Security of Bennett–Brassard 1984 Quantum-Key Distribution under a Collective-Rotation Noise Channel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Operation of the BB84 Protocol
2.1. Preparation and Measurement
2.2. Parameter Estimation
2.3. Sifting
2.4. Key Map
2.5. Error Correction
2.6. Privacy Amplification
3. Collective-Rotation Noise
4. Security Analysis of the Intercept-and-Resend Attack
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bennett, C.H.; Brassard, G. Quantum cryptography. Theor. Comput. Sci. 2014, 560, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisin, N.; Ribordy, G.; Tittel, W.; Zbinden, H. Quantum cryptography. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2002, 74, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirola, S.; Andersen, U.L.; Banchi, L.; Berta, M.; Bunar, D.; Colbeck, R.; Englund, D.; Gehring, T.; Lupo, C.; Ottaviani, C.; et al. Advances in quantum cryptography. Adv. Opt. Photonics 2020, 12, 1012–1236. [Google Scholar]
- Scarani, V.; Kurtsiefer, C. The black paper of quantum cryptography: Real implementation problems. Theor. Comput. Sci. 2014, 560, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Garhwal, S. State-of-the-art survey of quantum cryptography. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2021, 28, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, W.Y. Quantum key distribution with high loss: Toward global secure communication. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 91, 057901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoller, P.; Beth, T.; Binosi, D.; Blatt, R.; Briegel, H.; Bruss, D.; Calarco, T.; Cirac, J.I.; Deutsch, D.; Eisert, J.; et al. Quantum information processing and communication. Eur. Phys. J. D. 2005, 36, 203–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Śliwczyński, Ł.; Krehlik, P.; Lipiński, M. Optical fibers in time and frequency transfer. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2010, 21, 075302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngabireng, C.; Ambomo, S.; Dinda, P.T.; Moubissi, A. Loss effects in the spectra of polarization modulational instability in weakly birefringent optical fibers. J. Opt. 2011, 13, 085201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.W.; Hwang, T. Quantum dialogue protocols immune to collective noise. Quantum Inf. Process. 2013, 12, 2131–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertz, M.; Kampermann, H.; Shadman, Z.; Bruß, D. Quantum key distribution with finite resources: Taking advantage of quantum noise. Phys. Rev. A 2013, 87, 042312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruß, D. Optimal eavesdropping in quantum cryptography with six states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 81, 3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senekane, M.; Mafu, M.; Petruccione, F. Six-state symmetric quantum key distribution protocol. J. Quant. Inf. Sci. 2015, 5, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarani, V.; Acin, A.; Ribordy, G.; Gisin, N. Quantum cryptography protocols robust against photon number splitting attacks for weak laser pulse implementations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 57901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.C.W.; Curty, M.; Walenta, N.; Xu, F.; Zbinden, H. Concise security bounds for practical decoy-state quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 2014, 89, 022307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralph, T.C. Continuous variable quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. A 1999, 61, 010303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillery, M. Quantum cryptography with squeezed states. Phys. Rev. A 2000, 61, 022309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, L.D.S.; Borelli, L.F.; Roversi, J.A.; Vidiella-Barranco, A. Performance analysis of continuous-variable quantum key distribution using non-Gaussian states. Quantum Inf. Process. 2022, 21, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K.; Waks, E.; Yamamoto, Y. Differential phase shift quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 037902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stucki, D.; Brunner, N.; Gisin, N.; Scarani, V.; Zbinden, H. Fast and simple one-way quantum key distribution. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 194108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafu, M.; Marais, A.; Petruccione, F. A necessary condition for the security of coherent-one-way quantum key distribution protocol. Appl. Math. Inf. Sci. 2014, 8, 2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosshans, F.; Van Assche, G.; Wenger, J.; Brouri, R.; Cerf, N.J.; Grangier, P. Quantum key distribution using gaussian-modulated coherent states. Nature 2003, 421, 238–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laudenbach, F.; Pacher, C.; Fung, C.H.F.; Poppe, A.; Peev, M.; Schrenk, B.; Hübel, H. Continuous-Variable quantum key distribution with gaussian modulation—The theory of practical implementations. Adv. Quantum Technol. 2018, 1, 1870011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pironio, S.; Acín, A.; Brunner, N.; Gisin, N.; Massar, S.; Scarani, V. Device-independent quantum key distribution secure against collective attacks. N. J. Phys. 2009, 11, 045021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodhead, E.; Acín, A.; Pironio, S. Device-independent quantum key distribution with asymmetric CHSH inequalities. Quantum 2021, 5, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Shi, R.; Ruan, X.; Guo, Y.; Mao, Y.; Feng, Y. Monte Carlo-based security analysis for multi-mode continuous-variable quantum key distribution over underwater channel. Quantum Inf. Process. 2022, 21, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curty, M.; Xu, F.; Cui, W.; Lim, C.C.W.; Tamaki, K.; Lo, H.K. Finite-key analysis for measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, H.K.; Curty, M.; Qi, B. Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 130503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.H.; Qin, S.F.; Shi, W.M.; Yang, Y.G. Measurement-device-independent continuous variable semi-quantum key distribution protocol. Quant. Inf. Process. 2022, 21, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibson, P.; Erven, C.; Godfrey, M.; Miki, S.; Yamashita, T.; Fujiwara, M.; Thompson, M.G. Chip-based quantum key distribution. Nat. Comm. 2017, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenenko, H.; Sibson, P.; Hart, A.; Thompson, M.G.; Rarity, J.G.; Erven, C. Chip-based measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Optica 2020, 7, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwek, L.C.; Cao, L.; Luo, W.; Wang, Y.; Sun, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, A.Q. Chip-based quantum key distribution. AAPPS Bull. 2021, 31, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Zhou, L.; Zhong, W.; Sheng, Y.B. Faithful entanglement distribution using quantum multiplexing in noisy channel. Eur. Lett. 2021, 135, 40001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Huang, Y.; Du, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Geng, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, K. Advances in chip-based quantum key distribution. Entropy 2022, 24, 1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orieux, A.; Diamanti, E. Recent advances on integrated quantum communications. J. Opt. 2016, 18, 083002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaki, K.; Lütkenhaus, N. Unconditional security of the Bennett 1992 quantum key-distribution protocol over a lossy and noisy channel. Phys. Rev. A 2004, 69, 032316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.B. Fault tolerant quantum key distribution protocol with collective random unitary noise. Phys. Rev. A 2005, 72, 050304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasselli, F.; Kampermann, H.; Bruß, D. Finite-key effects in multipartite quantum key distribution protocols. N. J. Phys. 2018, 20, 113014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.J. Robust multiparty quantum secret key sharing over two collective-noise channels. Phys. A: Stat. Mech. Appl. 2006, 361, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Deng, F.G.; Zhou, H.Y. Efficient quantum key distribution over a collective noise channel. Phys. Rev. A 2008, 78, 022321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Xiu, X.M.; Gao, Y.J.; Chi, F. Deterministic secure quantum communication against collective-dephasing noise by using EPR pairs and auxiliary photons. Opt. Commun. 2009, 282, 1688–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, X.M.; Dong, L.; Gao, Y.J.; Chi, F. Quantum key distribution protocols with six-photon states against collective noise. Opt. Commun. 2009, 282, 4171–4174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.B.; Deng, F.G. Efficient quantum entanglement distribution over an arbitrary collective-noise channel. Phys. Rev. A 2010, 81, 042332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.K.; Dong, L.; Xiu, X.M.; Gao, Y.J. A deterministic secure quantum communication protocol through a collective rotation noise channel. Int. J. Quantum Inf. 2010, 8, 1389–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wen, Q.; Liu, B.; Gao, F.; Sun, Y. Robust and efficient quantum private comparison of equality with collective detection over collective-noise channels. Sci. China Phys. Mech. 2013, 56, 1670–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, G.; Huang, Y. Robust quantum secure direct communication with a quantum one-time pad over a collective-noise channel. Sci. China Physics, Mech. Astron. 2011, 54, 942–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Tsai, C.; Hwang, T. Fault tolerant two-step quantum secure direct communication protocol against collective noises. Sci. China Phys. Mech. 2011, 54, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Qiao-Yan, W.; Heng-Yue, J.; Su-Juan, Q.; Fei, G. Fault tolerant quantum secure direct communication with quantum encryption against collective noise. Chin. Phys. B 2012, 21, 100308. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, T. Fault tolerant channel-encrypting quantum dialogue against collective noise. Sci. China Phys. Mech. 2015, 58, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.Y. Quantum secure direct dialogue over collective noise channels based on logical Bell states. Quantum Inf. Process. 2015, 14, 1487–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Pan, Z.; Zheng, J.; Sun, F.; Ye, X.; Yuan, K. The security analysis of quantum SAGR04 protocol in collective-rotation noise channel. Chin. J. Electron. 2015, 24, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Chen, Y. Three stage quantum cryptography protocol under collective-rotation noise. Entropy 2015, 17, 2919–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garapo, K.; Mafu, M.; Petruccione, F. Intercept-resend attack on six-state quantum key distribution over collective-rotation noise channels. Chin. Phys. B 2016, 25, 070303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, J.; Li, C.; Li, H.; Yang, Y.; Chen, X. The security analysis of quantum B92 protocol in collective-rotation noise channel. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 2019, 58, 1326–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.G.; Gao, S.; Li, D.; Zhou, Y.H.; Shi, W.M. Three-party quantum secret sharing against collective noise. Quantum Inf. Process. 2019, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.F.; Ma, W.P. Multiparty quantum secure direct communication immune to collective noise. Quantum Inf. Process. 2019, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.W.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Tian, X.X.; Qian, Y.H.; Zheng, S.H. Fault tolerant controlled quantum dialogue against collective noise. Chin. Phys. B 2020, 29, 010304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, W.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ma, H. Development of quantum private queries protocol on collective-dephasing noise channel. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waks, E.; Zeevi, A.; Yamamoto, Y. Security of quantum key distribution with entangled photons against individual attacks. Phys. Rev. A 2002, 65, 052310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żukowski, M.; Zeilinger, A.; Horne, M.A.; Ekert, A.K. "Event-ready-detectors" Bell experiment via entanglement swapping. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1993, 71, 4287–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.; Pei, S.; Song, B.; Zhong, K. Deterministic secure quantum communication over a collective-noise channel. Sci. China Phys. Mech. 2009, 52, 1913–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, Y.H.; Pan, Z.S.; Sun, F.Q.; Li, N.; Li, L.L. Security analysis of BB84 protocol in the collective-rotation noise channel. Acta Phys. Sin. 2016, 65, 30302. [Google Scholar]
- Curty, M.; Lütkenhaus, N. Intercept-resend attacks in the Bennett-Brassard 1984 quantum-key-distribution protocol with weak coherent pulses. Phys. Rev. A 2005, 71, 062301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
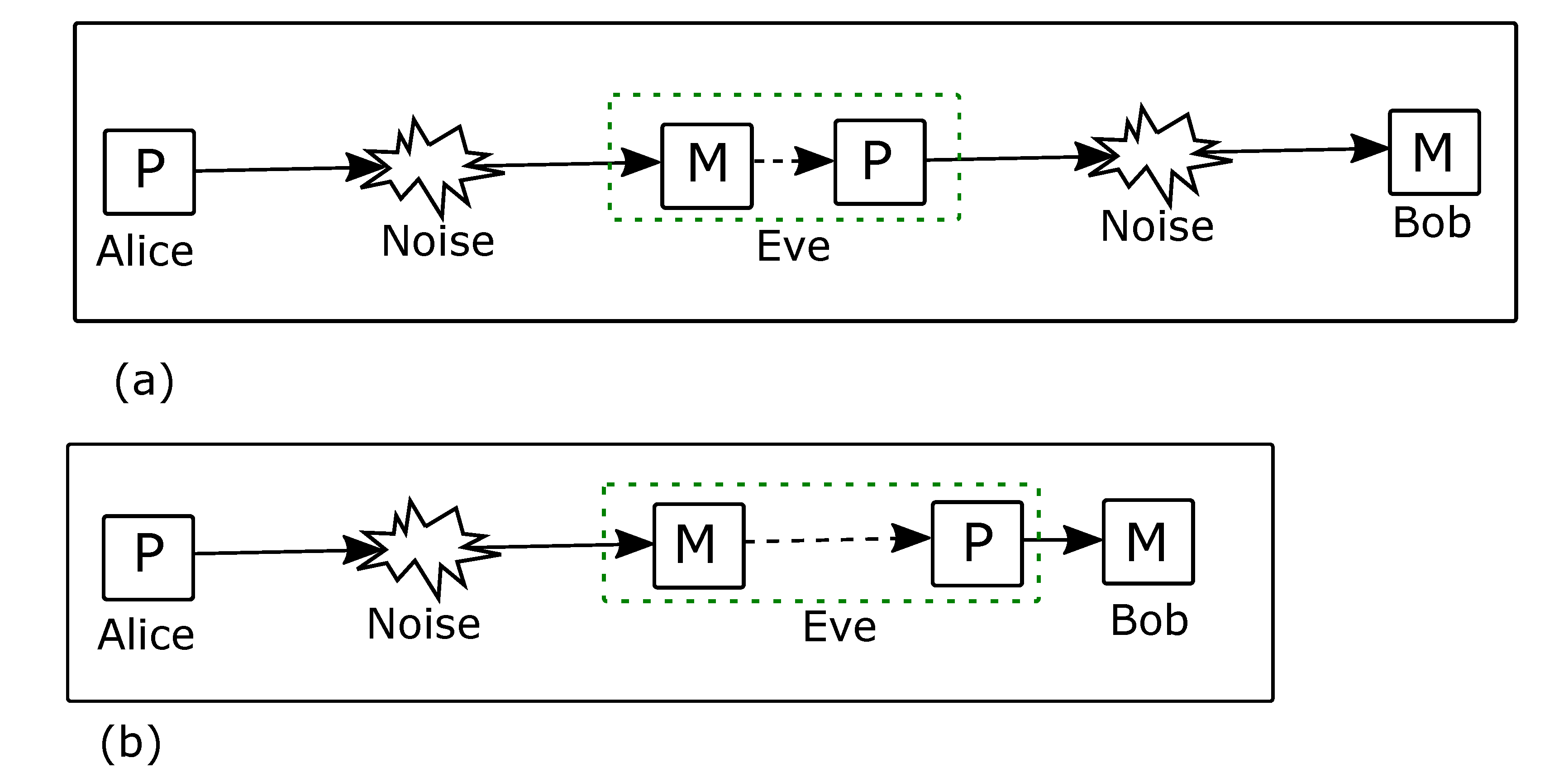
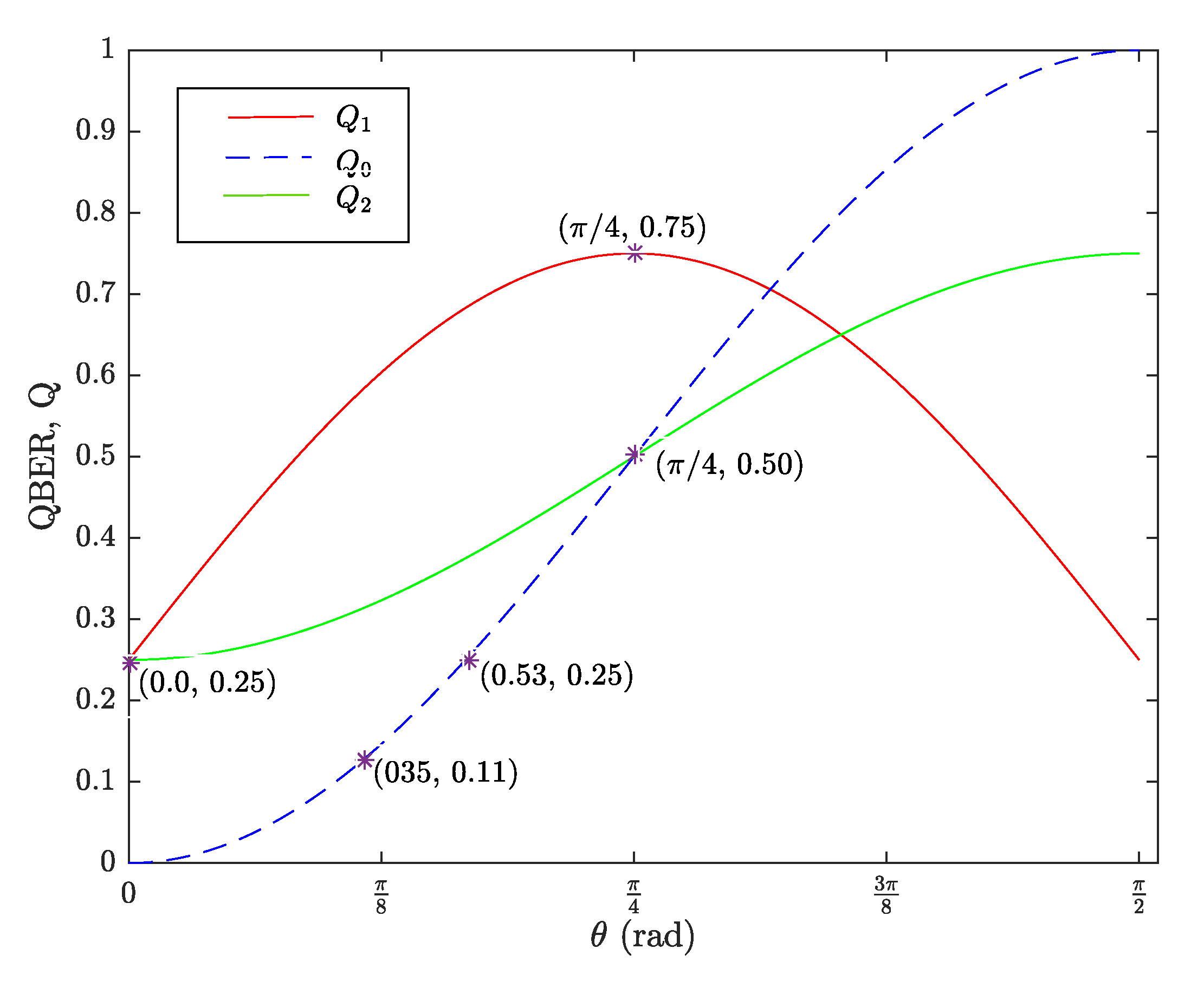
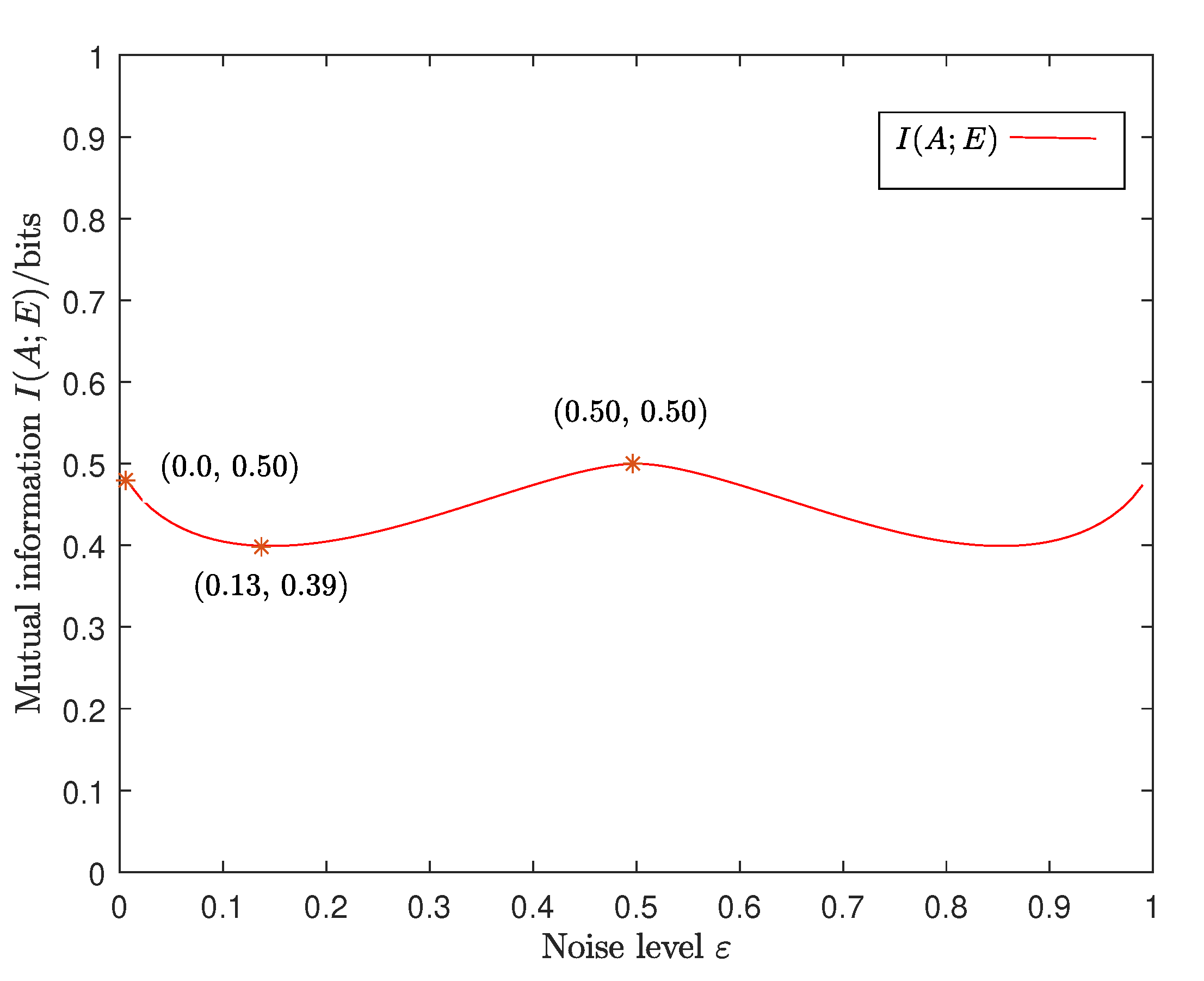
| Alice Sends | Eve Obtains | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| |0〉 | |1〉 | |+〉 | |−〉 | |
| Eve Sends | Bob Obtains | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| |0〉 | |1〉 | |+〉 | |−〉 | |
| Alice Sends | Bob Receives | |||
| |0〉 | |1〉 | |+〉 | |−〉 | |
| a | b | c | d | |
| b | a | d | c | |
| d | c | a | b | |
| c | d | b | a | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mafu, M.; Sekga, C.; Senekane, M. Security of Bennett–Brassard 1984 Quantum-Key Distribution under a Collective-Rotation Noise Channel. Photonics 2022, 9, 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9120941
Mafu M, Sekga C, Senekane M. Security of Bennett–Brassard 1984 Quantum-Key Distribution under a Collective-Rotation Noise Channel. Photonics. 2022; 9(12):941. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9120941
Chicago/Turabian StyleMafu, Mhlambululi, Comfort Sekga, and Makhamisa Senekane. 2022. "Security of Bennett–Brassard 1984 Quantum-Key Distribution under a Collective-Rotation Noise Channel" Photonics 9, no. 12: 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9120941
APA StyleMafu, M., Sekga, C., & Senekane, M. (2022). Security of Bennett–Brassard 1984 Quantum-Key Distribution under a Collective-Rotation Noise Channel. Photonics, 9(12), 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9120941





