Pincer Complexes Derived from Tridentate Schiff Bases for Their Use as Antimicrobial Metallopharmaceuticals
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. General Characteristics of Metallopharmaceuticals
1.2. Importance of Multidenticity of Ligands
2. General Aspects of Schiff Bases
2.1. Biological Importance of Schiff Bases
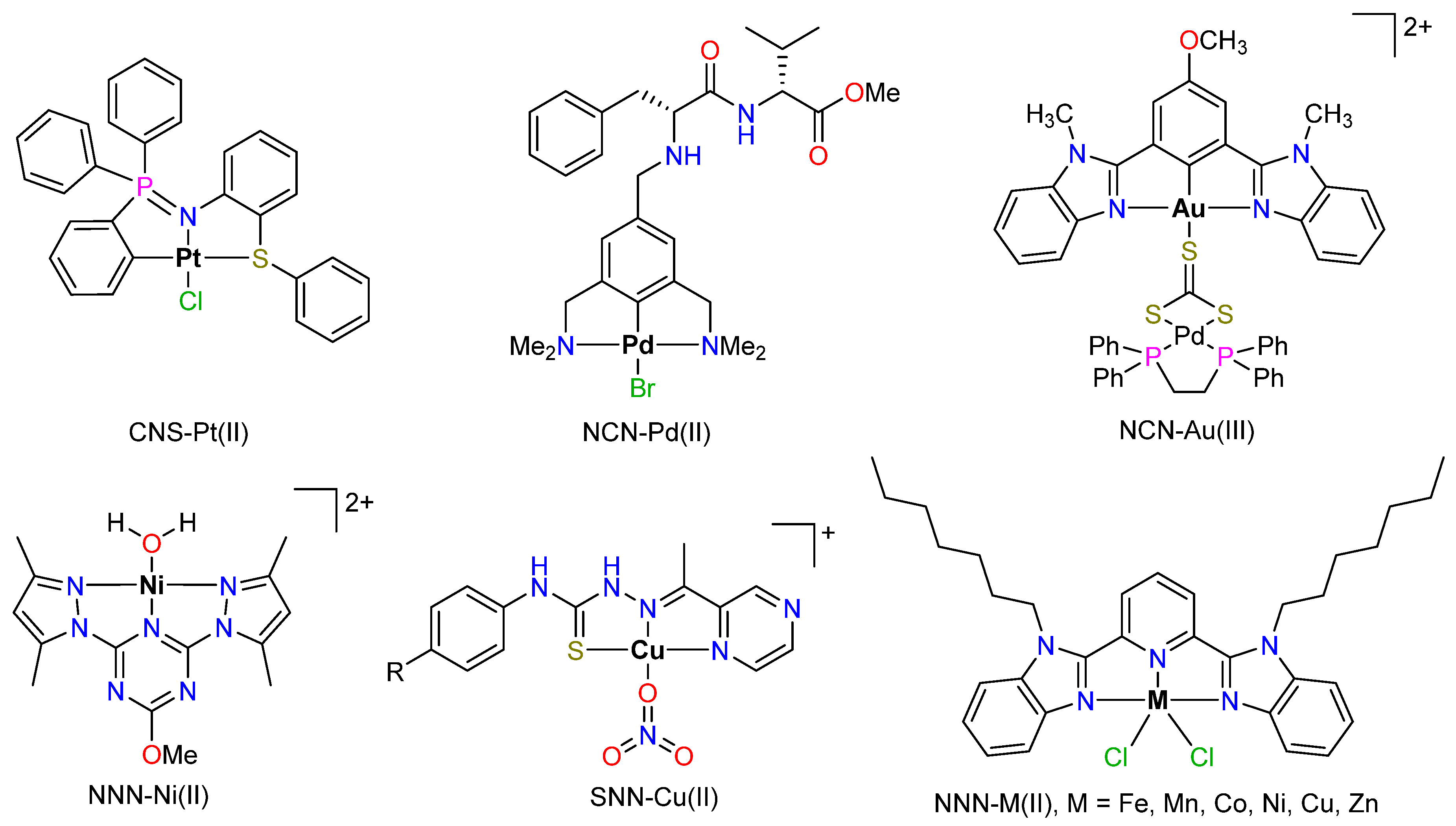
2.2. Schiff Bases as Tridentate Ligands
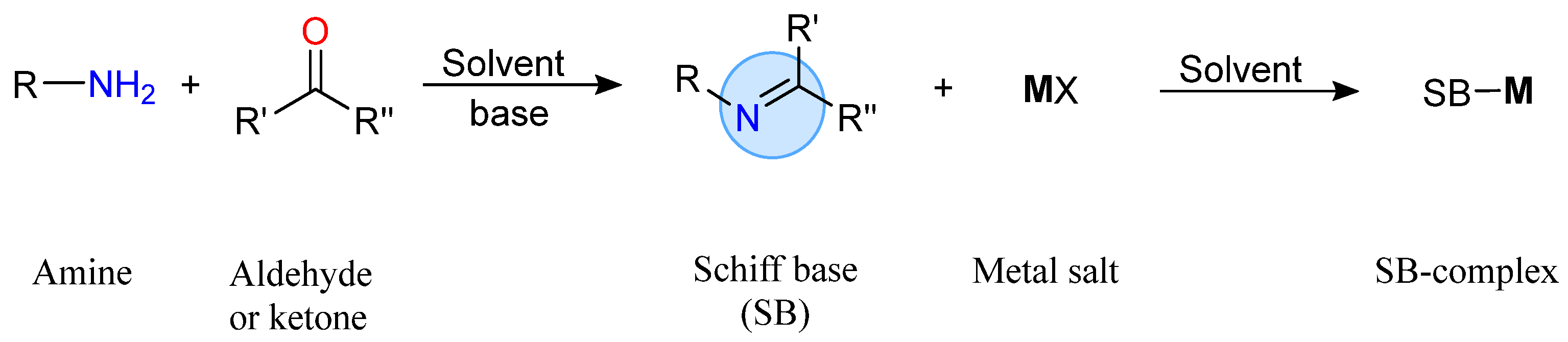
2.3. Synthesis of Metal Complexes Using Schiff Bases
2.3.1. Traditional Chemical Method
2.3.2. Microwave and Sonochemical Synthesis
3. Antimicrobial Metallopharmaceuticals with Tridentate Schiff Bases
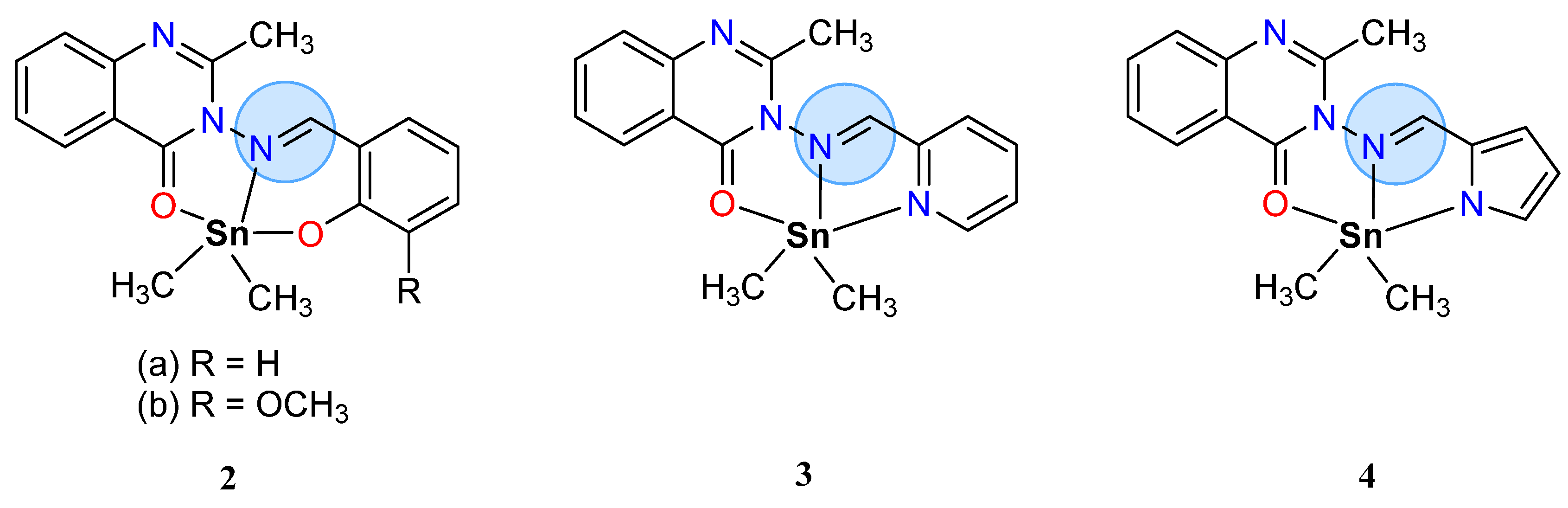
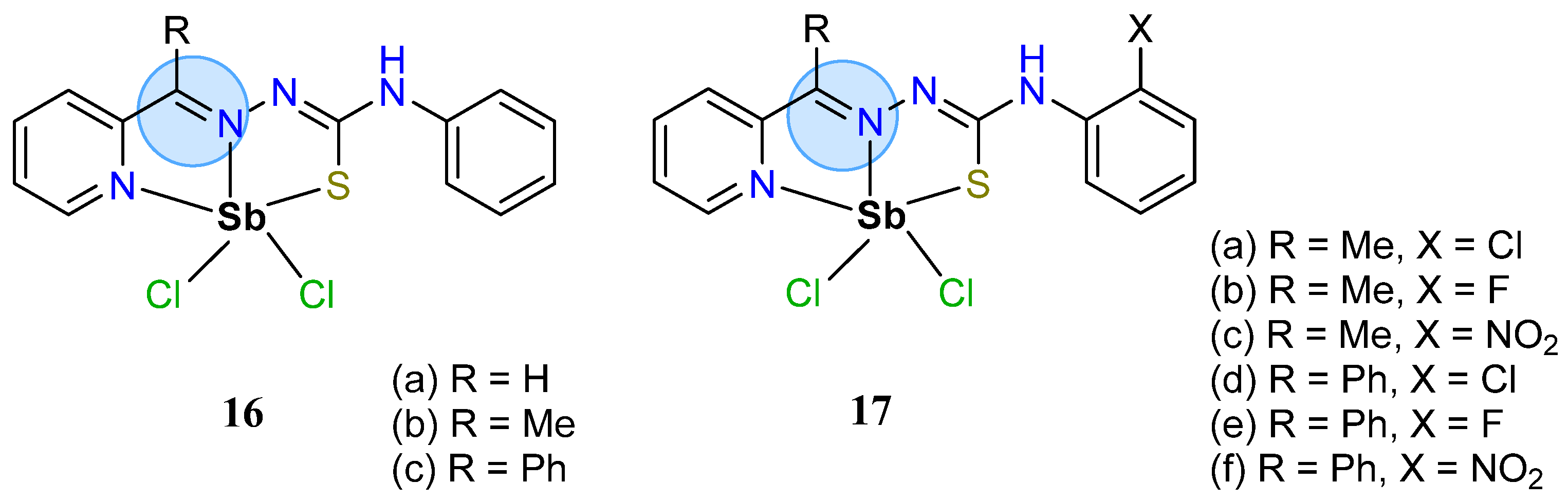
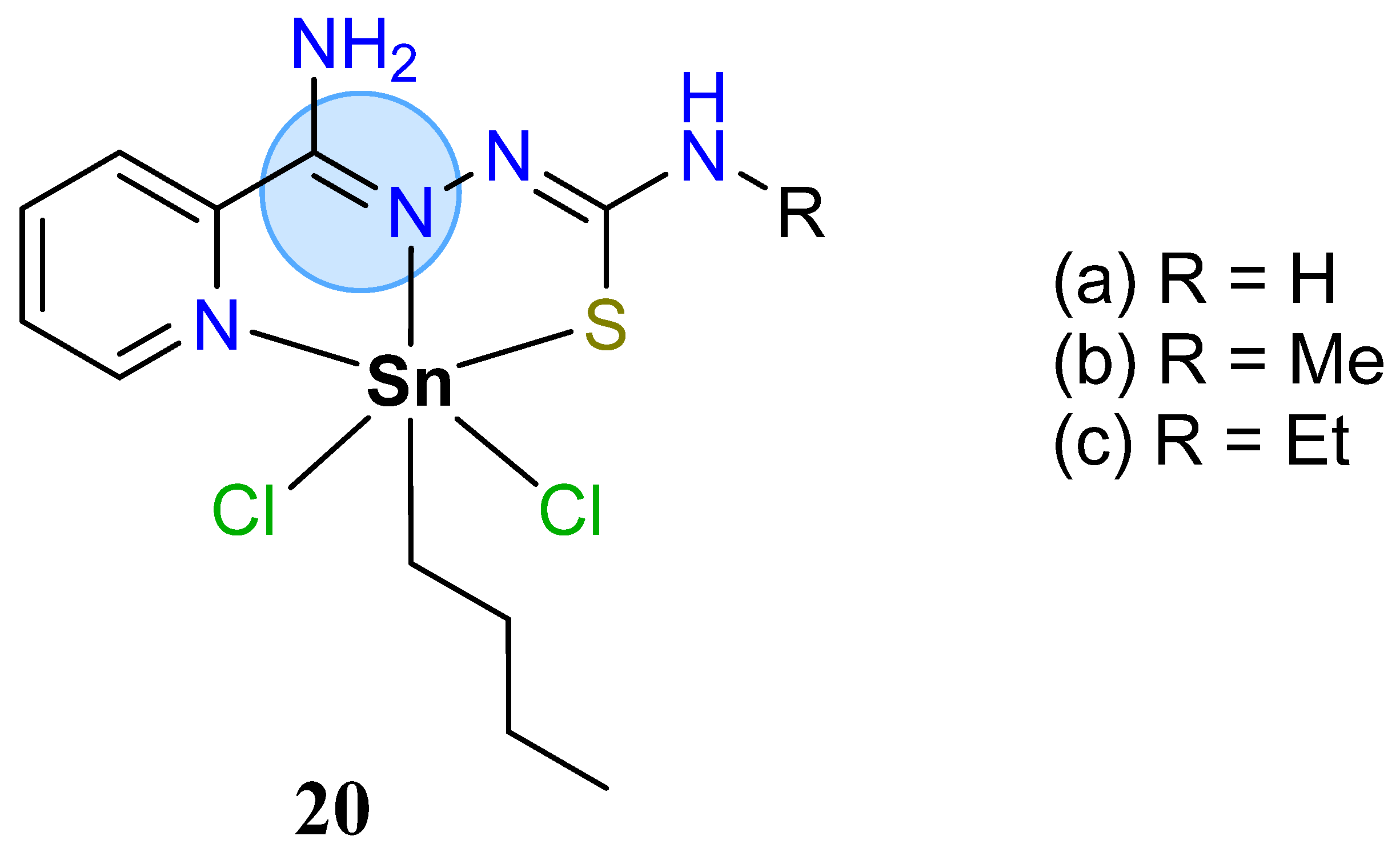
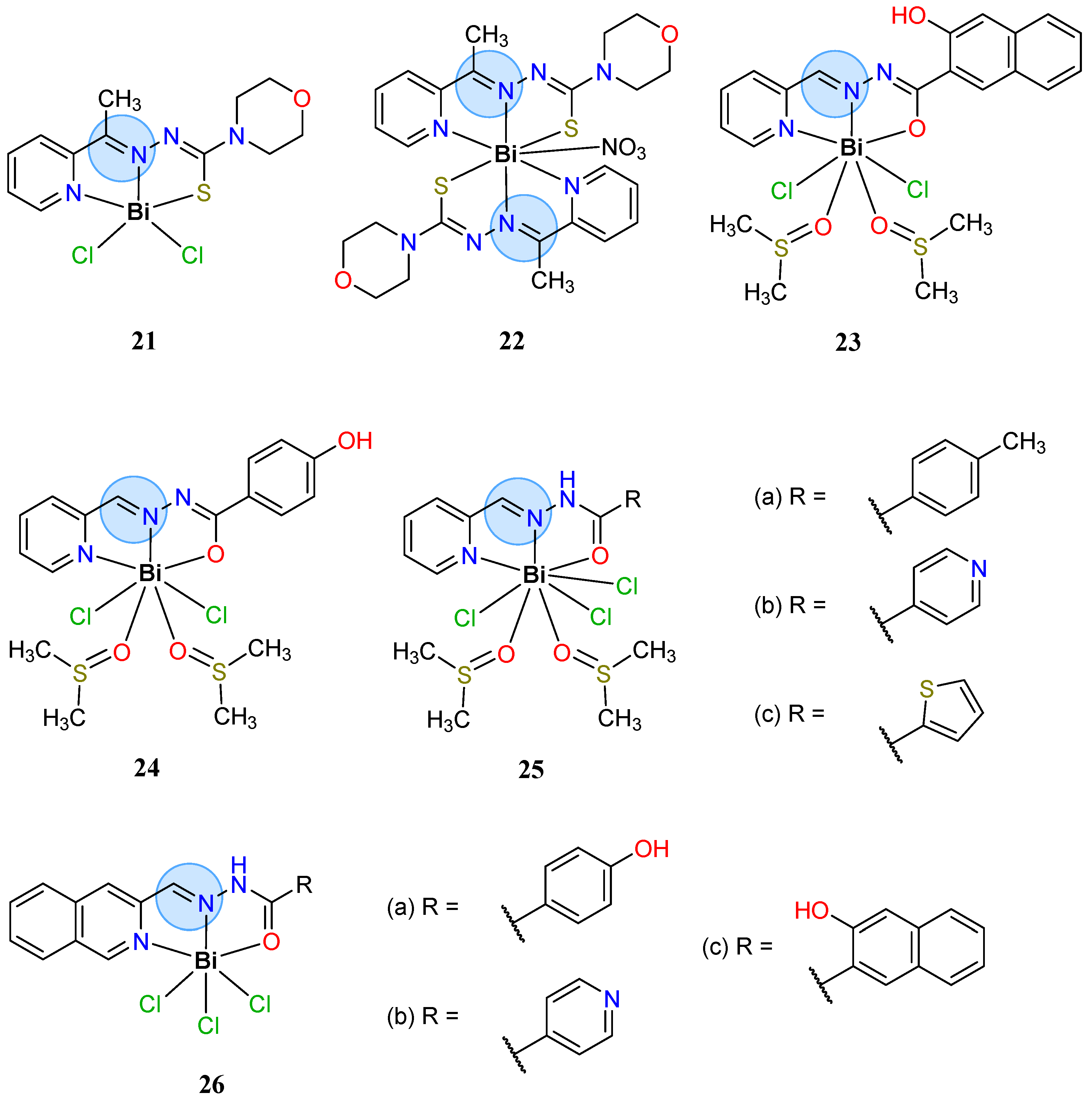
3.1. Main Group Elements
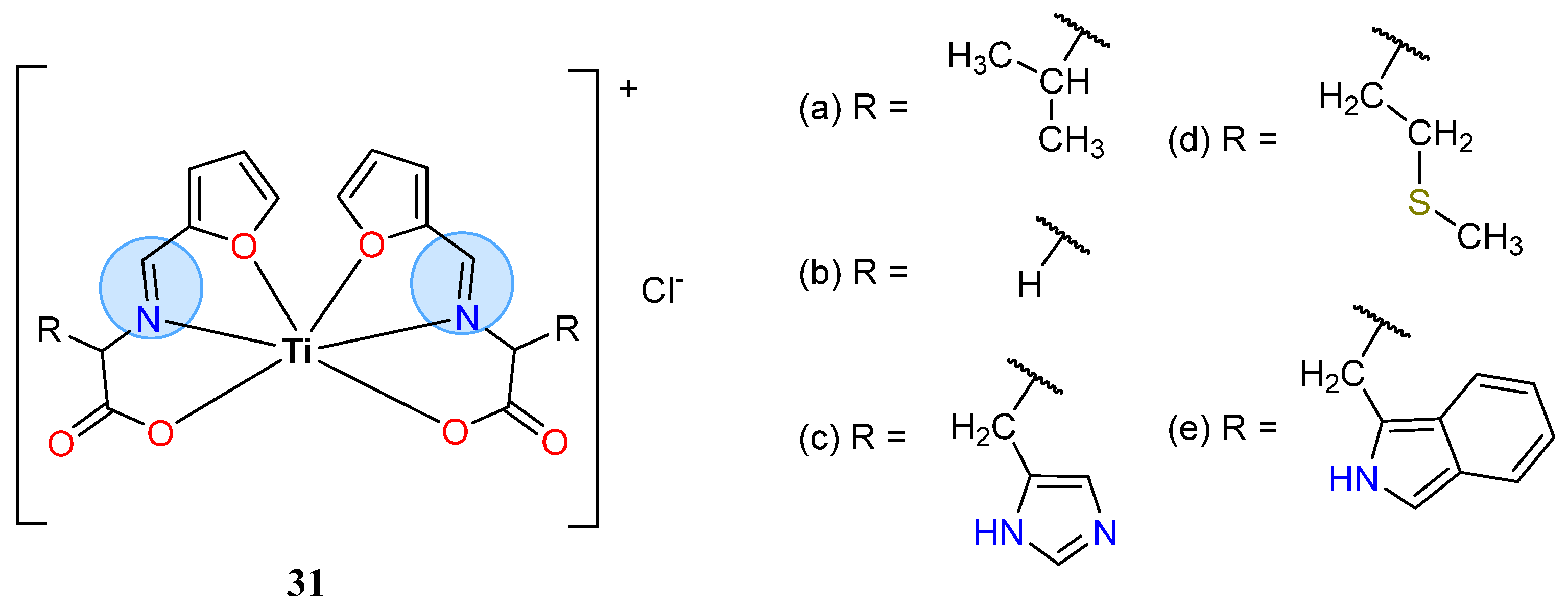
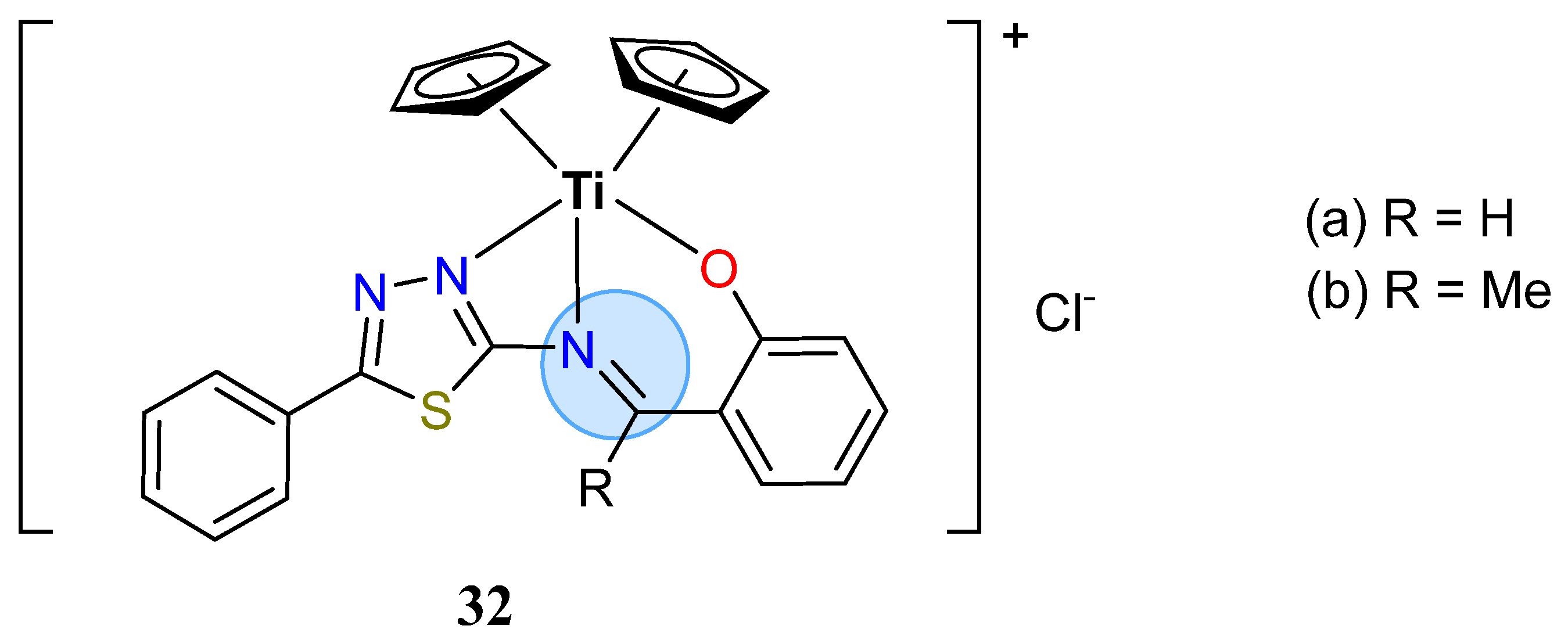
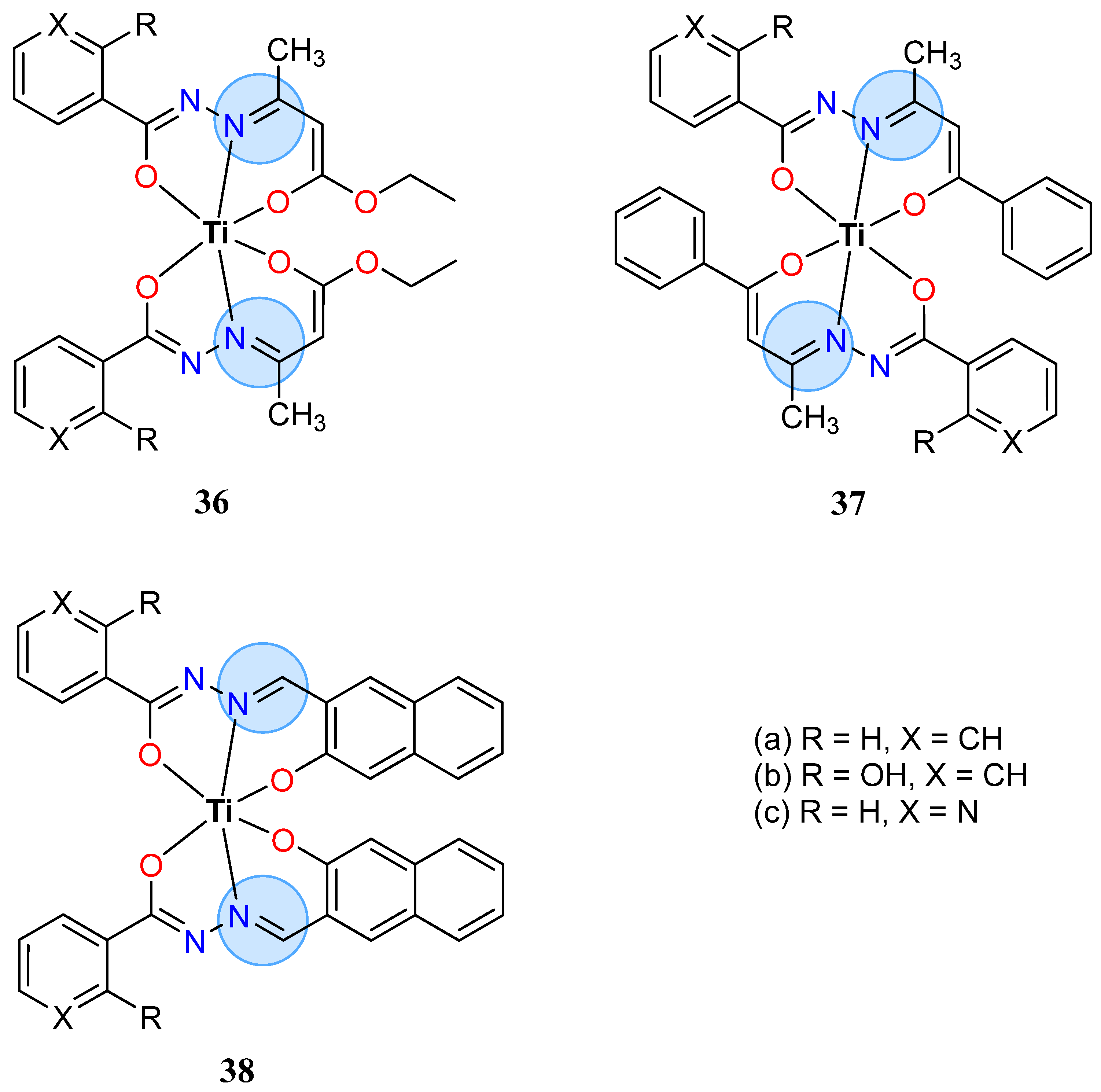
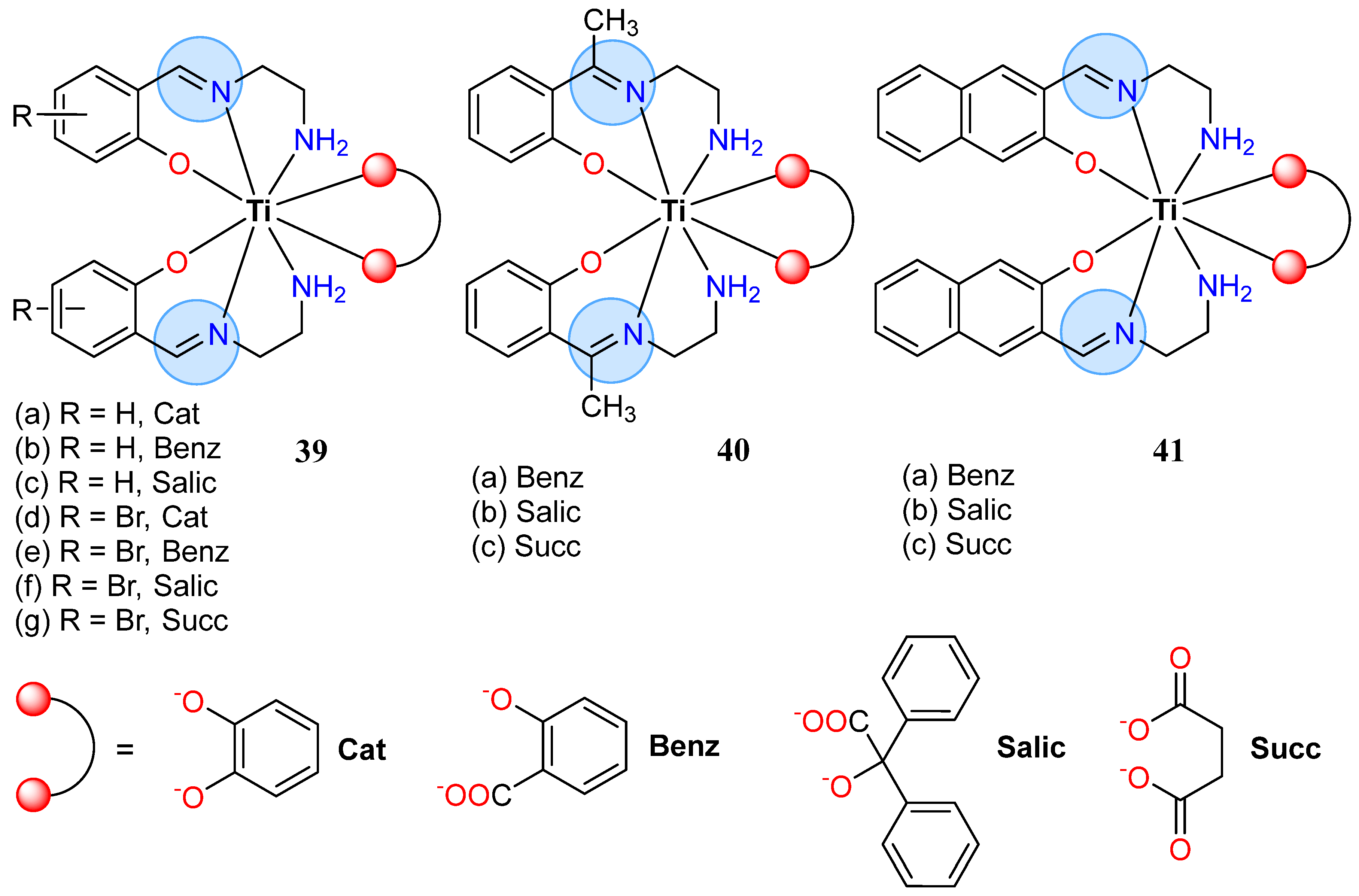
3.2. Titanium Group
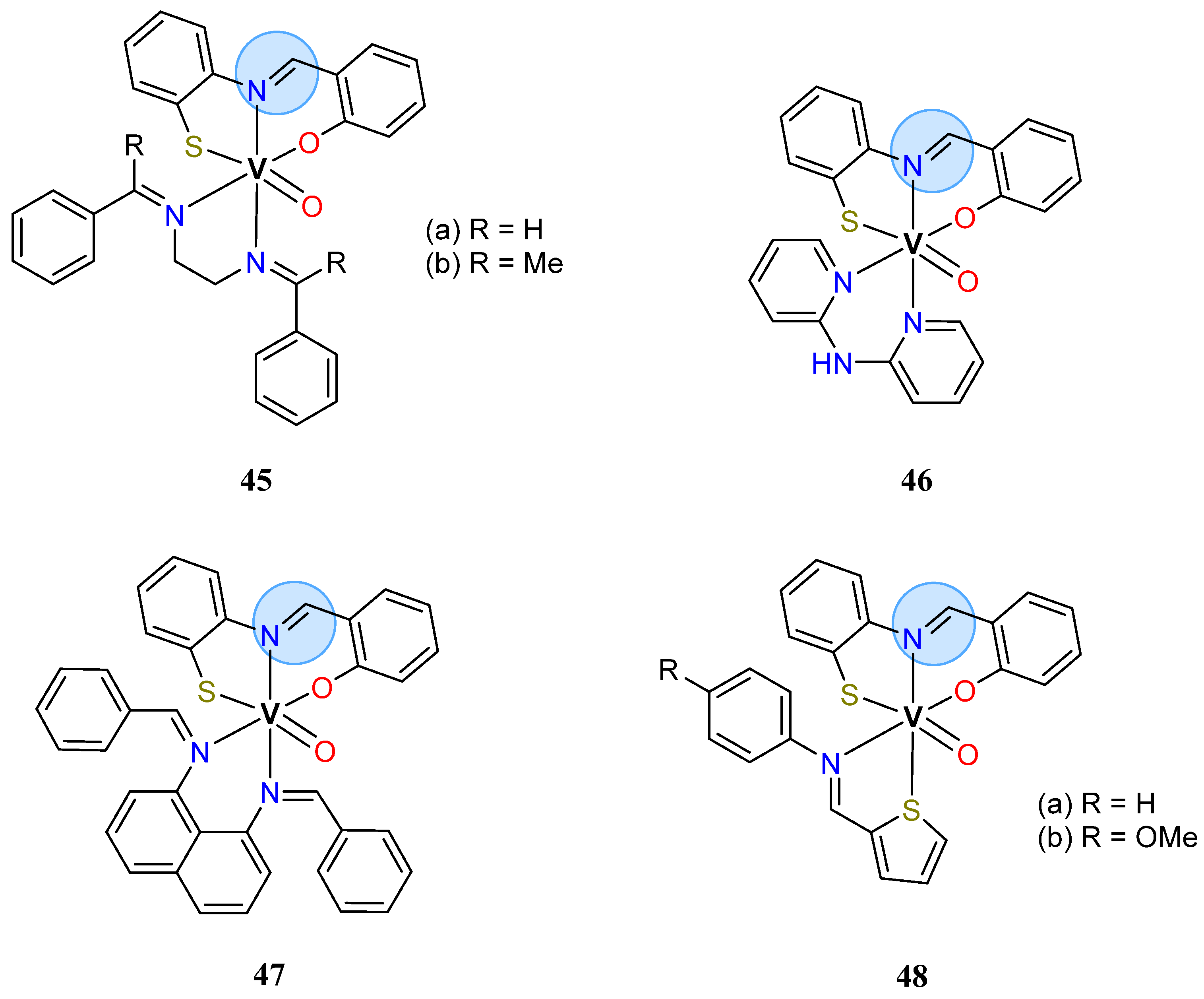
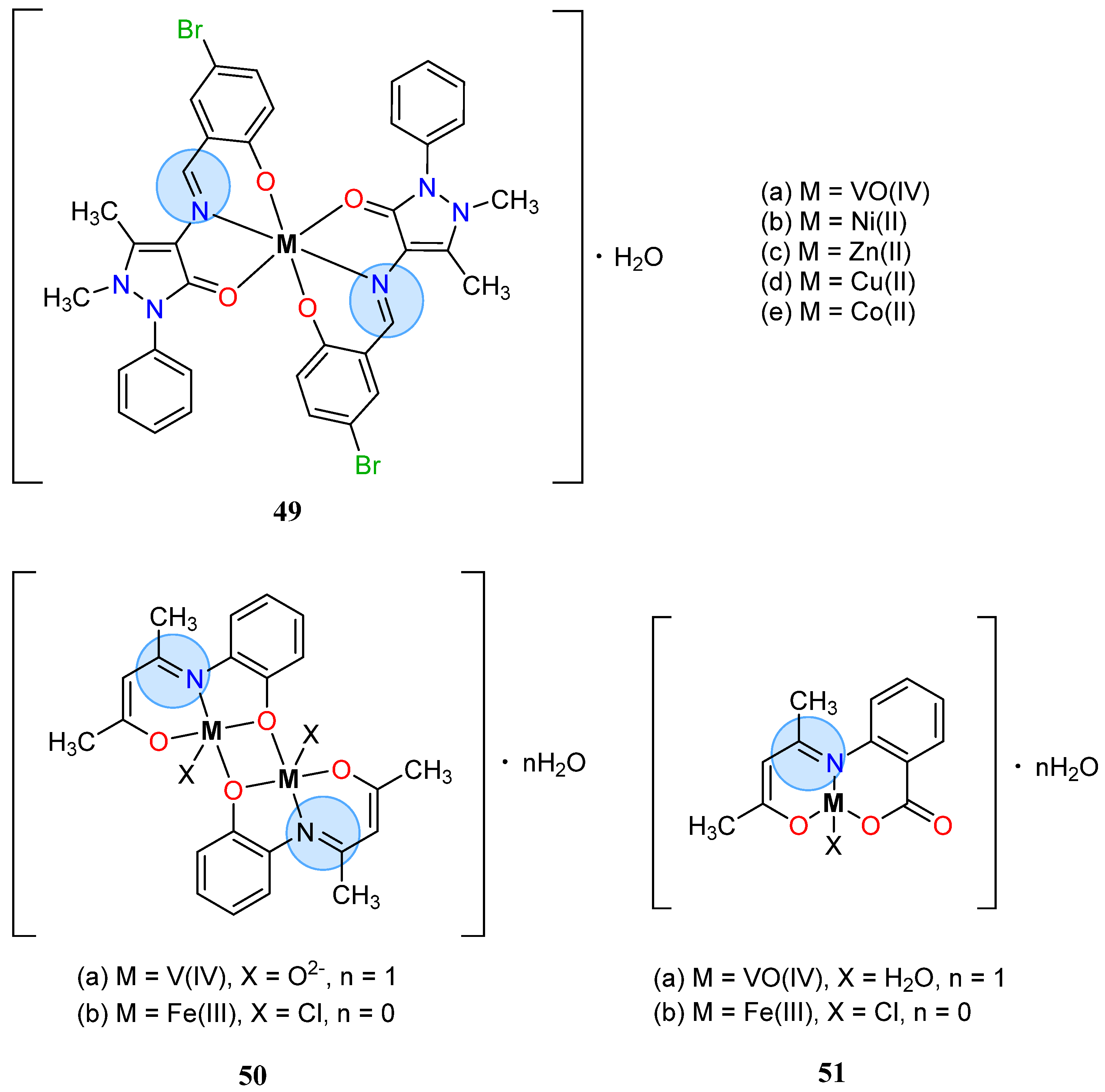
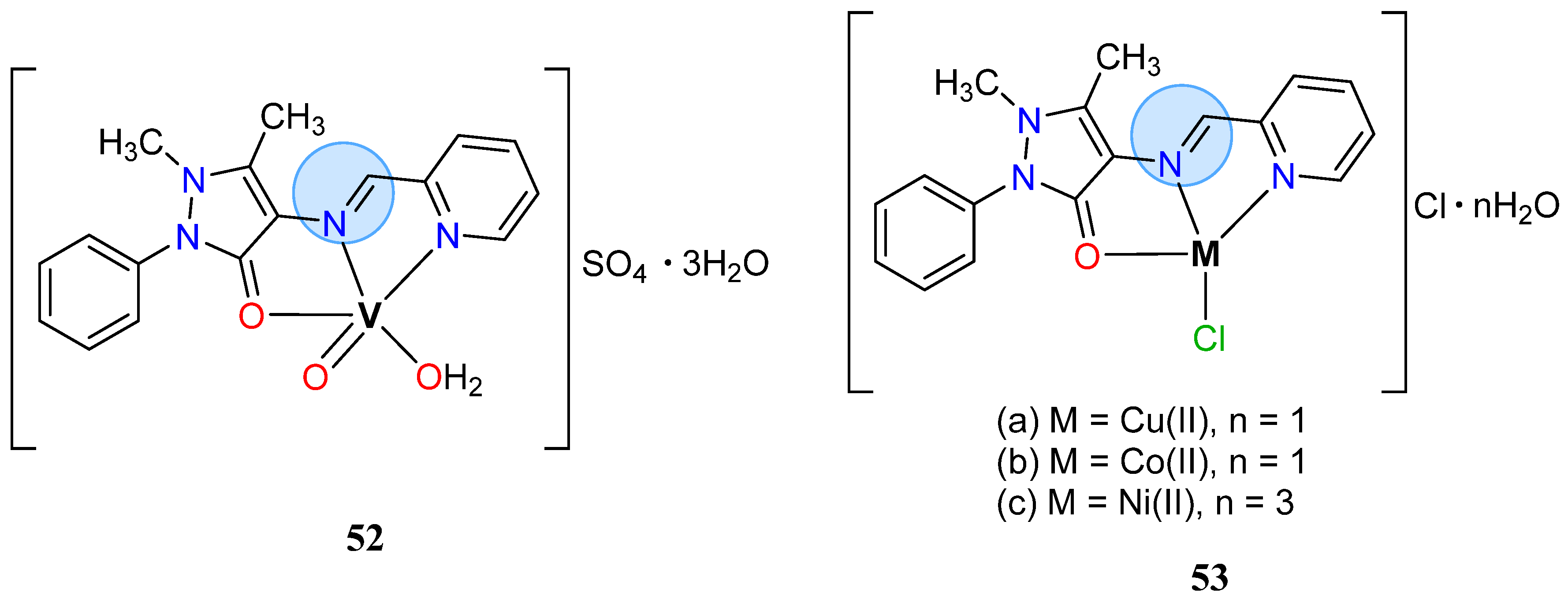
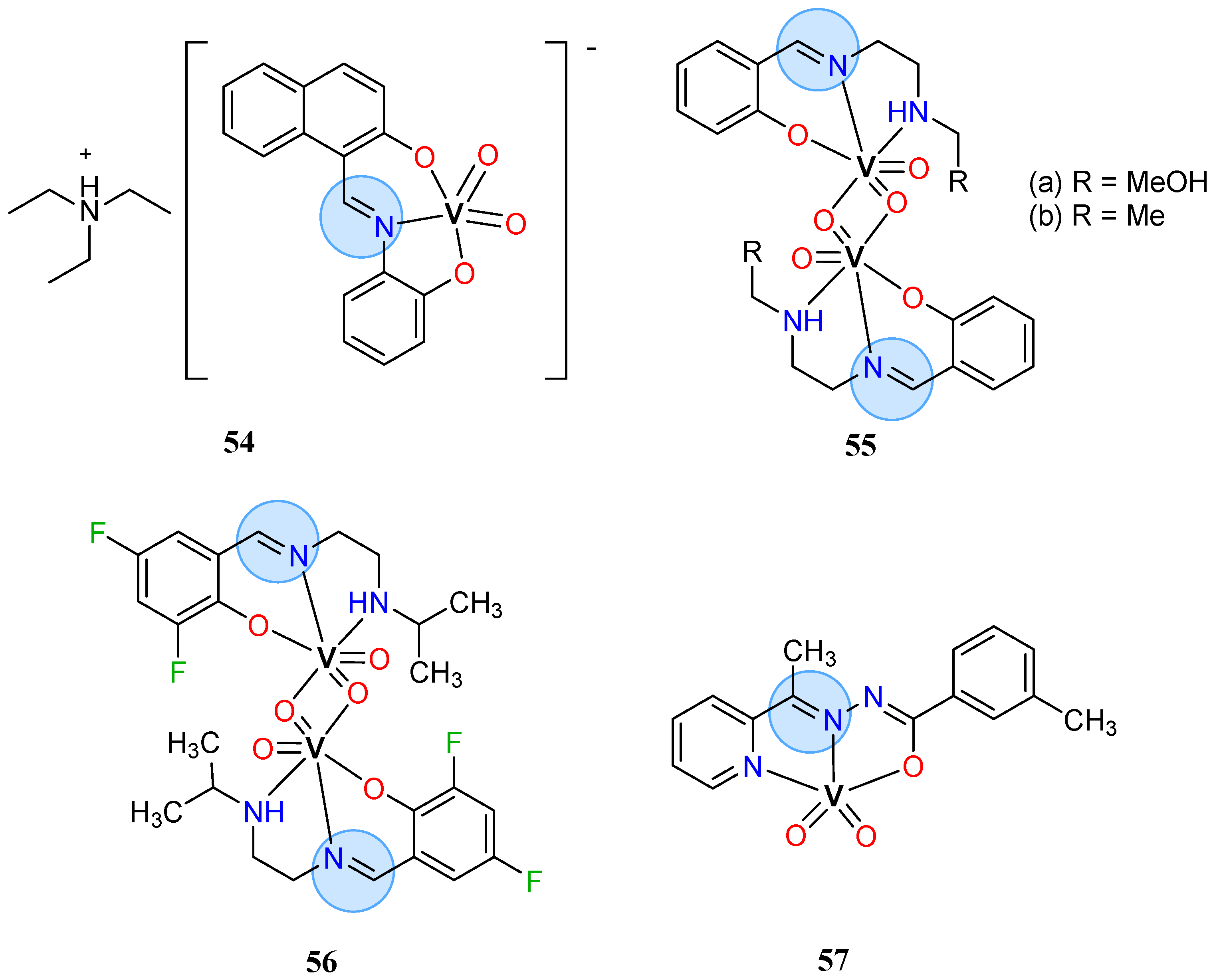
3.3. Vanadium Group
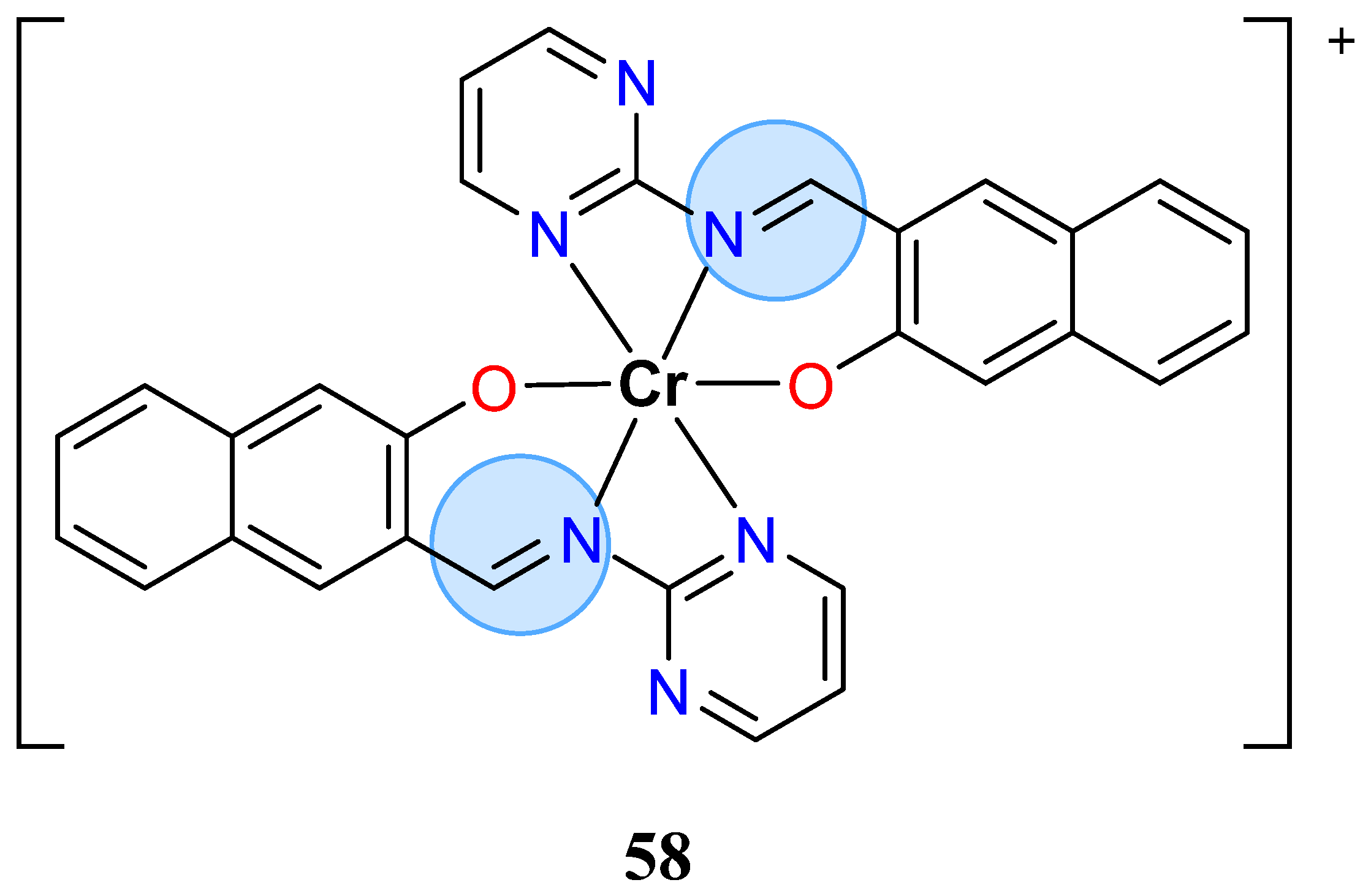
3.4. Chromium Group
3.5. Manganese Group
3.6. Iron Group
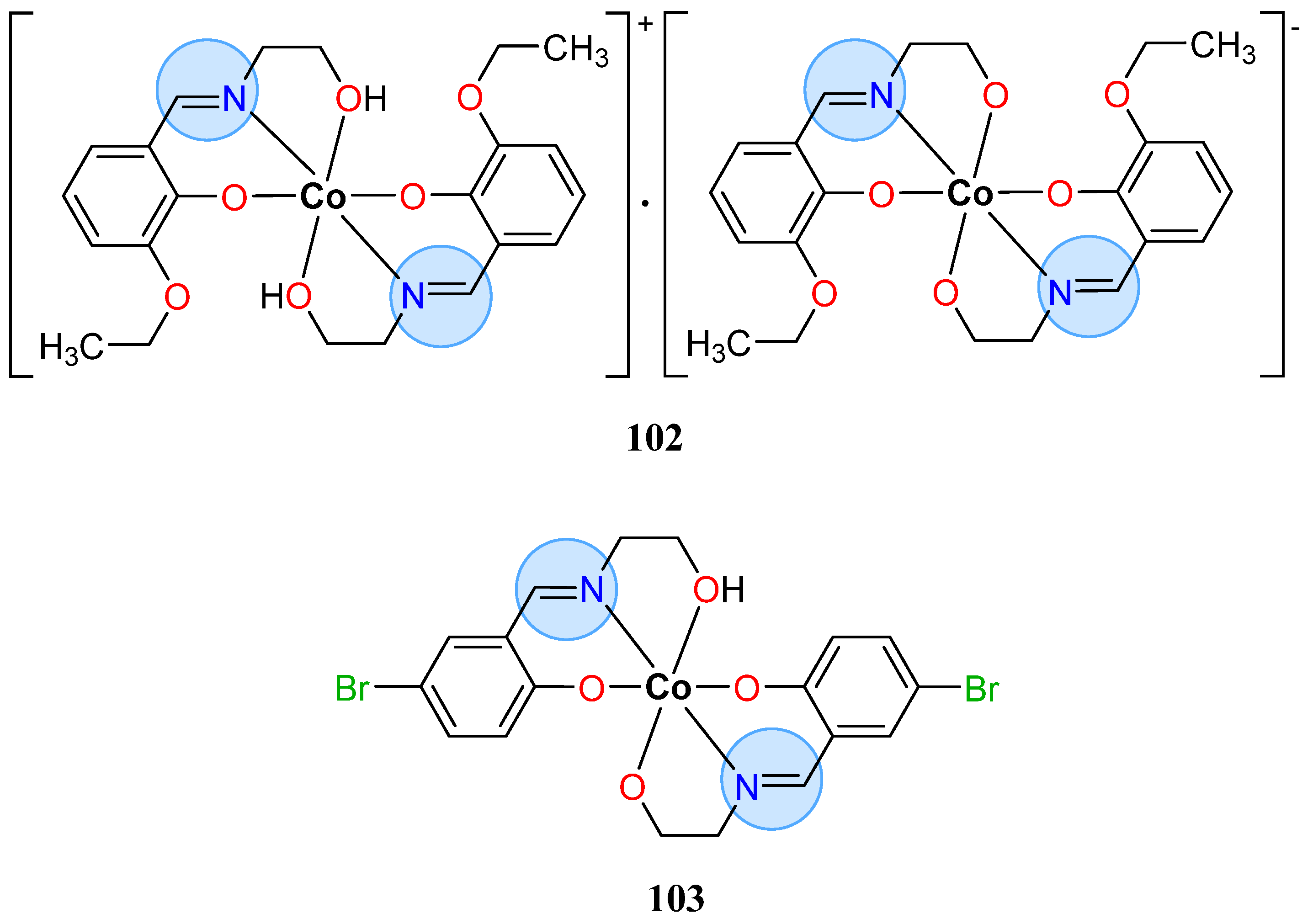
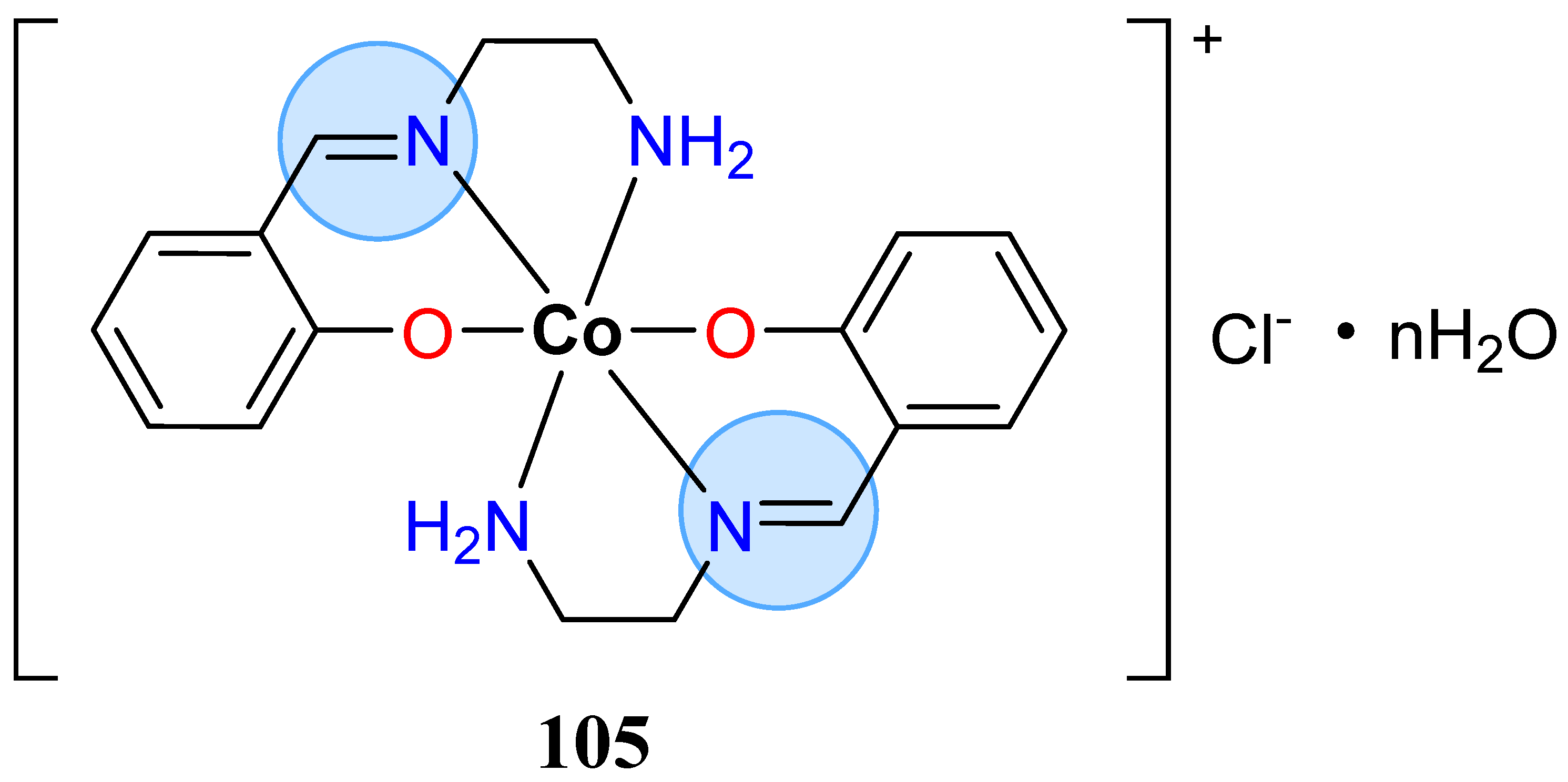
3.7. Cobalt Group
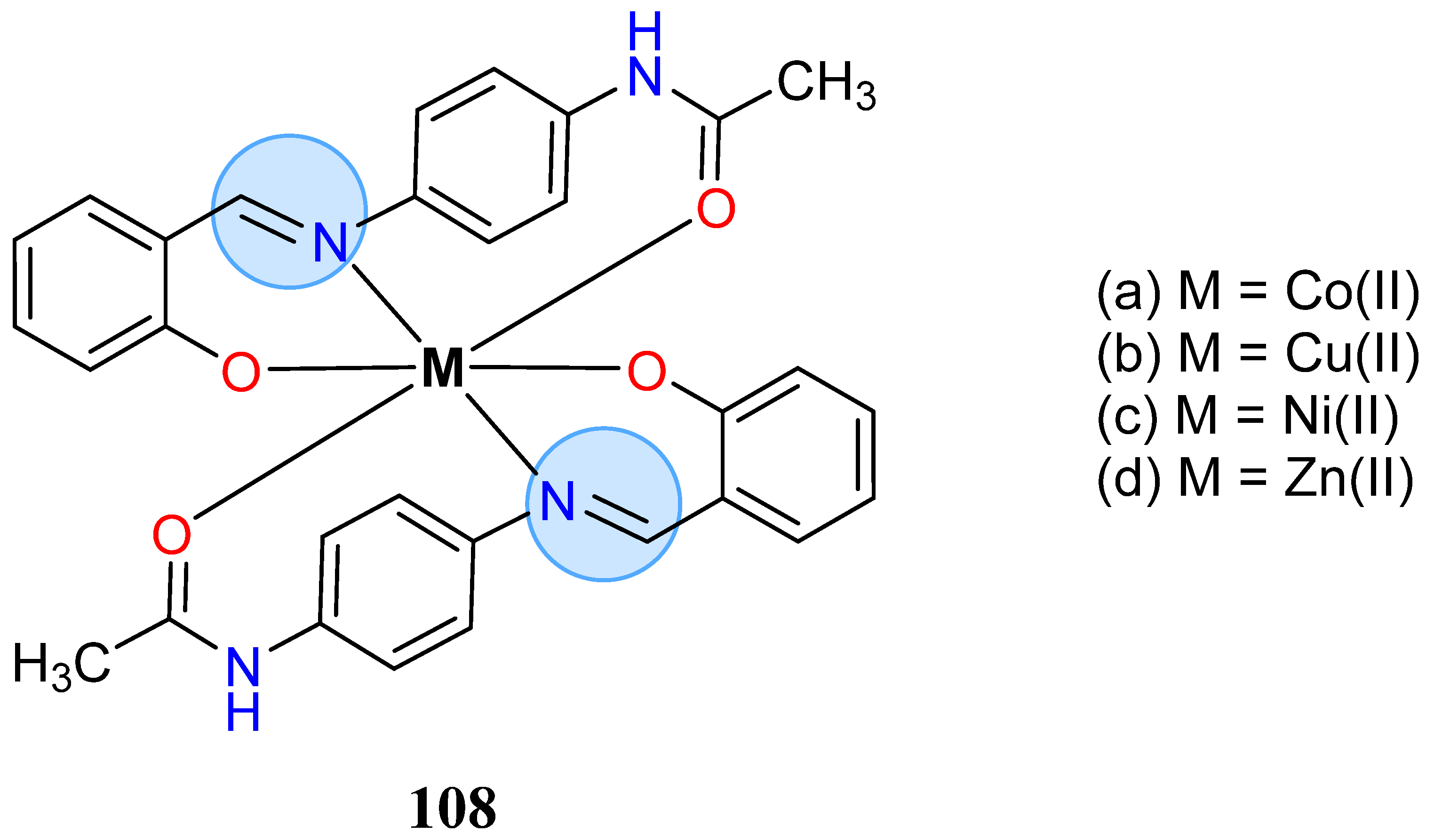
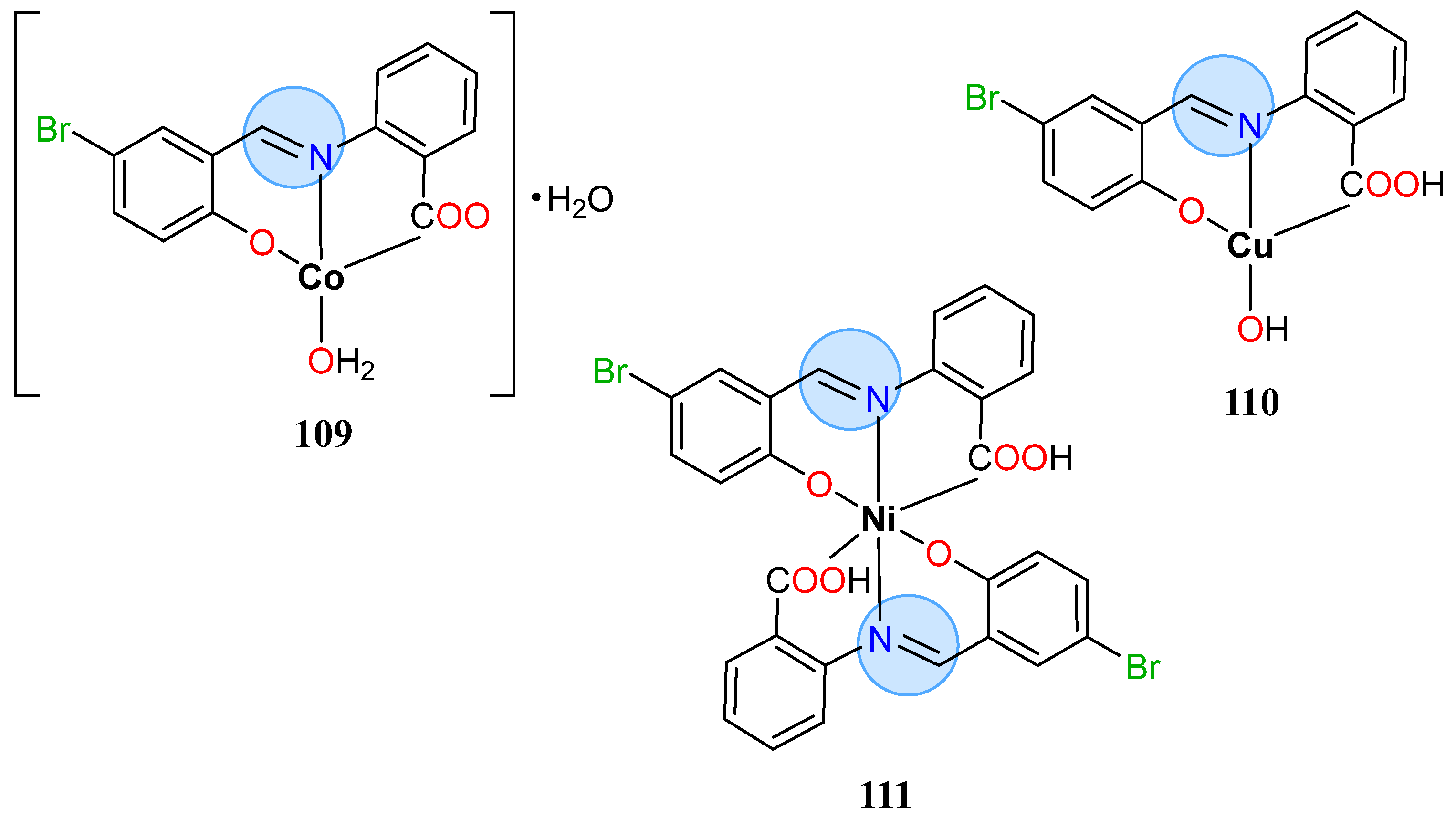
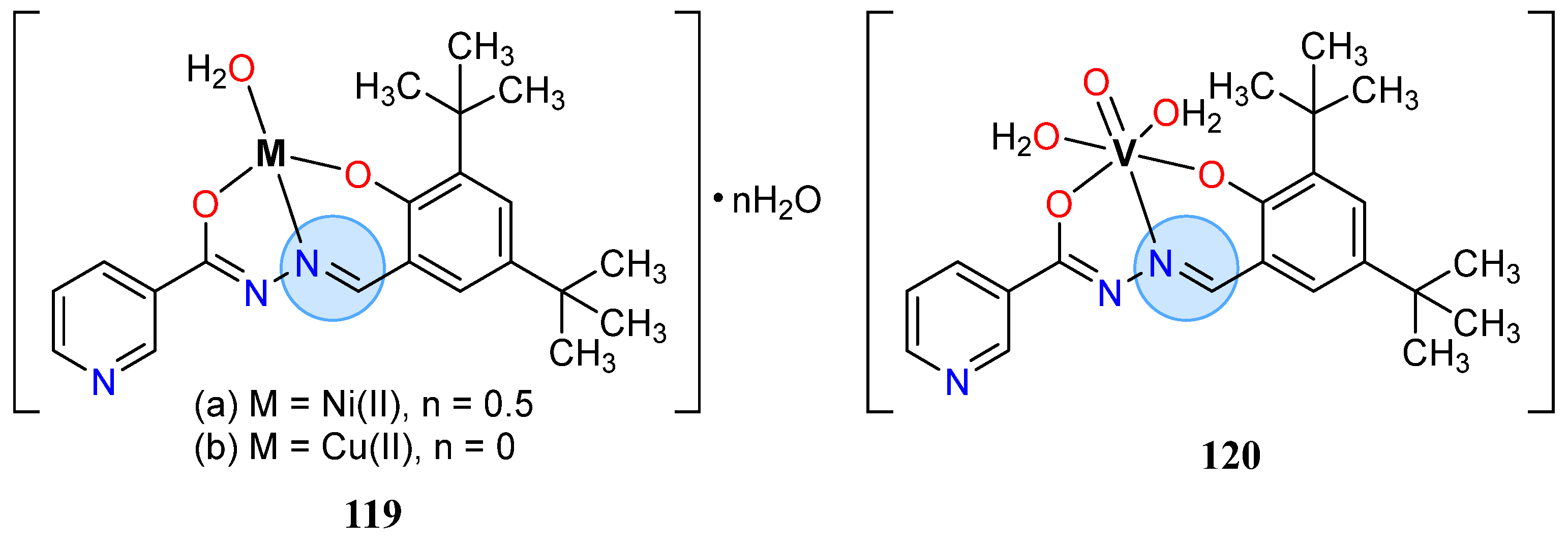
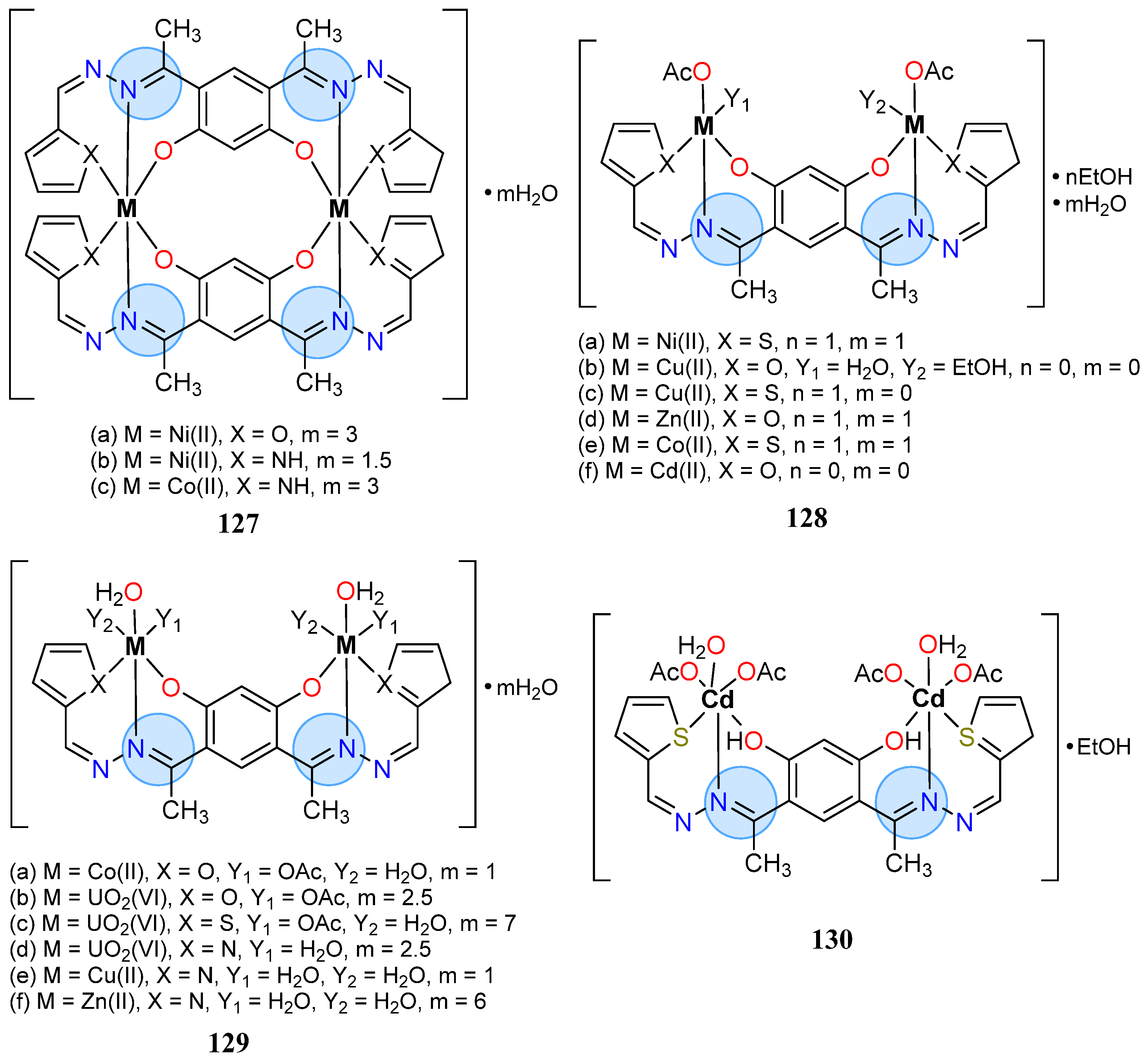
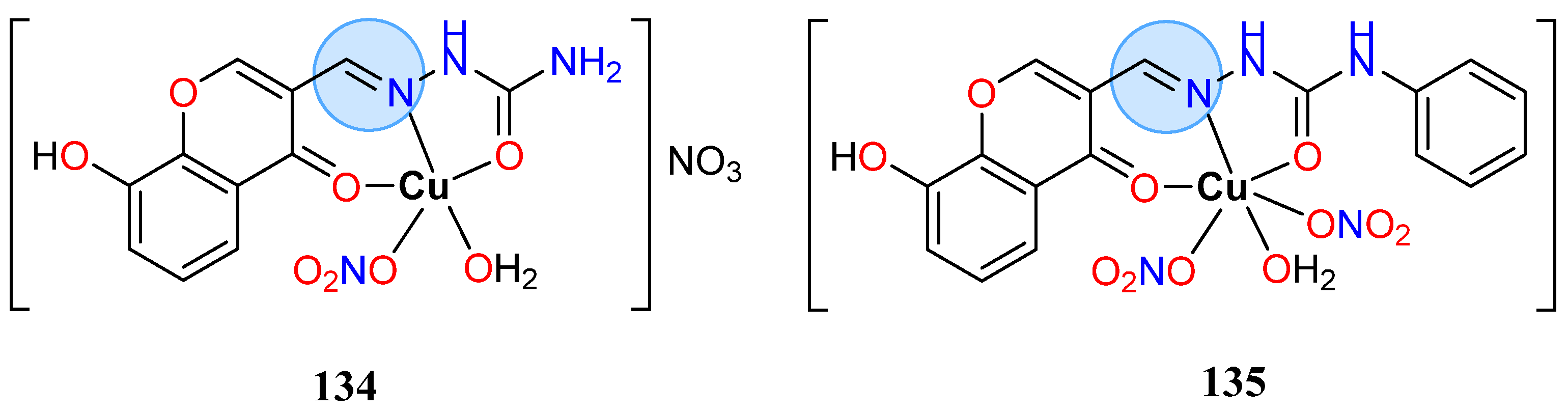
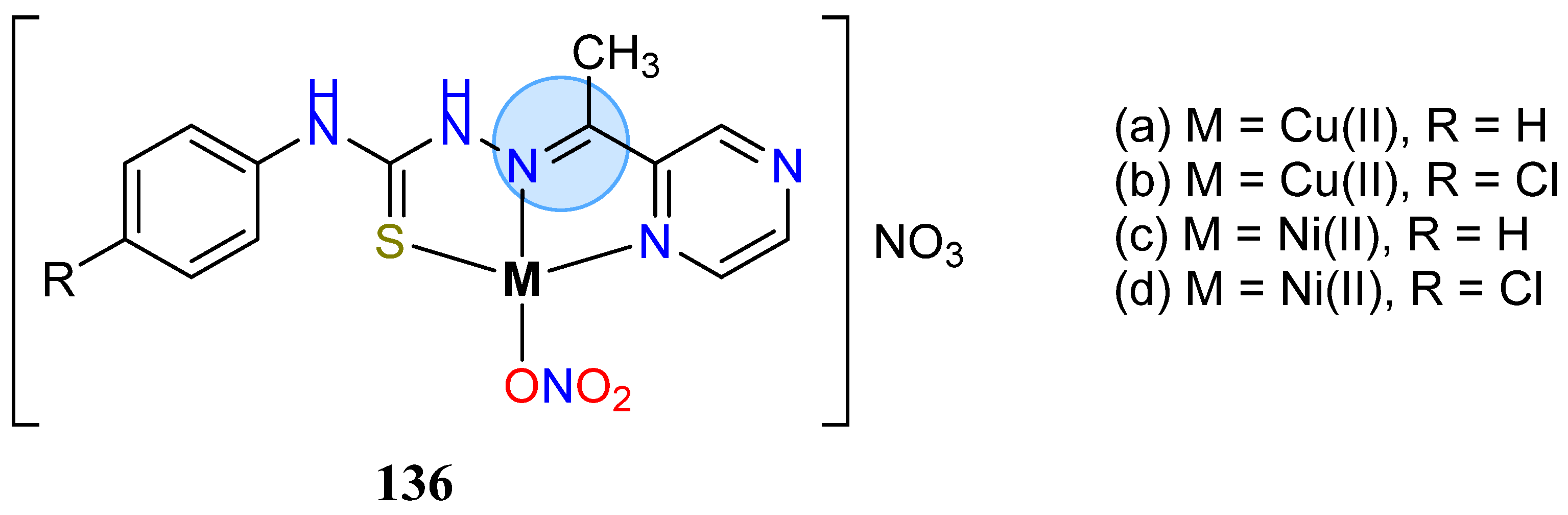
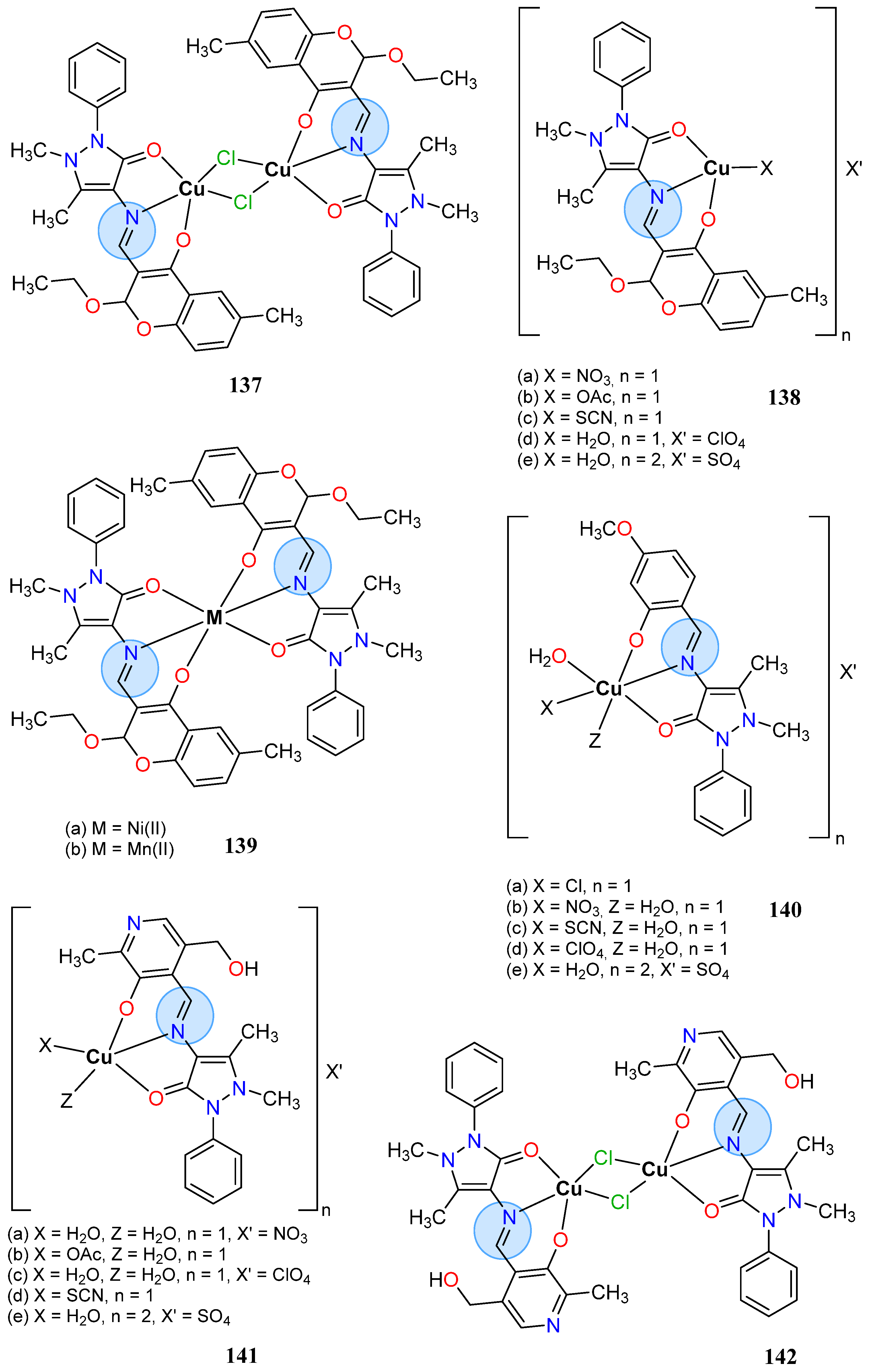
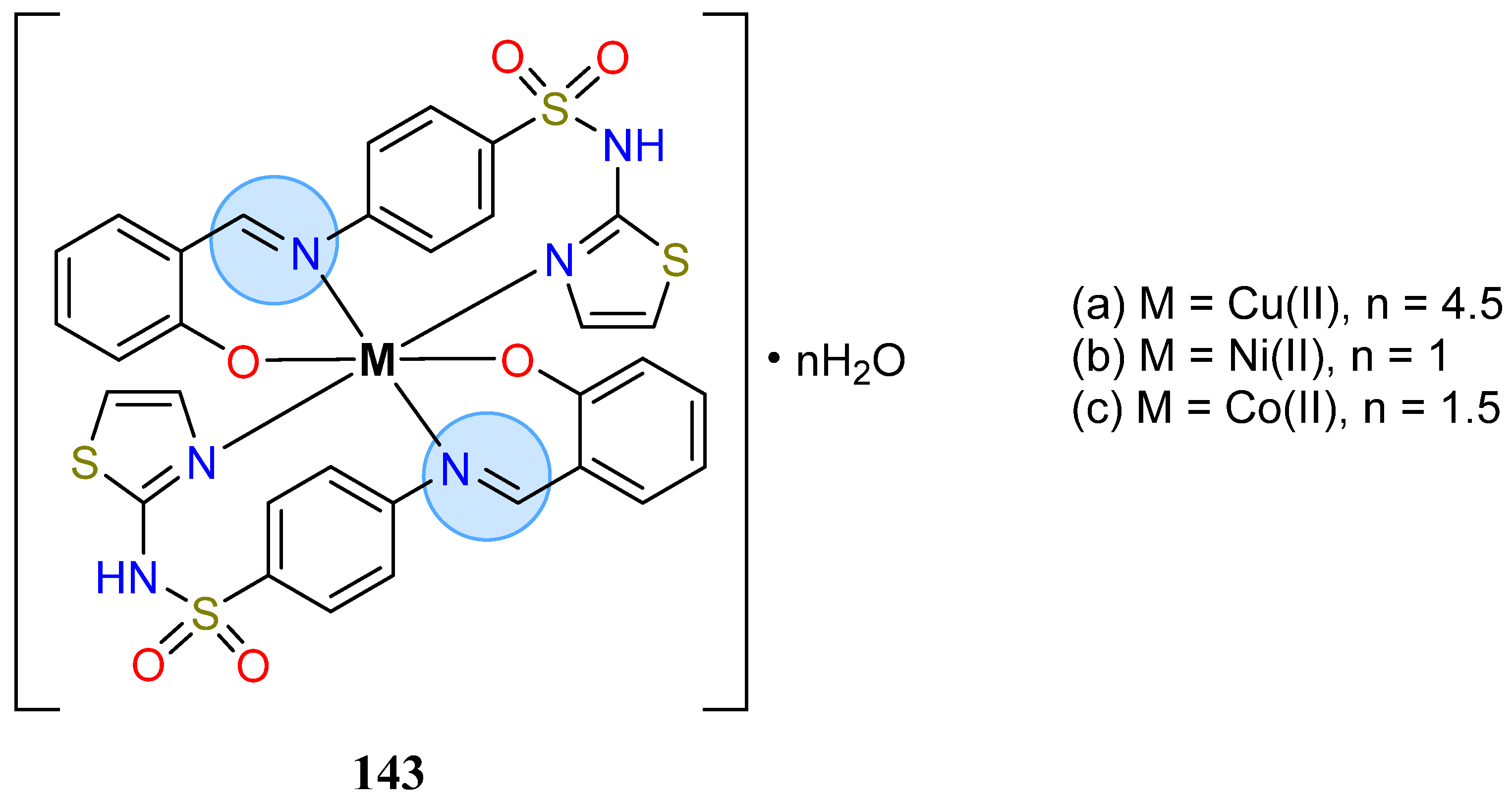
3.8. Nickel, Copper, and Zinc Groups
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Species | Short Name | Long Name |
|---|---|---|
| Gram-positive Bacteria | A. tumefaciens | Agrobacterium tumefaciens |
| B. cereus | Bacillus cereus | |
| B. simplex | Bacillus simplex | |
| B. subtilis | Bacillus subtilis | |
| E. faecalis | Enterococcus faecalis | |
| E. acetylicum | Exiguobacterium acetylicum | |
| M. tuberculosis | Mycobacterium tuberculosis | |
| L. monocytogenes | Listeria monocytogenes | |
| P. acnes | Propionibacterium acnes | |
| S. lutea | Sarcina lutea | |
| S. aureus | Staphylococcus aureus | |
| S. epidermis | Staphylococcus epidermis | |
| S. faecalis | Streptococcus faecalis | |
| S. pneumoniae | Streptococcus pneumoniae | |
| S. pyogenes | Streptococcus pyogenes | |
| S. viridans | Streptococcus viridans | |
| Gram-negative bacteria | A. aceti | Acetobacter aceti |
| A. baumannii | Acinetobacter baumannii | |
| A. hydrophila | Aeromonas hydrophila | |
| A. tumefaciens | Agrobacterium tumefaciens | |
| C. jejuni | Campylobacter jejuni | |
| C. israelensis | Chromohalobacter israelensis | |
| C. salexigens | Chromohalobacter salexigens | |
| E. aerogenes | Enterobacter aerogenes | |
| E. cloacae | Enterobacter cloacae | |
| E. caratovora | Erwinia caratovora | |
| E. coli | Escherichia coli | |
| H. halophila | Halomonas halophila | |
| H.s salina | Halomonas salina | |
| K. pneumoniae | Klebsiella pneumoniae | |
| N. gonorrhoeae | Neisseria gonorrhoeae | |
| P. mirabalis | Proteus mirabalis | |
| P. vulgaris | Proteus vulgaris | |
| P. aeruginosa | Pseudomonas aeruginosa | |
| P. fluorescens | Pseudomonas fluorescens | |
| P. phaseolicola | Pseudomonas phaseolicola | |
| P. putida | Pseudomonas putida | |
| R. solanacearum | Ralstonia solanacearum | |
| S. abony | Salmonella abony | |
| S. paratyphi | Salmonella paratyphi | |
| S. typhimurium | Salmonella typhimurium | |
| S. marcescens | Serratia marcescens | |
| S. dysenteriae | Shigella dysenteriae | |
| S. sonnei | Shigella sonnei | |
| X. vesicatoria | Xanthomonas vesicatoria | |
| Fungi | A. alternata | Alternaria alternata |
| A. solani | Alternaria solani | |
| A. clavatus | Aspergillus clavatus | |
| A. flavus | Aspergillus flavus | |
| A. fumigatus | Aspergillus fumigatus | |
| A. niger | Aspergillus niger | |
| B. cinerea | Botrytis cinerea | |
| C. albicans | Candida albicans | |
| C. dubliniensis | Candida dubliniensis | |
| C. glaberata | Candida glaberata | |
| C. krusei | Candida krusei | |
| C. lusitaniae | Candida lusitaniae | |
| C. parapsilosis | Candida parapsilosis | |
| C. tropicalis | Candida tropicalis | |
| C. utilis | Candida utilis | |
| C. lagenarium | Colletotrichum lagenarium | |
| Cryptococcus | Cryptococcus | |
| D. hansenii | Debaryomyces hansenii | |
| F. moniliforme | Fusarium moniliforme | |
| F. oxysporum | Fusarium oxysporum | |
| F. solani | Fusarium solani | |
| H. guilliermondii | Hanseniaspora guilliermondii | |
| H. oryzae | Heterodera oryzae | |
| K. fragilis | Kluyveromyces fragilis | |
| M. phaseolin | Macrophomina phaseolin | |
| M. phaseolina | Macrophomina phaseolina | |
| M. canis | Microsporum canis | |
| M. mucedo | Mucor mucedo | |
| P. chrysogenum | Penicilium chrysogenum | |
| P. expansum | Penicillium expansum | |
| P. funiculosum | Penicillium funiculosum | |
| P. lanosum | Penicillium lanosum | |
| P. notatum | Penicillium notatum | |
| P. oxalicum | Penicillium oxalicum | |
| R. bataticola | Rhizoctonia bataticola | |
| R. stolonifer | Rhizopus stolonifer | |
| R. stolonifera | Rhizopus stolonifera | |
| R. rubra | Rhodotorula rubra | |
| S. pulverlentum | Sporotrichum pulverlentum | |
| T. harzianum | Trichoderma harzianum | |
| T. polysporum | Trichoderma polysporum | |
| T. viride | Trichoderma viride | |
| T. longifolius | Trichophyton longifolius | |
| T. rubrum | Trichophyton rubrum | |
| Parasite | P. falciparum | Plasmodium falciparum |
| L. major | Leishmania major | |
| T. cruzi | Trypanosoma cruzi |
References
- Lüllmann, H.; Mohr, K.; Hein, L. Farmacología: Texto y Atlas, 6th ed.; Médica Panamericana S.A., Ed.; Elsevier: Barcelona, Spain, 2010; ISBN 978-2-257-00069-9. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, T.M. Bioquímica: Libro de Texto con Aplicaciones Clínicas, 4th ed.; Editorial Reverté, S.A.: Barcelona, Spain, 2004; ISBN 978-8-429-17208-9. [Google Scholar]
- Reygaert, W.C. An overview of the antimicrobial resistance mechanisms of bacteria. AIMS Microbiol. 2018, 4, 482–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mjos, K.D.; Orvig, C. Metallodrugs in Medicinal Inorganic Chemistry. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 4540–4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garner, J.P.; Heppell, P.S.J. The use of Flammacerium in British Burns Units. Burns 2005, 31, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrades, S. Uso y abuso de los antibióticos. Offarm 2001, 20, 82–93. [Google Scholar]
- Fong, K.Y.; Wright, D.W. Hemozoin and antimalarial drug discovery. Future Med. Chem. 2013, 5, 1437–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieites, M.; Otero, L.; Santos, D.; Olea-Azar, C.; Norambuena, E.; Aguirre, G.; Cerecetto, H.; González, M.; Kemmerling, U.; Morello, A.; et al. Platinum-based complexes of bioactive 3-(5-nitrofuryl)acroleine thiosemicarbazones showing anti-Trypanosoma cruzi activity. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2009, 103, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engels, D.; Savioli, L. Reconsidering the underestimated burden caused by neglected tropical diseases. Trends Parasitol. 2006, 22, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desjeux, P. The increase in risk factors for leishmaniasis worldwide. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2001, 95, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imberti, C.; Zhang, P.; Huang, H.; Sadler, P.J. New Designs for Phototherapeutic Transition Metal Complexes. Angew. Chem. 2020, 132, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronconi, L.; Sadler, P.J. Using coordination chemistry to design new medicines. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2007, 251, 1633–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, R.; Hazra, D.K.; Koner, S.; Helliwell, M.; Mukherjee, M.; Bhattacharjee, A. Hydrothermal synthesis of dimeric lanthanide compounds: X-ray structure, magnetic study and heterogeneous catalytic epoxidation of olefins. Polyhedron 2010, 29, 3183–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohshima, T.; Nemoto, T.; Tosaki, S.; Kakei, H.; Gnanadesikan, V.; Shibasaki, M. Catalytic asymmetric epoxidation of α, β-unsaturated carboxylic acid imidazolides and amides by lanthanide–BINOL complexes. Tetrahedron 2003, 59, 10485–10497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostova, I.; Momekov, G. Synthesis, characterization and cytotoxicity evaluation of new cerium(III), lanthanum(III) and neodymium(III) complexes. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2007, 21, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szpunar, J. Advances in analytical methodology for bioinorganic speciation analysis: Metallomics, metalloproteomics and heteroatom-tagged proteomics and metabolomics. Analyst 2005, 130, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, K.; Hashmi, W.; Ismail, H.; Mirza, B.; Twamley, B.; Akhter, Z.; Rozas, I.; Baker, R.J. Synthesis, DNA binding and antibacterial activity of metal(II) complexes of a benzimidazole Schiff base. Polyhedron 2019, 157, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervaiz, M.; Riaz, A.; Munir, A.; Saeed, Z.; Hussain, S.; Rashid, A.; Younas, U.; Adnan, A. Synthesis and characterization of sulfonamide metal complexes as antimicrobial agents. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1202, 127284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uivarosi, V. Metal Complexes of Quinolone Antibiotics and Their Applications: An Update. Molecules 2013, 18, 11153–11197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Rave, S.; Ramírez-Apan, M.T.; Tlahuext, H.; Morales-Morales, D.; Toscano, R.A.; Grévy, J.-M. Non-symmetric CNS-Pt(II) pincer complexes including thioether functionalized iminophosphoranes. Evaluation of their in vitro anticancer activity. J. Organomet. Chem. 2016, 814, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillena, G.; Rodríguez, G.; van Koten, G. Palladium(II) pincer complexes of α-amino acids: Towards the synthesis of catalytically active artificial peptides. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 3895–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, S.M.; Almarhoon, Z.; Sholkamy, E.N.; El-Faham, A. Bis-pyrazolyl-s-triazine Ni(II) pincer complexes as selective gram positive antibacterial agents; synthesis, structural and antimicrobial studies. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1195, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polo-Cerón, D. Cu(II) and Ni(II) Complexes with New Tridentate NNS Thiosemicarbazones: Synthesis, Characterisation, DNA Interaction, and Antibacterial Activity. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2019, 2019, 3520837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabrizi, L.; Chiniforoshan, H. The cytotoxicity and mechanism of action of new multinuclear Scaffold Au III, Pd II pincer complexes containing a bis(diphenylphosphino) ferrocene/non-ferrocene ligand. Dalt. Trans. 2017, 46, 14164–14173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobinikhaledi, A.; Jabbarpour, M.; Hamta, A. Synthesis of some novel and biologically active schiff bases bearing a 1,3,4-thiadiazole moiety under acidic and ptc conditions. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2011, 56, 812–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Gul, S.; Ali Khan, M. Schiff Bases and Their Metallic Derivatives: Highly Versatile Molecules with Biological and Abiological Perspective. In Stability and Applications of Coordination Compounds; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, N.; Kumar, R.; Dureja, P.; Rawat, D.S. Schiff Bases as Potential Fungicides and Nitrification Inhibitors. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 8520–8525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuamer, K.M.; Maihub, A.A.; El-Ajaily, M.M.; Etorki, A.M.; Abou-Krisha, M.M.; Almagani, M.A. The Role of Aromatic Schiff Bases in the Dyes Techniques. Int. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 04, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.C.; Sutar, A.K. Catalytic activities of Schiff base transition metal complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2008, 252, 1420–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raczuk, E.; Dmochowska, B.; Samaszko-Fiertek, J.; Madaj, J. Different Schiff Bases—Structure, Importance and Classification. Molecules 2022, 27, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Li, J. Molecular Assembly of Schiff Base Interactions: Construction and Application. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 1597–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, E.; Przybylski, P.; Brzezinski, B.; Bartl, F. Schiff Bases in Biological Systems. Curr. Org. Chem. 2009, 13, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.N.; Ahmed, S.S.; Alam, S.M.R. REVIEW: Biomedical applications of Schiff base metal complexes. J. Coord. Chem. 2020, 73, 3109–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altamimi, M.A.; Hussain, A.; Alshehri, S.; Imam, S.S.; Alnami, A.; Bari, A. Novel Hemocompatible Imine Compounds as Alternatives for Antimicrobial Therapy in Pharmaceutical Application. Processes 2020, 8, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, C.M.; da Silva, D.L.; Modolo, L.V.; Alves, R.B.; de Resende, M.A.; Martins, C.V.B.; de Fátima, Â. Schiff bases: A short review of their antimicrobial activities. J. Adv. Res. 2011, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bringmann, G.; Dreyer, M.; Faber, J.H.; Dalsgaard, P.W.; Stærk, D.; Jaroszewski, J.W.; Ndangalasi, H.; Mbago, F.; Brun, R.; Christensen, S.B. Ancistrotanzanine C and Related 5,1′- and 7,3′-Coupled Naphthylisoquinoline Alkaloids from Ancistrocladus t anzaniensis. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza, A.O.; Galetti, F.C.S.; Silva, C.L.; Bicalho, B.; Parma, M.M.; Fonseca, S.F.; Marsaioli, A.J.; Trindade, A.C.L.B.; Gil, R.P.F.; Bezerra, F.S.; et al. Antimycobacterial and cytotoxicity activity of synthetic and natural compounds. Quim. Nova 2007, 30, 1563–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andiappan, K.; Sanmugam, A.; Deivanayagam, E.; Karuppasamy, K.; Kim, H.-S.; Vikraman, D. In vitro cytotoxicity activity of novel Schiff base ligand–lanthanide complexes. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, A.; Chattopadhyay, S. Synthesis and characterization of mixed valence cobalt(III)/cobalt(II) complexes with N,O-donor Schiff base ligands. Polyhedron 2019, 159, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alterhoni, E.; Tavman, A.; Hacioglu, M.; Şahin, O.; Seher Birteksöz Tan, A. Synthesis, structural characterization and antimicrobial activity of Schiff bases and benzimidazole derivatives and their complexes with CoCl2, PdCl2, CuCl2 and ZnCl2. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1229, 129498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.A.; Dar, O.A.; Gull, P.; Wani, M.Y.; Hashmi, A.A. Heterocyclic Schiff base transition metal complexes in antimicrobial and anticancer chemotherapy. Medchemcomm 2018, 9, 409–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Barman, P. Recent Advances in Schiff Base Ruthenium Metal Complexes: Synthesis and Applications; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; Volume 379, ISBN 0123456789. [Google Scholar]
- Arunadevi, A.; Raman, N. Biological response of Schiff base metal complexes incorporating amino acids–a short review. J. Coord. Chem. 2020, 73, 2095–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Aziz, A.A.; El-Sayed, I.S.A.; Khalil, M.M.H. Some divalent metal(II) complexes of novel potentially tetradentate Schiff base N,N′-bis(2-carboxyphenylimine)-2,5-thiophenedicarboxaldhyde: Synthesis, spectroscopic characterization and bioactivities. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2017, 31, e3730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santha Lakshmi, S.; Geetha, K.; Mahadevi, P. Tridentate Schiff base (ONO) transition metal complexes: Synthesis, crystal structure, spectroscopic and larvicidal studies. J. Chem. Sci. 2016, 128, 1113–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Halim, H.F.; Omar, M.M.; Mohamed, G.G. Synthesis, structural, thermal studies and biological activity of a tridentate Schiff base ligand and their transition metal complexes. Spectrochim. Acta-Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2011, 78, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anacona, J.R.; Noriega, N.; Camus, J. Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of a tridentate Schiff base derived from cephalothin and sulfadiazine, and its transition metal complexes. Spectrochim. Acta-Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2015, 137, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munde, A.S.; Jagdale, A.N.; Jadhav, S.M.; Chondhekar, T.K. Synthesis, characterization and thermal study of some transition metal complexes of an asymmetrical tetradentate Schiff base ligand. J. Serbian Chem. Soc. 2010, 75, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galini, M.; Salehi, M.; Kubicki, M.; Amiri, A.; Khaleghian, A. Structural characterization and electrochemical studies of Co(II), Zn(II), Ni(II) and Cu(II) Schiff base complexes derived from 2-((E)-(2-methoxyphenylimino)methyl)-4-bromophenol; Evaluation of antioxidant and antibacterial properties. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2017, 461, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.T.; Pham Thi, P.N.; Nguyen, V.T. Synthesis, Characterization, and in Vitro Cytotoxicity of Unsymmetrical Tetradentate Schiff Base Cu(II) and Fe(III) Complexes. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2021, 2021, 6696344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiadis, N.C.; Granadeiro, C.M.; Mayans, J.; Raptopoulou, C.P.; Bekiari, V.; Cunha-Silva, L.; Psycharis, V.; Escuer, A.; Balula, S.S.; Konidaris, K.F.; et al. Multifunctionality in two families of dinuclear lanthanide(III) complexes with a tridentate schiff-base ligand. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 9581–9585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, W.C.; Lin, C.C. Preparation, characterization, and catalytic studies of magnesium complexes supported by NNO-tridentate schiff-base ligands. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 48, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, R.A.; Alaghaz, A.N.M.A.; Alturiqi, A.S. New dimeric Schiff base quinoline complexes: Synthesis, spectral characterization, electrochemistry and cytotoxicity. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 32, e4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Jamwal, D.; Rana, D.; Katoch, A. Microwave Synthesized Nanocomposites for Enhancing Oral Bioavailability of Drugs; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; ISBN 9780128137581. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, A.P.; Jain, R.K. Conventional and microwave synthesis, spectral, thermal and antimicrobial studies of some transition metal complexes containing 2-amino-5-methylthiazole moiety. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2014, 18, 814–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmi, N.; Shrivastava, S.; Meena, R.; Joshi, S.C.; Singh, R.V. Microwave assisted synthesis, spectroscopic characterization and biological aspects of some new chromium(iii) complexes derived from N⁁O donor Schiff bases. New J. Chem. 2013, 37, 1445–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, R.B.; Mahale, R.G.; Patil, S.R. Ultrasound assisted Schiff base metal complexes, organic reactions and nano-particles synthesis study—A Review. J. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 6, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Merzougui, M.; Ouari, K.; Weiss, J. Ultrasound assisted synthesis, characterization and electrochemical study of a tetradentate oxovanadium diazomethine complex. J. Mol. Struct. 2016, 1120, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rahman, L.H.; Abu-Dief, A.M.; El-Khatib, R.M.; Abdel-Fatah, S.M. Some new nano-sized Fe(II), Cd(II) and Zn(II) Schiff base complexes as precursor for metal oxides: Sonochemical synthesis, characterization, DNA interaction, in vitro antimicrobial and anticancer activities. Bioorg. Chem. 2016, 69, 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapila, A.; Kaur, M.; Kaur, H. Organotin(IV) complexes of tridentate (O,N,O) Schiff base ligand: Computational, spectroscopic and biological studies. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 40, S102–S106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, B.K.; Viciano, M.; Godard, C.; Castillón, S.; García-Ruiz, M.; Blanco González, M.D.; Claver, C. Metal complexes bearing ONO ligands as highly active catalysts in carbon dioxide and epoxide coupling reactions. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2021, 517, 120194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, H.; Bera, R.; Rizzoli, C.; Bieńko, D.; Adhikary, C. Double end-on azido derivative of a tridentate (NNO) Schiff base dimeric copper(II) complex: Synthesis, X-ray structure, magnetic property and catalytic effectiveness. J. Coord. Chem. 2020, 73, 3062–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messai, A.; Bilge, D.; Bilge, M.; Parlak, C. New Cu(II) coordination polymer by chiral tridentate Schiff base ligand. J. Mol. Struct. 2017, 1137, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongsuwan, S.; Chatwichien, J.; Pinchaipat, B.; Kumphune, S.; Harding, D.J.; Harding, P.; Boonmak, J.; Youngme, S.; Chotima, R. Synthesis, characterization and anticancer activity of Fe(II) and Fe(III) complexes containing N-(8-quinolyl)salicylaldimine Schiff base ligands. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 26, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarzewicz, J.; Jurowska, A.; Hodorowicz, M.; Kazek, G.; Głuch-Lutwin, M.; Sapa, J.; Papież, M. Tridentate ONO ligands in vanadium(III-V) complexes—Synthesis, characterization and biological activity. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1224, 129205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Performance Standars for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 31st ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Malvern, PA, USA, 2021; ISBN 978-1-68440-105-5. [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd, N.C.; Morgan, H.W.; Nicholson, B.K.; Ronimus, R.S. The composition of Ehrlich’s Salvarsan: Resolution of a century-old debate. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 941–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolliffe, D.M. A history of the use of arsenicals in man. J. R. Soc. Med. 1993, 86, 287–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wéry, M. Drug used in the treatment of sleeping sickness (human African trypanosomiasis: HAT). Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 1994, 4, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breinl, A.; Todd, J.L. Atoxyl in the treatment of trypanosomiasis. BMJ 1907, 1, 132–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Davies-Bolorunduro, O.F.; Osuolale, O.; Saibu, S.; Adeleye, I.A.; Aminah, N.S. Bioprospecting marine actinomycetes for antileishmanial drugs: Current perspectives and future prospects. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Zaki, L.; Saryazdi, A.K.P.; Tavakoli, P.; Tavajjohi, A.; Poursalehi, R.; Delavari, H.; Ghaffarifar, F. Efficacy of green synthesized silver nanoparticles via ginger rhizome extract against Leishmania major in vitro. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0255571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Yan, H.; Chang, G.; Li, Z.; Niu, M.; Hong, M. Organotin(IV) complexes derived from hydrazone Schiff base: Synthesis, crystal structure, in vitro cytotoxicity and DNA/BSA interactions. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2017, 464, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusof, E.N.M.; Page, A.J.; Sakoff, J.A.; Simone, M.I.; Veerakumarasivam, A.; Tiekink, E.R.T.; Ravoof, T.B.S.A. Tin(IV) compounds of tridentate thiosemicarbazone Schiff bases: Synthesis, characterization, in-silico analysis and in vitro cytotoxicity. Polyhedron 2020, 189, 114729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhanuka, S.; Khaturia, S.; Chahar, M.; Singh, H.L. Design, Spectroscopic Characterization and Theoretical Studies of Organotin(IV) and Organosilicon(IV) Complexes with Schiff Base Ligands Derived from Amino Acids. Asian J. Chem. 2020, 32, 2821–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatra, P.; Sharma, J.; Sharma, R.A.; Singh, Y. Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial activity of diorganotin(IV) derivatives of some bioactive bifunctional tridentate Schiff base ligands. Main Gr. Met. Chem. 2016, 39, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baul, T.S.B. Antimicrobial activity of organotin(IV) compounds: A review. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2008, 22, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manju; Mishra, N.; Kumar, D. Coordination chemistry of Schiff base tin complexes. Russ. J. Coord. Chem. Khimiya 2014, 40, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, J.; Yadav, J.; Singh, N. Synthesis, characterisation, in vitro antimicrobial, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of diorganotin(IV) complexes derived from salicylaldehyde Schiff bases. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2019, 45, 3943–3968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, K.S.; Kumar, L.S.; Chandan, S.; Jayalakshmi, B.; Revanasiddappa, H.D. Diorganotin(IV) complexes of biologically potent 4(3H)-quinazolinone derived Schiff bases: Synthesis, spectroscopic characterization, DNA interaction studies and antimicrobial activity. Spectrochim. Acta-Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2011, 81, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedaghat, T.; Aminian, M.; Bruno, G.; Amiri Rudbari, H. Binuclear organotin(IV) complexes with adipic dihydrazones: Synthesis, spectral characterization, crystal structures and antibacterial activity. J. Organomet. Chem. 2013, 737, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonika; Nidhi; Malhotra, R. Synthesis and structural studies on penta and hexa coordinated organotin (IV) complexes of alkyl pyruvate aroyl hydrazones. Pharma Chem. 2011, 3, 305–313. [Google Scholar]
- Khatkar, P.; Asija, S. New diorganotin(IV) complexes of tridentate Schiff bases derived from 1,3-indanedione derivative: Synthesis, spectral studies and in vitro antimicrobial activities. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2017, 192, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatkar, P.; Ahlawat, A.; Asija, S.; Singh, V. Synthesis, characterization, in vitro antimicrobial, DNA binding activity and QSAR studies of diorganotin(IV) complexes of Schiff bases derived from 2-benzoyl-1H-indene-1,3(2H)-dione and 4-substituted benzoic acid hydrazides. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2020, 196, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shujha, S.; Shah, A.; Zia-Ur-Rehman; Muhammad, N.; Ali, S.; Qureshi, R.; Khalid, N.; Meetsma, A. Diorganotin(IV) derivatives of ONO tridentate Schiff base: Synthesis, crystal structure, in vitro antimicrobial, anti-leishmanial and DNA binding studies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 2902–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shujah, S.; Zia-Ur-Rehman; Muhammad, N.; Ali, S.; Khalid, N.; Tahir, M.N. New dimeric and supramolecular organotin(IV) complexes with a tridentate schiff base as potential biocidal agents. J. Organomet. Chem. 2011, 696, 2772–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shujah, S.; Zia-ur-Rehman; Muhammad, N.; Shah, A.; Ali, S.; Khalid, N.; Meetsma, A. Bioactive hepta- and penta-coordinated supramolecular diorganotin(IV) Schiff bases. J. Organomet. Chem. 2013, 741–742, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Puri, P.; Kumar, Y.; Sharma, C. Hypercoordinated Organosilicon(IV) and Organotin(IV) Complexes: Syntheses, Spectral Studies, and Antimicrobial Activity In Vitro. ISRN Inorg. Chem. 2013, 2013, 356802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, J.K.; Singh, R.; Chahal, V.K.; Sharma, R.P. Novel hexacoordinate organosilicon(IV) complexes of diethylenetriamine schiff base with SiO2N3 skeleton. Arkivoc 2009, 2009, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, J.; Kumari, S.; Asijaa, S.; Malhotra, R. Synthetic, spectroscopic, and biological aspects of triorganosilicon(IV) complexes of tridentate schiff bases. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2012, 187, 1409–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Farhan, B.S.; Basha, M.T.; Abdel Rahman, L.H.; El-Saghier, A.M.M.; El-Ezz, D.A.; Marzouk, A.A.; Shehata, M.R.; Abdalla, E.M. Synthesis, dft calculations, antiproliferative, bactericidal activity and molecular docking of novel mixed-ligand salen/8-hydroxyquinoline metal complexes. Molecules 2021, 26, 4725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baiocco, P.; Colotti, G.; Franceschini, S.; Ilari, A. Molecular basis of antimony treatment in Leishmaniasis. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 2603–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessa, J.A.; Reis, D.C.; Mendes, I.C.; Speziali, N.L.; Rocha, L.F.; Pereira, V.R.A.; Melo, C.M.L.; Beraldo, H. Antimony(III) complexes with pyridine-derived thiosemicarbazones: Structural studies and investigation on the antitrypanosomal activity. Polyhedron 2011, 30, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrilha, G.L.; Dias, R.P.; Rocha, W.R.; Mendes, I.C.; Benítez, D.; Varela, J.; Cerecetto, H.; González, M.; Melo, C.M.L.; Neves, J.K.A.L.; et al. 2-Acetylpyridine- and 2-benzoylpyridine-derived thiosemicarbazones and their antimony(III) complexes exhibit high anti-trypanosomal activity. Polyhedron 2012, 31, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, K.S.O.; Silva, N.F.; Da Silva, J.G.; De Miranda, L.F.; Romeiro, C.F.D.; Souza-Fagundes, E.M.; Mendes, I.C.; Beraldo, H. Investigation on the pharmacological profile of 2,6-diacetylpyridine bis(benzoylhydrazone) derivatives and their antimony(III) and bismuth(III) complexes. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 53, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bastos, T.O.; Maria Soares, B.; Silva Cisalpino, P.; Castro Mendes, I.; dos Santos, R.G.; Beraldo, H. Coordination to gallium(III) strongly enhances the potency of 2-pyridineformamide thiosemicarbazones against Cryptococcus opportunistic fungi. Microbiol. Res. 2010, 165, 573–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, J.G.; Azzolini, L.S.; Wardell, S.M.S.V.; Wardell, J.L.; Beraldo, H. Increasing the antibacterial activity of gallium(III) against Pseudomonas aeruginosa upon coordination to pyridine-derived thiosemicarbazones. Polyhedron 2009, 28, 2301–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, I.C.; Costa, F.B.; de Lima, G.M.; Ardisson, J.D.; Garcia-Santos, I.; Castiñeiras, A.; Beraldo, H. Tin(IV) complexes with 2-pyridineformamide-derived thiosemicarbazones: Antimicrobial and potential antineoplasic activities. Polyhedron 2009, 28, 1179–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, I.C.; Moreira, J.P.; Ardisson, J.D.; dos Santos, R.G.; da Silva, P.R.O.; Garcia, I.; Castiñeiras, A.; Beraldo, H. Organotin(IV) complexes of 2-pyridineformamide-derived thiosemicarbazones: Antimicrobial and cytotoxic effects. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 43, 1454–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Rebolledo, A.; Piro, O.E.; Castellano, E.E.; Teixeira, L.R.; Batista, A.A.; Beraldo, H. Metal complexes of 2-benzoylpyridine semicarbazone: Spectral, electrochemical and structural studies. J. Mol. Struct. 2006, 794, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piló, E.D.L.; Recio-Despaigne, A.A.; Da Silva, J.G.; Ferreira, I.P.; Takahashi, J.A.; Beraldo, H. Effect of coordination to antimony(III) on the antifungal activity of 2-acetylpyridine- and 2-benzoylpyridine-derived hydrazones. Polyhedron 2015, 97, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seng, H.L.; Tiekink, E.R.T. Main-Group Medicinal Chemistry Including Li and Bi; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 3, ISBN 9780080965291. [Google Scholar]
- Nomiya, K.; Sekino, K.; Ishikawa, M.; Honda, A.; Yokoyama, M.; Kasuga, N.C.; Yokoyama, H.; Nakano, S.; Onodera, K. Syntheses, crystal structures and antimicrobial activities of monomeric 8-coordinate, and dimeric and monomeric 7-coordinate bismuth(III) complexes with tridentate and pentadentate thiosemicarbazones and pentadentate semicarbazone ligands. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2004, 98, 601–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.; Din, I.U.; Mehmood, M.; Rauf, M.K.; Azam, S.S.; Haq, I.-U.; Tahir, M.N.; Parvaiz, N. Synthesis, structural characterization, and molecular docking studies of bioactive bismuth(III) complexes with substituted hydrazones. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1230, 129870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.T.; Fang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Li, M.X.; Ji, Y.M.; Han, Q.X. Cu(II), Ga(III) and In(III) complexes of 2-acetylpyridine: N (4)-phenylthiosemicarbazone: Synthesis, spectral characterization and biological activities. Medchemcomm 2017, 8, 2125–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.A.; Perdigão, G.M.C.; Rodrigues, L.E.; Da Silva, J.G.; Souza-Fagundes, E.M.; Takahashi, J.A.; Rocha, W.R.; Beraldo, H. Cytotoxic and antimicrobial effects of indium(iii) complexes with 2-acetylpyridine-derived thiosemicarbazones. Dalt. Trans. 2017, 46, 918–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessa, J.A.; Soares, M.A.; Dos Santos, R.G.; Mendes, I.C.; Salum, L.B.; Daghestani, H.N.; Andricopulo, A.D.; Day, B.W.; Vogt, A.; Beraldo, H. Gallium(III) complexes with 2-acetylpyridine-derived thiosemicarbazones: Antimicrobial and cytotoxic effects and investigation on the interactions with tubulin. BioMetals 2013, 26, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damit, N.S.H.H.; Hamid, M.H.S.A.; Rahman, N.S.R.H.A.; Ilias, S.N.H.H.; Keasberry, N.A. Synthesis, structural characterisation and antibacterial activities of lead(II) and some transition metal complexes derived from quinoline-2-carboxaldehyde 4-methyl-3-thiosemicarbazone. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2021, 527, 120557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Saied, F.; Ayad, M.; Aly, S. Tin(IV), titanium(IV) and hafnium(IV) complexes of some aromatic Schiff bases derived from 4-aminoantipyrine. Transit. Met. Chem. 1993, 18, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hakimi, A.N.; Alminderej, F.; Aroua, L.; Alhag, S.K.; Alfaifi, M.Y.; Samir, O.M.; Mahyoub, J.A.; Elbehairi, S.E.I.; Alnafisah, A.S. Design, synthesis, characterization of zirconium (IV), cadmium (II) and iron (III) complexes derived from Schiff base 2-aminomethylbenzimidazole, 2-hydroxynaphtadehyde and evaluation of their biological activity. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 7378–7389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, A.; Ahmad, S.I.M. Physico-chemical and antimicrobial studies on Ni(II), Cu (II) and Ti(III) Schiff base complexes derived from 2- furfuraldehyde. Orient. J. Chem. 2009, 25, 391–395. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, A.K.; Pandey, O.P.; Sengupta, S.K. Synthesis, Spectral and Antimicrobial Studies of Bis(cyclopentadienyl)titanium(IV) Derivatives with Schiff Bases Derived from 2-Amino-5-phenyl-1,3,4-thiadiazole. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2005, 3, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaul, A.R.; Dhande, V.V.; Yaul, S.R.; Aswar, A.S. Transition metal complexes containing tridentate hydrazone Schiff bases: Synthesis, characterization and biological activity. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2011, 88, 775–780. [Google Scholar]
- Uddin, M.N.; Khandaker, S.; Moniruzzaman; Amin, M.S.; Shumi, W.; Rahman, M.A.; Rahman, S.M. Synthesis, characterization, molecular modeling, antioxidant and microbial properties of some Titanium(IV) complexes of schiff bases. J. Mol. Struct. 2018, 1166, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir Uddin, M.; Chowdhury, D.A.; Hossain, K. Titanium(IV) Complexes of Unsymmetrical Schiff Bases Derived from Ethylenediamine and o-Hydroxyaldehyde/Ketone and Their Anti-microbial Evaluation. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2012, 59, 1520–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shashidhara, G.M.; Goudar, T.R. Oxovanadium(IV) and Niobium(V) Complexes with Some New Schiff Bases. Synth. React. Inorg. Met. Chem. 2000, 30, 1581–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchal, P.K.; Parekh, H.M.; Pansuriya, P.B.; Patel, M.N. Bactericidal activity of different oxovanadium(IV) complexes with Schiff bases and application of chelation theory. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2006, 21, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebosie, N.P.; Ogwuegbu, M.O.C.; Onyedika, G.O.; Onwumere, F.C. Biological and analytical applications of Schiff base metal complexes derived from salicylidene-4-aminoantipyrine and its derivatives: A review. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2021, 18, 3145–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anupama, B.; Padmaja, M.; Kumari, C.G. Synthesis, Characterization, Biological Activity and DNA Binding Studies of Metal Complexes with 4-Aminoantipyrine Schiff Base Ligand. E-J. Chem. 2012, 9, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, C.R.; Goswami, P.; Sengupta, M. Synthesis, electrochemical and antimicrobial studies of mono and binuclear iron(III) and oxovanadium(IV) complexes of [ONO] donor tridentate Schiff-base ligands. J. Coord. Chem. 2010, 63, 3969–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.P.; Mishra, R.; Jain, R.; Gupta, S. Synthesis of New VO(II), Co(II), Ni(II) and Cu(II) Complexes with Isatin-3-Chloro-4-Floroaniline and 2-Pyridinecarboxylidene-4-Aminoantipyrine and their Antimicrobial Studies. Mycobiology 2012, 40, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khosravan, M.; Abdolahi, L.; Ebrahimipour, S.Y. A novel anionic di-oxido vanadium(V) Schiff base complex: Synthesis, spectral characterization, X ray crystal structure, catalytic activity for the preparation of tetrahydro-4H-chromene derivatives and antibacterial properties. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2021, 128, 108561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.-J.; Xue, L.-W.; Zhao, G.-Q. Synthesis, Structures, and Antimicrobial Activities of Dimeric Oxovanadium(V) Complexes With Tridentate Schiff Bases. Synth. React. Inorg. Met. Nano-Metal Chem. 2013, 43, 1344–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.-Q.; Liu, Q.-R.; Han, Y.-J.; Xue, L.-W. Vanadium complexes derived from fluoro-substituted Schiff bases: Synthesis, crystal structures, and antimicrobial activity. Inorg. Nano-Metal Chem. 2020, 50, 836–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-H.; Qiu, X.-Y.; Liu, S.-J. Synthesis, characterization and crystal structures of copper(II), zinc(II) and vanadium(V) complexes, derived from 3-methyl- N ′-(1-(pyridin-2-yl)ethylidene)benzohydrazide, with antibacterial activity. J. Coord. Chem. 2019, 72, 962–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Jiang, P.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, X. Molybdenum(VI) complex with a tridentate Schiff base ligand immobilized on SBA-15 as effective catalysts in epoxidation of alkenes. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2015, 206, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cindrić, M.; Strukan, N.; Vrdoljak, V.; Kajfež, T.; Kamenar, B. A Series of Molybdenum(VI) Complexes with Tridentate Schiff Base Ligands. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2002, 628, 2113–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAuliffe, C.A.; Sayle, B.J. Coordination chemistry of molybdenum and tungsten—VIII. Oxomolybdenum(V) complexes of 8-hydroxyquinoline and relevance of EPR spectra to binding sites in flavoenzymes. Bioinorg. Chem. 1978, 8, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, D.D.; Rastogi, R.; Gupta, V.K.; Singh, S. Olefin eooxidation catalyzed by dioxo- tungsten(VI) schiff base complexes 4. Indian J. Chem. 1999, 38, 369–372. [Google Scholar]
- Amini, M.; Bagherzadeh, M.; Eftekhari-Sis, B.; Ellern, A.; Keith Woo, L. Catalytic efficacy of an oxido-peroxido tungsten(VI) complex: Synthesis, X-ray structure and oxidation of sulfides and olefins. J. Coord. Chem. 2013, 66, 1897–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, M.S.; Prakash, V. Preparation and characterization of Cr(III), Mn(II), Co(III), Ni(II), Cu(II), Zn(II) and Cd(II) chelates of schiffs base derived from vanillin and 4-amino antipyrine. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 2010, 5, 2203–2211. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Dief, A.M.; El-khatib, R.M.; Aljohani, F.S.; Alzahrani, S.O.; Mahran, A.; Khalifa, M.E.; El-Metwaly, N.M. Synthesis and intensive characterization for novel Zn(II), Pd(II), Cr(III) and VO(II)-Schiff base complexes; DNA-interaction, DFT, drug-likeness and molecular docking studies. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1242, 130693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.Z.; Ding, T.; Chen, C.L.; Li, M.X.; Zhang, D.; Niu, J.Y. Biological activities of pyridine-2-carbaldehyde Schiff bases derived from S-methyl- and S-benzyldithiocarbazate and their zinc(II) and manganese(II) complexes. Crystal Structure of the Manganese(II) complex of pyridine-2-carbaldehyde S-benzyldithiocarbaz. Russ. J. Coord. Chem. 2011, 37, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refat, M.S.; El-Metwaly, N.M. Spectral, thermal and biological studies of Mn(II) and Cu(II) complexes with two thiosemicarbazide derivatives. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2012, 92, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Malik, S.; Singh, A. Spectral and biological behaviour of complexes some bivalent metals and Schiff base. Res. J. Chem. Environ. Sci. 2015, 3, 30–35. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.-L. Synthesis, crystal structures, and antibacterial activities of manganese(II) and copper(II) complexes derived from 2-bromo-4-chloro-6-[(2-hydroxyethylimino)methyl]phenol. Inorg. Nano-Metal Chem. 2017, 47, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; Kumar, D.; Chandra, S.; Misra, N. Experimental and theoretical studies of Mn(II) and Co(II) metal complexes of a tridentate Schiff’s base ligand and their biological activities. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 34, e5371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anacona, J.R.; Mago, K.; Camus, J. Antibacterial activity of transition metal complexes with a tridentate NNO amoxicillin derived Schiff base. Synthesis and characterization. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 32, e4374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, G.G.; Omar, M.M.; Ahmed, Y.M. Metal complexes of Tridentate Schiff base: Synthesis, Characterization, Biological Activity and Molecular Docking Studies with COVID-19 Protein Receptor. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2021, 647, 2201–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, K.M.; Patel, N.H.; Patel, K.N.; Patel, M.N. Synthesis, Structural Characterization and Biocidal Studies of Manganese(II), Iron(II), Cobalt(II), Nickel(II), Copper(II), Zinc(II) and Cadmium(II) Complexes with Tridentate Schiff Bases and 2,2′- Bipyridylamine. Synth. React. Inorg. Met. Chem. 2000, 30, 1953–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, G.G.; Omar, M.M.; Ibrahim, A.A. Biological activity studies on metal complexes of novel tridentate Schiff base ligand. Spectroscopic and thermal characterization. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 4801–4812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadhav, S.M.; Shelke, V.A.; Shankarwar, S.G.; Munde, A.S.; Chondhekar, T.K. Synthesis, spectral, thermal, potentiometric and antimicrobial studies of transition metal complexes of tridentate ligand. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2014, 18, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachare, A.-A.; Kumbalpuri, S.-A.; Shankarwar, S.-G.; Chondhekar, T.-K. Transition metal complexes of tridentate Schiff base ligand: Synthesis, spectral characterization and antimicrobial properties. ICAIJ 2016, 11, 010–018. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, S.; Islam, A.; Zakaria, C.-M.; Haque, M.-M.; Mannan, A.; Zahan, K.-E. Synthesis, Spectral and Thermal Characterization with Antimicrobial Studies on Mn(II), Fe(II), Co(II) and Sn(II) Complexes of Tridentate N,O Coordinating Novel Schiff Base Ligand. J. Chem. Biol. Phys. Sci. Sect. A 2017, 7, 041–052. [Google Scholar]
- Sumrra, S.H.; Suleman, A.; Chohan, Z.H.; Zafar, M.N.; Raza, M.A.; Iqbal, T. Triazole metal based complexes as antibacterial/antifungal agents. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2017, 87, 1281–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eugene-Osoikhia, T.T.; Akinpelu, I.O.; Odiaka, T.I. Synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial studies of transition metal complexes of Schiff base derived from salicylaldehyde and L-tyrosine amino acid. Niger. J. Chem. Res. 2019, 24, 46–56. [Google Scholar]
- Reshma, R.; Selwin Joseyphus, R.; Arish, D.; Reshmi Jaya, R.J.; Johnson, J. Tridentate imidazole-based Schiff base metal complexes: Molecular docking, structural and biological studies. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Y.M.; Mahmoud, W.H.; Omar, M.M.; Mohamed, G.G. Synthesis, Characterization and Biological Activity of Transition Metals Schiff Base Complexes Derived from 4,6-Diacetylresorcinol and 1,8-Naphthalenediamine. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2021, 31, 2339–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, J.D.; Sakthikumar, K. Synthesis of water soluble transition metal(II) complexes from morpholine condensed tridentate schiff base: Structural elucidation, antimicrobial, antioxidant and DNA interaction studies. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2015, 7, 23–34. [Google Scholar]
- Jamuna, K.; Naik, B.R.; Sreenu, B.; Seshaiah, K. Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity of Cu(II) and Fe(III) complexes of a new tridentate Schiff base ligand. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2012, 4, 4275–4282. [Google Scholar]
- Celen, S.; Gungor, E.; Kara, H.; Azaz, A.D. Synthesis, spectroscopic characterization, and antimicrobial activities of Ni(II) and Fe(II) complexes with N -(2-hydroxyethyl)-5-nitrosalicylaldimine. J. Coord. Chem. 2013, 66, 3170–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rahman, L.H.; Abu-Dief, A.M.; Newair, E.F.; Hamdan, S.K. Some new nano-sized Cr(III), Fe(II), Co(II), and Ni(II) complexes incorporating 2-((E)-(pyridine-2-ylimino)methyl)napthalen-1-ol ligand: Structural characterization, electrochemical, antioxidant, antimicrobial, antiviral assessment and DNA interaction. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2016, 160, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anacona, J.R.; Ruiz, K.; Loroño, M.; Celis, F. Antibacterial activity of transition metal complexes containing a tridentate NNO phenoxymethylpenicillin-based Schiff base. An anti-MRSA iron (II) complex. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2019, 33, e4744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alosaimi, A.M.; El Mannoubi, I.; Zabin, S.A. Synthesis, molluscicidaland, antimicrobial potentialities of iron triad mononuclear metal complexes incorporating tridentate asymmetrical Schiff base ligands containing soft sulfur coordinating atoms. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2020, 13, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Balasubramanian, K.P.; Karvembu, R.; Chinnusamy, V.; Natarajan, K. Synthesis, characterization, electrochemistry, catalytic and biological activities of ruthenium(III) complexes containing dibasic tridentate Schiff bases. Indian J. Chem.-Sect. A Inorg. Phys. Theor. Anal. Chem. 2005, 44, 2450–2454. [Google Scholar]
- Sathya, N.; Raja, G.; Padma Priya, N.; Jayabalakrishnan, C. Ruthenium(II) complexes incorporating tridentate Schiff base ligands: Synthesis, spectroscopic, redox, catalytic and biological properties. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2010, 24, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, V.V.; Balasubramanian, K.P.; Chinnusamy, V. Synthesis, characterization, electrochemistry, catalytic and biological activities of ruthenium(III) complexes with tridentate ONO Donar Schiff base ligands. Asian J. Chem. 2010, 22, 7318–7326. [Google Scholar]
- El-Sherif, A.A.; Shoukry, M.M.; Abd-Elgawad, M.M.A. Synthesis, characterization, biological activity and equilibrium studies of metal(II) ion complexes with tridentate hydrazone ligand derived from hydralazine. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2012, 98, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emam, S.M.; Abouel-Enein, S.A.; Abdel-Satar, E.M. Structural characterization, thermal investigation and biological activity of metal complexes containing Schiff Base ligand (Z)-3-(1-((4,6-dimethyl-1H-pyrazolo [3,4-b] pyridin-3-yl)imino)ethyl)-4-hydroxy-6-methyl-2H-pyran-2-one. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2019, 33, e4847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, M.; Dutkiewicz, G.; Rezaei, A.; Amoozadeh, A.; Rahmani, S.; Grivani, G.H.; Kubicki, M. Synthesis, Antibacterial Studies and Crystal Structures of Tridentate Schiff Base Ligand and It’s Cobalt(III) Complex. J. Chem. Crystallogr. 2012, 42, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanzadeh, M.; Salehi, M.; Kubicki, M.; Shahcheragh, S.M.; Dutkiewicz, G.; Pyziak, M.; Khaleghian, A. Synthesis, crystal structures, spectroscopic studies and antibacterial properties of a series of mononuclear cobalt(III) Schiff base complexes. Transit. Met. Chem. 2014, 39, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekri, R.; Salehi, M.; Asadi, A.; Kubicki, M. Spectroscopic studies, structural characterization and electrochemical studies of two cobalt (III) complexes with tridentate hydrazone Schiff base ligands: Evaluation of antibacterial activities, DNA-binding, BSA interaction and molecular docking. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 32, e4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J. Synthesis, Crystal Structures, and Antibacterial Activity of Cobalt and Copper Complexes With Tridentate Schiff Bases. Synth. React. Inorganic, Met. Nano-Metal Chem. 2012, 42, 1410–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaran, J.S.; Priya, S.; Jayachandramani, N.; Mahalakshmi, S. Synthesis, Spectroscopic Characterization and Biological Activities of Transition Metal Complexes Derived from a Tridentate Schiff Base. J. Chem. 2013, 2013, 260358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirubavathy, S.J.; Velmurugan, R.; Karvembu, R.; Bhuvanesh, N.S.P.; Parameswari, K.; Chitra, S. Synthesis, structure, and pharmacological evaluation of Co(III) complex containing tridentate Schiff base ligand. Russ. J. Coord. Chem. 2015, 41, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.M. Syntheses, Characterization, and Antibacterial Property of Polynuclear Cobalt(III) and Copper(II) Complexes Derived from Similar Tridentate Schiff Bases. Russ. J. Coord. Chem. 2018, 44, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munjal, M. Synthesis, characterization and Antifungal activity of transition metal (II) complexes of Schiff base derived from p-aminoacetanilide and salicylaldehyde. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2018, 7, 864–866. [Google Scholar]
- Prajapati, K.N.; Brahmbhatt, M.P.; Vora, J.J.; Prajapati, P.B. Synthesis, Catalysis And Biological Study of Transition Metal (II) Chelates With ONO-Tridentate Schiff Base Ligand. J. Pharm. Chem. Biol. Sci. 2019, 7, 110–124. [Google Scholar]
- Manimohan, M.; Pugalmani, S.; Sithique, M.A. Synthesis, Spectral Characterisation and Biological Activities of Novel Biomaterial/N, N, O Donor Tridentate Co (II), Ni (II) and Zn (II) Complexes of Hydrazide Based Biopolymer Schiff Base Ligand. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2020, 30, 4481–4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shebl, M.; Saif, M.; Nabeel, A.I.; Shokry, R. New non-toxic transition metal nanocomplexes and Zn complex-silica xerogel nanohybrid: Synthesis, spectral studies, antibacterial, and antitumor activities. J. Mol. Struct. 2016, 1118, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagesh, G.Y.; Mahadev, U.D.; Mruthyunjayaswamy, B.H.M. Mononuclear Metal (II) Schiff Base Complexes Derived from Thiazole and O-Vanillin Moieties: Synthesis, Characterization, Thermal Behaviour and Biological Evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2015, 31, 190–197. [Google Scholar]
- Chohan, Z.H.; Arif, M.; Akhtar, M.A.; Supuran, C.T. Metal-Based Antibacterial and Antifungal Agents: Synthesis, Characterization, and In Vitro Biological Evaluation of Co(II), Cu(II), Ni(II), and Zn(II) Complexes with Amino Acid-Derived Compounds. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2006, 2006, 83131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagesh, G.Y.; Mruthyunjayaswamy, B.H.M. Synthesis, characterization and biological relevance of some metal (II) complexes with oxygen, nitrogen and oxygen (ONO) donor Schiff base ligand derived from thiazole and 2-hydroxy-1-naphthaldehyde. J. Mol. Struct. 2015, 1085, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.N.; Gaur, P.; Raidas, M.L.; Chaurasia, B.; Bagri, S.S. Novel NNO pincer type Schiff base ligand and its complexes of Fe(IIl), Co(II) and Ni(II): Synthesis, spectroscopic characterization, DFT, antibacterial and anticorrosion study. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1240, 130582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, M.S.S.; Makhlouf, M.M.; Ullah, F.; El-Hady, O.M. Mononucleating nicotinohydazone complexes with VO2+, Cu2+, and Ni2+ ions. Characteristic, catalytic, and biological assessments. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 334, 116001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vančo, J.; Švajlenová, O.; Račanská, E.; Muselík, J.; Valentová, J. Antiradical activity of different copper(II) Schiff base complexes and their effect on alloxan-induced diabetes. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2004, 18, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, M.S.S.; Elsawy, H. Biological potential of oxo-vanadium salicylediene amino-acid complexes as cytotoxic, antimicrobial, antioxidant and DNA interaction. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2018, 184, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rahman, L.H.; Adam, M.S.S.; Abu-Dief, A.M.; Moustafa, H.; Basha, M.T.; Aboraia, A.S.; Al-Farhan, B.S.; Ahmed, H.E.-S. Synthesis, theoretical investigations, biocidal screening, DNA binding, in vitro cytotoxicity and molecular docking of novel Cu (II), Pd (II) and Ag (I) complexes of chlorobenzylidene Schiff base: Promising antibiotic and anticancer agents. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 32, e4527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shebl, M. Synthesis, spectral studies, and antimicrobial activity of binary and ternary Cu(II), Ni(II), and Fe(III) complexes of new hexadentate Schiff bases derived from 4,6-diacetylresorcinol and amino acids. J. Coord. Chem. 2009, 62, 3217–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shebl, M. Coordination behavior of new bis(tridentate ONO, ONS and ONN) donor hydrazones towards some transition metal ions: Synthesis, spectral, thermal, antimicrobial and antitumor studies. J. Mol. Struct. 2017, 1128, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samy, F.; Shebl, M. Synthesis, spectroscopic, biological, and theoretical studies of new complexes from (E)-3-(2-(5, 6-diphenyl-1,2,4-triazin-3-yl)hydrazono)butan-2-one oxime. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 34, e5502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftikhar, B.; Javed, K.; Khan, M.S.U.; Akhter, Z.; Mirza, B.; Mckee, V. Synthesis, characterization and biological assay of Salicylaldehyde Schiff base Cu(II) complexes and their precursors. J. Mol. Struct. 2018, 1155, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaiarasi, G.; Rex Jeya Rajkumar, S.; Dharani, S.; Rath, N.P.; Prabhakaran, R. New cationic and neutral copper(II) complexes containing 7-hydroxy-4-oxo-4[H]-chromene derived ONO pincer ligands: Synthesis, characterization and in vitro biological evaluations. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2018, 180, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahontu, E.M. Transition Metal Complexes with Antipyrine-Derived Schiff Bases: Synthesis and Antibacterial Activity. In Descriptive Inorganic Chemistry Researches of Metal Compounds; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Reiss, A.; Cioateră, N.; Dobrițescu, A.; Rotaru, M.; Carabet, A.C.; Parisi, F.; Gănescu, A.; Dăbuleanu, I.; Spînu, C.I.; Rotaru, P. Bioactive co(Ii), ni(ii), and cu(ii) complexes containing a tridentate sulfathiazole-based (onn) schiff base. Molecules 2021, 26, 3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


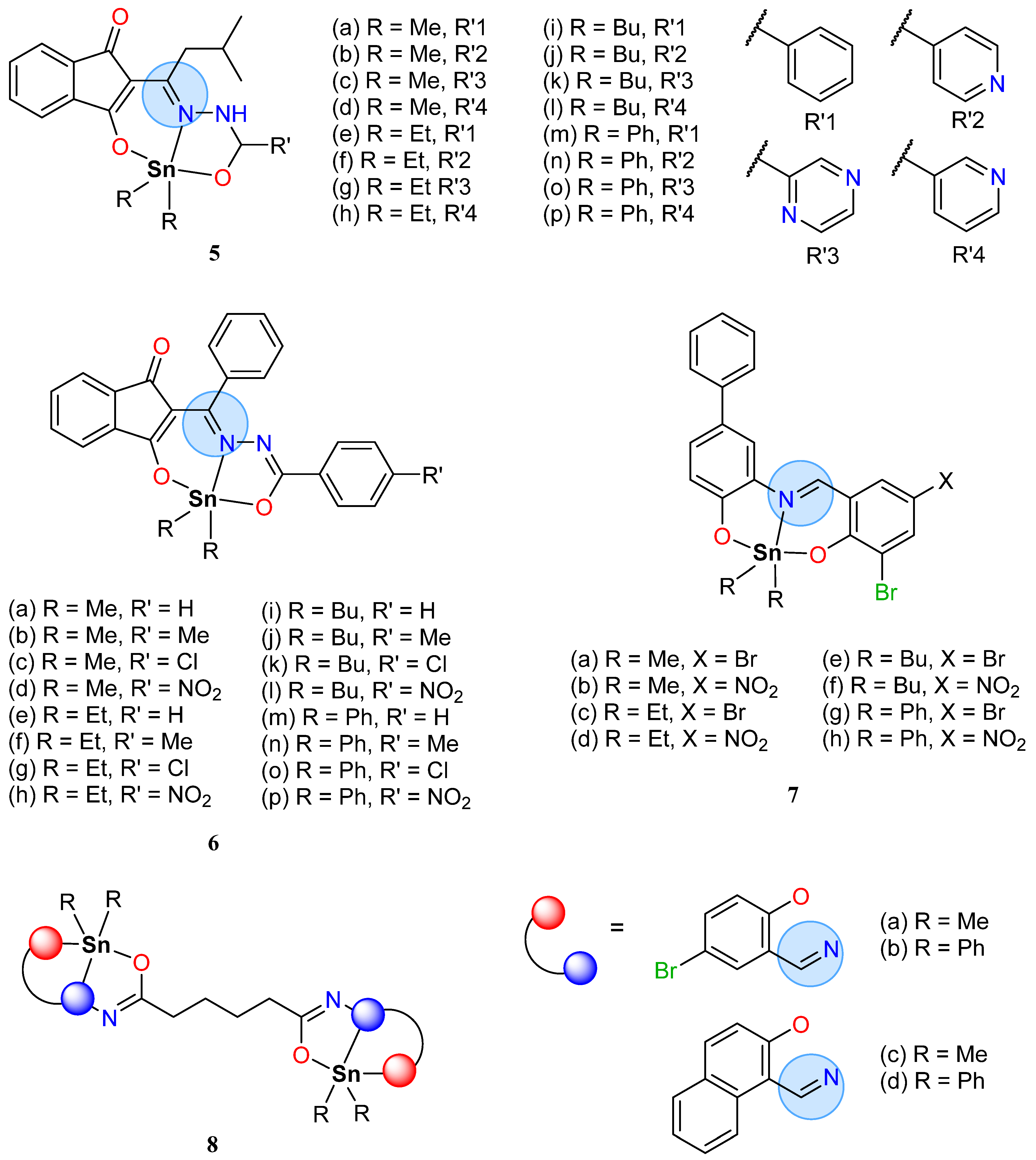
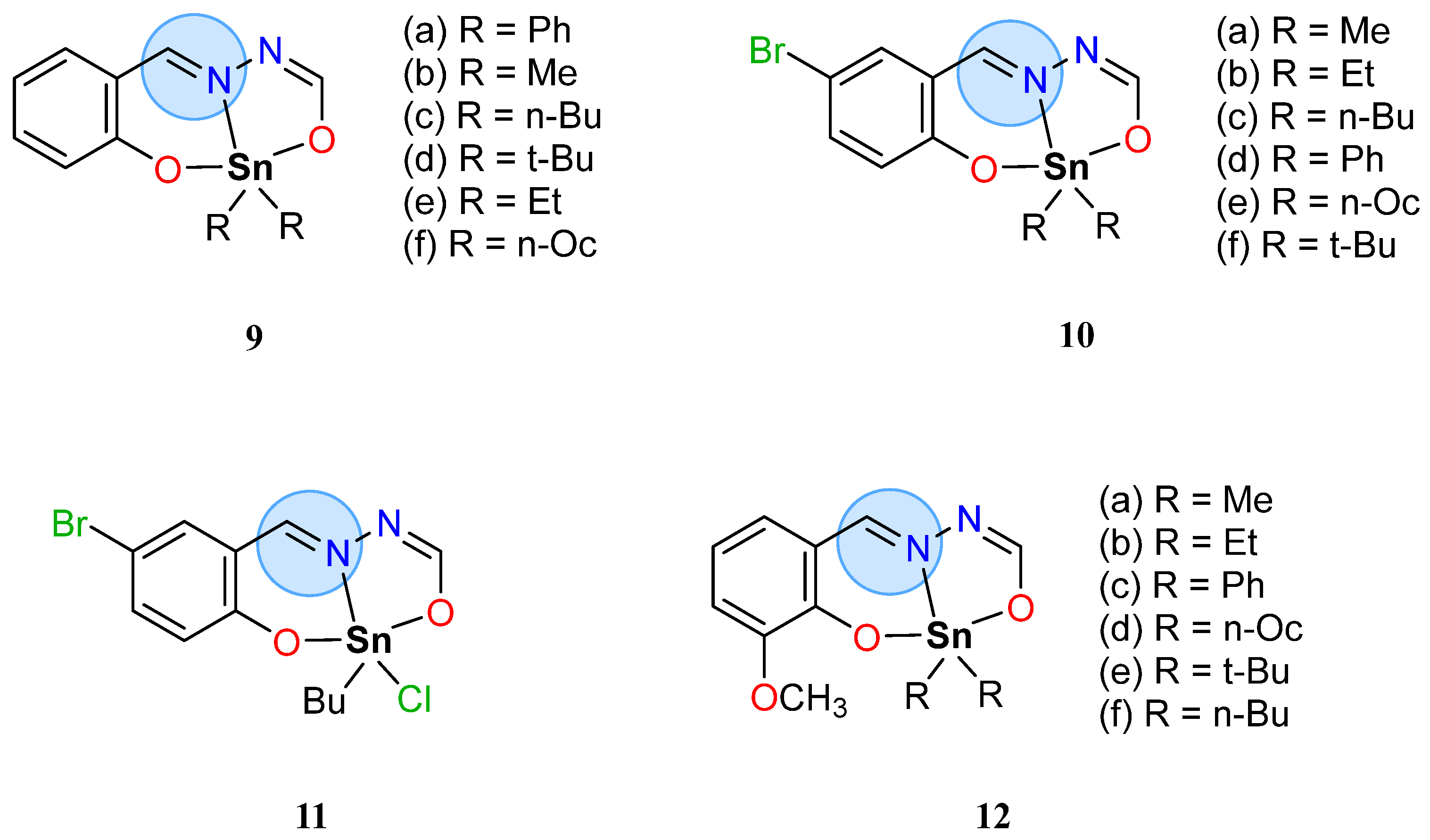
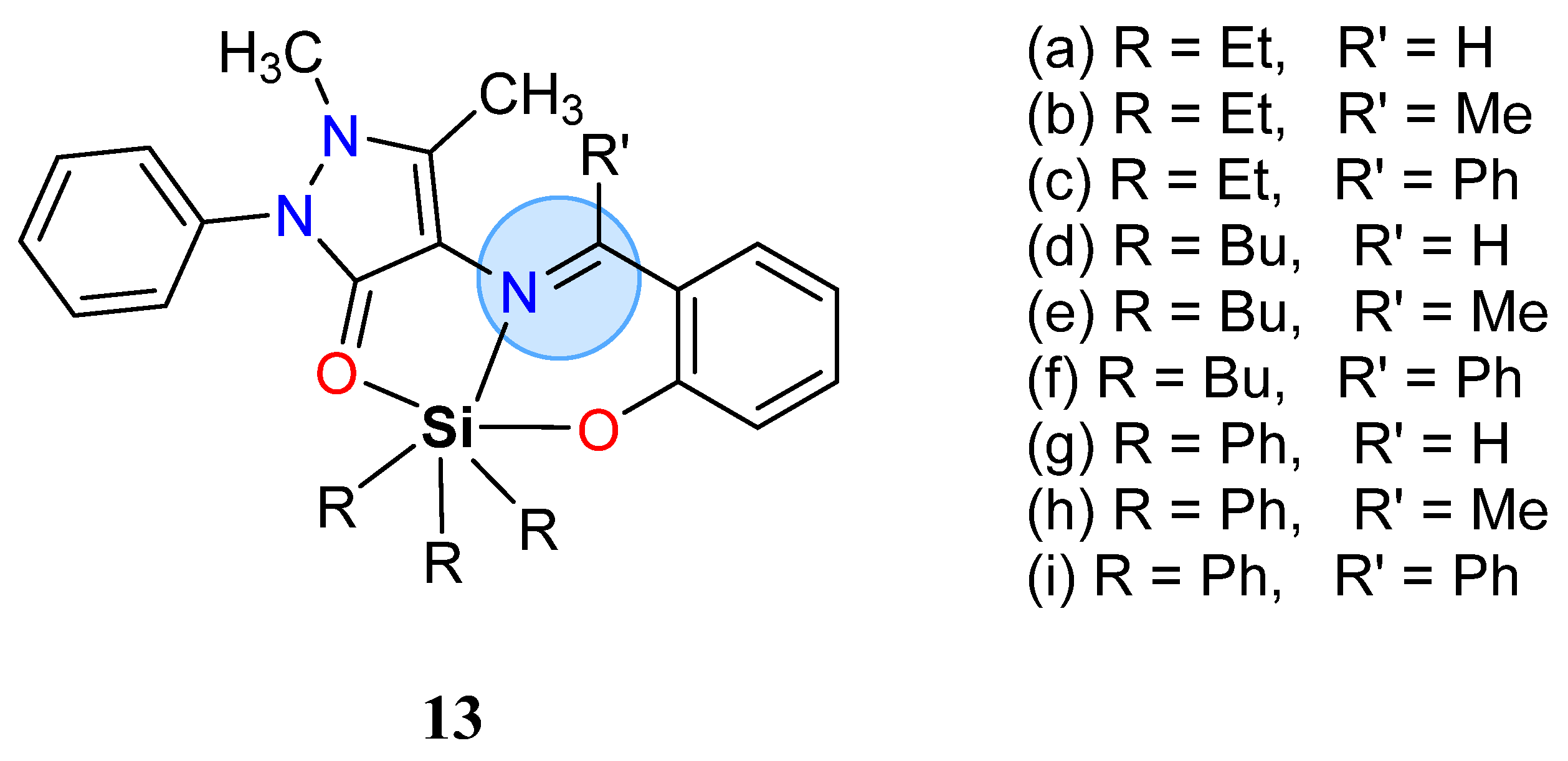
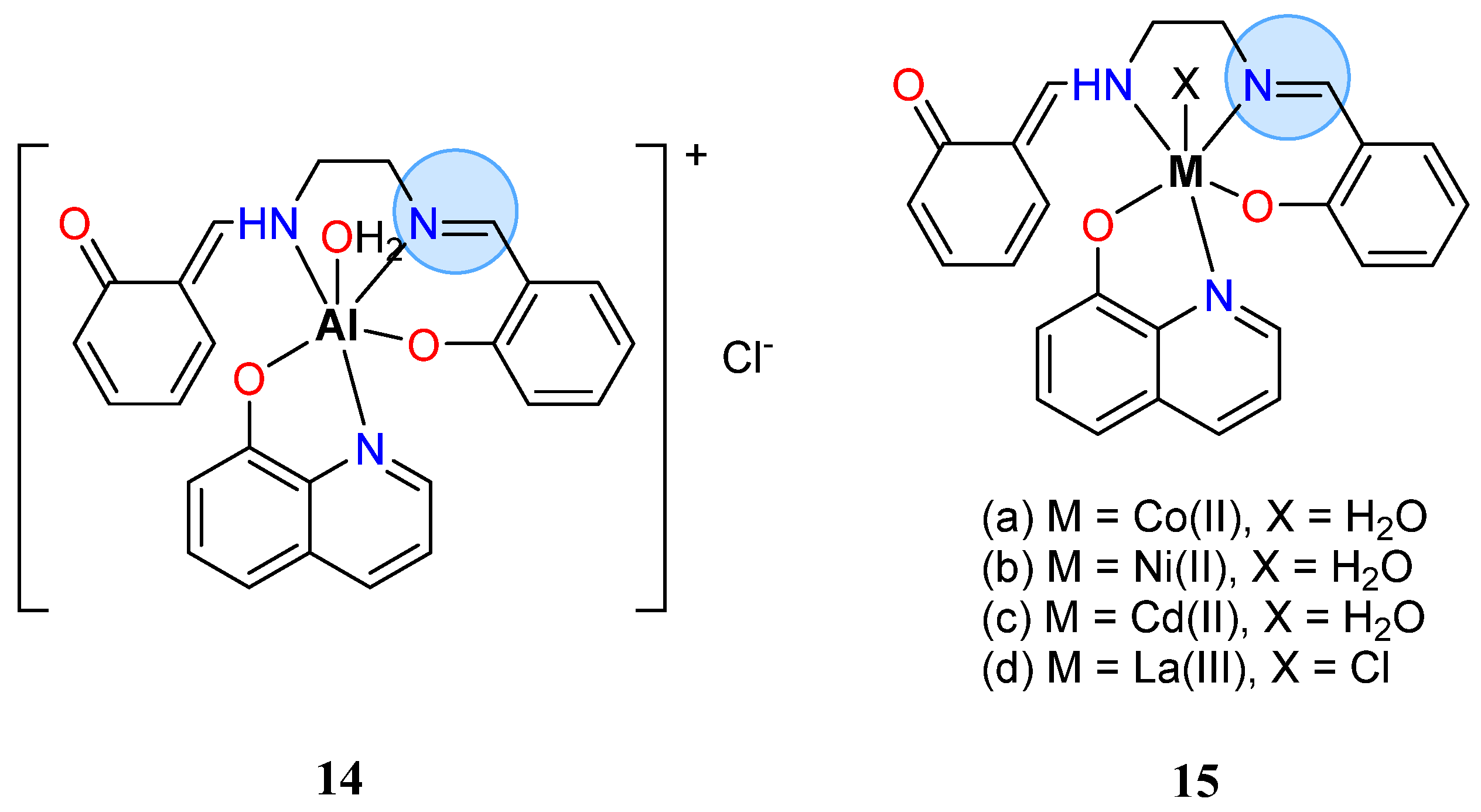






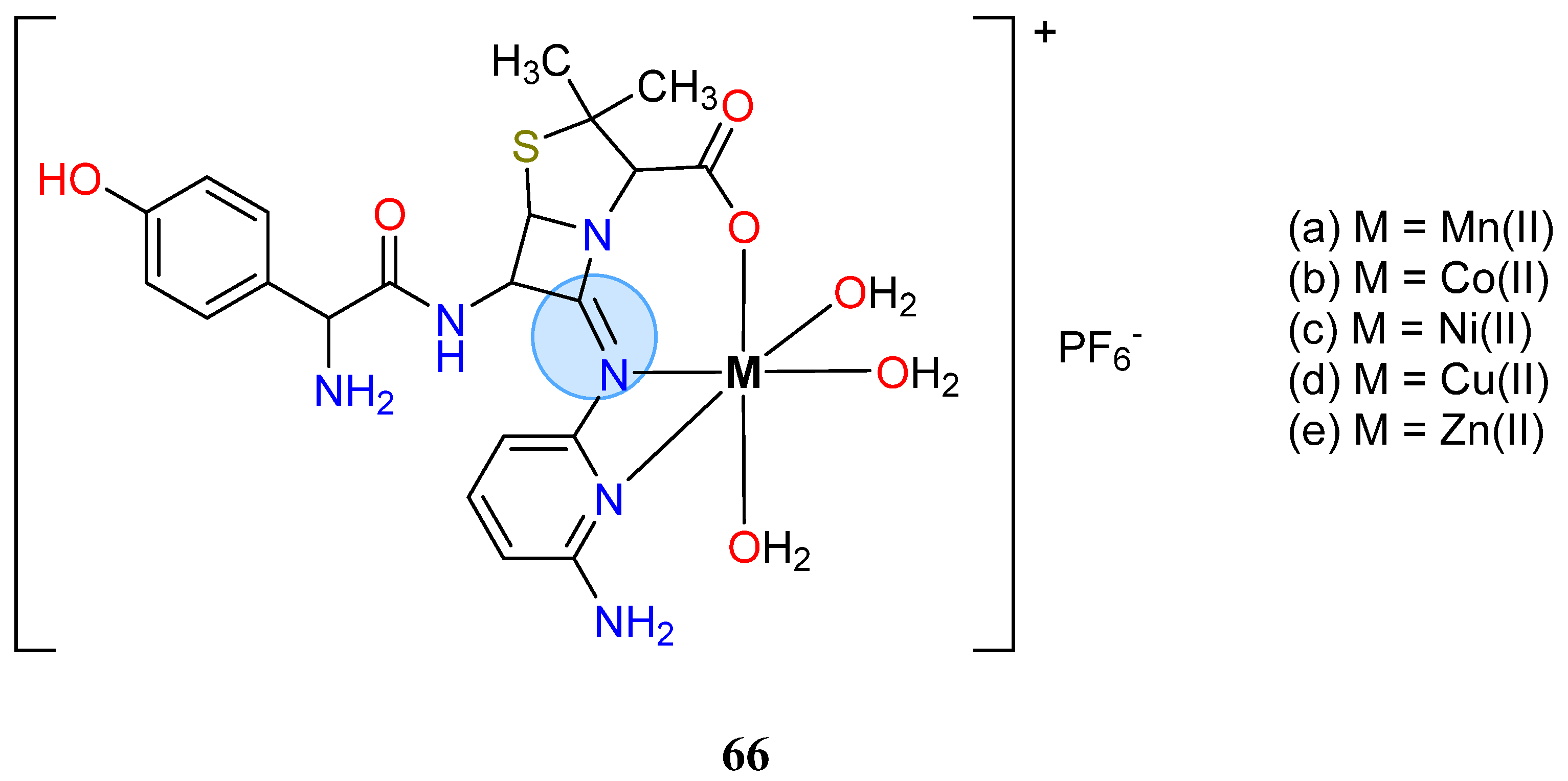
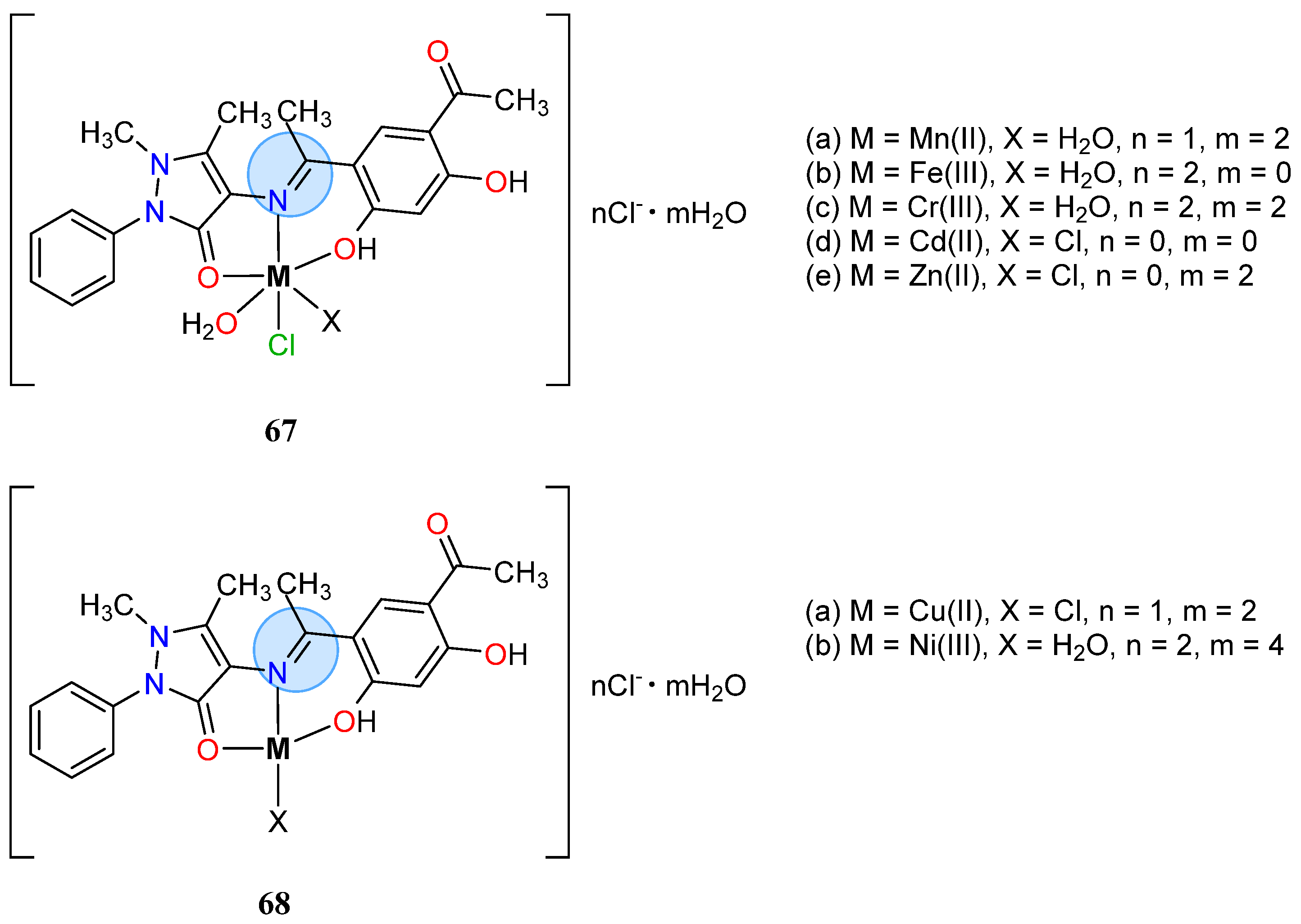
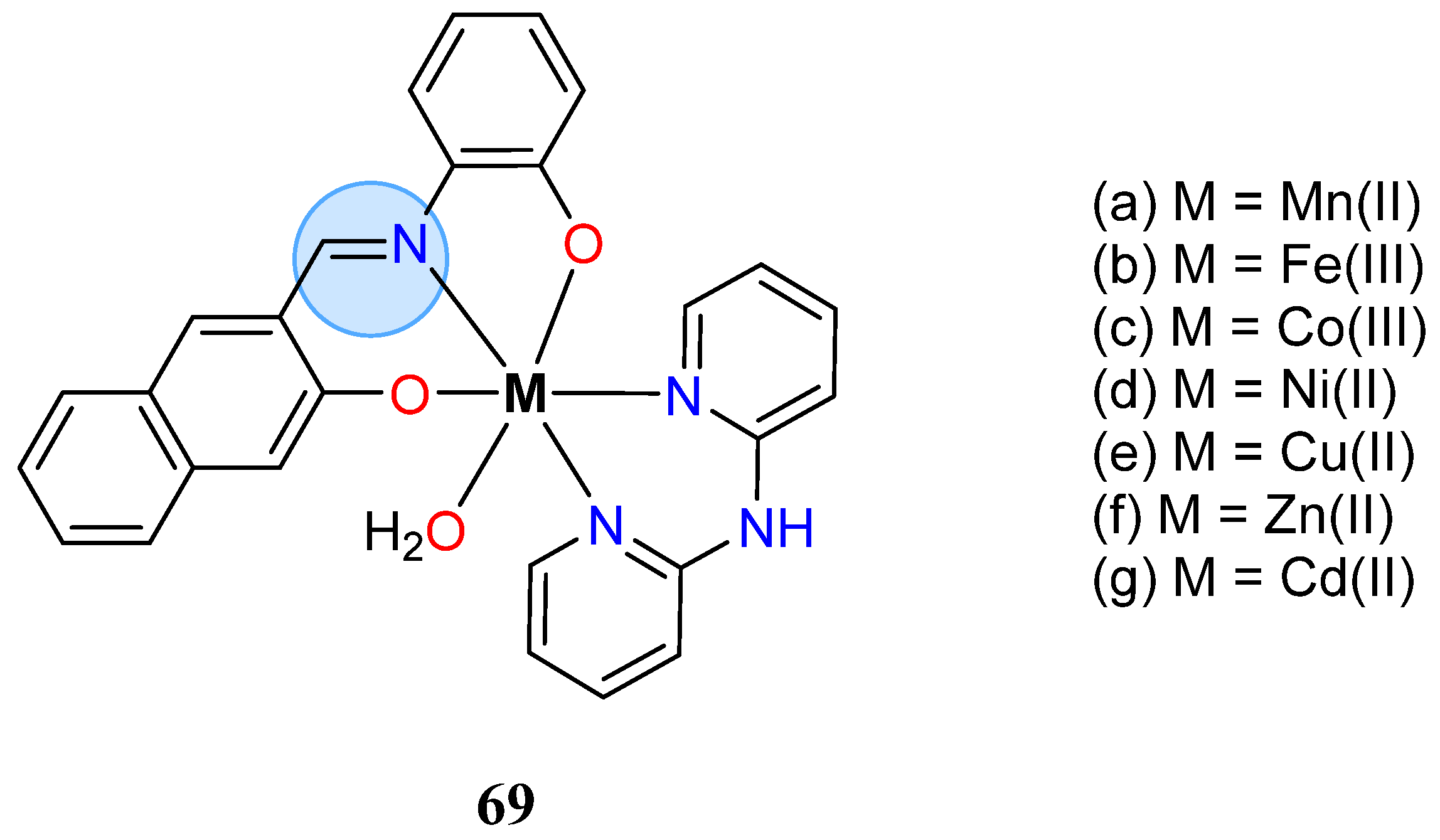
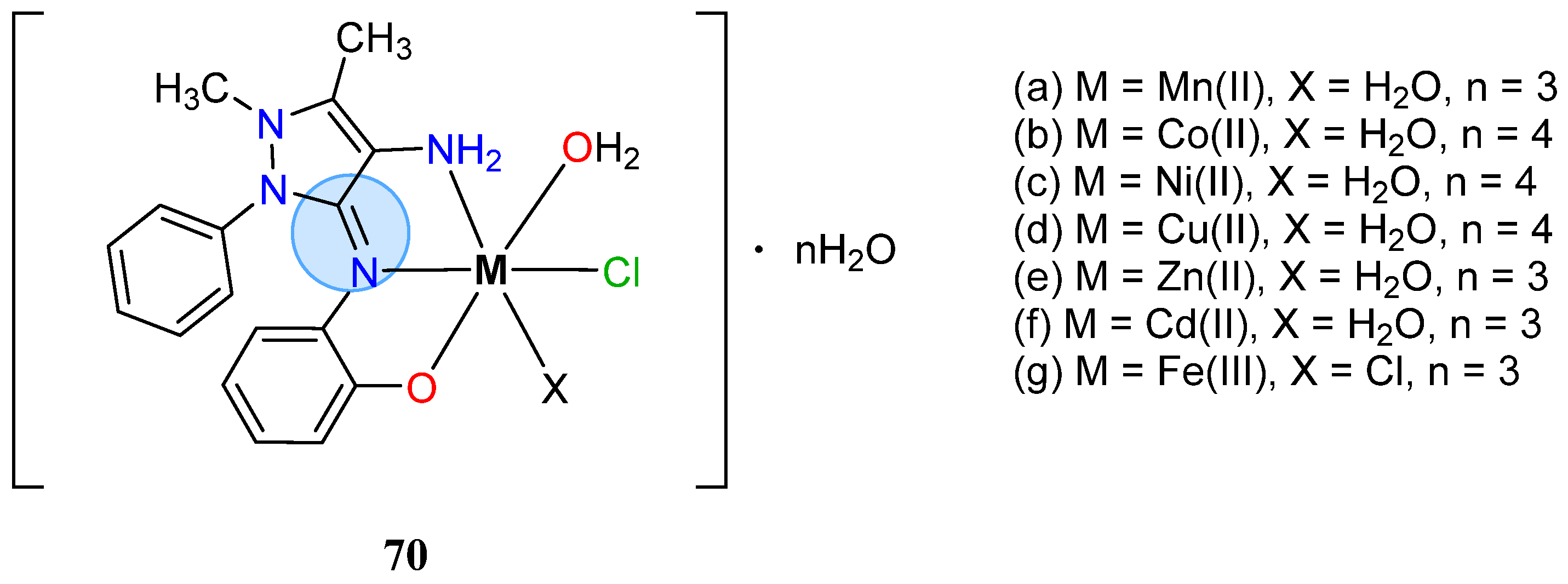
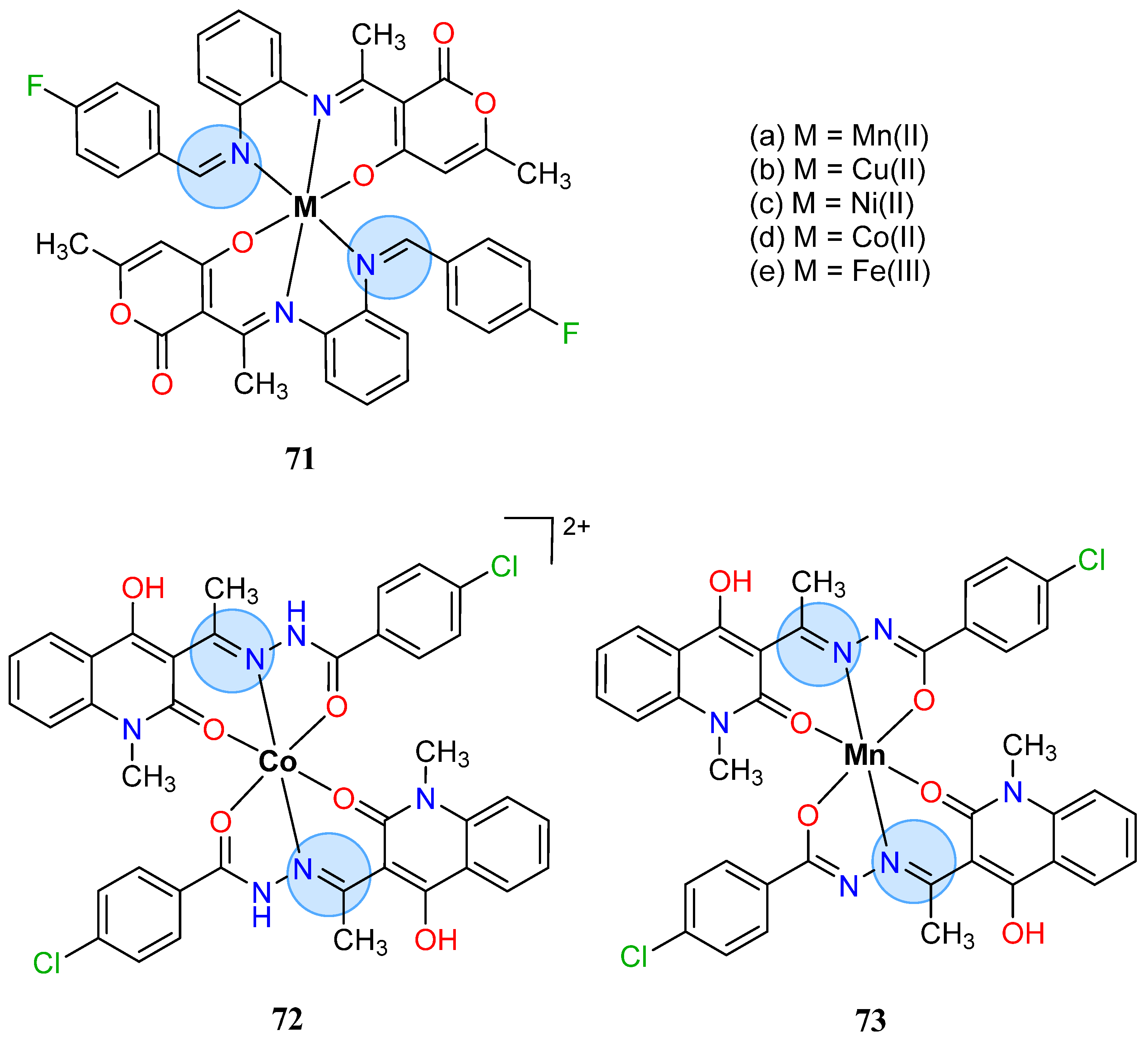
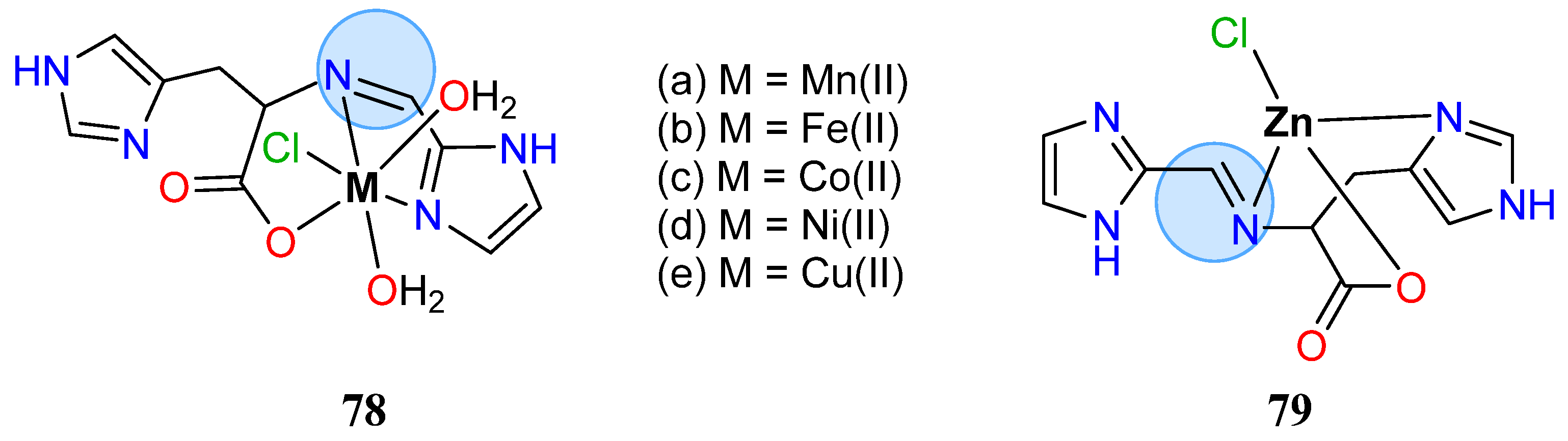
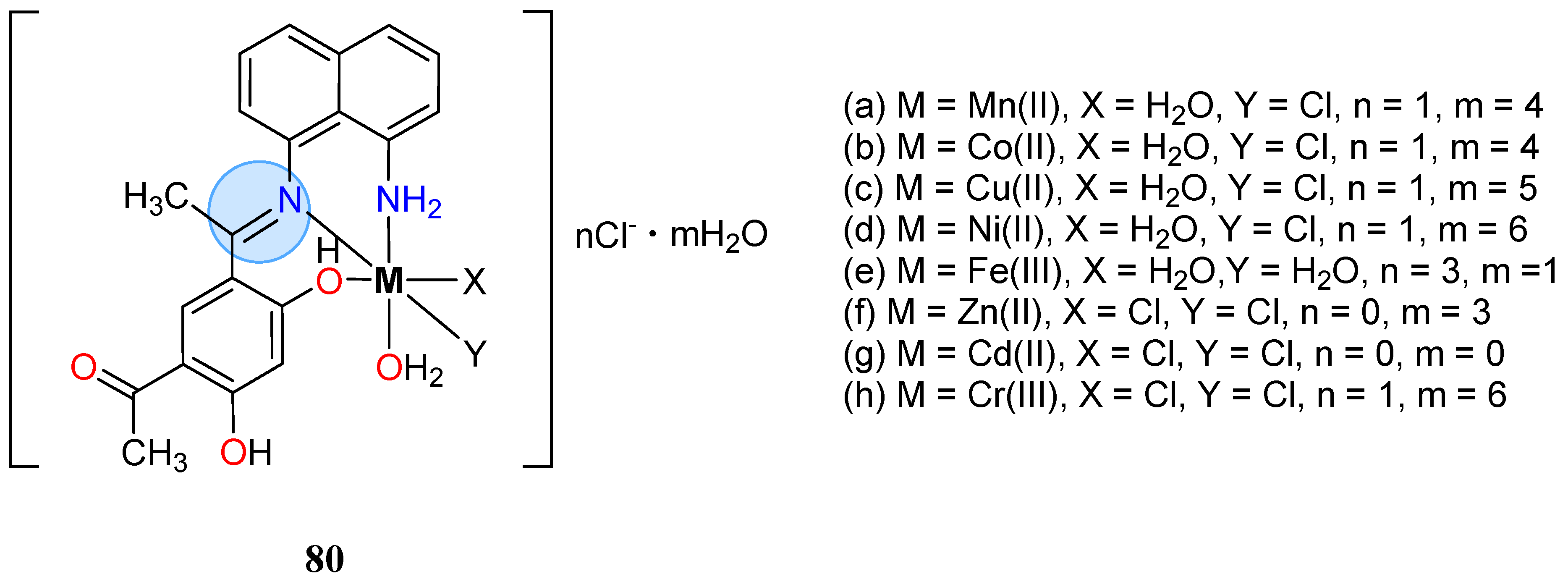



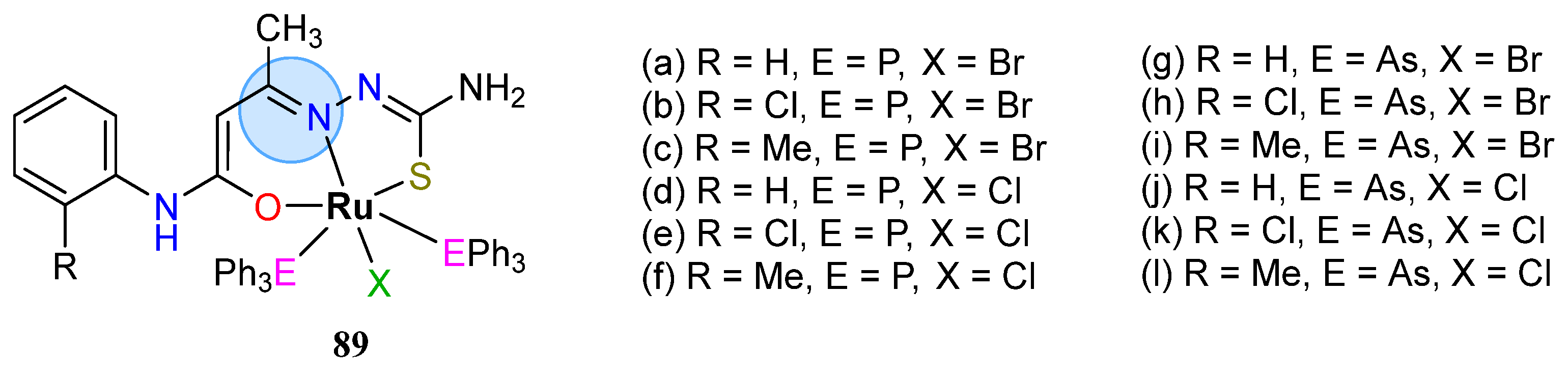




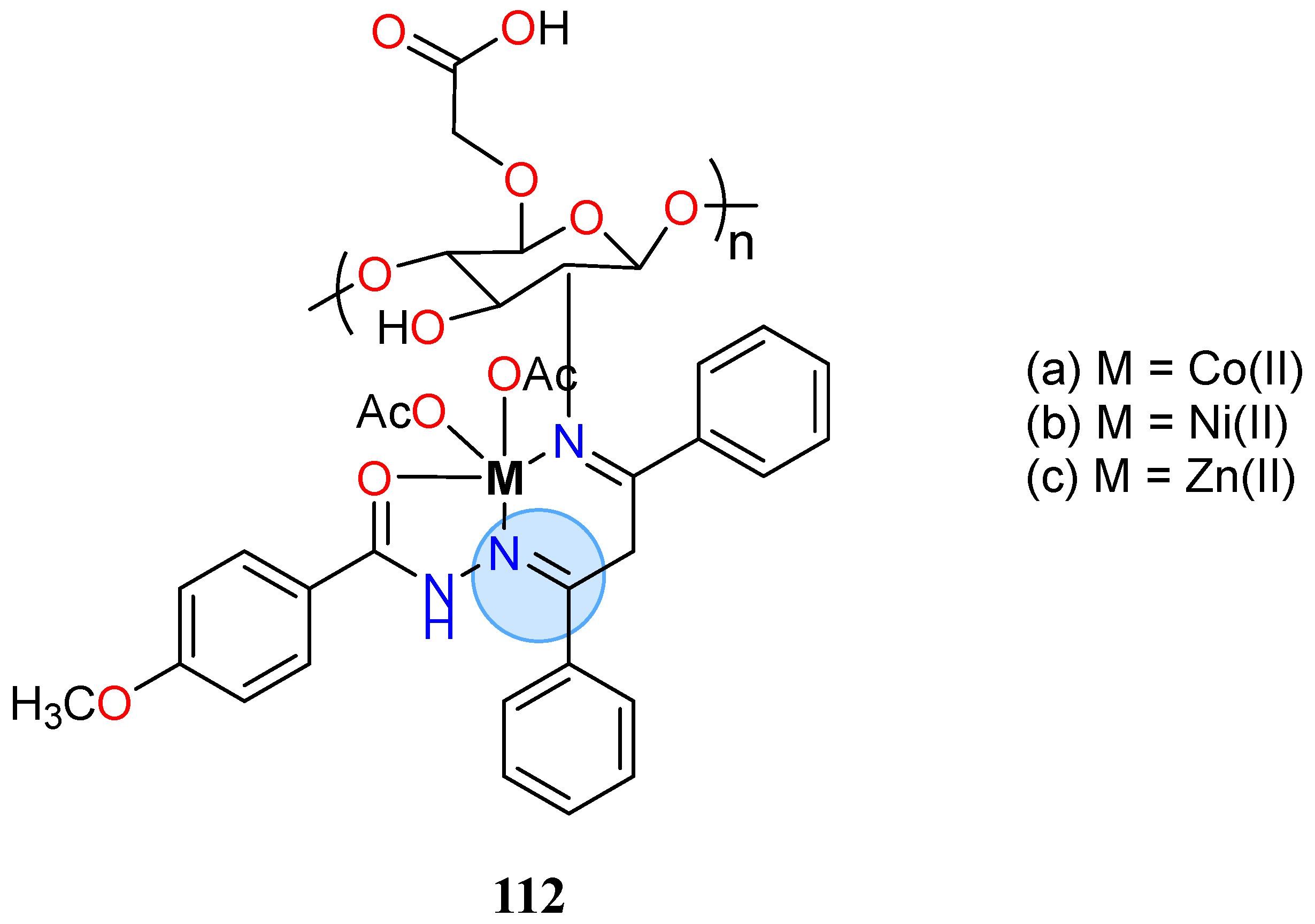
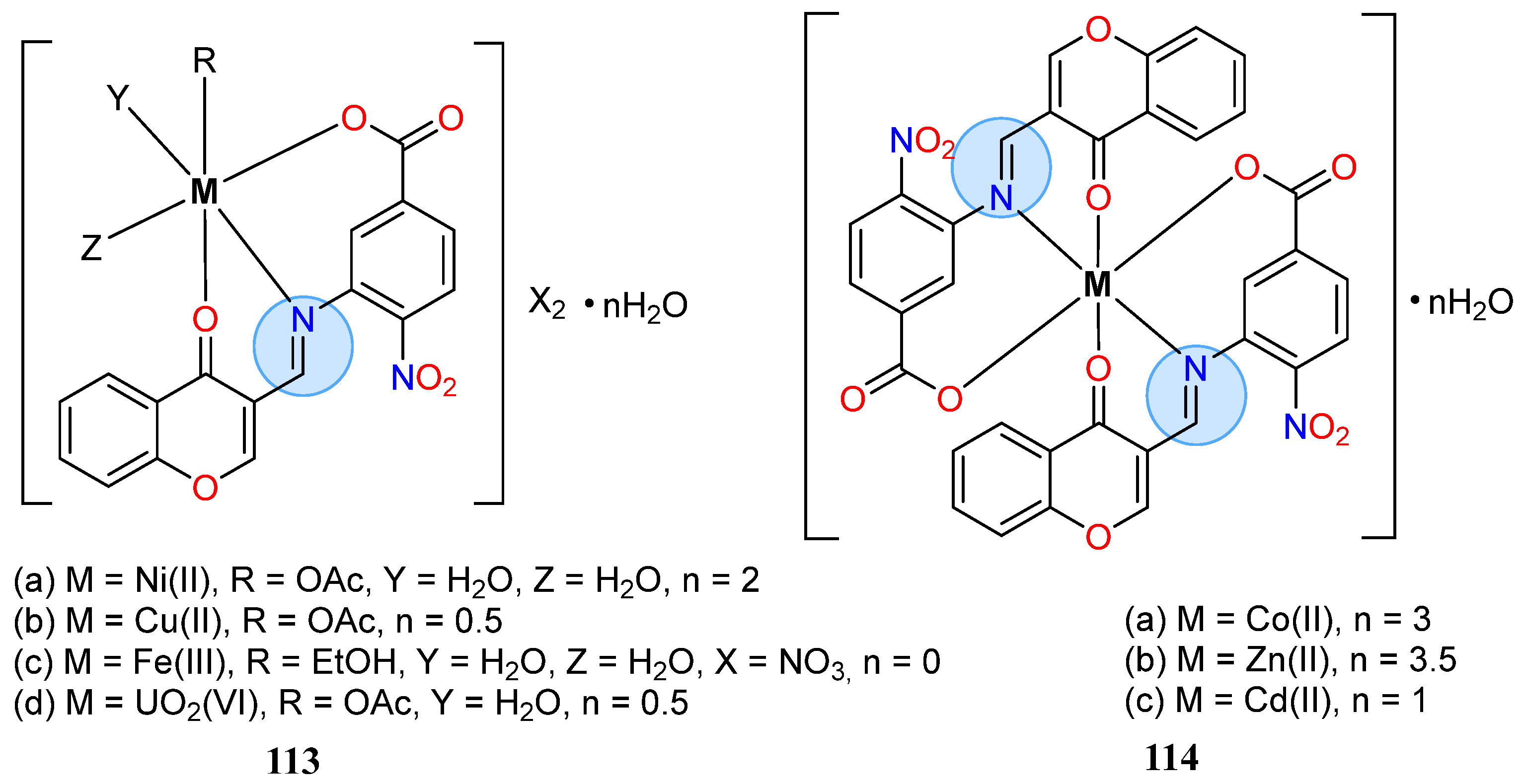
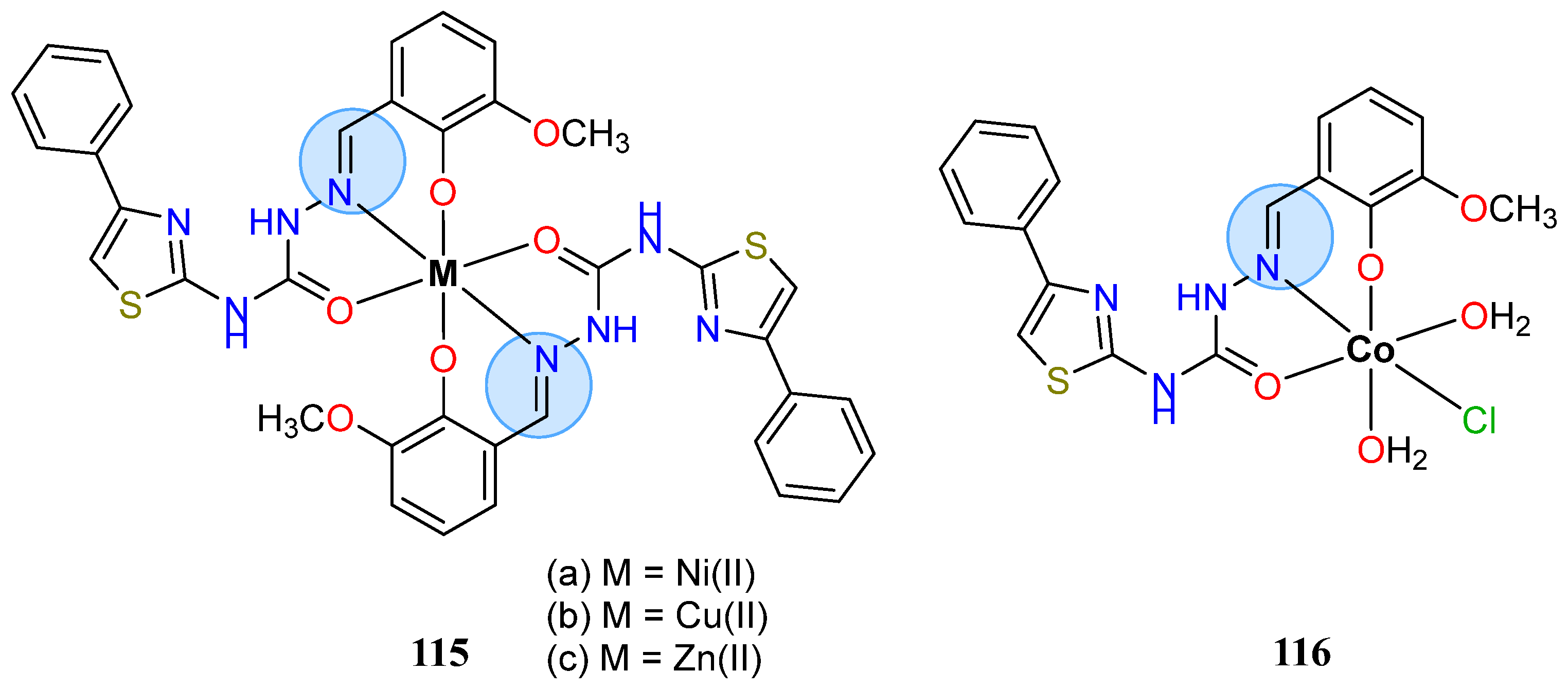
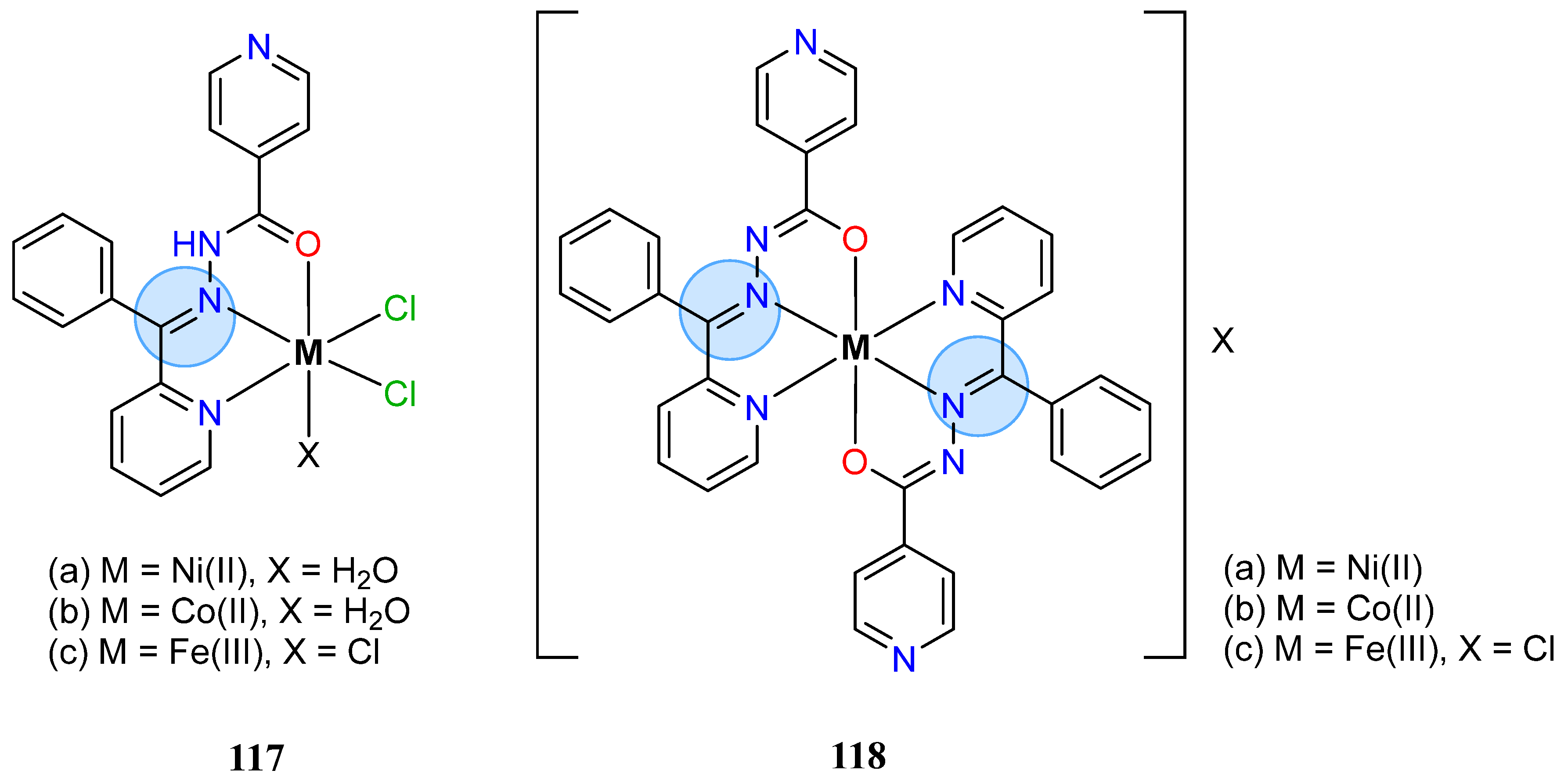


| Group in Periodic Table | Complex | Best Activity |
|---|---|---|
| Main Group | Organotin(IV): 8b | Inhibition zone = 23 mm for S. aureus |
| Organotin(IV): 10c | IC50 = 0.41 μg/mL for L. major | |
| Aluminium(III): 14 | Inhibition zone = 37 mm for A. flavus | |
| Antimony(III): 16b | IC50 = 1.23 μM for T. cruzi | |
| Indium(III): 27b | IC50 = 3.0 μM for C. parapsilosis | |
| Titanium Group | Titanium (IV): 32 | Inhibition zone = 16 mm for E. coli |
| Titanium (IV): 39d | Inhibition zone = 18 mm for B. cereus | |
| Vanadium Group | Oxovanadium(IV): 50a | MIC = 28 μg/mL for K. pneumoniae |
| Oxovanadium(V): 56 | MIC = 0.5 μg/mL for S. aureus | |
| Chromium Group | Chromium(III): 34b | Inhibition zone = 16.50 mm for A. niger |
| Chromium(III): 58 | Inhibition zone = 18 mm for M. luteus | |
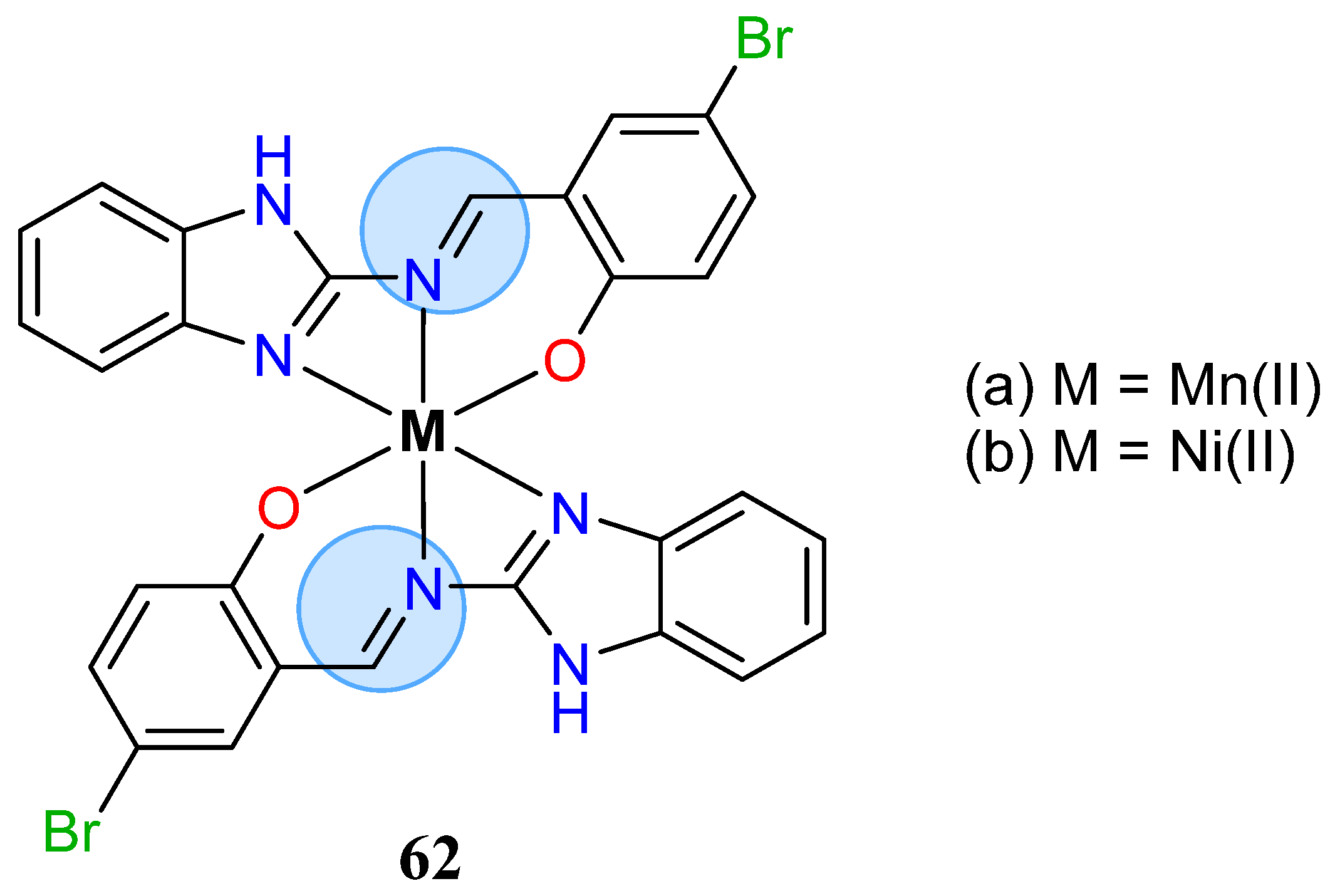
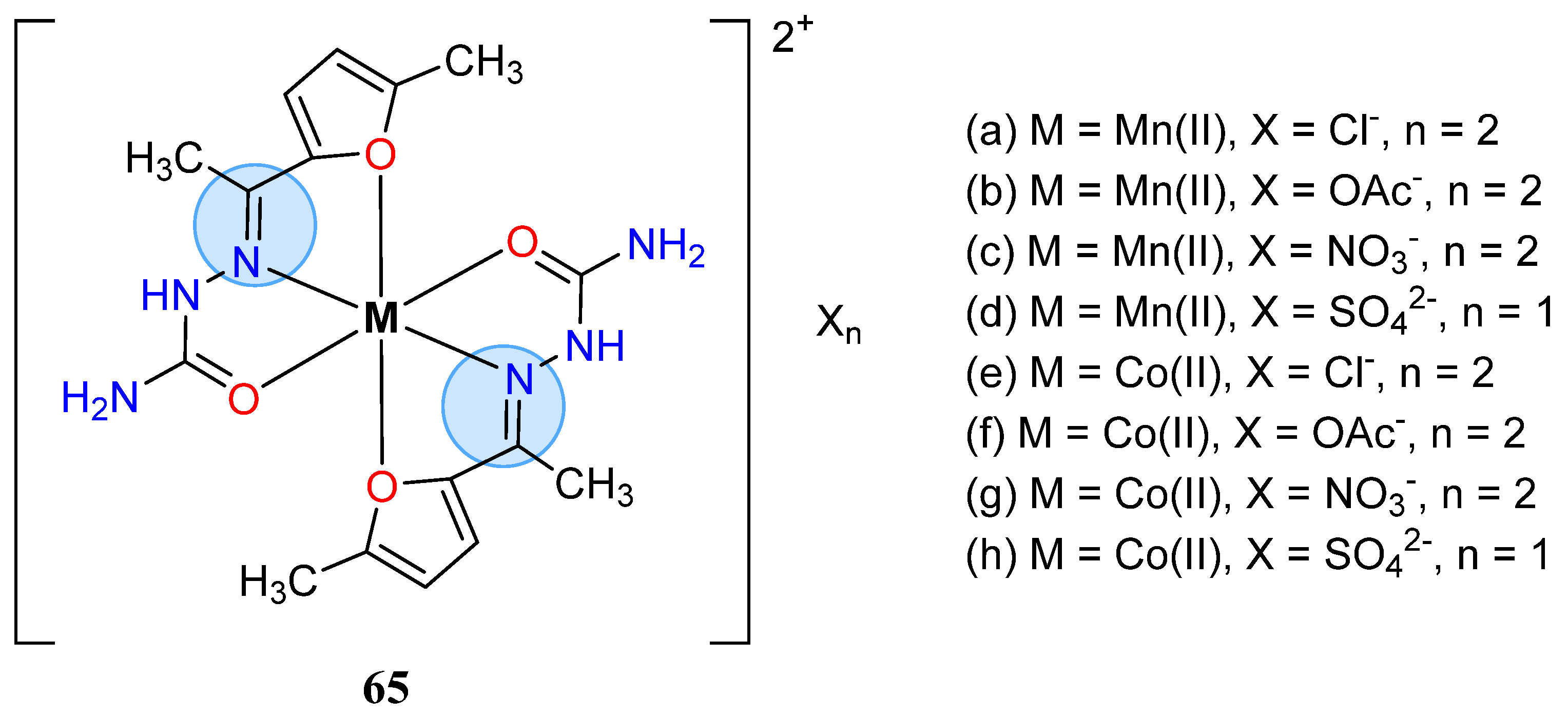
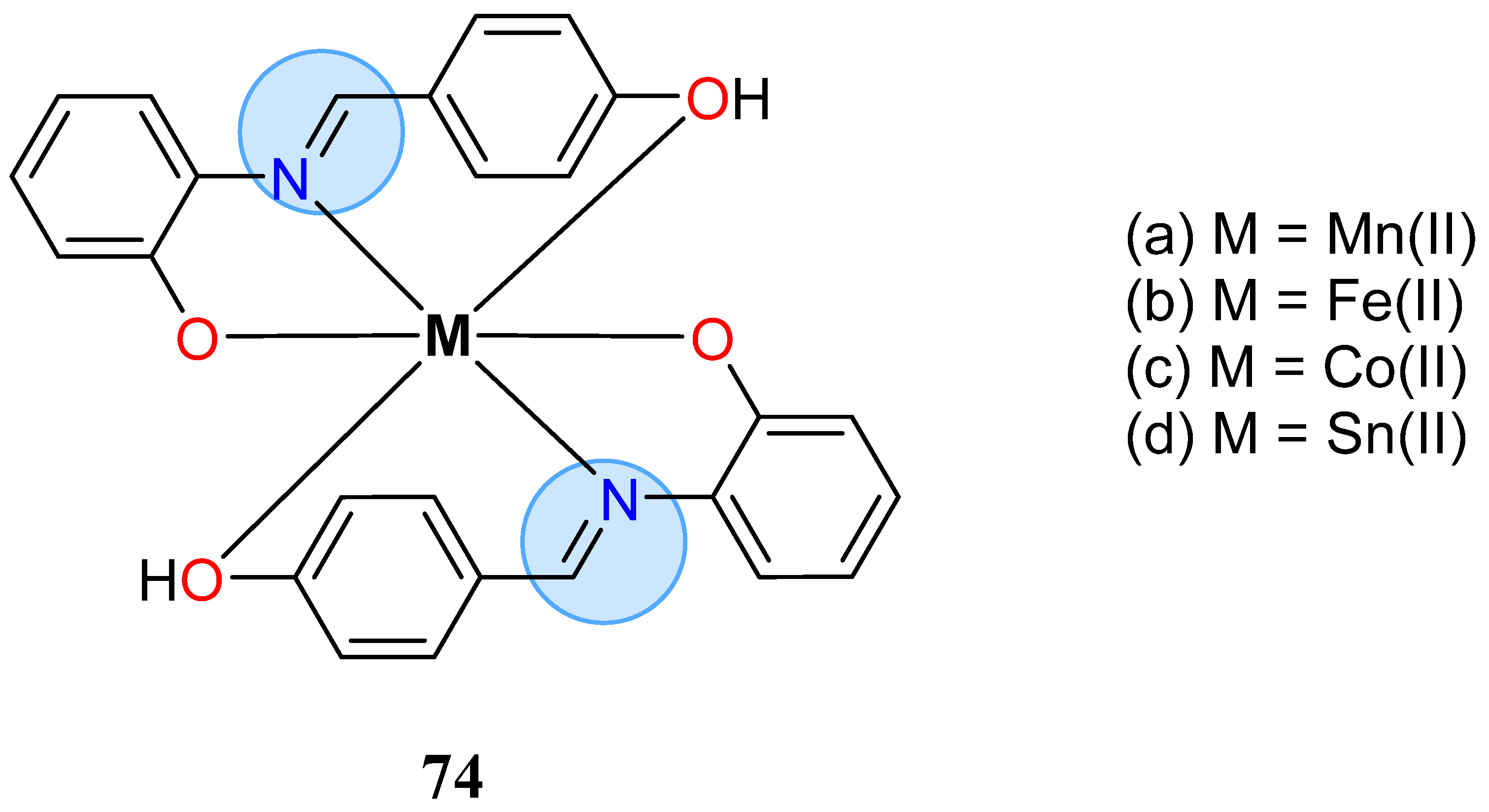
| Manganese Group | Manganese(II): 65c, 65d | Inhibition zone = 44 mm for P. aeruginosa |
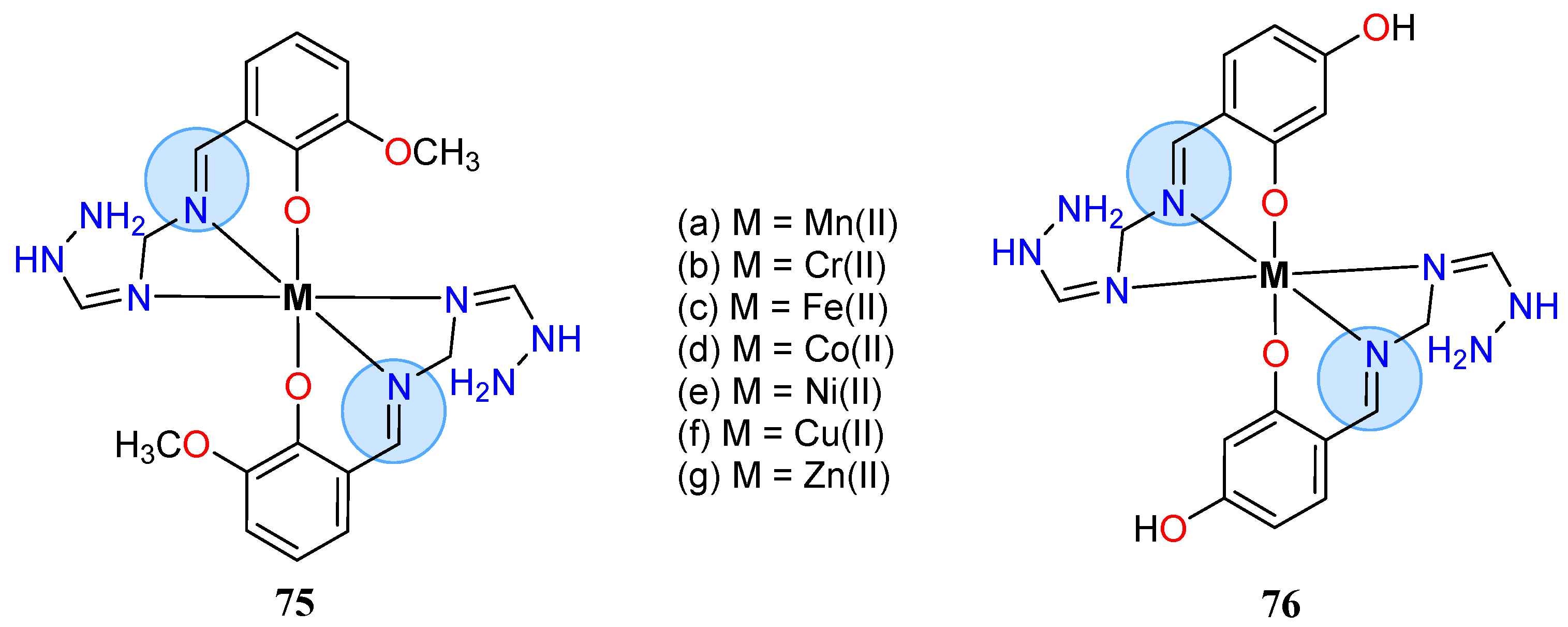
| Manganese(II): 74a | Inhibition zone = 12 mm for E. coli | |
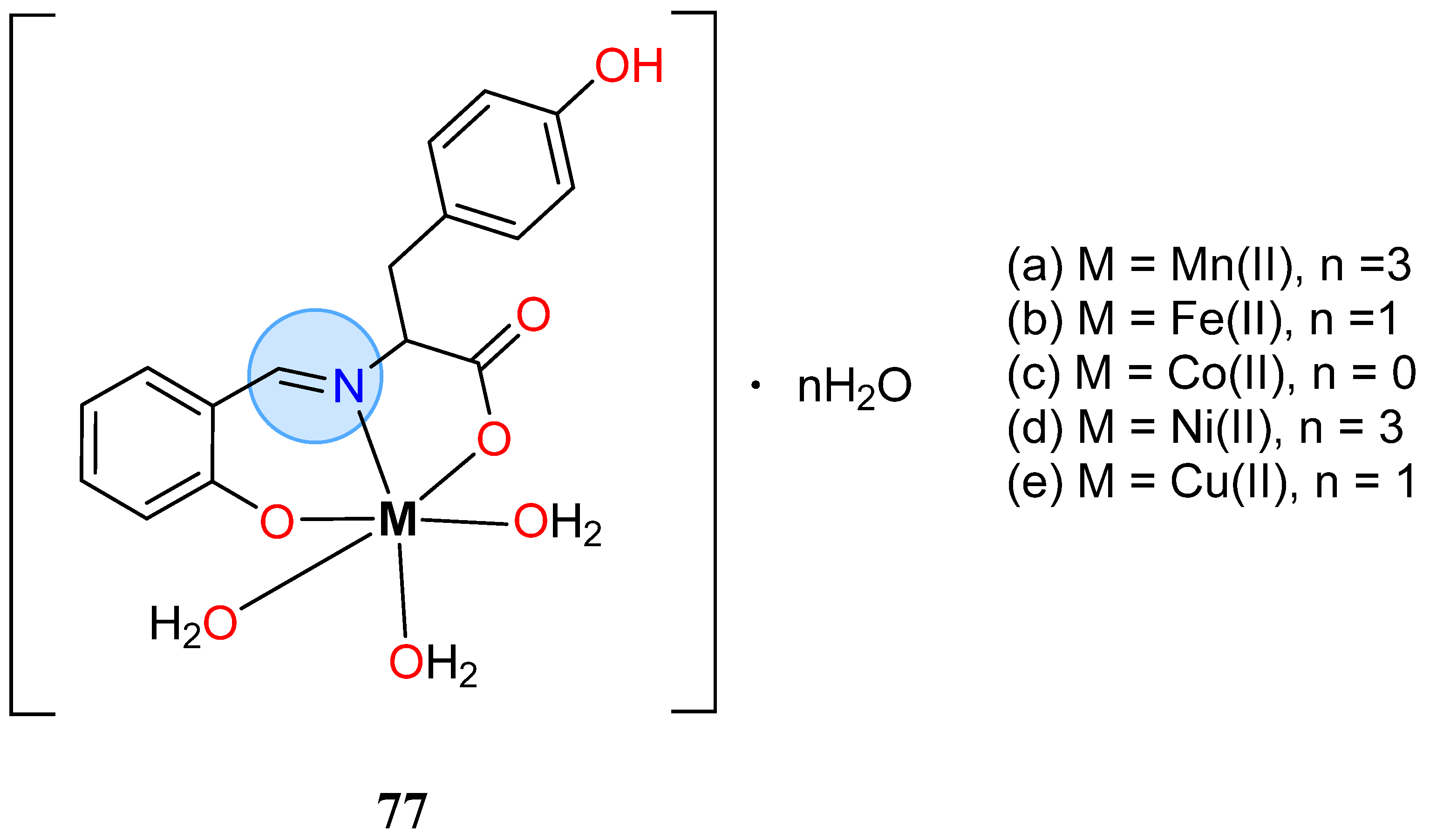
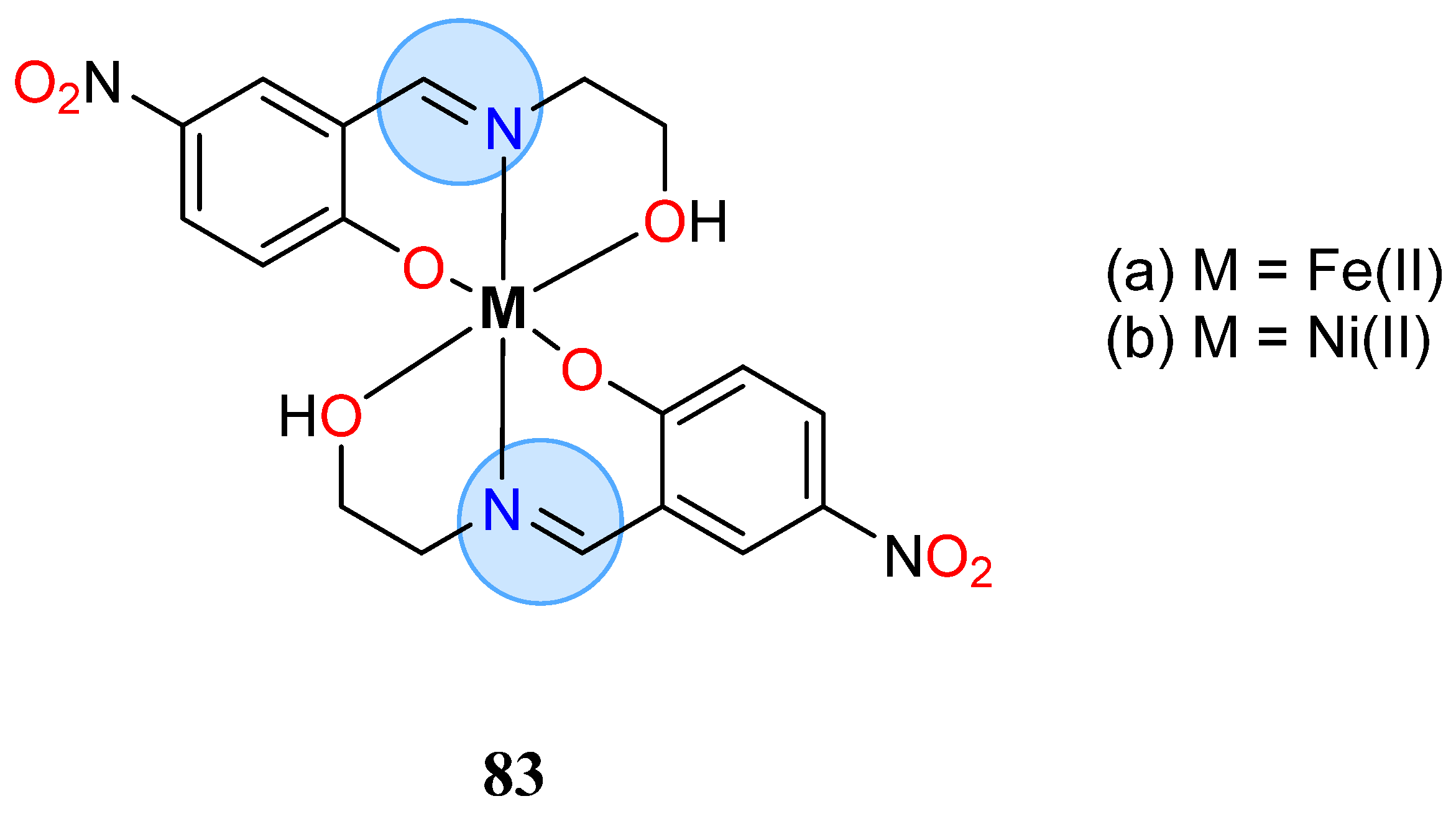
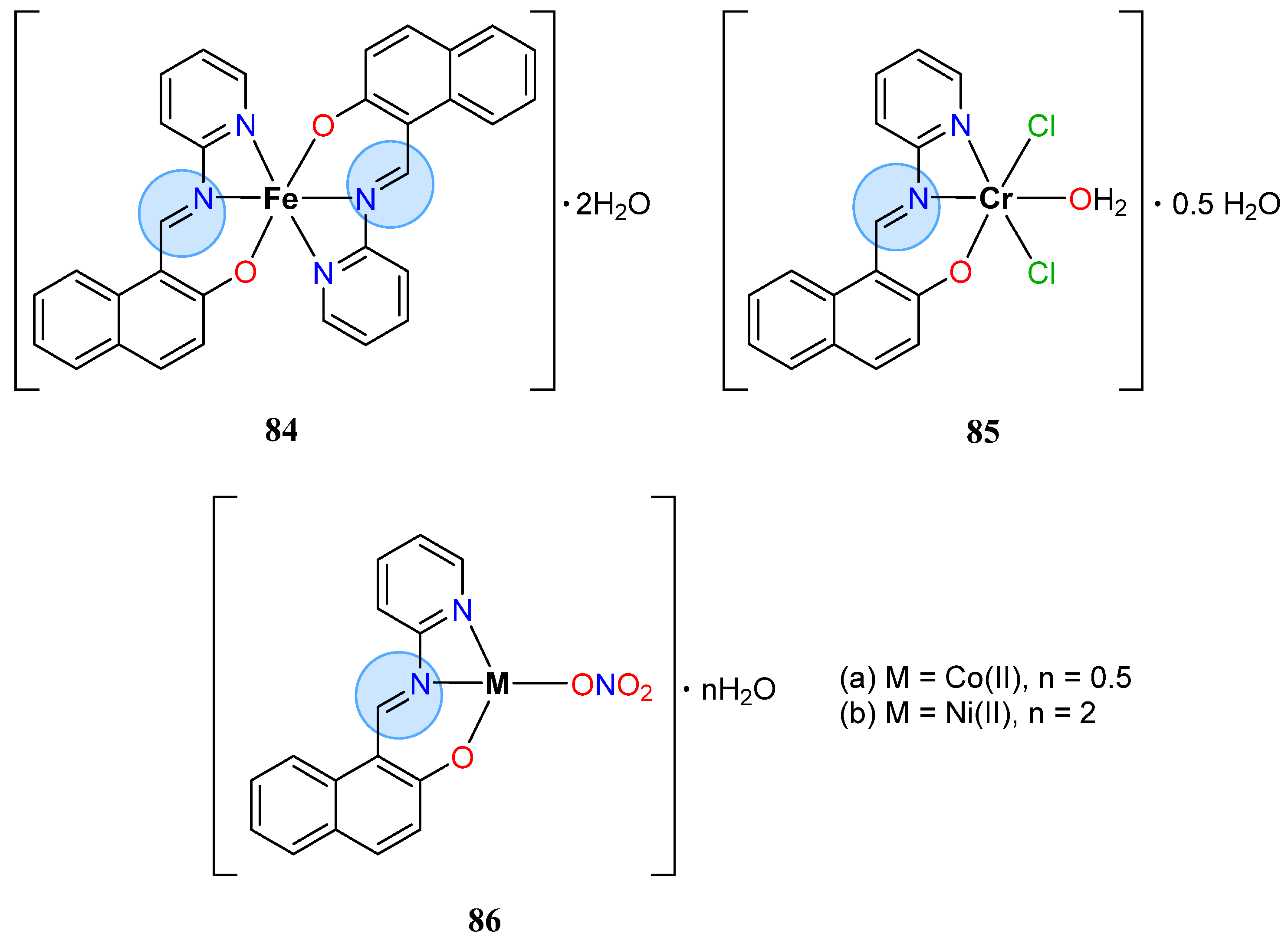
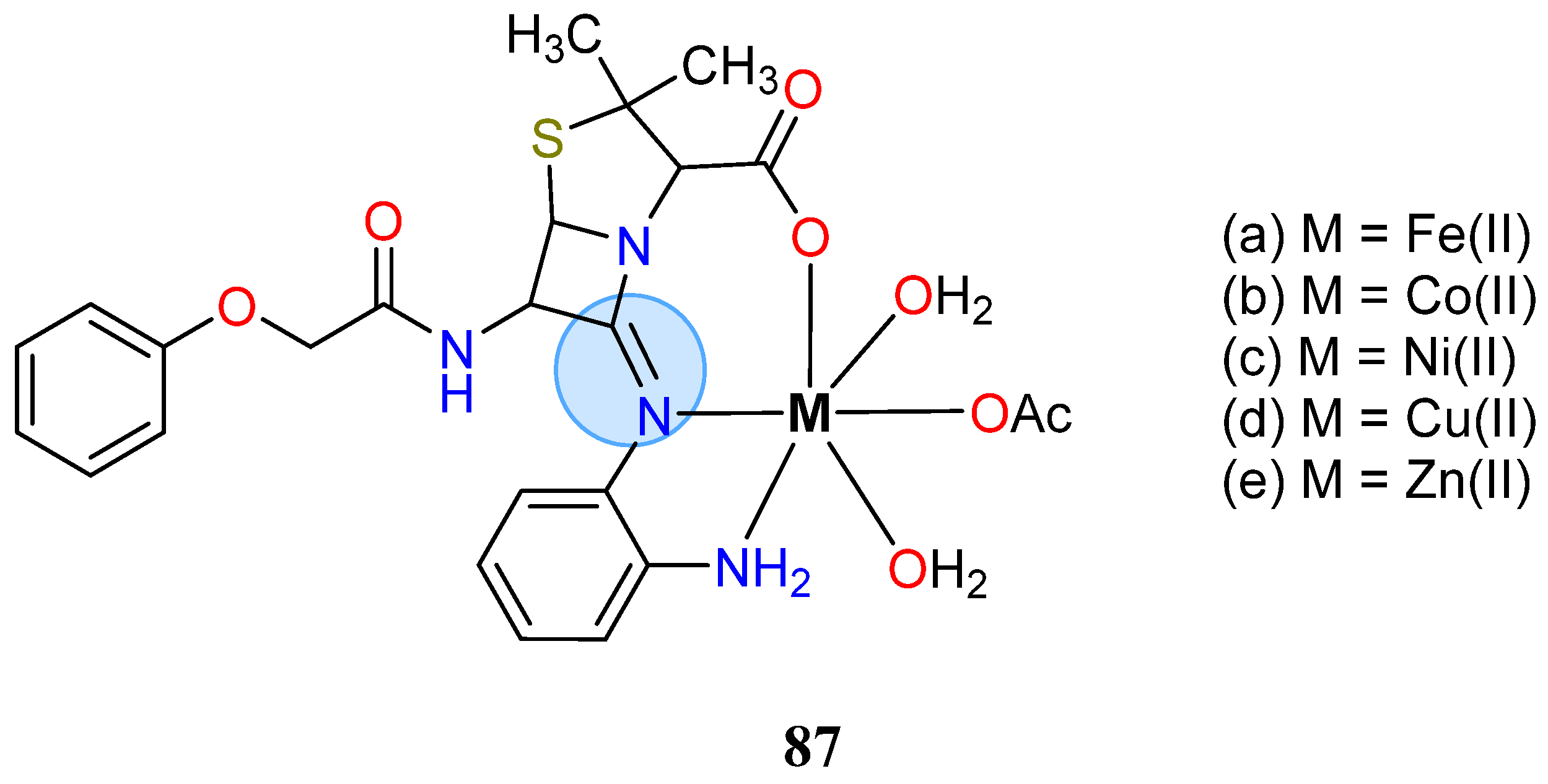
| Iron Group | Iron(II): 87a | MIC = 0.042 μmol/mL for S. aureus |
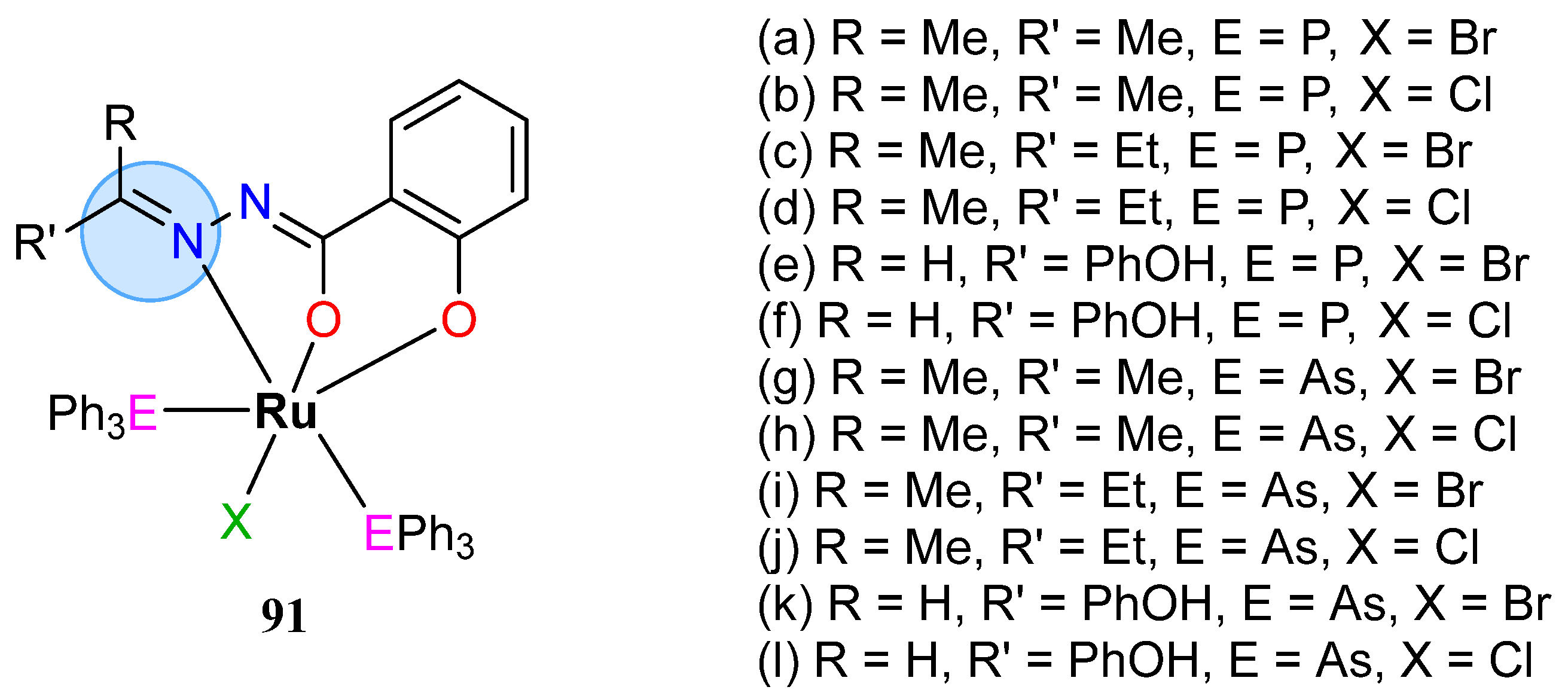
| Ruthenium(II): 90h, 90l | Inhibition zone = 15–17 mm for S. aureus | |
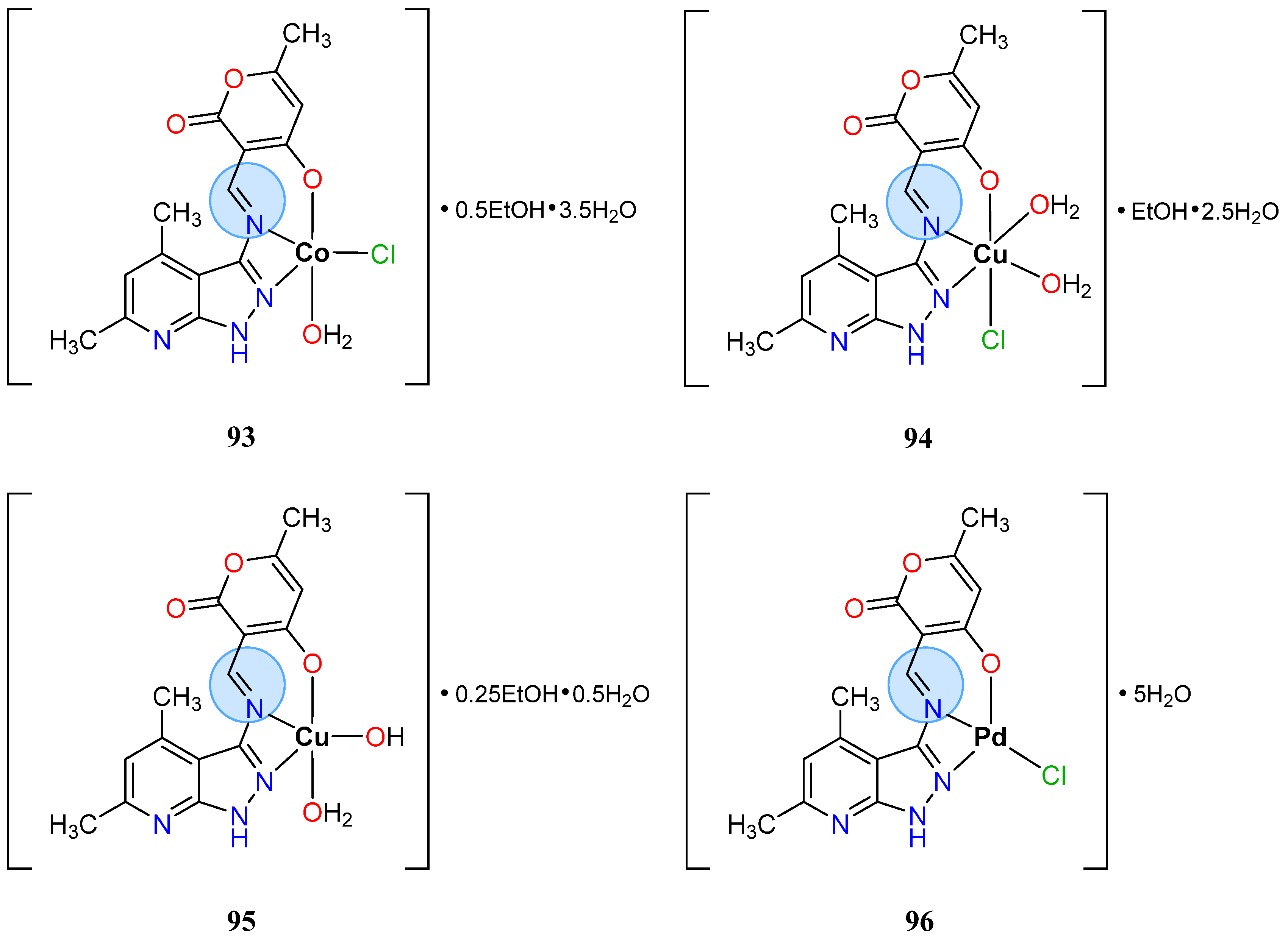
| Cobalt Group | Cobalt(II): 88f | Inhibition zone = 25 mm for E. faecalis |
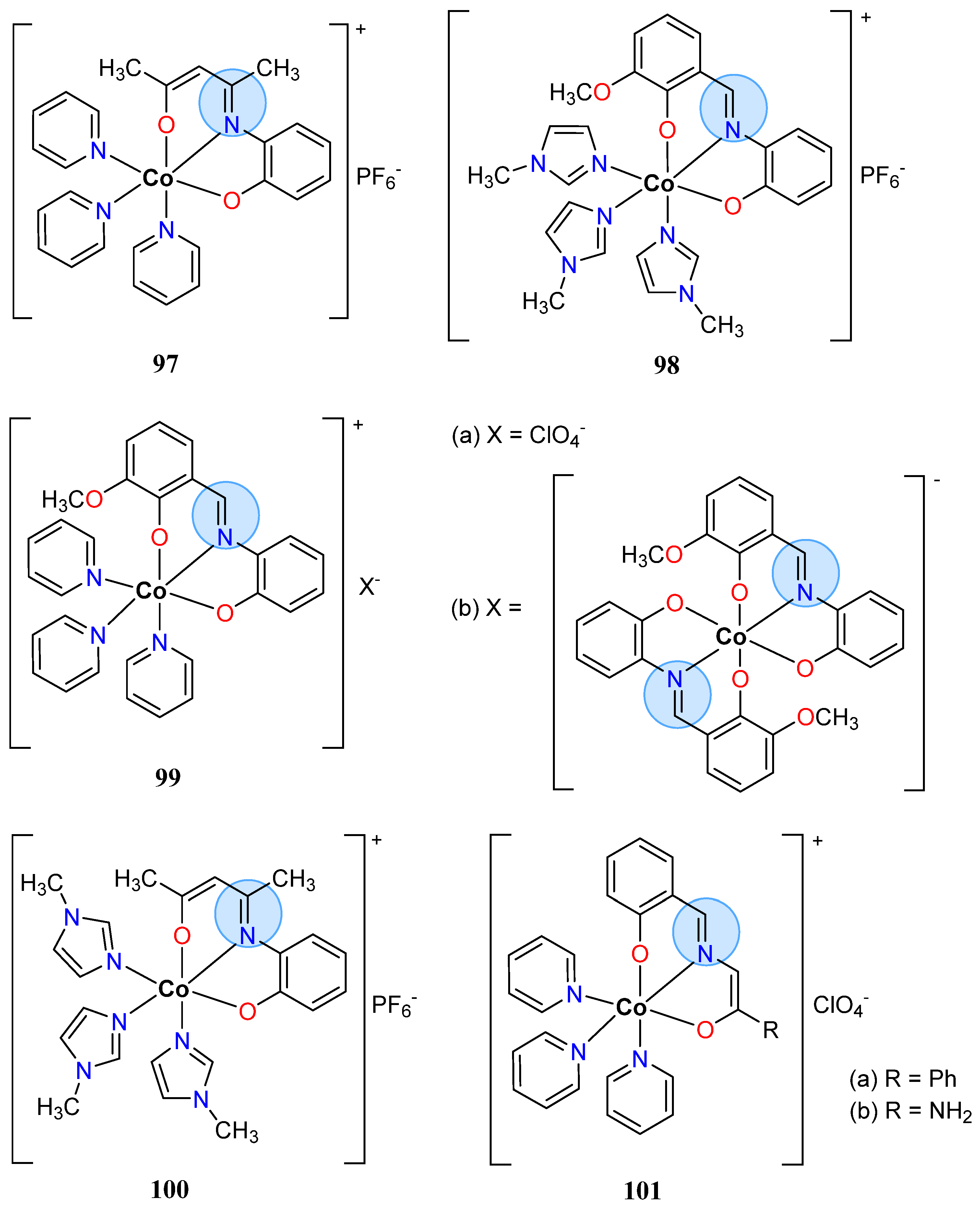
| Cobalt(III): 105 | Inhibition zone = 33 mm for A. niger | |
| Nickel Group | Nickel(II): 76e | Inhibition zone = 20 mm for S. aureus |
| Nickel(II): 112b | % of inhibition = 94.38% for C. albicans | |
| Nickel(II): 127b | MIC = 6 µg/mL for S. aureus | |
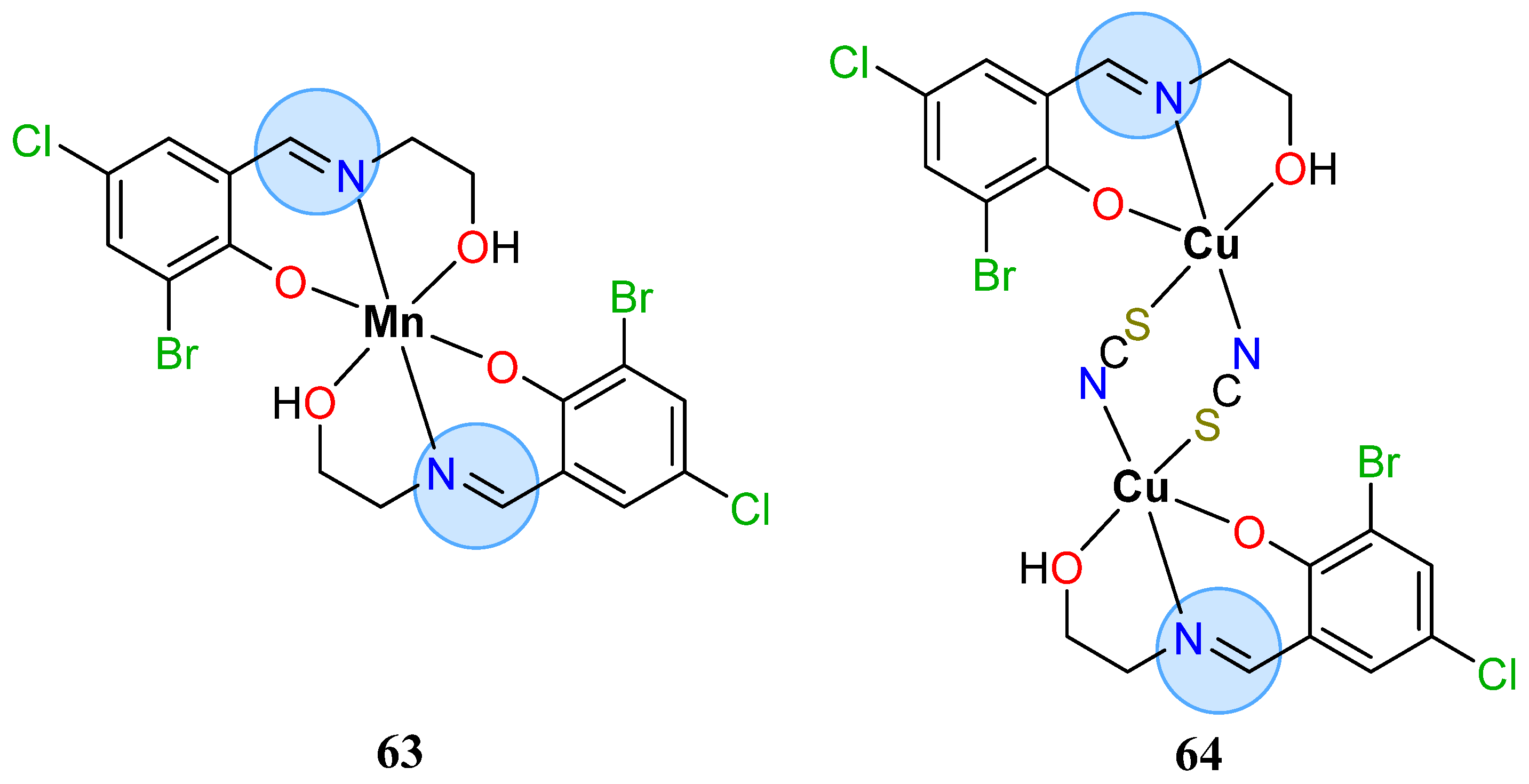
| Copper Group | Copper(II): 64 | MIC = 0.20 µg/mL for B. subtilis |
| Copper(II): 70d | Inhibition zone = 15 mm for P. putida | |
| Copper(II): 136a, 136b | MIC = 3.9 µg/mL for S. aureus/B. cereus | |
| Zinc Group | Cadmium(II): 67d | Inhibition zone = 24 mm for E. coli |
| Cadmium(II): 128f | MIC = 4 µg/mL for P. vulgaris | |
| Cadmium(II): 130 | MIC = 2 µg/mL for C. albicans |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aragón-Muriel, A.; Reyes-Márquez, V.; Cañavera-Buelvas, F.; Parra-Unda, J.R.; Cuenú-Cabezas, F.; Polo-Cerón, D.; Colorado-Peralta, R.; Suárez-Moreno, G.V.; Aguilar-Castillo, B.A.; Morales-Morales, D. Pincer Complexes Derived from Tridentate Schiff Bases for Their Use as Antimicrobial Metallopharmaceuticals. Inorganics 2022, 10, 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics10090134
Aragón-Muriel A, Reyes-Márquez V, Cañavera-Buelvas F, Parra-Unda JR, Cuenú-Cabezas F, Polo-Cerón D, Colorado-Peralta R, Suárez-Moreno GV, Aguilar-Castillo BA, Morales-Morales D. Pincer Complexes Derived from Tridentate Schiff Bases for Their Use as Antimicrobial Metallopharmaceuticals. Inorganics. 2022; 10(9):134. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics10090134
Chicago/Turabian StyleAragón-Muriel, Alberto, Viviana Reyes-Márquez, Farrah Cañavera-Buelvas, Jesús R. Parra-Unda, Fernando Cuenú-Cabezas, Dorian Polo-Cerón, Raúl Colorado-Peralta, Galdina V. Suárez-Moreno, Bethsy Adriana Aguilar-Castillo, and David Morales-Morales. 2022. "Pincer Complexes Derived from Tridentate Schiff Bases for Their Use as Antimicrobial Metallopharmaceuticals" Inorganics 10, no. 9: 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics10090134
APA StyleAragón-Muriel, A., Reyes-Márquez, V., Cañavera-Buelvas, F., Parra-Unda, J. R., Cuenú-Cabezas, F., Polo-Cerón, D., Colorado-Peralta, R., Suárez-Moreno, G. V., Aguilar-Castillo, B. A., & Morales-Morales, D. (2022). Pincer Complexes Derived from Tridentate Schiff Bases for Their Use as Antimicrobial Metallopharmaceuticals. Inorganics, 10(9), 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics10090134