Preparation of RGO/Fe3O4 Nanocomposites as a Microwave Absorbing Material
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
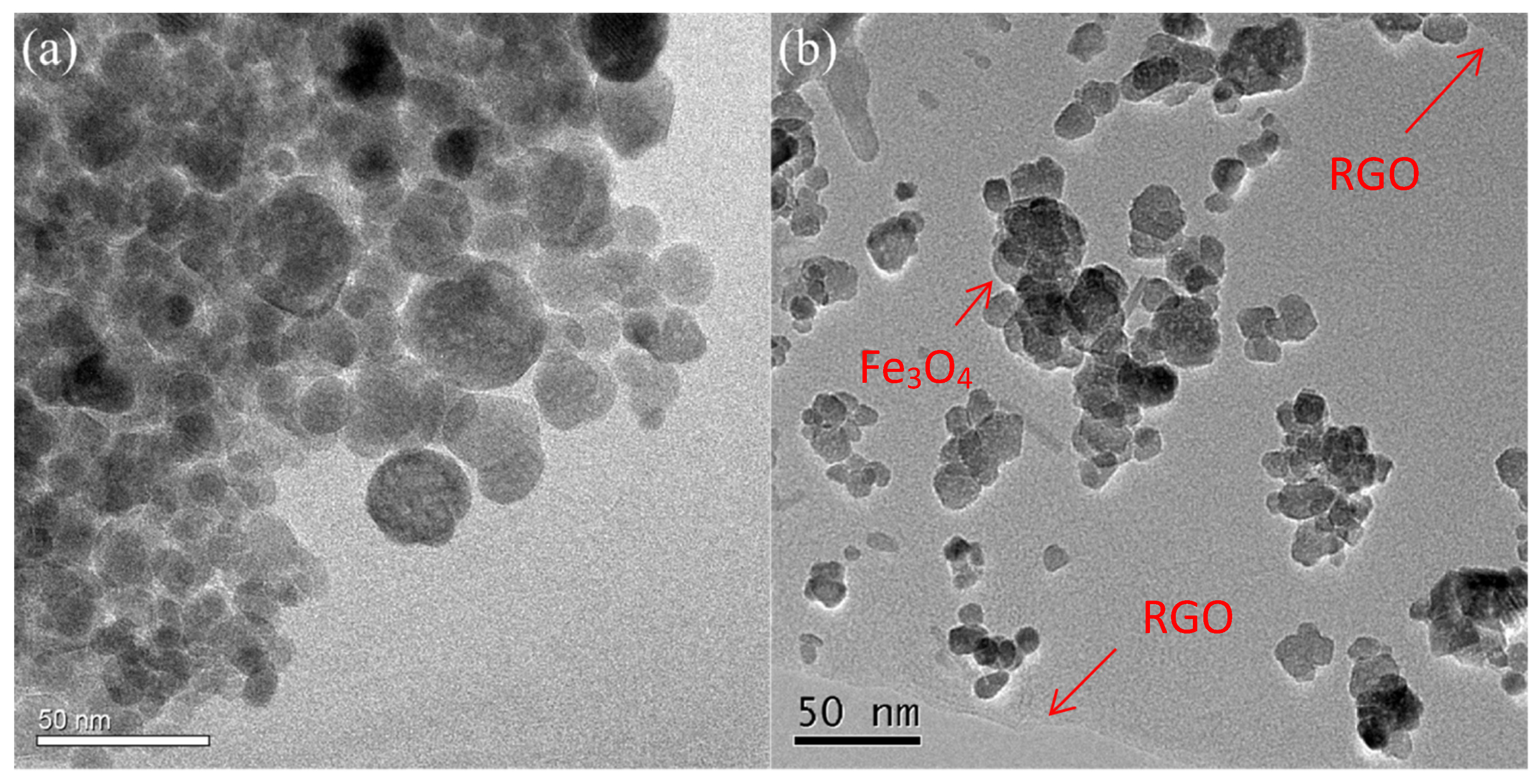
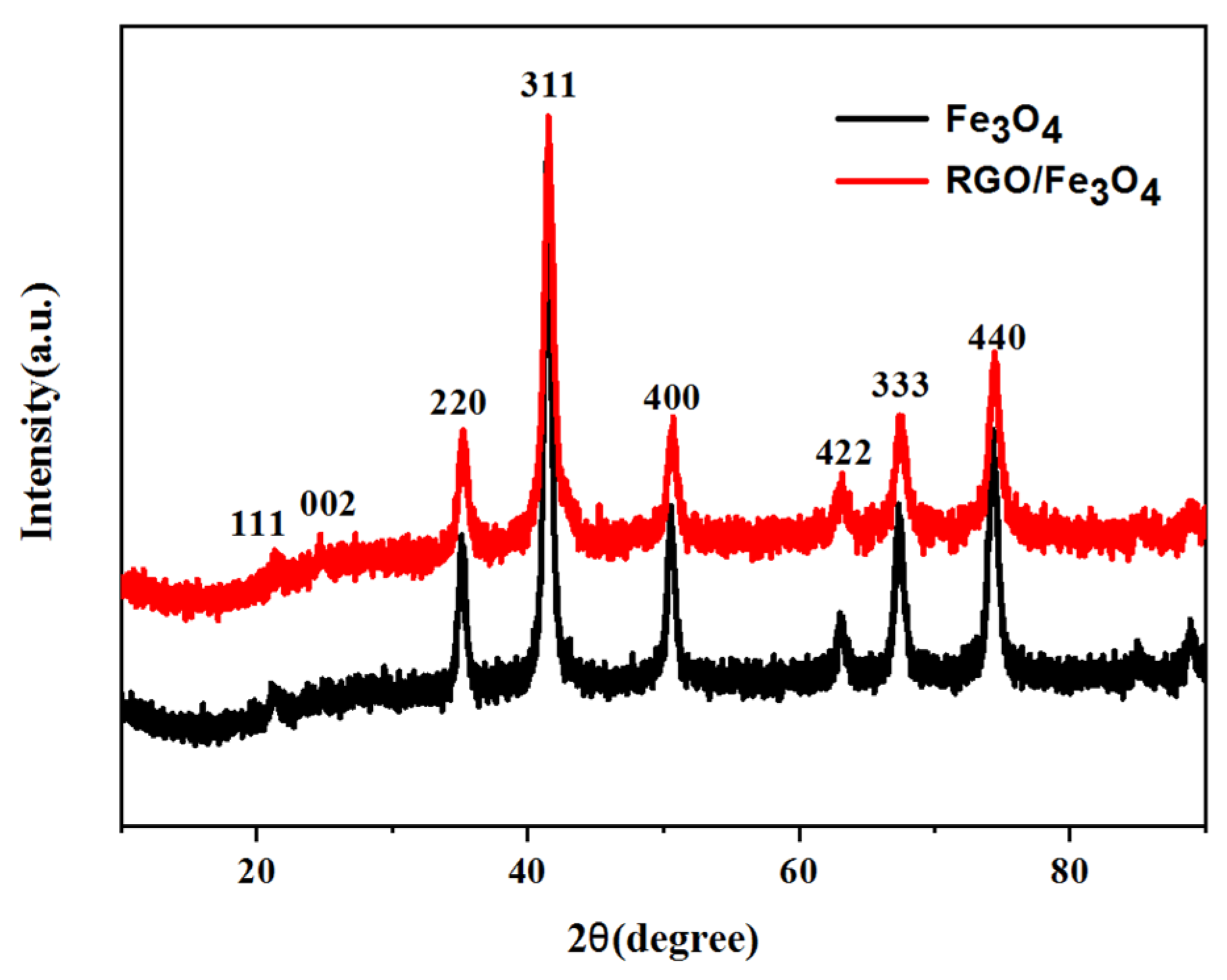
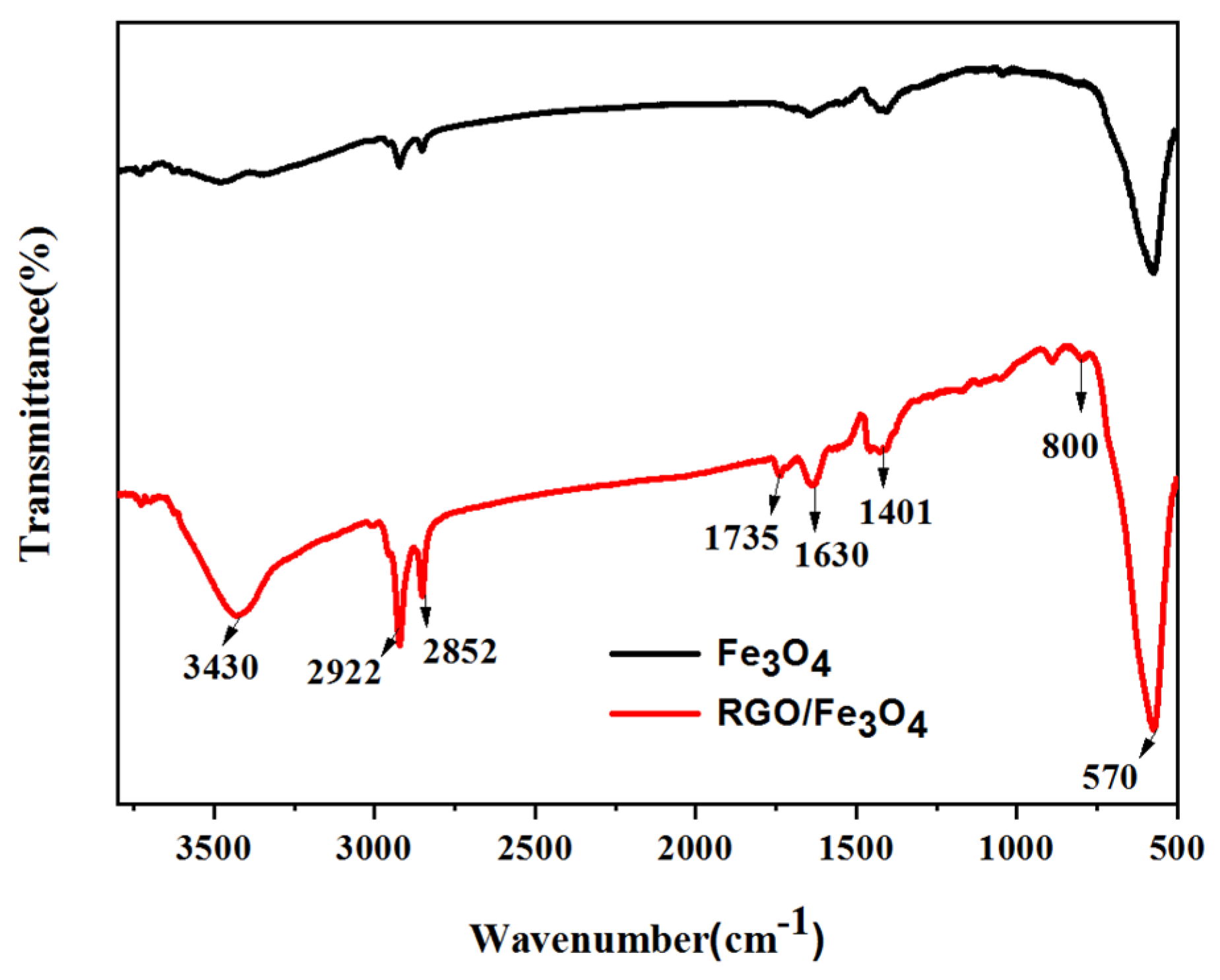
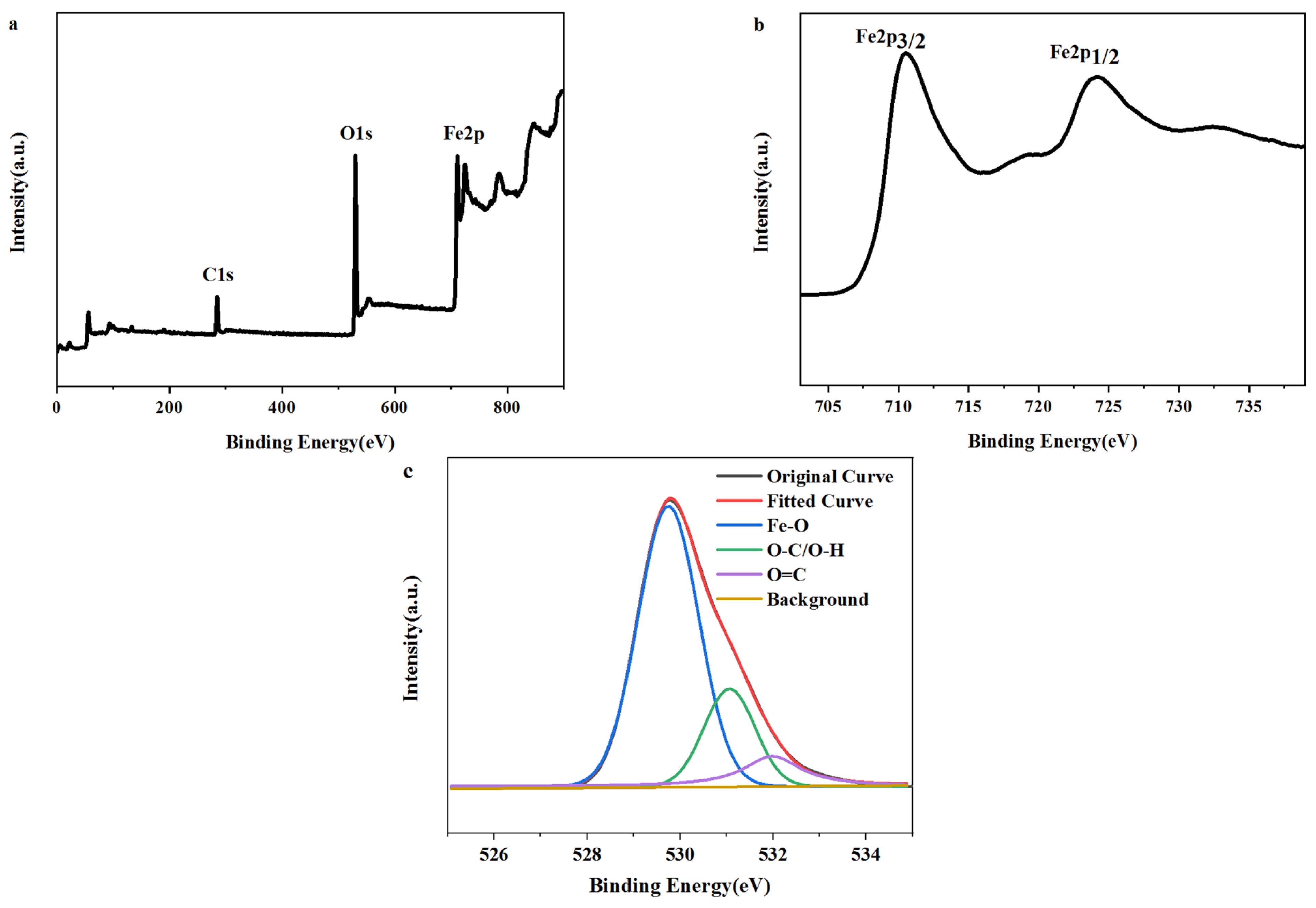
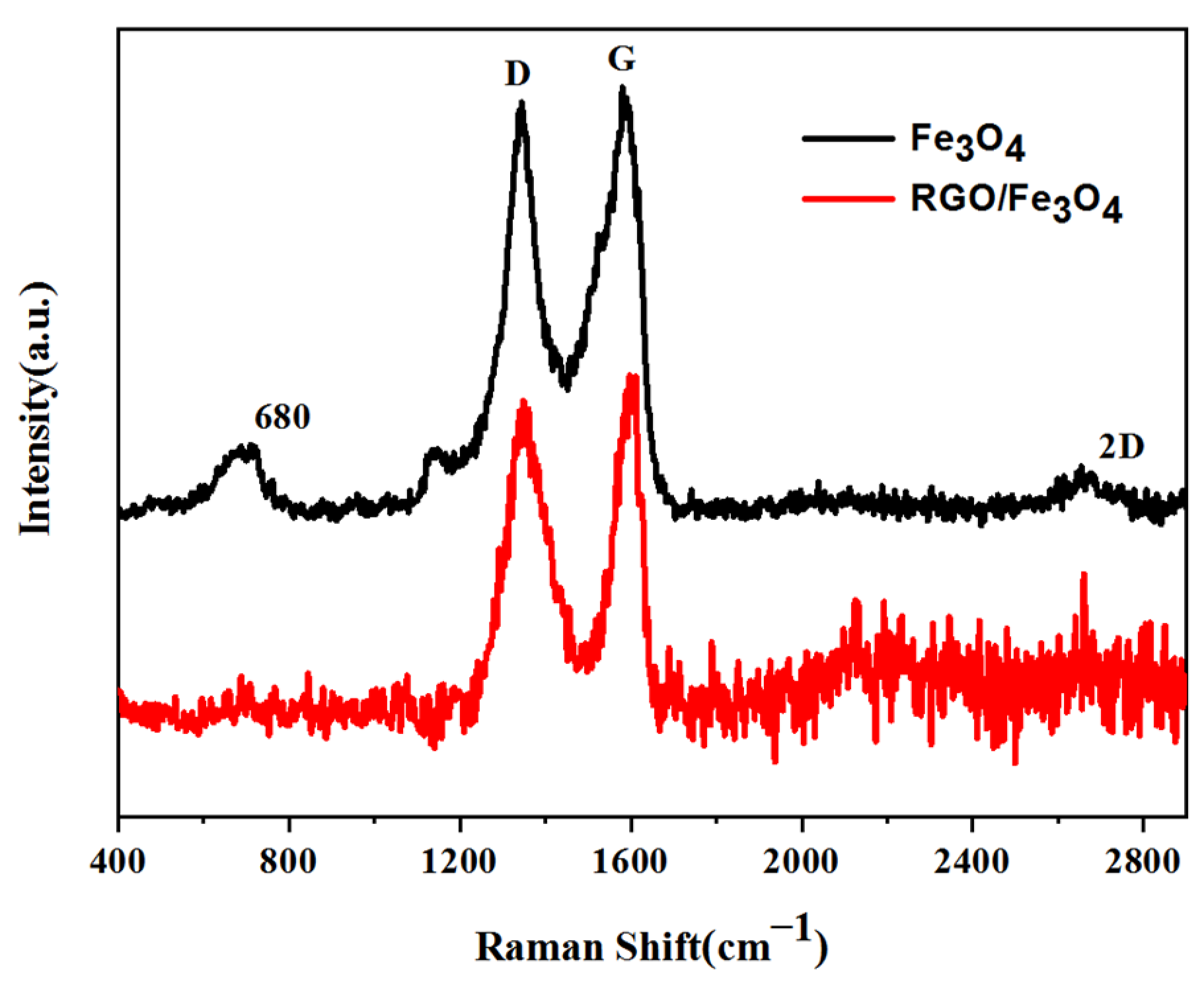
2.1. Morphology and Chemical Composition Analysis
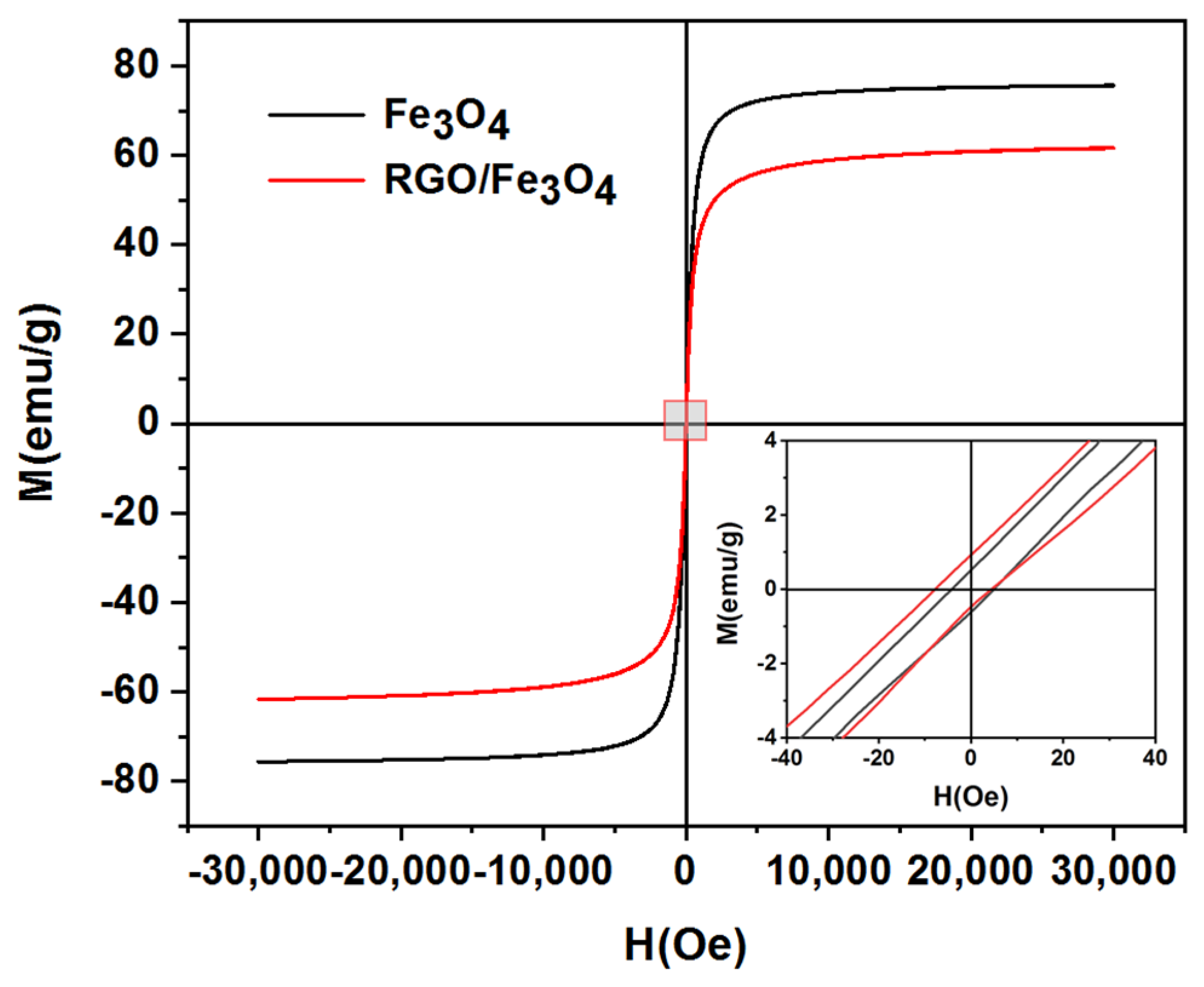
2.2. Magnetic Properties
2.3. Hydrophobic Properties
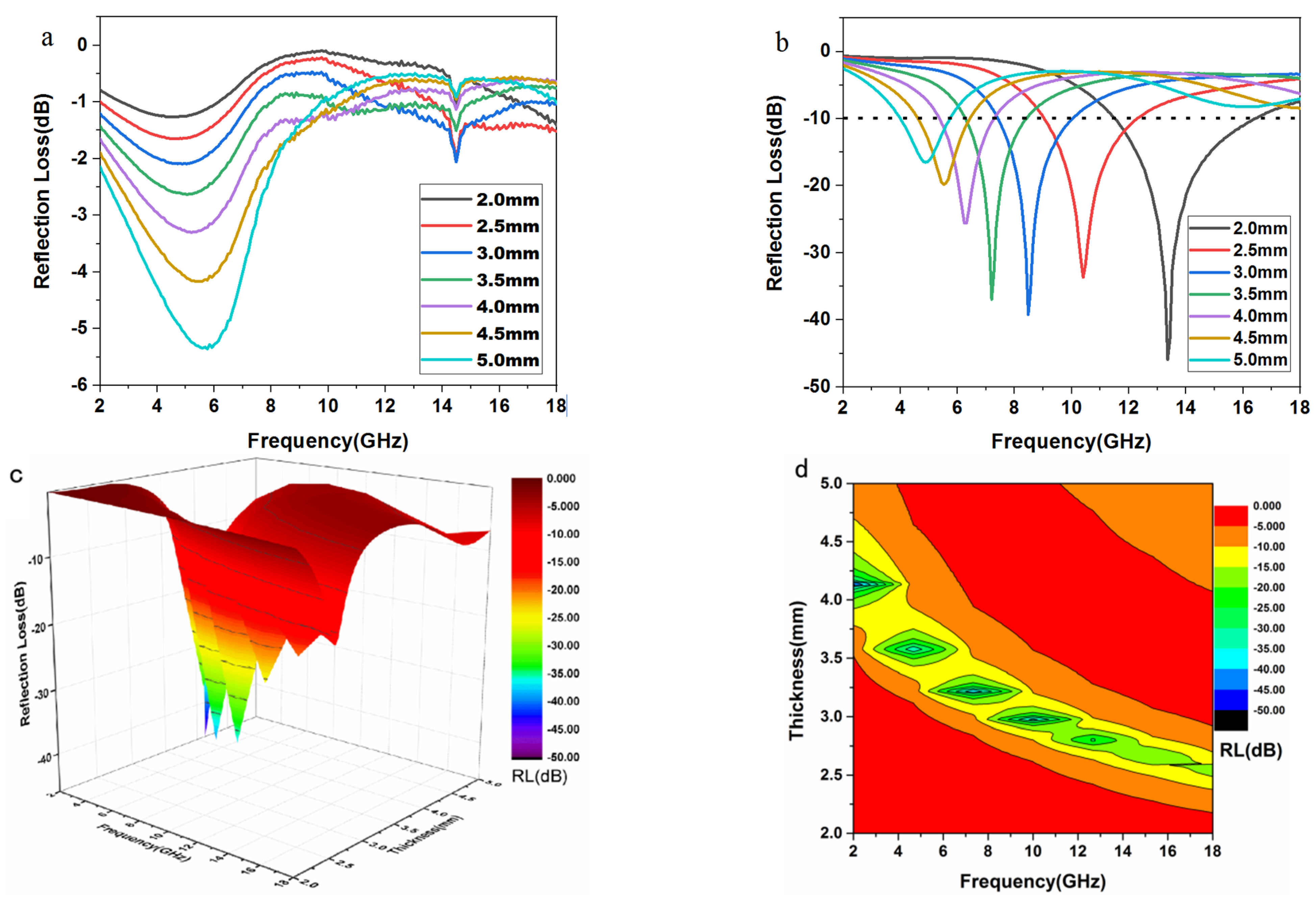
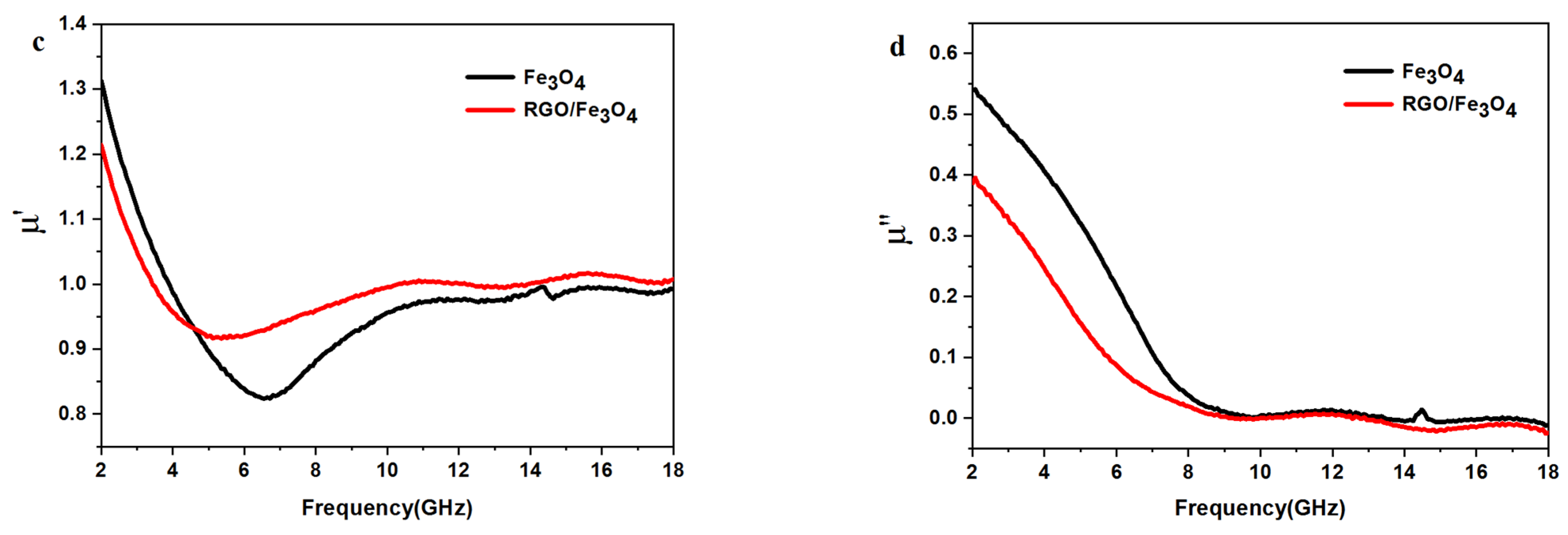
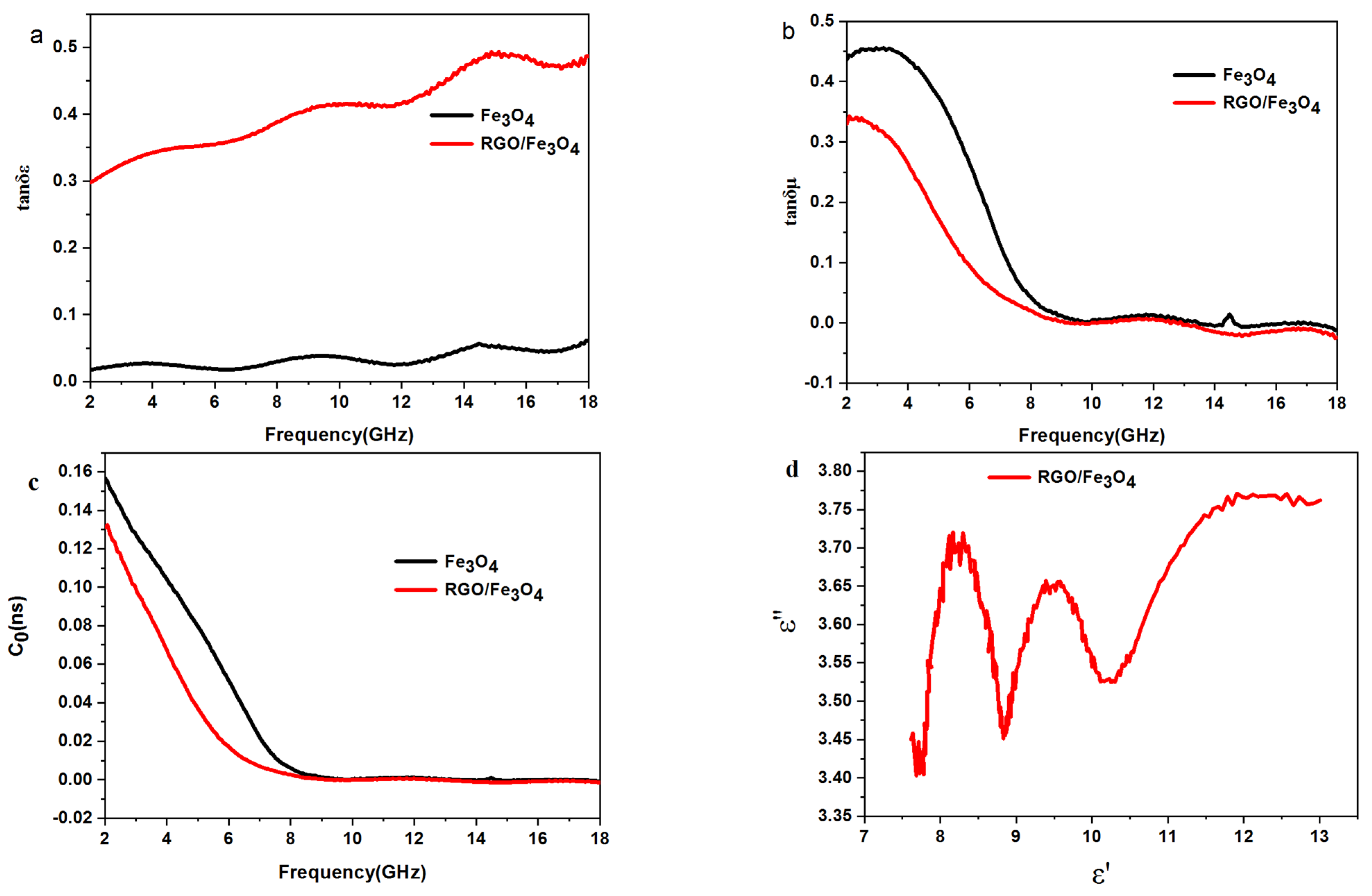
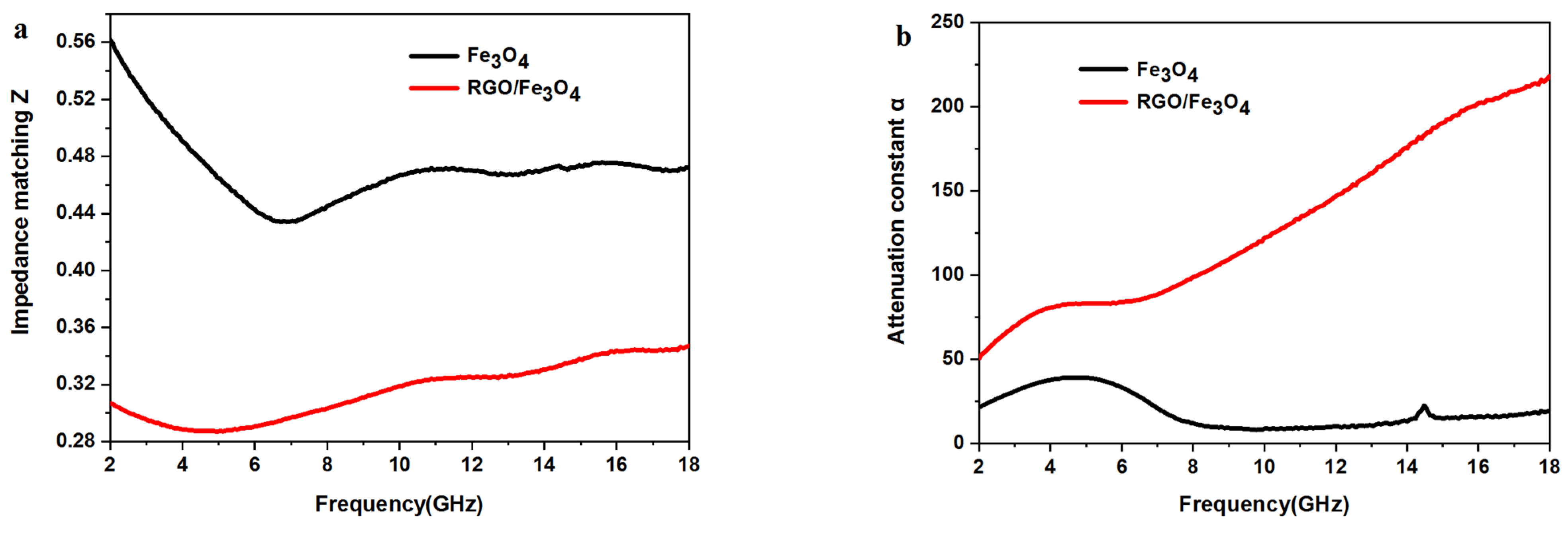
2.4. Analyses of Electromagnetic Parameters and Absorbing Properties
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Preparation of Hydrophobic RGO/Fe3O4 Nanocomposites
3.3. Characterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, R.; Huang, X.; Zhong, B.; Xia, L.; Wen, G.; Zhou, Y. Enhanced microwave absorption properties of ferroferric oxide/graphene composites with a controllable microstructure. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 16952–16962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liao, Q.; Zhang, G.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y. Electromagnetic wave absorption in reduced graphene oxide functionalized with Fe3O4/Fe nanorings. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 2018–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Wang, H.; Huang, F.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Z.; Hui, D.; Zhou, Z. Graphene-based microwave absorbing composites: A review and prospective. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2018, 137, 260–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Ren, B.; Wu, S.; Wang, W.; Zhou, X. Facile synthesis of rGO/SmFe5O12/CoFe2O4 ternary nanocomposites: Composition control for superior broadband microwave absorption performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 453, 464–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boruah, P.K.; Borah, D.J.; Handique, J.; Sharma, P.; Sengupta, P.; Das, M.R. Facile synthesis and characterization of Fe3O4 nanopowder and Fe3O4/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite for methyl blue adsorption: A comparative study. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 3, 1974–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Cao, J.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhao, H.; Ji, G.; Du, Y. The outside-in approach to construct Fe3O4 nanocrystals/mesoporous carbon hollow spheres core-shell hybrids toward microwave absorption. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 6, 1427–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.N.; Sharma, N.; Kumar, L. Synthesis of graphene oxide (GO) by modified hummers method and its thermal reduction to obtain reduced graphene oxide (rGO). Graphene 2017, 6, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Ren, B.; Cai, K.; Song, Y.F.; Wang, W. Synthesis of nonstoichiometric Co0.8Fe2.2O4/reduced graphene oxide (rGO) nanocomposites and their excellent electromagnetic wave absorption property. J. Alloys Comp. 2019, 774, 997–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Yao, Z.; Zhou, J.; Preparation of reduced graphene oxide/Ni0. 4Zn0.4Co0.2Fe2O4 nanocomposites and their excellent microwave absorption properties. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 13409–13416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Tri, P.; Tran, H.N.; Plamondon, C.O.; Tuduri, L.; Nanda, D.V.; Mishra, A.; Chao, H.P.; Bajpai, A.K. Recent progress in the preparation, properties and applications of superhydrophobic nano-based coatings and surfaces: A review. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 132, 235–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewmanee, T.; Wannapop, S.; Phuruangrat, A.; Thongtem, T.; Wiranwetchayan, O.; Promnopas, W.; Sansongsiri, S.; Thongtem, S. Effect of oleic acid content on manganese-zinc ferrite properties. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2019, 103, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S.M.; Sinha, B.B.; Phase, D.; Sen, D.; Sastry, P.U.; Kolekar, Y.D.; Ramana, C.V. Particle size, morphology, and chemical composition controlled CoFe2O4 nanoparticles with tunable magnetic properties via oleic acid based solvothermal synthesis for application in electronic devices. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2019, 2, 1828–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, F.Z.; Ahmad, I.; Siddiqui, J.J.; Ali, K.M.; Mudsar, M.; Arshad, H. Light weight RGO/Fe3O4 nanocomposite for efficient electromagnetic absorption coating in X-band. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 19775–19782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yi, H.; Zhang, J.; Feng, J.; Li, F.; Xue, D.; Zhang, H.; Peng, Y.; Mellors, N.J. Fe3O4-graphene hybrids: Nanoscale characterization and their enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption in gigahertz range. J. Nanopart. Res. 2013, 15, 1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, C.; Pan, E.; Jia, M. Fe3O4 nanoparticle/graphene aerogel composite with enhanced lithium storage performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 458, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.M.; Rasheed, M. Solid state reaction synthesis and characterization of Cu doped TiO2 nanomaterials. Mater. Chem. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1795, 021059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinca, T.F.; Chicinaş, H.F.; Neamţu, B.V.; Isnard, O.; Pascuta, P.; Lupu, N.; Stoian, G.; Chicinaş, I. Mechanosynthesis, structural, thermal and magnetic characteristics of oleic acid coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 171, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Y.; Li, B.; Shi, T.N.; Wang, Y.; Komarneni, S. Nanoparticles of magnetite anchored onto few-layer graphene: A highly efficient Fenton-like nanocomposite catalyst. J. Colloid Interface. Sci. 2018, 532, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, H.; Gan, D.; Guo, L.; Liu, M.; Chen, J.; Deng, F.; Zhou, N.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y. A facile strategy for preparation of magnetic graphene oxide composites and their potential for environmental adsorption. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 18571–18577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, M.; Shihab, S.; Sabah, O.W. An investigation of the structure, electrial and optical properties of graphene-oxide thin films using different solvents. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1795, 012052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Ng, V.M.H.; Yao, Z.; Zhou, J.; Lei, Y.; Yang, Z.; Kong, L.B. Microwave absorption properties of double-layer absorbers based on Co0.2Ni0.4Zn0.4Fe2O4 ferrite and reduced graphene oxide composites. J. Alloys Comp. 2017, 701, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuvaneswari, S.; Pratheeksha, P.M.; Anadan, S.; Rangappa, D.; Gopalan, R.; Rao, T.N. Efficient reduced graphene oxide grafted porous Fe3O4 composite as a high performance anode material for Li-ion batteries. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 5284–5294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Wang, H.; Xu, D.; Liao, K.; Wang, R.; He, B.; Gong, Y.; Yan, C. High-energy flexible quasi-solid-state lithium-ion capacitors enabled by a freestanding rGO-encapsulated Fe3O4 nanocube anode and a holey rGO film cathode. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 17814–17823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Lin, J.; Xiao, J.; Fan, H. Synthesis and electromagnetic, microwave absorbing properties of polyaniline/graphene oxide/ Fe3O4 nanocomposites. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 19345–19352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, S.; Sardar, M.; Satpati, B.; Kumar, S.; Banerjee, S. Magnetization enhancement of Fe3O4 by attaching on graphene oxide: An interfacial effect. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2018, 122, 21356–21365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xia, L.; Zhang, T.; Shi, B.; Huang, L.; Zhong, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Wen, G. Fe3O4@LAS/RGO composites with a multiple transmission-absorption mechanism and enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 352, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Shu, R.; Xie, Y.; Xia, H.; Gan, Y.; Shi, J.; He, J. Cubic MnFe2O4 particles decorated reduced graphene oxide with excellent microwave absorption properties. Mater. Lett. 2018, 23, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Wu, Y.; Cai, H.; Qu, X.; Ni, L.; Teng, C.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, L. Fe3O4 Nanopearl decorated carbon nanotuves stemming from carbon onions with self-cleaning and microwave absortpion properties. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 54175–54181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Kwon, J.S.; Lee, C.H.; Bae, K.; Sohn, S.; Kim, H.M. Optimization of super-hydrophobic property by two-step surface modification. J. Nanosci. Nanotechno. 2019, 19, 7192–7197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shooshtary Veisi, S.; Yousefi, M.; Amini, M.M.; Shakeri, A.R.; Bagherzadeh, M. Magnetic and microwave absorption properties of Cu/Zr doped M-type Ba/Sr hexaferrites prepared via sol-gel auto-combustion method. J. Alloys Comp. 2019, 773, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Singh, C.; Marwaha, A.; Narang, S.B.; Jotania, R.; Mishra, S.R.; Bai, Y.; Raju, K.C.J.; Singh, D.; Ghimire, M.; et al. Elucidation of microwave absorption mechanisms in Co-Ga substituted Ba–Sr hexaferrites in X-band. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 14995–15005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhao, H.; Yang, Z.; Lv, J.; Cao, J.; Qi, X.; Ji, G.; Du, Y. An unusual route to grow carbon shell on Fe3O4 microspheres with enhanced microwave absorption. J. Alloys Comp. 2018, 762, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, H.J.; Jun, G.H.; Lee, D.J.; Ryu, H.J.; Hong, S.H. Enhanced electromagnetic interference shielding behavior of graphehe nanoplatelet/Ni/Wax nanocomposites. J. Mater. Chem. C. 2017, 5, 6471–6479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.; Meng, X.; Lu, C. Exchange-coupled Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4/SrFe12O19 composites with enhanced microwave absorption performance. J. Alloys Comp. 2018, 768, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ye, Z.; Liu, Z.; Chen, J. The effect of GO loading on electromagnetic wave absorption properties of Fe3O4/reduced graphene oxide hybrids. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 13146–13153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Ye, M.; Han, A.; Guo, J.; Chen, C. Nanosheet architecture of Cu9S5 loaded with Fe3O4 microspheres for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 8803–8811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhong, K.; Shi, T.; Meng, X.; Wu, G.; Lu, Y. Enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance of core-shell Fe3O4@poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) microspheres/reduced graphene oxide composite. Carbon 2021, 178, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hen, J.; Gao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, H. N-doped residual carbon from coal gasification fine slag decorated with Fe3O4 nanoparticles for electromagnetic wave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 104, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, T.K.; Singh, B.P.; Singh, V.N.; Teotia, S.; Singh, A.P.; Elizabeth, I.; Dhakate, S.R.; Dhawan, S.K.; Mathur, R.B. MnO2 decorated graphene nanoribbons with superior permittivity and excellent microwave shielding properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 4256–4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.; Singh, A.P.; Singh, B.P.; Singh, V.N.; Dhawan, S.K. Conducting ferrofluid: A high-performance microwave shielding material. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 13159–13168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Singh, A.P.; Varshney, S.; Agrawal, N.; Sambyal, P.; Pandey, Y.; Singh, B.P.; Singh, V.N.; Gupta, B.K.; Dhawan, S.K. New insight into the shape-controlled synthesis and microwave shielding properties of iron oxide covered with reduced graphene oxide. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 62413–62422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi Afshar, S.R.; Hasheminiasari, M.; Masoudpanah, S.M. Structural, magnetic and microwave absorption properties of SrFe12O19/Ni0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4 composites prepared by one-pot solution combustion method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 466, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, A.; Jia, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Lv, H. Development of Fe/Fe3O4@C composite with excellent electromagnetic absorption performance. J. Alloys Comp. 2018, 745, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Zhu, D.; Zhou, W.; Min, D.; Luo, F. Enhanced impedance matching and microwave absorption properties of the MAMs by using ball-milled flaky carbonyl iron-BaFe12O19 as compound absorbent. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 467, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, K.; Qiao, X.J.; Sun, Z.G.; Guo, X.D.; Wei, L.; Qu, Y. Preparation and microwave absorbing properties of graphene oxides/ferrite composites. Appl. Phys. A 2017, 123, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandihalli, N.; Gregory, D.H.; Mori, T. Energy-saving pathways for thermoelectric nanomaterial synthesis: Hydrothermal/solvothermal, microwave-assisted, solution-based, and powder processing. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2106052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.J.; Vaidhyanathan, B.; Ganguli, M.; Ramakrishnan, P.A. Synthesis of inorganic solids using mcicrowaves. Chem. Mater. 1999, 11, 882–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadian, R.; Rahmani, S.; Seyed Dorraji, M.S.; Hajimiri, I. Microwave absorption properties of GO nanosheets-BaFe12O19-NiO nanocomposites based on epoxy resin: Optimization using Taguchi methodology. J. Mater. Sci-Mater. Electron. 2017, 29, 4583–4595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Huang, Z.H.; Lu, M.M.; Cao, W.Q.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, D.Q.; Cao, M.S. 3D Fe3O4 nanocrystals decorating carbon nanotubes to tune electromagnetic properties and enhance microwave absorption capacity. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 12621–12625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, R.; Zhang, G.; Wang, X.; Gao, X.; Wang, M.; Gan, Y.; Shi, J.; He, J. Fabrication of 3D net-like MWCNTs/ZnFe2O4 hybrid composites as high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbers. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 337, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, H.; Pang, W.; Zhang, B.; Ren, N. Excellent microwave absorption properties of the h-BN–GO–Fe3O4 ternary composite. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 11722–11730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xie, Y.; Lu, W.; Chou, T.W. Flexible electromagnetic wave absorbing composite based on 3D rGO-CNT-Fe3O4 ternary films. Carbon 2018, 129, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zong, M. Synthesis of holey reduced graphene oxide covered in the FeCo@SiO2 and their enhanced electromagnetic absorption properties. J. Compos. Mater. 2019, 53, 1973–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Xiong, X.; Chen, P.; Yu, Q.; Chu, H.; Yang, S.; Wang, Q. Superior corrosion-resistant 3D porous magnetic graphene foam-ferrite nanocomposite with tunable electromagnetic wave absorption properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2019, 469, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Peng, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Augustine, R.; Mahmoud, M.M.; Tang, H.; Rao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, G.; Jiang, T. Achieving ultra-high electromagnetic wave absorption by anchoring Co0.33Ni0.33Mn0.33Fe2O4 nanoparticles on graphene sheets using microwave-assisted polyol method. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 21015–21026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Guo, Y.; Wu, G.; Ji, G.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, Z. Interface polarization strategy to solve electromagnetic wave interference issue. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2017, 9, 5660–5668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, R.; Li, W.; Zhou, X.; Tian, D.; Zhang, G.; Gan, Y.; Shi, J.; He, J. Facile preparation and microwave absorption properties of RGO/MWCNTs/ZnFe2O4 hybrid nanocomposites. J. Alloys Comp. 2018, 743, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Dai, S.; Ji, G.; Zhao, H.; Cao, J.; Du, Y. Rationally regulating complex dielectric parameters of mesoporous carbon hollow spheres to carry out efficient microwave absorption. Carbon 2018, 127, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, F.W.; Lai, C.W.; Abd Hamid, S.B. Easy preparation of ultrathin reduced graphene oxide sheets at a high stirring speed. Ceram. Int. 2015, 41, 5798–5806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Samples | RLmin or Shielding Effectiveness(dB) | Bandwidth (RL < −10 dB, GHz) | Thickness (mm) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FeNR@rGO | −23.1 | 3.9 | 4.0 | [2] |
| Fe3O4/rGO | 22.7 | 3.1 | 3.0 | [35] |
| Cu9S5/Fe3O4 | −39.5 | 2.2 | 4.3 | [36] |
| Fe3O4@PEDOT/rGO | −48.8 | 4.3 | 2.9 | [37] |
| Fe3O4/NRC | −29.6 | 4.32 | 1.5 | [38] |
| MnO2/GNRs | −57 | 5.6 | 3.0 | [39] |
| Conducting ferrofluid composite | 41 | 4 | - | [40] |
| Iron oxide-RGO | 33.0 | −5.6 | - | [41] |
| RGO/Fe3O4 | −45.7 | 5 | 2.0 | this work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Du, S.; Hong, R.; Chen, H. Preparation of RGO/Fe3O4 Nanocomposites as a Microwave Absorbing Material. Inorganics 2023, 11, 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11040143
Chen X, Du S, Hong R, Chen H. Preparation of RGO/Fe3O4 Nanocomposites as a Microwave Absorbing Material. Inorganics. 2023; 11(4):143. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11040143
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xingtian, Shumin Du, Ruoyu Hong, and Huaiyin Chen. 2023. "Preparation of RGO/Fe3O4 Nanocomposites as a Microwave Absorbing Material" Inorganics 11, no. 4: 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11040143
APA StyleChen, X., Du, S., Hong, R., & Chen, H. (2023). Preparation of RGO/Fe3O4 Nanocomposites as a Microwave Absorbing Material. Inorganics, 11(4), 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11040143







