Mechano-Synthesis, Structure, and Thermal and Magnetic Behaviors of the New Compound Mn1.2Co0.05Fe0.7P0.45Si0.5B0.05
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. SEM Analysis
2.2. XRD Analysis
2.3. Thermal Analysis
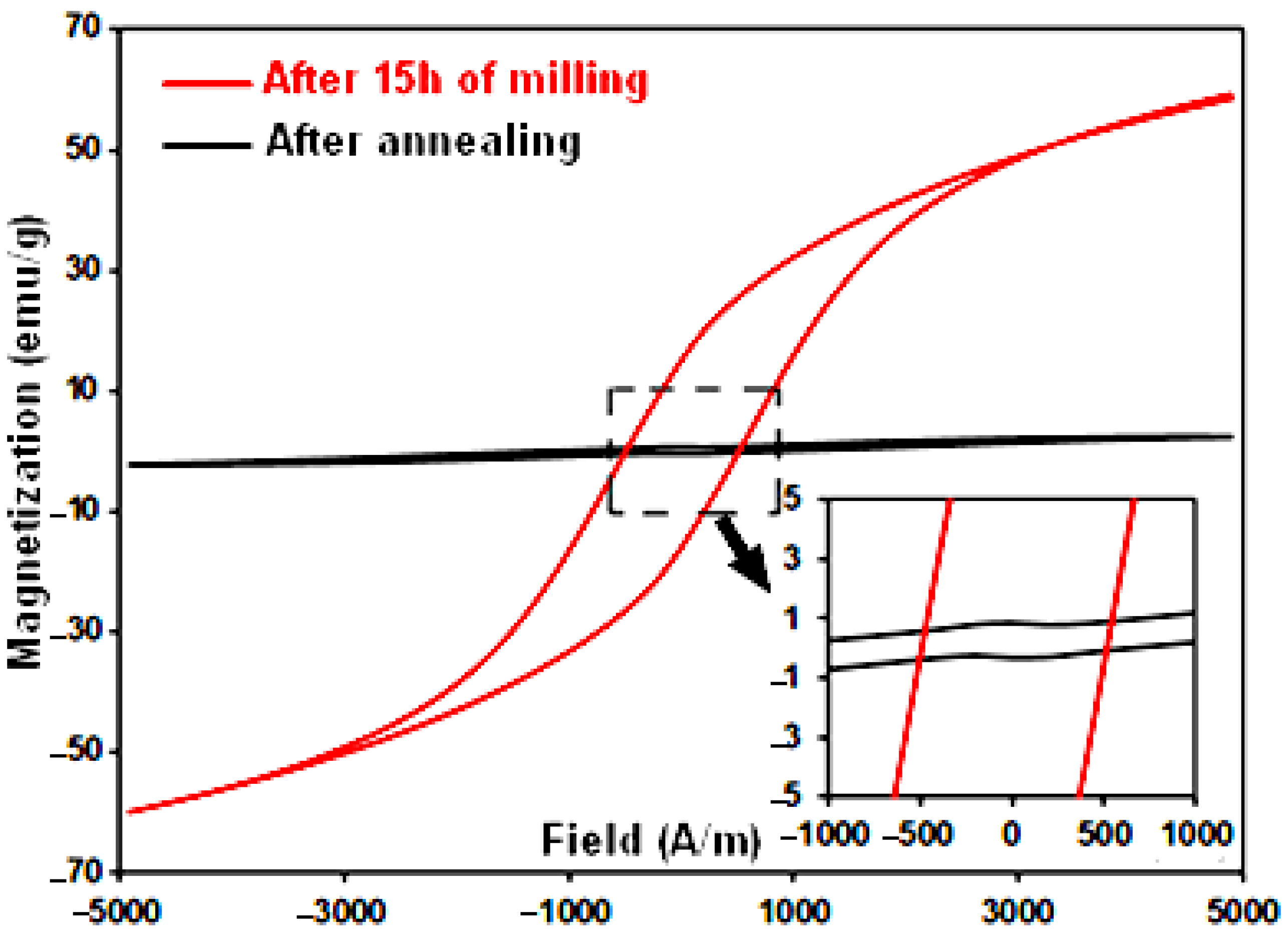
2.4. Magnetic Analysis
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brück, E. Developments in magnetocaloric refrigeration. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2005, 38, R381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brück, E.; Tegus, O.; Thanh, D.T.C.; Buschow, K.H.J. Magnetocaloric refrigeration near room temperature (invited). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2007, 310, 2793–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegus, O.; Bruck, E.; Buschow, K.H.J.; De Boer, F.R. Transition-metal-based magnetic refrigerants for room-temperature applications. Nat. Lond. 2002, 415, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gschneidner, K.A.; Pecharsky, V.K.; Tsokol, A.O. Recent developments in magnetocaloric materials. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2005, 68, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brück, E.; Tegus, O.; Thanh, D.T.C.; Trung, N.T.; Buschow, K.H.J. A review on Mn-based materials for magnetic refrigeration: Structure and properties. Int. J. Refrig. 2008, 31, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutfleisch, O.; Willard, M.A.; Brück, E.; Chen, C.H.; Sankar, S.G.; Liu, J.P. Magnetic Materials and Devices for the 21st Century: Stronger, Lighter, and More Energy Efficient. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trung, N.T.; Gortenmulder, Z.Q.; Ou, T.J.; Tegus, O.; Buschow, K.H.J.; Brück, E. Tunable thermal hysteresis in MnFe(P,Ge) compounds. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 102513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschall, T.; Skokov, K.P.; Fries, M.; Taubel, A.; Radulov, I.; Scheibel, F.; Benke, D.; Riegg, S.; Gutfleisch, O. Making a cool choice: The materials library of magnetic refrigeration. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1901322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillou, F.; Porcari, G.; Yibole, H.; van Dijk, N.; Brück, E. Taming the first-order transition in giant magnetocaloric materials. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 2671–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.F.; Caron, L.; Roy, P.; Dung, N.H.; Zhang, L.; Kockelmann, W.A.; De Groot, R.A.; van Dijk, N.H.; Brück, E. Tuning the phase transition in transition-metal-based magnetocaloric compounds. Phys. Rev. B 2014, 89, 174429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, L.; Trung, N.T.; Brück, E. Pressure-tuned magnetocaloric effect in Mn0.93Cr0.07CoGe. Phys. Rev. B 2011, 84, 020414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillou, F.; Wilhelm, F.; Tegus, O.; Rogalev, A. Microscopic mechanism of the giant magnetocaloric effect in MnCoGe alloys probed by x-ray magnetic circular dichroism. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 108, 122405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Gong, Y.Y.; Xu, G.Z.; Peng, G.; Shah, I.A.; UlHassan, N.; Xu, F. Realization of magnetostructural coupling by modifying structural transitions in MnNiSiCoNiGe system with a wide Curie-temperature window. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.K.; Wang, W.H.; Feng, L.; Zhu, W.; Li, G.J.; Chen, J.L.; Zhang, H.W.; Wu, G.H.; Jiang, C.B.; Xu, H.B.; et al. Stable magnetostructural coupling with tunable magnetoresponsive effects in hexagonal ferromagnets. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, V.; Fredbrick, C.G. Magnetic and crystallographic properties of ternary manganese silicides with ordered Co2P structure. Phys. Status Solidi A 1973, 20, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dung, N. Moment Formation and Giant Magnetocaloric Effects in Hexagonal Mn-Fe-P-Si Compounds. Ph.D. Thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wada, H.; Takahara, T.; Katagiri, K.; Ohnishi, T.; Soejima, K.; Yamashita, K. Recent progress of magnetocaloric effect and magnetic refrigerant materials of Mn compounds (invited). J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 117, 172606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillou, F.; Yibole, H.; van Dijk, N.H.; Brück, E. Effect of boron substitution on the ferromagnetic transition of MnFe0.95P2/3Si1/3. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 632, 717–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillou, F.; Yibole, H.; van Dijk, N.; Zhang, L.; Hardy, V.; Brück, E. About the mechanical stability of MnFe(P,Si,B) giant-magnetocaloric materials. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 617, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.F.; Hu, S.Y.; Xu, F.; Brück, E. Overview of magnetoelastic coupling in (Mn,Fe)2(P, Si)-type magnetocaloric materials. Rare Met. 2018, 37, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, S.; Asano, S.; Ishida, S. Electronic and magnetic properties of X2Mn1-xVxSi (X = Fe, Co). J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1994, 63, 1881–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rundqvist, S. X-ray investigations of Mn3P, Mn2P, and Ni2P. Acta Chem. Scand. 1962, 16, 992–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhanga, F.; Taake, C.; Huang, B.; You, X.; Ojiyed, H.; Shen, Q.; Dugulan, I.; Caronb, L.; Dijka, N.V.; Brück, E. Magnetocaloric effect in the (Mn,Fe)2(P,Si) system: From bulk to nano. Acta Mater. 2022, 224, 117532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.F.; Caron, L.; Cedervall, J.; Gubbens, P.C.M.; Dalmas de Réotier, P.; Yaouanc, A.; Qian, F.; Wildes, A.R.; Luetkens, H.; Amato, A.; et al. Short-range magnetic correlations and spin dynamics in the paramagnetic regime of (Mn,Fe)2(P, Si). Phys. Rev. B 2016, 94, 014426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, R.; Khitouni, M.; Kolsi, A.W.; Njah, N. The studies of crystallite size and microstrains in aluminum powder prepared by mechanical milling. Phys. Stat. Solidi C 2006, 3, 3325–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khitouni, M.; Kolsi, A.W.; Njah, N. The effects of boron additions on the disordering and crystallite refinement of Ni3AI powders during mechanical milling. Ann. De Chim. Sci. Matériaux 2003, 28, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berak, J.; Heumann, T. Über das System Mangan-Phosphor. Int. J. Mater. Res. 1950, 41, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.W.; Zheng, Z.G.; Huang, B.W.; Yu, H.Y.; Qiu, Z.G.; Mao, Y.L.; Zhang, S.; Xiao, F.M.; Zeng, D.C.; Goubitz, K.; et al. Microstructure formation and magnetocaloric effect of the Fe2P-type phase in (Mn,Fe)2(P, Si, B) alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 735, 2567–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowley, C.; Rode, K.; Lau, Y.C.; Thiyagarajah, N.; Betto, D.; Borisov, K.; Atcheson, G.; Kampert, E.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, Y.; et al. Magnetocrystalline anisotropy and exchange probed by high-field anomalous Hall effect in fully compensated half-metallic Mn2RuxGa thin films. Phys. Rev. B 2018, 98, 220406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betto, D.; Lau, Y.C.; Borisov, K.; Kummer, K.; Brookes, N.B.; Stamenov, P.; Coey, J.M.D.; Rode, K. Structure, site-specific magnetism, and magnetotransport properties of epitaxial D022-structure Mn2FexGa thin films. Phys. Rev. B 2017, 96, 024408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, E.E.; Bocarsly, J.D.; Grebenkemper, J.H.; Issa, R.; Wilson, S.D.; Pollock, T.M.; Seshadri, R. Structural coupling and magnetic tuning in Mn2−xCoxP magnetocalorics for thermomagnetic power generation. APL Mater. 2020, 8, 041106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Singh, V.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Lee, S.-C.; Singh, S.; Pandey, D. Effect of heat treatment on the phase purity of Fe2P powder. AIP Conf. Proc. 2020, 2265, 030021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutfleisch, O.; Gottschall, T.; Fries, M.; Benke, D.; Radulov, I.; Skokov, K.P.; Wende, H.; Gruner, M.; Acet, M.; Entel, P.; et al. Mastering hysteresis in magnetocaloric materials. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2016, 374, 20150308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, G.B.; McCormick, P.G. Mechanical alloying. Mater. Forum 1992, 16, 91–97. [Google Scholar]
- Coey, J.M.D. Magnetic materials. J. Alloys Compd. 2001, 326, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degauque, J. Magnétisme et matériaux magnétiques: Introduction. J. Phys. IV 1992, 2, C3-1–C3-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowroozi, M.A.; Shokrollahi, H. The effects of milling time and heat treatment on the micro-structural and magnetic behavior of Fe42Ni28Zr8Ta2B10C10 synthesized by mechanical alloying. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2013, 335, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.B.; Fu, Z.Y.; Zhang, J.Y.; Shi, J.; Wang, W.M.; Wanga, H.; Wang, Y.C.; Zhang, Q.J. Annealing on the structure and properties evolution of the CoCrFeNiCuAl high-entropy alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2010, 502, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Wang, W.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Fu, Z. Alloying behavior and novel properties of CoCrFeNiMn high-entropy alloy fabricated by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. Intermetallics 2015, 56, 24–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.J.; Gao, S.; Han, K.; Miao, Y.D.; Qi, J.Q.; Wei, F.X.; Ren, Y.J.; Zhan, Z.Z.; Sui, Y.W.; Sun, Z.; et al. Effects of minor B addition on microstructure and properties of Al19Co20Fe20Ni41 eutectic high-entropy alloy. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2021, 31, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.F.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Chen, G.L. Novel microstructure and properties of multicomponent CoCrCuFeNiTix alloys. Intermetallics 2007, 15, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zuo, T.T.; Tang, Z.; Gao, M.C.; Dahmen, K.A.; Liaw, P.K.; Lu, Z.P. Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2014, 61, 1–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, S.R.; Ogale, S.B.; Higgins, J.S.; Zheng, H.; Millis, A.J.; Kulkarni, V.N.; Ramesh, R.; Greene, R.L.; Venkatesan, T. Co-occurrence of superparamagnetism and anomalous Hall effect in highly reduced cobalt-doped rutile TiO2−δ films. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 166601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, H.; Hokabe, T.; Kamigaichi, T.; Okamoto, T. Magnetic Properties of Fe2P Single Crystal. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 1977, 43, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Tan, F.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, F. A novel strategy to fabricate gamma-Fe2O3-MWCNTs hybrids with selectively ferromagnetic or superparamagnetic properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 454, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, J.P.; Zhang, Q.; Altounian, Z. Fe magnetic moment formation and exchange interaction in Fe2P: A first-principles study. Phys. Lett. A 2013, 377, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolotti, M.; Lutterotti, L.; Pepponi, G. Combining XRD and XRF analysis in one Rietveld-like fitting. Powder Diffr. 2017, 32, S225–S230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietveld, H.M. A profile refinement method for nuclear and magnetic structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1969, 2, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, B.E.; Averbach, B.L. The Effect of Cold-Work Distortion on X-ray Patterns. J. Appl. Phys. 1950, 21, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, G.K.; Hall, W.H. X-ray line broadening from filed aluminium and wolfram. Acta Metall. 1953, 1, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
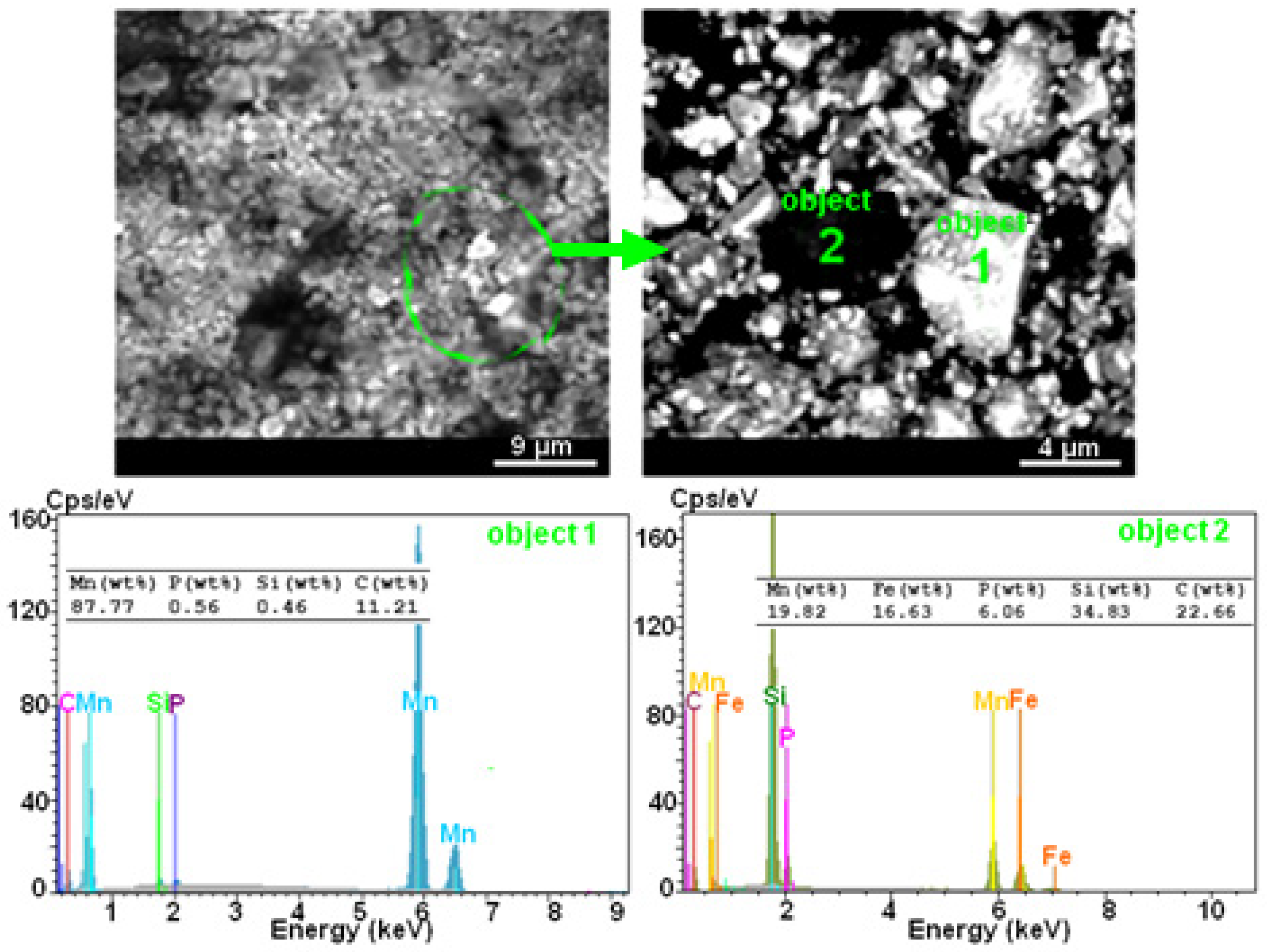
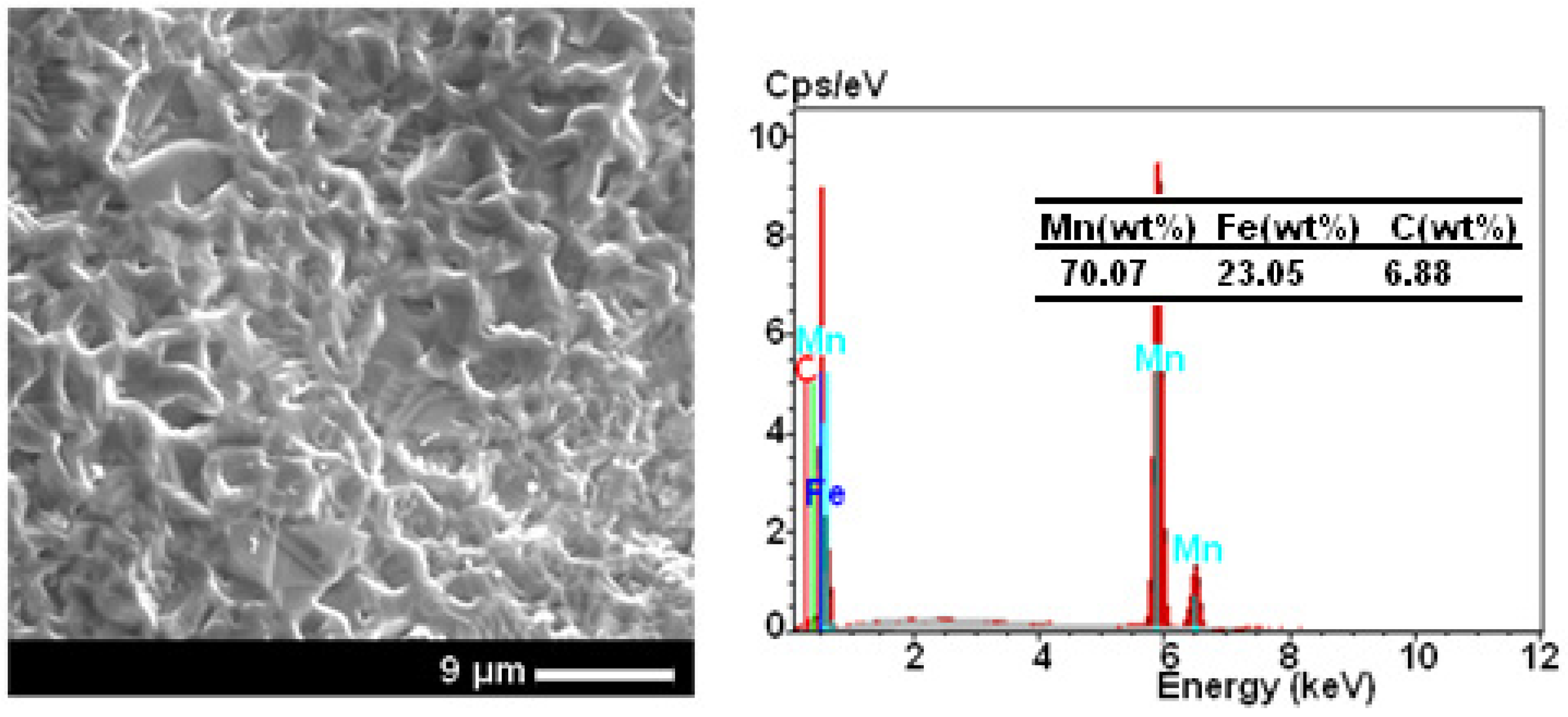

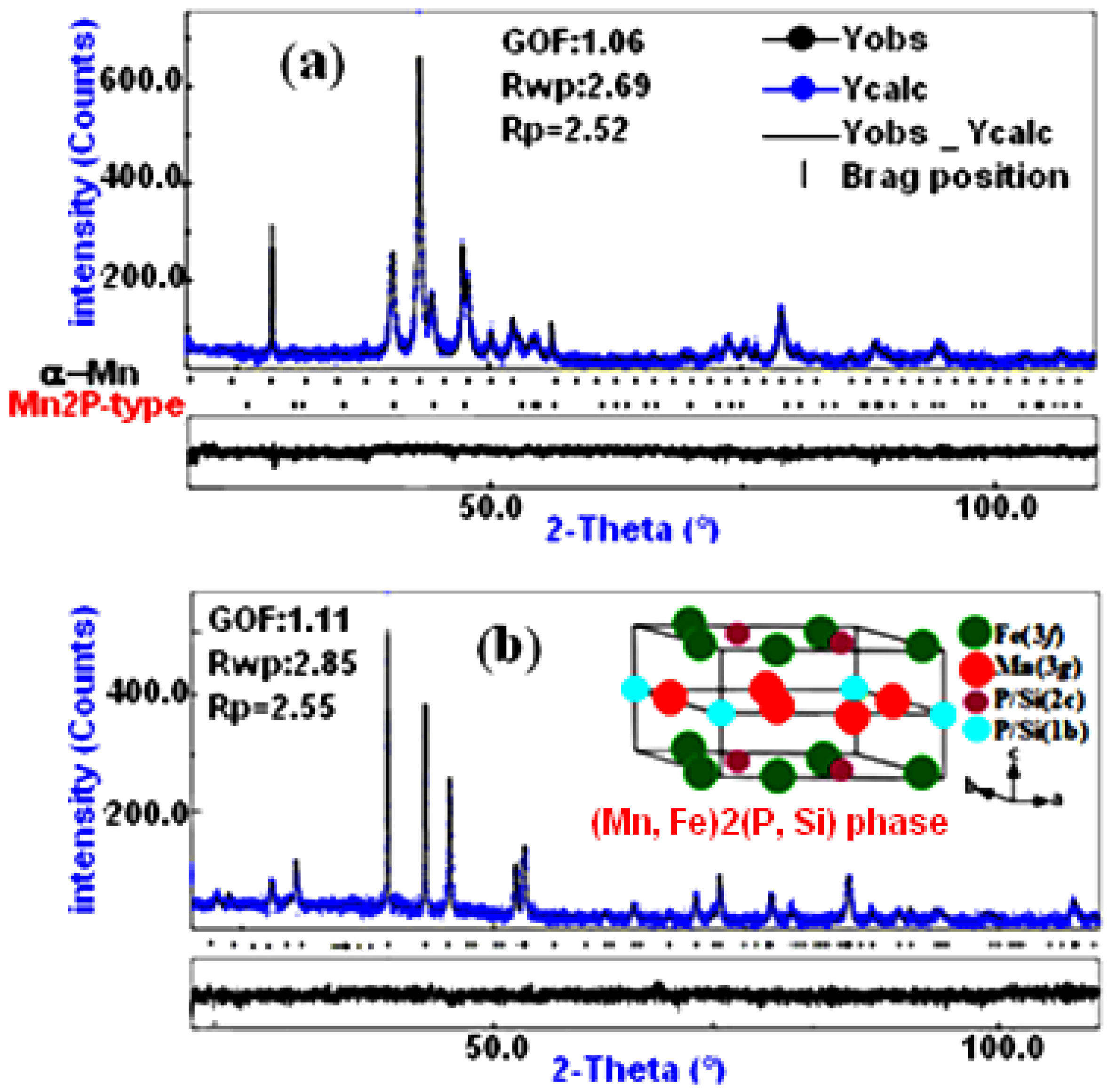
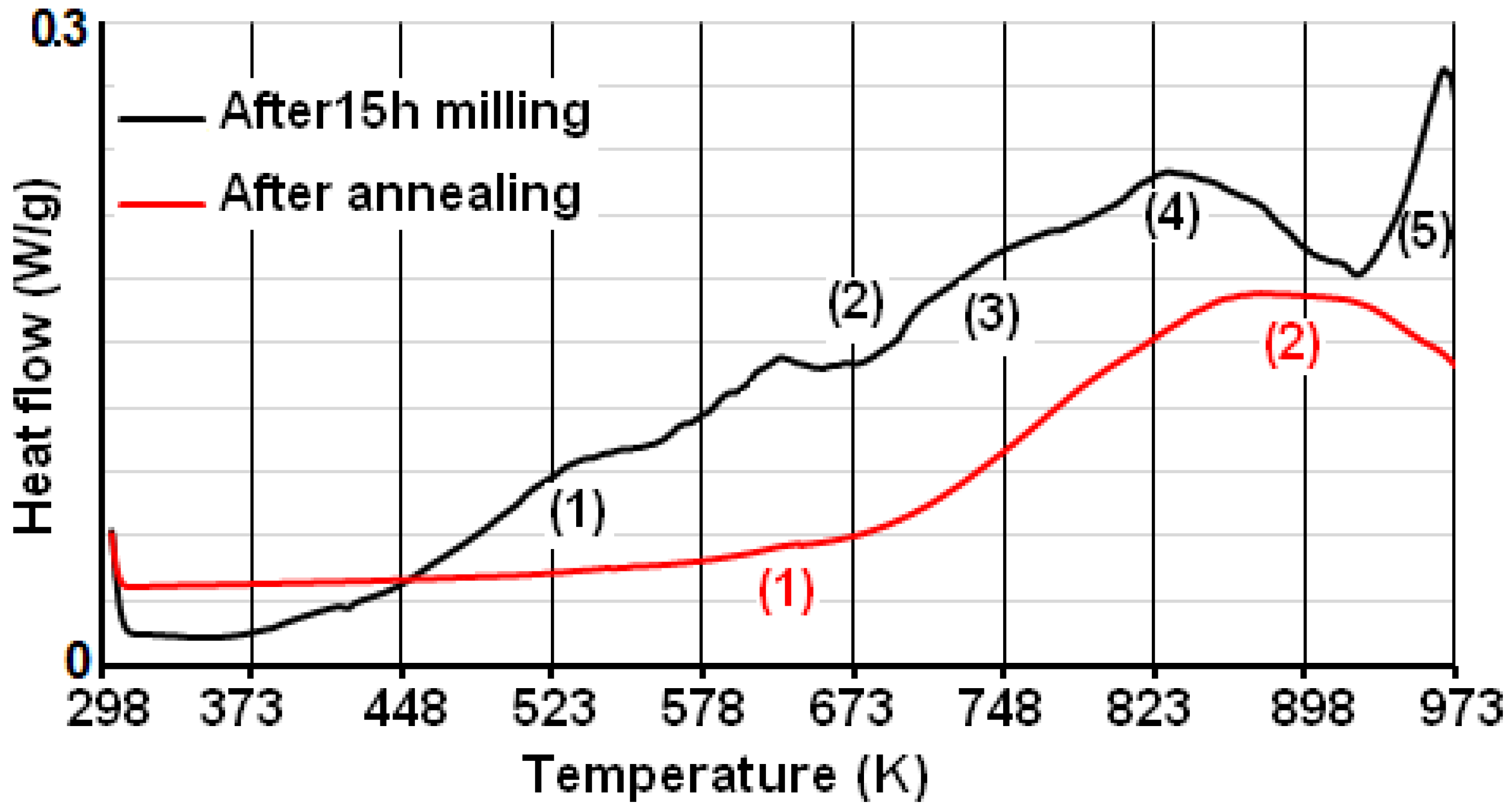
| Powder | Phase Type | a (nm) | c (nm) | c/a | Phase (%) | D (nm) | ε (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Milled powder | α-Mn3Fe2Si | 0.8935 (1) | - | - | 17.1 | 15 | 0.870 |
| hcp-Mn2P | 0.5875 (1) | 0.3642 (1) | 0.61 | 82.9 | 25 | 0.650 | |
| Annealed powder | hcp-(Mn,Fe)2(P,Si) | 0.6071 (1) | 0.3460 (1) | 0.56 | 100.0 | 95 | 0.085 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khitouni, N.; Almoneef, M.M.; Mili, A.; Khitouni, M.; Wederni, A.; Suñol, J.-J. Mechano-Synthesis, Structure, and Thermal and Magnetic Behaviors of the New Compound Mn1.2Co0.05Fe0.7P0.45Si0.5B0.05. Inorganics 2024, 12, 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics12030063
Khitouni N, Almoneef MM, Mili A, Khitouni M, Wederni A, Suñol J-J. Mechano-Synthesis, Structure, and Thermal and Magnetic Behaviors of the New Compound Mn1.2Co0.05Fe0.7P0.45Si0.5B0.05. Inorganics. 2024; 12(3):63. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics12030063
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhitouni, Nawel, Maha M. Almoneef, Amira Mili, Mohamed Khitouni, Asma Wederni, and Joan-Josep Suñol. 2024. "Mechano-Synthesis, Structure, and Thermal and Magnetic Behaviors of the New Compound Mn1.2Co0.05Fe0.7P0.45Si0.5B0.05" Inorganics 12, no. 3: 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics12030063
APA StyleKhitouni, N., Almoneef, M. M., Mili, A., Khitouni, M., Wederni, A., & Suñol, J.-J. (2024). Mechano-Synthesis, Structure, and Thermal and Magnetic Behaviors of the New Compound Mn1.2Co0.05Fe0.7P0.45Si0.5B0.05. Inorganics, 12(3), 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics12030063








