High Poisonous Cd Ions Removal by Ru-ZnO-g-C3N4 Nanocomposite: Description and Adsorption Mechanism
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
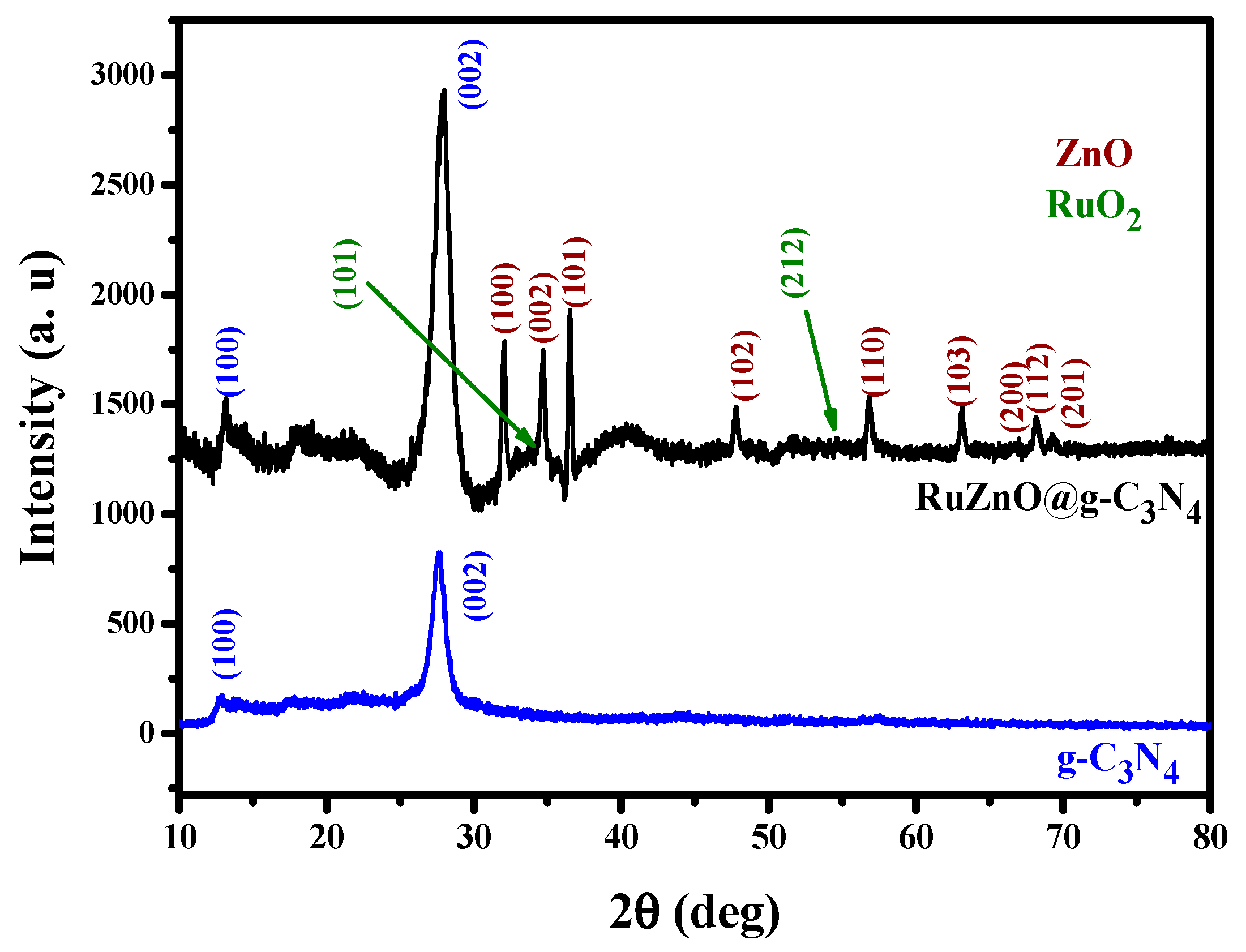
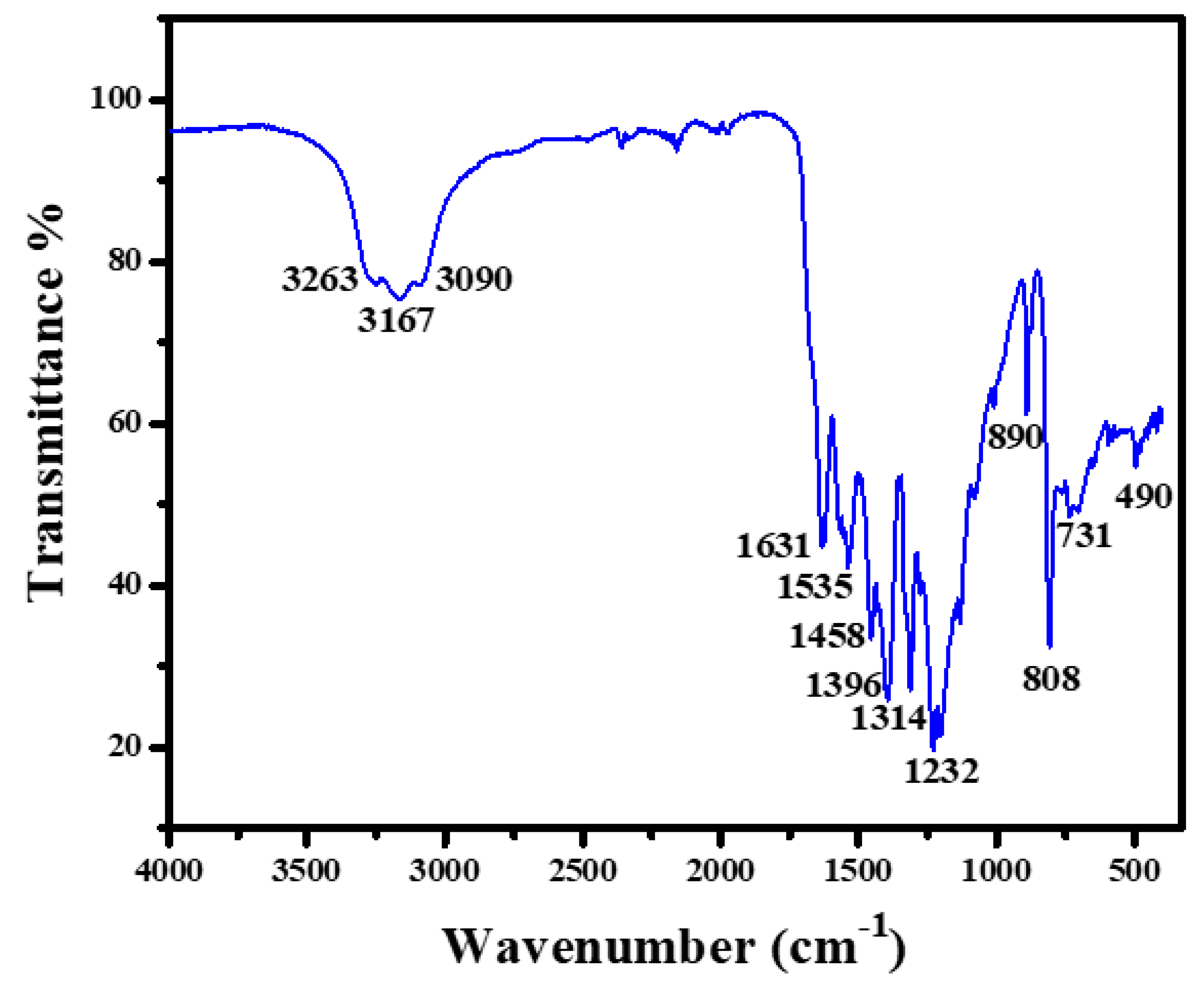
2.1. Ru-ZnO-g-C3N4 Nanosorbent Characteristics
2.2. Adsorption Capability of Ru-ZnO-g-C3N4 Nanocomposite
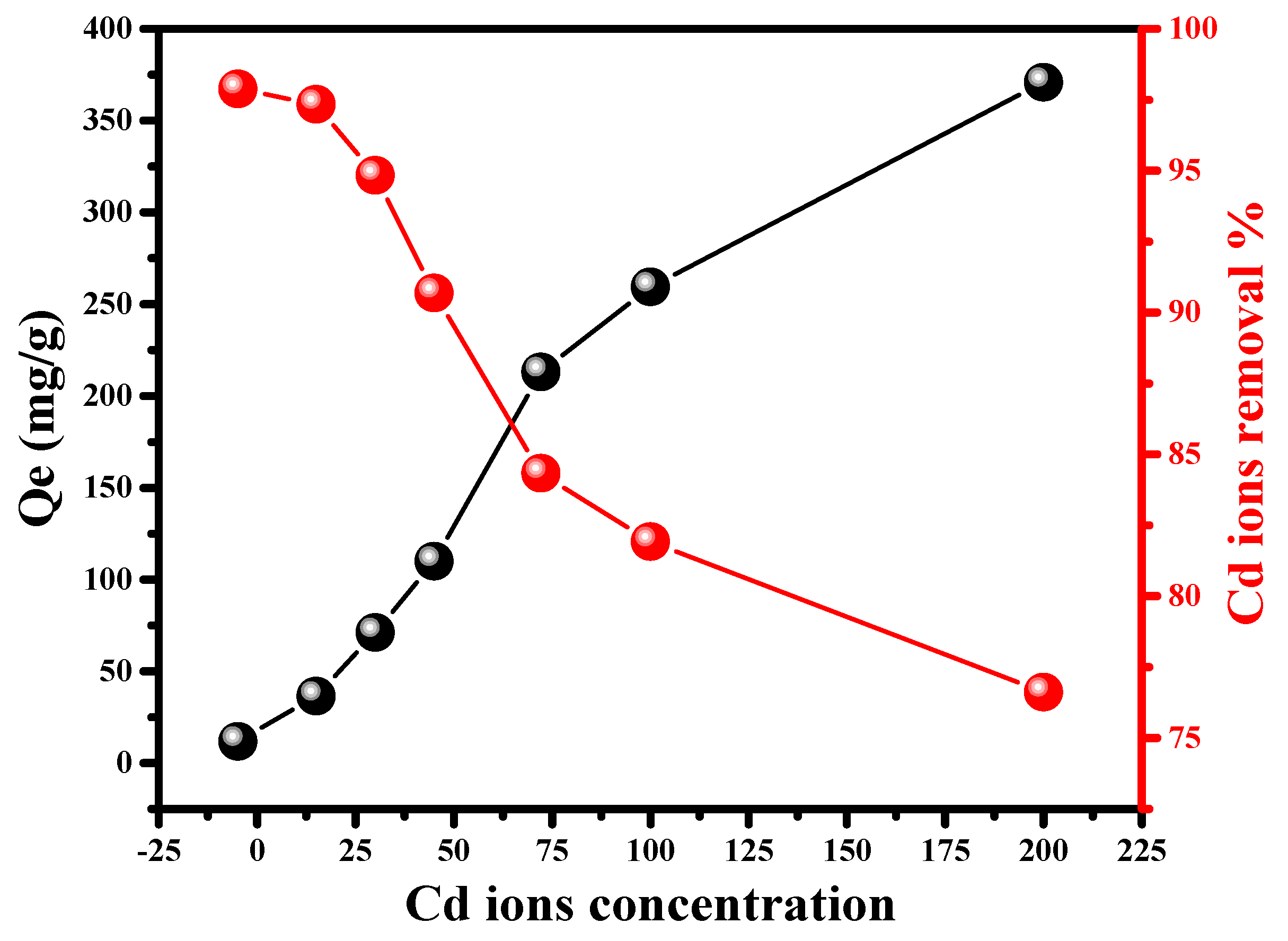
2.2.1. Impact of Initial Cd (II) Concentration
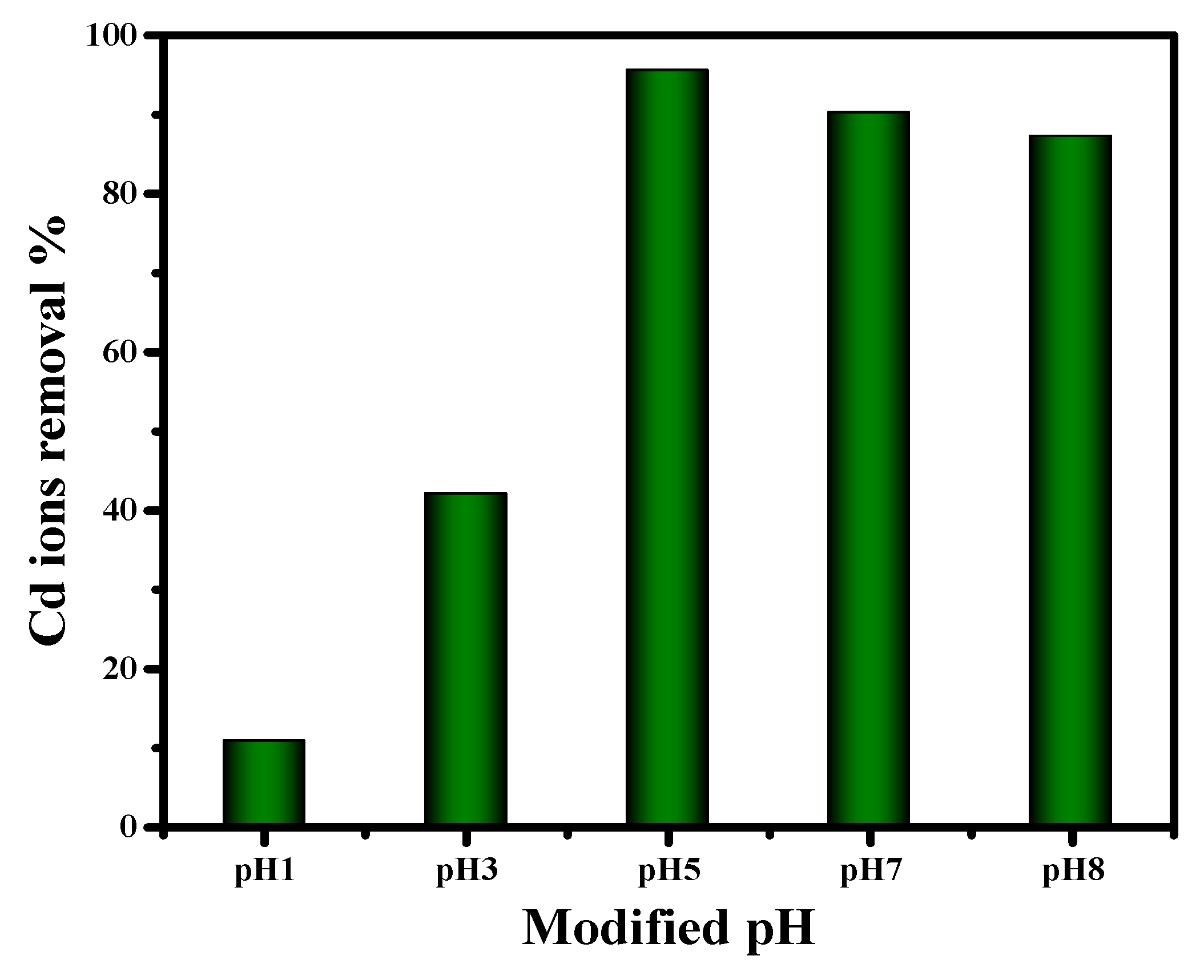
2.2.2. Impact of Difference pH on Cd (II) Removal
2.2.3. Adsorption Isotherms Modeling
2.2.4. Contact Time and Adsorption Kinetics Modeling
2.3. Adsorption Mechanism
2.4. Assessment Study
3. Experimental Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
3.2. Ru-ZnO-g-C3N4 Nanocomposites Construction
3.3. Ru-ZnO-g-C3N4 Nanocomposites Characterizations
3.4. Cd Ions Removal Procedures
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aldaghri, O.; Modwi, A.; Idriss, H.; Ali, M.; Ibnaouf, K. Cleanup of Cd II from water media using Y2O3@gC3N4 (YGCN) nanocomposite. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2022, 129, 109315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modwi, A.; Ismail, M.; Idriss, H.; Aissa, M.A.; Khezami, L.; Bououdina, M. Efficient Removal of Cd (II) from Aquatic Media by Heteronanostructure MgO@ TiO2@ g-C3N4. J. Nanomater. 2022, 2022, 1458442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, D.; Zhang, B.; Xu, G.; Wang, B.; Mao, K.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Feng, X.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, H. Efficient removal of Cd(II) from aqueous solution by pinecone biochar: Sorption performance and governing mechanisms. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 115001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandara, T.; Xu, J.; Potter, I.D.; Franks, A.; Chathurika, J.; Tang, C. Mechanisms for the removal of Cd(II) and Cu(II) from aqueous solution and mine water by biochars derived from agricultural wastes. Chemosphere 2020, 254, 126745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Lin, Q.; Zhong, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wen, X.; Luo, H. Removal of Cd(II) and Pb(II) from aqueous solution by modified attapulgite clay. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 4994–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Li, F.; Cui, J.; Yang, S.; Fang, L. Simultaneous removal of Cd(II) and As(III) by graphene-like biochar-supported zero-valent iron from irrigation waters under aerobic conditions: Synergistic effects and mechanisms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 395, 122623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balarak, D.; Chandrika, K.; Igwegbe, C.A.; Ahmadi, S.; Umembamalu, C.J. Biosorption of phenol using modified barley husk: Studies on equilibrium isotherm, kinetics, and thermodynamics of interactions. Sigma J. Eng. Nat. Sci. 2020, 38, 1161–1177. [Google Scholar]
- You, D.; Shi, H.; Yang, L.; Shao, P.; Luo, X.; Yin, K.; Luo, S. Tuning the effective utilization of adsorption sites in La-MOFs via a steric hindrance effect towards enhanced As(iii) removal. Environ. Sci. Nano 2021, 8, 3387–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, A.; Badawy, S.; Farag, S.; Mohamed, L.; Fletcher, A.; Taha, G. Non-linear adsorption characteristics of modified pine wood sawdust optimised for adsorption of Cd(II) from aqueous systems. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, S.; Younis, A.; Ali, R.; Elkady, E. Phenol removal from aqueous solution using amino modified silica nanoparticles. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 36, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alminderej, F.M.; Younis, A.M.; Albadri, A.E.; El-Sayed, W.A.; El-Ghoul, Y.; Ali, R.; Mohamed, A.M.; Saleh, S.M. The superior adsorption capacity of phenol from aqueous solution using Modified Date Palm Nanomaterials: A performance and kinetic study. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 104120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieszczycka, K.; Filipowiak, K.; Wojciechowska, I.; Aksamitowski, P. Novel ionic liquid-modified polymers for highly effective adsorption of heavy metals ions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, A.; Manzoor, T.; Malik, L.A.; Qureashi, A.; Pandith, A.H. Enhanced and selective adsorption of Zn (II), Pb (II), Cd (II), and Hg (II) ions by a dumbbell-and flower-shaped potato starch phosphate polymer: A combined experimental and DFT calculation study. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 4853–4867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Jobara, A.; Bekouche, H.; Allateef, M.A.; Ben Aissa, M.A.; Modwi, A. Impact of Cu Ions removal onto MgO nanostructures: Adsorption capacity and mechanism. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2022, 33, 12500–12512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khezami, L.; Elamin, N.; Modwi, A.; Taha, K.K.; Amer, M.S.; Bououdina, M. Mesoporous Sn@ TiO2 nanostructures as excellent adsorbent for Ba ions in aqueous solution. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 5805–5813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Modwi, A.; Idriss, H.; Aldaghri, O.; Ismail, M.; Ibnaouf, K. Detoxification of Pb (II) from aquatic media via CaMgO2@g-C3N4 nanocomposite. Mater. Lett. 2022, 322, 132501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abaker, Z.; Hussein, T.; Makawi, S.; Mustafa, B.; Modwi, A. Superior uptake of Cu (II) from aquatic media via Y2O3-ZnO nanostructures. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2022, 30, 100879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, B.; Modwi, A.; Ismail, M.; Makawi, S.; Hussein, T.; Abaker, Z.; Khezami, L. Adsorption performance and Kinetics study of Pb(II) by RuO2–ZnO nanocomposite: Construction and Recyclability. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 19, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamari, S.; Shahbazi, A. Biocompatible Fe3O4@ SiO2-NH2 nanocomposite as a green nanofiller embedded in PES–nanofiltration membrane matrix for salts, heavy metal ion and dye removal: Long–term operation and reusability tests. Chemosphere 2020, 243, 125282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmorsi, T.M.; Elsayed, M.; Bakr, M.F. Enhancing the removal of methylene blue by modified ZnO nanoparticles: Kinetics and equilibrium studies. Can. J. Chem. 2017, 95, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, P.; Zhang, L.; Liu, G.; Cheng, H.-M. Graphene-Like Carbon Nitride Nanosheets for Improved Photocatalytic Activities. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 4763–4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeisi-Kheirabadi, N.; Nezamzadeh-Ejhieh, A. A Z-scheme g-C3N4/Ag3PO4 nanocomposite: Its photocatalytic activity and capability for water splitting. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 33381–33395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-H.; Wang, X.; Antonietti, M. Solvent-free and metal-free oxidation of toluene using O2 and g-C3N4 with nanopores: Nanostructure boosts the catalytic selectivity. ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 2082–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, X.; Yan, Y.; Shi, W.; Wang, D.; Yang, L.; Lin, X.; Hua, Z.; Liu, Y. Surface imprinting of a g-C3N4 photocatalyst for enhanced photocatalytic activity and selectivity towards photodegradation of 2-mercaptobenzothiazole. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 40726–40736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva-Neto, M.L.; de Oliveira, M.C.; Dominguez, C.T.; Lins, R.E.; Rakov, N.; de Araújo, C.B.; Gomes, A.S. UV random laser emission from flexible ZnO-Ag-enriched electrospun cellulose acetate fiber matrix. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotomayor, F.J.; Cychosz, K.A.; Thommes, M. Characterization of micro/mesoporous materials by physisorption: Concepts and case studies. Acc. Mater. Surf. Res. 2018, 3, 34–50. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, C.V.; Quang, D.V.; Nguyen Thi, H.P.; Truong, T.N.; La, D.D. Effective removal of Pb (II) from aqueous media by a new design of Cu–Mg binary ferrite. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 7298–7306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, Y.N.; Yang, S.S.; Ding, J.; Zhao, S.Y.; Chen, C.X.; He, L.; Ren, N.Q. A biochar-promoted V2O5/gC3N4 Z-Scheme heterostructure for enhanced simulated solar light-driven photocatalytic activity. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 15106–15117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Gaashani, R.; Radiman, S.; Daud, A.; Tabet, N.; Al-Douri, Y. XPS and optical studies of different morphologies of ZnO nanostructures prepared by microwave methods. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 2283–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manríquez, M.E.; Noreña, L.E.; Wang, J.A.; Chen, L.; Salmones, J.; González-García, J.; Reza, C.; Tzompantzi, F.; Cortez, J.G.H.; Ye, L.; et al. One-Pot Synthesis of Ru-Doped ZnO Oxides for Photodegradation of 4-Chlorophenol. Int. J. Photoenergy 2018, 2018, 7605306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.T.; Nicolas, Y.; Olivier, C.; Toupance, T.; Müller, M.M.; Kleebe, H.J.; Jaegermann, W. Preparation of RuO2/TiO2 mesoporous heterostructures and rationalization of their enhanced photocatalytic properties by band alignment investigations. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 22098–22110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, C.; Wang, W.; Tan, F.; Luo, F.; Chen, J.; Qiao, X. Investigation on the efficiency and mechanism of Cd(II) and Pb(II) removal from aqueous solutions using MgO nanoparticles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 299, 664–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kataria, N.; Garg, V. Optimization of Pb (II) and Cd (II) adsorption onto ZnO nanoflowers using central composite design: Isotherms and kinetics modelling. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 271, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, D.; Kumar, H.; Sarswat, A.; Alexandre-Franco, M.; Pittman, C.U., Jr. Cadmium and lead remediation using magnetic oak wood and oak bark fast pyrolysis bio-chars. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 236, 513–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuh-Shan, H. Citation review of Lagergren kinetic rate equation on adsorption reactions. Scientometrics 2004, 59, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, A.R.; Sallam, A.S.; Al-Omran, A.; El-Naggar, A.H.; Alenazi, K.K.; Nadeem, M.; Al-Wabel, M.I. Chemically Modified Biochar Produced from Conocarpus Wastes: An Efficient Sorbent for Fe(II) Removal from Acidic Aqueous Solutions. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2013, 31, 625–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, B.; Salman, J.; Ahmad, A. Adsorption isotherm and kinetic modeling of 2,4-D pesticide on activated carbon derived from date stones. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sikaily, A.; El Nemr, A.; Khaled, A.; Abdelwehab, O. Removal of toxic chromium from wastewater using green alga Ulva lactuca and its activated carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 148, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahali, S.; Aissa, M.A.B.; Modwi, A.; Said, R.B.; Belhocine, Y. Application of mesoporous CaO@ g-C3N4 nanosorbent materials for high-efficiency removal of Pb (II) from aqueous solution. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 379, 121594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, S.M.; Albadri, A.E.; Aissa, M.A.B.; Modwi, A. Fabrication of Mesoporous V2O5@ g-C3N4 Nanocomposite as Photocatalyst for Dye Degradation. Crystals 2022, 12, 1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.Y.; Hung, J.T.; Chou, Y.C.; Shen, S.J.; Wu, W.T.; Liu, F.Y.; Chen, C.C. Synthesis of bismuth oxybromochloroiodide/graphitic carbon nitride quaternary composites (BiOxCly/BiOmBrn/BiOpIq/g-C3N4) enhances visible-light-driven photocatalytic activity. Catal. Commun. 2022, 163, 106418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arita, S.; Koike, T.; Kayaki, Y.; Ikariya, T. Aerobic Oxidative Kinetic Resolution of Racemic Secondary Alcohols with Chiral Bifunctional Amido Complexes. Angew. Chem. 2008, 120, 2481–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, A.; Tian, W.; Yang, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Li, Z. Molybdenum sulfide-modified metal-free graphitic carbon nitride/black phosphorus photocatalyst synthesized via high-energy ball-milling for efficient hydrogen evolution and hexavalent chromium reduction. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 413, 125400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.; Chen, C.; Wen, T.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, X.; Xu, A. Superior adsorption capacity of g-C3N4 for heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 456, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hameed, A.M.; Alharbi, A.; Abdelrahman, E.A.; Mabrouk, E.M.; Hegazey, R.M.; Algethami, F.K.; Al-Ghamdi, Y.O.; Youssef, H.M. Facile Hydrothermal Fabrication of Analcime and Zeolite X for Efficient Removal of Cd(II) Ions From Aqueous Media and Polluted Water. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020, 30, 4117–4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, E.A.; Subaihi, A. Application of geopolymers modified with chitosan as novel composites for efficient removal of Hg (II), Cd (II), and Pb (II) ions from aqueous media. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020, 30, 2440–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciesielczyk, F.; Bartczak, P.; Jesionowski, T. A comprehensive study of Cd(II) ions removal utilizing high-surface-area binary Mg–Si hybrid oxide adsorbent. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 3613–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallakpour, S.; Khadem, E. Chitosan reinforced with modified CaCO3 nanoparticles to enhance thermal, hydrophobicity properties and removal of cu(II) and cd(II) ions. J. Polym. Res. 2017, 24, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Nemr, A.; El-Assal, A.A.; El Sikaily, A.; Mahmoud, M.E.; Amira, M.F.; Ragab, S. New magnetic cellulose nanobiocomposites for Cu (II), Cd (II) and Pb (II) ions removal: Kinetics, thermodynamics and analytical evaluation. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 2021, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.; Sun, C.; Yan, Z. Adsorption characteristics of white pottery clay towards Pb (II), Cu (II), and Cd (II). Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Aissa, M.A.; Modwi, A.; Albadri, A.E.; Saleh, S.M. Dependency of Crystal Violet Dye Removal Behaviors onto Mesoporous V2O5-g-C3N4 Constructed by Simplistic Ultrasonic Method. Inorganics 2023, 11, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



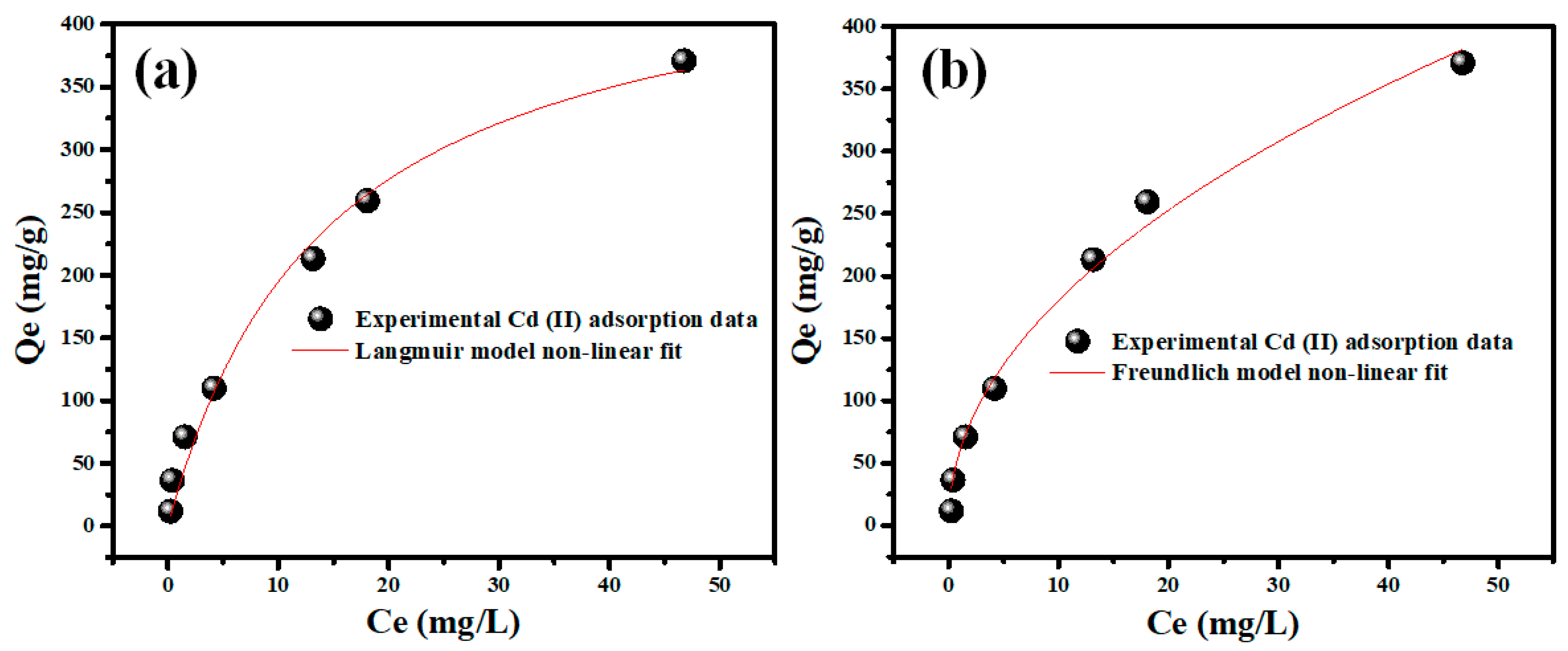
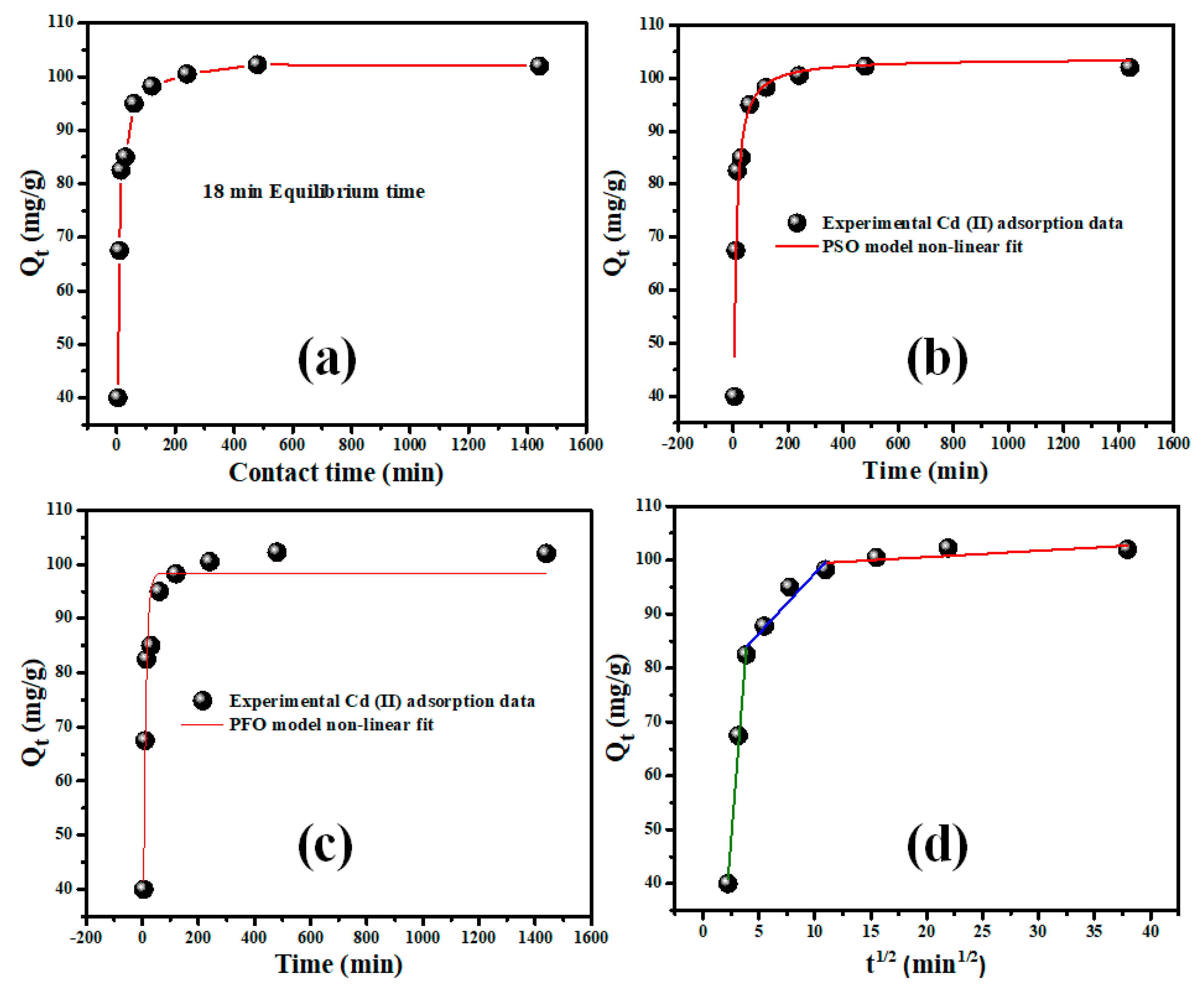

| Adsorption Model | Langmuir | Freundlich | PFO | PSO |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Qmax = 475.5 mg/g | n = 59.07 | Q = 98.34 | QCal = 103.7, QExp = 102.5 |
| KL = 0.069 | Kf = 0.485 | K1 = 0.109 | K2 = 0.0064 | |
| R2 | 0.9958 | 0.9911 | 0.9489 | 0.9945 |
| Chi-Sqr | 295.85 | 186.92 | 21.91 | 19.034 |
| Step | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| kdif (mg g−1 min−1/2) | 26.15 | 2.233 | 0.117 |
| C | 17.54 | 25.21 | 98.21 |
| R2 | 0.9923 | 0.9890 | 0.5682 |
| RSS | 7.900 | 10.178 | 4.371 |
| Materials Used | Pseudo-Second-Order | Langmuir Isotherm | Optimal pH | SBET (m2/g) | D (nm) | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k2 (g/mg/min) | R2 | qm (mg/g) | R2 | |||||
| Zeolite X | 0.002 | 0.999 | 62.814 | 0.953 | 6.5 | - | 94.85 | [46] |
| Geopolymers/Chitosan | 0.00012 | 0.982 | 166.11 | 0.992 | 8 | - | - | [47] |
| Binary Mg–Si hybrid oxide | 0.033 | 0.999 | 18.790 | 0.998 | 7 | 540 | 56.4 | [48] |
| Chitosan/CaCO3 nanoparticles | - | - | 29.41 | 0.980 | 6.5 | - | 60 | [49] |
| Magnetic cellulose nanocomposites | 0.811 | 1.000 | 103.1 | 0.820 | 6 | 7.72 | 30 | [50] |
| White pottery clay | 0.0124 | 0.999 | 26.991 | 0.999 | 5.5 | 56.58 | - | [51] |
| Ru-ZnO-g-C3N4 | 0.0064 | 0.9945 | 475.5 | 0.9958 | 5.00 | 257 | 6.61 | This paper |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ismail, M.; Albadri, A.; Ben Aissa, M.A.; Modwi, A.; Saleh, S.M. High Poisonous Cd Ions Removal by Ru-ZnO-g-C3N4 Nanocomposite: Description and Adsorption Mechanism. Inorganics 2023, 11, 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11040176
Ismail M, Albadri A, Ben Aissa MA, Modwi A, Saleh SM. High Poisonous Cd Ions Removal by Ru-ZnO-g-C3N4 Nanocomposite: Description and Adsorption Mechanism. Inorganics. 2023; 11(4):176. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11040176
Chicago/Turabian StyleIsmail, Mukhtar, Abuzar Albadri, Mohamed Ali Ben Aissa, Abueliz Modwi, and Sayed M. Saleh. 2023. "High Poisonous Cd Ions Removal by Ru-ZnO-g-C3N4 Nanocomposite: Description and Adsorption Mechanism" Inorganics 11, no. 4: 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11040176
APA StyleIsmail, M., Albadri, A., Ben Aissa, M. A., Modwi, A., & Saleh, S. M. (2023). High Poisonous Cd Ions Removal by Ru-ZnO-g-C3N4 Nanocomposite: Description and Adsorption Mechanism. Inorganics, 11(4), 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11040176