies of the Binding of a Lipophilic Gd-AAZTA Complex to Fatted and Defatted Human Serum Albumin. Chem. A Eur. J. 2007, 13, 5785–5797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artali, R.; Bombieri, G.; Giovenzana, G.B.; Galli, M.; Lattuada, L.; Meneghetti, F. Preparation, Crystallographic and Theoretical Study on a Bifunctional Gd-AAZTA Derivative as Potential MRI Contrast Agent Precursor. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2013, 407, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minazzi, P.; Lattuada, L.; Menegotto, I.G.; Giovenzana, G.B. An Enzymatic Approach to Bifunctional Chelating Agents. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 12, 6915–6921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovenzana, G.B.; Lattuada, L.; Negri, R. Recent Advances in Bifunctional Paramagnetic Chelates for MRI. Isr. J. Chem. 2017, 57, 825–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travagin, F.; Lattuada, L.; Giovenzana, G.B. AAZTA: The Rise of Mesocyclic Chelating Agents for Metal Coordination in Medicine. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 438, 213908–213931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranyai, Z.; Uggeri, F.; Maiocchi, A.; Giovenzana, G.B.; Cavallotti, C.; Takács, A.; Tóth, I.; Bányai, I.; Bényei, A.; Brucher, E.; et al. Equilibrium, Kinetic and Structural Studies of AAZTA Complexes with Ga3+, In3+ and Cu2+. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 2013, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, G.; Szikra, D.; Trencsényi, G.; Fekete, A.; Garai, I.; Giani, A.M.; Negri, R.; Masciocchi, N.; Maiocchi, A.; Uggeri, F.; et al. AAZTA: An Ideal Chelating Agent for the Development of 44Sc PET Imaging Agents. Angew. Chem. 2017, 56, 2118–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfister, J.; Summer, D.; Rangger, C.; Petrik, M.; von Guggenberg, E.; Minazzi, P.; Giovenzana, G.B.; Aloj, L.; Decristoforo, C. Influence of a Novel, Versatile Bifunctional Chelator on Theranostic Properties of a Minigastrin Analogue. EJNMMI Res. 2015, 5, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horváth, D.; Vágner, A.; Szikra, D.; Trencsényi, G.; Demitri, N.; Guidolin, N.; Maiocchi, A.; Ghiani, S.; Travagin, F.; Giovenzana, G.B.; et al. Boosting Bismuth(III) Complexation for Targeted α-Therapy (TAT) Applications with the Mesocyclic Chelating Agent AAZTA. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202207120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fersing, C.; Masurier, N.; Rubira, L.; Deshayes, E.; Lisowski, V. AAZTA-Derived Chelators for the Design of Innovative Radiopharmaceuticals with Theranostic Applications. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoni, L.; Belvisi, L.; Arosio, D.; Bartolomeo, M.P.; Bianchi, A.; Brioschi, C.; Buonsanti, F.; Cabella, C.; Casagrande, C.; Civera, M.; et al. Synthesis of Gd and 68Ga Complexes in Conjugation with a Conformationally Optimized RGD Sequence as Potential MRI and PET Tumor-Imaging Probes. ChemMedChem 2012, 7, 1084–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nock, B.A.; Kaloudi, A.; Nagel, J.; Sinnes, J.-P.; Roesch, F.; Maina, T. Novel Bifunctional DATA Chelator for Quick Access to Site-Directed PET 68Ga-Radiotracers: Preclinical Proof-of-Principle with [Tyr3]Octreotide. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 14584–14590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinnes, J.-P.; Nagel, J.; Waldron, B.P.; Maina, T.; Nock, B.A.; Bergmann, R.K.; Ullrich, M.; Pietzsch, J.; Bachmann, M.; Baum, R.P.; et al. Instant Kit Preparation of 68Ga-Radiopharmaceuticals via the Hybrid Chelator DATA: Clinical Translation of [68Ga]Ga-DATA-TOC. EJNMMI Res. 2019, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klasen, B.; Moon, E.S.; Rösch, F. AAZTA5-Squaramide Ester Competing with DOTA-, DTPA- and CHX-A″-DTPA-Analogues: Promising Tool for 177Lu-Labeling of Monoclonal Antibodies under Mild Conditions. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2021, 96–97, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greifenstein, L.; Kramer, C.S.; Moon, E.S.; Rösch, F.; Klega, A.; Landvogt, C.; Müller, C.; Baum, R.P. From Automated Synthesis to In Vivo Application in Multiple Types of Cancer—Clinical Results with [68Ga]Ga-DATA5m.SA.FAPi. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nock, B.A.; Kanellopoulos, P.; Moon, E.S.; Rouchota, M.; Loudos, G.; Ballal, S.; Yadav, M.P.; Bal, C.; Mishra, P.; Sheokand, P.; et al. [111In]In/[177Lu]Lu-AAZTA5-LM4 SST2R-Antagonists in Cancer Theranostics: From Preclinical Testing to First Patient Results. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovenzana, G.B.; Palmisano, G.; Sisti, M.; Cavallotti, C.; Aime, S.; Calabi, L.; Swenson, R.; Kondareddiar, R.; Lattuada, L.; Morosini, P. Multidentate Aza Ligands Able to Complex Metal Ions and the Use Thereof in Diagnostics and Therapy. U.S. Patent US20060034773A1, 16 February 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kock, F.V.C.; Forgács, A.; Guidolin, N.; Stefania, R.; Vágner, A.; Gianolio, E.; Aime, S.; Baranyai, Z. [Gd(AAZTA)]− Derivatives with n-Alkyl Acid Side Chains Show Improved Properties for Their Application as MRI Contrast Agents. Chem. A Eur. J. 2021, 27, 1849–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, E.; Nagel, J.; Waldron, B.P.; Parker, D.; Tóth, I.; Brücher, E.; Rösch, F.; Baranyai, Z. Equilibrium, Kinetic and Structural Properties of Gallium(III) and Some Divalent Metal Complexes Formed with the New DATAm and DATA5m Ligands. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 10358–10371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vágner, A.; D’Alessandria, C.; Gambino, G.; Schwaiger, M.; Aime, S.; Maiocchi, A.; Tóth, I.; Baranyai, Z.; Tei, L. A Rigidified AAZTA-like Ligand as Efficient Chelator for 68Ga Radiopharmaceuticals. ChemistrySelect 2016, 1, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vágner, A.; Gianolio, E.; Aime, S.; Maiocchi, A.; Tóth, I.; Baranyai, Z.; Tei, L. High Kinetic Inertness of a Bis-Hydrated Gd-Complex with a Constrained AAZTA-like Ligand. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 11235–11238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranyai, Z.; Pálinkás, Z.; Uggeri, F.; Brücher, E. Equilibrium Studies on the Gd3+, Cu2+ and Zn2+ Complexes of BOPTA, DTPA and DTPA-BMA Ligands: Kinetics of Metal-Exchange Reactions of [Gd(BOPTA)]2−. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 2010, 1948–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tei, L.; Gugliotta, G.; Fekete, M.; Kálmán, F.K.; Botta, M. Mn(II) Complexes of Novel Hexadentate AAZTA-like Chelators: A Solution Thermodynamics and Relaxometric Study. Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 2025–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irving, H.M.; Miles, M.G.; Pettit, L.D. A Study of Some Problems in Determining the Stoicheiometric Proton Dissociation Constants of Complexes by Potentiometric Titrations Using a Glass Electrode. Anal. Chim. Acta 1967, 38, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zekany, L.; Nagypal, I. PSEQUAD. In Computational Methods for the Determination of Formation Constants; Leggett, D.J., Ed.; Modern Inorganic Chemistry; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1985; pp. 291–353. ISBN 978-1-4684-4934-1. [Google Scholar]
- Baranyai, Z.; Pálinkás, Z.; Uggeri, F.; Maiocchi, A.; Aime, S.; Brücher, E. Dissociation Kinetics of Open-Chain and Macrocyclic Gadolinium(III)-Aminopolycarboxylate Complexes Related to Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Catalytic Effect of Endogenous Ligands. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 16426–16435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarka, L.; Burai, L.; Brücher, E. The Rates of the Exchange Reactions between [Gd(DTPA)]2− and the Endogenous Ions Cu2+ and Zn2+: A Kinetic Model for the Prediction of the In Vivo Stability of [Gd(DTPA)]2−, Used as a Contrast Agent in Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Chem. Eur. J. 2000, 6, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brücher, E.; Laurenczy, G. Aminopolycarboxylates of Rare Earths—VIII: Kinetic Study of Exchange Reactions between Eu3+ Ions and Lanthanide(III) Diethylenetriaminepentaacetate Complexes. J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem. 1981, 43, 2089–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
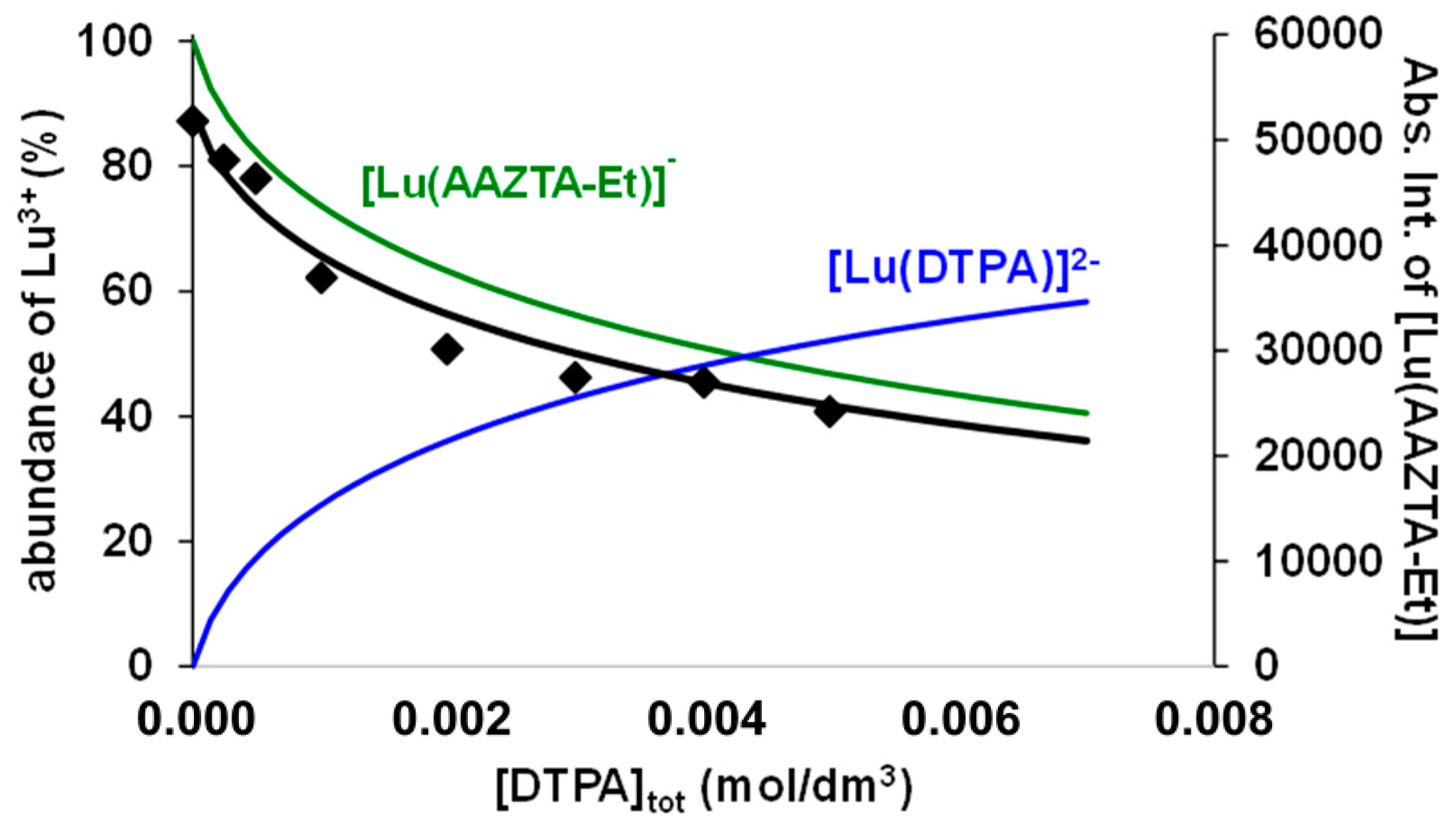
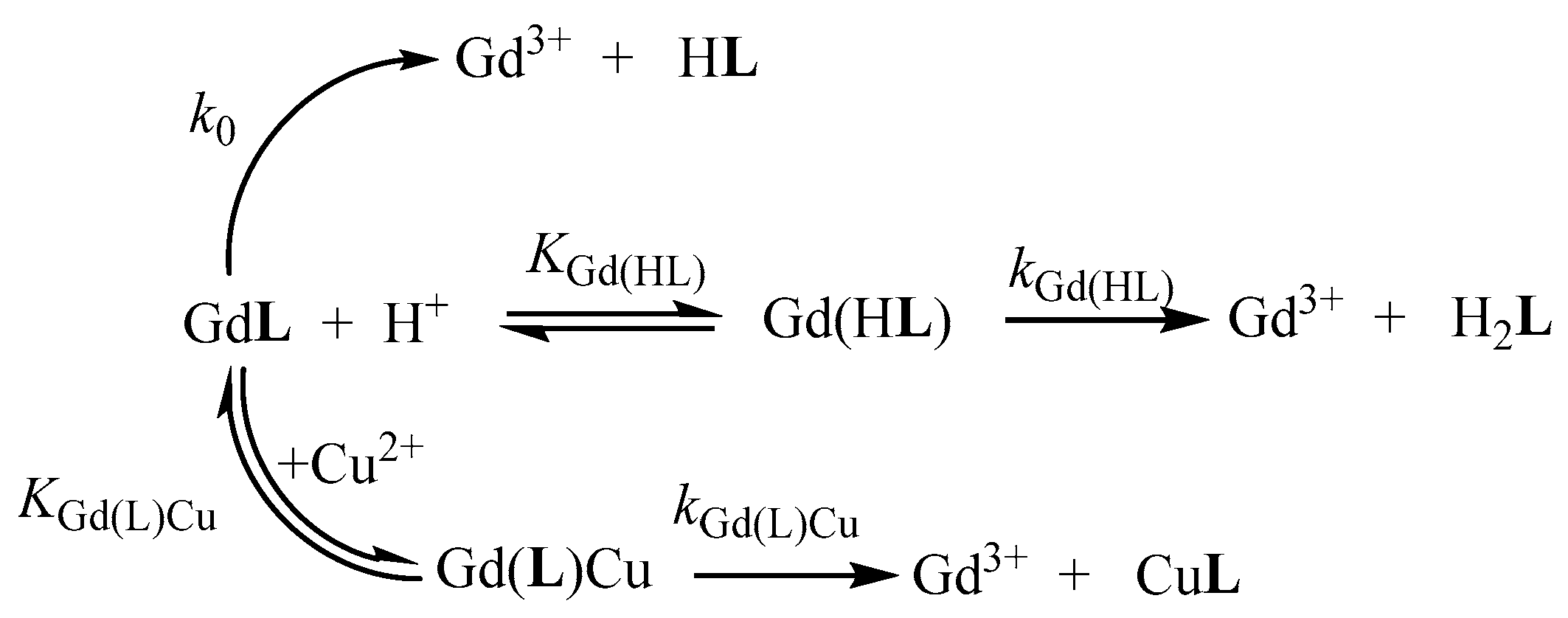
| AAZTA-Et | AAZTA-Bn | AAZTA-C2-COOH [a] | AAZTA-C4-COOH [a] | AAZTA-Me | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 0.15 M NaCl | 0.15 M NaCl [b] | 0.1 M KCl [c] | |||
| logK1H | 10.61 (1) | 10.20 (2) | 10.22 | 10.48 | 10.06 | 11.23 |
| logK2H | 6.56 (2) | 6.54 (3) | 6.53 | 6.90 | 6.50 | 6.52 |
| logK3H | 3.68 (2) | 3.55 (3) | 4.33 [d] | 4.68 [d] | 3.77 | 3.78 |
| logK4H | 2.43 (2) | 2.34 (4) | 3.62 | 3.73 | 2.33 | 2.24 |
| logK5H | 0.57 (8) | − | 2.91 | 2.60 | 1.51 | 1.56 |
| logK6H | − | − | 2.03 | 1.80 | − | − |
| logK7H | − | − | 1.23 | 1.09 | − | − |
| ΣlogKiH | 23.85 | 22.62 | 30.86 | 31.27 | 24.16 | 25.33 |
| AAZTA-Et | AAZTA-Bn | AAZTA-C2-COOH [a] | AAZTA-C4-COOH [a] | AAZTA-Me | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 0.15 M NaCl | 0.15 M NaCl [b] | 0.1 M KCl [c] | |||
| CaL | 11.86 (1) | 12.02 (1) | 11.91 | 12.05 | 11.75 | 12.76 |
| CaHL | 3.33 (3) | 3.35 (2) | 4.36 [f] | 4.77 [f] | 3.41 | 3.34 |
| CaH2L | − | − | 3.58 | 3.27 | − | − |
| MnL | 14.61 (2) | 14.74 (1) | − | − | 14.19 [d] | 15.44 |
| MnHL | 2.80 (5) | 2.44 (5) | − | − | 2.61 [d] | 2.83 |
| ZnL | 16.84 (2) | 17.22 (5) | 16.93 | 17.05 | 16.02 | 18.01 |
| ZnHL | 3.49 (1) | 3.74 (4) | 4.48 [f] | 4.74 [f] | 3.95 | 3.87 |
| ZnH2L | 2.37 (2) | 2.64 (4) | 3.61 | 3.76 | 2.53 | 2.36 |
| ZnH3L | − | − | 2.74 | 2.76 | − | − |
| ZnLH−1 | 11.53 (5) | 12.14(8) | 11.44 | 11.39 | 11.36 | 11.25 |
| CuL | 18.92 (2) | 17.78 (9) | 19.96 | 18.94 | 20.60 | 22.27 |
| CuHL | 4.03 (2) | 4.11 (4) | 4.54 [f] | 4.79 [f] | 3.86 | 4.00 |
| CuH2L | 2.58 (2) | 2.76 (4) | 3.86 | 3.91 | 2.43 | 2.72 |
| CuH3L | − | − | 2.94 | 2.88 | 1.37 | − |
| CuH4L | − | − | 1.40 | 1.31 | − | − |
| CuLH−1 | 11.13 (3) | 11.24 (3) | 11.23 | 11.02 | 10.62 | 10.81 |
| LaL | 16.70 (1) | 16.68 (1) | 16.98 | 17.24 | 16.48 | 17.53 |
| LaHL | 2.04 (2) | 2.08 (2) | 4.36 [f] | 4.68 [f] | 1.90 | 1.97 |
| LaH2L | − | − | 2.59 | 2.37 | − | − |
| GdL | 19.71 (1)/19.4 (2) [g] | 19.4 (1) [g] | 20.06 | 20.33 | 18.93 | 20.24 |
| GdHL | 1.91 (1) | − | 4.45 [f] | 4.74 [f] | 2.18 | 1.89 |
| GdH2L | − | − | 2.11 | 2.07 | − | − |
| LuL | 21.52 (3) | 21.48 (9) | 21.65 | 22.06 | 21.22 | 21.85 |
| LuHL | − | − | 4.47 [f] | 4.65 [f] | − | − |
| pGd [e] | 17.08 | 17.50 | 18.14 | 18.08 | 17.17 | 17.31 |
| [Gd(AAZTA-Et)]− | [Gd(AAZTA-Bn)]− | [Gd(AAZTA-C4-COOH)]− [a] | [Gd(AAZTA-C2-COOH)]− [a] | [Gd(AAZTA)]− [b] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | 0.15 M NaCl | 0.1 M KCl | |||
| k1/M−1s−1 | 0.91 ± 0.08 | 0.33 ± 0.05 | 0.37 | 0.47 | 1.05 |
| k2/M−2s−1 | − | − | 123 | − | − |
| k3Cu/M−1s−1 | (3 ± 1) × 10−4 | − | − | 4 × 10−5 | 1.9 × 10−4 |
| KGdHL/M−1 | 140 ± 30 | 283 ± 50 | 118 (KGdH2L) | 128 (KGdH2L) | 233 |
| KGd(L)Cu/M−1 | 34 ± 5 | 38 ± 9 | − | 20 ± 6 | 9 ± 2 |
| kd/s−1 pH = 7.4 | 3.6 × 10−8 | 1.3 × 10−8 | 1.4 × 10−8 | 1.9 × 10−8 | 4.0 × 10−8 |
| t1/2/h pH = 7.4 | 5.3 × 103 | 1.4 × 104 | 1.3 × 104 | 1.0 × 104 | 4.3 × 103 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Forgione, F.; Ranga, M.; Travagin, F.; Boccalon, M.; Baranyai, Z.; Giovenzana, G.B.; Lattuada, L. The Legacy of AAZTA—Synthesis and Coordination Chemistry of Two AAZTA Structural Analogs. Inorganics 2024, 12, 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics12090235
Forgione F, Ranga M, Travagin F, Boccalon M, Baranyai Z, Giovenzana GB, Lattuada L. The Legacy of AAZTA—Synthesis and Coordination Chemistry of Two AAZTA Structural Analogs. Inorganics. 2024; 12(9):235. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics12090235
Chicago/Turabian StyleForgione, Federico, Madalina Ranga, Fabio Travagin, Mariangela Boccalon, Zsolt Baranyai, Giovanni B. Giovenzana, and Luciano Lattuada. 2024. "The Legacy of AAZTA—Synthesis and Coordination Chemistry of Two AAZTA Structural Analogs" Inorganics 12, no. 9: 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics12090235
APA StyleForgione, F., Ranga, M., Travagin, F., Boccalon, M., Baranyai, Z., Giovenzana, G. B., & Lattuada, L. (2024). The Legacy of AAZTA—Synthesis and Coordination Chemistry of Two AAZTA Structural Analogs. Inorganics, 12(9), 235. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics12090235








