Facile Synthesis of CuFe2O4 Nanoparticles for Efficient Removal of Acid Blue 113 and Malachite Green Dyes from Aqueous Media
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
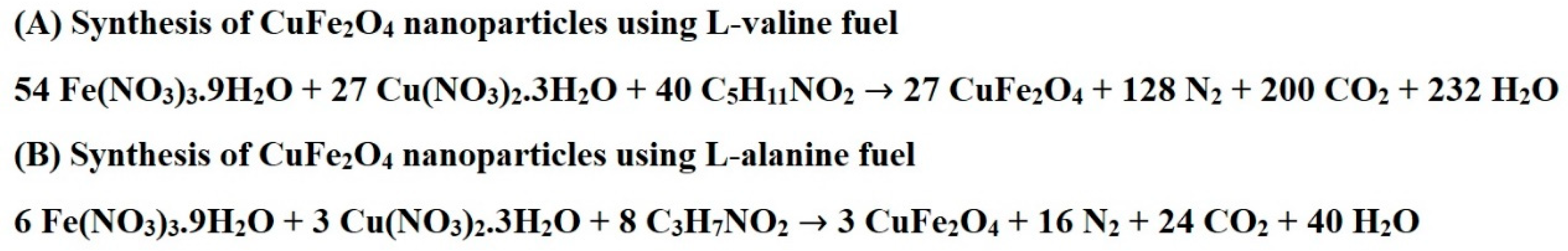
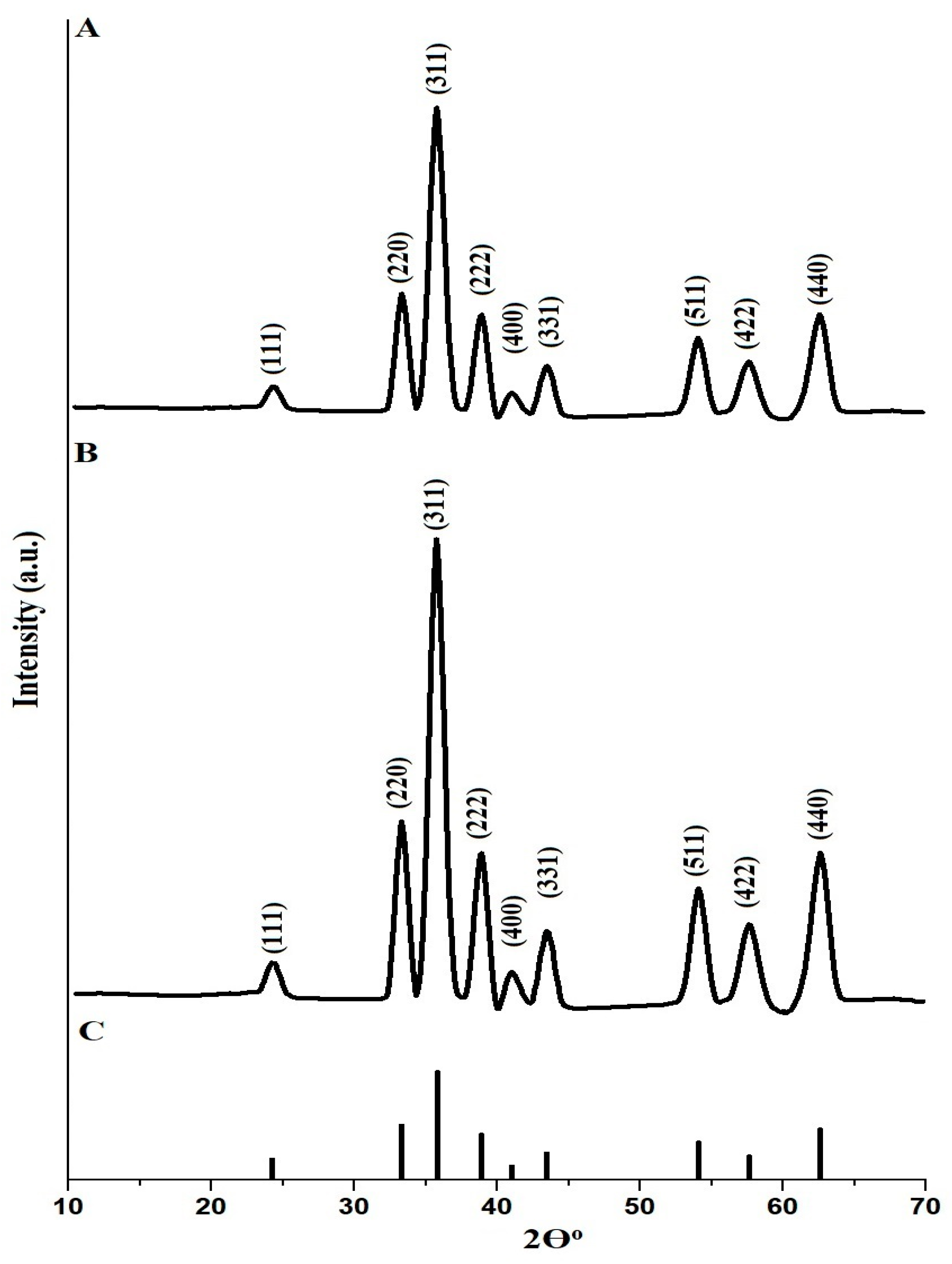
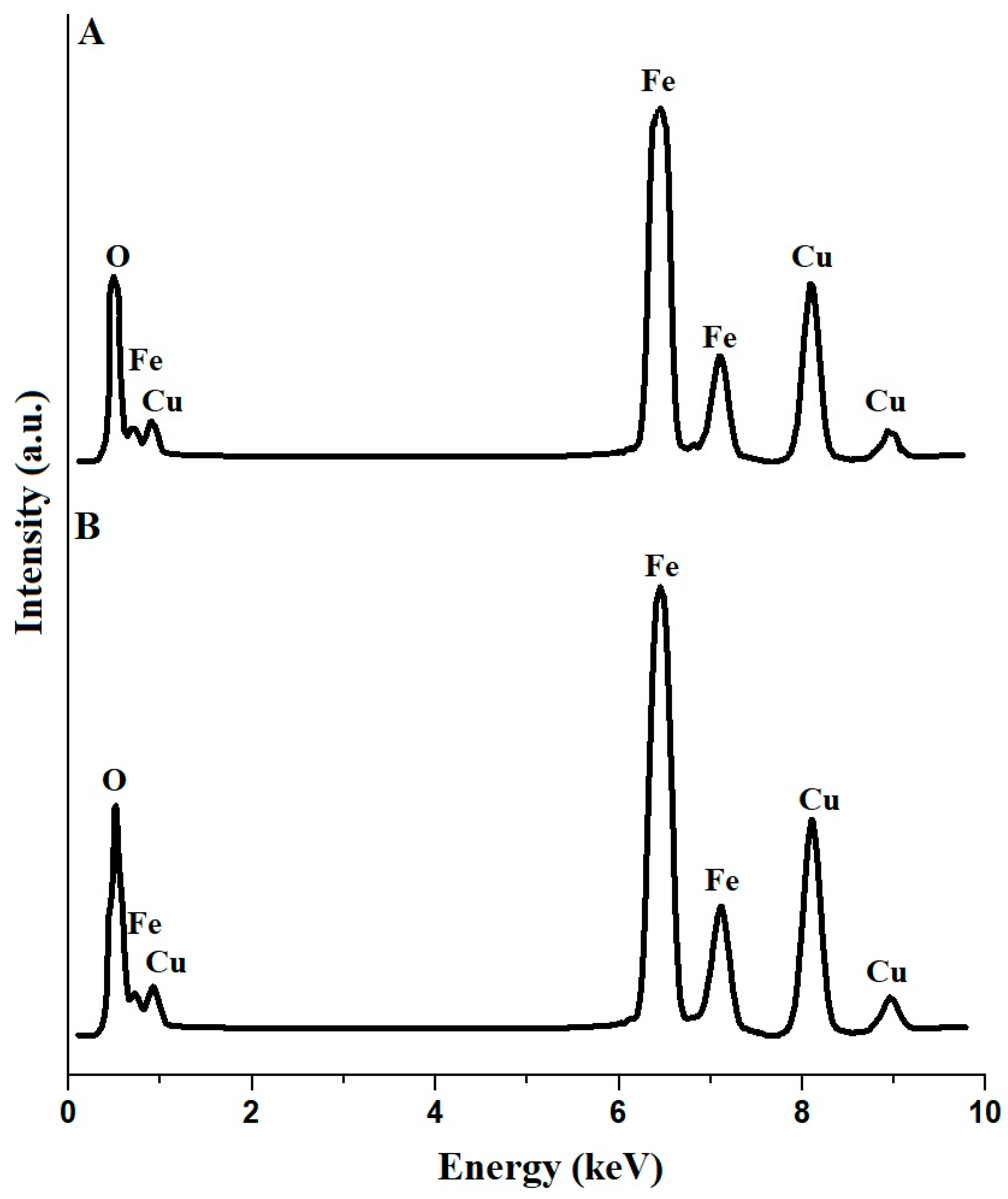
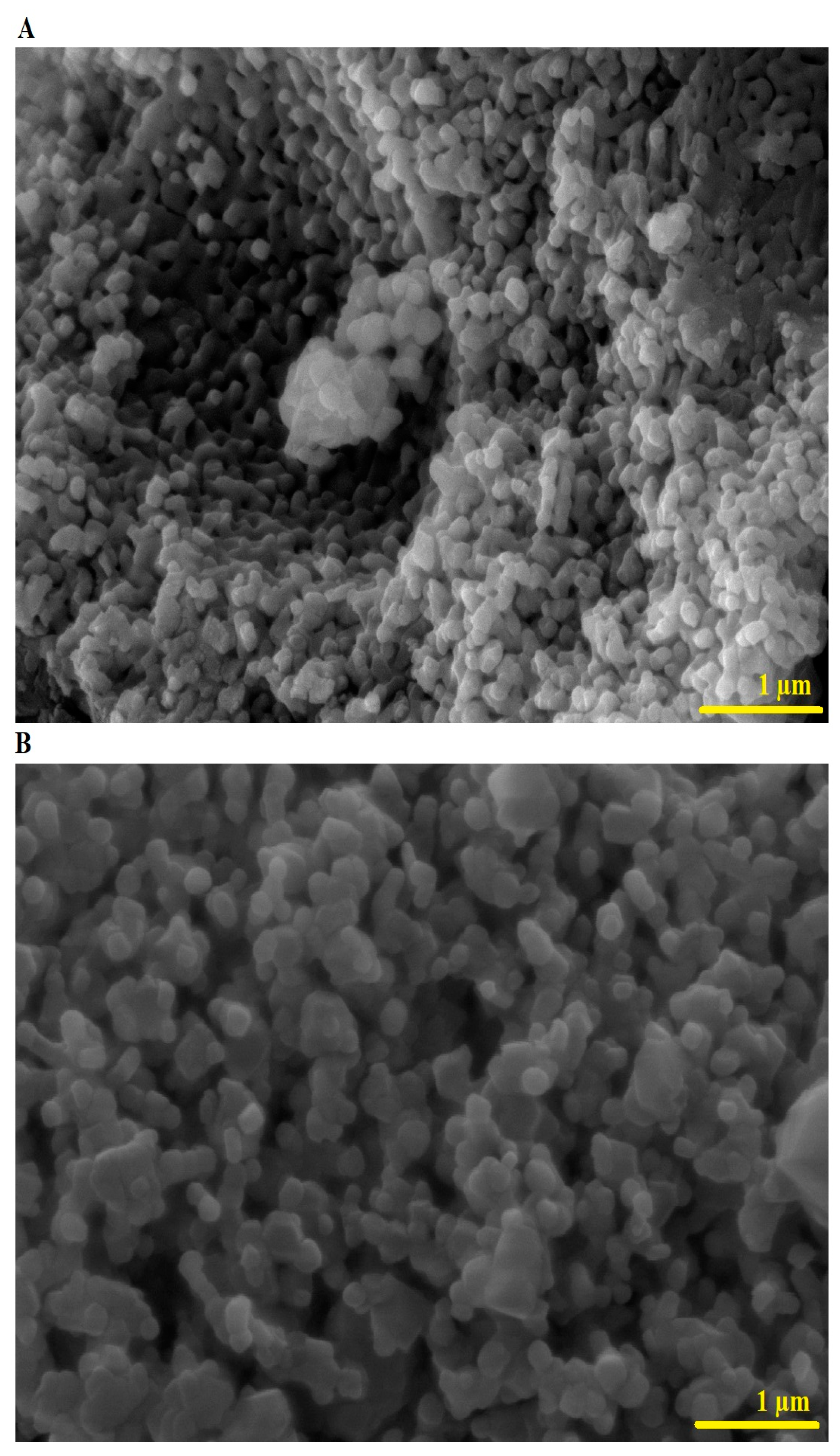
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of CuFe2O4 Nanoparticles
2.2. Removal of Acid Blue 113 and Malachite Green Dyes from Aqueous Media
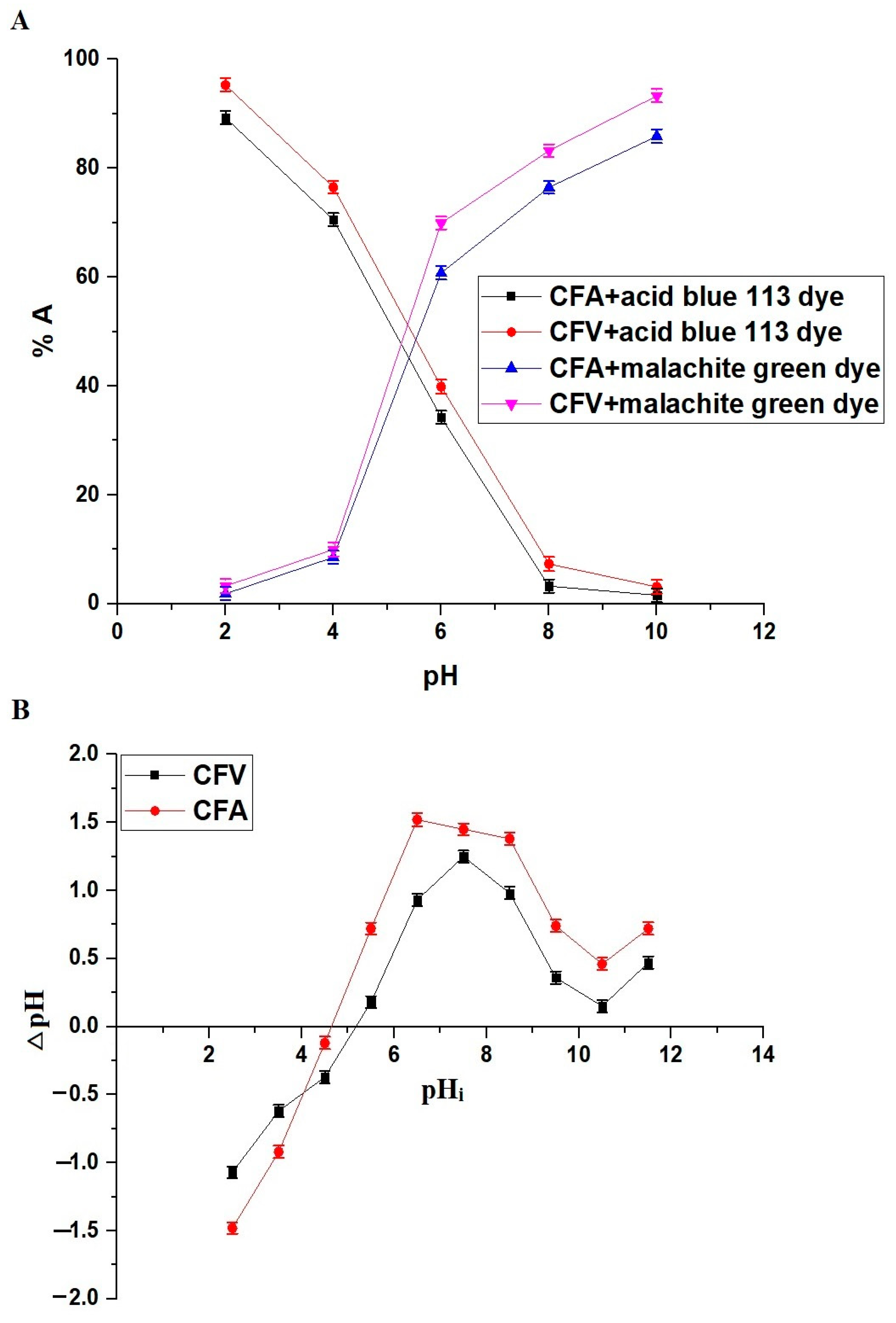
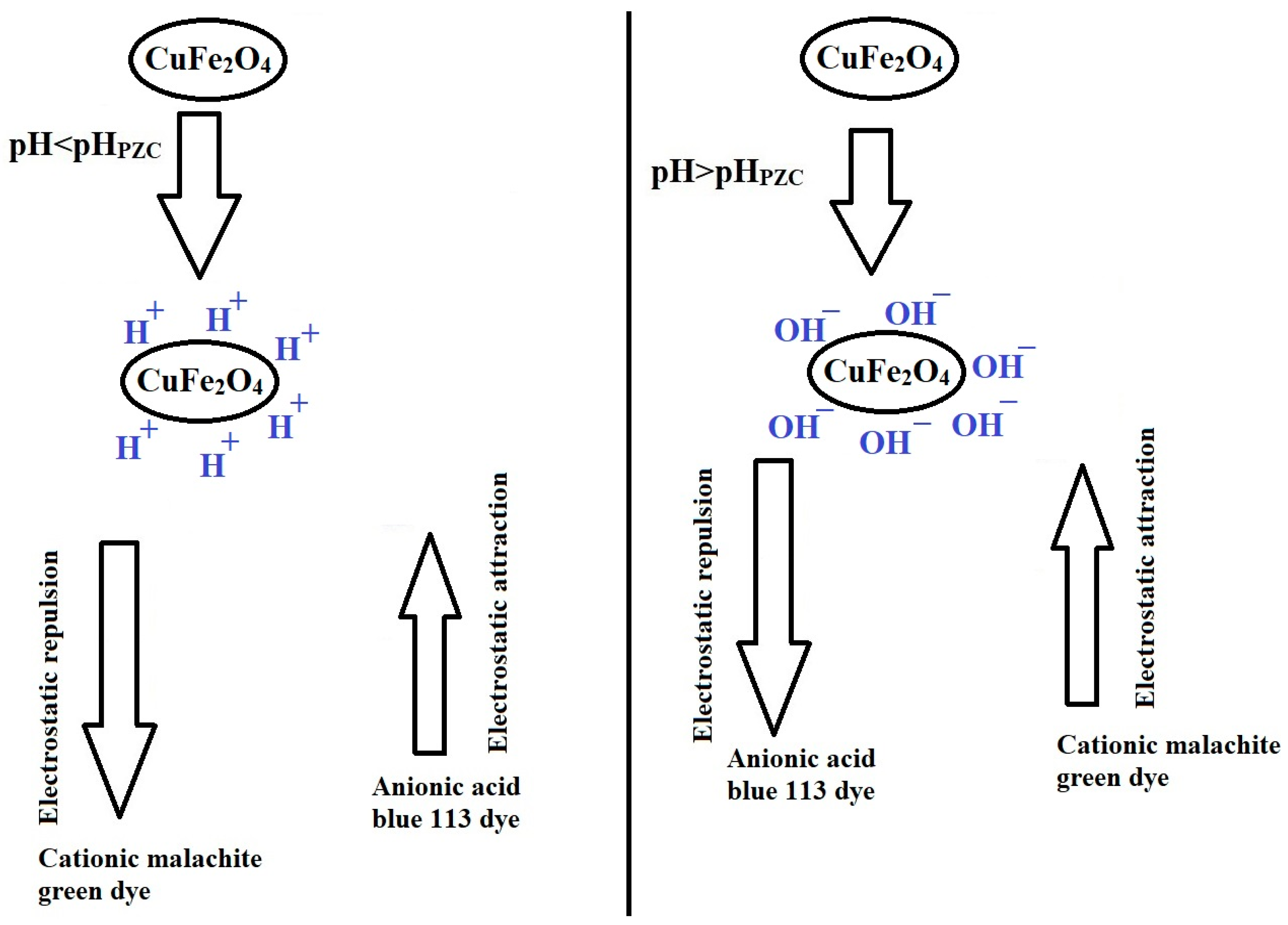
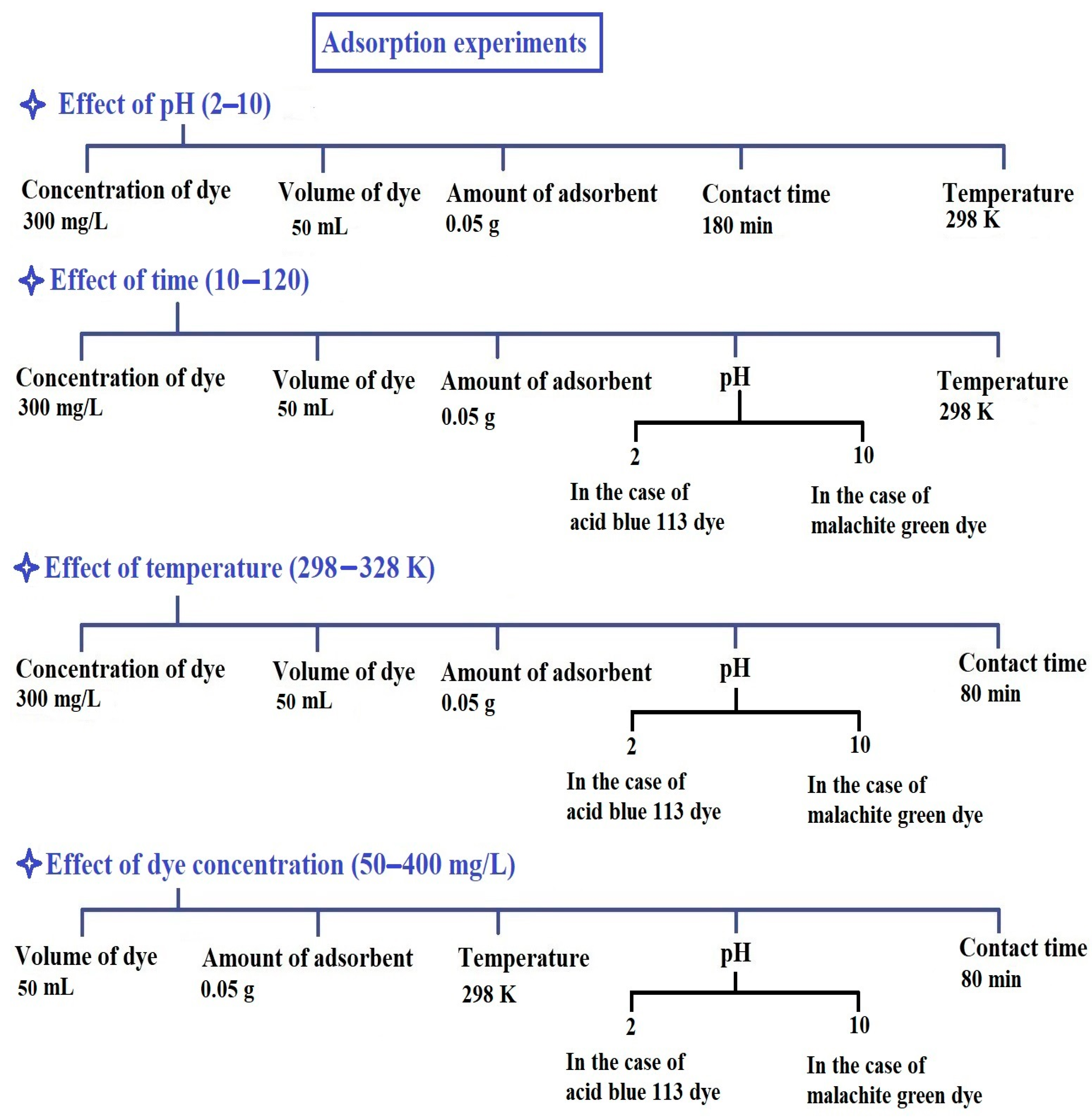
2.2.1. Influence of pH
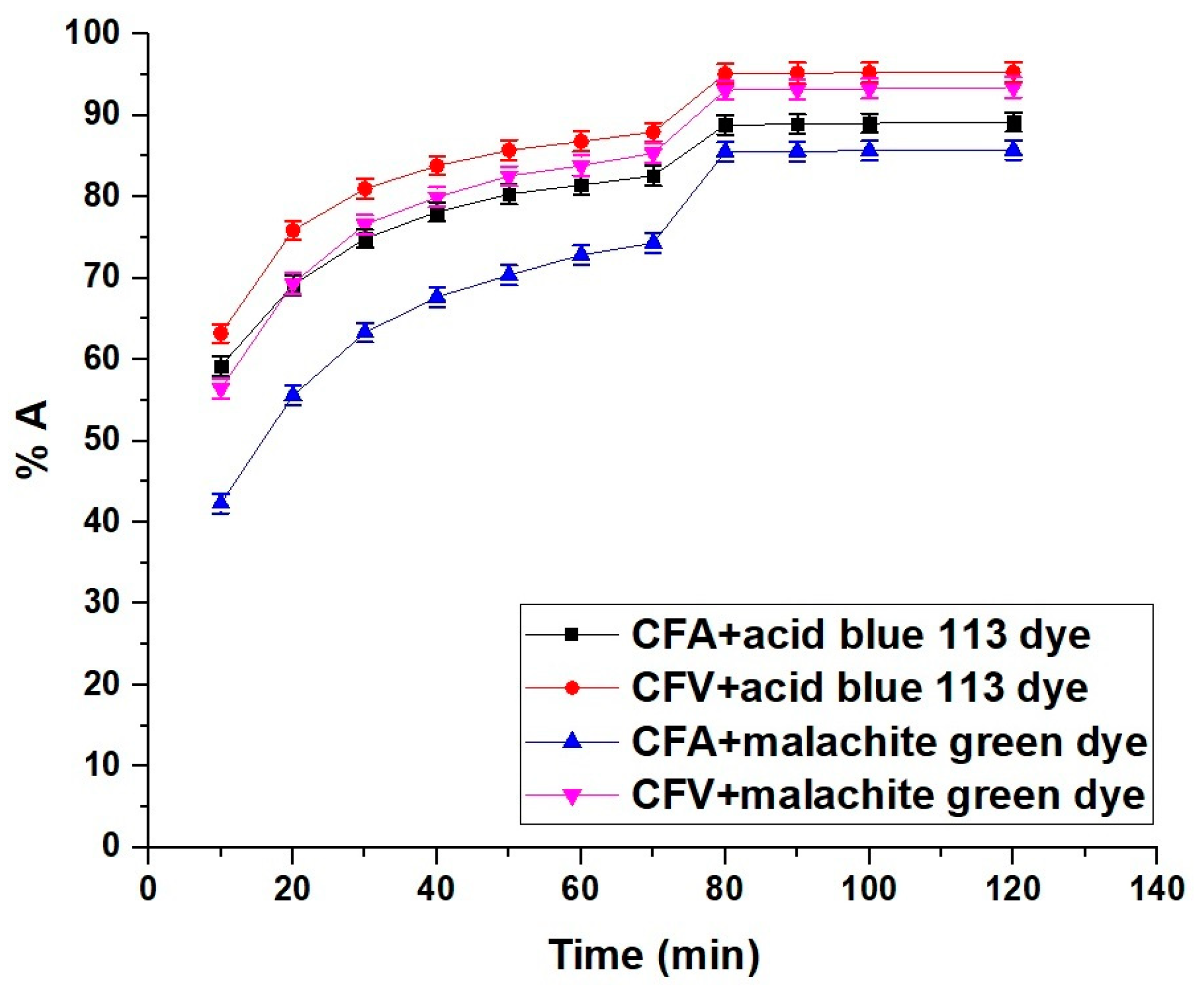
2.2.2. Influence of Contact Time
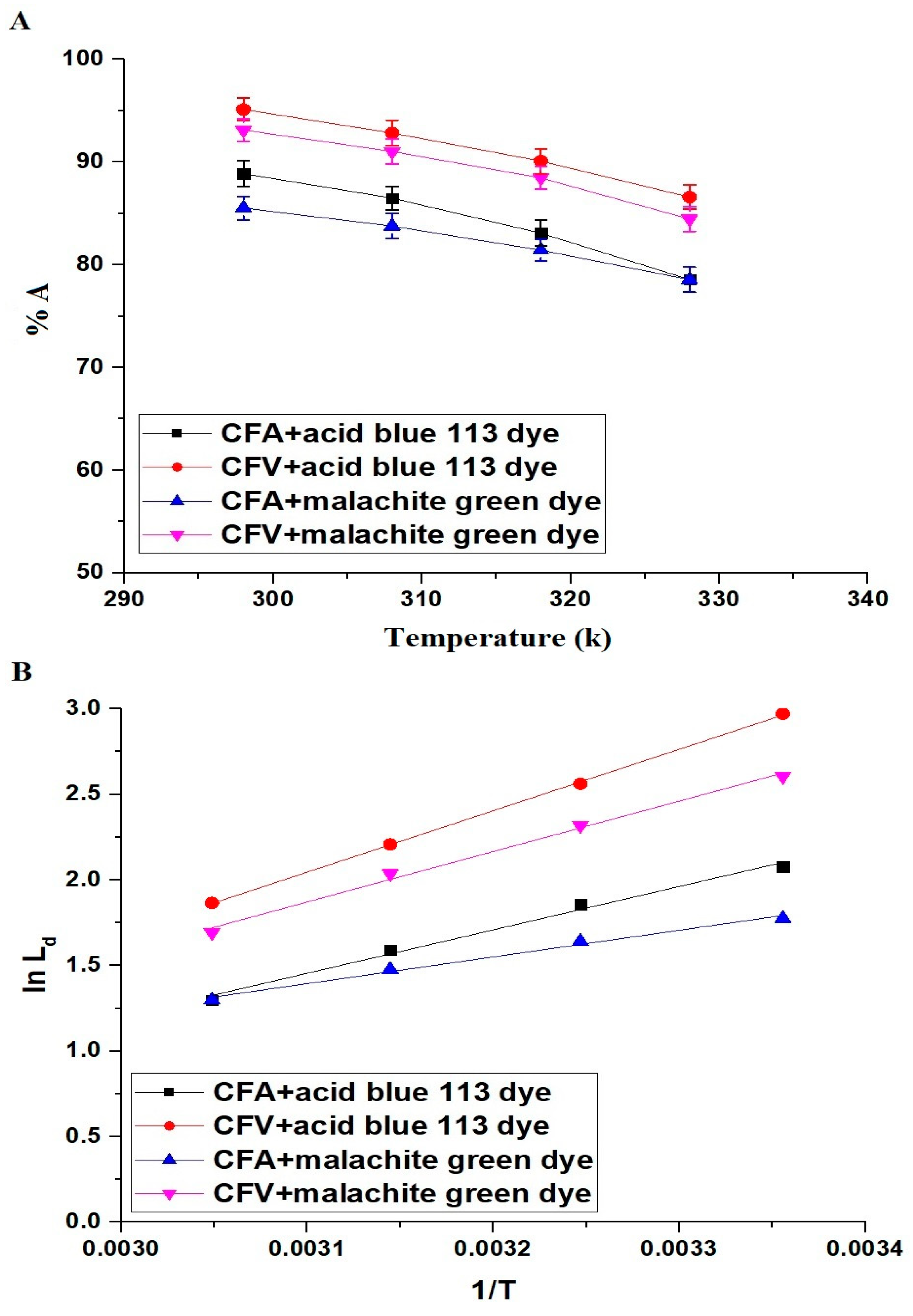
2.2.3. Influence of Temperature
2.2.4. Influence of Concentration
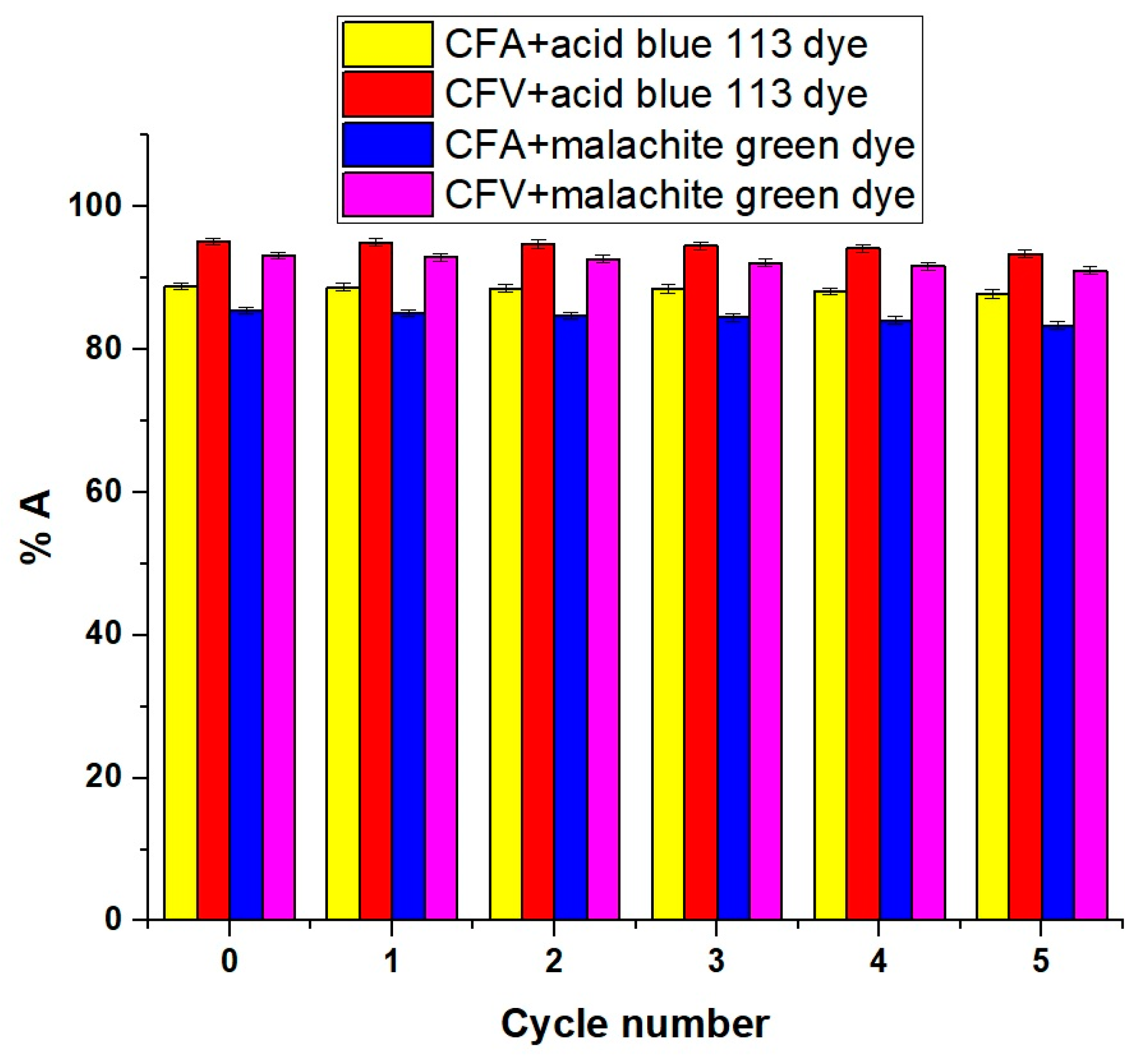
2.2.5. Effect of Regeneration and Reusability
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials
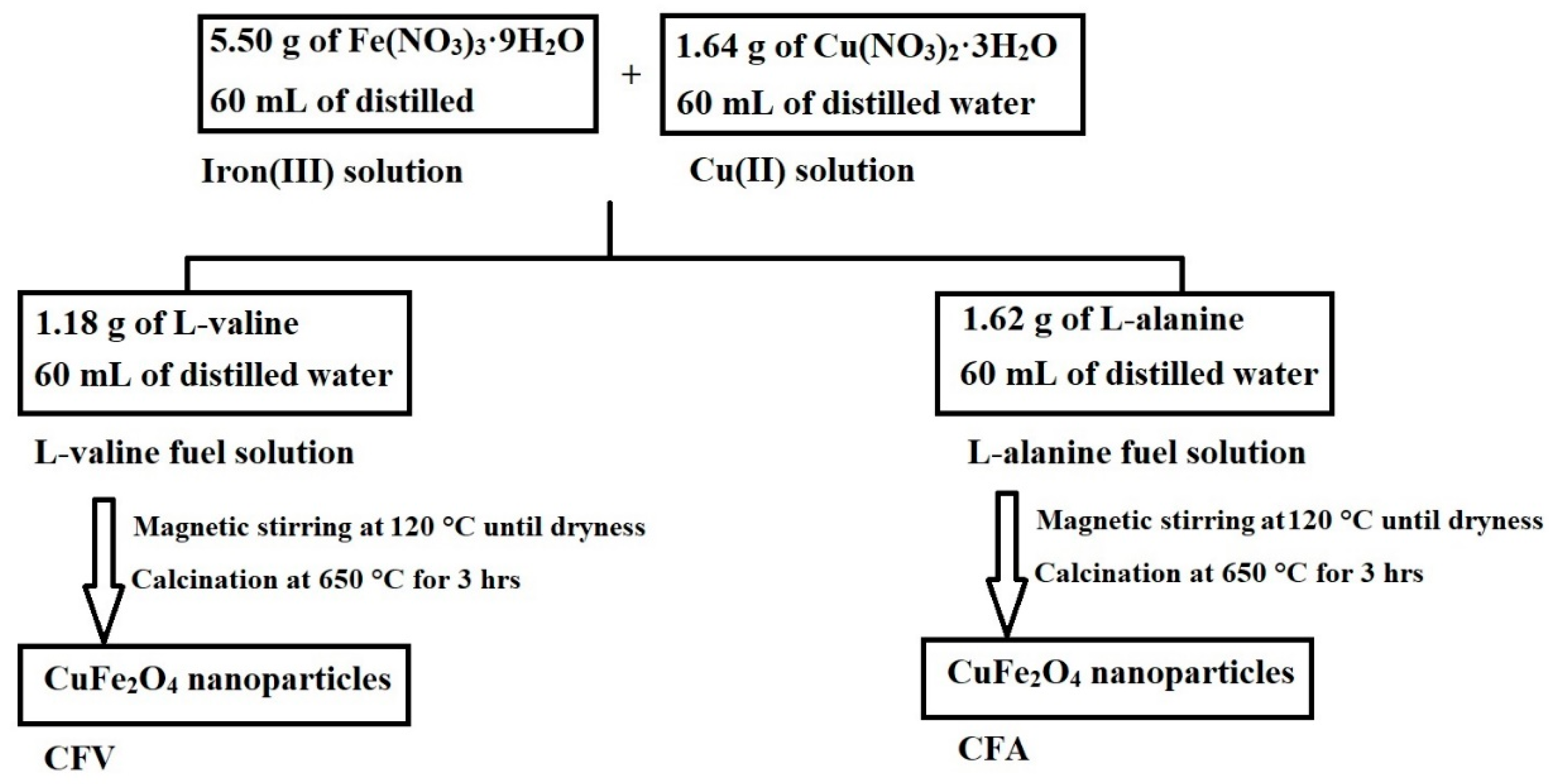
3.2. Synthesis of Copper Ferrite (CuFe2O4) Nanoparticles
3.3. Instrumentation
3.4. Removal of Acid Blue 113 and Malachite Green Dyes from Aqueous Media
3.5. Point of Zero Charge (pHPZC) of the CFV and CFA Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, D.; Nam, S.N.; Jung, B.; Soo Choi, J.; Min Park, C.; Earn Choong, C.; Jang, M.; Cho, K.S.; Jun, B.M.; Yoon, Y. Removal of Selected Contaminants of Dyes and Pharmaceuticals Using MXene-Based Nanoadsorbents: A Review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 341, 126864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radoor, S.; Karayil, J.; Jayakumar, A.; Siengchin, S. Journal of Water Process Engineering Efficient Removal of Dyes, Heavy Metals and Oil-Water from Wastewater Using Electrospun Nanofiber Membranes: A Review. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 59, 104983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian, M.; Jaymand, M. Interpenetrating Polymer Network Hydrogels for Removal of Synthetic Dyes: A Comprehensive Review. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 486, 215152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kausar, A.; Zohra, S.T.; Ijaz, S.; Iqbal, M.; Iqbal, J.; Bibi, I.; Nouren, S.; El Messaoudi, N.; Nazir, A. Cellulose-Based Materials and Their Adsorptive Removal Efficiency for Dyes: A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 224, 1337–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriram, G.; Bendre, A.; Mariappan, E.; Altalhi, T.; Kigga, M.; Ching, Y.C.; Jung, H.Y.; Bhaduri, B.; Kurkuri, M. Recent Trends in the Application of Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs) for the Removal of Toxic Dyes and Their Removal Mechanism—A Review. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2022, 31, e00378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reghioua, A.; Atia, D.; Hamidi, A.; Jawad, A.H.; Abdulhameed, A.S.; Mbuvi, H.M. Production of Eco-Friendly Adsorbent of Kaolin Clay and Cellulose Extracted from Peanut Shells for Removal of Methylene Blue and Congo Red Removal Dyes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 263, 130304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marey, A.; Gado, W.S.; Soliman, A.G.; Masoud, A.M.; El-Zahhar, A.A.; Al-Hazmi, G.A.A.M.; Taha, M.H.; El Naggar, A.M.A. Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue Dye from Wastewater Specimen Using Polystyrene Coated Nanoparticles of Silica. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2024, 160, 112018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.M.; Vasu, D.; Chan, S.Y.; Liu, Y.C.; Jiang, J.; You, Y.F.; Chiu, T.W.; Chen, S.C. Two-Dimensional Heterojunction Layered Graphene Oxide/Graphitic Carbon Nitride Photocatalyst for Removal of Toxic Environmental Dye Methylene Blue. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 345, 123556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagherzadeh, M.; Salehi, G.; Rabiee, N. Rapid and Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue Dye from Aqueous Solutions Using Extract-Modified Zn–Al LDH. Chemosphere 2024, 350, 141011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, S.; Kularkar, A.; Devi, S.; Nagababu, P. Photoluminescence and Photocatalytic Degradation Studies of Zn-Based Nanoparticles on Malachite Green Dye. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2024, 188, 111929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekaran, C.; Vishnu, D.; Dhandapani, B.; Alagesan, T.; Balaji, G. Facile Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Glycerol as Cross-Linker and the Kinetic Studies for the Photocatalytic Degradation of Acid Blue 113 Dye. Results Chem. 2022, 4, 100377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihaddaden, S.; Aberkane, D.; Boukerroui, A.; Robert, D. Removal of Methylene Blue (Basic Dye) by Coagulation-Flocculation with Biomaterials (Bentonite and Opuntia Ficus Indica). J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 102952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustos-Terrones, Y.A.; Hermosillo-Nevárez, J.J.; Ramírez-Pereda, B.; Vaca, M.; Rangel-Peraza, J.G.; Bustos-Terrones, V.; Rojas-Valencia, M.N. Removal of BB9 Textile Dye by Biological, Physical, Chemical, and Electrochemical Treatments. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2021, 121, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Saud Abdulhameed, A.; ALOthman, Z.A.; Yong, S.K.; Wilson, L.D.; Jawad, A.H.; Algburi, S. Chitosan-Schiff Base Nano Silica Hybrid System for Azo Acid Dye Removal: Multivariable Optimization, Desirability Function, and Adsorption Mechanism. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2024, 162, 112237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, Q.; Xu, S.; Wu, X.; Wang, S.; Jin, D.; Wang, P.; Wu, D.; Dong, F. Electrochemical Removal of Synthetic Methyl Orange Dyeing Wastewater by Reverse Electrodialysis Reactor: Experiment and Mineralizing Model. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 114064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Wang, J.J.; Dangal, P.; Lomnicki, S.; Roy, A.D.; Park, J.H. A Novel Sugarcane Residue-Derived Bimetallic Fe/Mn-Biochar Composite for Activation of Peroxymonosulfate in Advanced Oxidation Process Removal of Azo Dye: Degradation Behavior and Mechanism. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 58, 104740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurav, R.; Bhatia, S.K.; Choi, T.R.; Choi, Y.K.; Kim, H.J.; Song, H.S.; Lee, S.M.; Lee Park, S.; Lee, H.S.; Koh, J.; et al. Application of Macroalgal Biomass Derived Biochar and Bioelectrochemical System with Shewanella for the Adsorptive Removal and Biodegradation of Toxic Azo Dye. Chemosphere 2021, 264, 128539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyakairu, G.W.A.; Kapanga, P.M.; Ntale, M.; Lusamba, S.N.; Tshimanga, R.M.; Ammari, A.; Shehu, Z. Synthesis, Characterization and Application of Zeolite/Bi2O3 Nanocomposite in Removal of Rhodamine B Dye from Wastewater. Clean. Water 2024, 1, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, V.L.; Kieu, T.T.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Truong, T.T.T.; Hoang, D.T.; Vu, T.L.C.; Nguyen, T.M.T.; Le, T.S.; Doan, T.H.Y.; Pham, T.D. Surface Modification of Zeolite by Cationic Surfactant and the Application on Adsorptive Removal of Azo Dye Ponceau 4R. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1304, 137619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kadhi, N.S.; Al-Senani, G.M.; Algethami, F.K.; Shah, R.K.; Saad, F.A.; Munshi, A.M.; Rehman, K.; Khezami, L.; Abdelrahman, E.A. Calcium Ferrite Nanoparticles: A Simple Synthesis Approach for the Effective Disposal of Congo Red Dye from Aqueous Environments. Inorganics 2024, 12, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghanmi, R.M.; Abdelrahman, E.A. Simple Production and Characterization of ZnO/MgO Nanocomposite as a Highly Effective Adsorbent for Eliminating Congo Red Dye from Water-Based Solutions. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2024, 161, 112137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazey, R.M.; Abdelrahman, E.A.; Kotp, Y.H.; Hameed, A.M.; Subaihi, A. Facile Fabrication of Hematite Nanoparticles from Egyptian Insecticide Cans for Efficient Photocatalytic Degradation of Rhodamine B Dye. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 1652–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, T.; Joseph, S.; Mathew, S. Structural and Microwave Properties of Copper Ferrite Nanoparticles Prepared by Sol-Gel Synthesis. J. Metastable Nanocrystalline Mater. 2005, 23, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajik, S.; Beitollahi, H. Hydrothermal Synthesis of CuFe2O4 Nanoparticles for Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Detection of Sunset Yellow. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 165, 113048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanuri, S.; Dinda, S.; Singh, S.A.; Roy, S.; Chakraborty, C.; Datta, S.P. Microrod Networks CuO–ZnO–Al2O3 Catalyst for Methanol Synthesis from CO2: Synthesis, Characterization, and Performance Demonstration. Mater. Today Chem. 2024, 36, 101959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sani, L.A.; Bai, H.; Xu, Z.; Fu, L.; Sun, Y.; Huang, X.; Gao, H.; Liu, X.; Bai, D.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Optimized Combustion Temperature in the Facile Synthesis of Ni/Al2O3 Catalyst for CO2 Methanation. J. CO2 Util. 2024, 80, 102678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergis, B.R.; Hari Krishna, R.; Kottam, N.; Nagabhushana, B.M.; Sharath, R.; Darukaprasad, B. Removal of Malachite Green from Aqueous Solution by Magnetic CuFe2O4 Nano-Adsorbent Synthesized by One Pot Solution Combustion Method. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2018, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, X.; Che, Y.; Liu, H.; Zuo, W.; Zhang, Y. The Methyl Blue Adsorption Performance and Mechanism of NaX Zeolite Synthesized from Huadian Oil Shale Ash. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2023, 147, 104904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Xu, F.; Wei, W.; Gao, H.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, G.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, P. Efficient and Fast Adsorption of Methylene Blue Dye onto a Nanosheet MFI Zeolite. J. Solid State Chem. 2021, 295, 121917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, Y.; Boricha, H.; Suryavanshi, A.; Gajare, A.; Jain, S.; Suresh, K. Synthesis, Characterization and Adsorption Studies on Activated Carbon Adsorbent Synthesized from Kigelia Africana for Removal of Acid Blue 113 Dye from Synthetic Solution. Mater. Today Proc. 2023; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Açıkel, Y.S.; Göze, B. Removal of Methyl Red, a Cationic Dye, Acid Blue 113, an Anionic Dye, from Wastewaters Using Chitin and Chitosan: Influence of Copper Ions. Desalin. Water Treat. 2017, 73, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, S.; Kini, M.S.; Rangasamy, G.; Selvaraj, R. Mesoporous Calcium Hydroxide Nanoparticle Synthesis from Waste Bivalve Clamshells and Evaluation of Its Adsorptive Potential for the Removal of Acid Blue 113 Dye. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, T.Y.; Raman, A.A.A.; Bello, M.M.; Buthiyappan, A. Magnetic Graphene Oxide-Biomass Activated Carbon Composite for Dye Removal. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 37, 2179–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinayagam, R.; Pai, S.; Murugesan, G.; Varadavenkatesan, T.; Kaviyarasu, K.; Selvaraj, R. Green Synthesized Hydroxyapatite Nanoadsorbent for the Adsorptive Removal of AB113 Dye for Environmental Applications. Environ. Res. 2022, 212, 113274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Musawi, T.J.; Mengelizadeh, N.; Al Rawi, O.; Balarak, D. Capacity and Modeling of Acid Blue 113 Dye Adsorption onto Chitosan Magnetized by Fe2O3 Nanoparticles. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 344–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, M.; Mirza, B.; Mahanpoor, K.; Mirjalili, M.; Najafi, F.; Moradi, O.; Sadegh, H.; Shahryari-ghoshekandi, R.; Asif, M.; Tyagi, I.; et al. Adsorption of Malachite Green from Aqueous Solution by Carboxylate Group Functionalized Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes: Determination of Equilibrium and Kinetics Parameters. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 34, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.S.K.; Jiang, S.J. Chitosan-Functionalized Graphene Oxide: A Novel Adsorbent an Efficient Adsorption of Arsenic from Aqueous Solution. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1698–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Dinh, D.M.; Hsieh, Y. Lo Adsorption and Desorption of Cationic Malachite Green Dye on Cellulose Nanofibril Aerogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 173, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadegh, N.; Haddadi, H.; Sadegh, F.; Asfaram, A. Synthesis of Graphene/Fe3O4/Polyaniline Nanocomposite for Simultaneous Removal of a Binary Mixture of Malachite Green Cationic Dye and Acid Red 1 Anionic Dye from Aqueous Solutions. Polyhedron 2024, 248, 116671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubakar, H.L.; Tijani, J.O.; Abdulkareem, A.S.; Egbosiuba, T.C.; Abdullahi, M.; Mustapha, S.; Ajiboye, E.A. Effective Removal of Malachite Green from Local Dyeing Wastewater Using Zinc-Tungstate Based Materials. Heliyon 2023, 9, e19167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rout, D.R.; Jena, H.M. Removal of Malachite Green Dye from Aqueous Solution Using Reduced Graphene Oxide as an Adsorbent. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 47, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

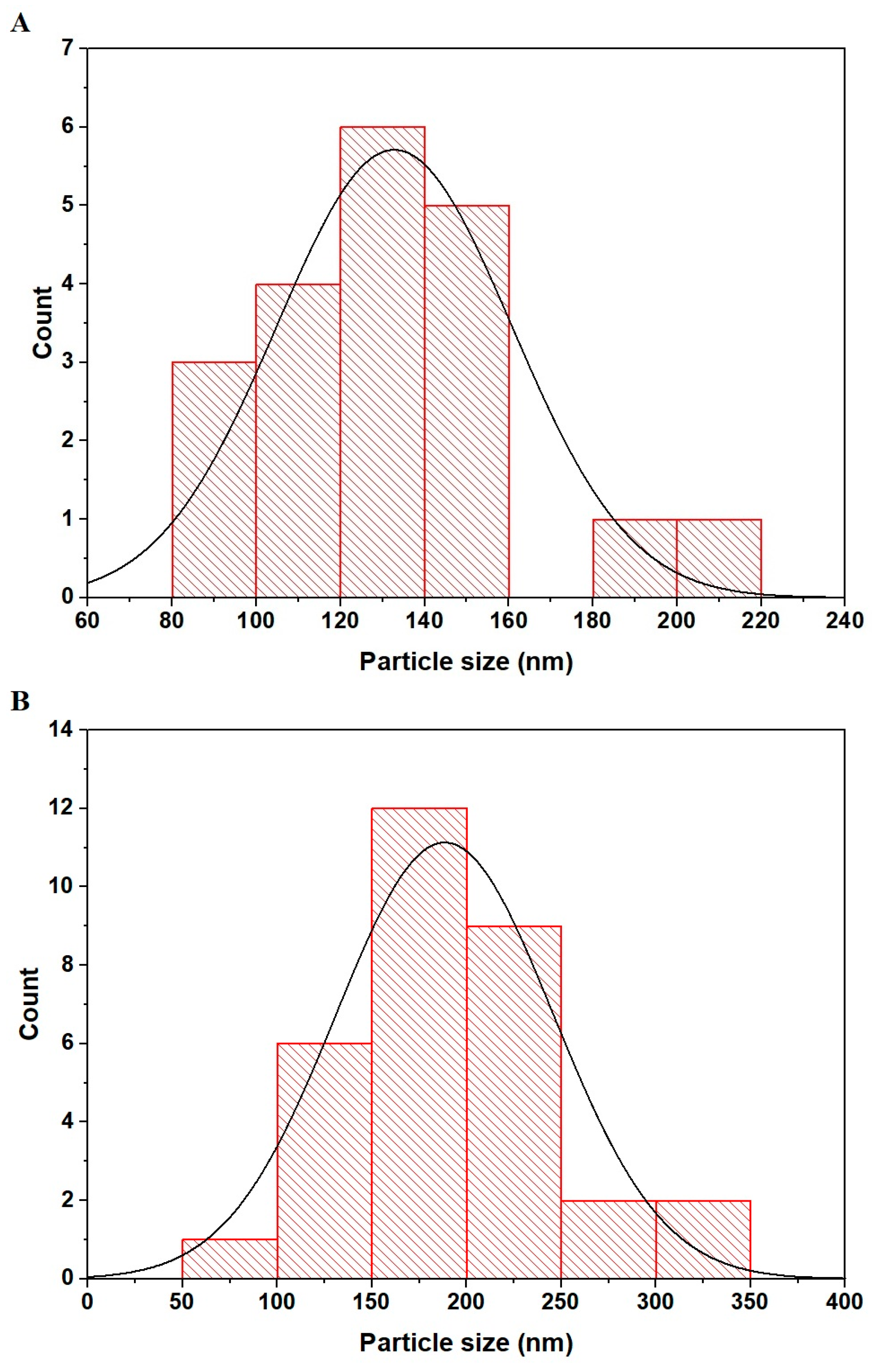

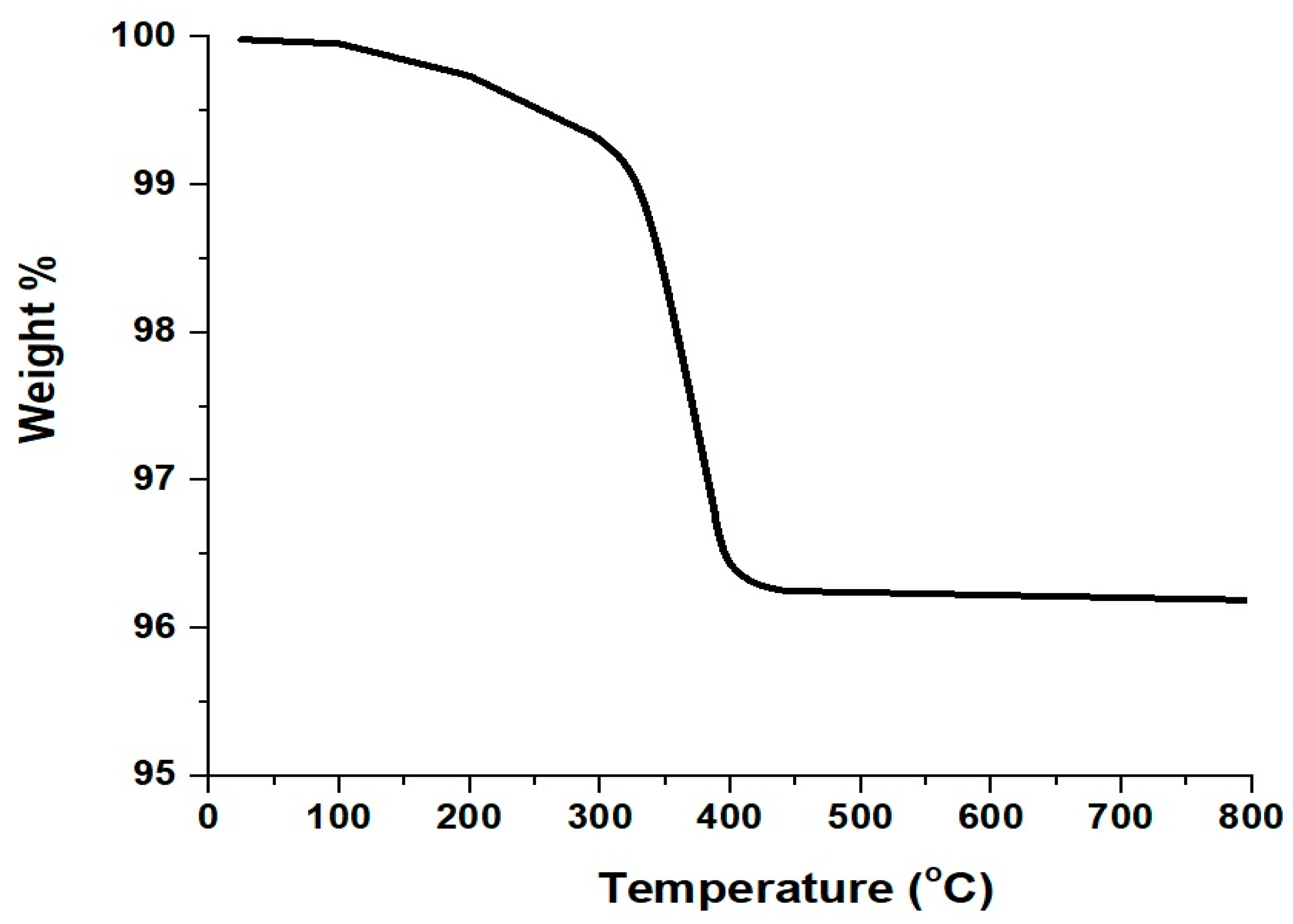




| Sample | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Total Pore Volume (cc/g) | Average Pore Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CFV | 69.38 | 0.1232 | 3.34 |
| CFA | 39.78 | 0.068 | 2.89 |
| Samples | OExp (mg/g) | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 (1/min) | Oe (mg/g) | R2 | L2 (g/mg·min) | Oe (mg/g) | R2 | ||
| CFA | 266.58 | 0.0254 | 99.06 | 0.9589 | 0.000695 | 266.67 | 0.9998 |
| CFV | 285.37 | 0.0235 | 97.79 | 0.9244 | 0.000740 | 281.69 | 0.9999 |
| Samples | OExp (mg/g) | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 (1/min) | Oe (mg/g) | R2 | L2 (g/mg.min) | Oe (mg/g) | R2 | ||
| CFA | 256.58 | 0.0219 | 141.49 | 0.9602 | 0.00037 | 255.75 | 0.9999 |
| CFV | 279.36 | 0.0249 | 119.24 | 0.9493 | 0.00053 | 280.11 | 0.9999 |
| Samples | △So (KJ/molK) | △Ho (KJ/mol) | △Go (KJ/mol) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | 308 | 318 | 328 | |||
| CFA | 0.0535 | −21.19 | −37.14 | −37.67 | −38.21 | −38.74 |
| CFV | 0.0759 | −30.01 | −52.63 | −53.39 | −54.15 | −54.91 |
| Samples | △So (KJ/molK) | △Ho (KJ/mol) | △Go (KJ/mol) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | 308 | 318 | 328 | |||
| CFA | 0.0287 | −13.02 | −21.58 | −21.87 | −22.16 | −22.44 |
| CFV | 0.0607 | −24.63 | −42.73 | −43.34 | −43.94 | −44.55 |
| Samples | Langmuir | Freundlich | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Omax (mg/g) | L4 (L/mg) | R2 | Omax (mg/g) | L3 (mg/g)(L/mg)1/n | 1/Z | R2 | |
| CFA | 281.69 | 0.2141 | 0.9990 | 475.15 | 67.60 | 0.3419 | 0.8112 |
| CFV | 297.62 | 0.3114 | 0.9986 | 565.15 | 81.50 | 0.3395 | 0.7037 |
| Samples | Langmuir | Freundlich | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Omax (mg/g) | L4 (L/mg) | R2 | Omax (mg/g) | L3 (mg/g)(L/mg)1/n | 1/Z | R2 | |
| CFA | 280.11 | 0.1082 | 0.9973 | 463.37 | 47.23 | 0.4004 | 0.8719 |
| CFV | 294.99 | 0.2038 | 0.9976 | 556.00 | 66.01 | 0.3736 | 0.7611 |
| Adsorbent | Omax (mg/g) | Ref |
|---|---|---|
| Activated carbon | 188.89 | [30] |
| Chitosan | 143.00 | [31] |
| Calcium hydroxide | 153.53 | [32] |
| Magnetic graphene oxide/biomass-activated carbon | 32.20 | [33] |
| Hydroxyapatite | 120.48 | [34] |
| Magnetite | 128.00 | [35] |
| CFA | 281.69 | This study |
| CFV | 297.62 | This study |
| Adsorbent | Omax (mg/g) | Ref |
|---|---|---|
| Carboxylate functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes | 11.70 | [36] |
| Chitosan-functionalized graphene oxide | 71.90 | [37] |
| Cellulose nanofibril aerogel | 212.70 | [38] |
| Graphene/Fe3O4/polyaniline nanocomposite | 150.27 | [39] |
| Zinc-tungstate based materials | 251.758 | [40] |
| Reduced graphene oxide | 279.85 | [41] |
| CFA | 280.11 | This study |
| CFV | 294.99 | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Wasidi, A.S.; Shah, R.K.; Abdelrahman, E.A.; Mabrouk, E.-S.M. Facile Synthesis of CuFe2O4 Nanoparticles for Efficient Removal of Acid Blue 113 and Malachite Green Dyes from Aqueous Media. Inorganics 2024, 12, 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics12060143
Al-Wasidi AS, Shah RK, Abdelrahman EA, Mabrouk E-SM. Facile Synthesis of CuFe2O4 Nanoparticles for Efficient Removal of Acid Blue 113 and Malachite Green Dyes from Aqueous Media. Inorganics. 2024; 12(6):143. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics12060143
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Wasidi, Asma S., Reem K. Shah, Ehab A. Abdelrahman, and El-Sayed M. Mabrouk. 2024. "Facile Synthesis of CuFe2O4 Nanoparticles for Efficient Removal of Acid Blue 113 and Malachite Green Dyes from Aqueous Media" Inorganics 12, no. 6: 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics12060143
APA StyleAl-Wasidi, A. S., Shah, R. K., Abdelrahman, E. A., & Mabrouk, E.-S. M. (2024). Facile Synthesis of CuFe2O4 Nanoparticles for Efficient Removal of Acid Blue 113 and Malachite Green Dyes from Aqueous Media. Inorganics, 12(6), 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics12060143







