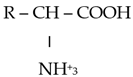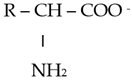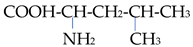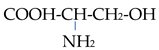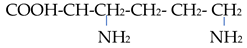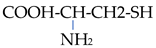1. Introduction
The basis of the economy of Kazakhstan is its mining and metallurgical complex, which plays an important and, in several industries, strategic role not only in Kazakhstan but also globally [
1].
However, the reserves of high-quality ores in the republic have decreased from year to year, and the share of difficult-to-process and low-grade ores has increased, which requires the involvement of substandard raw materials during production. In particular, the extraction of precious metals is expanding due to the involvement of low-grade ores during processing in new primary and off-balance areas of exploited deposits, old ore dumps, the stale tailings of processing plants, refractory (difficult to process) ores, and technogenic waste [
2].
Involving low-grade raw materials in production requires new approaches for the development of easy-to-use and effective technologies.
Currently, with respect to global practice, a significant amount of gold-containing raw materials is processed using sodium cyanide [
3,
4,
5,
6,
7]. The cyanidation process is the main method for extracting gold from ores and concentrates. The essence of the process is that crushed material containing noble metals is brought into contact with dilute alkaline solutions of sodium cyanide; under this influence, gold and silver enter the solution.
The relative selectivity of sodium cyanide as a solvent, the successful combination of the processes of dissolution and the precipitation of noble metals, and the simplicity of the equipment and other advantages of cyanidation render this process very effective and productive, providing the possibility of applying this technology not only to concentrates but also to gold ores; in a number of cases, this process can also be applied to technogenic raw materials.
Due to the technological and economic advantages over other alternative options for the metallurgical processing of gold ore raw materials, cyanidation has firmly occupied a central place in gold production technology for more than 110 years. Over the past 20 years, more than 90% of the world’s metal was mined using this method. Currently, out of many hundreds of operating gold extraction factories, only a few operate without the use of cyanidation. This trend will continue for many years to come [
6].
The gold mining industries of South Africa, Canada, the USA, Australia, and other countries that are the main producers of gold, use the cyanide process. In the Soviet Union, in 1990, more than 85% of all gold ores were processed via cyanidation. Currently, in Russia and CIS countries, this value has increased to 95% [
7].
In Kazakhstan, as in general world practice, sodium cyanide remains the main chemical tool for extracting gold from ores and concentrates [
8]. The presence of gold in raw materials that can be easily opened allows it to be extracted by directly exposing the raw material to an alkaline solution of sodium cyanide, i.e., the direct cyanidation method is used. However, due to the depletion of quality raw material reserves, ores in which gold is concentrated in fine association with sulfide minerals, such as iron, arsenic, copper, and other non-ferrous metals (pyrite, arsenopyrite, chalcopyrite, etc.), are increasingly involved in production. In a number of deposits, carbon is present. The fine association between gold and minerals (fine dissemination of gold in minerals) and the presence of carbon and other impurities in lower valency forms (Fe, As, and S) create insurmountable difficulties for the extraction of gold via direct cyanidation. These types of ore are usually classified as refractory types of raw materials. Deposits with refractory ores in Kazakhstan include more than a third of the republic’s explored gold reserves. As a rule, the processing of refractory ores, as well as technogenic and low-grade raw materials, is characterized by low gold recovery rates during cyanide leaching and requires the use of a number of additional techniques.
Traditional methods for preparing refractory ores are flotation enrichment and oxidative roasting [
9,
10,
11]. Flotation enrichment is based on how minerals can be retained on the interphase surface due to the different wettability of minerals. The flotation method for extracting metals from ore is a complex process that is influenced by many factors. The flotation of complex polymetallic ores depends, first of all, on the mineralogical composition and type of host rocks; flotation conditions also have a significant impact on flotation, i.e., the technological mode of the process and, of course, reagent support. The reagents used in flotation ensure high selectivity, stability, and efficiency with respect to the flotation process, and they also create the greatest opportunities for improving and intensifying this enrichment method. The influence of flotation reagents makes it possible to change the surface properties of minerals over a wide range, which makes flotation the most universal method for the beneficiation of minerals. At the same time, the use of classical flotation reagents for processing refractory and low-grade raw materials increases the cost of the flotation process. In addition, it is not always possible to achieve the desired results.
The most studied and widely used industrial method for preparing refractory gold ores for cyanide stripping is oxidative roasting [
11]. During the roasting process, sulfur and arsenic are transferred into the gas phase in the form of arsenic trioxide and sulfur dioxide. Gold is easily extracted from the resulting cinder via cyanidation. The firing method is quite simple and well mastered, and it is still used in Canada, South Africa, Australia, etc. However, its popularity is declining due to the need for the strict control of SO
2 and As
2O
3 emissions.
In recent years, there has been a steady tendency to reduce the use of roasting for the pre-processing of refractory gold-containing raw materials due to its serious disadvantages: low gold recovery due to the formation of fusible compound films on the opened gold’s surface and the carryover of gold into arsenic sublimes; inevitable environmental pollution with the emission of arsenic and sulfur; and the need for the expensive disposal of highly toxic arsenic trioxide [
12].
Since the late 1980s, hydrometallurgical autoclave and bacterial dissection technologies have been gradually introduced into the preparatory process of processing gold-containing raw materials [
13,
14]. Processes such as Albion, Leachox, etc., have also been proposed [
15,
16].
The essence of the autoclave method for opening refractory gold is the oxidation of gold-containing sulfide concentrates in an aqueous environment under the influence of oxygen at elevated temperatures. As a result of the autoclave’s opening, the submicroscopic and solid-soluble gold associated with sulfides is released and made available for subsequent leaching with a cyanide solution. The first industrial plant for processing refractory gold-bearing raw materials was built at the McLaughlin Gold Mine (USA) in 1986 [
7].
Compared to roasting, the autoclave opening method has the following advantages: higher gold recovery; no gas emissions of arsenic and sulfur compounds; the removal of arsenic in the form of low-toxicity iron arsenate, which can be discharged into a conventional tailings pond; low sensitivity to the presence of impurities, such as antimony and lead in raw materials (which reduce gold recovery when roasting is used); and the possibility of processing both flotation concentrates and ores of different composition and quality. A significant disadvantage of this method is the need to use expensive acid-resistant equipment. In addition, operating an autoclave under high-pressure conditions creates additional dangerous circumstances [
16].
The Albion process [
16,
17] is a combination of ultrafine grinding and oxidative leaching at atmospheric pressure; in this case, sulfides, as in the autoclave method, are oxidized, releasing metals for subsequent extraction via cyanidation. The ultrafine grinding of raw materials is carried out in mills up to 80% of the size class at 10–20 microns, which is accompanied by an increase in the number of grain cracks and lattice defects in the mineral compared to unground minerals. Due to the increase in the surface area of minerals, the rate of oxidation of the finely ground product increases. Fine grinding also prevents sulfide passivation, which occurs when oxidation products such as iron oxides and elemental sulfur are deposited on the surface of the sulfide mineral.
Leachox technology, similarly to Albion, is based on the ultrafine grinding of materials up to 95% of the size class at 20 microns and atmospheric oxidation with oxygen (cavitation feed) in special column reactors at 25 °C towards an oxidation degree of 5–15%, with respect to the processed product [
17].
In recent years, the use of biotechnology in the processing of refractory gold ores has increased due to the significant advantages of these technologies in terms of economic efficiency and environmental security. The process is based on oxidation via the bacteria of minerals in which gold is embedded. In summary, these are sulfides contained in refractory ores, due to which gold is released, turning into their native form. The gold is then extracted using cyanidation. Bioleaching is an attractive alternative to the traditional physical and chemical methods of ore beneficiation due to the reduced resource intensity of the technology and fewer harmful effects induced upon the environment [
18,
19].
Biotechnologies not only involve the microorganisms’ impact on raw materials but also the impact of bioadditives. Recently, scientists have become interested in studying the leaching of low-grade raw materials in the presence of natural organic substances—bioreagents. Organic additives promote the effect of chemically active substances on raw materials and stimulate processes such as hydrolysis and oxidation. Among dietary supplements, amino acids occupy one of the main positions. The most popular amino acid is glycine [
20,
21,
22,
23,
24].
Glycine has a unique ability to form complexes with the ions of precious, rare, and non-ferrous metals, which, combined with non-toxicity, makes it the most promising new-generation leaching reagent. Glycine can effectively leach copper, gold, and other important elements from various types of raw materials. The main advantages of using glycine as an alternative to traditional leaching reagents is its availability, low cost, and the fact that it does not react with non-metallic minerals (clays, carbonates, and oxides and hydroxides of iron), which simplifies the processing of the resulting solutions by eliminating purification operations from impure elements.
The authors of [
25] studied the leaching of gold with alkaline amino acid–peroxide solutions at low concentrations. It was observed that amino acids (glycine, alanine, and histidine) can dissolve gold in alkaline conditions at low and moderate temperatures. Heating the leaching solution from 40 to 600 °C significantly increases the dissolution of gold in alkaline amino acid–peroxide solutions. It was also observed that gold dissolution increases with increasing amino acid, peroxide, and pH concentrations and that histidine enhances gold dissolution when used in equimolar amounts with glycine.
In another study by these authors [
26], the use of strong oxidizing agents for leaching gold in glycine solutions was studied. The effects of oxidizing agents, such as potassium permanganate, hydrogen peroxide, sodium chlorate, potassium iodide, and potassium ferricyanide, were initially assessed in a screening test. The highest gold leaching rate (85.1%) was observed using 1.5 kg/t glycine and 3 kg/t potassium permanganate at a pH of 10.5 and ambient temperatures. This value is close to the value for the recovery of gold from the same raw materials under similar conditions via cyanidation (87.4%). If potassium permanganate is in molar excess, the leaching rate is greatly reduced due to glycine oxidation. Gold is recovered from leaching solutions via conventional adsorption on activated carbon.
The main goal of the authors of [
22] (Mojtaba Sarvar, Ziaedin Shafaei Tonkaboni, Mohammad Noaparast, Ali Reza Badiei, and Ahmad Amiri) was to investigate the ability of a number of amino acids to recover gold during leaching. For this purpose, eight amino acids were used to leach native gold: glycine, alanine, valine, phenylalanine, histidine, asparagine, aspartic acid, and cysteine. The studied parameters were as follows: temperature, the concentration of hydrogen peroxide (as an oxidizing agent), pH values, and the concentration of amino acids. The results showed that the presence of hydrogen peroxide, moderate temperature, and an alkaline environment were key factors for gold leaching. It should be noted that cysteine can dissolve gold at ambient temperatures and in the absence of hydrogen peroxide. It was also observed that the order of amino acids during gold leaching was asparagine > glycine > histidine > cysteine > phenylalanine > valine > aspartic acid > alanine. The authors of [
27] studied the leaching of complex gold ores using cyanide and glycine. It was shown that gold recovery during cyanide leaching increased from 6.47 to 62.21% relative to an increase in cyanide concentrations from 250 to 4500 g/t. At a cyanide concentration of 2000 g/t and a glycine concentration of 0.5 mol/L in the absence of H
2O
2, gold recovery was 78% and increased to 88% and 93% with an increase in H
2O
2 concentrations to 1 and 1.5%, respectively.
Much attention has been focused on the glycinate leaching processes of gold in the research reported by the Mining and Process Solutions company (MPS, Perth, Australia). The company has patented metal leaching methods: GlyLeach and GlyCat [
27]. The GlyLeach process completely eliminates the use of NaCN and is promising for the development of gold ore deposits using heap leaching (HI) and in situ leaching (IF), which was successfully tested in 2019; its use at a pH value of 12.5 ensured the extraction of ~85% Au into a solution.
The GlyCat process involves leaching base and noble metals with glycine solutions via the addition of a small amount of NaCN (0.15–0.2 g/L NaCN, pH 9–12). Pilot tests of the GlyCat process were carried out in 2017–2019 at the Telfer gold mining enterprise. As a result, the degree of Au recovery from the collective copper–pyrite flotation concentrate was achieved: 83–90%. The process was carried out in the agitation mode at a pH value of 10.5. The leaching duration was 48 h at 35 °C.
Analyzing different gold ore processing methods, it was observed that the advantages of the cyanide gold leaching process, as paradoxical as it may sound at first glance, include its environmental friendliness. Spent cyanide solutions that are removed from the technological process are relatively easily decomposed via various chemical oxidizing agents (chlorine, ozone, hydrogen peroxide, etc.), and the eventual formation of nitrogen-containing compounds and carbon dioxide occurs, which not only does not pose a danger to the environment but, on the contrary, promotes the development of flora and fauna. This fact—combined with the relatively low concentration of cyanide in working solutions, the non-aggressiveness of cyanide solutions towards various structural materials, and the real possibility of their chemical purification relative to the required MPC standards—makes the use of cyanide in gold production technology more convenient compared to acids and concentrated alkalis or saline solutions. Despite the disadvantages, such as the length of the process, the cumbersomeness of the equipment, the low extraction of gold from poor ores, etc., it was not possible to create a process that is generally competitive relative to cyanide.
Thus, the cyanidation process of gold ores, mastered by the industry many years ago, now not only does not lose its importance but, on the contrary, is tending towards further development and improvement, occupying a dominant position among other metallurgical processing methods with respect to raw gold ore materials.
2. Results and Discussion
The purpose of this study was to study the possibility of using amino acids of different structures in the cyanide leaching of gold from low-grade ores to increase the efficiency of the process.
During the first stage, the physical and chemical studies of the initial low-grade gold ore from a Kazakhstan deposit were carried out. According to X-ray phase analyses (
Table 1), the main component of the sample was quartz, i.e., the ore was dominated by silicate rocks, and muscovite and clinochlore were contained in lower quantities.
The elemental composition of the ore is presented in
Table 2. The main elements in the ore were silicon, potassium, calcium, sodium, magnesium, and iron, as shown in the table.
The gold content in the ore was 1.28 g/t, according to chemical analyses.
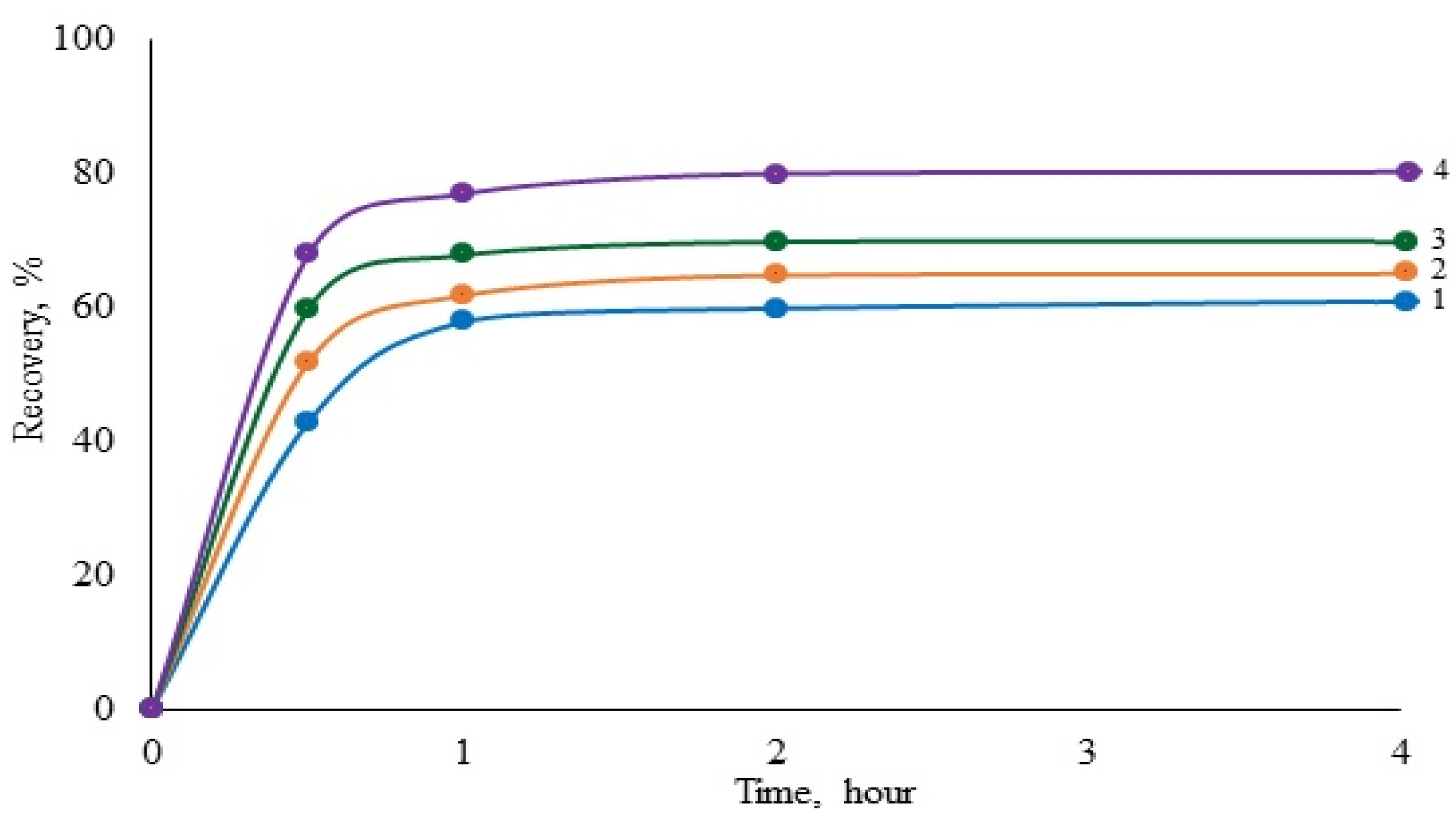
Ore leaching was conducted with a solution of sodium cyanide in the presence of glycine. The study determined the effect of glycine concentrations on the gold’s cyanide leaching degree. The glycine concentration varied within the range of 0.05–0.5 M. The results obtained are presented in
Figure 1, from which it follows that an increase in glycine concentrations from 0.05 to 0.5 M/dm
3 helps increase the gold’s recovery degree.
The chemical properties of amino acids were determined primarily via the presence of a carboxyl group and an amino group. Differences in the reactivity and individual behavior of each amino acid were also determined via the specificity of its side radical. Amino acids are amphoteric; in an acidic environment, where dissociation at the COOH group is suppressed, they behave similarly to a base and become positively charged:
In an alkaline environment, they behave similarly to an acid and are negatively charged:
In this regard, amino acids can form salts with both bases and acids: (NH3 CHRCOOH)Cl and (NH2 CHRCOO)Na. In addition to ordinary salts, amino acids can form intracomplex salts with metal cations:
In this case, the bond in the complex is carried out due to the electrostatic attraction of the metal ion via the oxygen atom of the carboxyl group and its donor–acceptor interaction with the nitrogen atom. Compounds with non-cyclic metals with respect to the coordination of amino acids via the nitrogen atom are also known: Me-NH
2·CHRCOOH [
1,
2,
6].
During the research study, systems based on the following amino acids were studied (
Table 3). As observed in the table, the systems included amino acids of different structures. Amino acids comprise elements, such as carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen, and only one amino acid—cysteine—along with the described elements, includes sulfur.
When gold cyanide is dissolved in an alkaline solution (pH 11.0), a complex ion [Au(CN)
2] is formed, and during interactions with amino acids, it is possible to form complexes based on amino acids and mixed complexes [
28,
29].
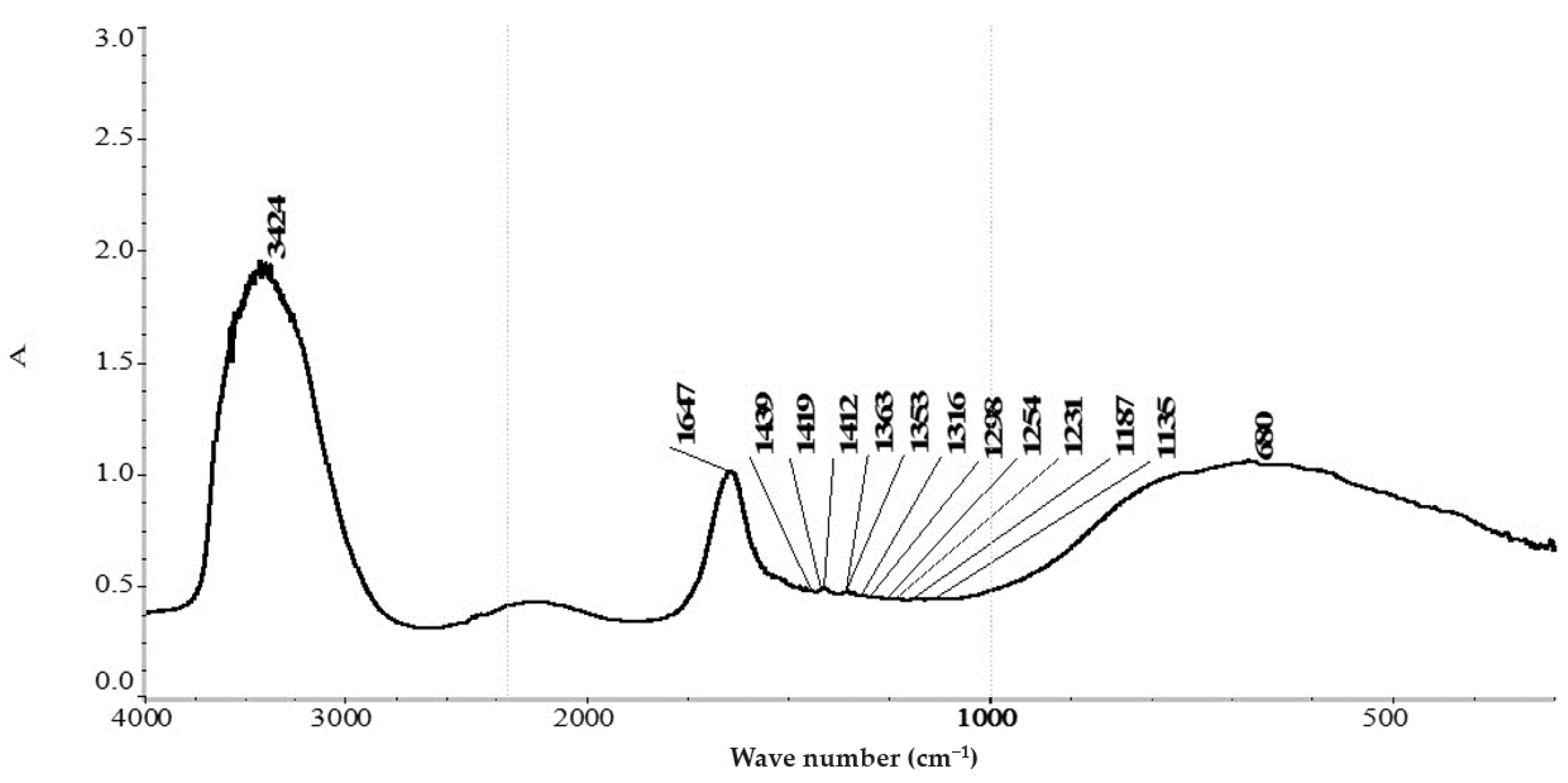
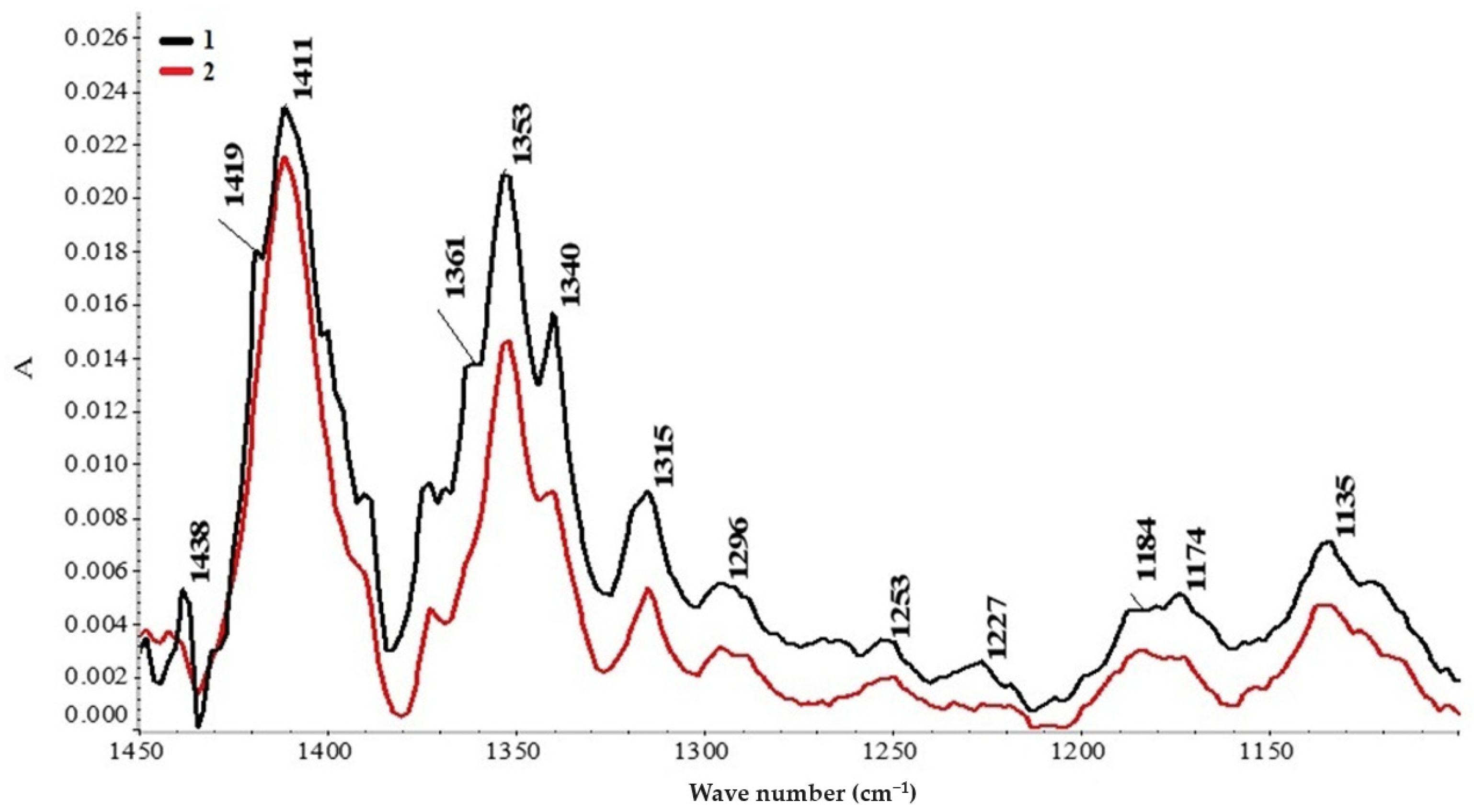
Figure 2 shows the spectrum of the system: water –leucine–gold cyanide.
The spectrum of a system containing the amino acid leucine (
Figure 2) contains stretching absorption bands of ν(OH) (3424 cm
−1), the deformation of δHOH (1647 cm
−1), and the libration of νLH
2O, with a maximum wave number of 680 cm
−1 relative to the vibrations of molecular water [
28]. Absorption bands that characterize the νs(COO
−) vibration at 1412 and 1419 cm
−1 were also recorded. It is known that in the spectrum of the L-Leucine compound, the νs(COO
−) band is observed at 1407 cm
−1 [
29], and the splitting and the appearance of the band are observed at 1419 cm
−1, which correspond to the symmetric stretching vibration of νs(COO
−) in peptides and polysaccharides according to [
29]; in our system, it probably corresponds to the appearance of complex structures in aqueous solutions that are similar to peptide chains [
30].
Figure 3 shows a fragment of the obtained spectrum as a result of the automatic correction of the baseline within the range of 1450–1100 cm
−1, immediately after the formation of the system, and after a month. It follows from the figure that within a month, the metastable system reaches equilibrium. Moreover, an increase in the intensity of the absorption band near a wave number of 1419 cm
−1 is observed, and a noticeably unequal increase in the intensity of the absorption bands of νs(COO
−) is observed at 1419 and 1411 cm
−1. A band is observed at 1353 cm
−1, which falls into the manifestation region of valence C–O, deformation C–H, and deformation N–H [
29], which can be explained by a change in the ratio between cyclic and linear complexes with respect to gold; in particular, a decrease in the content of the gold–salt intracomplex in the solution is observed. There is information in the literature about the variety of gold compounds in systems with amino acids [
31]. During the formation of linear complexes such as Me-NH
2∙CHRCOOH [
31], it is natural to increase the intensities of the νs(COO
−) absorption bands since the content of non-metal-coordinated COO
− groups in the solution increases.
Figure 4 compares the spectra of the samples after automatic corrections within the range of 1450–1100 cm
−1 and obtained within one month.
A decrease in the intensity of the absorption band of the symmetrical stretching vibration νs(COO−) near wave number 1419 cm−1 is observed for all gold-containing systems in the following series: leucine, asparagine, histidine, serine, lysine, and cysteine. The resulting dependence can be explained as follows.
Complex compounds based on the [Au(CN)2]− anion and amino acids are formed in the system during the interaction process. The connection in the complex is carried out due to the carboxyl group (ionic bond) and an amino group (donor–acceptor). The first amino acid in this series, leucine, belongs to the aliphatic amino acid series. The magnitude of the absorption band characterizing the vibration νs(COO−) at 1419 cm−1 is at its maximum, i.e., the main contribution to bond formation is provided by the carboxyl group, and the ionic bond predominates.
The next amino acids in the series under consideration are asparagine and histidine. An amide group (asparagine) and an imidazole ring (histidine) appear in the side radical. The effect of covalent bonds increases, and the effect of ionic bonds decreases. The strongest effect of the side radical’s covalent bond is expressed in cysteine due to the presence of a sulfur atom in the side radical.
It is known that oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur atoms have the most strongly expressed covalent bonds due to their structure, i.e., the strength of the ionic bond decreases, and the strength of the covalent bond increases in the specified series. The intensity of the absorption band of the symmetrical stretching vibration ν
s(COO
−) near a wave number of 1419 cm
−1 decreases. The results of studies on the effect of amino acids on the gold leaching degree of leucine, histidine, asparagine, and cysteine are presented in
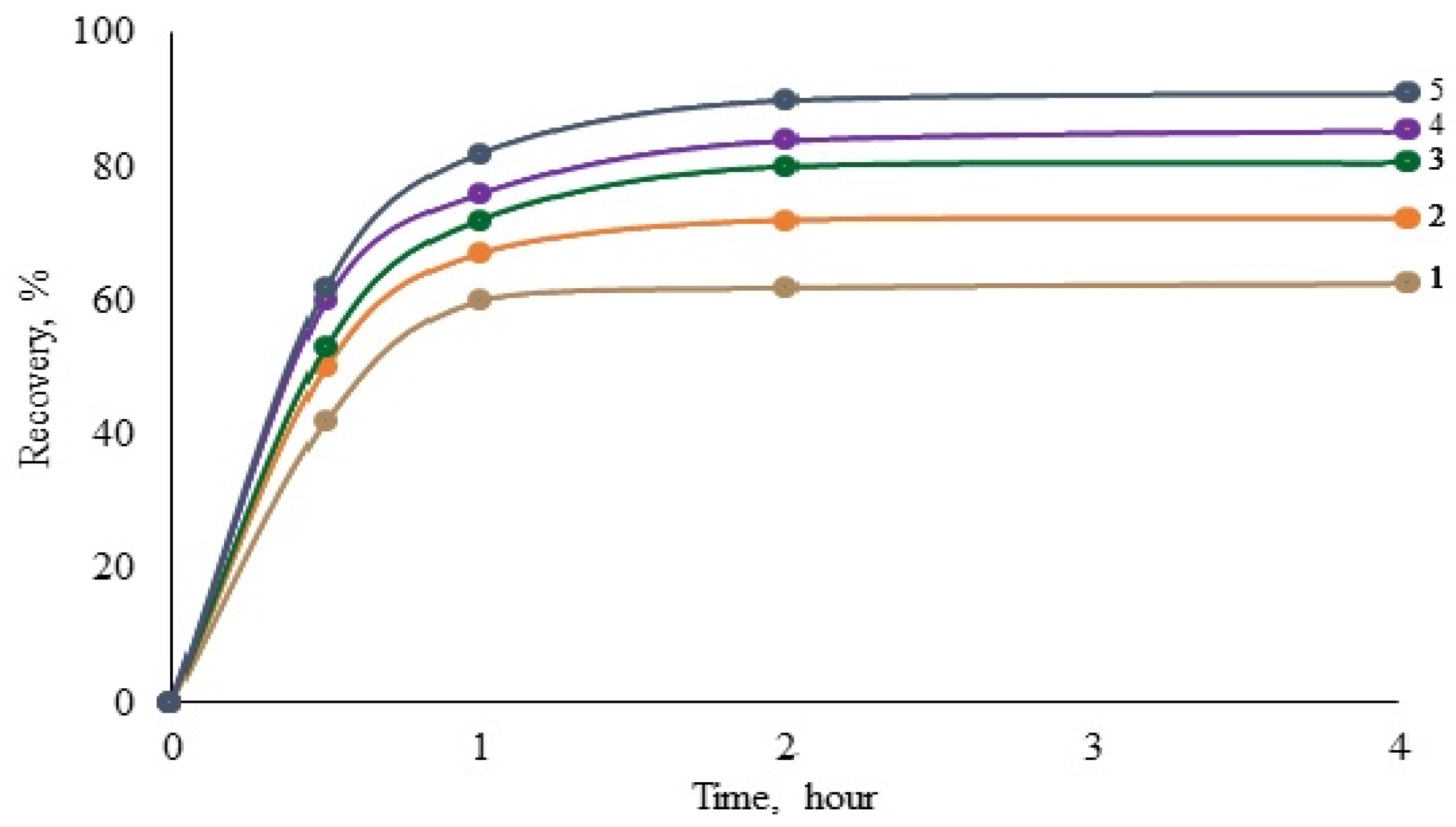
Figure 5. It follows from the figure that the gold recovery degree increases in the leucine–asparagine–histidine–cysteine series, which is consistent with the data shown above.
Thus, from the obtained results, it follows that the higher the contribution of covalent bonds to the formation of gold complexes with amino acids, the higher the positive effect of the amino acid on the degree of gold recovery during cyanide leaching. The contribution degree of covalent and ionic bonds can be assessed via the IR spectroscopic studies of the corresponding systems: gold cyanide–amino acid. By comparing the intensity of bands at a wave number of 1419 cm−1 in different systems, indirectly predicting the effect of a particular amino acid on the process of gold leaching is possible.