Abstract
Quantum key distribution (QKD) offers information-theoretical security, while real systems are thought not to promise practical security effectively. In the practical continuous-variable (CV) QKD system, the deviations between realistic devices and idealized models might introduce vulnerabilities for eavesdroppers and stressors for two parties. However, the common quantum hacking strategies and countermeasures inevitably increase the complexity of practical CV systems. Machine-learning techniques are utilized to explore how to perceive practical imperfections. Here, we review recent works on secure CVQKD systems with machine learning, where the methods for detections and attacks were studied.
1. Introduction
Quantum key distribution (QKD) is an unconditionally secure quantum communication technology to transmit secure keys between the authorized sender (Alice) and receiver (Bob). Its information-theoretical security is harnessed by some fundamental laws of quantum mechanics such as the Heisenberg uncertainty principle, the quantum no-cloning theorem, and the association and nonlocality of particle entanglement [1]. QKD is divided into two classes, namely discrete-variable QKD [2,3] and continuous-variable (CV) QKD [4,5]. CVQKD has a series of theoretical, experimental, and implemental achievements promising a higher key and simpler and safer detecting techniques [6]. The Gaussian-modulated coherent state (GMCS) protocol is one of the most favorable CVQKD schemes to date, which in theory has been proven secure against arbitrary collective attacks and coherent attacks based on some basic assumptions [7].
However, a new challenge is the practical security proof for real CV systems in a more rigorous manner. In practice, realistic devices are not modeled as absolutely secure and perfect. There are security loopholes exposed by the imperfect devices for Eve to successfully steal secret key information, which is an effective quantum hacking strategy. These various attacks are against various components such as sources, detectors, and channels. For example, in practical CV systems, Eve may try to exploit the imperfections to launch local oscillator (LO) fluctuation attacks [8], wavelength attacks [9,10], and calibration attacks [11] related to LO signals; saturation attacks [12] and homodyne-detector-blinding attacks [13] in imperfections of homodyne detectors. In the last two decades, the rise of quantum hacking strategies has gone hand in hand with miscellaneous landmarks such as the maximum possible distance [14,15] and the standardization of QKD [16]; a review on the subject is given in [17].
To prevent or catch such attacks, many approaches have been proposed [17]. The first is to patch existent protocols, such as addition or modification in hardware [18,19]. The second is to devise novel QKD schemes, such as device-independent QKD [20] and measurement-device-independent QKD [21]. A more universal countermeasure consists of placing additional optical devices on the system. A wavelength filter is effective against the wavelength attack, and a proper monitor at detections may counter the homodyne-detector-blinding attack. However, this approach is limited by our understanding of the devices and complete knowledge of attacks. Although a security patch could defeat a certain type of attack, patched countermeasures themselves might open other loopholes and add burden to the system. Besides, the performance of the traditional approaches is difficult to quantify.
Machine learning, one of the most swiftly developed interdisciplinary concepts, has been a powerful tool for face recognition, autonomous driving, medical imaging, and so on. In recent years, the cross-cutting studies of machine learning and quantum communication [22], quantum computation [23], and quantum optics [24], have become a brand-new idea and paradigm after theories, experiments, and computational simulations. In 2018, Reference [25] used support vector regression to predict parameters in practical CV systems for the first time, which effectively replaces extra monitoring devices. Many teams respectively proposed that different neural networks and random forest models be used for real-time parameter optimization [26,27,28]. Besides, in [29], a distance-weighted k-nearest-neighbors-based machine-learning detector was proposed to directly deal with the raw secret key, but not the system parameters, which is a new idea for improving the performance of CV systems. Reference [30] employed a backpropagation neural network to adjust the modulation variance to an optimal value and to furnish a higher achievable key rate and a more efficient parameter optimization than the local search algorithm in the practical four-state CVQKD system.
Based on these schemes, the efficient performance of machine learning for secure communication in the CVQKD system has been confirmed. Many researchers are aware that machine-learning techniques would have huge advantages in attack and defense in practical CV systems. In this paper, we review recent works on secure CVQKD with machine learning, focusing mainly on the practical imperfections. We briefly introduce the most commonly used distribution protocol flow of CVQKD and security analysis in Section 2. In Section 3.1, we review countermeasures that utilize machine-learning techniques to perceive a certain typical attack and multiple typical attacks, respectively. Then, we turn to improving the success rate of quantum hacking attacks fueled by machine-learning advances in Section 3.2. Finally, we give a brief conclusion in Section 4.
2. Background
This section briefly introduces the protocol and security in continuous-variable quantum information theory.
2.1. Protocol
CVQKD protocols can be divided into several types depending on the prepared state: the modulation schemes, the detection strategies, etc. More protocols can be found in an earlier review [7]. We describe the distribution protocol flow of the CVQKD protocol based on the most commonly used GG02 protocol [4]. The GG02 protocol is a Gaussian modulation protocol based on the coherent state rather than the squeezed state.
Alice prepares 2N random variables , , where the random numbers follow the Gaussian distribution with variance .
Alice sends the N coherent states distributed in phase space coordinates to Bob through the untrusted quantum channel.
Bob first prepares the corresponding N random binary variables . The prepared and the homodyne detector are used to achieve random measurement of the X and P regular components of the quantum state sent by Alice. Then, Bob obtains N corresponding to .
Bob sends his modulation of N random binary variables to Alice. After Alice obtains the measurement-based selection information, the selected measurement-based information is matched and filtered with her modulation information. Alice and Bob complete the quantum state preparation, sending, and measurement process. The legal parties simultaneously obtain N pairs of raw keys .
Alice and Bob perform data postprocessing on shared random variables such as parameter estimation, data negotiation, error correction, privacy amplification, and so on.
2.2. Security Analysis
This paper mainly considered the security of the CVQKD protocol under the collective attack. Eve prepares N auxiliary states, performs individual operations on the quantum states sent by Alice to the channel, and stores the output states in the quantum memory. Eve monitors the channel, and after the legal parties complete the classical negotiation and privacy amplification, Eve performs the joint measurement on the saved states.
We performed the secure information under the collective attack in the asymptotic case of reverse reconciliation, without the finite length effect [31]. The formula for the security key rate is:
where is the Shannon mutual information between Alice and Bob and is the Holevo bound [32] for Eve’s accessible information. is expressed as:
is expressed as:
where . are the symplectic eigenvalues given by:
with:
are the symplectic eigenvalues given by:
with:
The last symplectic eigenvalue .
The experimental parameters of the system involved in the above formulas include: , where is Alice’s modulation variance.
is the total noise referring to the channel input, where T is the quantum channel transmittance. is the detection-added noise referring to the channel input, where is the efficiency of Bob’s homodyne detector and is the detector’s electronic noise.
is the channel-added noise referring to the channel input, where is the excess noise of the system, and its value does not include Bob’s internal noise.
Based on the above equation, we are able to obtain the security key rate for the asymptotic case Equation (1) under the collective attack. Besides, the security in the finite key case based on the uncertainty principle and the composable security were proven against collective attacks [33,34].
3. Quantum Hacking Attacks and Countermeasures with Machine Learning
Studies focused on the practical vulnerabilities in CVQKD systems, which can start from two perspectives. On the one hand, legitimate distant parties (Alice and Bob) want to securely communicate in the presence of Eve. Once having perceived the type of certain attack, they must interrupt or defend accordingly. On the other hand, eavesdroppers (Eve) want to steal the fractional or intact key information without being detected by Alice and Bob. The application of machine learning is both a severe challenge and a golden opportunity from two perspectives. The following provides the recent works.
3.1. Countermeasures with Machine Learning
3.1.1. Countermeasures on a Targeted Attack
For example, consider the wavelength attack. The linear discriminant analysis support vector machine (LDA-SVM) algorithm was applied to successfully detect the wavelength attack via analyzing optical spectrum signals in practical CVQKD systems by He et al. [35].
Targeting the wavelength-independent properties of the beam-splitter (BS), Eve launches the wavelength attack by switching LO signals and different wavelengths sent from Alice, which is unsuspected by Alice and Bob [9]. To prevent wavelength attacks, one of the known countermeasures is to randomly add a wavelength filter and monitor the LO intensity in the practical CV system. A more general solution is to perform the real-time shot noise measurement [36]. As we mentioned above, this kind of patched countermeasure increases the complexity of the system.
The traditional machine learning model is divided into two parts, namely feature extraction and classification, which correspond here to LDA and the SVM [37]. SVMs have gained prominence in the field of data classification and are constantly evolving [38,39,40]. These methods seek to find an optimal hyperplane that maximizes the Euclidean distance from the hyperplane to the support vectors. If its generalization lies on nonlinear hypersurfaces, SVMs are combined with different kernel functions such as the linear, polynomial, sigmoid, and radial basis functions [41]. LDA maps the digital spectrum data with labels in a high-dimensional space onto a low-dimensional space, which maximizes the between-class scatter and minimizes the within-class scatter. The preprocessed features are used as the input to train and test the SVM classifier.
Therefore, He et al. [35] proposed an intelligent monitoring model with the LDA-SVM algorithm embedded in it based on an optical spectrum analyzer (OSA). They collected normal signal spectra and the forged signal spectra of the wavelength attack by Eve as the dataset. Optical spectrum signals were transformed into digital optical spectrum data by OSA. Figure 1 shows the procedure of the algorithm’s processing module. The dataset was divided into the training set and the testing set and input into the LDA algorithm module to extract the features. The SVM detector was trained and evaluated on these specially selected features. Having superior performance, the optical spectrum intelligent monitoring model can be deployed in a common communication environment. This intelligent model can identify abnormal optical spectrum signals in the center wavelength of the signals of 1528.0 nm, 1540.5 nm, and 1548.5 nm and even 1549.1 nm and 1550.1 nm, for safe communication in CVQKD systems (the recognition accuracy is 100%). In theory, except for the center wavelength of the signals, the model based on the LDA-SVM can deal with signal intensities, peak values, and other important indexes.
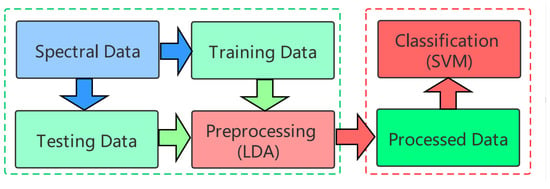
Figure 1.
Training and predicting procedure of the algorithm’s processing module. The LDA algorithm preprocesses the spectral data and inputs them into the SVM classifier. From [35].
The other typical attack is the calibration attack. A hidden Markov-model (HMM) was utilized to detect the calibration attack in real CV systems by Mao et al. [42].
The calibration attack is a powerful attack that arises from the loopholes of the LO intensity calibration and the clock generation processing in the practical CVQKD setup [11]. In calibration attacks, Eve intercepts a fraction of the signal pulses during quantum transmission when launching a partial intercept–resend attack [43]. Then, Eve prepares the perfect shape of quantum states and resends this to Bob, while Bob’s shot noise estimation remains unchanged. This allows Eve to control the shot noise estimated by two parties. One of the presented strategies to solve this is to add the second homodyne detector on a split part of Bob’s LO to monitor the real-time shot noise [36].
As a typical machine-learning model for classification, the HMM is a reasonable model for describing the transient processing and dynamic properties of the problems, which are the building blocks of detecting anomaly intrusions in time series [44,45,46]. Its targeted problems have two characteristics: one is based on computational sequence analysis; the other is that there exist two kinds of data, namely observed sequences (quadrature values measured by Bob) and the underlying state path (interference factors).
After analysis, Mao et al. [42] found that the variation of the measured quadrature values reflected whether the calibration attack was performed. However, Bob’s measurement values are affected by environmental disturbances, the drawbacks of devices, and the attacks by eavesdroppers. Based on this, Mao et al. established an HMM-based calibration attack recognition, which sufficiently analyzes training data only influenced by common interferences but eavesdroppers. If Eve launches the calibration attack, the trained model will detect the interference values according to the changed quadrature values of Bob’s measurement. The whole procedure has two parts, as illustrated in Figure 2. The offline training process is the top-half part above the dotted line, while the recognition process is the bottom-half part below the dotted line. During the training, Mao et al. collected the normal dataset of previous communication processing by the peak–valley-seeking method and then trained the parameters of the HMM with the Baum–Welch algorithm. Normally, a well-trained HMM will output a high probability value for normal data and a low probability value for attacked data. When the predicted probability value is smaller than a certain threshold, the system is attacked and the received attacked sequences are discarded. The HMM-based calibration attack recognition can precisely detect almost all of the attacked data under 30 km with a high recognition precision of 98.735%. According to this idea, if the unattacked training data under the condition of a certain attack can be collected, this proposed model also applies to the analysis of other attacks.
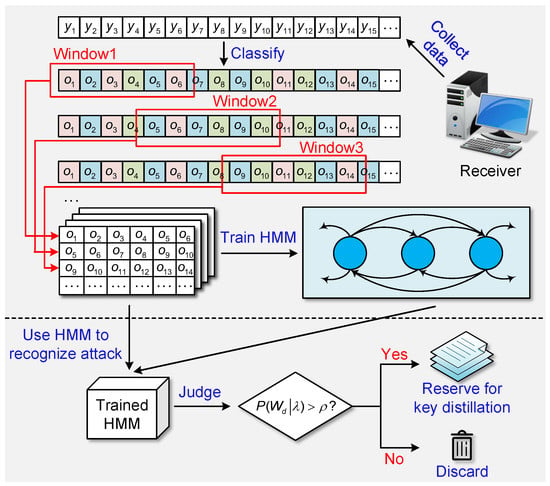
Figure 2.
The HMM-based calibration attack recognition model includes two parts. The first is the training process above the dotted line, and the second is the recognition process below the dotted line. From [42].
3.1.2. Countermeasures on Multiple Attacks
The above-mentioned recognition models only detect a certain given attack, but which kinds of attacks were launched by Eve are not predictable. Nonetheless, it must be emphasized that we need a universal defense scheme to detect multiple attacks as much as possible. For this purpose, an artificial-neural-network (ANN)-based universal defense scheme for CVQKD systems was proposed by Mao et al. [47].
In [47], multiple attacks involving three typical attack strategies against CV systems with imperfections of the homodyne detector, the calibration attack, the LO intensity attack, and the saturation attack, were considered, as well as two hybrid attacks [13,48]. Mao et al. further investigated some classical features of the pulses and deviations of these features between normal unattacked pulses and abnormal attacked pulses. The results indicated that there were four features influenced by different attack strategies, called the LO intensity , the shot noise variance , and the mean and variance of Bob’s measurement. Table 1 shows the impacts of multiple attacks on the four features. The top four attack strategies affect different features, and there are different levels of impact on the same features between the hybrid attack and the saturation attack.

Table 1.
The impacts of multiple attacks on the four features. From [47].
The ANN is an information-processing model that imitates the biological nervous system function of the human brain [49]. The ANN architecture is connected through several layers, and each layer contains a certain amount of neurons. The three-layer nonlinear ANN multiclassifier designed in this paper consisted of the input, output, and hidden layers, using a soft-max function to properly distinguish multiple attacks.
The ANN model for attack detection was trained and tested as depicted in Figure 3 from [47]. Bob’s received keys were used as the input and put into the model in order. Once having perceiving abnormal data, the transmitted processing terminates immediately with both time and resource efficiency. The precision and recall of these multiple attacks reached the maximum of one when the number of neurons in the hidden layer was fifteen. Besides, the security analysis of a CVQKD system that employed the ANN-based attack detection model was performed and compared with a system without any countermeasures against attacks. In both the asymptotic and finite size cases, the secret key rate and transmission distance of the proposed model decreased, but the overall defense capability of the system was enhanced, as shown in Figure 4a. The composable secret key rates of this ANN model were less than those in the asymptotic and finite size limit, but gradually increased as the number of exchanged signals increased, as shown in Figure 4b. All in all, compared with the CV systems without detecting strategies, the common ANN defense scheme constructed an integral defense model against most known attacks and obviously improved the systems’ security, but at the small expense of the key rate and transmit distance.
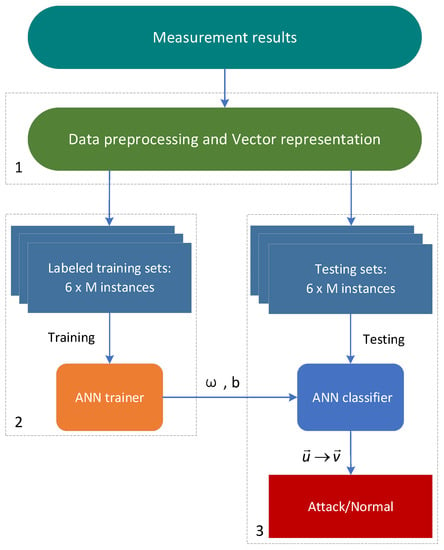
Figure 3.
The training and testing processing of the ANN model for multiple attacks’ recognition. From [47].
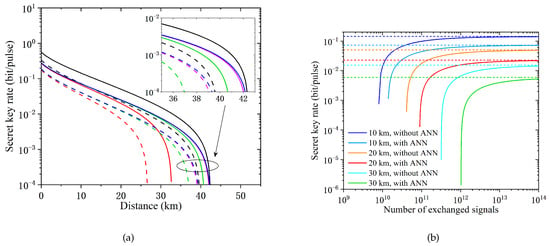
Figure 4.
(a) The secret key rates against collective attacks under the asymptotic and finite size case. The solid lines represent the system performance without any countermeasures, and the dashed lines represent the system performance with the ANN-based attack detection model. From left to right, the curves represent the number of exchanged signals, N = , N = , N = , and N = , and the asymptotic case, respectively. (b) Composable secret key rates of a CVQKD system with and without the ANN-based attack detection model. The solid lines from left to right represent the composable secret key rates with and without the ANN-based attack detection model at transmission distances of 10 km, 20 km, and 30 km, respectively. The dashed lines with the same color as the solid lines are their corresponding asymptotic secret key rates under the same conditions. In all the simulations, the insertion loss of the AM on Bob’s signal path was set to a typical value of 2.7 dB. From [47].
3.2. Quantum Hacking with Machine Learning
In Section 3.1, we introduced several cases of how to exploit machine-learning techniques to perceive one certain or several typical attacks, thereby restoring the high-accuracy and robust defense performance in CVQKD systems. We now discuss the machine-learning application to enhance the success rate of a quantum hacking attempt. Huang et al. [50] demonstrated a convolutional neural network (CNN)-based entanglement distillation attack in the horizontal link GMCS-CVQKD system, in which the CNN can help Eve choose the best opportunity to launch the entanglement distillation attack.
In the theoretical analysis of the security, the lossy quantum channel has a transmission efficiency with constant attenuation and excess noise. However, in practical free space CVQKD systems, a security problem is the instability of the signals’ physical parameters, especially in the weak and strong-turbulence free space [51]. The transmission efficiency fluctuates according to time, resulting in transmitted states degrading with a certain probability to non-Gaussian mixed states [52]. Eve can perform the entanglement distillation attack on the transmitted non-Gaussian mixed states.
The CNN, a deep learning algorithm that has quickly been developing, has performed various complex tasks especially in image recognition [53,54]. The designed CNN architecture combines five components: an input layer, two convolutional layers, two max-pooling layers, a fully connected layer, and a soft-max output layer. It achieves feature extraction hierarchically and indicates the classes of the input variables.
Figure 5 displays the CNN-based entanglement distillation attack model from [50]. Eve extracts part of the light beam B1 and measures one of the quadrature values. The well-trained CNN model takes the measurements as the input, and determines whether transmitted states are a non-Gaussian mixture to be used as the outputs. If they are, Eve will launch the attack; otherwise, she terminates the attach (the classification accuracy was 97.8%). Compared to traditional methods based on statistical analysis, the time complexity and time loss of this model are less influenced by the data size and its simpler implementation in existing technologies. To verify the practicability of the system, Huang et al. performed a security analysis showing that the region bounds of security were significantly impacted by the tap beam splitter transmissivity and the threshold value of for discarding the remaining state , as shown in Figure 6. The shorter the transmit distance, the more reliable the system is during the entanglement distillation attack. If some parameters, such as and , are adjusted to a proper random value, Eve can gain a non-negligible amount information about the final secret key without Alice’s and Bob’s realization.
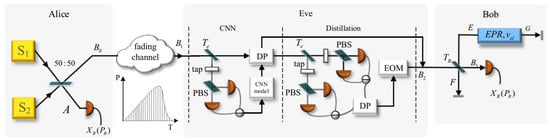
Figure 5.
Schematic diagram of the CNN-based entanglement distillation attack model. Alice prepares the entangled states and sends them to Bob through a fluctuating lossy channel. Eve uses the measurement of the light beam B1 as input to the CNN model. If the transmitted states are non-Gaussian, the entanglement distillation attack is launched. From [50].
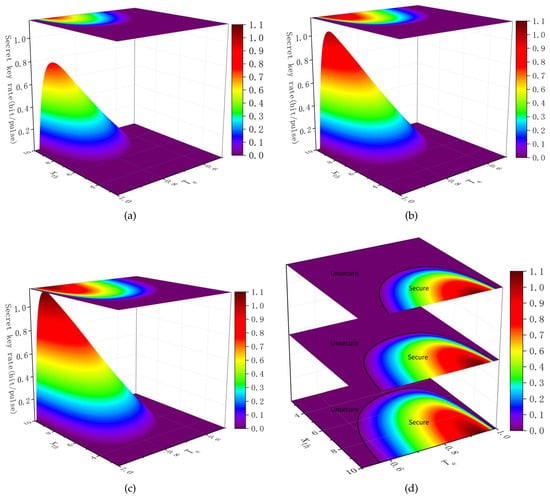
Figure 6.
Simulation under the elliptical beam model. (a–c) Performing the system performances at different transmission distances of 8 km, 10 km, and 12 km, respectively. (d) Security region bounds of the QKD system under the entanglement distillation attack at different distances of 8 km, 10 km, and 12 km, from bottom to top, respectively. The black solid lines represent the bounds between the positive and negative secret key rates. From [50].
4. Conclusions
In this review, we discussed how to perceive the imperfections of devices with machine-learning techniques in practical CVQKD systems. These range from countermeasures to quantum hacking attacks.
Firstly, we briefly described a classical distribution protocol flow based on the GG02 protocol and an example of the security proof: the asymptotic case against collective attacks. Secondly, after analyzing the abnormal behaviors of Eve, we reviewed the countermeasures on a certain attack and multiple attacks with several classical machine learning models. These recognition models can effectively identify and classify attacks with high precision and recall values. The application of machine learning is at the software level and does not require any additional equipment, addressing the vulnerabilities and system burden associated with traditional patched countermeasures. Later, we introduced how to improve the success rate of quantum hacking attacks with machine learning in order to reach the particular required conditions. We emphasized that the purpose of the analysis of quantum hacking is not to disrupt the communication process, but to prevent bugs and loopholes in the future in the implementation of QKD systems. Our aim is to use machine learning to reduce the complexity of CV systems to a certain degree and improve the performance to ensure the security of quantum secure communication.
As mentioned above in Section 3, the proposed machine-learning models can be used to perceive other vulnerabilities under certain conditions. How to achieve these conditions, e.g., how to collect training data under a certain attack and how to find the necessary loopholes to launch an attack, is crucial. Besides, the deployment of CVQKD systems with machine-learning models in the real world also deserves thoughtful consideration. Are these methods effective, and how should they be strengthened if faced with stronger attacks from Eve? All of the above are issues that need to be considered in future research, and many unexpected prospects may emerge. It is also quite certain that machine learning will have a huge advantage in relevant data processing and data analysis in the attack and defense of practical CV systems.
Similarly, there are practical security issues such as those in DVQKD and several corresponding classic countermeasures [17]. Attention was also given to the fact that machine-learning approaches can help tackle difficulties such as parameter estimation in DV systems, such as developing a new operating mode called “predicting-and-updating” with a long short-term memory network to handle the phase drift problem [55]. Given this, why not apply machine-learning techniques to real-world security issues in practical DVQKD? We are excited about what the future holds.
All in all, machine learning has gradually played an important role in the quantum safe encryption transmission for real CV systems, paving the way for secure QKD with realistic devices. Meanwhile, we expect that in the future, the study of machine learning will continue to lead to many new unexpected insights in the subfields of QKD.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (61972418, 61977062, 61872390, and 61801522), the National Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, China (2019JJ40352), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of Central South University (2019zzts278).
Acknowledgments
The authors express appreciation to Z. He, Y. Mao, and W. Huang for their pioneering research. Furthermore, we thank the reviewers of this work for their valuable comments and suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Gisin, N.; Ribordy, G.; Tittel, W.; Zbinden, H. Quantum cryptography. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2002, 74, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bennett, C.H.; Brassard, G. Quantum cryptography. Theor. Comput. Sci. 2014, 560, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Curty, M.; Qi, B.; Qian, L.; Lo, H.K. Discrete and continuous variables for measurement-device-independent quantum cryptography. Nat. Photonics 2015, 9, 772–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grosshans, F.; Grangier, P. Continuous variable quantum cryptography using coherent states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 057902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lance, A.M.; Symul, T.; Sharma, V.; Weedbrook, C.; Ralph, T.C.; Lam, P.K. No-switching quantum key distribution using broadband modulated coherent light. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 95, 180503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Huang, P.; Huang, D.; Lin, D.; Zeng, G. Practical security of continuous-variable quantum key distribution with finite sampling bandwidth effects. Phys. Rev. A 2016, 93, 022315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weedbrook, C.; Pirandola, S.; García-Patrón, R.; Cerf, N.J.; Ralph, T.C.; Shapiro, J.H.; Lloyd, S. Gaussian quantum information. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2012, 84, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.C.; Sun, S.H.; Jiang, M.S.; Liang, L.M. Local oscillator fluctuation opens a loophole for Eve in practical continuous-variable quantum-key-distribution systems. Phys. Rev. A 2013, 88, 022339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, J.Z.; Weedbrook, C.; Yin, Z.Q.; Wang, S.; Li, H.W.; Chen, W.; Guo, G.C.; Han, Z.F. Quantum hacking of a continuous-variable quantum-key-distribution system using a wavelength attack. Phys. Rev. A 2013, 87, 062329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.C.; Sun, S.H.; Jiang, M.S.; Liang, L.M. Wavelength attack on practical continuous-variable quantum-key-distribution system with a heterodyne protocol. Phys. Rev. A 2013, 87, 052309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jouguet, P.; Kunz-Jacques, S.; Diamanti, E. Preventing calibration attacks on the local oscillator in continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 2013, 87, 062313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, H.; Kumar, R.; Alléaume, R. Quantum hacking: Saturation attack on practical continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 2016, 94, 012325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, H.; Kumar, R.; Makarov, V.; Alléaume, R. Homodyne-detector-blinding attack in continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 2018, 98, 012312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jouguet, P.; Kunz-Jacques, S.; Leverrier, A.; Grangier, P.; Diamanti, E. Experimental demonstration of long-distance continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Nat. Photonics 2013, 7, 378–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Huang, P.; Lin, D.; Zeng, G. Long-distance continuous-variable quantum key distribution by controlling excess noise. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campagna, M.; Chen, L.; Dagdelen, O.; Ding, J.; Fernick, J.; Gisin, N.; Hayford, D.; Jennewein, T.; Lütkenhaus, N.; Mosca, M.; et al. Quantum Safe Cryptography and Security: An introduction, benefits, enablers and challenges. Eur. Telecommun. Stand. Inst. 2015, 8, 1–64. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, F.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Q.; Lo, H.K.; Pan, J.W. Secure quantum key distribution with realistic devices. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2020, 92, 025002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerhardt, I.; Liu, Q.; Lamas-Linares, A.; Skaar, J.; Kurtsiefer, C.; Makarov, V. Full-field implementation of a perfect eavesdropper on a quantum cryptography system. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lydersen, L.; Wiechers, C.; Wittmann, C.; Elser, D.; Skaar, J.; Makarov, V. Hacking commercial quantum cryptography systems by tailored bright illumination. Nat. Photonics 2010, 4, 686–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Acín, A.; Brunner, N.; Gisin, N.; Massar, S.; Pironio, S.; Scarani, V. Device-independent security of quantum cryptography against collective attacks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 230501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lo, H.K.; Curty, M.; Qi, B. Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 108, 130503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wallnöfer, J.; Melnikov, A.A.; Dür, W.; Briegel, H.J. Machine learning for long-distance quantum communication. PRX Quantum 2020, 1, 010301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biamonte, J.; Wittek, P.; Pancotti, N.; Rebentrost, P.; Wiebe, N.; Lloyd, S. Quantum machine learning. Nature 2017, 549, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordani, T.; Suprano, A.; Polino, E.; Acanfora, F.; Innocenti, L.; Ferraro, A.; Paternostro, M.; Spagnolo, N.; Sciarrino, F. Machine learning-based classification of vector vortex beams. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2020, 124, 160401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Huang, P.; Peng, J.; Fan, J.; Zeng, G. Integrating machine learning to achieve an automatic parameter prediction for practical continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 2018, 97, 022316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.Y.; Yin, Z.Q.; Wang, C.; Cui, C.H.; Teng, J.; Wang, S.; Chen, W.; Huang, W.; Xu, B.J.; Guo, G.C.; et al. Parameter optimization and real-time calibration of a measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution network based on a back propagation artificial neural network. JOSA B 2019, 36, B92–B98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lo, H.K. Machine learning for optimal parameter prediction in quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 2019, 100, 062334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, H.J.; Liu, J.Y.; Zhang, C.M.; Wang, Q. Predicting optimal parameters with random forest for quantum key distribution. Quantum Inf. Process. 2020, 19, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guo, Y.; Wang, X.; Xie, C.; Zhang, L.; Huang, D. Discrete-modulated continuous-variable quantum key distribution with a machine-learning-based detector. Opt. Eng. 2018, 57, 066109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Guo, Y.; Huang, D. Parameter Optimization Based BPNN of Atmosphere Continuous-Variable Quantum Key Distribution. Entropy 2019, 21, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fossier, S.; Diamanti, E.; Debuisschert, T.; Tualle-Brouri, R.; Grangier, P. Improvement of continuous-variable quantum key distribution systems by using optical preamplifiers. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2009, 42, 114014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holevo, A.S. Bounds for the quantity of information transmitted by a quantum communication channel. Probl. Peredachi Informatsii 1973, 9, 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Leverrier, A.; Grosshans, F.; Grangier, P. Finite-size analysis of a continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 2010, 81, 062343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leverrier, A. Composable security proof for continuous-variable quantum key distribution with coherent states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 114, 070501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, Z.; Wang, Y.; Huang, D. Wavelength attack recognition based on machine learning optical spectrum analysis for the practical continuous-variable quantum key distribution system. JOSA B 2020, 37, 1689–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz-Jacques, S.; Jouguet, P. Robust shot noise measurement for continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 2015, 91, 022307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouzalmat, A.; Kharroubi, J.; Zarghili, A. Comparative study of PCA, ICA, LDA using SVM classifier. J. Emerg. Technol. Web Intell. 2014, 6, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, C.C.; Lin, C.J. LIBSVM: A library for support vector machines. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. (TIST) 2011, 2, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smola, A.J.; Schölkopf, B. A tutorial on support vector regression. Stat. Comput. 2004, 14, 199–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.F.; Kwok, J.T.; Zhou, Z.H. Semi-supervised learning using label mean. In Proceedings of the 26th Annual International Conference on Machine Learning, Montreal, QC, Canada, 14–18 June 2009; pp. 633–640. [Google Scholar]
- Soman, K.; Loganathan, R.; Ajay, V. Machine Learning with SVM and Other Kernel Methods; PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd.: Delhi, India, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, W.; Qin, H.; Huang, D.; Guo, Y. Hidden-Markov-model-based calibration-attack recognition for continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 2020, 101, 062320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodewyck, J.; Debuisschert, T.; Garcia-Patron, R.; Tualle-Brouri, R.; Cerf, N.J.; Grangier, P. Experimental implementation of non-Gaussian attacks on a continuous-variable quantum-key-distribution system. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 030503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haider, W.; Hu, J.; Xie, Y.; Yu, X.; Wu, Q. Detecting anomalous behavior in cloud servers by nested-arc hidden semi-Markov model with state summarization. IEEE Trans. Big Data 2017, 5, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Pedrycz, W.; Jamal, I. Multivariate time series anomaly detection: A framework of Hidden Markov Models. Appl. Soft Comput. 2017, 60, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holgado, P.; Villagrá, V.A.; Vazquez, L. Real-time multistep attack prediction based on hidden markov models. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput. 2017, 17, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Huang, W.; Zhong, H.; Wang, Y.; Qin, H.; Guo, Y.; Huang, D. Detecting quantum attacks: A machine learning based defense strategy for practical continuous-variable quantum key distribution. New J. Phys. 2020, 22, 083073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.Z.; Kunz-Jacques, S.; Jouguet, P.; Weedbrook, C.; Yin, Z.Q.; Wang, S.; Chen, W.; Guo, G.C.; Han, Z.F. Quantum hacking on quantum key distribution using homodyne detection. Phys. Rev. A 2014, 89, 032304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saritas, M.M.; Yasar, A. Performance analysis of ANN and Naive Bayes classification algorithm for data classification. Int. J. Intell. Syst. Appl. Eng. 2019, 7, 88–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, W.; Mao, Y.; Xie, C.; Huang, D. Quantum hacking of free-space continuous-variable quantum key distribution by using a machine-learning technique. Phys. Rev. A 2019, 100, 012316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasylyev, D.; Semenov, A.; Vogel, W. Atmospheric quantum channels with weak and strong turbulence. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 117, 090501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Xie, C.; Liao, Q.; Zhao, W.; Zeng, G.; Huang, D. Entanglement-distillation attack on continuous-variable quantum key distribution in a turbulent atmospheric channel. Phys. Rev. A 2017, 96, 022320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. Deep learning face representation from predicting 10,000 classes. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 1891–1898. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 25, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y.; Ding, H.J.; Zhang, C.M.; Xie, S.P.; Wang, Q. Practical phase-modulation stabilization in quantum key distribution via machine learning. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2019, 12, 014059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).