Noise Reduction of OCT Images Based on the External Patch Prior Guided Internal Clustering and Morphological Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
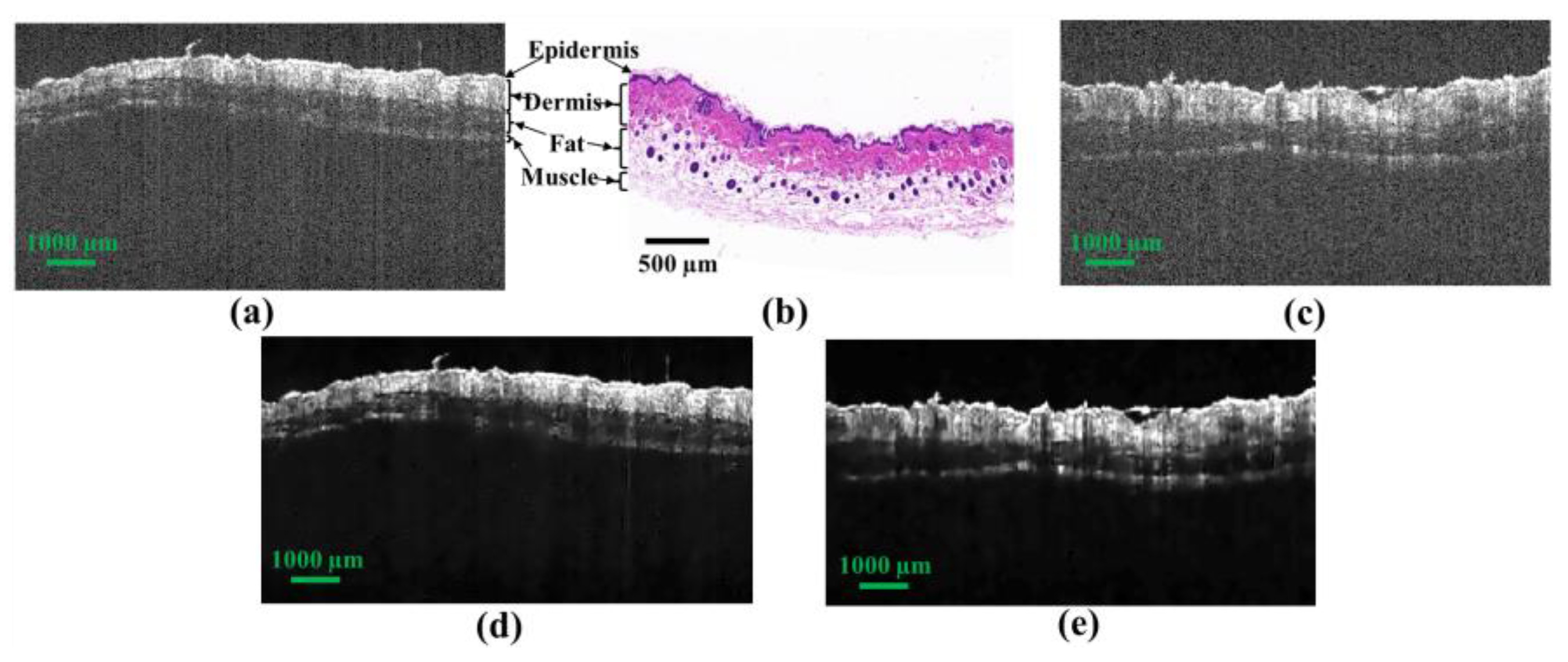
2.1. Biological Tissue Preparation and OCT Imaging
2.2. Acquisition and Preprocessing of OCT Images
2.3. Noise Reduction Algorithm Based on E2PGICMA
| Algorithm 1: Proposed algorithm for denoising of OCT images |
| 1. Input: noisy image y, noise standard deviation σ, learned GMM model parameter Θ’ and K. |
| 2. Initialization: |
| (1) Choose a reasonable scaling factor γ for controlling the re-estimation of noise variance; |
| (2) Initialize x0 = y; σ0 = σ. |
| 3. Optimization and Compute xl via Equation (1); |
| 4. Update σl, such that (σl)2 = γ(σ2 − ). |
| 5. Beginning the background reduction |
| (1) Input the speckle-reduced OCT image, |
| (2) Image binarization with Ostu algorithm, |
| (3) Region filling (Mask: 5 × 5) and finding the upper boundary of OCT image, |
| (4) Reset the gray level above the upper boundary of the OCT image to zero. |
| 6. Output: denoised image x. |
2.4. Validation for the Noise Reduction of OCT Images
3. Experimental Results
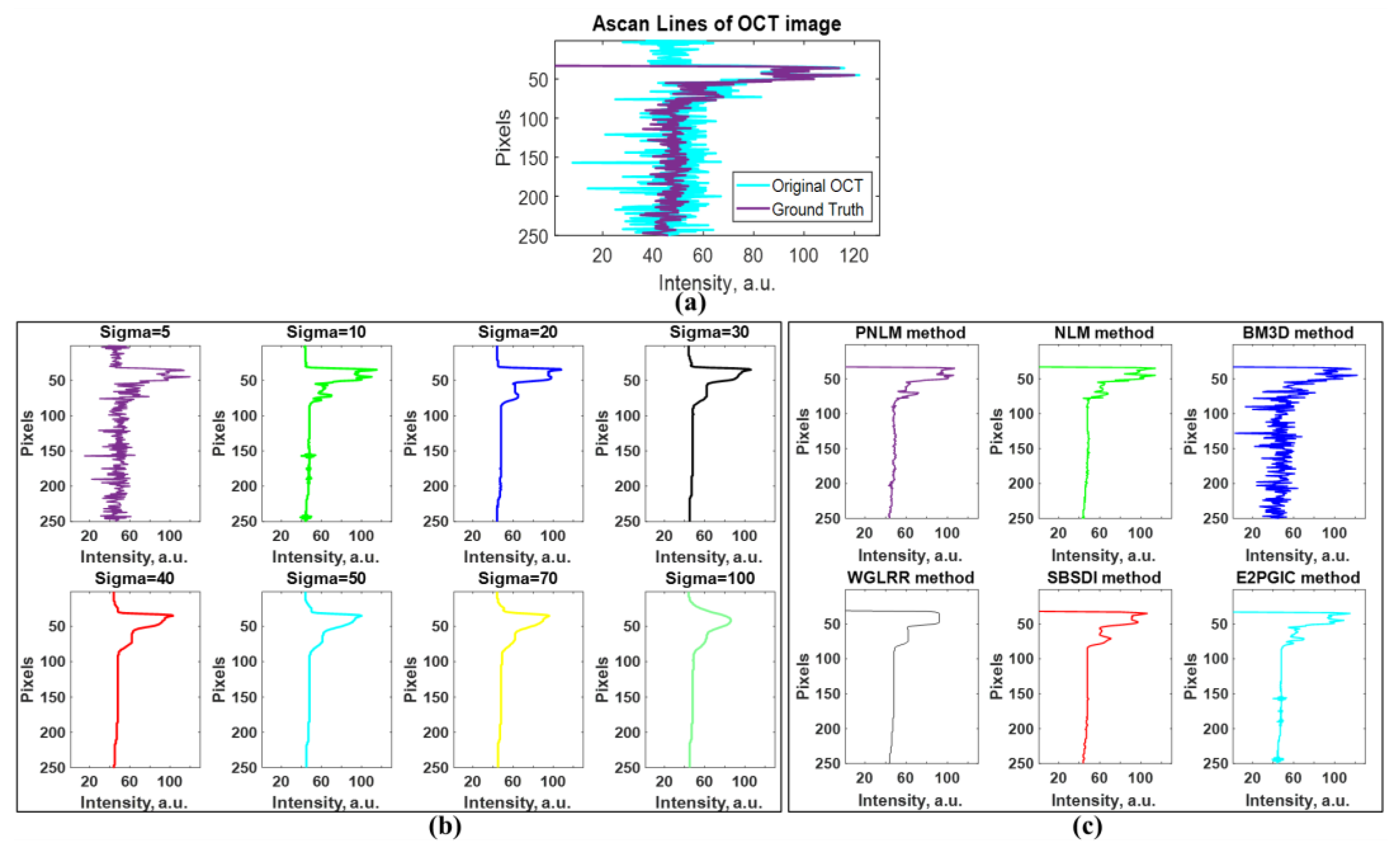
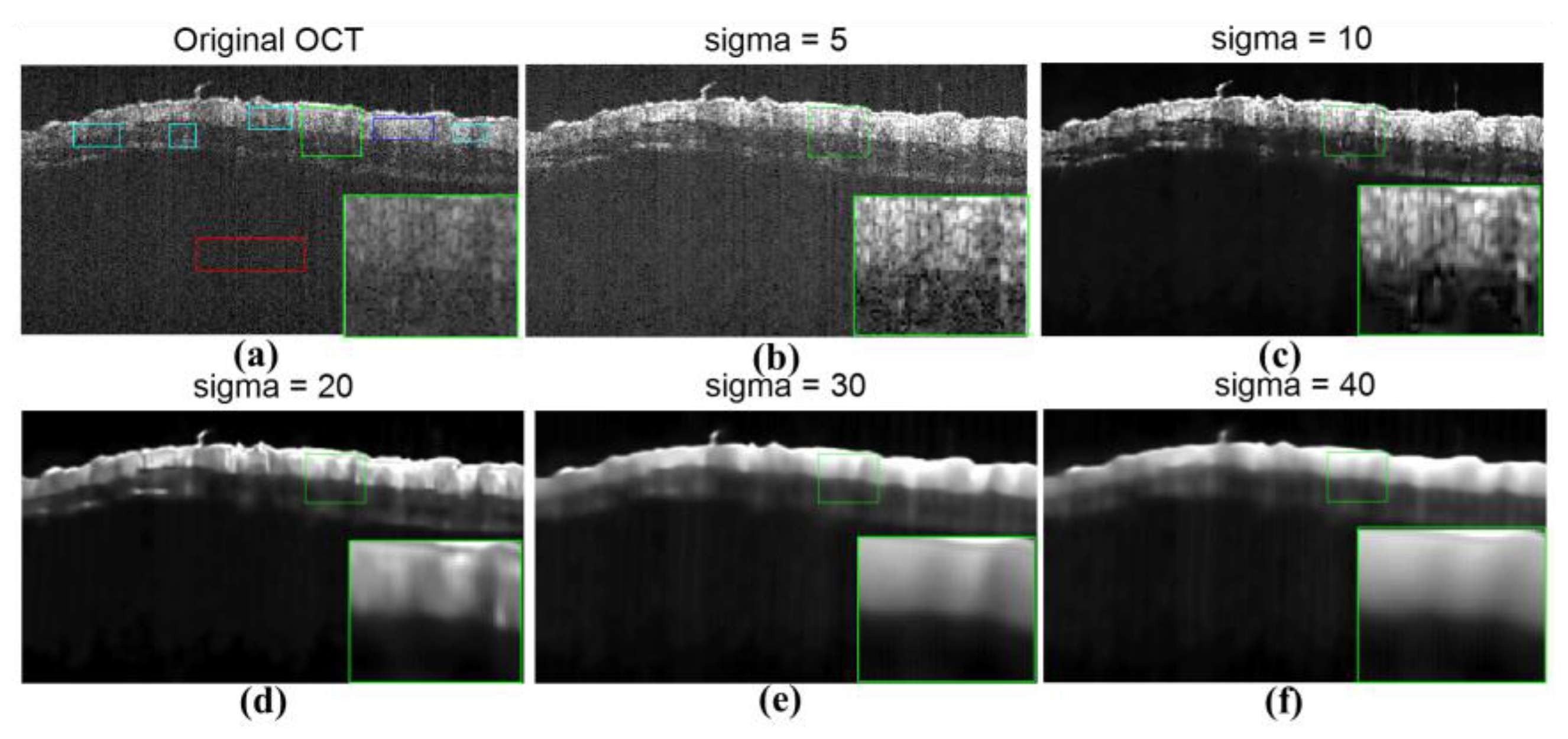
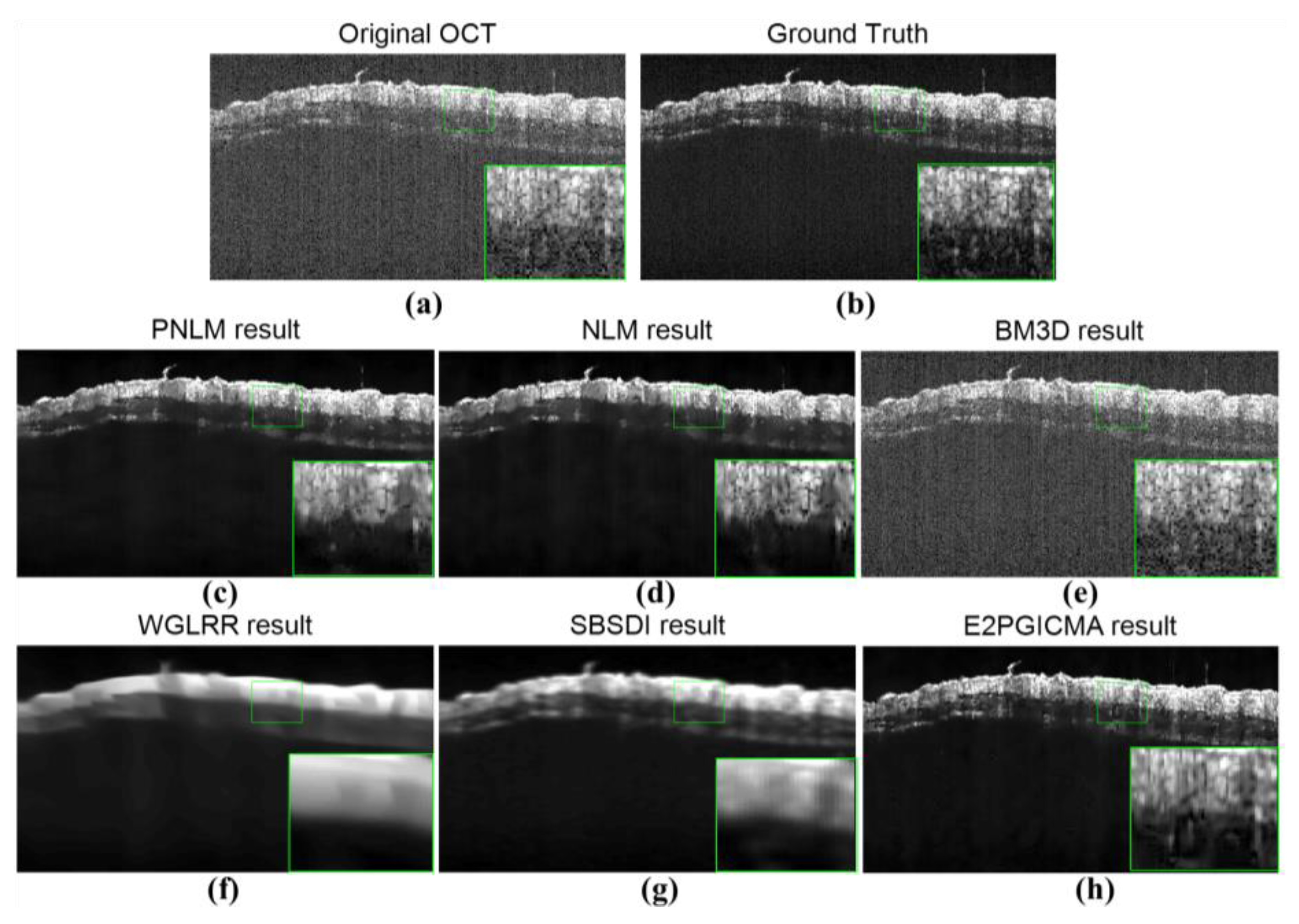
3.1. Results of Speckle Noise Reduction with the E2PGICMA-Based Method
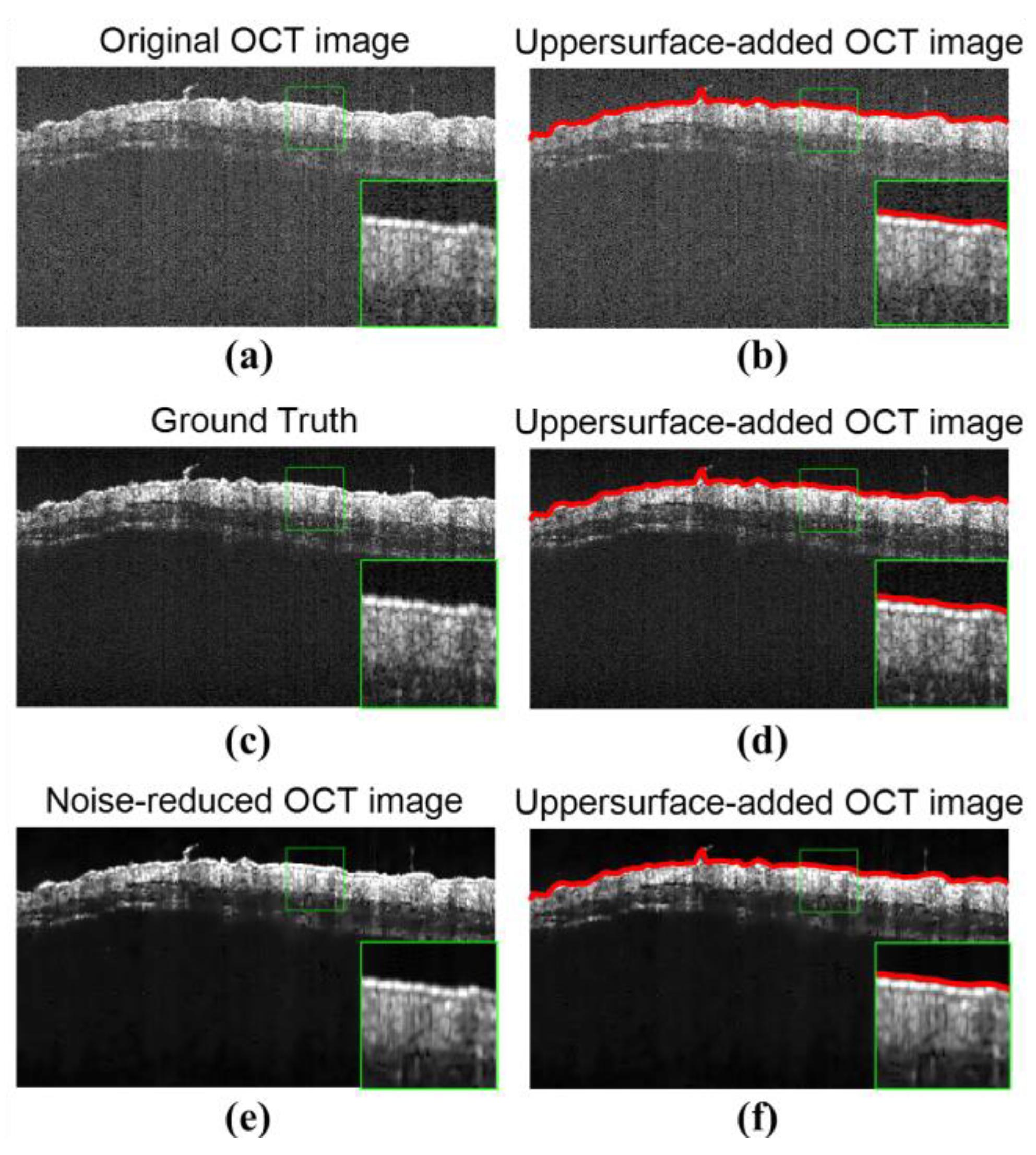
3.2. Results of Background Reduction with the Region Filling Algorithm
3.3. Quantitative Validation of Noise Reduction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, D.; Swanson, E.A.; Lin, C.P.; Schuman, J.S.; Stinson, W.G.; Chang, W.; Hee, M.R.; Flotte, T.; Gregory, K.; Fujimoto, G. Optical coherence tomography. Science 1991, 254, 1178–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chou, H.Y.; Huang, S.L.; Tjiu, J.W.; Chen, H.H. Dermal epidermal junction detection for full-field optical coherence tomography data of human skin by deep learning. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2021, 87, 101833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sleman, A.A.; Soliman, A.; Elsharkawy, M.; Giridharan, G.; Ghazal, M.; Sandhu, H.; Schaal, S.; Keynton, R.; Elmaghraby, A.; El-Baz, A. A novel 3D segmentation approach for extracting retinal layers from optical coherence tomography images. Med. Phys. 2021, 48, 1584–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Hui, H.; Jing, J.; Tian, F.; Jiang, J.; Yang, X.; Chen, Y.; Tian, J. Structure attention co-training neural network for neovascularization segmentation in intravascular optical coherence tomography. Med. Phys. 2022, 46, 1723–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrasco-Zevallos, O.M.; Viehland, C.; Keller, B.; Draelos, M.; Kuo, A.N.; Toth, C.A.; Izatt, J.A. Review of intraoperative optical coherence tomography: Technology and applications [Invited]. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 1607–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmitt, J.M.; Xiang, S.H.; Yung, K.M. Speckle in optical coherence tomography. J. Biomed. Opt. 1999, 4, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yin, H.; Hong, J.; Wang, C.; He, B.; Chen, Z.; Li, Q.; Xue, P.; Zhang, X. Speckle reducing OCT using optical chopper. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 4021–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iftimia, N.; Bouma, B.E.; Tearney, G.J. Speckle reduction in optical coherence tomography by “path length encoded” angular compounding. J. Biomed. Opt. 2003, 8, 260–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desjardins, A.E.; Vakoc, B.J.; Oh, W.Y.; Motaghiannezam, S.M.; Tearney, G.J.; Bouma, B.E. Angle-resolved optical coherence tomography with sequential angular selectivity for speckle reduction. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 6200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kennedy, B.F.; Hillman, T.R.; Curatolo, A.; Sampson, D.D. Speckle reduction in optical coherence tomography by strain compounding. Opt. Lett. 2010, 35, 2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Caneiro, D.; Read, S.A.; Collins, M.J. Speckle reduction in optical coherence tomography imaging by affine-motion image registration. J. Biomed. Opt. 2011, 16, 116027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pircher, M.; Gotzinger, E.; Leitgeb, R.A.; Fercher, A.F.; Hitzenberger, C.K. Speckle reduction in optical coherence tomography by frequency compounding. J. Biomed. Opt. 2003, 8, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Ou, H.; Sun, C.; Chui, P.C.; Yang, V.X.D.; Lam, E.Y.; Wong, K.K.Y. Wavelet domain compounding for speckle reduction in optical coherence tomography. J. Biomed. Opt. 2013, 18, 096002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, J.; Tao, D.; Quan, Y.; Wong, D.W.K.; Cheung, G.C.M.; Akiba, M.; Liu, J. Speckle reduction in 3D optical coherence tomography of retina by A-scan reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 35, 2270–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhu, W.; Cheng, X.; Xiang, D.; Shi, F. Speckle noise reduction in optical coherence tomography images based on edge-sensitive cGAN. Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 5129–5146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, B.; Zhu, Y.K. Speckle reduction in optical coherence tomography images of human finger skin by wavelet modified BM3D filter. Opt. Commun. 2013, 291, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Li, S.; McNabb, R.P.; Nie, Q.; Kuo, A.N.; Toth, C.A.; Izatt, J.A.; Farsiu, S. Fast acquisition and reconstruction of optical coherence tomography images via sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2013, 32, 2034–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anantrasirichai, N.; Nicholson, L.; Morgan, J.E.; Erchova, I.; Mortlock, K.; North, R.V.; Albon, J.; Achim, A. Adaptive-weighted bilateral filtering and other pre-processing techniques for optical coherence tomography. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2014, 38, 526–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, M.; Tang, C.; Chen, M.; Qiu, Y.; Lei, Z. Texture preservation and speckle reduction in optical coherence tomography using the shearlet-based total variation algorithm. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2019, 122, 265–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aum, J.; Kim, J.H.; Jeong, J. Effective speckle noise suppression in optical coherence tomography images using non-local means denoising filter with double Gaussian anisotropic kernels. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, D43–D50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Gao, J.; Li, A. Probability-based non-local means filter for speckle noise suppression in optical coherence tomography images. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 994–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.; Li, S.; Nie, Q.; Izatt, J.A.; Toth, C.A.; Farsiu, S. Sparsity based denoising of spectral domain optical coherence tomography images. Biomed. Opt. Express 2012, 3, 927–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kafieh, R.; Rabbani, H.; Selesnick, I. Three-dimensional data-driven multi scale atomic representation of optical coherence tomography. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2015, 34, 1042–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, F.; Cai, N.; Gu, Y.; Hu, D.; Ma, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X. DeSpecNet: A CNN-based method for speckle reduction in retinal optical coherence tomography images. Phys. Med. Biol. 2019, 64, 175010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Huang, Z.; Liu, X.; Meng, X.; You, Y.; Liu, G.; Yang, K.; Maier, A.; Ren, Q.; Lu, Y. Noise reduction in optical coherence tomography images using a deep neural network with perceptually-sensitive loss function. Biomed. Opt. Express 2020, 11, 817–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhu, W.; Yu, K.; Chen, Z.; Shi, F.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, Y.; Peng, Y.; Bao, D.; Feng, S.; et al. Semi-supervised capsule cGAN for speckle noise reduction in retinal OCT images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2021, 40, 1168–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Tang, C.; Hao, F.; Chen, M.; Lei, Z. Texture preservation and speckle reduction in poor optical coherence tomography using the convolutional neural network. Med. Image Anal. 2020, 64, 101727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Bang, H.; Lee, E.; Won, Y.; Kim, K.; Park, S.; Yoo, H.; Lee, S. Lateral image reconstruction of optical coherence tomography using one-dimensional deep deconvolution network. Lasers Surg. Med. 2022, 54, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, T.; Singh, M.; Çetintaş, E.; Luo, Y.; Rivenson, Y.; Larin, K.V.; Ozcan, A. Neural network-based image reconstruction in swept-source optical coherence tomography using undersampled spectral data. Light Sci. Appl. 2021, 10, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhang, L.; Yu, H. External patch prior guided internal clustering for image denoising. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 603–611. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.W.; Ma, L.F.; Jiang, W.P.; Luo, S.T.; Zhang, X.R.; Liao, H.E. Optimized optical coherence tomography imaging with Hough transform-based fixed-pattern noise reduction. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 32087–32096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheimariotis, G.; Chatzizisis, Y.S.; Koutkias, V.G.; Toutouzas, K.; Giannopoulos, A.; Riga, M.; Chouvarda, I.; Antoniadis, A.P.; Doulaverakis, C.; Tsamboulatidis, I.; et al. Automatic detection of lumen border in intravascular OCT images. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2017, 151, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, A.G.; Conjeti, S.; Carlier, S.G.; Dutta, P.K.; Kastrati, A.; Laine, A.F.; Navab, N.; Katouzian, A.; Sheet, D. Lumen segmentation in intravascular optical coherence tomography using backscattering tracked and initialized random walks. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2016, 20, 606–614. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.; Luo, S.; Huo, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Xie, H.; Kang, H. An imaging analysis and reconstruction method for multiple-micro-electro-mechanical system mirrors-based off-centre scanning optical coherence tomography probe. Laser Phys. Lett. 2020, 17, 075601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Ma, Q.; Li, M.; Luan, D.; Kang, H. Quantitative investigation of laser ablation based on real-time temperature variations and OCT images for laser treatment applications. Lasers Surg. Med. 2022, 54, 459–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoran, D.; Weiss, Y. From learning models of natural image patches to whole image restoration. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pizurica, A.; Jovanov, L.; Huysmans, B.; Zlokolica, V.; De Keyser, P.; Dhaenens, F.; Philips, W. Multiresolution denoising for optical coherence tomography: A review and evaluation. Curr. Med. Imaging Rev. 2008, 4, 270–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Cao, L.; Chen, J.; Zheng, X. Speckle noise reduction for optical coherence tomography images via non-local weighted group low-rank representation. Laser Phys. Lett. 2017, 14, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, B.; Mandal, M.; Mitra, P.; Chatterjee, J. Attenuation corrected-optical coherence tomography for quantitative assessment of skin wound healing and scar morphology. J. Biophotonics. 2021, 14, e202000357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kande, N.A.; Dakhane, R.; Dukkipati, A.; Yalavarthy, P.K. SiameseGAN: A generative model for denoising of spectral domain optical coherence tomography images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2021, 40, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zeng, Z.; Shen, H.; Zheng, X.; Dai, P.; Ouyang, P. DN-GAN: Denoising generative adversarial networks for speckle noise reduction in optical coherence tomography images. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2020, 55, 101632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.W.; Ma, Q.; Xin, S.H.; Peng, R.Y.; Kang, H.X. Quantitative and qualitative evaluation of supercontinuum laser-induced cutaneous thermal injuries and their repair with OCT images. Lasers Surg. Med. 2021, 53, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boppart, S.A.; Brown, J.Q.; Farah, C.S.; Kho, E.; Marcu, L.; Saunders, C.M.; Sterenborg, H.J.C.M. Label-free optical imaging technologies for rapid translation and use during intraoperative surgical and tumor margin assessment. J. Biomed. Opt. 2017, 23, 021104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

| σ | SNR | PSNR | CNR | SSIM | EPI | ENL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original (σ = 5) | 17.93 | 31.21 | 3.65 | 257.36 | 1.52 | 27.59 |
| 5 | 17.93 | 31.21 | 3.66 | 257.39 | 1.53 | 27.60 |
| Original (σ = 10) | 20.99 | 34.27 | 6.65 | 249.38 | 0.30 | 37.84 |
| 10 | 20.99 | 34.27 | 6.63 | 249.40 | 0.31 | 37.87 |
| Original (σ = 20) | 17.93 | 31.21 | 3.66 | 257.36 | 1.53 | 27.60 |
| 20 | 18.90 | 32.18 | 10.96 | 223.87 | 0.11 | 72.04 |
| Original (σ = 30) | 18.05 | 31.33 | 13.91 | 211.14 | 0.09 | 93.61 |
| 30 | 18.05 | 31.33 | 13.88 | 210.95 | 0.09 | 92.99 |
| Original (σ = 40) | 17.69 | 30.97 | 15.14 | 203.81 | 0.08 | 97.84 |
| 40 | 17.69 | 30.97 | 15.13 | 203.77 | 0.09 | 97.79 |
| Original (σ = 50) | 17.41 | 30.69 | 15.73 | 197.80 | 0.08 | 106.17 |
| 50 | 17.41 | 30.69 | 15.75 | 197.75 | 0.08 | 105.89 |
| Original (σ = 70) | 17.03 | 30.31 | 16.87 | 189.25 | 0.07 | 127.29 |
| 70 | 17.04 | 30.33 | 17.07 | 189.24 | 0.07 | 131.24 |
| Original (σ = 100) | 16.42 | 29.70 | 17.81 | 168.30 | 0.06 | 168.28 |
| 100 | 16.43 | 29.71 | 18.04 | 168.56 | 0.07 | 166.04 |
| Methods | SNR | PSNR | XCOR | CNR | SSIM | EPI | ENL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original | 20.99 | 34.27 | 0.9958 | 6.65 | 249.38 | 0.30 | 37.84 |
| BM3D | 15.85 | 18.99 | 0.9867 | 2.32 | 254.04 | 0.49 | 23.42 |
| PNLM | 20.69 | 33.97 | 0.9953 | 8.27 | 243.87 | 0.24 | 45.50 |
| NLM | 20.77 | 34.05 | 0.9952 | 6.96 | 248.44 | 0.26 | 34.98 |
| WGLRR | 17.37 | 30.65 | 0.9924 | 15.31 | 200.18 | 0.05 | 83.82 |
| SBSDI | 17.22 | 30.40 | 0.9916 | 4.17 | 207.00 | 0.08 | 14.06 |
| Proposed method (σ = 10) | 20.99 | 34.27 | 0.9959 | 6.63 | 249.40 | 0.31 | 37.87 |
| σ | 5 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 70 | 100 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Times cost (s) | 35.74 | 41.27 | 78.04 | 216.11 | 255.74 | 288.10 | 354.83 | 553.90 |
| Method | BM3D | PNLM | WGLRR | NLM | SBSDI | E2PGICMA (σ = 10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Times cost (s) | 3.61 | 3.04 | 29.92 | 38.22 | 12.94 | 41.27 |
| Methods | BM3D | PNLM | NLM | WGLLR | SBSDI | This Method (σ = 10) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NRR [%] | 89.12 | 88.94 | 90.23 | 88.80 | 88.88 | 89.99 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, Y.; Li, Y.; Gao, T.; Tang, X. Noise Reduction of OCT Images Based on the External Patch Prior Guided Internal Clustering and Morphological Analysis. Photonics 2022, 9, 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9080543
Fan Y, Li Y, Gao T, Tang X. Noise Reduction of OCT Images Based on the External Patch Prior Guided Internal Clustering and Morphological Analysis. Photonics. 2022; 9(8):543. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9080543
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Yingwei, Yangxi Li, Tianxin Gao, and Xiaoying Tang. 2022. "Noise Reduction of OCT Images Based on the External Patch Prior Guided Internal Clustering and Morphological Analysis" Photonics 9, no. 8: 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9080543
APA StyleFan, Y., Li, Y., Gao, T., & Tang, X. (2022). Noise Reduction of OCT Images Based on the External Patch Prior Guided Internal Clustering and Morphological Analysis. Photonics, 9(8), 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9080543





