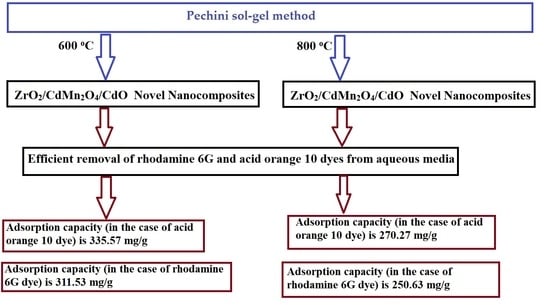
Efficient Disposal of Rhodamine 6G and Acid Orange 10 Dyes from Aqueous Media Using ZrO2/CdMn2O4/CdO as Novel and Facilely Synthesized Nanocomposites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Chemicals
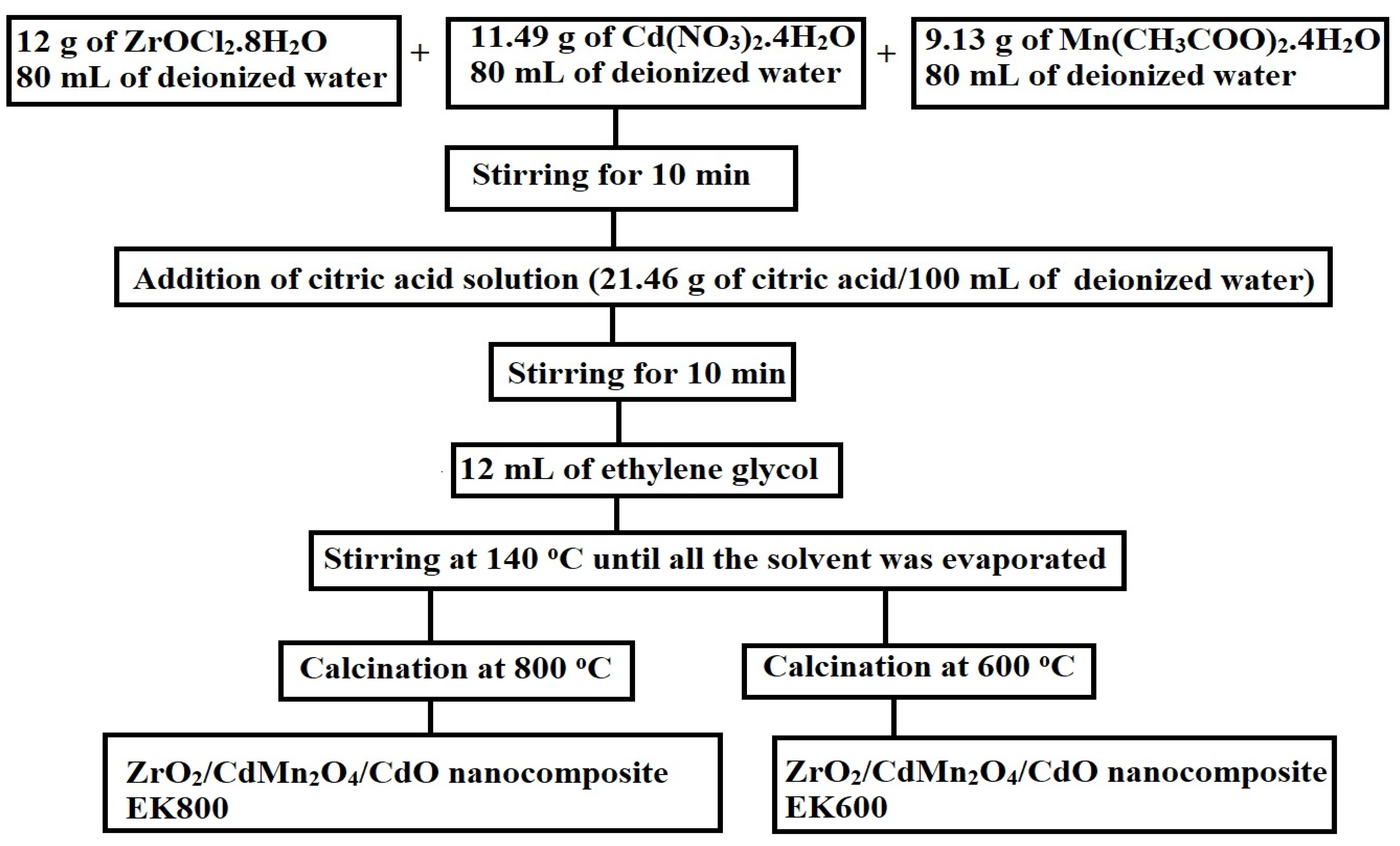
2.2. Synthesis of Adsorbents
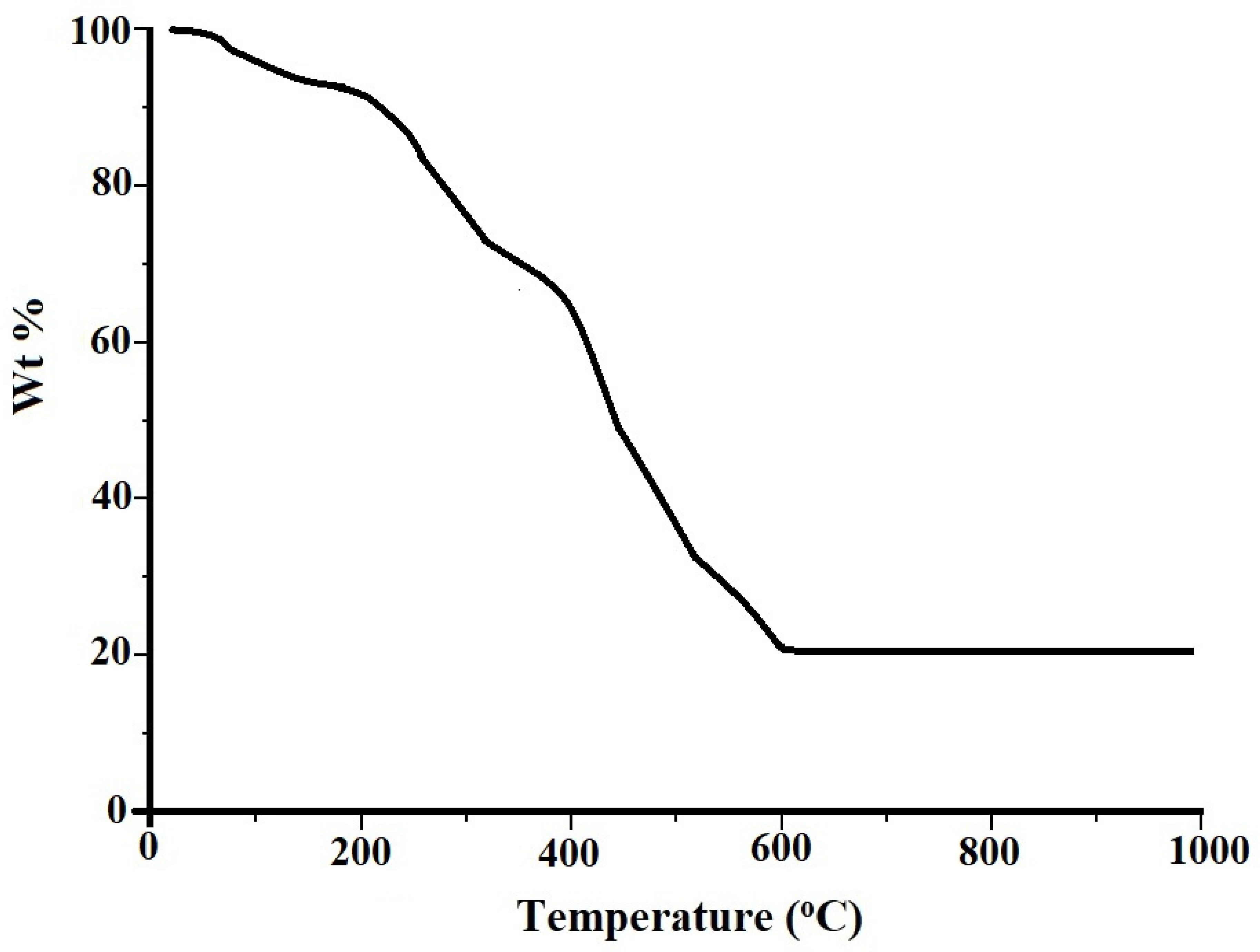
2.3. Characterization of Adsorbents
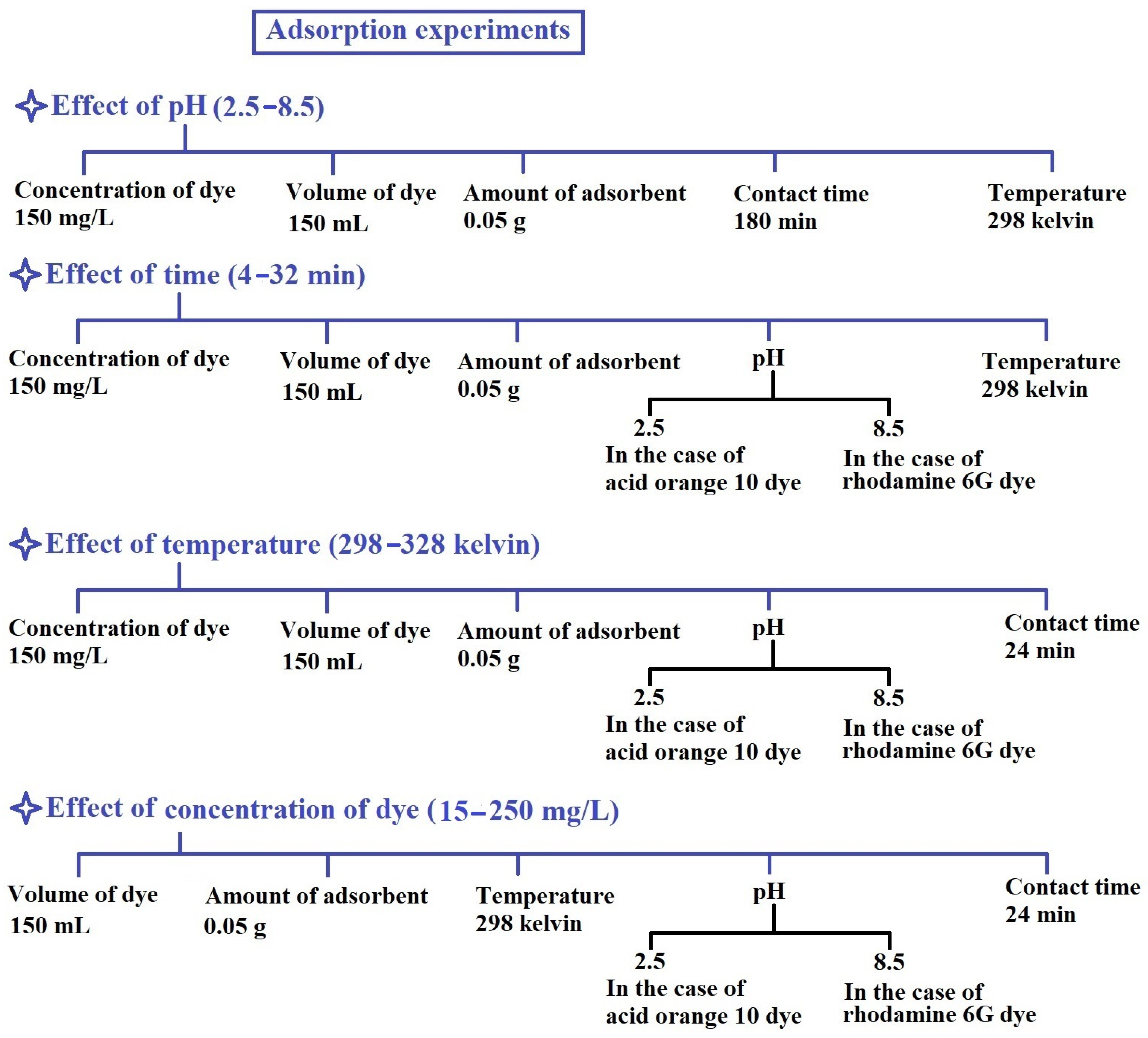
2.4. Removal of Rhodamine 6G and Acid Orange 10 Dyes from Aqueous Solutions
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of the Synthesized Samples
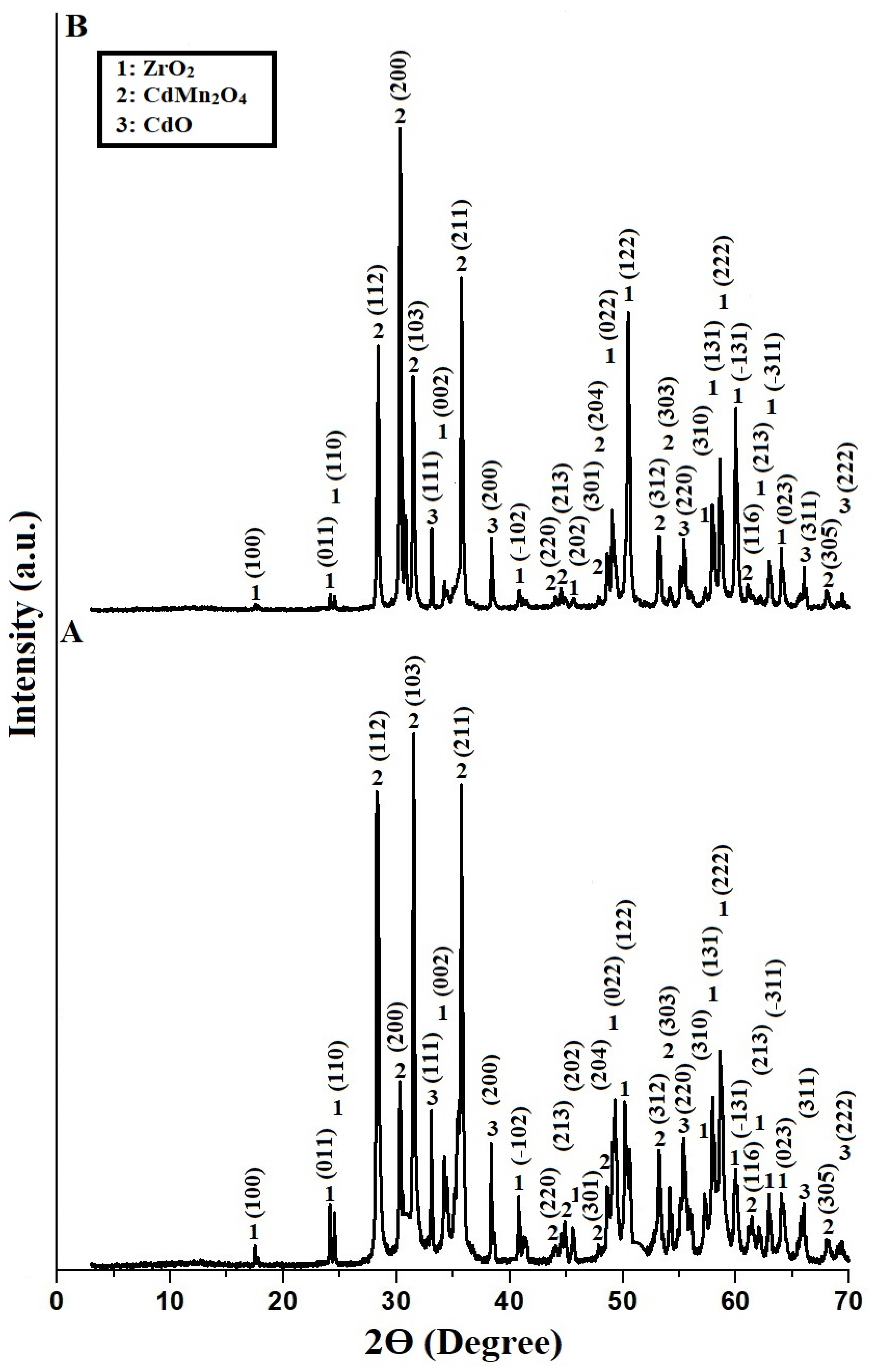
3.1.1. XRD
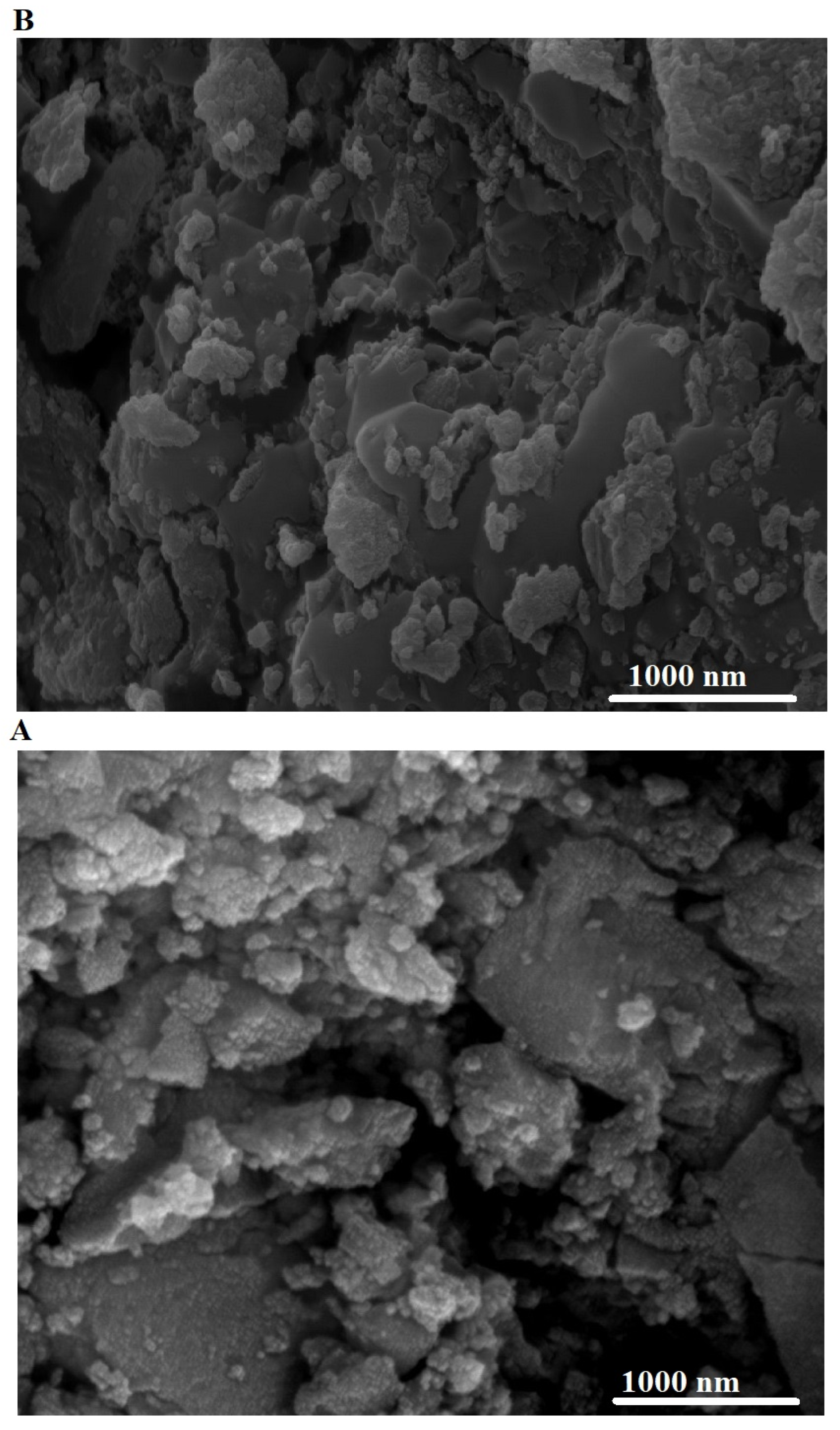
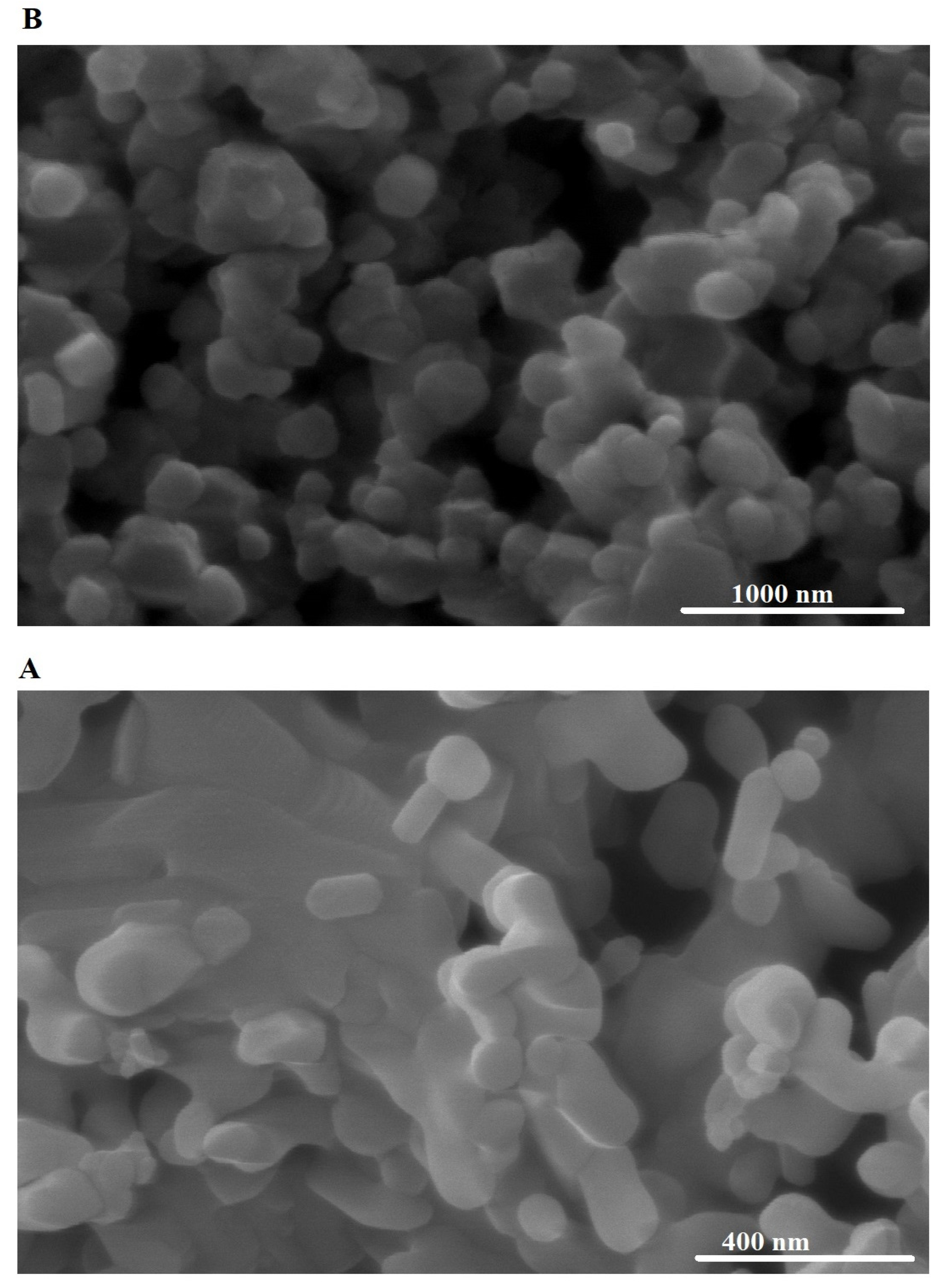
3.1.2. FE-SEM and EDS
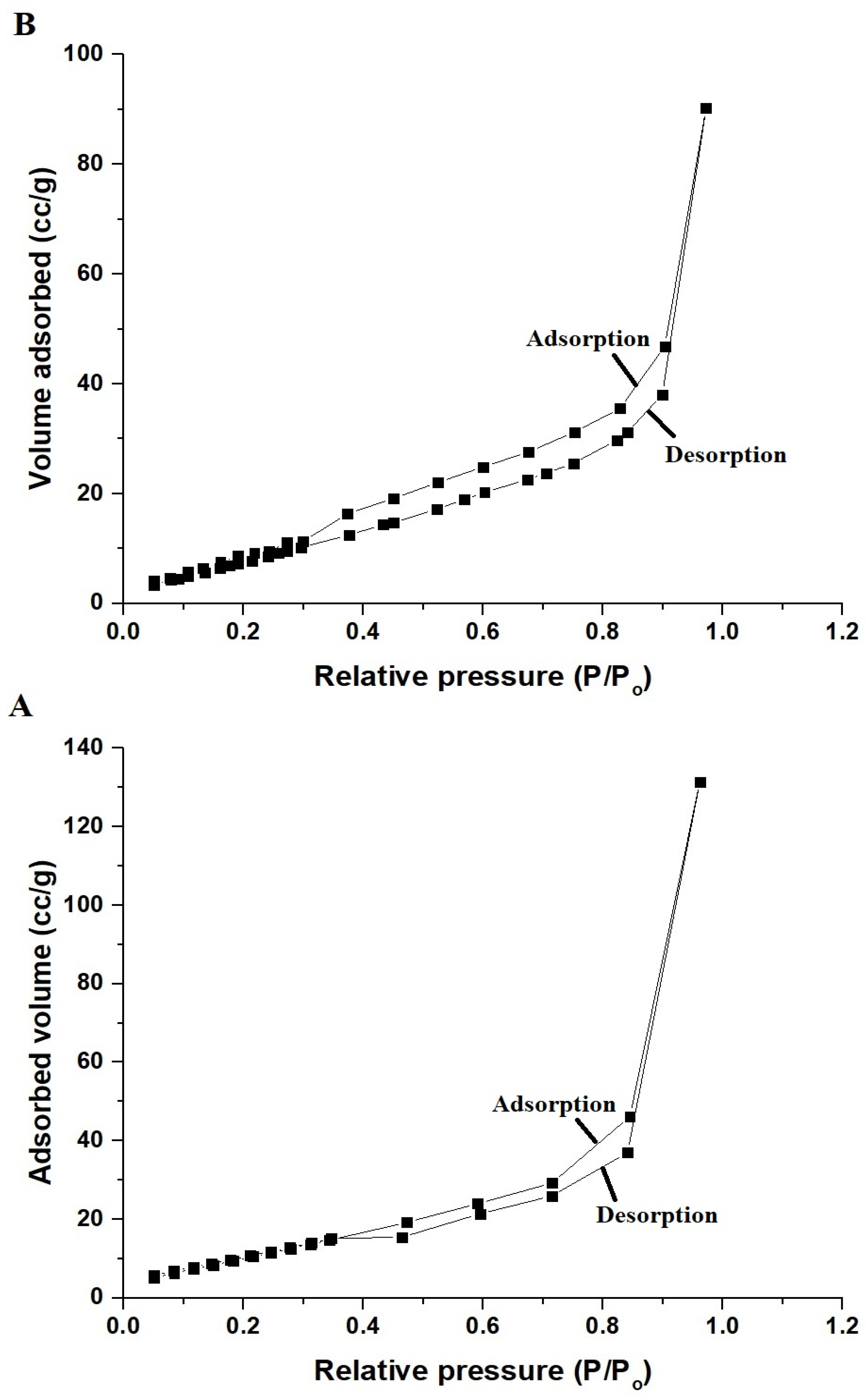
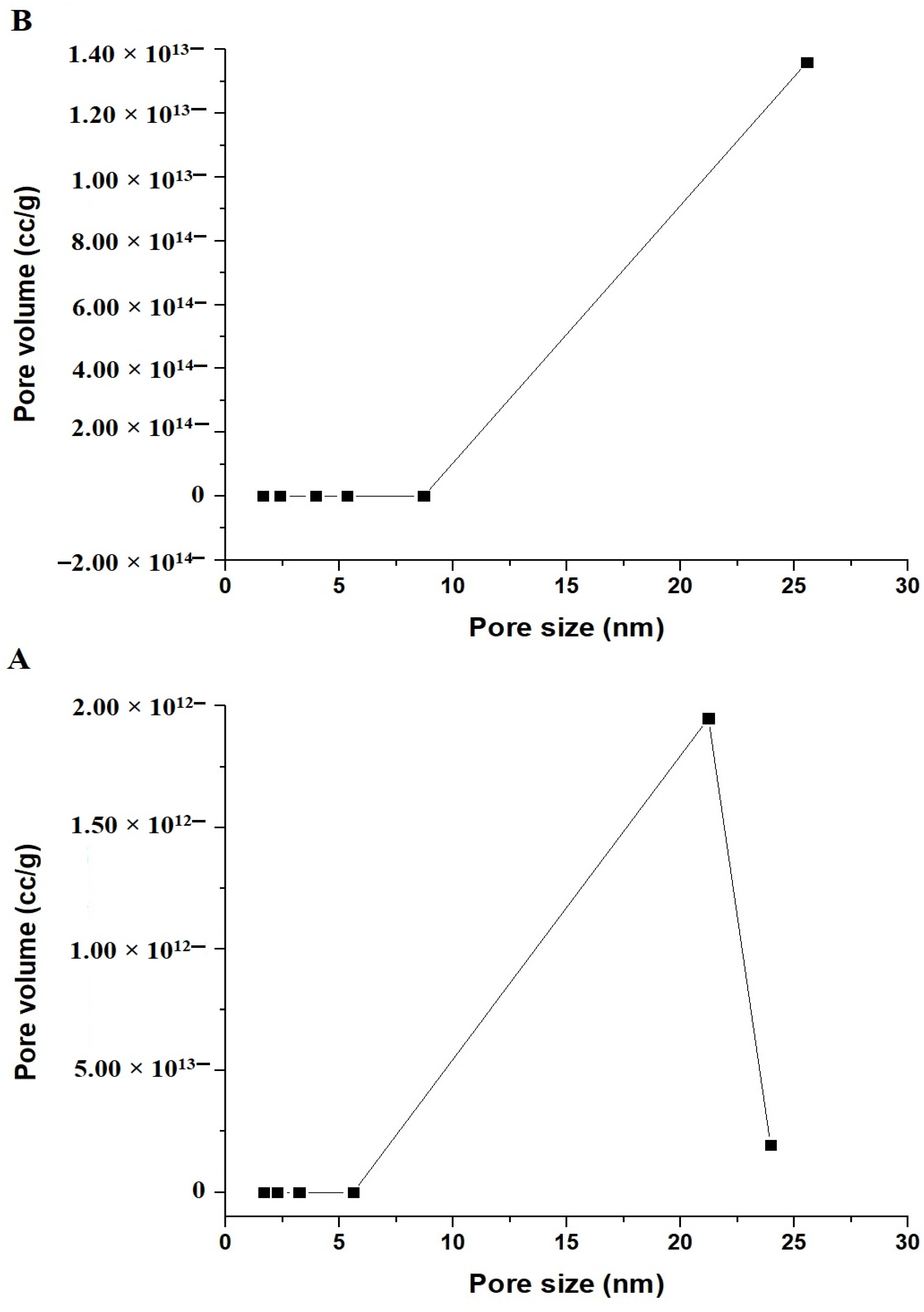
3.1.3. Nitrogen Adsorption/Desorption
3.2. Removal of Rhodamine 6G and Acid Orange 10 Dyes from Aqueous Solutions
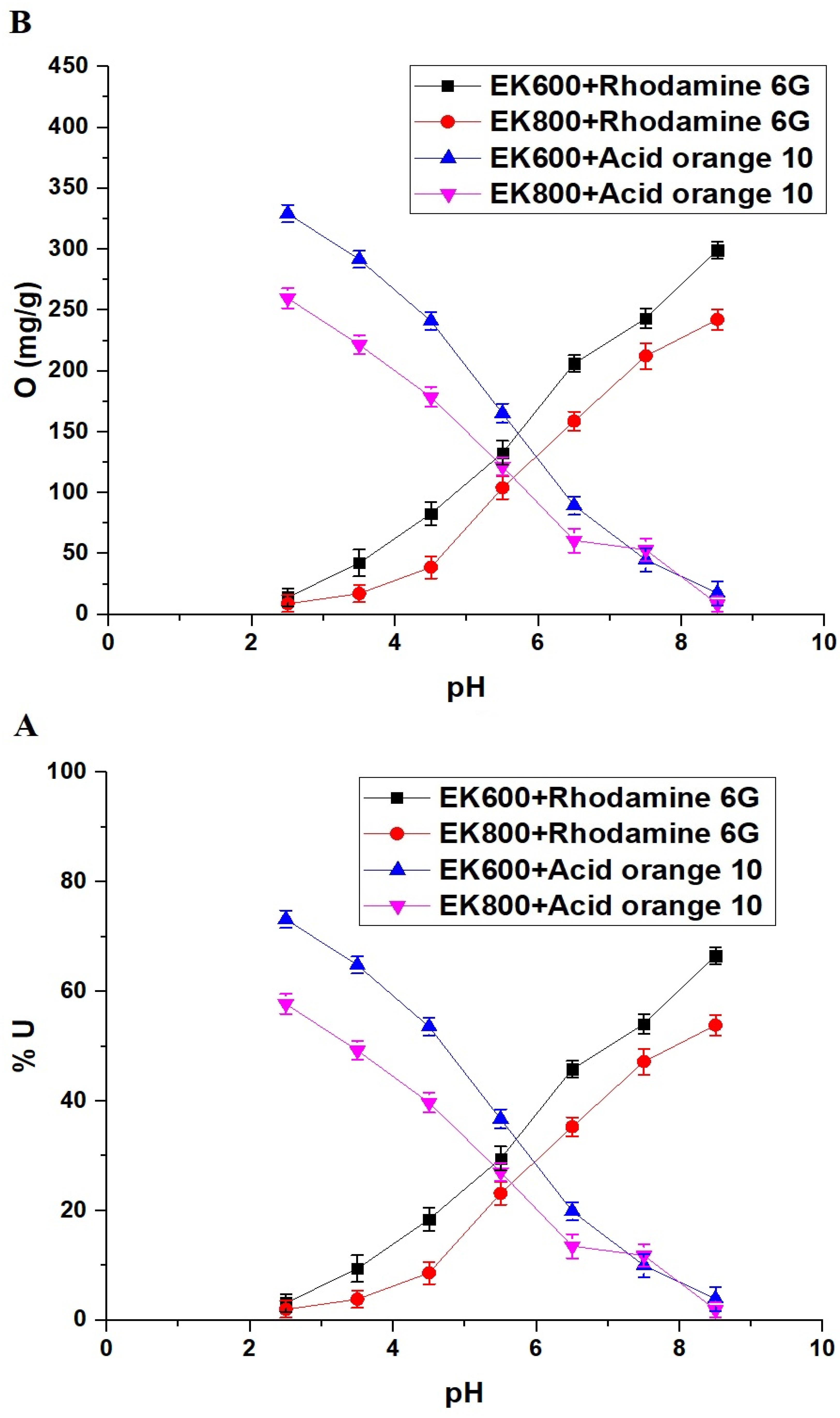
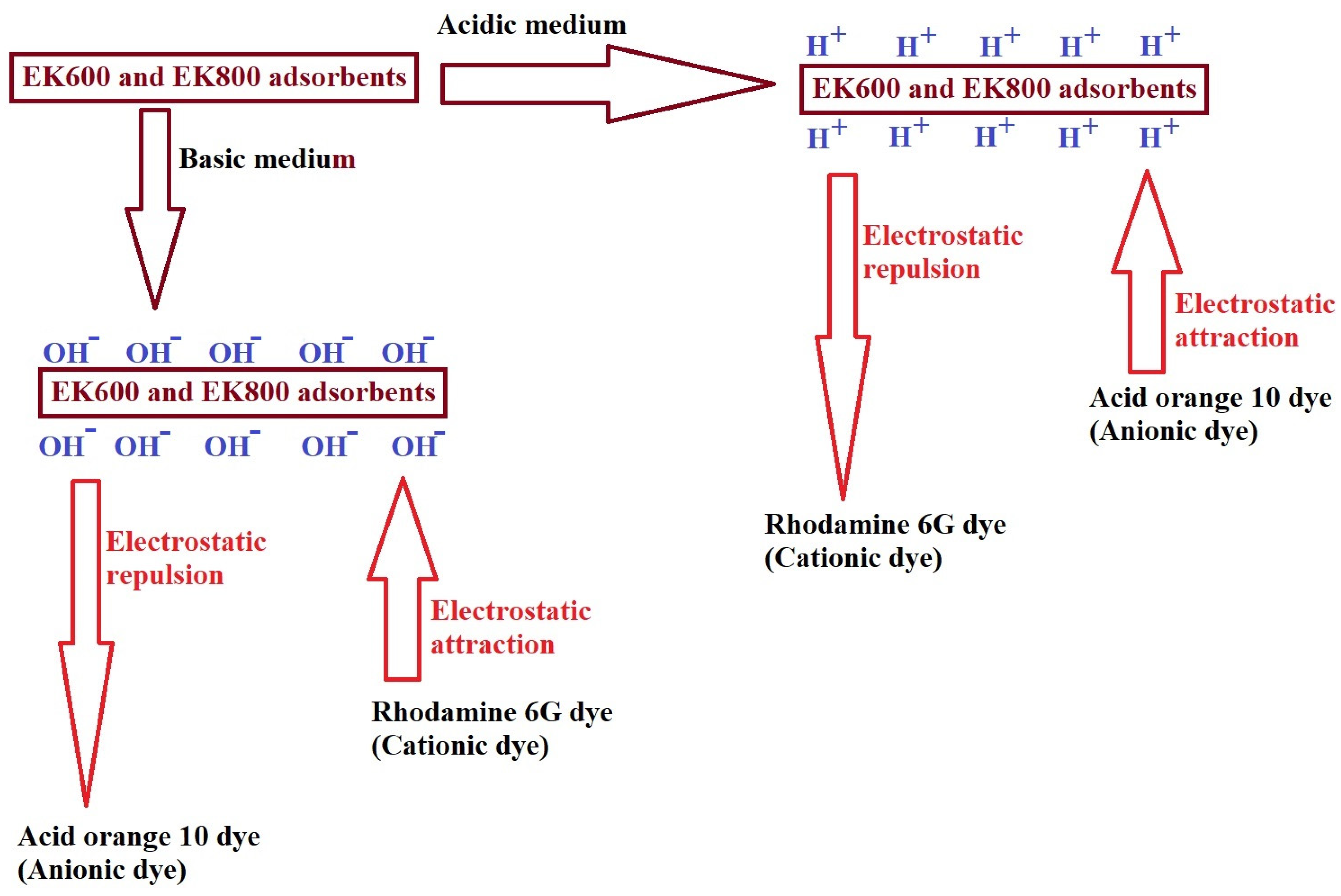
3.2.1. Effect of pH
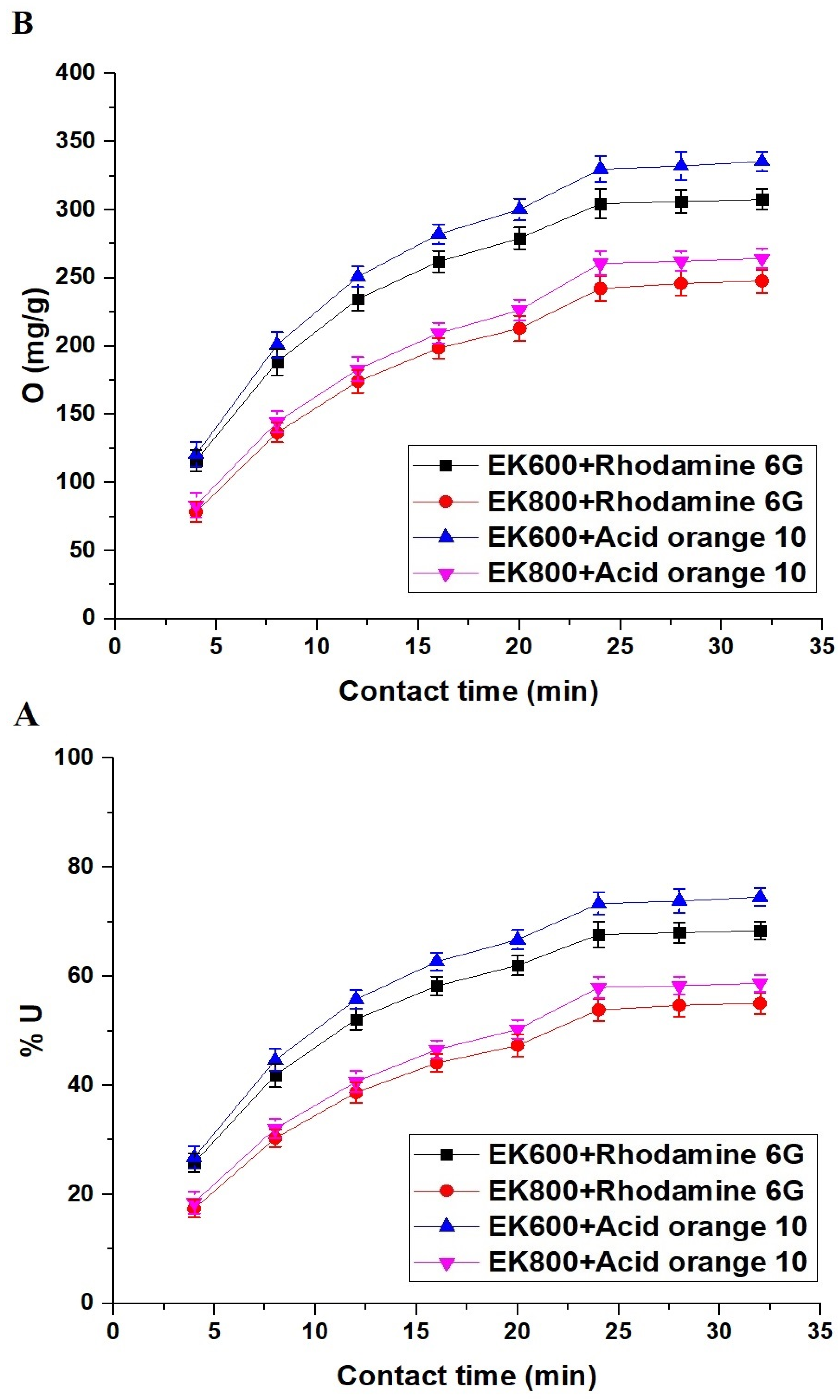
3.2.2. Effect of Contact Time
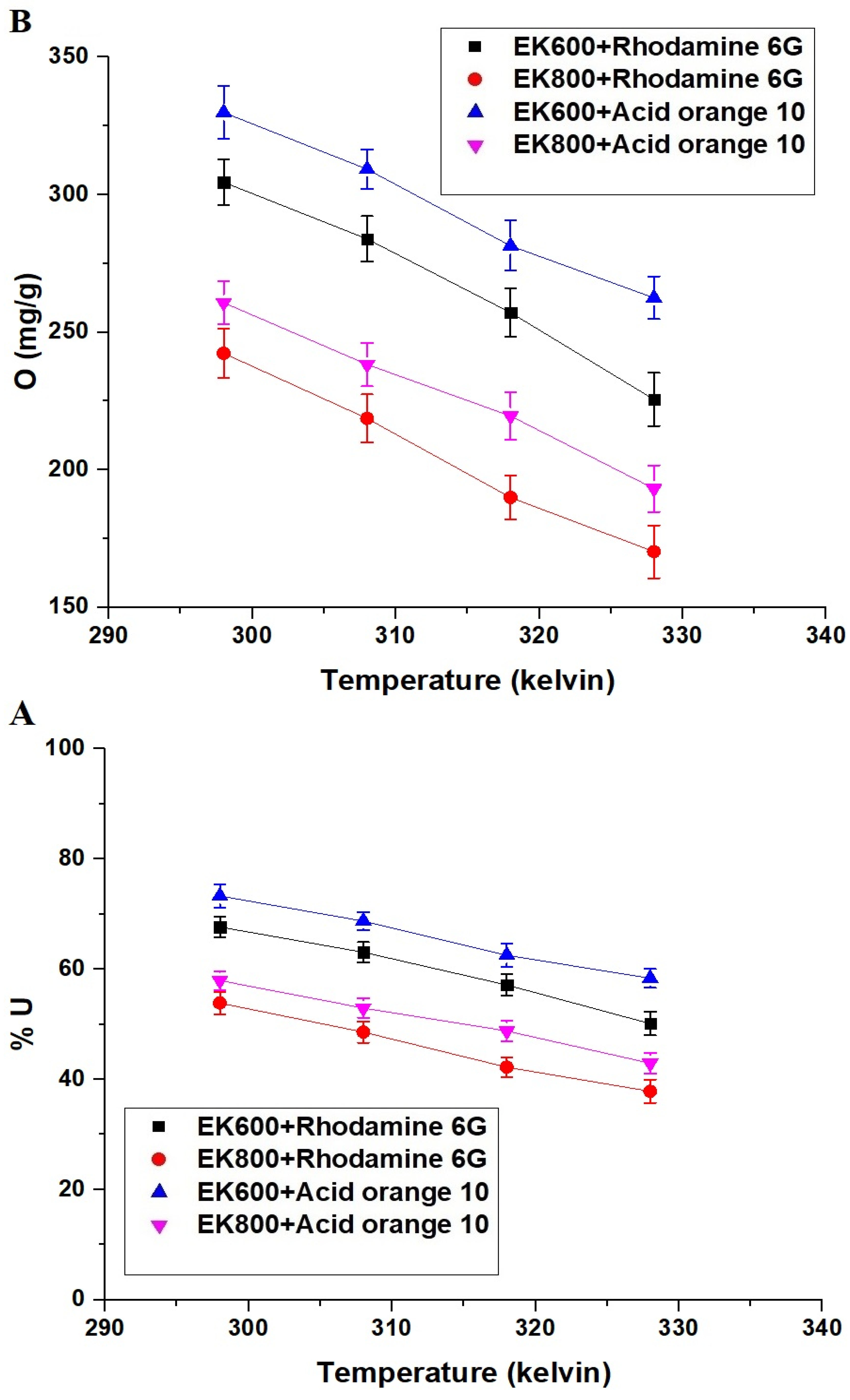
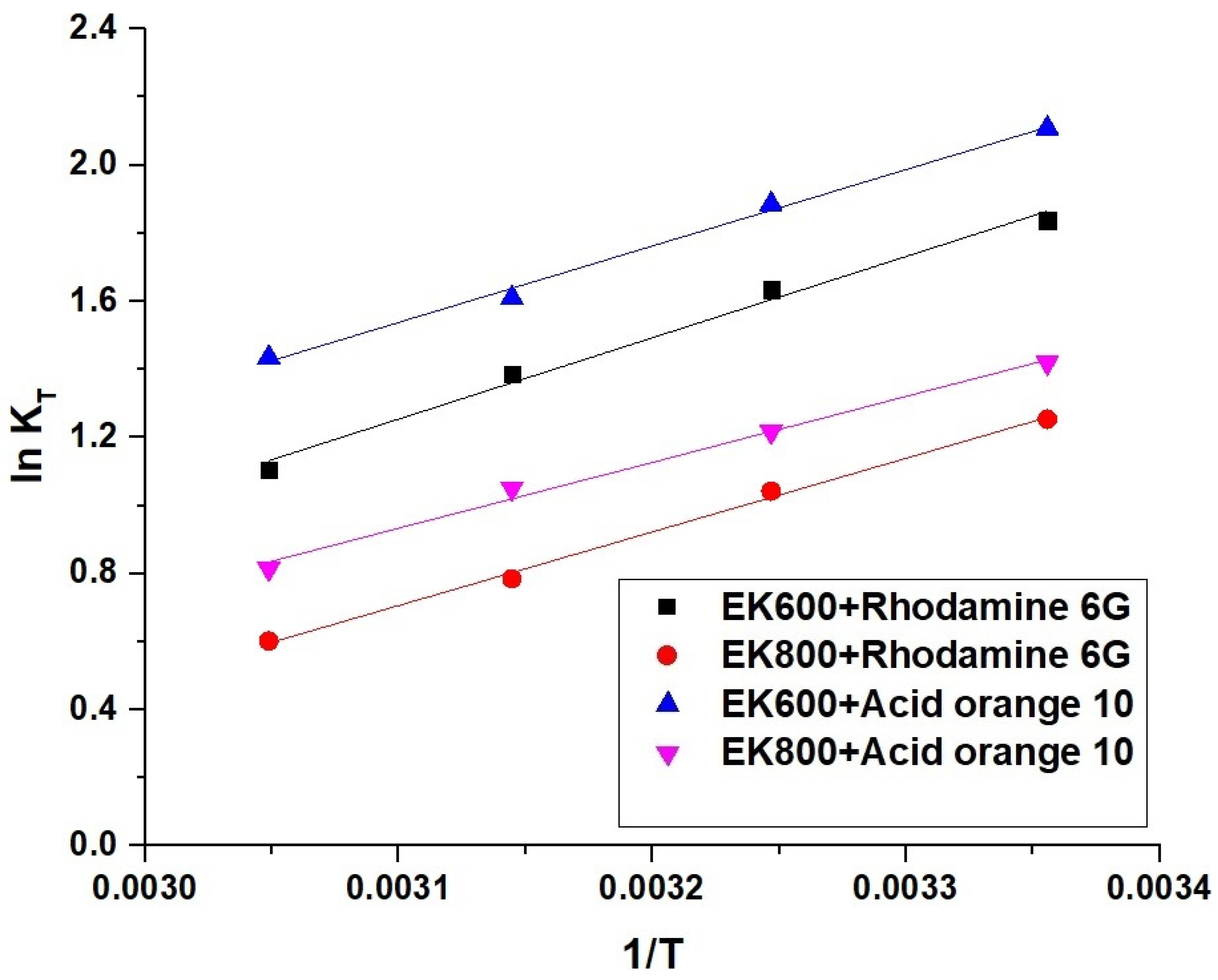
3.2.3. Effect of Temperature
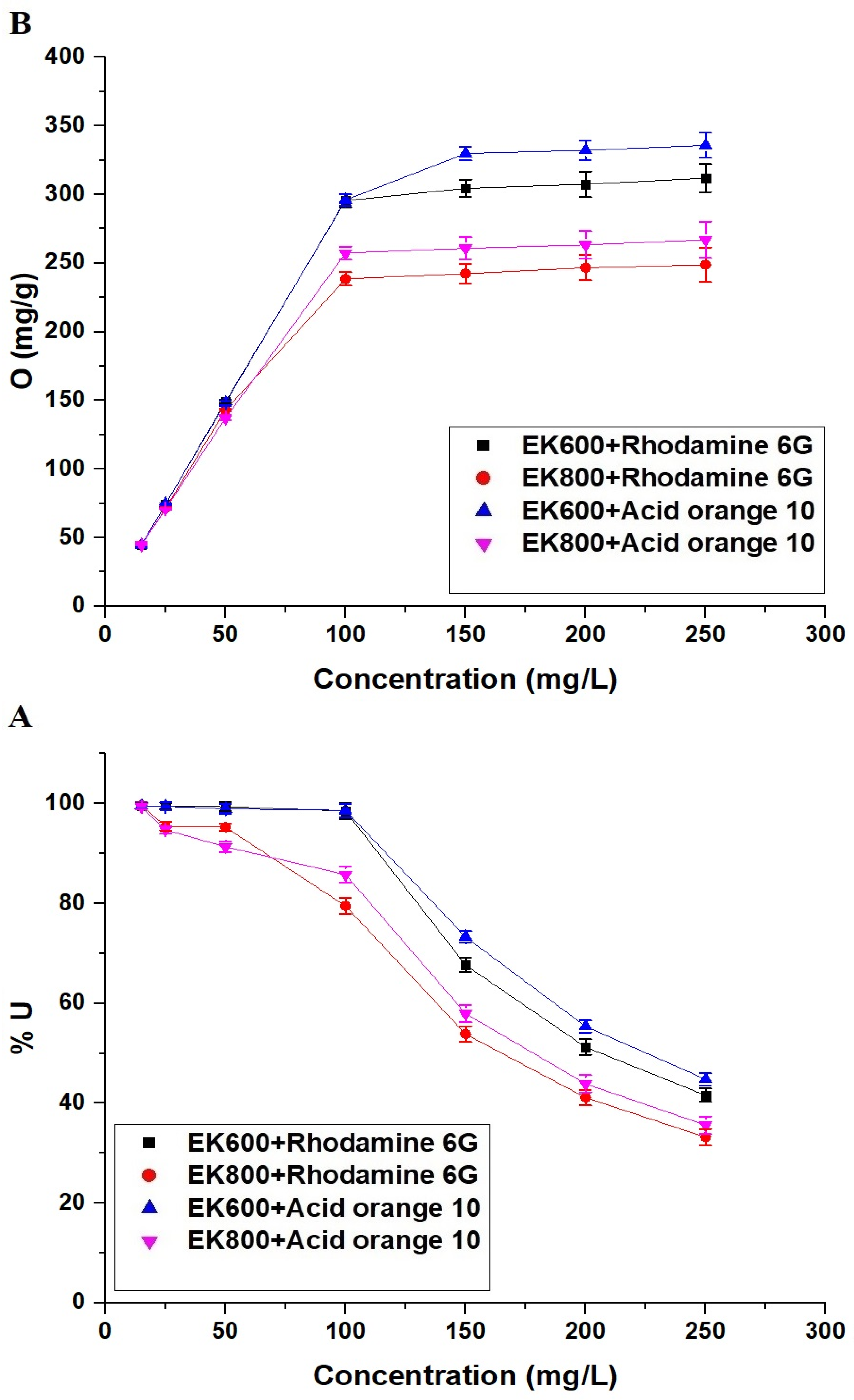
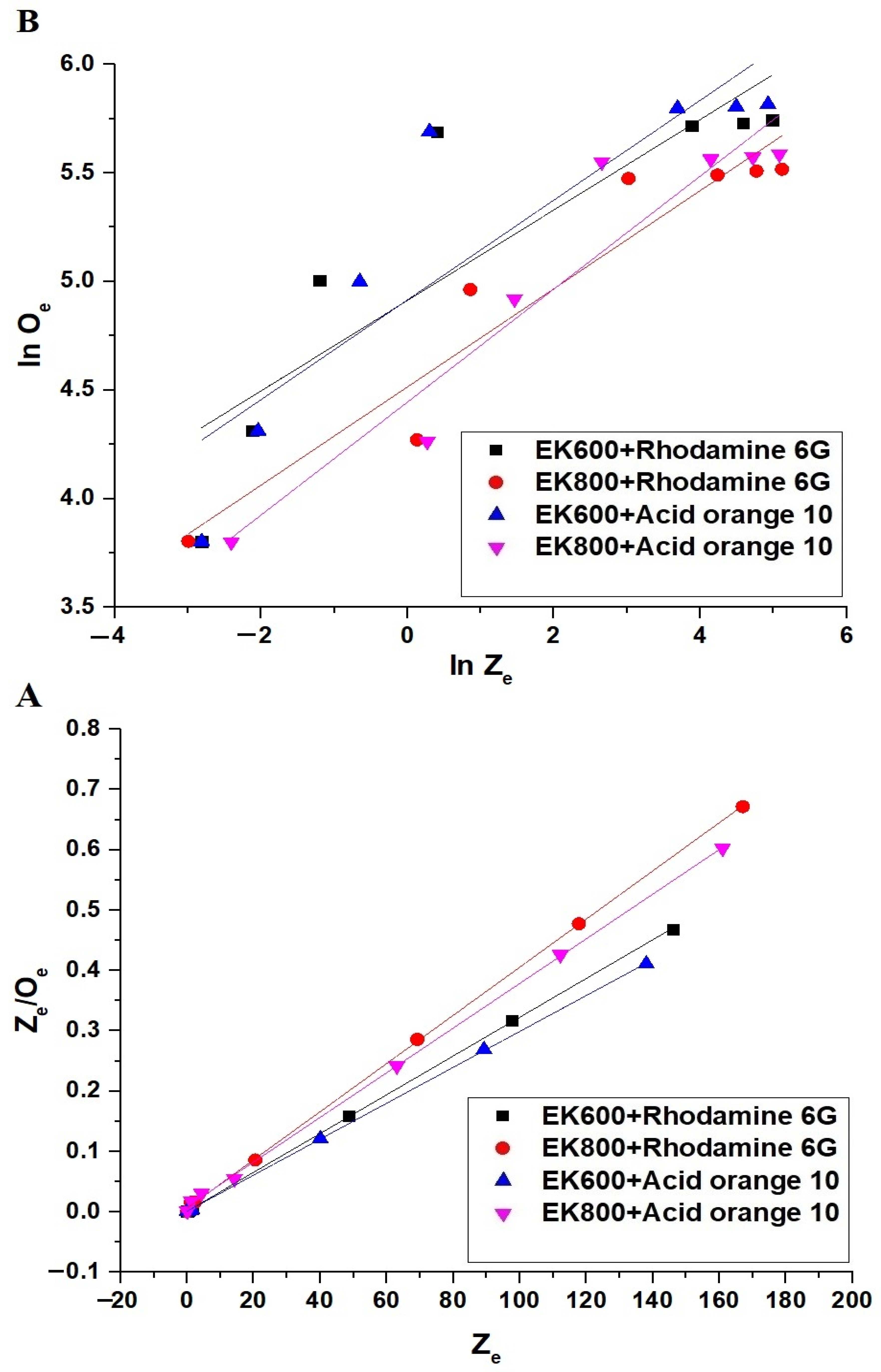
3.2.4. Effect of Dye Concentration
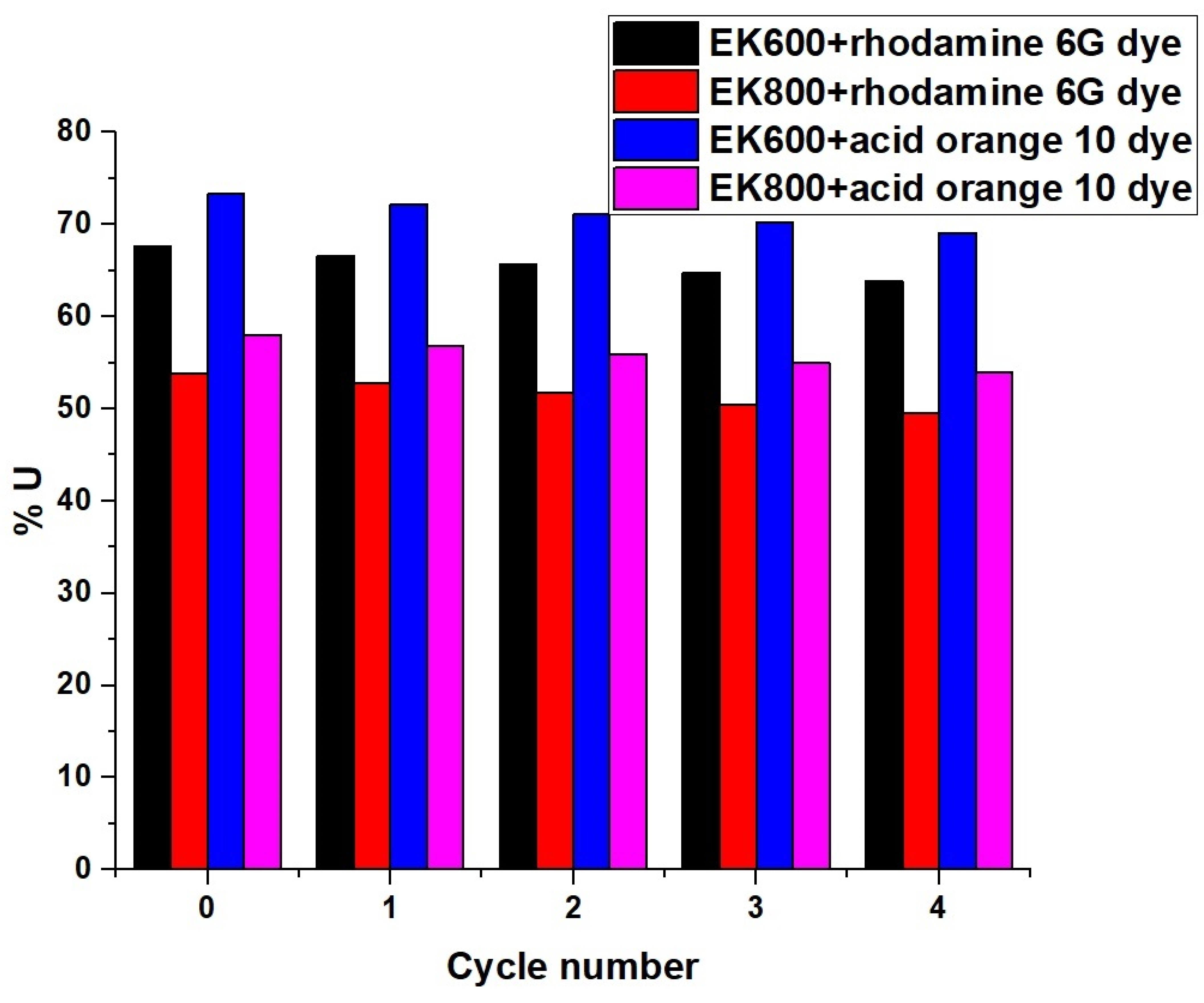
3.2.5. Effect of Desorption and Reusability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hasanpour, M.; Hatami, M. Photocatalytic Performance of Aerogels for Organic Dyes Removal from Wastewaters: Review Study. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 309, 113094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wazir, M.B.; Daud, M.; Ali, F.; Al-Harthi, M.A. Dendrimer Assisted Dye-Removal: A Critical Review of Adsorption and Catalytic Degradation for Wastewater Treatment. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 315, 113775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.F.; Khandaker, S.; Sarker, F.; Islam, A.; Rahman, M.T.; Awual, M.R. Current Treatment Technologies and Mechanisms for Removal of Indigo Carmine Dyes from Wastewater: A Review. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 318, 114061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadhom, M.; Albayati, N.; Alalwan, H.; Al-Furaiji, M. Removal of Dyes by Agricultural Waste. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2020, 16, 100259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahlot, R.; Taki, K.; Kumar, M. Efficacy of Nanoclays as the Potential Adsorbent for Dyes and Metal Removal from the Wastewater: A Review. Environ. Nanotechn. Monit. Manag. 2020, 14, 100339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Zhang, G.; Wen, J.; Li, X.; Zhu, J.; Wu, Z. Simultaneous Removal of Aqueous Same Ionic Type Heavy Metals and Dyes by a Magnetic Chitosan/Polyethyleneimine Embedded Hydrophobic Sodium Alginate Composite: Performance, Interaction and Mechanism. Chemosphere 2023, 318, 137869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiraja, N.; Saravana Sathiya Prabhahar, R.; Joshua, A. Preparation and Physio–Chemical Characterisation of Activated Carbon Derived from Prosopis Juliflora Stem for the Removal of Methylene Blue Dye and Heavy Metal Containing Textile Industry Effluent. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 397, 136579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastopoulos, I.; Ahmed, M.J.; Hummadi, E.H. Eucalyptus-Based Materials as Adsorbents for Heavy Metals and Dyes Removal from (Waste)Waters. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 356, 118864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garba, Z.N.; Lawan, I.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, M.; Wang, L.; Yuan, Z. Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC) Based Materials as Emerging Adsorbents for the Removal of Dyes and Heavy Metals–A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 135070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian, M.; Jaymand, M. Interpenetrating Polymer Network Hydrogels for Removal of Synthetic Dyes: A Comprehensive Review. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 486, 215152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Ihsanullah, I.; Hassan Shah, M.U.; Bhaskar Reddy, A.V.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Recent Advances in the Removal of Dyes from Wastewater Using Low-Cost Adsorbents. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 321, 115981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, D.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Chen, Q.; Wang, C.; Wu, T.; Xu, M. Adsorptive Removal of Organic Dyes via Porous Materials for Wastewater Treatment in Recent Decades: A Review on Species, Mechanisms and Perspectives. Chemosphere 2022, 293, 133464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Naim, A.F. Mesoporous and Nanoflowers (ZnO2) via a Hydrothermal Technique for Dye Removal and Antibacterial Applications. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 151, 110575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aramesh, N.; Bagheri, A.R.; Bilal, M. Chitosan-Based Hybrid Materials for Adsorptive Removal of Dyes and Underlying Interaction Mechanisms. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 183, 399–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, M.J.; Ampiaw, R.E.; Lee, W. Adsorptive Removal of Dyes from Wastewater Using a Metal-Organic Framework: A Review. Chemosphere 2021, 284, 131314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyewo, O.A.; Elemike, E.E.; Onwudiwe, D.C.; Onyango, M.S. Metal Oxide-Cellulose Nanocomposites for the Removal of Toxic Metals and Dyes from Wastewater. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 2477–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, C.; Dutta, S.; Saxena, V.K. A Review on Biosorptive Removal of Dyes and Heavy Metals from Wastewater Using Watermelon Rind as Biosorbent. Environ. Adv. 2020, 2, 100007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, A.; Sabouri, Z.; Hosseini, H.A.; Hashemzadeh, A.; Khatami, M.; Darroudi, M. Effect of Nickel Oxide Nanoparticles as a Photocatalyst in Dyes Degradation and Evaluation of Effective Parameters in Their Removal from Aqueous Environments. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2020, 115, 107867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihsanullah, I.; Jamal, A.; Ilyas, M.; Zubair, M.; Khan, G.; Atieh, M.A. Bioremediation of Dyes: Current Status and Prospects. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 38, 101680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitam, C.N.C.; Jalil, A.A. A Review on Exploration of Fe2O3 Photocatalyst towards Degradation of Dyes and Organic Contaminants. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 258, 110050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, B.; Rahimi, N.R.; Ebrahimi, A. Catalytic Reduction of Hazardous Acid Orange 10 Dye by BiVO4/TiO2 Nanocrystalline Heterojunction and Influence of Aeration, FeSO4, H2O2 and FeCl3 on Removal Efficiency: A Novel and Environmentally Friendly Process. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 104003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada-Cabrera, E.; Torres-Ferrer, L.R.; Luna-Barcenas, G.; Ramirez-Bon, R. Cellulose Dialysis Membrane Containing Raw Clinoptilolite Enhances the Removal of Rhodamine 6G from Aqueous Solutions. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2021, 321, 111113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merzouk, B.; Gourich, B.; Madani, K.; Vial, C.; Sekki, A. Removal of a Disperse Red Dye from Synthetic Wastewater by Chemical Coagulation and Continuous Electrocoagulation. A Comparative Study. Desalination 2011, 272, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nataraj, S.K.; Hosamani, K.M.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Nanofiltration and Reverse Osmosis Thin Film Composite Membrane Module for the Removal of Dye and Salts from the Simulated Mixtures. Desalination 2009, 249, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, J.; He, M.; Li, M.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, L. Growth of BiOBr/ZIF-67 Nanocomposites on Carbon Fiber Cloth as Filter-Membrane-Shaped Photocatalyst for Degrading Pollutants in Flowing Wastewater. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2022, 4, 1620–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, H.; Liu, Z.; Xu, L.; Liu, T.; Fan, Y.; Jin, L.; Dong, R.; Yi, Y.; Li, Y. Waste Textile Reutilization Via a Scalable Dyeing Technology: A Strategy to Enhance Dyestuffs Degradation Efficiency. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2022, 4, 1595–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bastaki, N. Removal of Methyl Orange Dye and Na2SO4 Salt from Synthetic Waste Water Using Reverse Osmosis. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2004, 43, 1561–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Chen, Z.; Yu, Q.; Zhu, W.; Li, S.; Han, L.; Lu, X.; Li, S.; Wu, Y.; Lv, Z.; et al. Enhanced Electrochemical Removal of Dye Wastewater by PbO2 Anodes Using Halloysite Nanotubes with Different Surface Charge Properties. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2022, 923, 116816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustos-Terrones, Y.A.; Hermosillo-Nevárez, J.J.; Ramírez-Pereda, B.; Vaca, M.; Rangel-Peraza, J.G.; Bustos-Terrones, V.; Rojas-Valencia, M.N. Removal of BB9 Textile Dye by Biological, Physical, Chemical, and Electrochemical Treatments. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2021, 121, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, E.A.; Hegazey, R.M.; Ismail, S.H.; El-Feky, H.H.; Khedr, A.M.; Khairy, M.; Ammar, A.M. Facile Synthesis and Characterization of β-Cobalt Hydroxide/Hydrohausmannite/Ramsdellitee/Spertiniite and Tenorite/Cobalt Manganese Oxide/Manganese Oxide as Novel Nanocomposites for Efficient Photocatalytic Degradation of Methylene Blue Dye. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 104372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazey, R.M.; Abdelrahman, E.A.; Kotp, Y.H.; Hameed, A.M.; Subaihi, A. Facile Fabrication of Hematite Nanoparticles from Egyptian Insecticide Cans for Efficient Photocatalytic Degradation of Rhodamine B Dye. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 1652–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, A.; Abdelrahman, E.A. Efficient Photocatalytic Degradation of Malachite Green Dye Using Facilely Synthesized Hematite Nanoparticles from Egyptian Insecticide Cans. Spectrochim. Acta-Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 226, 117612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, E.A.; Hegazey, R.M.; Kotp, Y.H.; Alharbi, A. Facile Synthesis of Fe2O3 Nanoparticles from Egyptian Insecticide Cans for Efficient Photocatalytic Degradation of Methylene Blue and Crystal Violet Dyes. Spectrochim. Acta-Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 222, 117195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelrahman, E.A.; Hegazey, R.M.; El-Azabawy, R.E. Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue Dye from Aqueous Media Using Fe/Si, Cr/Si, Ni/Si, and Zn/Si Amorphous Novel Adsorbents. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 5301–5313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, E.A. Synthesis of Zeolite Nanostructures from Waste Aluminum Cans for Efficient Removal of Malachite Green Dye from Aqueous Media. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 253, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Nada, A.; Abdala, A.; McKay, G. Removal of Phenols and Dyes from Aqueous Solutions Using Graphene and Graphene Composite Adsorption: A Review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagub, M.T.; Sen, T.K.; Afroze, S.; Ang, H.M. Dye and Its Removal from Aqueous Solution by Adsorption: A Review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 209, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, X.; Che, Y.; Liu, H.; Zuo, W.; Zhang, Y. The Methyl Blue Adsorption Performance and Mechanism of NaX Zeolite Synthesized from Huadian Oil Shale Ash. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2023, 147, 104904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jubouri, S.M.; Al-Jendeel, H.A.; Rashid, S.A.; Al-Batty, S. Green Synthesis of Porous Carbon Cross-Linked Y Zeolite Nanocrystals Material and Its Performance for Adsorptive Removal of a Methyl Violet Dye from Water. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2023, 356, 112587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboelfetoh, E.F.; El-Attar, H.G.; Okba, E.A. Facile Synthesis of Magnetic and Porous Zeolite/SnFe2O4 Nanocomposite for Cationic and Anionic Dyes Deterioration. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2023, 357, 112611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Xu, F.; Wei, W.; Gao, H.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, G.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, P. Efficient and Fast Adsorption of Methylene Blue Dye onto a Nanosheet MFI Zeolite. J. Solid State Chem. 2021, 295, 121917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Sun, J.; Jin, X.; Chen, Q.; Wu, X.; Tian, F.; Zhang, X.; Li, P.; Sheng, H. Adsorption Enhancement of Congo Red Dye from Wastewater Based on Edamame Shell Originated Activated Carbon by the Cations: Experimental and Theoretical Studies. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2023, 136, 109930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimzim; Singh, J.; Mittal, S.; Singh, H. Robust Removal of Cationic Dyes by Zinc Ferrite Composites in Single and Ternary Dye Systems. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 153, 110756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, H.E.; Abdel Aziz, M.S. Non-Toxic Chitosan-Pyrazole Adsorbent Enriched with Greenly Synthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for Dye Removal from Wastewater. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 241, 124632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inamdar, A.K.; Hulsure, N.R.; Kadam, A.S.; Thabet, A.E.; Shelke, S.B.; Inamdar, S.N. Cobalt Oxide Nanoparticles by Flame Pyrolysis for Efficient Removal of Mixed Dyes. Mater. Today Proc. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandão, W.Q.; Maciel, B.G.; Lima, E.M.d.A.; Mojica-Sánchez, L.C.; da Silva, R.J.; de Melo, C.P. Carboxymethylcellulose Magnetic Composite for Adsorptive Removal of Cationic Toluidine Blue Dye. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2023, 303, 127782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oviedo, L.R.; Oviedo, V.R.; Dalla Nora, L.D.; da Silva, W.L. Adsorption of Organic Dyes onto Nanozeolites: A Machine Learning Study. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 315, 123712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Xie, Z.; Xue, S.; Long, J.; Shi, W.; Liu, Y. Preparation of Benzenesulfonyl Hydrazone Modified Guar Gum and Its Adsorption Properties for Dyes and Phytotoxicity Assays. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 234, 123700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollakota, A.R.K.; Munagapati, V.S.; Gautam, S.; Wen, J.C.; Shu, C.M. Hydrothermal Tuning of Morphology of Aluminophosphate (AlPO-14) Framework for the Adsorption of Rhodamine 6G Dye. Adv. Powder Technol. 2021, 32, 3002–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanamudan, A.; Bandwala, K.; Pamidimukkala, P. Adsorption Property of Rhodamine 6G onto Chitosan-g-(N-Vinyl Pyrrolidone)/Montmorillonite Composite. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 69, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annadurai, G.; Juang, R.S.; Lee, D.J. Adsorption of Rhodamine 6G from Aqueous Solutions on Activated Carbon. J. Environ. Sci. Heal.-Part A Toxic/Hazardous Subst. Environ. Eng. 2001, 36, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gollakota, A.R.K.; Volli, V.; Munagapati, V.S.; Wen, J.C.; Shu, C.M. Synthesis of Novel ZSM-22 Zeolite from Taiwanese Coal Fly Ash for the Selective Separation of Rhodamine 6G. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 15381–15393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Zheng, H.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S. Enhanced Adsorption of Orange G from Aqueous Solutions by Quaternary Ammonium Group-Rich Magnetic Nanoparticles. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2019, 580, 123746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulkumar, M.; Sathishkumar, P.; Palvannan, T. Optimization of Orange G Dye Adsorption by Activated Carbon of Thespesia Populnea Pods Using Response Surface Methodology. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Dubey, S.; Gautam, R.K.; Chattopadhyaya, M.C.; Sharma, Y.C. Adsorption Characteristics of Alumina Nanoparticles for the Removal of Hazardous Dye, Orange G from Aqueous Solutions. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 5339–5354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imgharn, A.; Anchoum, L.; Hsini, A.; Naciri, Y.; Laabd, M.; Mobarak, M.; Aarab, N.; Bouziani, A.; Szunerits, S.; Boukherroub, R.; et al. Effectiveness of a Novel Polyaniline@Fe-ZSM-5 Hybrid Composite for Orange G Dye Removal from Aqueous Media: Experimental Study and Advanced Statistical Physics Insights. Chemosphere 2022, 295, 133786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaei, B.; Miri, R.; Bazyari, A.; Thompson, L.T. Asphaltene Adsorption on MgO, CaO, SiO2, and Al2O3 Nanoparticles Synthesized via the Pechini-Type Sol−Gel Method. Fuel 2022, 321, 124136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Gwon, Y.R.; Cho, S.K. Photoelectrochemical Water Oxidation on PbCrO4 Thin Film Photoanode Fabricated via Pechini Method: Various Solution-Processes for PbCrO4 Film Synthesis. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 878, 114601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhaji, A.; Razavi, R.S.; Ghasemi, A.; Loghman-Estarki, M.R. Modification of Pechini Sol–Gel Process for the Synthesis of MgO-Y2O3 Composite Nanopowder Using Sucrose-Mediated Technique. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 2541–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Sharma, R.; Kumar, S.; Kaur, M.; Sharma, J.D. Enhancement in the Photocatalytic Activity of Bi2Ti2O7 Nanopowders Synthesised via Pechini vs Co-Precipitation Method. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 20386–20395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.K.; Naglah, A.M.; Al-Omar, M.A.; Almehizia, A.A.; AlReshaidan, S.; Subaihi, A.; Alharbi, A.; Hameed, A.M.; Alkabli, J.; Fetoh, M.E.; et al. Efficient Removal of Ni(II) Ions from Aqueous Solutions Using Analcime Modified with Dimethylglyoxime Composite. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
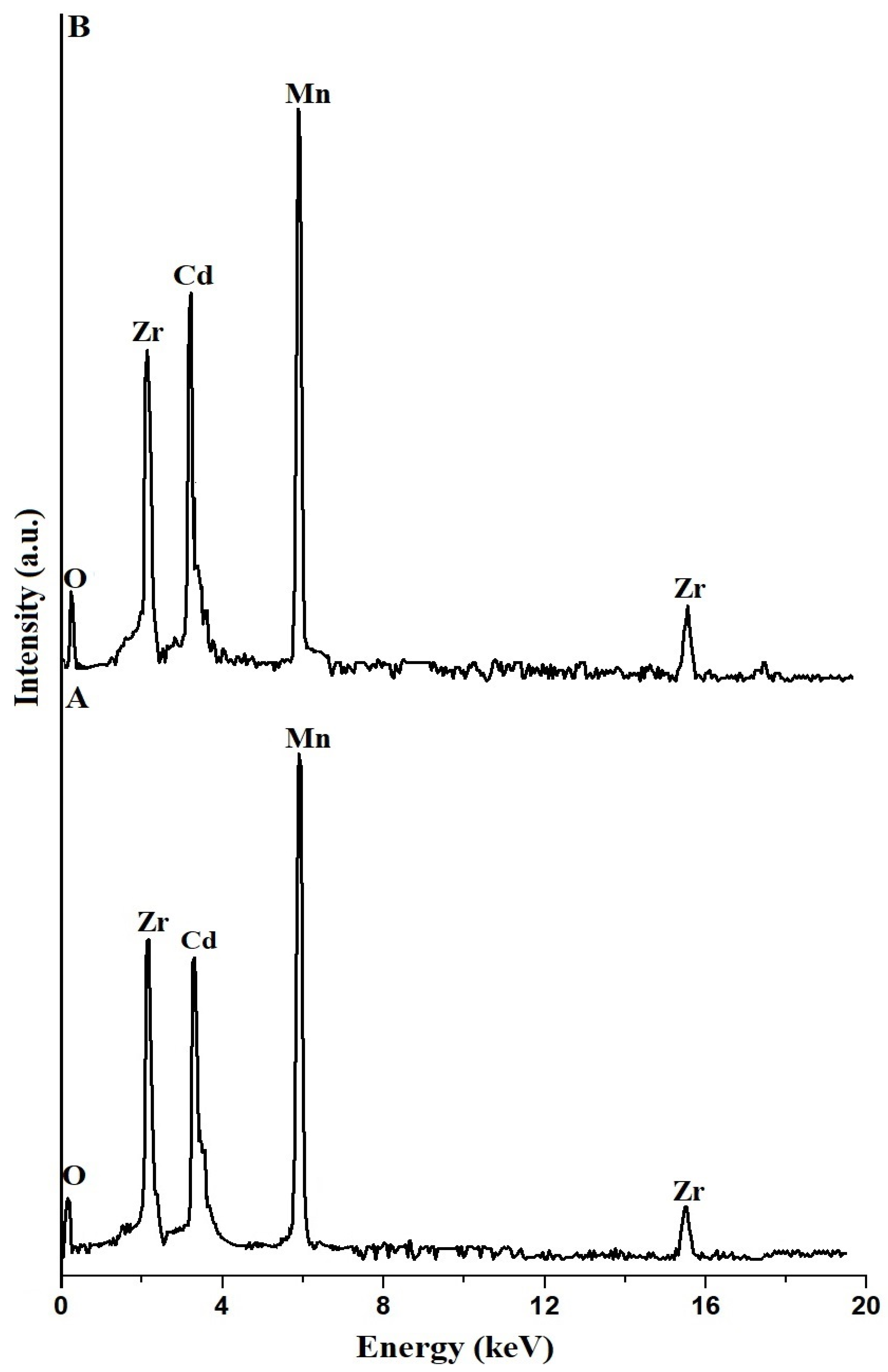


| Samples | % O | % Mn | % Cd | % Zr |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EK600 | 14.68 | 21.90 | 25.71 | 37.71 |
| EK800 | 13.98 | 21.64 | 27.43 | 36.95 |
| Sample | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Total Pore Volume (cc/g) | Average Pore Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| EK600 | 46.33 | 0.2037 | 8.79 |
| EK800 | 38.49 | 0.1398 | 7.27 |
| Conditions | Pseudo-First Order | Pseudo-Second Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 (1/min) | Oe (mg/g) | R2 | k2 (g/mg.min) | Oe (mg/g) | R2 | |
| EK600+ Rhodamine 6G | 0.1254 | 313.60 | 0.9999 | 0.00022 | 429.18 | 0.9955 |
| EK800+ Rhodamine 6G | 0.1081 | 250.93 | 0.9996 | 0.00019 | 371.75 | 0.9864 |
| EK600+ Acid orange 10 | 0.1227 | 342.68 | 0.9999 | 0.00018 | 478.47 | 0.9927 |
| EK800+ Acid orange 10 | 0.1024 | 265.35 | 0.9999 | 0.00018 | 392.16 | 0.9911 |
| Conditions | ΔH° (kJ/mol) | ΔS° (kJ/mol kelvin) | ΔG° (kJ/mol) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 298 | 308 | 318 | 328 | |||
| EK600+ Rhodamine 6G | −19.95 | 0.0514 | −35.26 | −35.78 | −36.29 | −36.81 |
| EK800+ Rhodamine 6G | −18.07 | 0.0501 | −33.00 | −33.50 | −34.00 | −34.51 |
| EK600+ Acid orange 10 | −18.76 | 0.0453 | −32.26 | −32.71 | −33.16 | −33.62 |
| EK800+ Acid orange 10 | −16.18 | 0.0423 | −28.79 | −29.22 | −29.64 | −30.06 |
| Langmuir Isotherm | Freundlich Isotherm | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conditions | Omax (mg/g) | k3 (L/mg) | R2 | Omax (mg/g) | k4 (mg/g)(L/mg)1/n | R2 |
| EK600+ Rhodamine 6G | 311.53 | 2.1837 | 0.9999 | 386.22 | 136.07 | 0.7504 |
| EK800+ Rhodamine 6G | 250.63 | 0.6196 | 0.9998 | 283.51 | 91.37 | 0.9159 |
| EK600+ Acid orange 10 | 335.57 | 1.9477 | 0.9999 | 431.32 | 136.44 | 0.7905 |
| EK800+ Acid orange 10 | 270.27 | 0.4302 | 0.9995 | 313.67 | 85.23 | 0.9118 |
| Adsorbent | O(mg/g) towards Rhodamine 6G Dye | O(mg/g) towards Acid Orange 10 Dye | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminophosphate | 208.11 | ---- | [49] |
| Chitosan-g-(N-vinylpyrrolidone)/montmorillonite composite | 36.60 | ---- | [50] |
| Activated carbon | 44.70 | ---- | [51] |
| ZSM-22 zeolite | 195.30 | ---- | [52] |
| Quaternary ammonium group-rich magnetic nanoparticles | ---- | 98.70 | [53] |
| Activated carbon | ---- | 17.60 | [54] |
| Alumina nanoparticles | ---- | 93.30 | [55] |
| Polyaniline/Fe-ZSM-5 composite | ---- | 217 | [56] |
| EK600 | 311.53 | 335.57 | This study |
| EK800 | 250.63 | 268.09 | This study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdelrahman, E.A.; Algethami, F.K.; AlSalem, H.S.; Binkadem, M.S.; Khairy, M.; Saad, F.A.; El-Sayyad, G.S.; Alqahtani, Z. Efficient Disposal of Rhodamine 6G and Acid Orange 10 Dyes from Aqueous Media Using ZrO2/CdMn2O4/CdO as Novel and Facilely Synthesized Nanocomposites. Inorganics 2023, 11, 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11080333
Abdelrahman EA, Algethami FK, AlSalem HS, Binkadem MS, Khairy M, Saad FA, El-Sayyad GS, Alqahtani Z. Efficient Disposal of Rhodamine 6G and Acid Orange 10 Dyes from Aqueous Media Using ZrO2/CdMn2O4/CdO as Novel and Facilely Synthesized Nanocomposites. Inorganics. 2023; 11(8):333. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11080333
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdelrahman, Ehab A., Faisal K. Algethami, Huda S. AlSalem, Mona S. Binkadem, Mohamed Khairy, Fawaz A. Saad, Gharieb S. El-Sayyad, and Zahrah Alqahtani. 2023. "Efficient Disposal of Rhodamine 6G and Acid Orange 10 Dyes from Aqueous Media Using ZrO2/CdMn2O4/CdO as Novel and Facilely Synthesized Nanocomposites" Inorganics 11, no. 8: 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11080333
APA StyleAbdelrahman, E. A., Algethami, F. K., AlSalem, H. S., Binkadem, M. S., Khairy, M., Saad, F. A., El-Sayyad, G. S., & Alqahtani, Z. (2023). Efficient Disposal of Rhodamine 6G and Acid Orange 10 Dyes from Aqueous Media Using ZrO2/CdMn2O4/CdO as Novel and Facilely Synthesized Nanocomposites. Inorganics, 11(8), 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11080333