Cadmium Depth Separation Method in Polymetallic Sulfate Solution: Flow-Electric Field Enhanced Cementation Combined with M5640 Extraction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Material
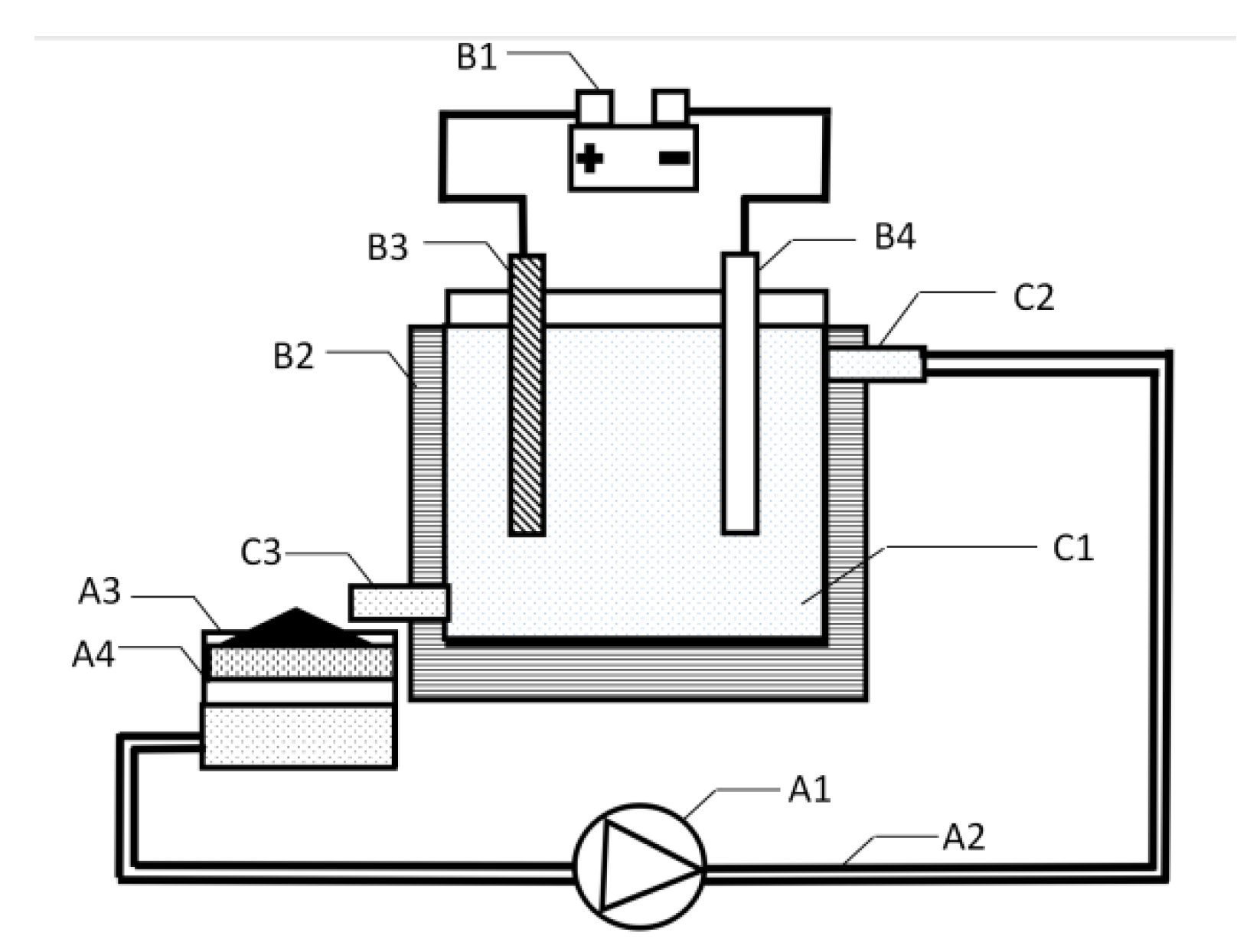
2.2. Process
3. Results and Discussion
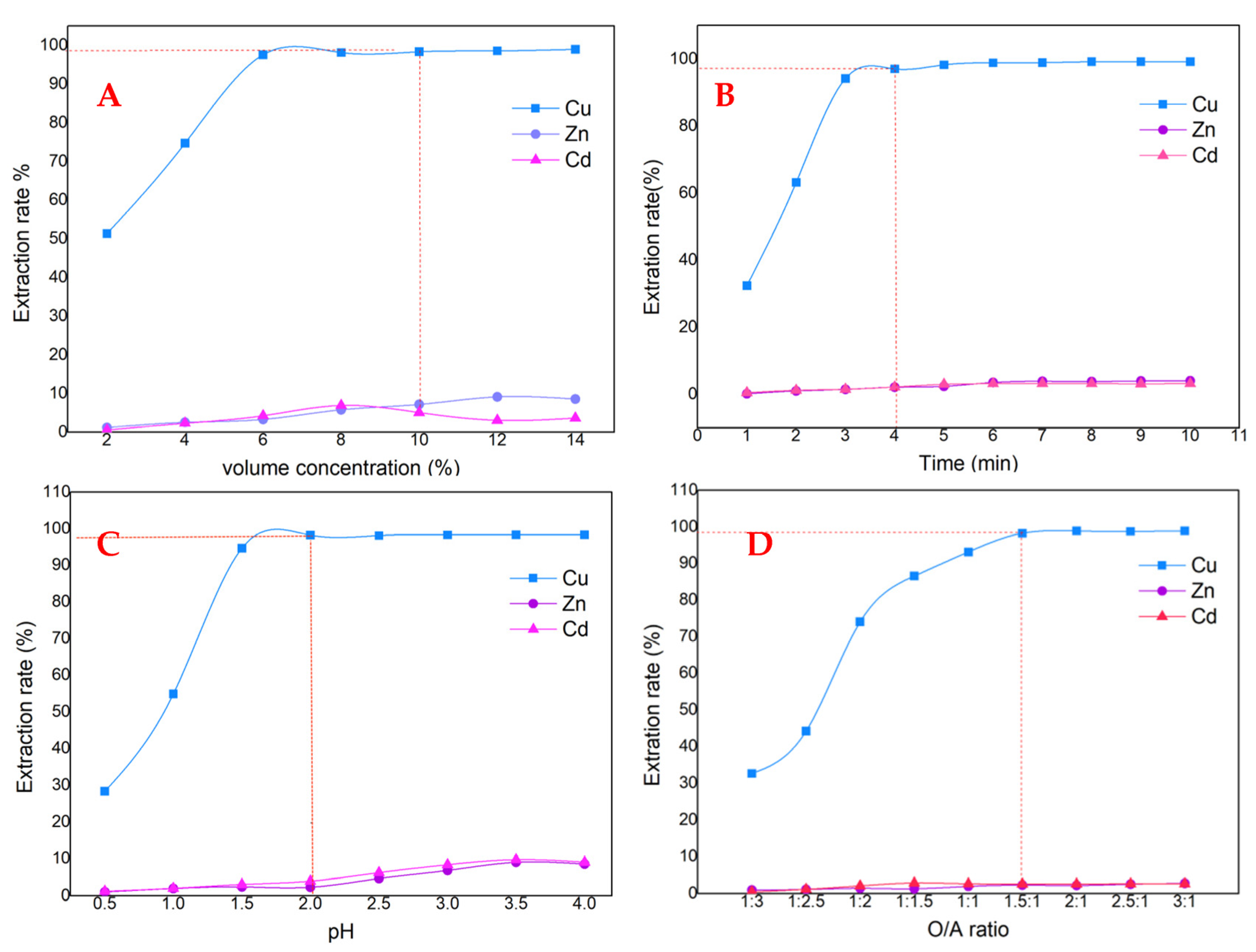
3.1. Copper Removal by M5640
3.1.1. Copper Removal Test Utilizing M5640
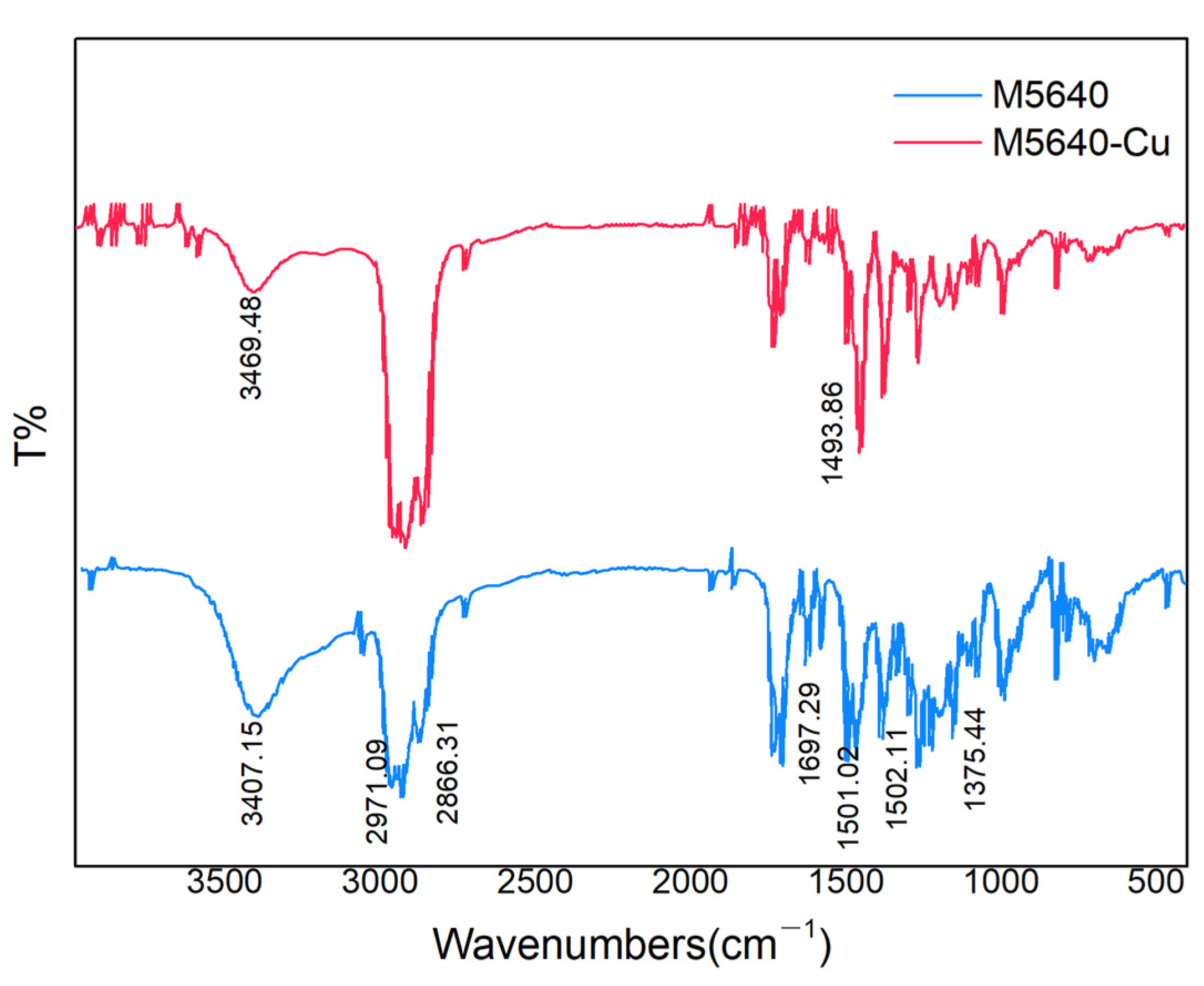
3.1.2. Extraction Mechanism and Characterization
3.2. Cadmium Cementation Enhanced by Flow-Electric Field Coupling
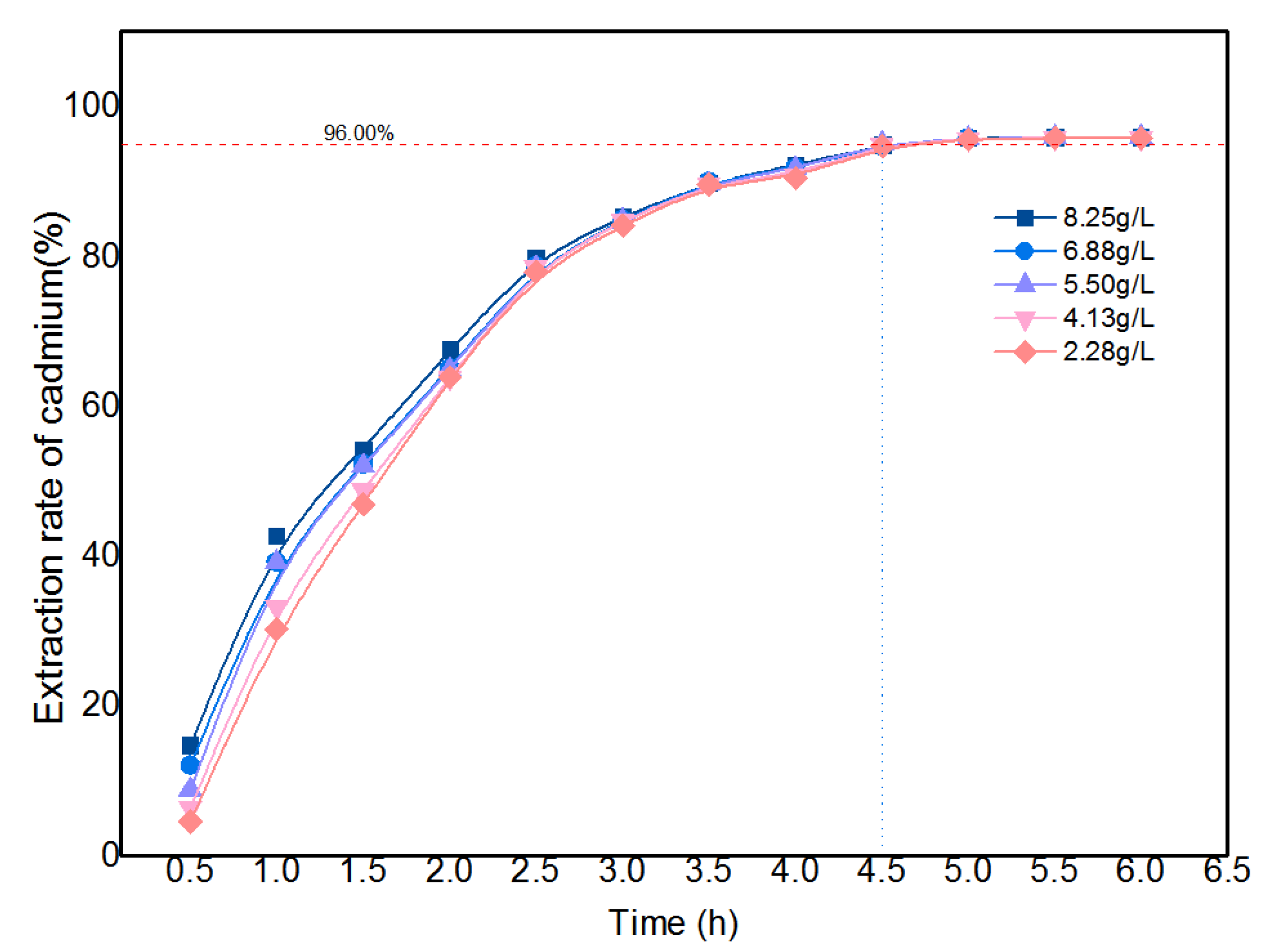
3.2.1. Determination of the Initial Cd Concentration and Reaction Time
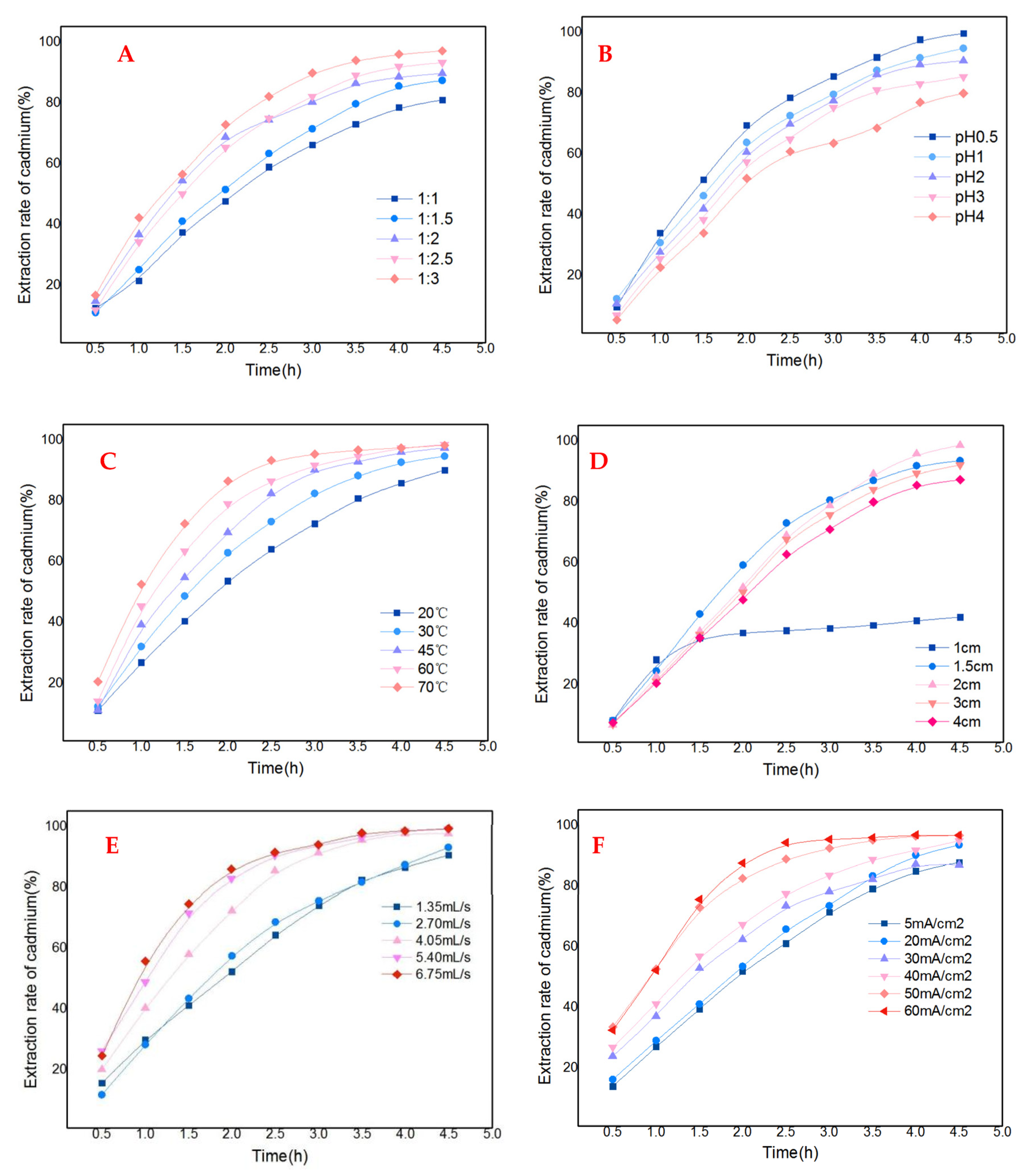
3.2.2. Single-Factor Experimental Analysis
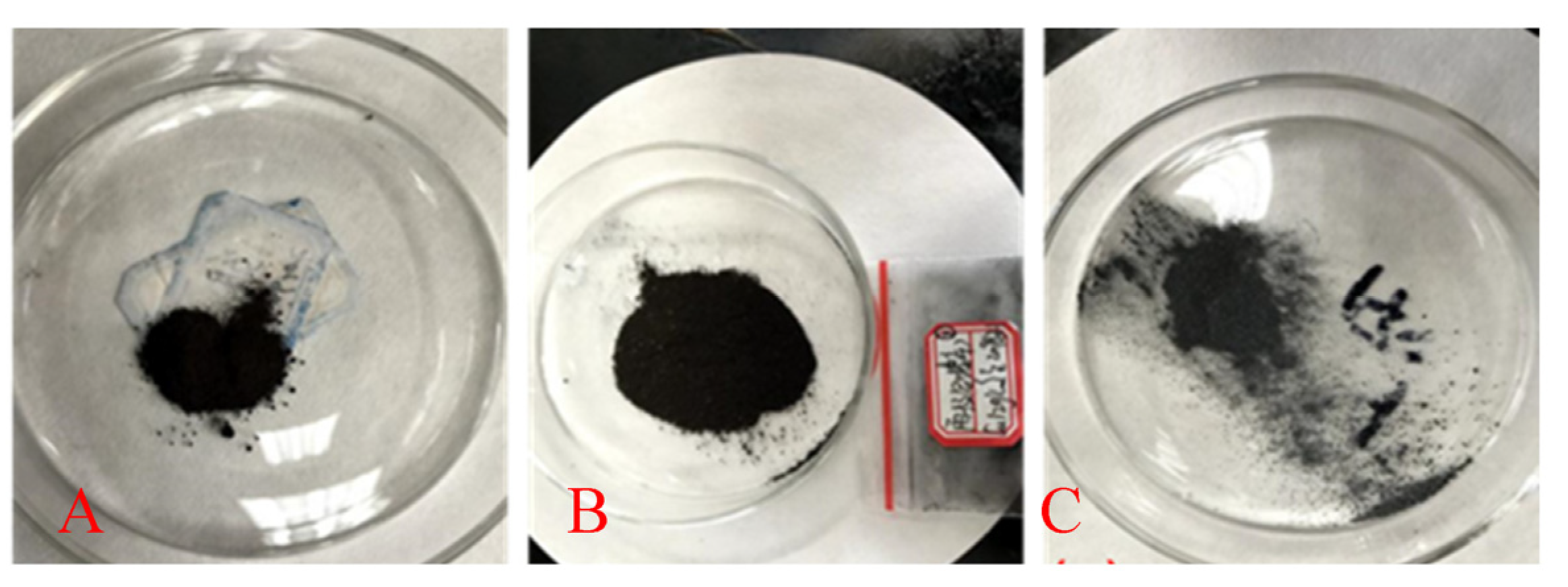
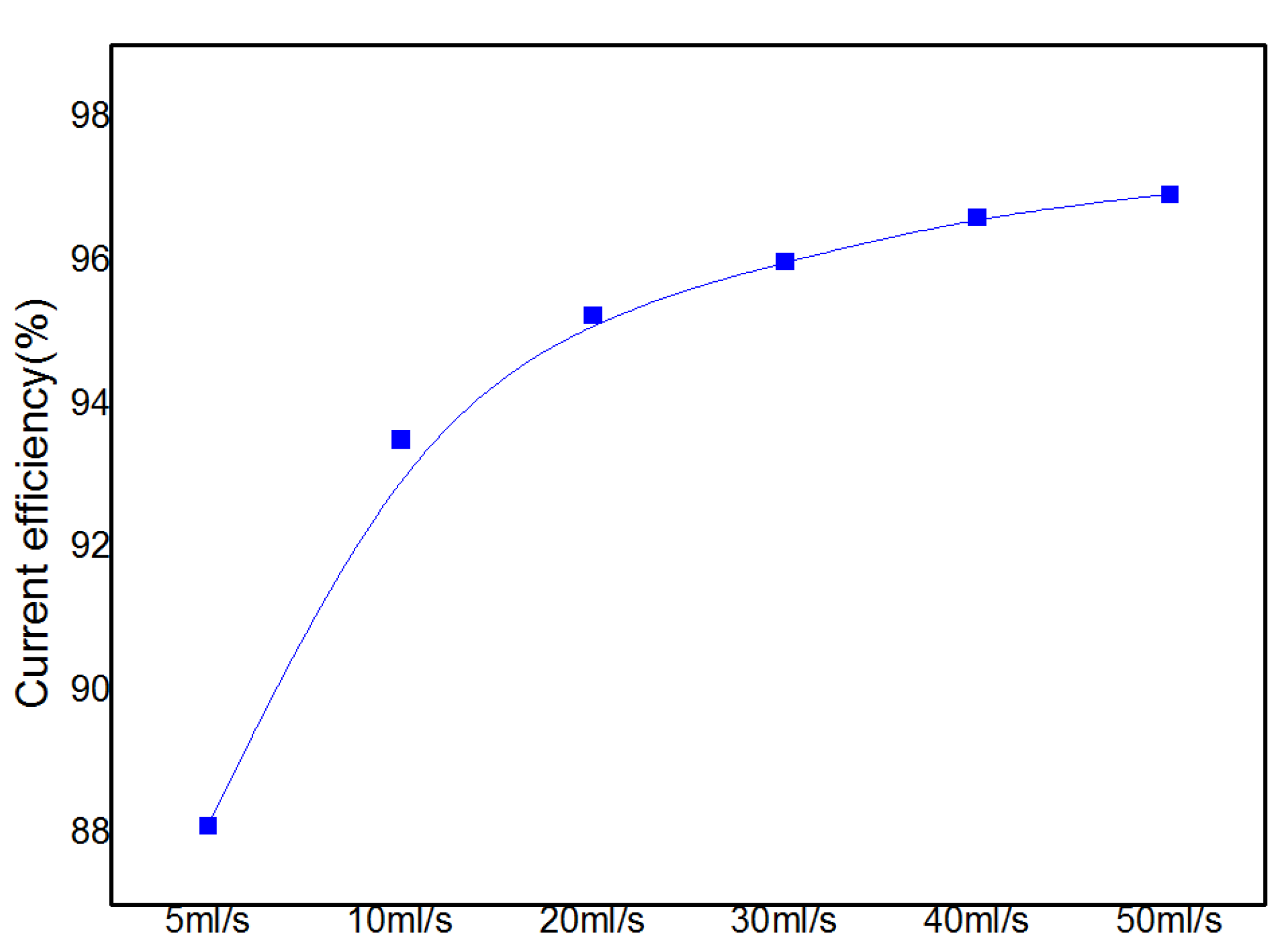
3.2.3. Current Efficiency and Cadmium Sponge Distribution
3.3. Response Surface Optimization of Coupled Fluid-Electric Field Cementation
3.3.1. Response Surface Method
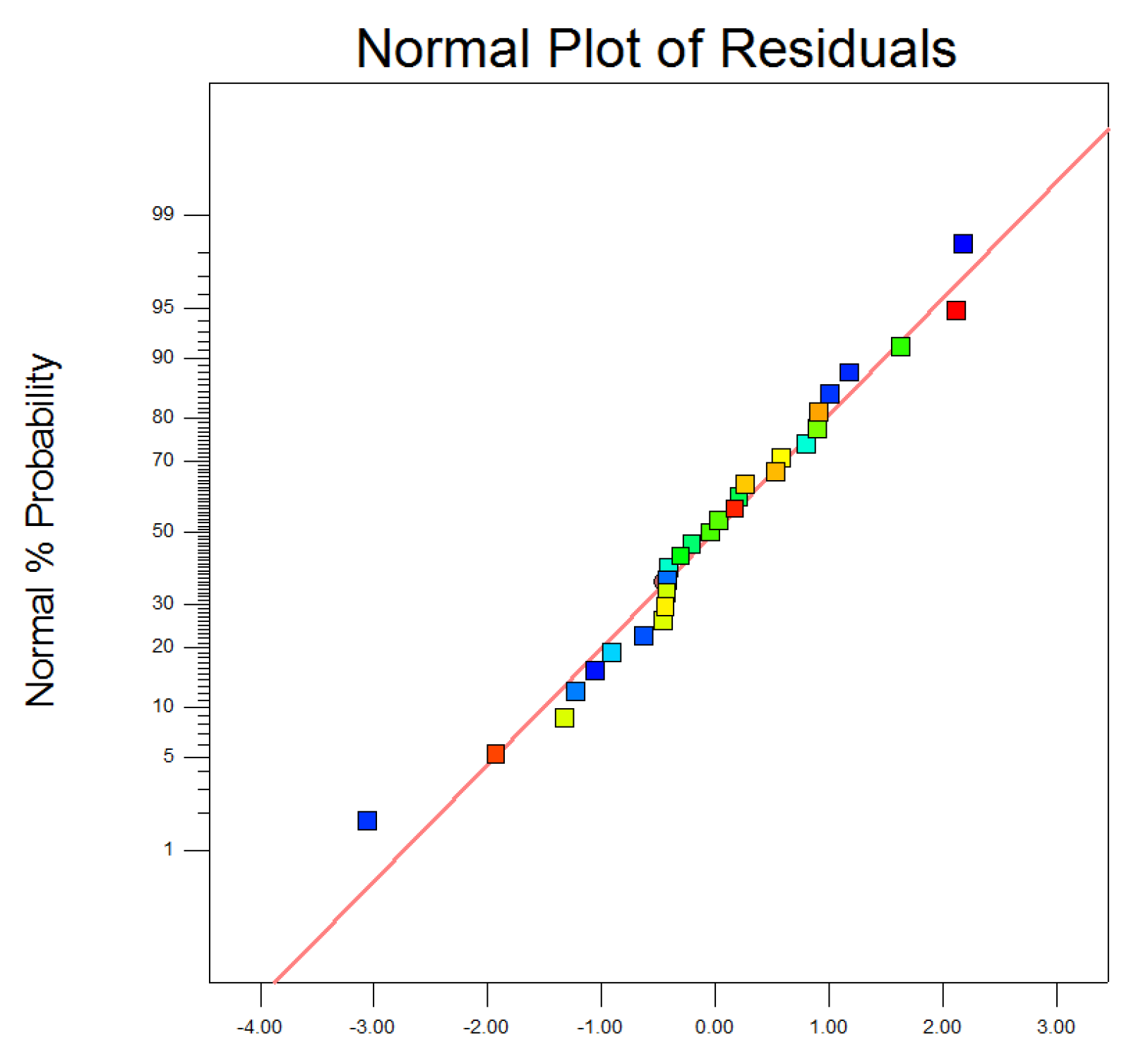
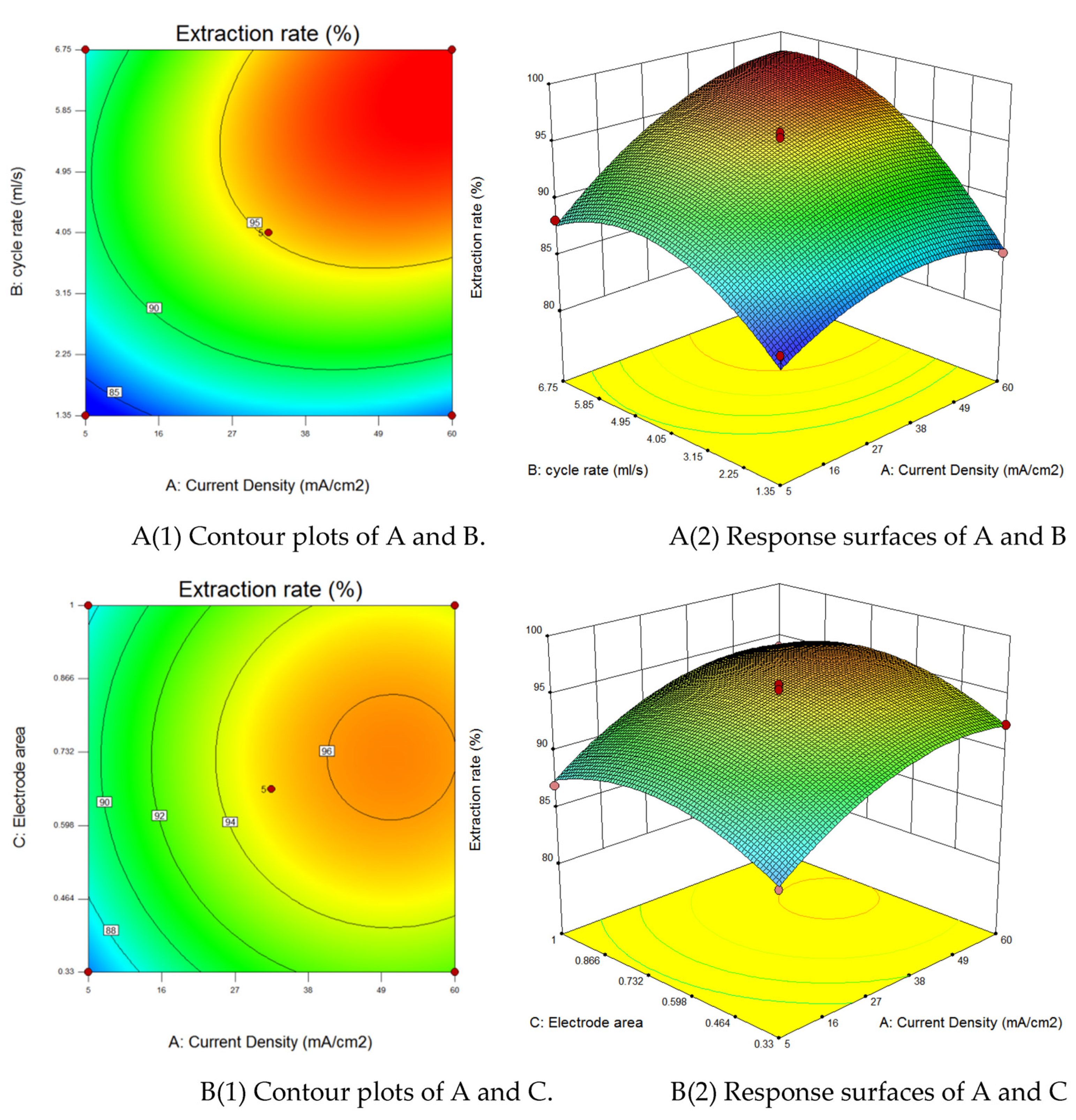
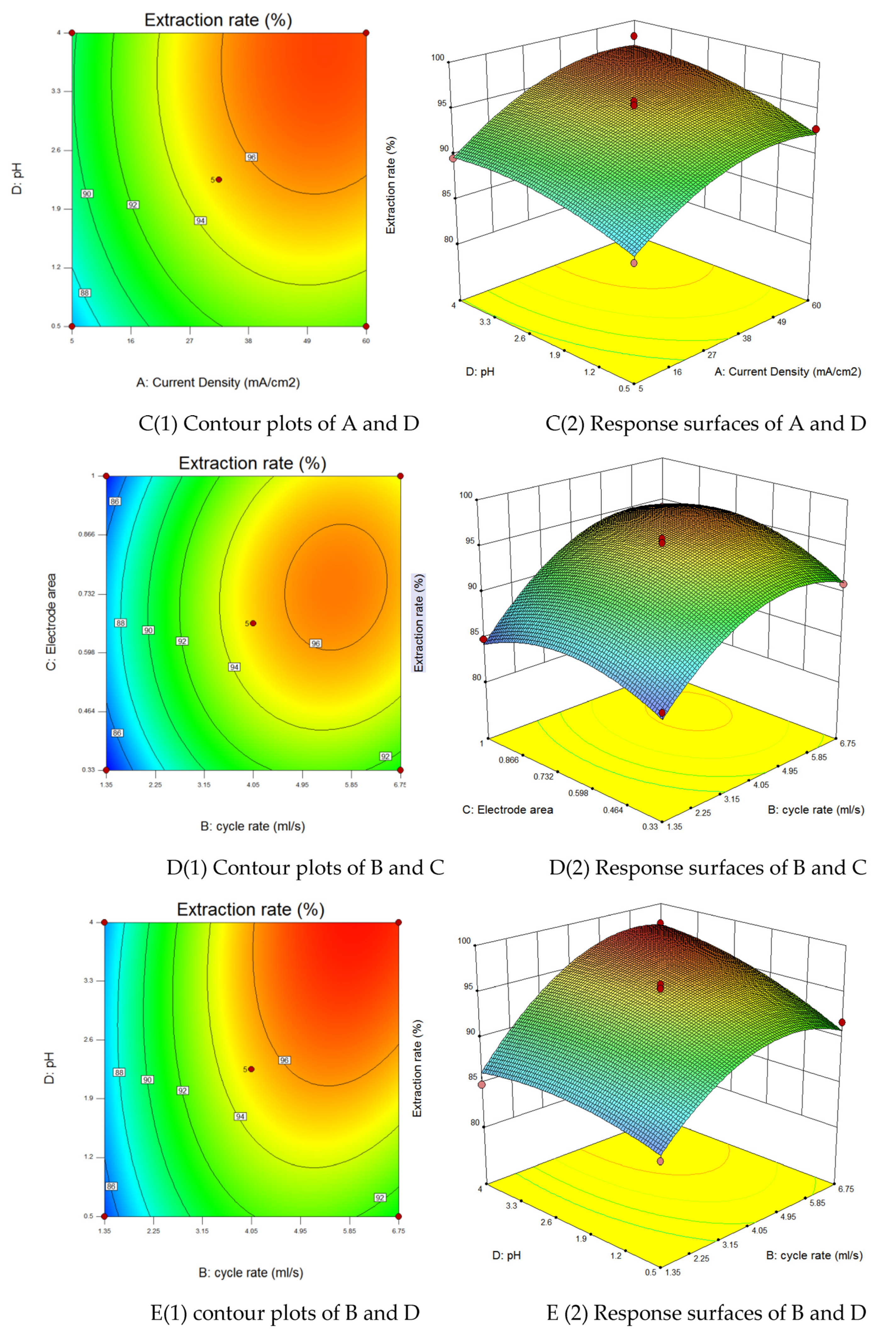
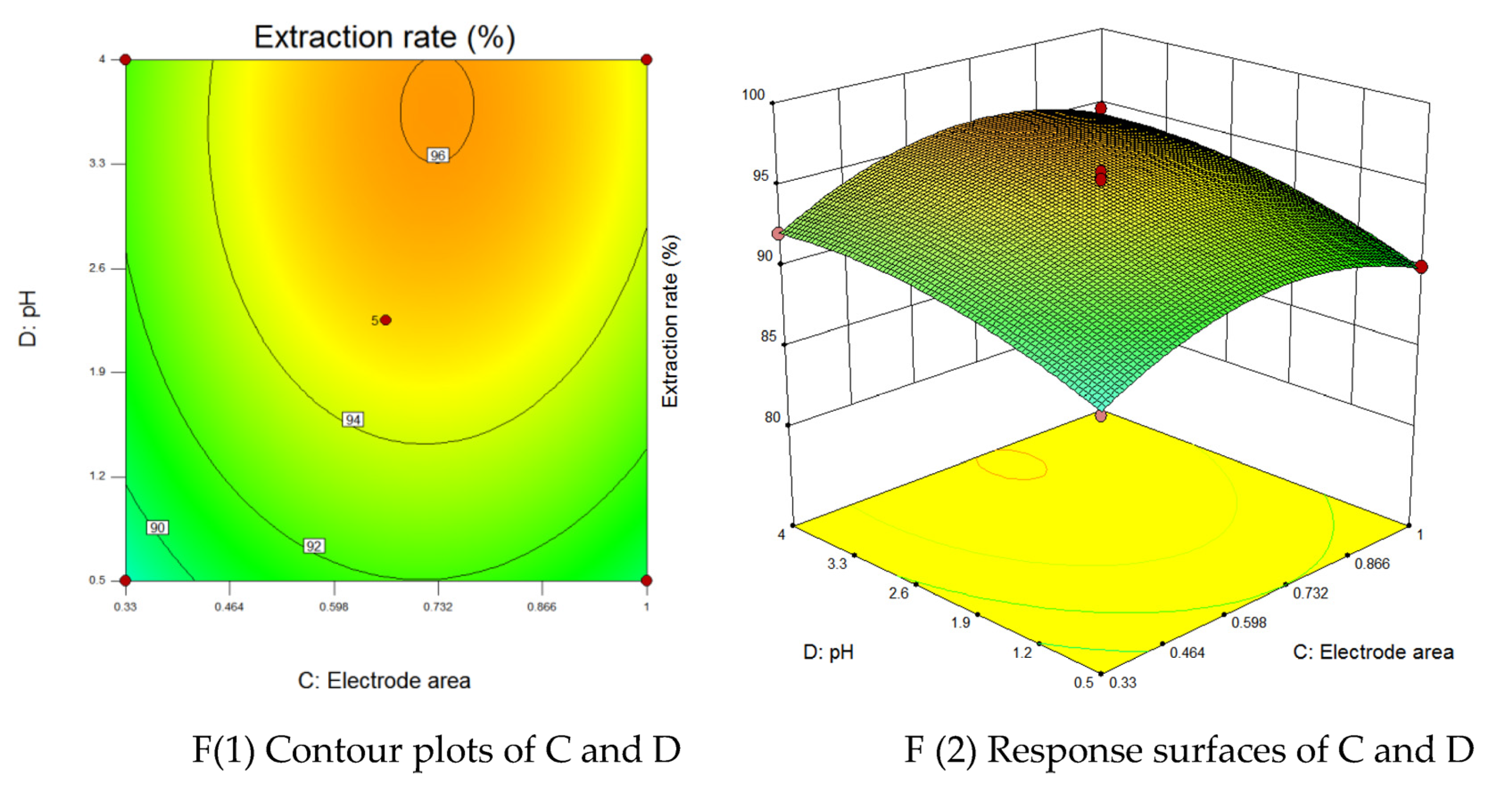
3.3.2. Analysis of Variance and Parameter Interactions
3.3.3. Validation of Process Parameter Predictions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, J.; She, J.; Yin, M.; Fang, F.; Xiao, T.; Song, G.; Liu, J. Geochemical Transfer of Cadmium in River Sediments near a Lead-Zinc Smelter. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 196, 110529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.-M.; Fu, R.-B.; Liu, H.-Q.; Guo, X.-P. Current Knowledge from Heavy Metal Pollution in Chinese Smelter Contaminated Soils, Health Risk Implications and Associated Remediation Progress in Recent Decades: A Critical Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 286, 124989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparajith, B.; Kumar, A.; Hodder, D.; Gupta, M.L. Recovery of Cadmium from Hydrometallurgical Zinc Smelter by Selective Leaching. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 102, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Guo, Z.; Jiang, L.; Sarkodie, E.K.; Li, K.; Shi, J.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, H.; Liang, Y.; et al. Cadmium, Lead and Arsenic Contamination in an Abandoned Nonferrous Metal Smelting Site in Southern China: Chemical Speciation and Mobility. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 239, 113617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karavasteva, M. The Effect of Certain Surfactants on the Cementation of Cobalt from Zinc Sulphate Solutions by Suspended Zinc Particles in the Presence of Copper or Antimony. Can. Metall. Q. 2001, 40, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouvea, L.R.; Morais, C.A. Recovery of Zinc and Cadmium from Industrial Waste by Leaching/Cementation. Miner. Eng. 2007, 20, 956–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.; Deandrade, J.; Korn, M.; Pereira, M.; Lemos, V.; Santos, W.; Rodrigues, F.; Souza, A.; Ferreira, H.; Dasilva, E. Review of Procedures Involving Separation and Preconcentration for the Determination of Cadmium Using Spectrometric Techniques. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 145, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weibel, G.; Eggenberger, U.; Kulik, D.A.; Hummel, W.; Schlumberger, S.; Klink, W.; Fisch, M.; Mäder, U.K. Extraction of Heavy Metals from MSWI Fly Ash Using Hydrochloric Acid and Sodium Chloride Solution. Waste Manag. 2018, 76, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, S.; Mishra, S. A Review on Extraction and Separation Studies of Copper with Various Commercial Extractants. Metall. Res. Technol. 2015, 112, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, T.G. The Hydrometallurgical Extraction of Zinc by Ammonium Carbonate: A Review of the Schnabel Process. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2006, 27, 231–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Liao, R.; Yang, B.; Fang, C.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wu, B.; Wang, J.; Qiu, G. Chalcocite (Bio)Hydrometallurgy—Current State, Mechanism, and Future Directions: A Review. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 41, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Liu, X.; Lyu, X.; Gao, W.; Su, H.; Li, C. Extraction and Separation of Copper and Iron from Copper Smelting Slag: A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 368, 133095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neira, A.; Pizarro, D.; Quezada, V.; Velásquez-Yévenes, L. Pretreatment of Copper Sulphide Ores prior to Heap Leaching: A Review. Metals 2021, 11, 1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, D.J.; Cook, N.J.; Grano, S.R.; Ehrig, K. Selective Leaching of Penalty Elements from Copper Concentrates: A Review. Miner. Eng. 2016, 98, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babakhani, A.; Rashchi, F.; Zakeri, A.; Vahidi, E. Selective Separation of Nickel and Cadmium from Sulfate Solutions of Spent Nickel–Cadmium Batteries Using Mixtures of D2EHPA and Cyanex 302. J. Power Sources 2014, 247, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, S.; Zeng, W.; Li, B.; Li, K.; Hu, H.; Ding, W. Experimental Analysis of the Performance of Innovative Circulation Configurations for Cleaner Copper Electrolysis. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 189, 105145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abaza, S.F.; Ahmed, A.M. Effect of Magnetic Field on the Rate of Production of Cadmium Powder from Cadmium Solutions by Cementation of Zinc. Asian J. Chem. 2014, 26, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, N.K.; El-Ashtoukhy, E.-S.Z.; Abdelwahab, O. Rate of Cadmium Ions Removal from Dilute Solutions by Cementation on Zinc Using a Rotating Fixed Bed Reactor. Hydrometallurgy 2007, 89, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadegh Safarzadeh, M.; Bafghi, M.S.; Moradkhani, D.; Ojaghi Ilkhchi, M. A Review on Hydrometallurgical Extraction and Recovery of Cadmium from Various Resources. Miner. Eng. 2007, 20, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Hadi, P.; Chen, G.; McKay, G. Removal of Cadmium Ions from Wastewater Using Innovative Electronic Waste-Derived Material. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 273, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xia, L.; Deen, K.M.; Asselin, E.; Ma, B.; Wang, C. Enhanced Removal of Cadmium from Wastewater by Electro-Assisted Cementation Process: A Peculiar Cd Reduction on Zn Anode. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 139692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casaroli, S.J.G.; Cohen, B.; Tong, A.R.; Linkson, P.; Petrie, J.G. Cementation for Metal Removal in Zinc Electrowinning Circuits. Miner. Eng. 2005, 18, 1282–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, T.; Yang, J.; Wang, W.; Li, L.; Yang, J. Process and Anodic Reaction Mechanism of Cadmium Electrically Enhanced Cementation on Zinc Plate under an Ultrasonic Field in Ammoniacal System. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2019, 29, 1967–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colantonio, N.; Kim, Y. Cadmium (II) Removal Mechanisms in Microbial Electrolysis Cells. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 311, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Geng, Y.; Han, G.; Cao, Y.; Peng, W.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, T.; Dou, Z. A Perspective of Stepwise Utilization of Hazardous Zinc Plant Purification Residue Based on Selective Alkaline Leaching of Zinc. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 122090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Xu, B.; Yang, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, B.; Liu, G.; Ma, Y.; Jiang, T. Comprehensive Recovery of Valuable Metals from Copper Smelting Open-Circuit Dust with a Clean and Economical Hydrometallurgical Process. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 424, 130411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, M.R.; Fritt-Rasmussen, J.; Nielsen, S.; Ottosen, L.M. Electrodialytic Removal of Cadmium from Wastewater Sludge. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 106, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgariu, L.; Bulgariu, D. Selective Extraction of Hg(II), Cd(II) and Zn(II) Ions from Aqueous Media by a Green Chemistry Procedure Using Aqueous Two-Phase Systems. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 118, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Q.; Xue, J.; Guo, Y.; Li, G.; Cui, H. A Two-Step Approach for Copper and Nickel Extracting and Recovering by Emulsion Liquid Membrane. Water Sci. Technol. 2016, 74, 2454–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zeng, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, T.; Yang, Y.; Tang, K. Simultaneously Enhanced ELM Selectivity and Stability by Difunctional Additives for Batch and Continuous Separation of Cd(II)/Cu(II). Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2018, 140, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Wu, J.; Wu, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhai, J. Solvent Extraction Process for the Selective Recovery of Copper and Cobalt from Carrollite Leach Solution. Metall. Res. Technol. 2019, 116, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Liu, Q.; Luo, L.; Liu, L.; Tang, K. Enhancement Mechanism of an Improved Liquid Membrane Using Selective Permeation Retardant for Heavy Metal Ions Separation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2019, 201, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Wang, S.; Duan, H.; Yuan, X.; Huang, Z.; Guo, H.; Yang, X. Efficient Separation of Copper and Nickel from Ammonium Chloride Solutions through the Antagonistic Effect of TRPO on Acorga M5640. Hydrometallurgy 2016, 163, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Ferreira, A.E.; Santos, S.M.C.; Reis, M.T.A.; Ismael, M.R.C.; Correia, M.J.N.; Carvalho, J.M.R. Separation and Recovery of Copper from Zinc Leach Liquor by Solvent Extraction Using Acorga M5640. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2010, 97, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Dwivedi, J.; Shukla, K.; Malviya, P. X-Ray Diffraction and Fourier Transformation Infrared Spectroscopy Studies of Copper (II) Thiourea Chloro and Sulphate Complexes. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2014, 534, 012014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deep, A.; Kumar, P.; Carvalho, J.M.R. Recovery of Copper from Zinc Leaching Liquor Using ACORGA M5640. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 76, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Reis, M.T.A.; Ismael, M.R.C.; Correia, M.J.N.; Carvalho, J.M.R. Modeling of the Extraction Equilibrium of Copper from Sulfate Solutions with Acorga M5640. Solvent Extr. Ion Exch. 2012, 30, 536–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, W.H.; Liu, Q.J.; Ding, P. Separation Test of Copper-Zinc-Sulfur Mixed Concentrate in Kazakhstan. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 683, 565–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.E.; Agarwal, S.; Machado, R.M.; Gameiro, M.L.F.; Santos, S.M.C.; Reis, M.T.A.; Ismael, M.R.C.; Correia, M.J.N.; Carvalho, J.M.R. Extraction of Copper from Acidic Leach Solution with Acorga M5640 Using a Pulsed Sieve Plate Column. Hydrometallurgy 2010, 104, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yang, S.; Wang, S.; Luo, T.; Chen, Y. Facile Method for the Cadmium Separation from Zinc- and Cadmium-Bearing Dust by Zinc Plate Electroreplacement (ZPER) Process. JOM 2022, 74, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Jiao, X.; Kapitanova, O.O.; Wang, J.; Volkov, V.S.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, S. Diffusion Limited Current Density: A Watershed in Electrodeposition of Lithium Metal Anode. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2200244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S.; Suwa, Y.; Endo, M. Cu/Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube Composite Films Fabricated by Pulse-Reverse Electrodeposition. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2011, 158, D49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, M.B.J.G.; Rosalém, S.F. Electrochemical Recovery of Cadmium from Spent Ni–Cd Batteries. J. Power Sources 2005, 139, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, Y.; Wu, M.-H.; Shen, Y.-S. A Study on the Cadmium Removal from Aqueous Solutions by Zinc Cementation. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2002, 37, 571–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shazly, A.H.; Mubarak, A.A.; Bamufleh, H.S. Improving the Diffusion Controlled Cementation of Cadmium Ions Using Reciprocating Fixed Bed of Zinc Rings. Defect Diffus. Forum 2011, 312–315, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Wang, H.; Liu, G.; Wang, Z. Box–Behnken Response Surface Design for the Optimization of Electrochemical Detection of Cadmium by Square Wave Anodic Stripping Voltammetry on Bismuth Film/Glassy Carbon Electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 235, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ince, O.K.; Ince, M.; Karaaslan, N.M.; Yonten, V. Optimization of Cadmium Removal from Water by Hydroxyapatite Using Experimental Design Methodology. Anal. Lett. 2016, 49, 2513–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Xin, X.; Xu, J.; Bian, Y.; Bian, Z. Cadmium Ion Adsorption by Amine-Modified Activated Carbon. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 1675–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Zn | Cd | Cu | Co | Ni | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 25,087 | 17,363 | 738.2 | 217.9 | 175.89 |
| 2 | 26,376 | 18,762 | 819.4 | 141.6 | 165.76 |
| 3 | 24,754 | 16,541 | 855.9 | 198.3 | 177.09 |
| Avg | 25,405.67 | 17,555.33 | 804.50 | 185.93 | 172.91 |
| Factor | Electrolyte Flow Rate | Current Density | pH | Cathode/Anode Area Ratio | Plate Spacing | Temperature |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| value | 5.40 mL/s | 20 mA/cm2 | 2 | 1:3 | 6 cm | 45 °C |
| Code | Electrolyte Cycle Rate (mL/s) | Current Density (mA/cm2) | Electrode Area Ratio | pH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 1.35 | 30 | 0.33 | 0.5 |
| 0 | 4.05 | 32.5 | 0.665 | 2.25 |
| 1 | 6.75 | 45 | 1 | 4 |
| Test No. | Electrolyte Cycle Rate (mL/s) | Current Density (mA/cm2) | Electrode Area Ratio | pH | Extraction Rate of Cadmium% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 | 1.35 | 0.665 | 2.25 | 84.13 |
| 2 | 60 | 1.35 | 0.665 | 2.25 | 85.26 |
| 3 | 5 | 6.75 | 0.665 | 2.25 | 88.18 |
| 4 | 60 | 6.75 | 0.665 | 2.25 | 97.21 |
| 5 | 32.5 | 4.05 | 0.33 | 0.5 | 88.34 |
| 6 | 32.5 | 4.05 | 1 | 0.5 | 90.08 |
| 7 | 32.5 | 4.05 | 0.33 | 4 | 92.13 |
| 8 | 32.5 | 4.05 | 1 | 4 | 94.65 |
| 9 | 5 | 4.05 | 0.665 | 0.5 | 85.87 |
| 10 | 60 | 4.05 | 0.665 | 0.5 | 92.83 |
| 11 | 5 | 4.05 | 0.665 | 4 | 89.62 |
| 12 | 60 | 4.05 | 0.665 | 4 | 98.13 |
| 13 | 32.5 | 1.35 | 0.33 | 2.25 | 84.69 |
| 14 | 32.5 | 6.75 | 0.33 | 2.25 | 90.98 |
| 15 | 32.5 | 1.35 | 1 | 2.25 | 84.86 |
| 16 | 32.5 | 6.75 | 1 | 2.25 | 94.17 |
| 17 | 5 | 4.05 | 0.33 | 2.25 | 85.65 |
| 18 | 60 | 4.05 | 0.33 | 2.25 | 92.34 |
| 19 | 5 | 4.05 | 1 | 2.25 | 87.03 |
| 20 | 60 | 4.05 | 1 | 2.25 | 93.96 |
| 21 | 32.5 | 1.35 | 0.665 | 0.5 | 84.37 |
| 22 | 32.5 | 6.75 | 0.665 | 0.5 | 91.75 |
| 23 | 32.5 | 1.35 | 0.665 | 4 | 84.83 |
| 24 | 32.5 | 6.75 | 0.665 | 4 | 97.67 |
| 25 | 32.5 | 4.05 | 0.665 | 2.25 | 95.59 |
| 26 | 32.5 | 4.05 | 0.665 | 2.25 | 94.15 |
| 27 | 32.5 | 4.05 | 0.665 | 2.25 | 95.88 |
| 28 | 32.5 | 4.05 | 0.665 | 2.25 | 95.38 |
| 29 | 32.5 | 4.05 | 0.665 | 2.25 | 94.81 |
| Source | Std. Dev. | R2 | R2Adj | R2Pre | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear | 2.74 | 0.6939 | 0.6429 | 0.6001 | |
| 2FI | 2.93 | 0.7382 | 0.5928 | 0.4936 | |
| Quadratic | 0.88 | 0.9817 | 0.9634 | 0.908 | Suggested |
| Cubic | 0.67 | 0.9954 | 0.9785 | 0.7949 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F Value | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 578.2 | 14 | 41.3 | 53.58 | <0.0001 | significant |
| A-Current Density | 128.38 | 1 | 128.38 | 166.54 | <0.0001 | |
| B-cycle rate | 223.78 | 1 | 223.78 | 290.29 | <0.0001 | |
| Electrode area ratio | 9.4 | 1 | 9.4 | 12.19 | 0.0036 | |
| D-pH | 47.16 | 1 | 47.16 | 61.18 | <0.0001 | |
| AB | 15.6 | 1 | 15.6 | 20.24 | 0.0005 | |
| AC | 0.014 | 1 | 0.014 | 0.019 | 0.8932 | |
| AD | 0.6 | 1 | 0.6 | 0.78 | 0.3923 | |
| BC | 2.28 | 1 | 2.28 | 2.96 | 0.1075 | |
| BD | 7.45 | 1 | 7.45 | 9.67 | 0.0077 | |
| CD | 0.15 | 1 | 0.15 | 0.2 | 0.6637 | |
| A2 | 40.6 | 1 | 40.6 | 52.67 | <0.0001 | |
| B2 | 104.59 | 1 | 104.59 | 135.68 | <0.0001 | |
| C2 | 46.18 | 1 | 46.18 | 59.9 | <0.0001 | |
| D2 | 10.04 | 1 | 10.04 | 13.03 | 0.0028 | |
| Residual | 10.79 | 14 | 0.77 | |||
| Lack of Fit | 8.9 | 10 | 0.89 | 1.88 | 0.2847 | not significant |
| Pure Error | 1.89 | 4 | 0.47 | |||
| Cor Total | 588.99 | 28 |
| No. | Circulating Flow Rate mL/s | Current Density mA/cm2 | pH | Electrode Area Ratio | Predicted Extraction Rate% | Actual Extraction Rate% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6.227 | 48.142 | 3.148 | 0.93 | 98.974 | 98.801 |
| 2 | 4.858 | 41.005 | 3.840 | 0.717 | 98.454 | 98.507 |
| 3 | 4.967 | 56.081 | 2.896 | 0.764 | 98.600 | 98.713 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, W.; Zeng, W.; Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Chen, B.; Zheng, X. Cadmium Depth Separation Method in Polymetallic Sulfate Solution: Flow-Electric Field Enhanced Cementation Combined with M5640 Extraction. Inorganics 2023, 11, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11010012
Ding W, Zeng W, Wang Y, Xu H, Chen B, Zheng X. Cadmium Depth Separation Method in Polymetallic Sulfate Solution: Flow-Electric Field Enhanced Cementation Combined with M5640 Extraction. Inorganics. 2023; 11(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Wenjie, Weizhi Zeng, Yunyan Wang, Hui Xu, Bingxin Chen, and Xie Zheng. 2023. "Cadmium Depth Separation Method in Polymetallic Sulfate Solution: Flow-Electric Field Enhanced Cementation Combined with M5640 Extraction" Inorganics 11, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11010012
APA StyleDing, W., Zeng, W., Wang, Y., Xu, H., Chen, B., & Zheng, X. (2023). Cadmium Depth Separation Method in Polymetallic Sulfate Solution: Flow-Electric Field Enhanced Cementation Combined with M5640 Extraction. Inorganics, 11(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11010012






