Theoretical Study of the Pre-Plasma Density Scale Length’s Influence on the Absorption Efficiency in Laser–Solid Interaction at Relativistic Laser Intensities for PW-Class Lasers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
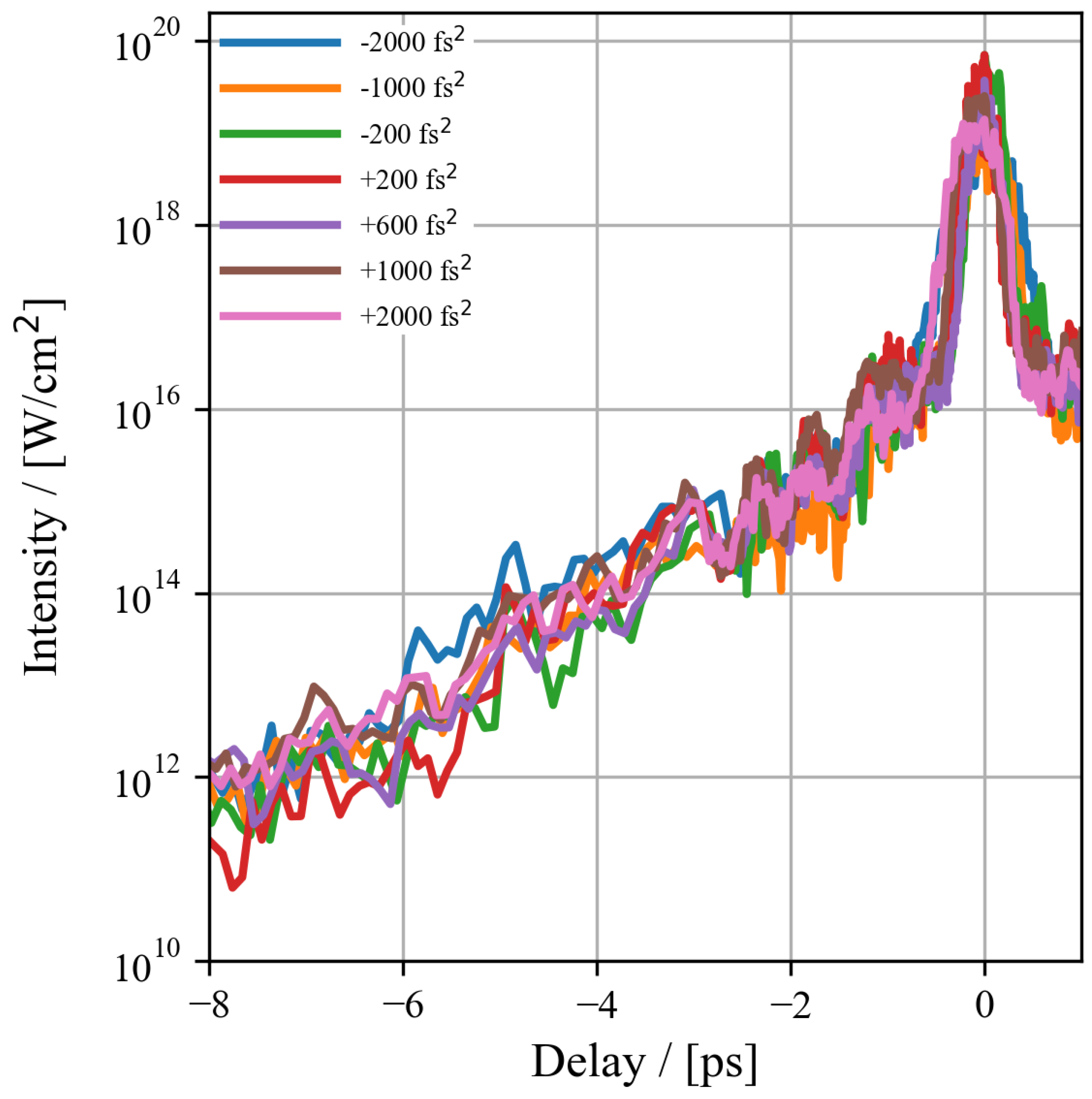
2.1. Experimental Measurements of Laser Parameters
2.2. Numerical Simulations
2.2.1. Laser–Matter Interaction Through Hydrodynamic Simulations
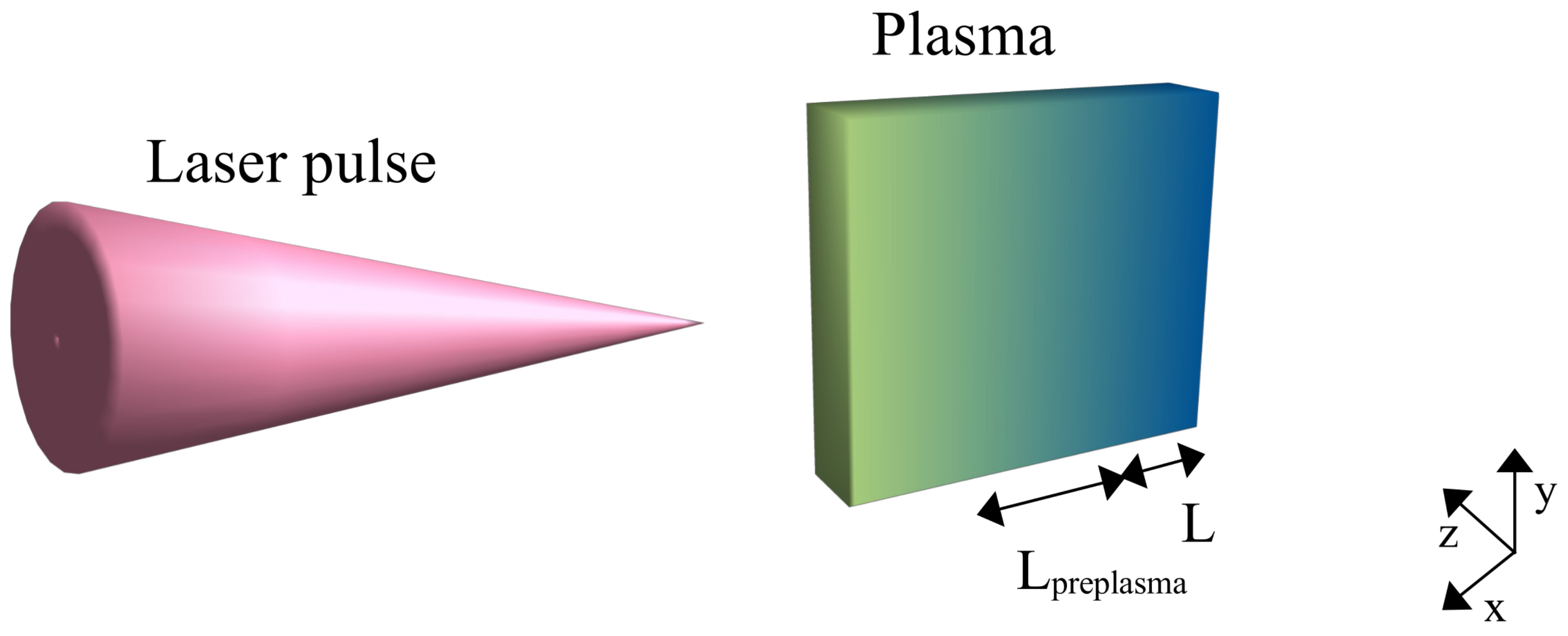
2.2.2. Laser–Plasma Interaction Through PIC Simulations
3. Results and Discussion
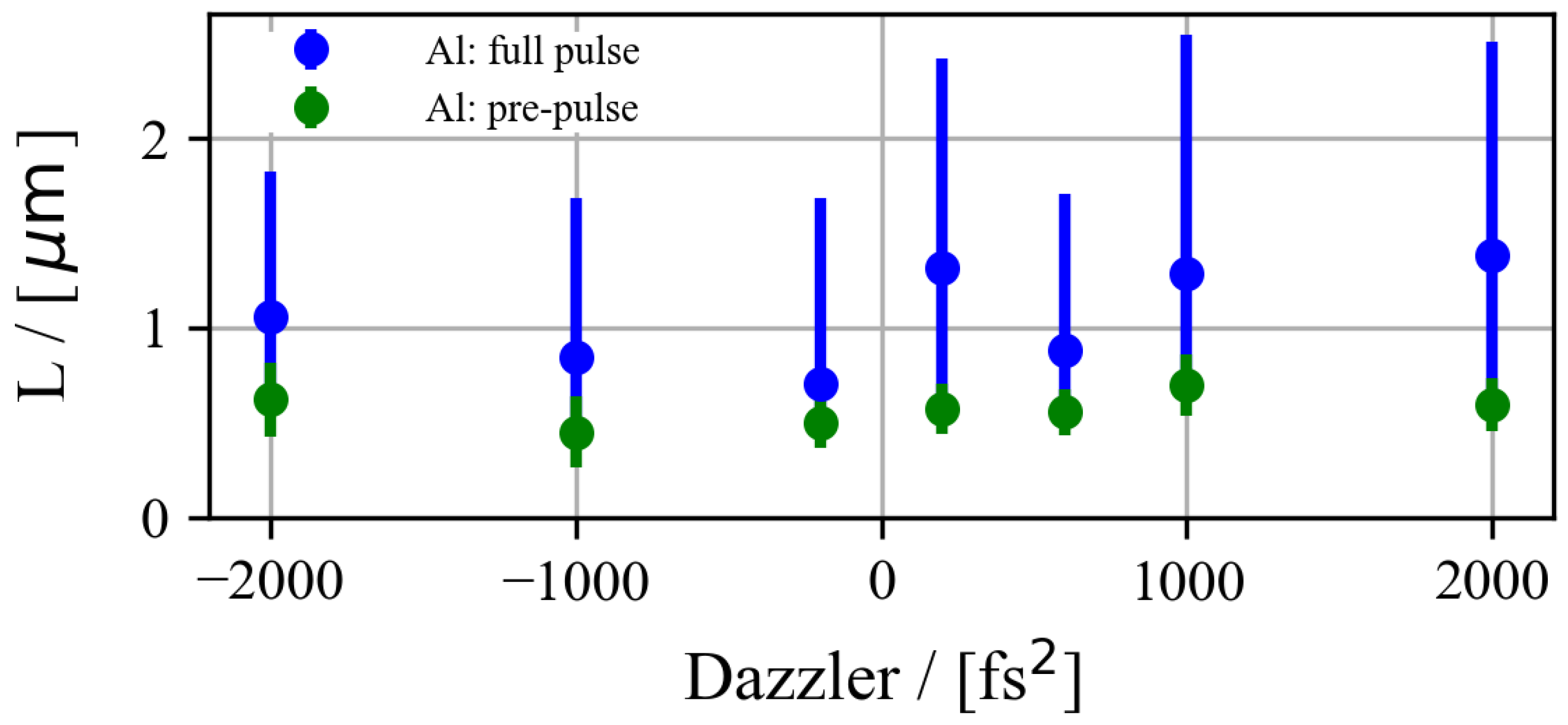
3.1. Estimation of the Pre-Plasma Density Scale Length
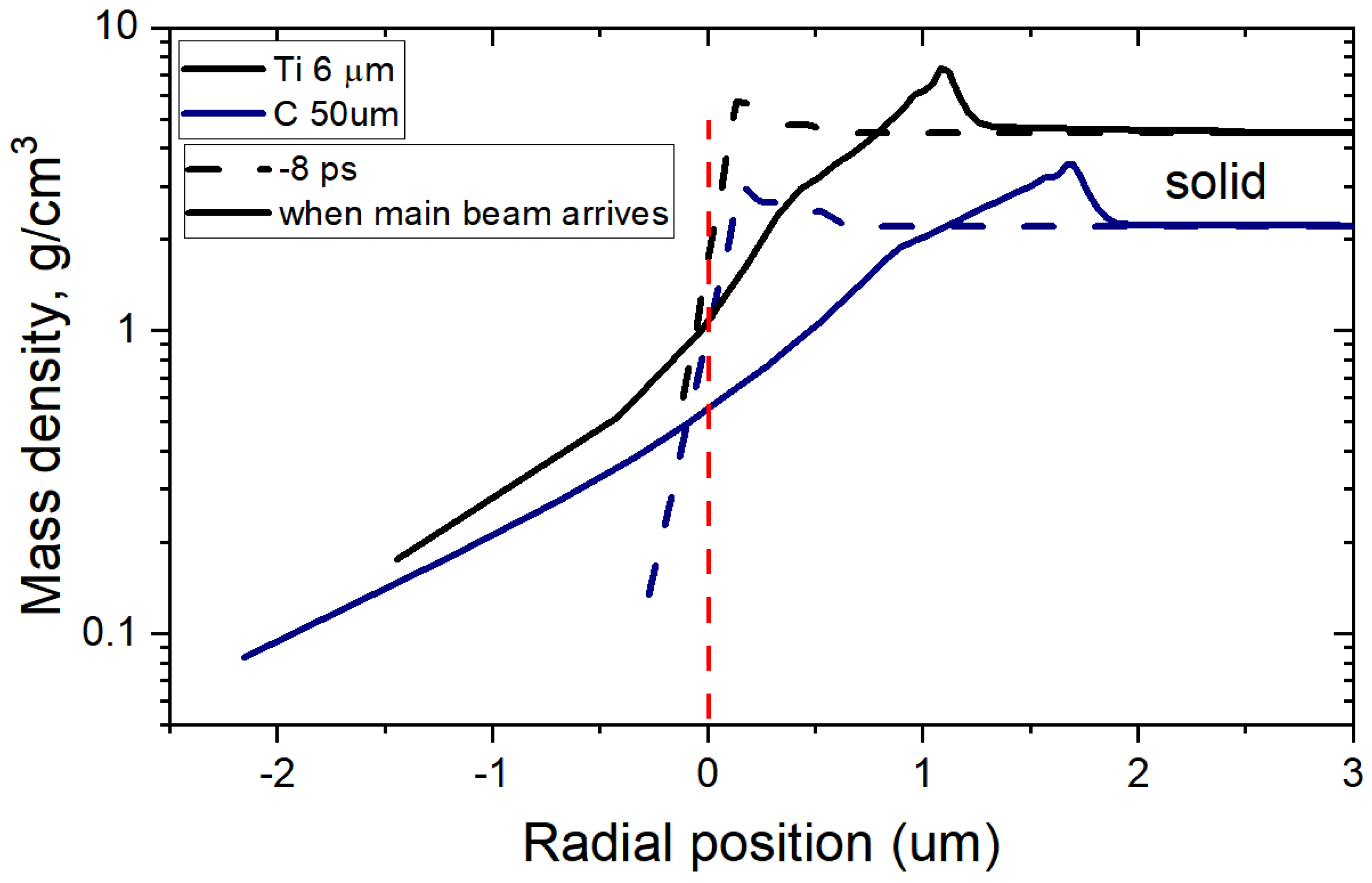
3.2. Hydrodynamic Simulations
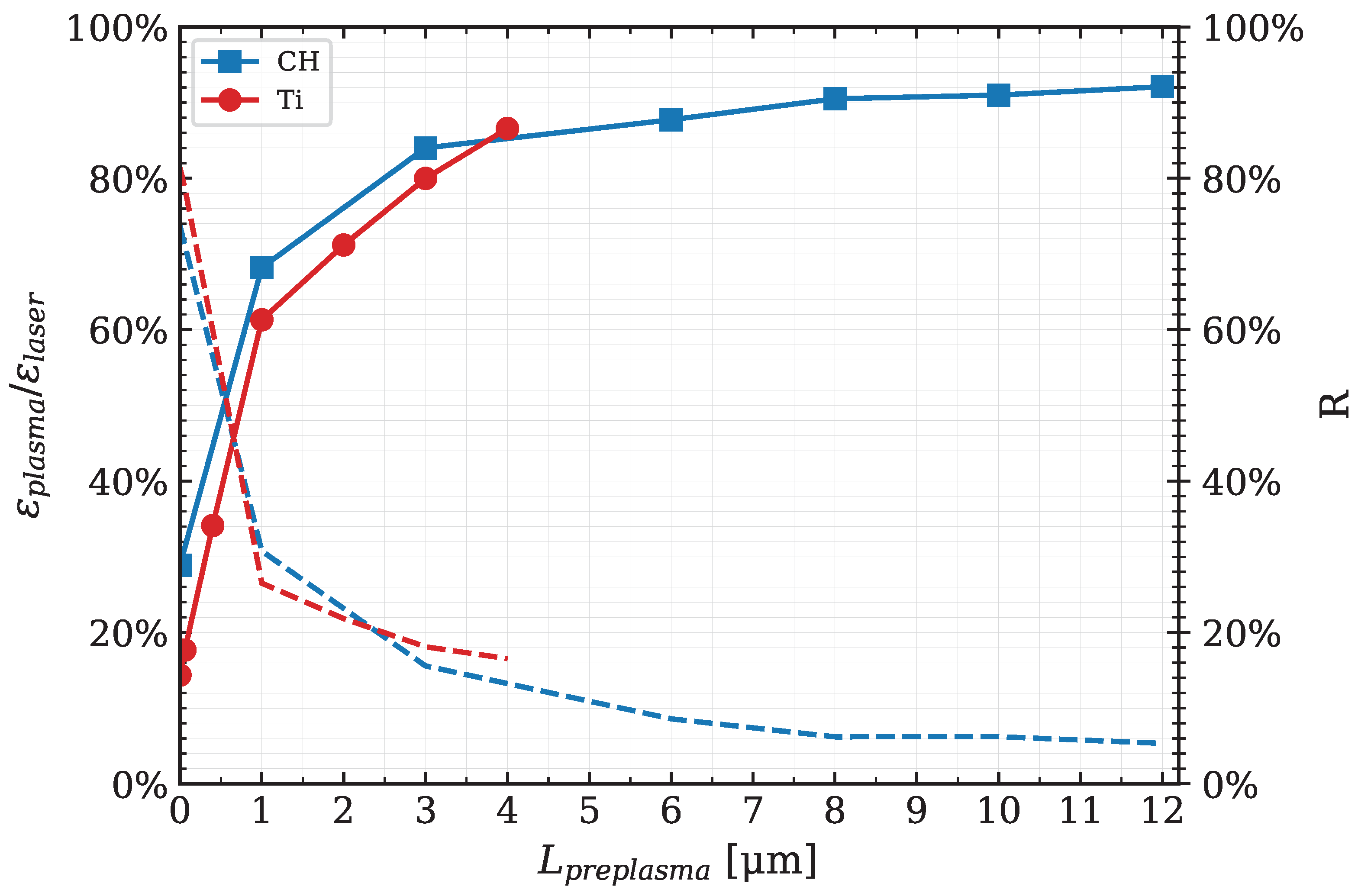
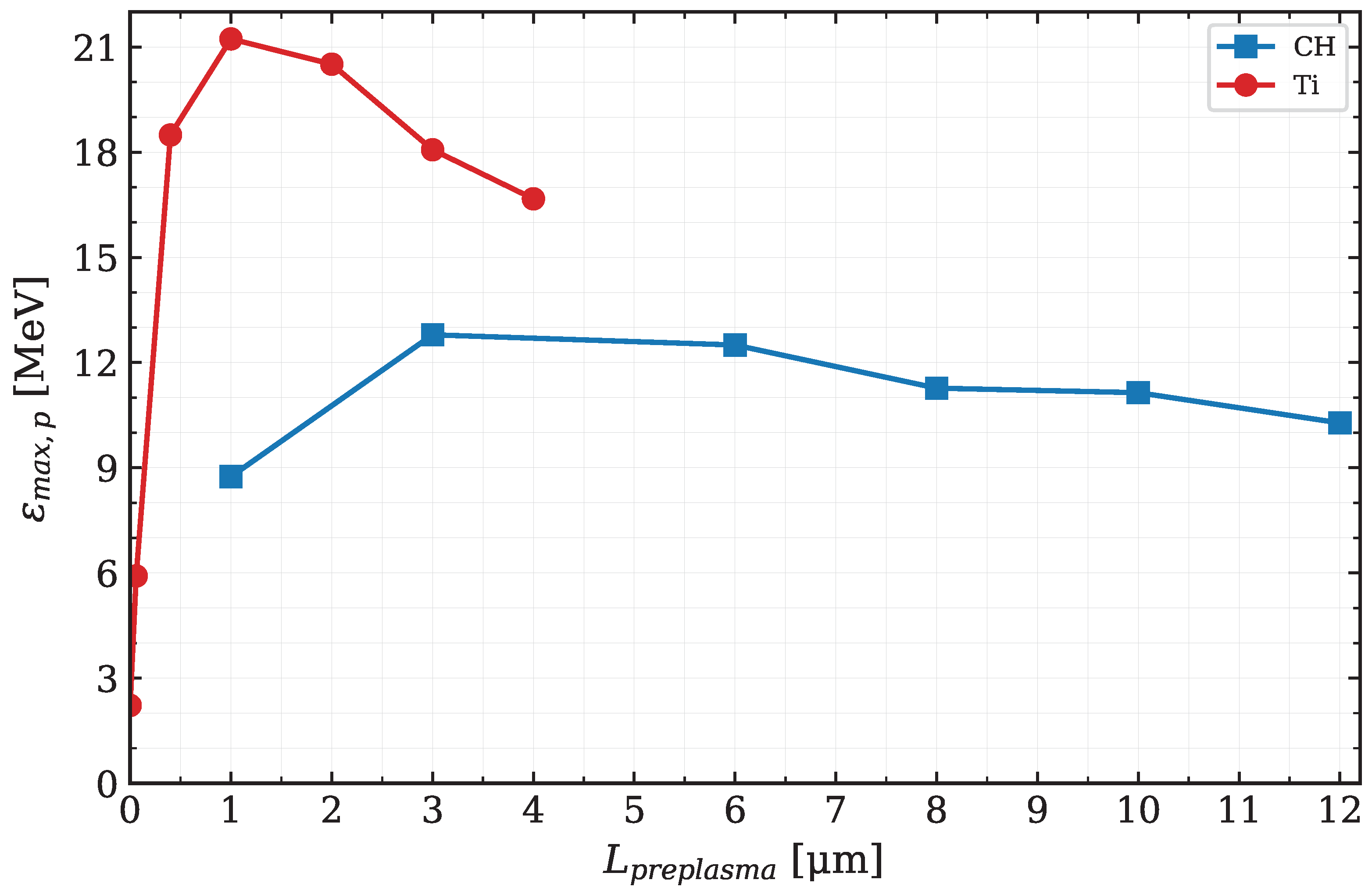
3.3. Pre-Plasma Influence on the Laser–Plasma Interaction
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Norreys, P.A.; Santala, M.; Clark, E.; Zepf, M.; Watts, I.; Beg, F.N.; Krushelnick, K.; Tatarakis, M.; Dangor, A.E.; Fang, X.; et al. Observation of a highly directional γ-ray beam from ultrashort, ultraintense laser pulse interactions with solids. Phys. Plasmas 1999, 6, 2150–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladisavlevici, I.M.; Ribeyre, X.; Vizman, D.; d’Humières, E. Investigation of γ-photon sources using near-critical density targets towards the optimization of the linear Breit–Wheeler process. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 2024, 66, 035009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daido, H.; Nishiuchi, M.P.A. Review of laser-driven ion sources and their applications. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2012, 75, 056401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghesi, M. Ion Acceleration: TNSA and Beyond. Springer Proc. Phys. 2019, 231, 143–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajima, T.; Malka, V. Laser plasma accelerators. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 2012, 62, 034004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichters, R.; Meyer-ter-Vehn, J.; Pukhov, A. Short-pulse laser harmonics from oscillating plasma surfaces driven at relativistic intensity. Plasmas 1996, 3, 3425–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norreys, P.A.; Zepf, M.; Moustaizis, S.; Fews, A.P.; Zhang, J.; Lee, P.; Bakarezos, M.; Danson, C.N.; Dyson, A.; Gibbon, P.; et al. Efficient Extreme UV Harmonics Generated from Picosecond Laser Pulse Interactions with Solid Targets. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 76, 1832–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corkum, P.B.; Krausz, F. Attosecond Science. Nat. Phys. 2007, 3, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beg, F.N.; Bell, A.R.; Dangor, A.E.; Danson, C.N.; Fews, A.P.; Glinsky, M.E.; Hammel, B.A.; Lee, P.; Norreys, P.A.; Tatarakis, M. A study of picosecond laser-solid interactions up to 1019 Wcm−2. Phys. Plasmas 1997, 4, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleko, V.; Karataev, P.; Konkov, A.; Kruchinin, K.; Naumenko, G.; Potylitsyn, A.; Vaughan, T. Coherent Cherenkov radiation as an intense THz source. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2016, 732, 012006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consoli, F.; Tikhonchuk, V.T.; Bardon, M.; Bradford, P.; Carroll, D.C.; Cikhardt, J.; Cipriani, M.; Clarke, R.J.; Cowan, T.E.; Danson, C.N.; et al. Laser produced electromagnetic pulses: Generation, detection and mitigation. High Power Laser Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehret, M.; Cikhardt, J.; Bradford, P.; Vladisavlevici, I.-M.; Burian, T.; de Luis, D.; Henares, J.L.; Martin, R.H.; Apiñaniz, J.I.; Lera, R.; et al. High-repetition-rate source of nanosecond duration kA-current pulses driven by relativistic laser pulses. High Power Laser Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, e33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, J.; Obst-Huebl, L.; Mao, J.-H.; Nakamura, K.; Geulig, L.D.; Chang, H.; Ji, Q.; He, L.; Chant, J.D.; Kober, Z.; et al. A new platform for ultra-high dose rate radiobiological research using the BELLA PW laser proton beamline. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Streeter, M.J.V.; Ettlinger, O.C.; Ahmed, H.; Astbury, S.; Borghesi, M.; Bourgeois, N.; Curry, C.B.; Dann, S.J.D.; Dover, N.P.; et al. Versatile tape-drive target for high-repetition-rate laser-driven proton acceleration. High Power Laser Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehret, M.; de Luis, D.; Apiñaniz, J.I.; Henares, J.L.; Lera, R.; Pérez-Hernández, J.A.; Puyuelo-Valdes, P.; Volpe, L.; Gatti, G. Stability and debris-mitigation of a solid tape target delivery system for intense laser-matter interactions towards high-repetition-rate. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 2024, 66, 045003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haney, S.J.; Berger, K.W.; Kubiak, G.D.; Rockett, P.D.; Hunter, J. Prototype high-speed tape target transport for a laser plasma soft-x-ray projection lithography source. Appl. Opt. 1993, 32, 6934–6937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Lee, T.; Li, W.; Ketwaroo, G.; Rose-Petruck, C.G. High-average-power 2-kHz laser for generation of ultrashort x-ray pulses. Opt. Lett. 2002, 27, 963–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujioka, S.; Nishimura, H.; Nishihara, K.; Miyanaga, N.; Izawa, Y.; Mima, K.; Shimada, Y.; Sunahara, A. Laser Production of Extreme Ultraviolet Light Source for the Next Generation Lithography Application. Plasma Fusion Res. 2009, 4, 048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemoto, K.; Maksimchuk, A.; Banerjee, S.; Flippo, K.; Mourou, G.; Umstadter, D.; Bychenkov, V.Y. Laser-triggered ion acceleration and table top isotope production. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 78, 595–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santala, M.I.K.; Zepf, M.; Beg, F.N.; Clark, E.L.; Dangor, A.E.; Krushelnick, K.; Tatarakis, M.; Watts, I.; Ledingham, K.W.D.; McCanny, T.; et al. Production of radioactive nuclides by energetic protons generated from intense laser-plasma interactions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 78, 19–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrill, F.E.; Golubev, A.A.; Mariam, F.G.; Turtikov, V.I.; Varentsov, D.; Collaboration, H. Proton Microscopy at Fair. AIP Conf. Proc. 2009, 1195, 667–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirani, F.; Maffini, A.; Casamichiela, F.; Pazzaglia, A.; Formenti, A.; Dellasega, D.; Russo, V.; Vavassori, D.; Bortot, D.; Huault, M.; et al. Integrated quantitative PIXE analysis and EDX spectroscopy using a laser-driven particle source. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabc8660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, M.; Cowan, T.E.; Key, M.H.; Hatchett, S.P.; Brown, C.; Fountain, W.; Johnson, J.; Pennington, D.M.; Snavely, R.A.; Wilks, S.C.; et al. Fast Ignition by Intense Laser-Accelerated Proton Beams. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 86, 436–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftekhari-Zadeh, E.; Blümcke, M.S.; Samsonova, Z.; Loetzsch, R.; Uschmann, I.; Zapf, M.; Ronning, C.; Rosmej, O.N.; Kartashov, D.; Spielmann, C. Laser energy absorption and x-ray generation in nanowire arrays irradiated by relativistically intense ultra-high contrast femtosecond laser pulses. Phys. Plasmas 2022, 29, 013301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter Mulser and Dieter Bauer. High Power Laser-Matter Interaction; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2010; Volume 238. [Google Scholar]
- Pape, S.L.; Tsui, Y.Y.; Macphee, A.; Hey, D.; Patel, P.; Mackinnon, A.; Key, M.; Wei, M.; Ma, T.; Beg, F.N.; et al. Characterization of the preformed plasma for high-intensity laser-plasma interaction. Opt. Lett. 2009, 34, 2997–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bocoum, M.; Böhle, F.; Vernier, A.; Jullien, A.; Faure, J.; Lopez-Martens, R. Spatial-domain interferometer for measuring plasma mirror expansion. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 3009–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forestier-Colleoni, P.; Batani, D.; Burgy, F.; Froustey, F.; Hulin, S.; d’Humières, E.; Jakubowska, K.; Merzeau, L.; Mishchik, K.; Santos, J.J. Polarimetry measurements of surfacic strong magnetic field produced by high power laser. In Proceedings of the Science for the First EPS Conference on Plasma Diagnostics—1st ECPD, Rome, Italy, 14–17 April 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hornung, J.; Zobus, Y.; Roeder, S.; Kleinschmidt, A.; Bertini, D.; Zepf, M.; Bagnoud, V. Time-resolved study of holeboring in realistic experimental conditions. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, Y.; Shepherd, R.; Lasinski, B.F.; Tabak, M.; Chen, H.; Chung, H.K.; Fournier, K.B.; Hansen, S.B.; Kemp, A.; Liedahl, D.A.; et al. Absorption of Short Laser Pulses on Solid Targets in the Ultrarelativistic Regime. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 085004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, R.; Takahashi, K.; Tanaka, K.A.; Tsukamoto, M.; Hashimoto, H.; Kato, Y.; Mima, K. Study of Laser-Hole Boring into Overdense Plasmas. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 4906–4909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Yu, W.; Chang, W.-W.; Ma, Y.-Y. Effects of Pre-plasma on Energetic Electrons Generation in Ultra-short Ultra-intense Laser–Solid Interactions. Phys. Scr. 2003, 67, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culfa, O.; Tallents, G.J.; Rossall, A.K.; Wagenaars, E.; Ridgers, C.P.; Murphy, C.D.; Dance, R.J.; Gray, R.J.; McKenna, P.; Brown, C.D.R.; et al. Plasma scale-length effects on electron energy spectra in high-irradiance laser plasmas. Phys. Rev. E 2016, 93, 043201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peebles, J.; Wei, M.S.; Arefiev, A.V.; McGuffey, C.; Stephens, R.B.; Theobald, W.; Haberberger, D.; Jarrott, L.C.; Link, A.; Chen, H. Investigation of laser pulse length and pre-plasma scale length impact on hot electron generation on OMEGA-EP. New J. Phys. 2017, 19, 023008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuter, R.; Gremillet, L.; Combis, P.; Drouin, M.; Lefebvre, E.; Flacco, A.; Malka, V. Influence of a preplasma on electron heating and proton acceleration in ultraintense laser-foil interaction. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 104, 103307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovchinnikov, V.M.; Schumacher, D.W.; McMahon, M.; Chowdhury, E.A.; Chen, C.D.; Morace, A.; Freeman, R.R. Effects of Preplasma Scale Length and Laser Intensity on the Divergence of Laser-Generated Hot Electrons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 110, 065007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debayle, A.; Honrubia, J.J.; d’Humières, E.; Tikhonchuk, V.T. Divergence of laser-driven relativistic electron beams. Phys. Rev. E 2010, 82, 036405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santala, M.I.; Zepf, M.; Watts, I.I.; Beg, F.N.; Clark, E.; Tatarakis, M.; Krushelnick, K.; Dangor, A.E.; McCanny, T.; Spencer, I.I.; et al. Effect of the Plasma Density Scale Length on the Direction of Fast Electrons in Relativistic Laser-Solid Interactions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2000, 84, 1459–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantono, G.; Fedeli, L.; Sgattoni, A.; Denoeud, A.; Chopineau, L.; Réau, F.; Ceccotti, T.; Macchi, A. Extreme Ultraviolet Beam Enhancement by Relativistic Surface Plasmons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 120, 264803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-B.; Hu, G.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-M.; Gu, Y.-Q.; Zhao, B.; Zuo, Y.; Zheng, J. Gamma-ray generation from ultraintense laser-irradiated solid targets with preplasma. High Power Laser Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjisolomou, P.; Tsygvintsev, I.; Sasorov, P.; Gasilov, V.; Korn, G.; Bulanov, S. Preplasma effects on laser ion generation from thin foil targets. Phys. Plasmas 2020, 27, 013107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaluza, M.; Schreiber, J.; Santala, M.I.K.; Tsakiris, G.D.; Eidmann, K.; Meyer-ter Vehn, J.; Witte, K.J. Influence of the Laser Prepulse on Proton Acceleration in Thin-Foil Experiments. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 93, 045003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenna, P.; Lindau, F.; Lundh, O.; Neely, D.; Persson, A.; Wahlström, C.G. High-intensity laser-driven proton acceleration: Influence of pulse contrast. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2006, 364, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culfa, O.; Tallents, G.; Korkmaz, M.; Rossall, A.; Wagenaars, E.; Ridgers, C.; Murphy, C.; Booth, N.; Carroll, D.; Wilson, L.; et al. Plasma scale length effects on protons generated in ultra-intense laser–plasmas. Laser Part. Beams 2017, 35, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.A.; Kodama, R.; Fujita, H.; Heya, M.; Izumi, N.; Kato, Y.; Kitagawa, Y.; Mima, K.; Miyanaga, N.; Norimatsu, T.; et al. Studies of ultra-intense laser plasma interactions for fast ignition. Phys. Plasmas 2000, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macphee, A.G.; Divol, L.; Kemp, A.J.; Akli, K.U.; Beg, F.N.; Chen, C.D.; Chen, H.; Hey, D.S.; Fedosejevs, R.J.; Freeman, R.R.; et al. Limitation on Prepulse Level for Cone-Guided Fast-Ignition Inertial Confinement Fusion. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 055002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roso, L. High repetition rate petawatt lasers. Eur. Phys. J. Web Conf. 2018, 167, 01001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Hernández, J.A.; Henares, J.L.; Vladisavlevici, I.-M.; et al. Pulse duration influence on protons driven by PW-fs lasers. 2025; to be submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Verluise, F.; Laude, V.; Cheng, Z.; Spielmann, C.; Tournois, P. Amplitude and phase control of ultrashort pulses by use of an acousto-optic programmable dispersive filter: Pulse compression and shaping. Opt. Lett. 2000, 25, 575–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, S.; Hutchinson, M.H.R.; Smith, R.A.; Zhou, F. High dynamic range third-order correlation measurement of picosecond laser pulse shapes. Meas. Sci. Technol. 1993, 4, 1426–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Gong, Z.; Lee, S.G.; Shou, Y.; Geng, Y.; Jeon, C.; Kim, I.J.; Lee, H.W.; Yoon, J.W.; Sung, J.H.; et al. Super-Heavy Ions Acceleration Driven by Ultrashort Laser Pulses at Ultrahigh Intensity. Phys. Rev. X 2021, 11, 021049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derouillat, J.; Beck, A.; Pérez, F.; Vinci, T.; Chiaramello, M.; Grassi, A.; Flé, M.; Bouchard, G.; Plotnikov, I.; Aunai, N.; et al. SMILEI: A collaborative, open-source, multi-purpose particle-in-cell code for plasma simulation. Comput. Phys. Commun. 2018, 222, 351–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supercomputación Castilla y León (SCAYLE). Available online: https://www.scayle.es/manual/es/hpc/infraestructura (accessed on 12 November 2024).
- Mishra, R.; Fiuza, F.; Glenzer, S. Enhanced ion acceleration in transition from opaque to transparent plasmas. New J. Phys. 2018, 20, 043047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forslund, D.W.; Kindel, J.M.; Lee, K. Theory of Hot-Electron Spectra at High Laser Intensity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1977, 39, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilks, S.C.; Kruer, W.L.; Tabak, M.; Langdon, A.B. Absorption of ultra-intense laser pulses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1992, 69, 1383–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunel, F. Not-so-resonant, resonant absorption. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1987, 59, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malka, G.; Miquel, J.L. Experimental Confirmation of Ponderomotive-Force Electrons Produced by an Ultrarelativistic Laser Pulse on a Solid Target. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilks, S.C.; Kruer, W.L. Absorption of ultrashort, ultra-intense laser light by solids and overdense plasmas. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 1997, 33, 1954–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, R.P. High-Energy-Density Physics, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliezer, S. The Thomas-Fermi and Related Models. In Strongly Coupled Plasma Physics; Rogers, F.J., Dewitt, H.E., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1987; pp. 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.K.; Stone, P.M. Ionization of boron, aluminum, gallium, and indium by electron impact. Phys. Rev. A 2001, 64, 052707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Z.-M.; Weng, S.-M.; Yu, L.-L.; Wang, W.-M.; Cui, Y.-Q.; Chen, M.; Zhang, J. Absorption of ultrashort intense lasers in laser–solid interactions. Chin. Phys. B 2015, 24, 015201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladisavlevici, I.M.; Vizman, D.; d’Humières, E. Theoretical investigation of the interaction of ultra-high intensity laser pulses with near critical density plasmas. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 2023, 65, 045012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brantov, A.; Govras, E.; Bychenkov, V.; Rozmus, W. Ion energy scaling under optimum conditions of laser plasma acceleration. Phys. Rev. Spec. Top. Accel. Beams 2015, 18, 021301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Humières, E.; Lefebvre, E.; Gremillet, L.; Malka, V. Proton acceleration mechanisms in high-intensity laser interaction with thin foils. Phys. Plasmas 2005, 12, 062704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackinnon, A.J.; Sentoku, Y.; Patel, P.K.; Price, D.W.; Hatchett, S.; Key, M.H.; Andersen, C.; Snavely, R.; Freeman, R.R. Enhancement of Proton Acceleration by Hot-Electron Recirculation in Thin Foils Irradiated by Ultraintense Laser Pulses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 215006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flacco, A.; Sylla, F.; Veltcheva, M.; Carrié, M.; Nuter, R.; Lefebvre, E.; Batani, D.; Malka, V. Dependence on pulse duration and foil thickness in high-contrast-laser proton acceleration. Phys. Rev. E 2010, 81, 036405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| GDD | ASE Pre-Pulse | ps-Pedestal | Main Pulse | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| / | / | /fs | / | /fs | / | /fs | /fs |
| (3.6 ± 0.6) × | 781 ± 23 | (2.6 ± 0.2) × | 336 ± 25 | (3.1 ± 0.2) × | 12 ± 8 | 196 ± 8 | |
| −1000 | (2.9 ± 0.4) × | 833 ± 25 | (6.8 ± 0.7) × | 267 ± 14 | (3.1 ± 0.2) × | 31 ± 1 | 170 ± 16 |
| −200 | (0.8 ± 0.2) × | 681 ± 26 | (1.4 ± 0.2) × | 351 ± 26 | (8.2 ± 0.4) × | 27 ± 6 | 79 ± 7 |
| 200 | (3.5 ± 0.8) × | 593 ± 17 | (2.0 ± 0.2) × | 344 ± 19 | (7.9 ± 1.9) × | −77 ± 34 | 99 ± 28 |
| 600 | (7.9 ± 1.5) × | 648 ± 18 | (2.0 ± 0.2) × | 401 ± 18 | (3.8 ± 0.4) × | −11 ± 8 | 97 ± 9 |
| 1000 | (5.5 ± 0.9) × | 862 ± 27 | (4.1 ± 0.3) × | 506 ± 33 | (1.4 ± 0.3) × | −82 ± 10 | 117 ± 7 |
| 2000 | (5.4 ± 0.6) × | 830 ± 18 | (2.6 ± 0.1) × | 465 ± 29 | (1.4 ± 0.3) × | −96 ± 8 | 156 ± 5 |
| Target Material | C | Al | Si | Ti | Ni | Cu | Au |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| /nm | 1081 ± 362 | 982 ± 369 | 1081 ± 357 | 827 ± 310 | 660 ± 249 | 659 ± 249 | 511 ± 193 |
| /nm | 658 ± 130 | 585 ± 154 | 599 ± 166 | 493 ± 130 | 393 ± 104 | 393 ± 104 | 303 ± 80 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vladisavlevici, I.-M.; Ehret, M.; Filippov, E.; García-García, E.; Mendez, C.; Ruíz, M.O.; Varela, Ó.; Volpe, L.; Pérez-Hernández, J.A. Theoretical Study of the Pre-Plasma Density Scale Length’s Influence on the Absorption Efficiency in Laser–Solid Interaction at Relativistic Laser Intensities for PW-Class Lasers. Photonics 2025, 12, 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12010071
Vladisavlevici I-M, Ehret M, Filippov E, García-García E, Mendez C, Ruíz MO, Varela Ó, Volpe L, Pérez-Hernández JA. Theoretical Study of the Pre-Plasma Density Scale Length’s Influence on the Absorption Efficiency in Laser–Solid Interaction at Relativistic Laser Intensities for PW-Class Lasers. Photonics. 2025; 12(1):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12010071
Chicago/Turabian StyleVladisavlevici, Iuliana-Mariana, Michael Ehret, Evgeny Filippov, Enrique García-García, Cruz Mendez, Marta Olivar Ruíz, Óscar Varela, Luca Volpe, and Jose Antonio Pérez-Hernández. 2025. "Theoretical Study of the Pre-Plasma Density Scale Length’s Influence on the Absorption Efficiency in Laser–Solid Interaction at Relativistic Laser Intensities for PW-Class Lasers" Photonics 12, no. 1: 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12010071
APA StyleVladisavlevici, I.-M., Ehret, M., Filippov, E., García-García, E., Mendez, C., Ruíz, M. O., Varela, Ó., Volpe, L., & Pérez-Hernández, J. A. (2025). Theoretical Study of the Pre-Plasma Density Scale Length’s Influence on the Absorption Efficiency in Laser–Solid Interaction at Relativistic Laser Intensities for PW-Class Lasers. Photonics, 12(1), 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12010071






