Abstract
This work details the synthesis and the crystal structures of the quaternary Zintl phases Na2CaCdSb2, Na2SrCdSb2 and Na2EuCdSb2. They are isostructural and their noncentrosymmetric structure is with the space group Pmc21 (Pearson code oP12). All structural work is carried out via single-crystal X-ray diffraction methods. The structure features [CdSb2]4– layers of corner-shared CdSb4 tetrahedra, which are stacked along the b-crystallographic axis and are separated by cations. The results from the structure refinements suggest that in addition to full cation ordering, which is typical for this structure, there also exists a possibility for an accommodation of a small degree of cation disorder.
1. Introduction
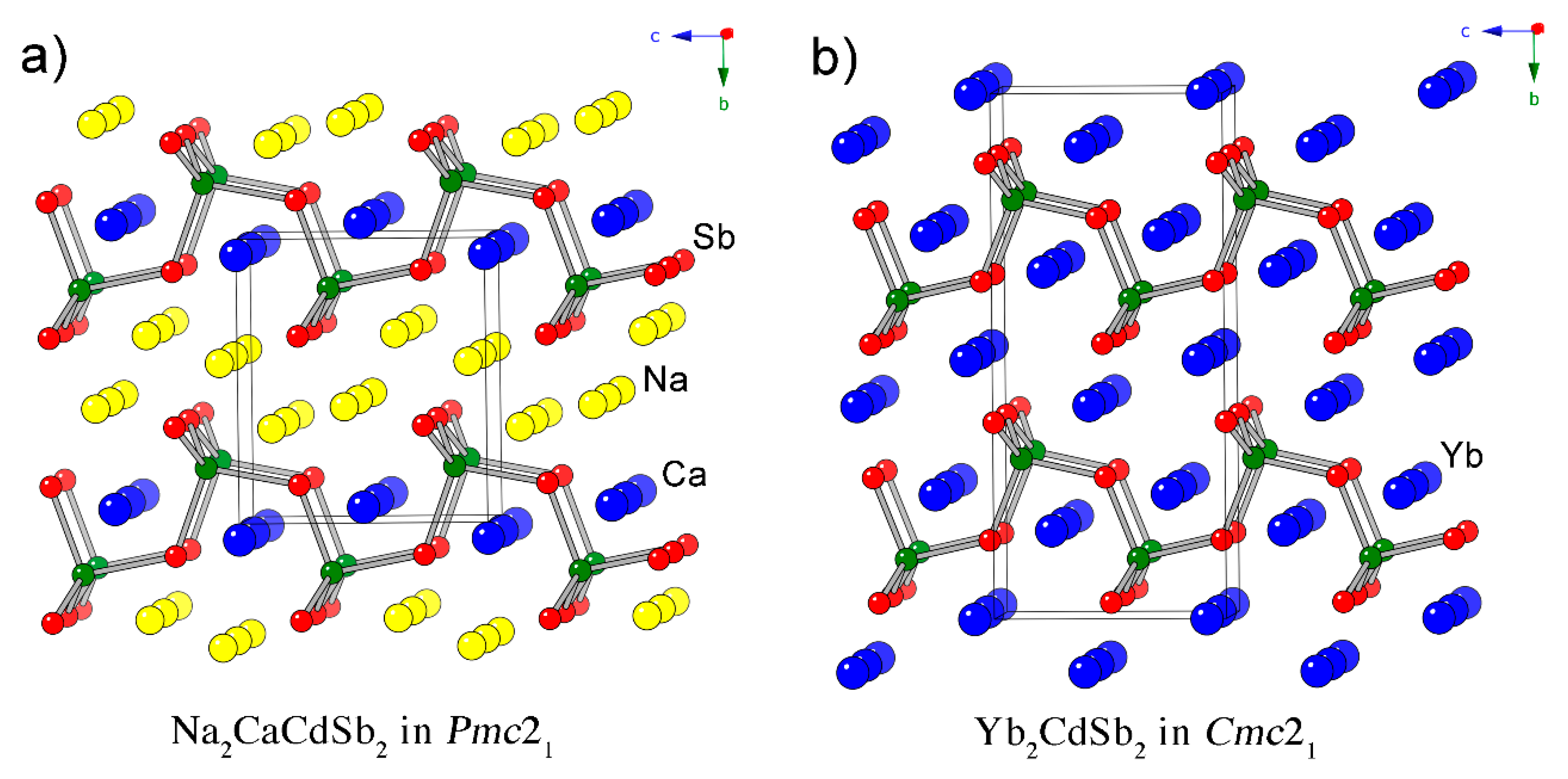
Since the discovery of Yb2CdSb2 and Ca2CdSb2 [1], which adopt different structures with similar motifs—Yb2CdSb2 crystallizes in the noncentrosymmetric space group Cmc21, whereas Ca2CdSb2 crystallizes in the centrosymmetric space group Pnma—our group has been conducting systematic studies on related quaternary compounds [2,3,4,5,6,7,8]. First, we investigated the solid solutions AxM2–xCdSb2, where A and M stand for the alkaline-earth metals Ca, Sr and Ba, and the nominally divalent rare-earth metals Eu and Yb [2]. The structures of all currently found AxM2–xCdSb2 phases are isotypic with the Yb2CdSb2 structure, featuring [CdSb2]4– layers of corner-shared CdSb4 tetrahedra. The layers are stacked along the b-crystallographic axis and are separated by cations (Figure 1). The placement of the different cations in all cases point at site preferences governed by simple spatial requirements—the larger cations prefer the crystallographic position with octahedral coordination of Sb atoms, which is referred to as the “interlayer” site. The smaller cations prefer to occupy the more compact site with square pyramidal arrangement of Sb atoms surrounding it, which is referred to as the “intralayer” site. For a more comprehensive treatment of the cation site preferences from a computational perspective, the reader is directed to the paper dealing with those problems in the related phosphides BaxSr2–xCdP2 [7,8]. Of note is the fact that the “2-1-2” structure in question has become synonymous with low thermal conductivity, which is an important facet in modern thermoelectrics development. As a result, other research teams have utilized the flexibility of the structure to design new materials for thermoelectric energy conversion [9,10,11,12] and second harmonic generation [13].
Figure 1.
Side-by-side comparison between the crystal structure of Na2CaCdSb2 (a) and that of Yb2CdSb2 (b). Both projections are along the a-crystallographic axis. Bonds are drawn only between Cd (green) and Sb (red) atoms, emphasizing the polyanionic [CdSb2]4– layers. Unit cells are outlined.
Extensions of the above work in a slightly different direction were the experiments directed at heterovalent substitutions of the divalent metal cations in Yb2CdSb2 and Ca2CdSb2. To date, we have succeeded in the synthesis and the accurate structural characterization of the Zintl compounds K2SrCdSb2, K2BaCdSb2 and Na2YbCdSb2 [2]. These quaternary phases crystallize with a novel type, with a noncentrosymmetric orthorhombic structure akin to that of Yb2CdSb2, where the mono- and divalent cations are ordered and occupy distinct crystallographic sites. The experimental data for Na2CaCdSb2, Na2SrCdSb2 and Na2EuCdSb2 at that time were insufficient to unequivocally establish the crystal structure, and only the unit-cell parameters were available for the latter.
With this paper, we report the structures of these three compounds, established from single-crystal X-ray diffraction methods. The new results suggest that, in addition to full cation ordering, the structure is also able to accommodate some cation disorder.
2. Results
Details of the data collection and selected crystallographic parameters are summarized in Table 1 and Table 2. For brevity, throughout the text, the simplified chemical formulae Na2CaCdSb2, Na2SrCdSb2 and Na2EuCdSb2 will be used instead of the refined formulae.

Table 1.
Selected single-crystal data collection and structure refinement parameters for Na2CaCdSb2 and Na2SrCdSb2.

Table 2.
Selected single-crystal data collection and structure refinement parameters for two independent samples of Na2EuCdSb2.
As discussed previously, the structure is very much alike to that of Yb2CdSb2, which is also noncentrosymmetric and crystallizes orthorhombically [1]. The latter has the space group Cmc21 (Pearson symbol oC20), while the structure under consideration herein has the space group Pmc21 (Pearson symbol oP12). In both, there are [CdSb2]4– layers made of corner-shared CdSb4 tetrahedra, which are stacked along the b-crystallographic axis. In both structures, the polyanionic layers are separated by slabs of cations. The main difference is that there are two divalent cations per formula unit in the Cmc21 structure, while in the Pmc21 one, there are three—two monovalent sodium cations formally substitute one alkaline-earth or rare-earth. The additional cation positions in Na2CaCdSb2, Na2SrCdSb2 and Na2EuCdSb2 necessitate the removal of the base-centering and halving the unit-cell volume. This is the most distinguishable difference between these two structures, which are schematically represented side-by-side in Figure 1.
There are six unique crystallographic positions in the asymmetric unit (Table 3), including two sodium, one calcium (or strontium or europium), one cadmium and two antimony sites, all in special positions with site symmetries m. All refined anisotropic displacement parameters are normal, despite the observed disorder (a figure showing a structural representation with anisotropic displacement parameters is provided as Supplementary Material). Na1 exhibits a somewhat enlarged atomic displacement parameter compared to Na2, but this must be an artifact of the greater coordination number (CN), since Ueq for Na2 is larger than Ueq for Na1 in all refined structures (Table 3). Another noteworthy crystallographic feature is the uneven variation of the unit-cell vectors a, b and c as a function of the size of the alkaline-earth metal. This is not unexpected, considering the fact that the magnitude of the a- and c-lattice parameters should correlate most strongly with the size of Ca, Sr and Eu, while the b-lattice parameter will be in correlation with the cation disorder, which is not uniform across the series.

Table 3.
Atomic coordinates of the atoms and their equivalent isotropic displacement parameters Ueq a for Na2CaCdSb2, Na2SrCdSb2 and Na2EuCdSb2.
As discussed already, the simplest way to relate the structure to that of the parent Yb2CdSb2 is to consider the aliovalent substitution of the interlayer Yb2+ cations by twice as many Na+ cations in way that the overall electron count is preserved. Using Na2CaCdSb2 and Yb2CdSb2 as examples, the following formulae breakdowns can be suggested: (Na+)2(Ca2+)(Cd2+)(Sb3–)2 and (Yb2+)2(Cd2+)(Sb3–)2.
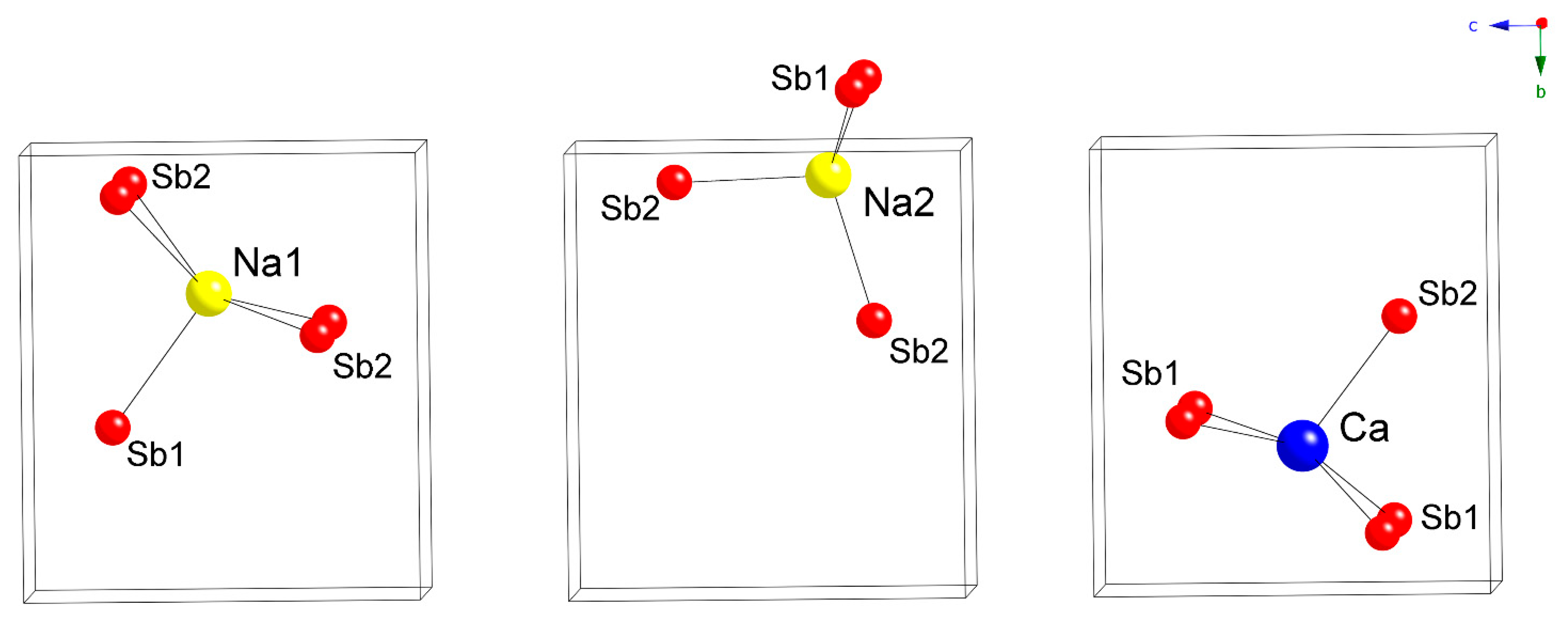
Since the [CdSb2]4– layers made of corner-shared CdSb4 tetrahedra are the same in both structures, it is obvious that packing of the interlayer Yb2+ cations in Yb2CdSb2 will have to differ from that of the Na+ cations in Na2CaCdSb2. Indeed, in Yb2CdSb2, the interlayer Yb atoms have CN6 (distorted octahedral), while in Na2CaCdSb2, Na1 has CN5 (distorted square-pyramidal) and Na2 has CN4 (distorted tetrahedral). Relevant distances from all four refined structures are tabulated in Table 4 and Table 5. The coordination environments of the three cationic sites in Na2CaCdSb2 are depicted in Figure 2. Careful inspection of the data shows that Na2 in particular is very tightly coordinated by the neighboring Sb atoms with Na2–Sb distances approaching the sum of the single-bonded radii of Sb (Pauling radius 1.39 Å) and Na (Pauling radius 1.57 Å) [14]. For the two known structures with K, namely, K2SrCdSb2 and K2BaCdSb2, the respective K2–Sb distances are on the order of 3.4 Å [2], also matching the sum of the single-bonded radii of Sb and K (Pauling radius 2.02 Å) [14]. This finding is unusual, since the electronic structure calculations for K2SrCdSb2 and K2BaCdSb2 indicate the mostly “passive” (i.e., space-filler and electron-donor) role of the alkali metals in these compounds, with minimal contribution from K near the Fermi level [2]. By comparison, the Sr and Ba atoms make more significant contributions to the DOS in the same energy window. This has also been the case for some other ternary antimonides such as Ba3Cd2Sb4 [15], Ba2Cd2Sb3 [16] and Ba2ZnSb2 [17], which we have studied as well.

Table 4.
Selected interatomic distances (Å) in Na2CaCdSb2 and Na2SrCdSb2.

Table 5.
Selected interatomic distances (Å) in for two independent samples of Na2EuCdSb2.
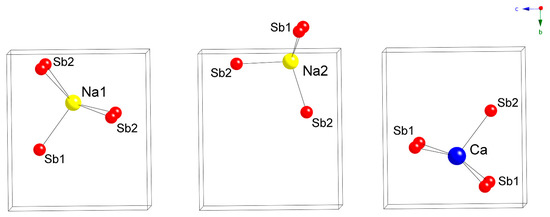
Figure 2.
Cation coordination polyhedra in the crystal structure of Na2CaCdSb2.
3. Discussion
The observations above imply that, although the title compounds fit the classical description of Zintl phases [18], some degree of covalency of the interactions for the presumed "cations” should also be expected.
In the context of the presented results, it is instructive to draw attention to the fact that, in three of the four refined structures, Na2 is the position that shows “heavier” electron density than Na. In the case of the Ca-bearing compound, the freely refined site occupation factor (SOF) for Na2 was 112%, but in the case of the Eu-bearing compound, the freely refined SOF for Na2 was 156%. At the same time, Na1 had an SOF that did not deviate much from unity and never showed a tendency to be over 100%. The same applies to the Sb and Cd positions as well. The SOF of Ca in Na2CaCdSb2 was 98%, the SOF of Sr in Na2SrCdSb2 was 96% and the SOF of Eu in Na2EuCdSb2 was 84%. There was another Na2EuCdSb2 crystal, from an independent experiment with a different Na:Eu ratio, that showed no SOF deviations (Table 2). Given the above, we proposed a model with a statistical admixture of Na/Ca, Na/Sr and Na/Eu on both Ca (Sr and Eu) and Na2 sites, which was refined successfully (Table 1 and Table 2). All final refined compositions are very close to the ideal “2-1-1-2”, indicating that the number of available valance electrons is still near the optimal value despite the disorder on both cation sites.
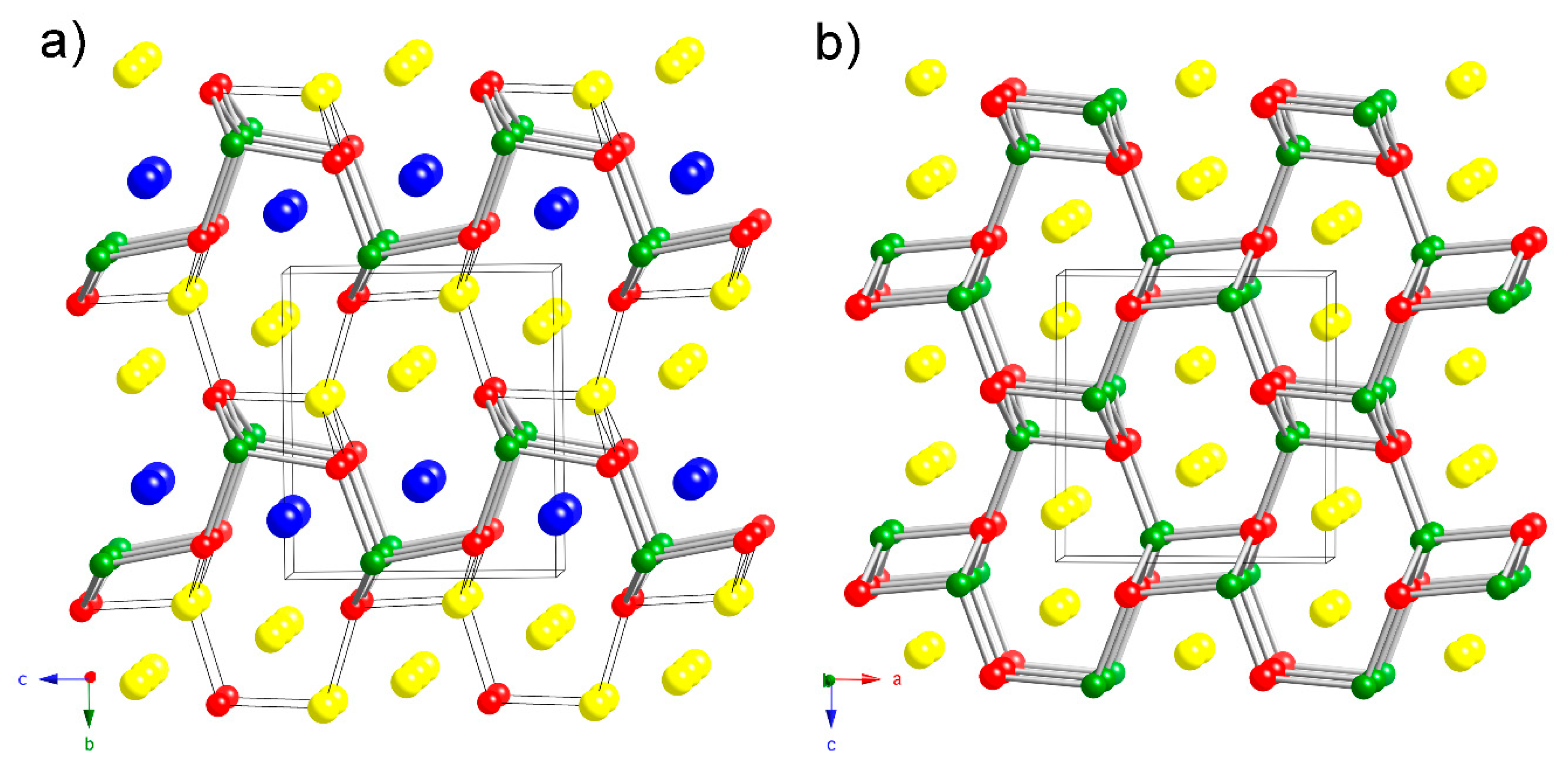
There are other possible structural models that can be proposed to explain the experimental observations described in the previous paragraph. Although the previous electronic structure calculations have suggested little covalency of the K–Sb interactions, one may notice that Na2–Sb and Cd–Sb distances are not too far off (Table 4 and Table 5). In our schematic representation of the structure in Figure 1 and Figure 2, only bonds that can be considered as mostly covalent (i.e., Cd–Sb interactions) are drawn. If one takes the liberty to consider the 3.1 Å Na2–Sb bond as covalent, a different schematic representation emerges, as seen in Figure 3. In this view, the structure can now be said to be more 3D, rather than layered, and derived from the well-known TiNiSi structure type (ternary variant of CeCu2) [19]. From the many compounds adopting that structure, the most useful comparison that can be made is to the structure of NaCdSb [20]. Simply put, in NaCdSb (= Na2Cd2Sb2), if 50% of the Cd atoms are replaced by Na atoms, the resultant chemical formula will be Na3CdSb2. Naturally, since the chemical bonding for this arrangement requires 18 electrons per formula unit for TiNiSi: 4(Ti) + 10(Ni) + 4(Si) = 18; and 8 electrons per formula for NaCdSb: 1(Na) + 2(Cd) + 5(Sb) = 8, as shown by Nuspl et al. [19], the bonding in the derived Na3CdSb2 will not be optimized. The dimensionality of the framework must be reduced as a result, and further steps must be taken to satisfy the octets of all atoms.
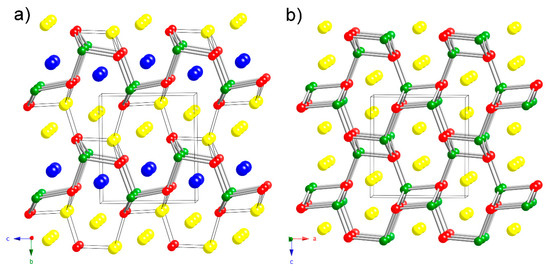
Figure 3.
Side-by-side comparison between the crystal structure of Na2CaCdSb2 (a) and that of NaCdSb (TiNiSi-structure type) (b). The judiciously drawn Cd–Sb bonds (cylinders) and the 3.1 Å Na2–Sb bonds (black lines) emphasize the [NaCdSb2]3– framework in Na2CaCdSb2 (a) and its similarity to the [Cd2Sb2]2– framework in NaCdSb (b). Unit cells are outlined and the origin of the unit cell in (a) is shifted in order to facilitate the comparison. Color code: Na in yellow, Ca in blue, Cd in green and Sb in red.
Considering the structural analogy drawn between Na2CaCdSb2 and NaCdSb, we may propose a different explanation for the observed anomalies concerning the SOF on Na2 site—what if the “heavy” Na2 was a partially occupied Cd, i.e., NaCaCd2–xSb2? Model refinements showed that the SOF of this Cd atom in NaCaCd2–xSb2 was just 26%, while in NaEuCd2–xSb2, where the Na-overoccupancy was extreme, the SOF of the Cd atom refined instead of Na was ca. 36%. This means that such hypothetical structures will be severely deprived of valence electrons to exist as variants of NaCdSb. Therefore, we argue that NaCaCd2–xSb2, NaSrCd2–xSb2 and NaEuCd2–xSb2 are unlikely structural models, even though precedents for similar structures with a large amount of vacancies exist, such as NaIn0.67Bi [21], for example.
We also considered models with statistical admixtures of Na/Cd on the Na2 site, as well as statistical admixtures Na/Ca, Na/Sr and Na/Eu on the Ca, Sr and Eu sites. They could be refined satisfactorily and the CIFs are provided as Supplementary Material. Here, we will just give the final refined formulae from these trial refinements: Na1.96Ca0.98Cd1.04Sb2, Na2.01Sr0.94Cd1.05Sb2 and Na2.05Eu0.81Cd1.14Sb2. Distinguishing these refined compositions from the ones in Table 1 and Table 2 via independent chemical analyses is clearly impossible. Both structural scenarios are plausible from the chemical bonding point of view, as the electron counts are nearly identical and satisfy the valence rules. The observation that the overoccupancy on the Na2 site was observed to increase in the order Ca > Sr > Eu, i.e., from lighter to heavier, taken together with the fact that we were able to obtain two crystals from two independent samples of Na2EuCdSb2, where the nominal Na: Eu were varied and the resultant structure refinements were in correlation with that (Table 2) appear to support the hypothesis for Na/Ca, Na/Sr and Na/Eu disorder on both sites. However, the model with statistical admixtures of Na/Cd on the Na2 site, and Na/Ca, Na/Sr and Na/Eu on the Ca, Sr and Eu sites, cannot be ruled out completely. This requires additional experimental and computational work, which is beyond the scope of this study.
4. Materials and Methods
The synthesis is described in detail in the prior publication focused on the synthesis and the crystal structures of K2SrCdSb2, K2BaCdSb2 and Na2YbCdSb2 [2]. The experimental data for making Na2CaCdSb2, Na2SrCdSb2 and Na2EuCdSb2 are mentioned there as well, and the existence of these compounds with the same crystal structure as K2SrCdSb2, K2BaCdSb2 and Na2YbCdSb2 was inferred from the respective unit-cell parameters. Here, we only reiterate the need to maintain inert atmosphere every step of the way, because most of the complications with the synthesis and the crystallographic studies arise from the extreme air- and moisture-sensitivity, which necessitates due diligence—work in a glove-box filled with argon gas (with oxygen and moisture levels below 1 ppm) or under vacuum with both starting materials and reaction products.
In the earlier study, X-ray powder diffraction data were taken using a Rigaku MiniFlex powder diffractometer, which was operated inside a nitrogen-filled glove box to prevent contact of the samples with air and moisture. For this follow up work, X-ray powder diffraction patterns were not pursued. All the characterization steps were done via single-crystal X-ray diffraction.
The crystals were small and did not have well defined morphologies. Air stability was an issue (vide supra), therefore single crystals were selected in the glove-box (under a microscope) and cut to desired dimensions (around 0.1 mm) with a scalpel. This was easily done because the crystals were very brittle. Two techniques were used to handle the crystals prior to mounting them on the goniometer—either covering them in dry Paratone-N oil and scooping them with MitiGen plastic loops or sealing them in thin-walled glass capillaries.
The intensity data were acquired using a nitrogen gas stream to alleviate the problem with air-sensitivity. Temperature was maintained at 170 K throughout the experiments. Multiple crystals had to be tried before the ones with the best quality were identified. Intensity data were collected using a Bruker SMART CCD diffractometer. The Bruker-supplied software packages [22,23] were used to manage data collection and for the integration of the measured reflections. Absorption correction was applied using SADABS [24]. Refinements by least-square minimizations on F2 were carried out with the aid of the SHELXL program [25]. The atomic coordinates from the previous reports on related antimonide phases [2] were suitable starting models, and the first refinement cycles quickly yielded reasonable conventional residual factors. However, there were some issues with the displacement parameters, which required checking the site occupation factors (SOFs) of all atomic positions. In three of the four refinements, the site occupied by the divalent metals (Ca, Sr and Eu) were found to be slightly underoccupied, while one of the two Na-sites exhibited unphysical overoccupancy (SOF exceeded 150% in the case of the Eu-compound). Considering the Zintl concept and the drive for attaining optimized bonding in this structure, the metal sites had to be modeled as statistically distributed Ca/Na, Sr/Na and Eu/Na on these two positions. Doing so allowed us to achieve proper fitting and very reasonable agreement between the displacement parameters for all atoms in each structure (Table 3). Final difference Fourier maps, in all cases, were featureless, and the final refined formulae are listed in Table 1 and Table 2. Alternative structural models with Cd contributing to the “heavy” Na2 were also considered, as discussed in Section 3. The results from these trial refinements are available as supporting information.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/inorganics10120265/s1, Figure showing a structural representation of Na1.96Ca0.98Cd1.04Sb2 with anisotropic displacement parameters; CIF from the refinements for Na2EuCdSb2 (cation-ordered) where the Eu and Na2 sites are refined with freed SOFs. CIFs from the refinements for Na1.96Ca0.98Cd1.04Sb2, Na2.01Sr0.94Cd1.05Sb2 and Na2.05Eu0.81Cd1.14Sb2, where disorder was modeled as statistical admixtures of Na/Cd on the Na2 site, and Na/Ca, Na/Sr and Na/Eu admixing on the Ca, Sr and Eu sites.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.S. and S.B.; methodology, formal analysis, B.S. and S.B.; investigation, B.S. and S.B.; resources, S.B.; data curation, S.B.; writing—original draft preparation, S.B.; writing—review and editing, S.B.; supervision, S.B.; project administration, S.B.; funding acquisition, S.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the US Department of Energy through a grant DE-SC0008885.
Data Availability Statement
The corresponding crystallographic information files (CIF) for all structures have been deposited with CSD, and the data for this paper can be obtained free of charge via http://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/conts/retrieving.html (accessed on 13 December 2022) (or from the CCDC, 12 Union Road, Cambridge CB2 1 EZ, UK; Fax: +44-1223-336033; E-mail: deposit@ccdc.cam.ac.uk). Depository numbers are 2215538–2215541.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Xia, S.-Q.; Bobev, S. Cation-anion interactions as structure directing factors: Structure and bonding of Ca2CdSb2 and Yb2CdSb2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 4049–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saparov, B.; Saito, M.; Bobev, S. Syntheses, and crystal and electronic structures of the new Zintl phases Na2ACdSb2 and K2ACdSb2 (A = Ca, Sr, Ba, Eu, Yb): Structural relationship with Yb2CdSb2 and the solid solutions Sr2–xAxCdSb2, Ba2–xAxCdSb2 and Eu2–xYbxCdSb2. J. Solid State Chem. 2011, 184, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunbunmi, M.O.; Baranets, S.; Bobev, S. Structural complexity and tuned thermoelectric properties of a new polymorph of the Zintl phase Ca2CdSb2 with a non-centrosymmetric monoclinic structure. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 61, 10888–10897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovchinnikov, A.; Darone, G.; Saparov, B.; Bobev, S. Exploratory work in the quaternary system of Ca–Eu–Cd–Sb: Synthesis, crystal, and electronic structures of new Zintl solid solutions. Materials 2018, 11, 2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, M.; Pan, M.-Y.; Xia, S.-Q.; Tao, X.-T.; He, H.; Darone, G.M.; Bobev, S. Synthesis, crystal and electronic structures, and properties, of the new pnictide semiconductors A2CdPn2 (A = Ca, Sr, Ba, Eu; Pn = P, As). Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 8020–8027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saparov, B.; Broda, M.; Ramanujachary, K.V.; Bobev, S. New quaternary Zintl phases—Synthesis, crystal and electronic structures of KA2Cd2Sb3 (A = Ca, Sr, Ba, Eu, Yb). Polyhedron 2010, 29, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balvanz, A.; Qu, J.; Baranets, S.; Ertekin, E.; Gorai, P.; Bobev, S. New n-type Zintl phases for thermoelectrics: Discovery, structural characterization, and band engineering of the compounds A2CdP2 (A = Sr, Ba, Eu). Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 10697–10707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Balvanz, A.; Baranets, S.; Bobev, S.; Gorai, P. Computational design of thermoelectric alloys through optimization of transport and dupability. Mater. Horiz. 2022, 9, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooley, J.A.; Promkhan, P.; Gangopadhyay, S.; Donadio, D.; Pickett, W.E.; Ortiz, B.R.; Toberer, E.S.; Kauzlarich, S.M. High Seebeck coefficient and unusually low thermal conductivity near ambient temperatures in layered compound Yb2–xEuxCdSb2. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Lee, J.; Shin, S.; Jo, H.; Moon, D.; Ok, K.M.; You, T.-S. Chemical driving force for phase-transition in the Ca2–xRExCdSb2 (RE = Yb, Eu; 0.11(1) ≤ x ≤ 1.36(2)) system. Cryst. Growth Des. 2020, 20, 746–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, K.P.; Chen, S.; Donadio, D.; Kauzlarich, S.M. Solid solution Yb2–xCaxCdSb2: Structure, thermoelectric properties, and quality factor. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 13596–13606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauble, A.K.; Crawford, C.M.; Adamczyk, J.M.; Wood, M.; Fettinger, J.C.; Toberer, E.S.; Kauzlarich, S.M. Deciphering defects in Yb2–xCaxCdSb2and their impact on thermoelectric properties. Chem. Mater. 2022, 34, 9228–9239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Lin, C.; Chen, J.; Xu, F.; Yang, S.; Li, B.; Yang, G.; Luo, M.; Ye, N. α-Ca2CdP2 and β-Ca2CdP2: Two polymorphic phosphide-based infrared nonlinear crystals with distorted NLO-active tetrahedral motifs realizing large second harmonic generation effects and suitable band gaps. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 60, 7553–7560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauling, L. The Nature of the Chemical Bond, 3rd ed.; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Saparov, B.; Xia, S.-Q.; Bobev, S. Synthesis, structure and bonding of the Zintl phase Ba3Cd2Sb4. Inorg. Chem. 2008, 47, 11237–11244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saparov, B.; He, H.; Zhang, H.; Greene, R.; Bobev, S. Synthesis, crystallographic and theoretical studies of the new Zintl phases Ba2Cd2Pn3 (Pn = As, Sb), and the solid solutions (Ba1–xSrx)2Cd2Sb3 and Ba2Cd2(Sb1–xAsx)3. Dalton Trans. 2010, 39, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saparov, B.; Bobev, S. Isolated [ZnPn2]4– chains in the Zintl phases Ba2ZnPn2 (Pn = As, Sb, Bi)—Synthesis, structure and bonding. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 5173–5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesper, R. The Zintl-Klemm concept—A historical survey. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2014, 640, 2639–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuspl, G.; Polborn, K.; Evers, J.; Landrum, G.A.; Hoffmann, R. The four-connected net in the CeCu2 structure and its ternary derivatives. Its electronic and structural properties. Inorg. Chem. 1996, 35, 6922–6932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savelsberg, G.; Schäfer, H. Ternaere Pnictude und Chalkogenide von Alkalimetallen und IB-bzw. IIB-Elementen. Z. Naturforsch. 1978, 33B, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobev, S.; Sevov, S.C. Five ternary Zintl phases in the systems alkali metal–indium–bismuth. J. Solid State Chem. 2002, 163, 436–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SMART, Version 2.10; Bruker Analytical X-ray Systems, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2003.
- SAINT, Version 6.45; Bruker Analytical X-ray Systems, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2003.
- SADABS, Version 2.10; Bruker Analytical X-ray Systems, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2003.
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. C 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).