Parameters Synthesis of Na-Magadiite Materials for Water Treatment and Removal of Basic Blue-41: Properties and Single-Batch Design Adsorber
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Effect of Temperature
2.2. Effect of NaOH
2.3. Effect of Water Content
2.4. FTIR Spectra
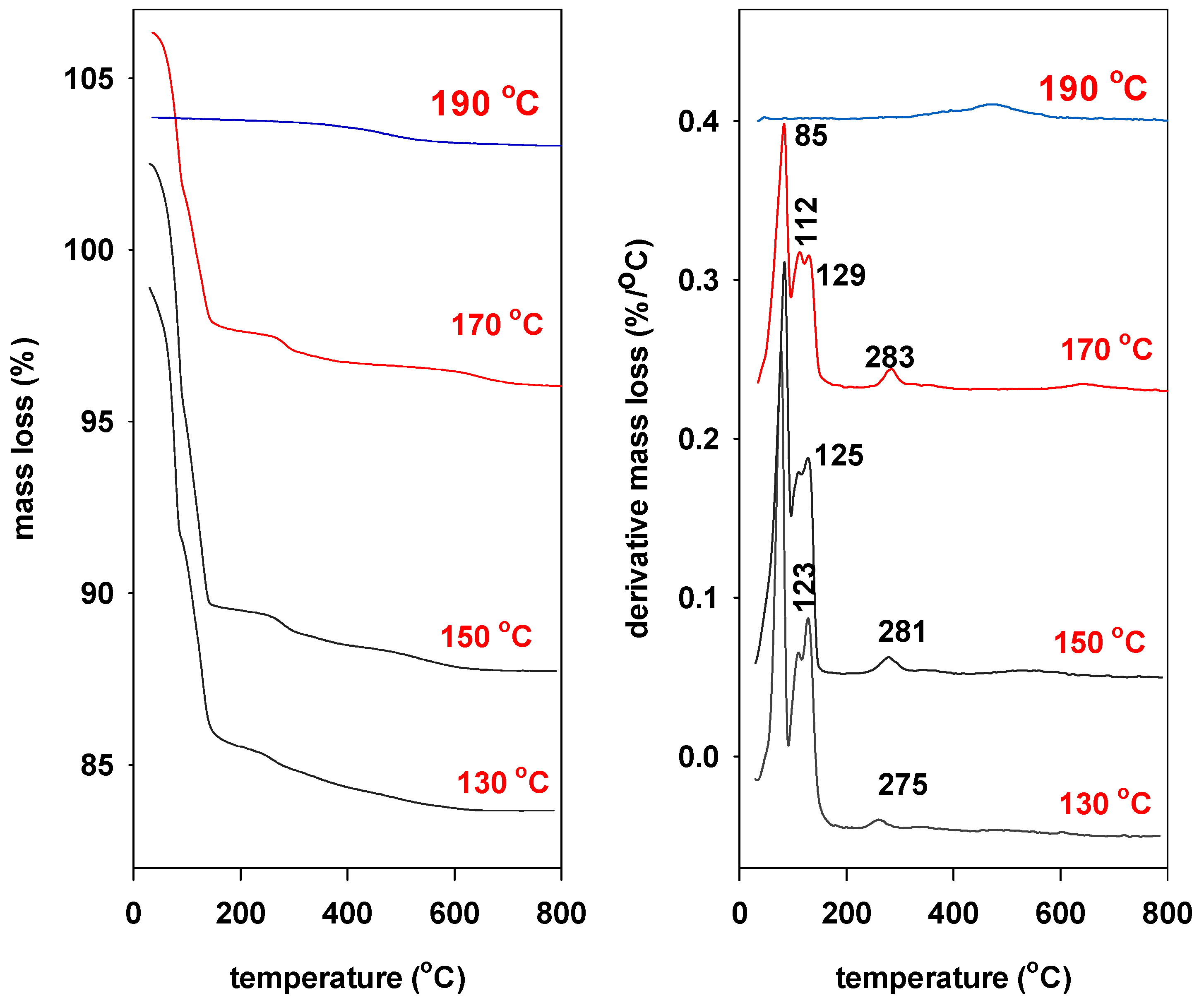
2.5. Thermogravimetric Analysis
2.6. 29Si MAS NMR Data
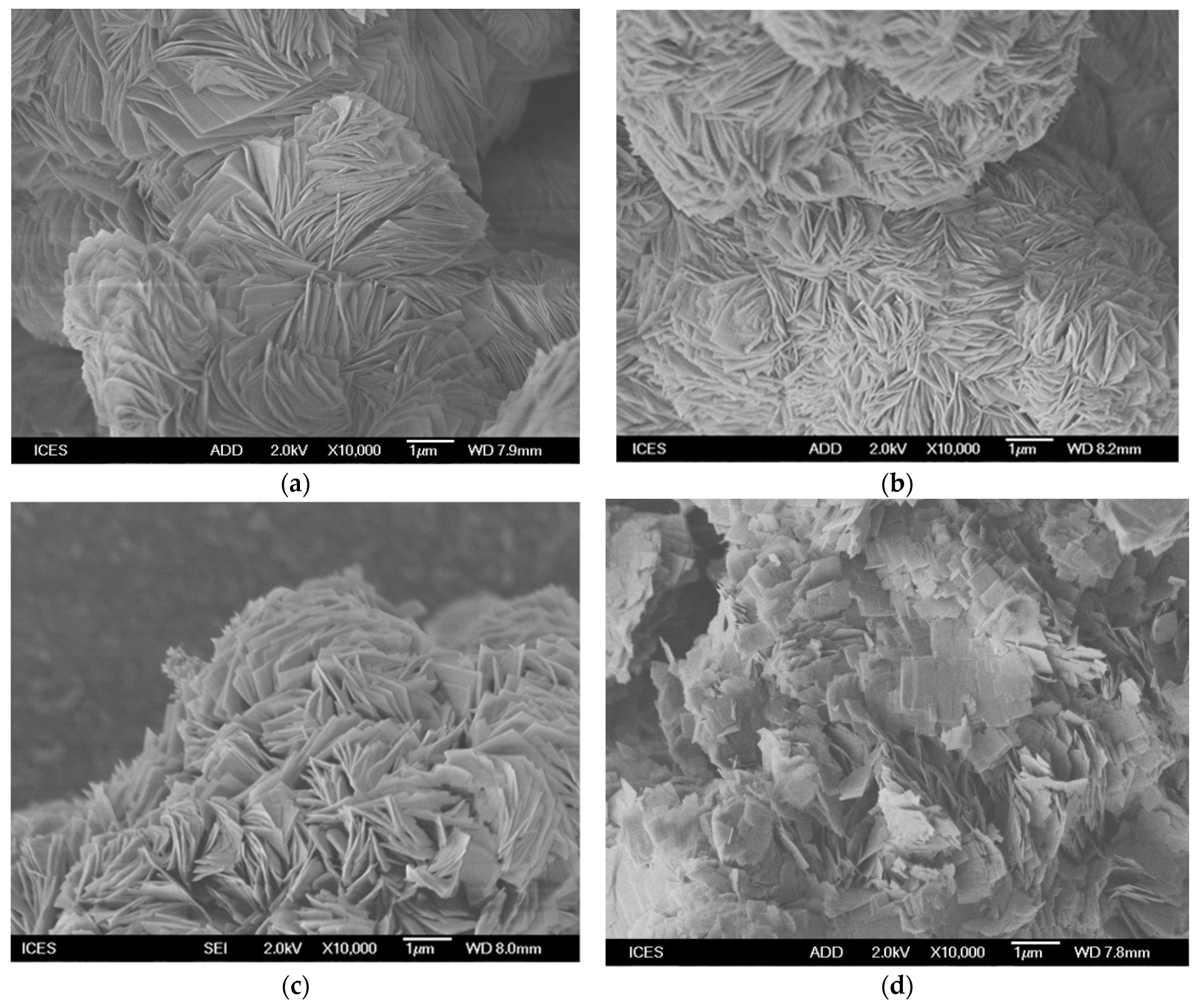
2.7. SEM-EDX Analysis
2.8. Surface Properties
3. Removal Properties of Na-Magadiite Materials
3.1. Effect of Initial Concentration of BB-41
3.2. Effect of Na-Magadiite Dose
3.3. Effect of pH
3.4. Effect of Silica Sources
3.5. Effect of Morphology Shape
3.6. Langmuir Adsorption Models
3.7. Regeneration Data
3.8. Batch Adsorber Design
4. Experimental Procedure and Characterization
4.1. Materials
4.2. Synthesis of Layered Silicate
4.3. Removal of Basic-Blue 41 Procedure
4.4. Regeneration Procedure
4.5. Characterization Techniques
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jing, X.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, X.; Mu, Y.; Liu, X.; Meng, C. Layered silicate magadiite–derived three-dimensional honeycomb-like cobalt–nickel silicates as excellent cathode for hybrid supercapacitors. Mater. Today Chem. 2021, 22, 100550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirinakorn, T.; Imwiset, K.; Bureekaew, S.; Ogawa, M. Inorganic modification of layered silicates toward functional inorganic-inorganic hybrids. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 153, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, A.; Abdelkrim, S.; Hachemaoui, M.; Adjdir, M.; Zahraoui, M.; Boukoussa, B. Layered silicate magadiite and its composites for pollutants removal and antimicrobial properties: A Review. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 198, 105823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, T.G.; de Assis, G.C.; da Silva, A.O.S.; Meneghetti, S.M.P. Progress in development of magadiite to produce multifunctional lamellar materials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 15, 43234–43250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.; Song, W.; Wang, K.; Zhu, R.; Zhang, X.; Yang, X.; Bae, J.W.; Gao, X.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, J.; et al. Highly efficient synthesis of high-value olefins from syngas over layered Fe-Mn/magadiite catalyst. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2023, 46, 1886–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Cao, L.; Du, M.; Hu, G.; Jahangir Alam, S.M. Adsorptive characterization of a pure magadiite and an organic modified magadiite on removal of methylene blue from related aqueous solution. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 217, 533–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.W.; Jung, J.H.; Kim, S.K.; Kwon, O.Y. Interlamellar silylation of magadiite by octyl triethoxysilane in the presence of dodecylamine. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 46, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Tang, W.; Du, M.; Liang, G.; Hu, G.; Jahangir Alam, S.M. Research on 5-fluorouracil as a drug carrier materials with its in vitro release properties on organic modified magadiite. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 130, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, T.; Jing, X.; Meng, C. In situ preparation and optical properties of metal-8-hydroxyquinoline decoration of layered silicate: Self-assembly in the magadiite interface by solid-solid reaction. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2017, 246, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooli, F.; Liu, Y.; Abboudi, M.; Rakass, S.; Oudghiri Hassani, H.; Ibrahim, S.M.; Al-Faze, R. Application of organo-magadiites for the removal of eosin dye from aqueous solutions: Thermal treatment and regeneration. Molecules 2018, 23, 2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Xi, Z.; Zhu, C.; Liang, G.; Yang, Y.; Hu, G.; Jamal, L.; Jahangir Alam, S.M. Adsorption process and properties analyses of a pure magadiite and a modified magadiite on rhodamine-B from an aqueous solution. Processes 2019, 7, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, M. Application of synthetic layered sodium silicate magadiite nanosheets for environmental remediation of methylene blue dye in water. Materials 2017, 10, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- França, D.B.; Torres, S.M.; Silva Filho, E.C.; Fonseca, M.G.; Jaber, M. Understanding the interactions between ranitidine and magadiite: Sodic and acidic crystalline lamellar magadiite adsorbents for the removal of methylene blue from aqueous solutions: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. Chemosphere 2019, 222, 980–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okrut, A.; Grosso-Giordano, N.A.; Schöttle, C.; Zones, S.; Katz, A. Understanding the role of Zn2+ in surfactant-free layered silicate delamination: Exfoliation of magadiite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2019, 283, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, D.L.; Ferrreira, J.N.; Pereira, M.J.; Viana, R.R.; Airoldi, C. Use of natural and modified magadiite as adsorbents to remove Th(IV), U(VI), and Eu(III) from aqueous media—Thermodynamic and equilibrium study. Clays Clay Miner. 2010, 58, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Blanchard, J.; Lambert, J.F.; Yannick Millot, Y.; Casale, S.; Zeng, S.; Nie, H.; Li, D. Role of the Al source in the synthesis of aluminum magadiite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 57, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Cao, L.; Du, M.; Hu, G.; Jahangir Alam, S.M. Competitive adsorption analyses of a pure magadiite and a new silylated magadiite on methylene blue and phenol from related aqueous solution. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 217, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.; Balkus, K.J. Synthesis of kenyaite, magadiite and octosilicate using poly(ethylene glycol) as a template. J. Porous Mater. 2003, 10, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, O.Y.; Park, K.W. Synthesis of layered silicates from sodium silicate solution. Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2004, 25, 25–26. [Google Scholar]
- Kooli, F.; Mianhui, L.; Plevert, J. Comparative studies on the synthesis of Na-magadiite, Na-kenyaite and RUB-18 phases. Clay Sci. 2006, 12 (Suppl. 2), 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, C. A comparative study of MFI zeolite derived from different silica sources: Synthesis, characterization and catalytic performance. Catalysts 2019, 9, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.; Asl, N.R. Sonochemical degradation of Basic Blue 41 dye assisted by nanoTiO2 and H2O2. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 153, 942–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vikrant, K.; Giri, B.S.; Raza, N.; Roy, K.; Kim, K.H.; Rai, B.N.; Singh, R.S. Recent advancements in bioremediation of dye: Current status and challenges. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 253, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shindy, H.A. Fundamentals in the chemistry of cyanine dyes: A review. Dyes Pigment. 2017, 145, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popoola, S.A.; Al Dmour, H.; Rakass, S.; Fatimah, I.; Liu, Y.; Mohmoud, A.; Kooli, F. Enhancement properties of Zr modified porous clay heterostructures for adsorption of Basic-Blue 41 dye: Equilibrium, regeneration, and single batch design adsorber. Materials 2022, 15, 5567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krysiak, Y.; Maslyk, M.; Silva, B.N.; Plana-Ruiz, S.; Moura, H.M.; Munsignatti, E.O.; Vaiss, V.S.; Kolb, U.; Tremel, W.; Palatinus, L.; et al. The Elusive structure of magadiite, solved by 3d electron diffraction and model building. Chem. Mater. 2021, 33, 3207–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marler, B.; Grosskreuz, I.; Gies, H. The crystal structure of synthetic kenyaite, Na2Si20O40(OH)2⋅8H2O. J. Solid State Chem. 2021, 300, 122215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, A.O.; Prado, A.G.S. Effect of thermal dehydration and rehydration on Na-magadiite structure. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 330, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, B.N.N.; Pastore, H.O.; Leitão, A.A. The role of hydration water in inorganic M+n-magadiites (M+n = K+, Ca2+, Mg2+): Advances in structural and electronic analysis by DFT calculations. Appl. Clay Sci. 2023, 231, 106749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, H.; Seo, J.D.; Kim, J.; Park, M. Adsorption behavior of kenyaite for Cu2+ and Pb2+. J. Porous Mater. 2022, 29, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Superti, G.B.; Oliveira, E.C.; Pastore, H.O.; Bordo, A.; Bisio, C.; Marchese, L. Aluminum magadiite: An acid solid layered material. Chem. Mater. 2007, 19, 4300–4315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eypert-Blaison, C.; Humbert, B.; Michot, L.J.; Pelletier, M.; Sauzeat, E.; Villieras, F. Structural Role of Hydration Water in Na- and H-Magadiite: A Spectroscopic Study. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 4439–4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooli, F.; Liu, Y.; Hbaieb, K.; Ching, O.; Al-Faze, R. Characterization of organo-kenyaites: Thermal stability and their effects on eosin removal characteristics. Clay Miner. 2018, 53, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, S.M.; Stephens, W.E.; Richardson, N.V. X-ray photoelectron and infrared spectroscopies of quartz samples of contrasting toxicity. Environ. Health 2009, 8 (Suppl. 1), S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attar, K.; Bouazza, D.; Miloudi, H.; Tayeb, A.; Boos, A.; Sastre, A.M.; Demey, H. Cadmium removal by a low-cost magadiite-based material: Characterization and sorption applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5351–5360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooli, F.; Mianhui, L.; Alshahateet, S.F.; Chen, F.; Yinghuai, Z. Characterization and thermal stability properties of intercalated Na-magadiite with cetyltrimethylammonium (C16TMA) surfactants. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2006, 67, 926–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binette, M.J.; Detellier, D. Lamellar polysilicate nanocomposite materials: Intercalation of polyethylene glycols into protonated magadiite. Can. J. Chem. 2002, 80, 1708–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins de Souza e Silva, J.; Paul, G.; Bendall, J.; Bisio, C.; Marchese, L.; Pastore, H.O. Novel insights on magadiite disaggregation: A multitechnique study on thermal stability. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 13434–13445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizukia, D.; Kuroda, K. Design of silicate nanostructures by interlayer alkoxysilylation of layered silicates (magadiite and kenyaite) and subsequent hydrolysis of alkoxy groups. New J. Chem. 2006, 30, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassi, M.; Miehe -Brendle, J.; Patarin, J.; Bengueddach, A. Na-magadiite prepared in a water/alcohol medium: Synthesis, characterization and use as a host material to prepare alkyltrimethylammonium- and Si-pillared derivates. Clay Miner. 2005, 40, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Wang, X.; Du, M.; Liang, G.; Hu, G.; Jahangir Alam, S.M. Adsorption analyses of phenol from aqueous solutions using magadiite modified with organo-functional groups: Kinetic and equilibrium studies. Materials 2018, 12, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Wang, Y.; Hu, T.; Meng, C. Metal oxide decorated layered silicate magadiite for enhanced properties: Insight from ZnO and CuO decoration. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 4303–4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, M.; Wang, X.; Du, M.; Liang, G.; Hu, G.; Jahangir Alam, S.M. Effects on the Mechanical Properties of Nacre-Like Bio-Hybrid Membranes with Inter-Penetrating Petal Structure Based on Magadiite. Materials 2019, 12, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kooli, F.; Liu, Y.; Abboudi, M.; Oudghiri Hassani, H.; Rakass, S.; Ibrahim, S.M.; Al Wadaani, F. Waste bricks applied as removal agent of Basic Blue 41 from aqueous solutions: Base treatment and their regeneration efficiency. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rápó, E.; Tonk, S. Factors affecting synthetic dye adsorption; desorption studies: A review of results from the last five years (2017–2021). Molecules 2021, 26, 5419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kooli, F.; Yan, L.; Al-Faze, R.; Al-Sehimi, A. Removal enhancement of basic blue 41 by brick waste from an aqueous solution. Arab. J. Chem. 2015, 8, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, A.R.; Araújo, K.R.O.; Moura, A.O.; Prado, A.G.S. Magadiite as a support for the controlled release of herbicides. Chem. Pap. 2018, 72, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, C.; El Kurdi, R.; Patra, D. Effect of pH on the removal of anionic and cationic dyes using zinc curcumin oxide nanoparticles as adsorbent. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 277, 125504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraishi, H. Crystallization of silica gel in alkaline solutions at 100 to 180 °C: Characterization of SiO2-Y by comparison to magadiite. Am. Mineral. 1989, 74, 1147–1151. [Google Scholar]
- Hans, S.; Stadie, N.P. Langmuir’s Theory of Adsorption: A Centennial Review. Langmuir 2019, 35, 5409–5426. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.Z. Avoiding spurious correlation in analysis of chemical kinetic data. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 6861–6863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benvenutia, J.; Adriano Fischb, A.; dos Santosc, J.H.Z.; Gutterresa, M. Silica-based adsorbent material with grape bagasse encapsulated by the sol gel method for the adsorption of Basic Blue 41 dye. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooli, F.; Liu, Y.; Al-Faze, R.; Al Suhaimi, A. Effect of acid activation of Saudi local clay mineral on removal properties of basic blue 41 from an aqueous solution. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 116, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humelnicu, L.; Baiceanu, A.; Ignat, M.; Dulman, V. The Removal of Basic Blue 41 Textile Dye from Aqueous Solution by Adsorption onto Natural Zeolitic Tuff: Kinetics and Thermodynamics. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 105, 274–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarezadeh-Mehrizi, M.; Badiei, A.R. Highly efficient removal of Basic Blue 41 with nanoporous silica. Water Resour. Ind. 2014, 5, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kul, A.R.; Aldemir, A.; Koyuncu, H. An investigation of natural and modified diatomite performance for adsorption of Basic Blue 41: Isotherm, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies. Desalination Water Treat. 2021, 229, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshin, S.; Rashtbari, Y.; Vosoughi, M.; Rehman, R.; Ramavandi, B.; Behzad, A.; Mitu, L. Removal of Basic Blue-41 dye from water by stabilized magnetic iron nanoparticles on clinoptilolite zeolite. Rev. Chim. 2020, 71, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mersin, G.; Acikel, U.; Levent, M. Efficient adsorption of basic blue 41 from textile wastewaters by natural and magnetically modified Manisa-Gordes clinoptilolite. Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2021, 169, 108632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskar, A.V.; Bolan, N.; Hoang, S.A.; Sooriyakumar, P.; Kumar, M.; Singh, L.; Jasemizad, T.; Padhye, L.P.; Singh, G.; Vinu, A.; et al. Recovery, regeneration and sustainable management of spent adsorbents from wastewater treatment streams: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 822, 153555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momina, S.M.; Isamil, S. Regeneration performance of clay-based adsorbents for the removal of industrial dyes: A review. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 24571–24587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkika, D.A.; Athanasios, C.; Mitropoulos, A.C.; Kyzas, G.Z. Why reuse spent adsorbents? The latest challenges and limitation. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 822, 153612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Dmour, H.; Kooli, F.; Mohmoud, A.; Liu, Y.; Popoola, S.A. Al and Zr porous clay heterostructures as removal agents of basic blue-41 dye from an artificially polluted solution: Regeneration properties and batch design. Materials 2021, 14, 2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debnath, S.; Ballav, N.; Maity, A.; Pillay, K. Single stage batch adsorber design for efficient Eosin yellow removal by polyaniline coated ligno-cellulose. Int. J. Biol Macromol. 2015, 72, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansour, R.A.; Aboeleneen, N.M.; AbdelMonem, N.M. Adsorption of cationic dye from aqueous solutions by date pits: Equilibrium, kinetic, thermodynamic studies, and batch adsorber design. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2018, 20, 1062–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İlknur, S.; Alzein, M. Adsorptive removal of basic blue 41 using pistachio shell adsorbent—Performance in batch and column system. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2020, 16, 100254. [Google Scholar]
















| Run No. | Synthesis Conditions (Initial Gels) | Products | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silica Source | SiO2 (g) | NaOH (g) | H2O (g) | Temp. | Time | ||
| 1 | Fumed silica | 45 | 4.8 | 105 | 150 | 1 day | Mag |
| 2 | 45 | 4.8 | 105 | 150 | 2 days | mag (MAG-FS) | |
| 3 | 45 | 4.8 | 105 | 150 | 3 days | Mag + ken | |
| 4 | 45 | 4.8 | 105 | 150 | 5 days | Mag + ken | |
| 5 | 45 | 4.8 | 105 | 150 | 7 days | Ken | |
| 6 | 45 | 4.8 | 105 | 150 | 10 days | Ken + silica | |
| 7 | 45 | 4.8 | 105 | 130 | 2 days | Mag + amorph. silica | |
| 8 | 45 | 4.8 | 105 | 170 | 2 days | ken | |
| 9 | 45 | 4.8 | 105 | 185 | 2 days | Crystalline silica | |
| 10 | 45 | 4.8 | 105 | 190 | 2 days | Crystalline quartz | |
| 11 | 45 | 4.8 | 105 | 200 | 2 days | crystalline quartz | |
| 12 | 45 | 1.05 | 105 | 150 | 2 days | Amorph. silica | |
| 13 | 45 | 2.5 | 105 | 150 | 2 days | Mag | |
| 14 | 45 | 7.2 | 105 | 150 | 2 days | no solid was obtained | |
| 15 | 45 | 9.6 | 105 | 150 | 2 days | no solid was obtained | |
| 16 | 45 | 4.8 | 20 | 150 | 2 days | Ken | |
| 17 | 45 | 4.8 | 40 | 150 | 2 days | Ken + Mag | |
| 18 | 45 | 4.8 | 50 | 150 | 2 days | Mag | |
| 19 | 45 | 4.8 | 60 | 150 | 2 days | Mag | |
| 20 | Ludox HS-40% | 45 | 4.8 | 105 | 150 | 1 day | Mag |
| 21 | 45 | 4.8 | 105 | 150 | 2 days | mag (MAG-HS) | |
| 22 | 45 | 4.8 | 105 | 150 | 3 days | Mag + silica | |
| 23 | 45 | 4.8 | 105 | 150 | 5 days | Mag + ken + silica | |
| 24 | 45 | 4.8 | 105 | 150 | 7 days | Ken + silica | |
| Run No. | Synthesis Conditions (Initial Gels) | Products | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silica Source | SiO2 (g) | NaOH (g) | H2O (g) | Temp. | Time | ||
| 24 | Ludox AS-40% | 45 | 4.8 | 105 | 150 | 1 day | Mag |
| 25 | 45 | 4.8 | 105 | 150 | 2 days | mag (MAG-AS) | |
| 26 | 45 | 4.8 | 105 | 150 | 3 days | Mag | |
| 27 | 45 | 4.8 | 105 | 150 | 5 days | Mag + ken + silica | |
| 28 | 45 | 4.8 | 105 | 130 | 10 days | Ken + silica | |
| 29 | Colloidal Silica | 45 | 4.8 | 105 | 150 | 1 day | Mag |
| 30 | 45 | 4.8 | 105 | 150 | 2 days | mag (MAG-CS) | |
| 31 | 45 | 4.8 | 105 | 150 | 3 days | mag + ken + tr (SiO2) | |
| 32 | 45 | 4.8 | 105 | 150 | 5 days | mag + ken + SiO2 | |
| 33 | 45 | 4.8 | 105 | 150 | 7 days | mag + ken + SiO2 | |
| 34 | 45 | 4.8 | 105 | 150 | 10 days | Ken + SiO2 (quartz) | |
| 35 | 45 | 4.8 | 105 | 130 | 2 days | mag + amorp SiO2 | |
| 36 | 45 | 4.8 | 105 | 140 | 2 days | Mag | |
| 37 | 45 | 4.8 | 105 | 170 | 2 days | Ken | |
| 38 | 45 | 4.8 | 105 | 200 | 2 days | quartz + tr (ken) | |
| 39 | 45 | 1.2 | 105 | 150 | 2 days | Amorphous silica | |
| 40 | 45 | 2.4 | 105 | 150 | 2 days | Mag | |
| 41 | 45 | 7.2 | 105 | 150 | 2 days | Mag | |
| 42 | 45 | 9.2 | 105 | 150 | 2 days | Mag | |
| 43 | 45 | 4.8 | 0 | 150 | 2 days | Mag | |
| Sample | SBET (m2/g) | T.P.V. (cc/g) | A.P.D (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAG-AS | 35 | 0.183 | 20.7 |
| MAG-HS | 38 | 0.230 | 23.9 |
| MAG-CS | 40 | 0.263 | 25.8 |
| MAG-FS | 33 | 0.221 | 26.7 |
| MAG-FS (130 °C) * | 42 | 0.211 | 20.1 |
| MAG-FS(60 g) + | 29 | 0.202 | 27.4 |
| Samples | qmax (mg/g) | KL (L/g) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAG-AS | 222 (219) * | 0.068 (0.112) | 0.9172 (0.9998) |
| MAG-HS | 212 (210) | 0.065 (0.098) | 0.831 (0.9985) |
| MAG-CS | 205 (208) | 0.065 (0.112) | 0.9491 (0.9978) |
| MAG-FS | 172 (167) | (0.061) (0.064) | 0.9386 (0.9889) |
| MAG-FS (130 °C) | 220 217 | 0.071 (0.142) | 0.9453 (0.9857) |
| MAG-FS (60 g) | 153 (150) | 0.063 (0.066) | 0.9406 (0.9987) |
| Material | Removal Capacity (mg/g) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Na-magadiites | 150–220 | This work |
| Sol gel silica material from grape bagasse | 268 | [52] |
| Saudi local clay mineral | 74 | [53] |
| Zeolite tuff | 192 | [54] |
| Brick waste materials | 60–70 | [46] |
| Nanoporous silica | 345 | [55] |
| Mn-modified diatomite | 62 | [56] |
| Clinoptilolite//Fe2O3 nanoparticles | 93 | [57] |
| Natural Gordes zeolite | 149 | [58] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alanazi, A.M.; Al Dmour, H.; Popoola, S.A.; Oudghiri Hassani, H.; Rakass, S.; Al-Faze, R.; Kooli, F. Parameters Synthesis of Na-Magadiite Materials for Water Treatment and Removal of Basic Blue-41: Properties and Single-Batch Design Adsorber. Inorganics 2023, 11, 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11110423
Alanazi AM, Al Dmour H, Popoola SA, Oudghiri Hassani H, Rakass S, Al-Faze R, Kooli F. Parameters Synthesis of Na-Magadiite Materials for Water Treatment and Removal of Basic Blue-41: Properties and Single-Batch Design Adsorber. Inorganics. 2023; 11(11):423. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11110423
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlanazi, Abdulaziz M., Hmoud Al Dmour, Saheed A. Popoola, Hicham Oudghiri Hassani, Souad Rakass, Rawan Al-Faze, and Fethi Kooli. 2023. "Parameters Synthesis of Na-Magadiite Materials for Water Treatment and Removal of Basic Blue-41: Properties and Single-Batch Design Adsorber" Inorganics 11, no. 11: 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11110423
APA StyleAlanazi, A. M., Al Dmour, H., Popoola, S. A., Oudghiri Hassani, H., Rakass, S., Al-Faze, R., & Kooli, F. (2023). Parameters Synthesis of Na-Magadiite Materials for Water Treatment and Removal of Basic Blue-41: Properties and Single-Batch Design Adsorber. Inorganics, 11(11), 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11110423







