Polymer Materials for U-Shaped Optic Fiber Sensors: A Review
Abstract
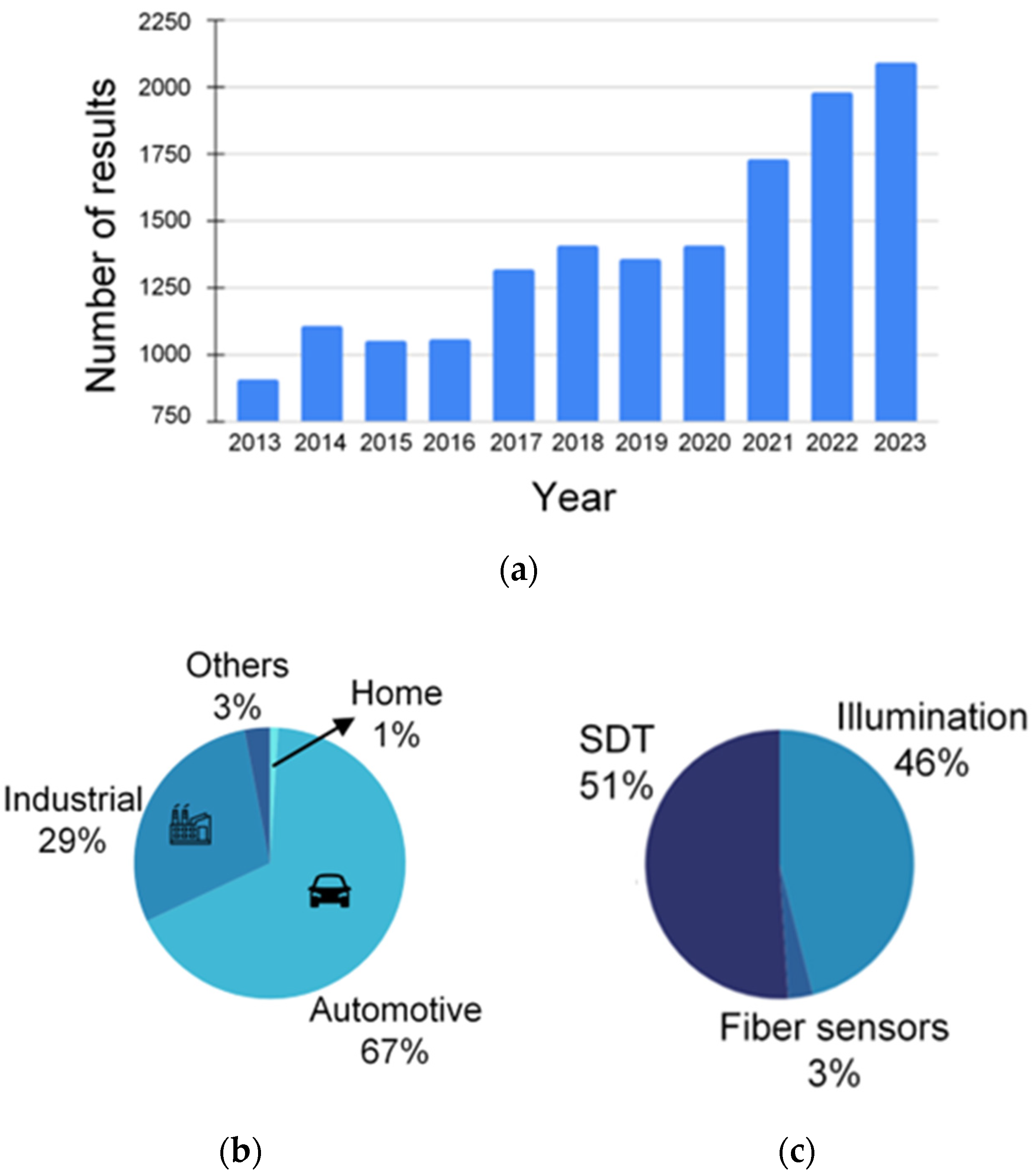
1. Introduction
2. POF U-Shaped Sensor Principles
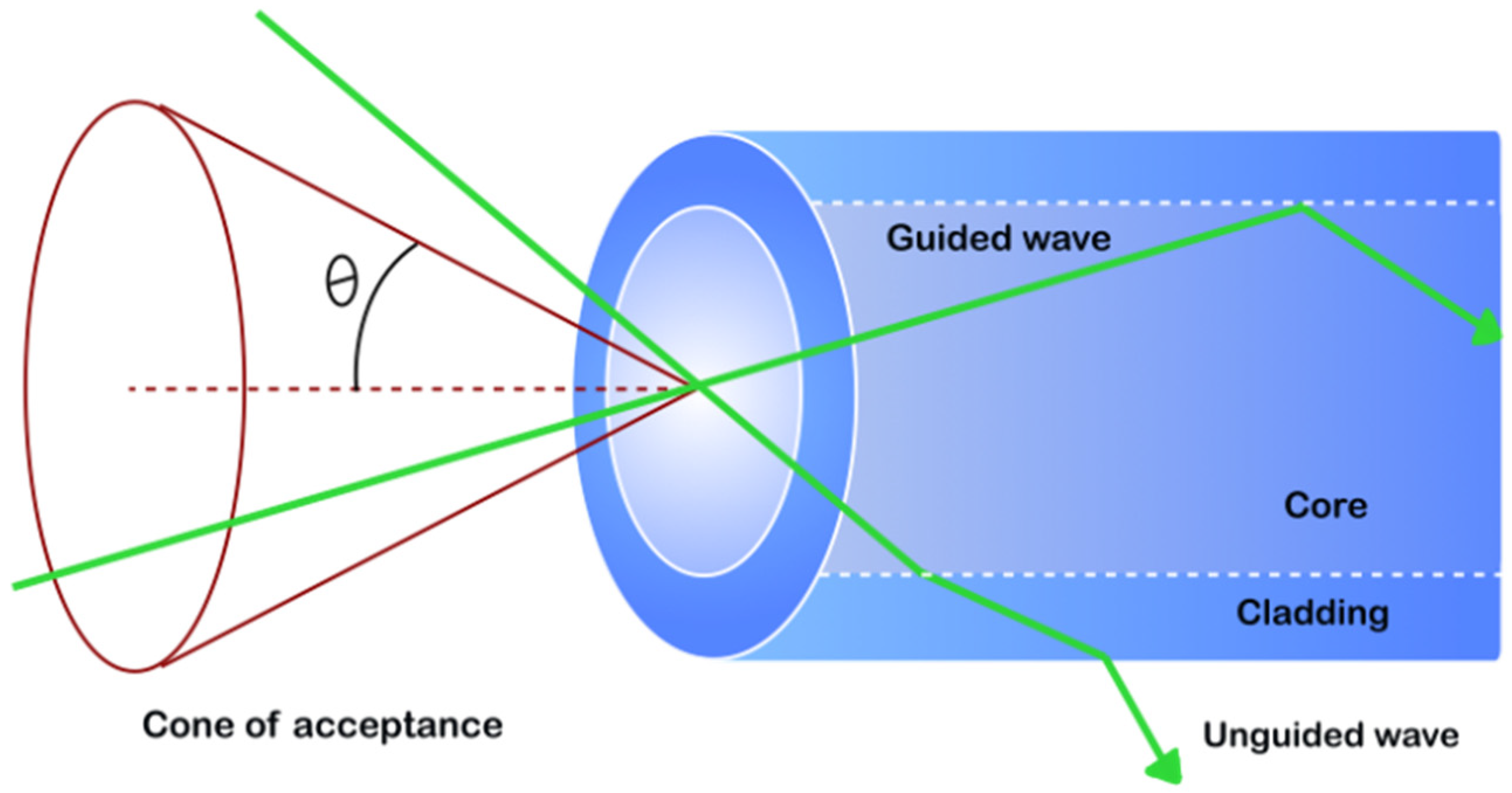
2.1. Sensing with Propagation Conditions in the Fiber
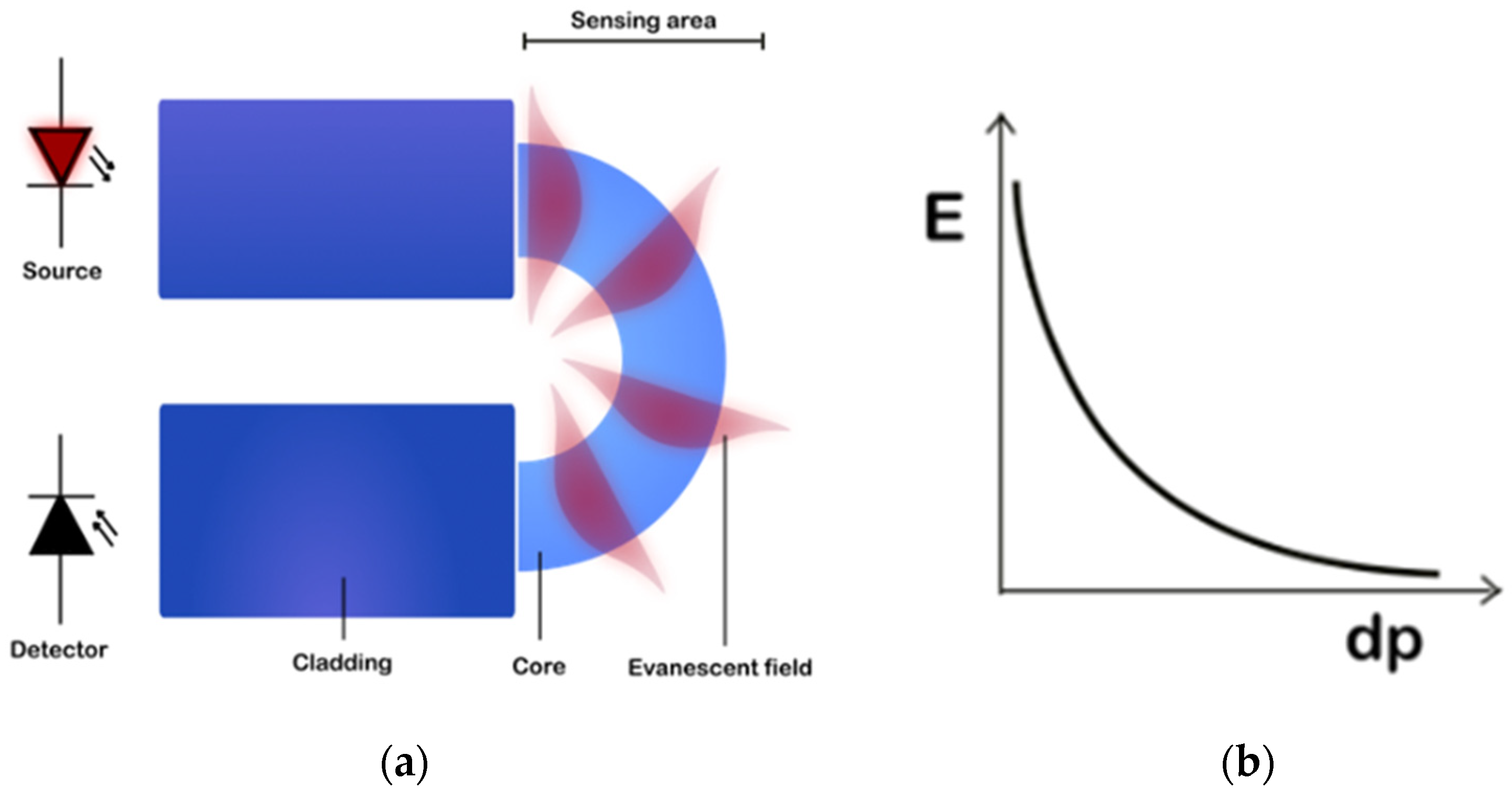
2.2. Sensing with Evanescent Field
2.3. U-Shaped Fabrication
3. Applications for U-Shaped POF
4. Materials for Polymer Optic Fibers
4.1. Conventional POFs
4.2. Hydrogel Optical Fibers (HOFs)
4.3. Biopolymer Optic Fibers (BIOPOFs)
4.4. High-Performance Polymer POFs (HPPPOFs)
4.5. Other POFs (UV-Curable and Sol–Gel-Based Acrylics, Water-Based Polymers and Urethanes)
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kallweit, J.; Pätzel, M.; Pursche, F.; Jabban, J.; Morobeid, M.; Gries, T. An Overview on Methods for Producing Side-Emitting Polymer Optical Fibers. Textiles 2021, 1, 337–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, J.R.; Zhong, L.S.; Wen, X.M.; Xu, C.X. Study on Surface Fluorinating for Reducing Attenuation of Polymethyl Methacrylate Polymer Optic Fiber. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 98, 2369–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coring SMF-28 Product Information. Available online: https://www.corning.com/media/worldwide/coc/documents/Fiber/product-information-sheets/PI-1424-AEN.pdf (accessed on 7 February 2024).
- Chu, F.; Yang, J. Coil-Shaped Plastic Optical Fiber Sensor Heads for Fluorescence Quenching Based TNT Sensing. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2012, 175, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, P.; Wu, B.; Bao, H.; Zheng, J. Screw-Shaped Plastic Optical Fibers for Refractive Index Sensing. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 5237–5242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Google Scholar. Available online: https://scholar.google.com/ (accessed on 27 February 2024).
- Habel, W.R.; Krebber, K. Photonic Sensors Review Fiber-Optic Sensor Applications in Civil and Geotechnical Engineering. Photonic Sens. 2011, 1, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cochrane, C.; Mordon, S.R.; Lesage, J.C.; Koncar, V. New Design of Textile Light Diffusers for Photodynamic Therapy. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2013, 33, 1170–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowri, A.; Rajamani, A.S.; Ramakrishna, B.; Sai, V.V.R. U-Bent Plastic Optical Fiber Probes as Refractive Index Based Fat Sensor for Milk Quality Monitoring. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2019, 47, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orelma, H.; Hokkanen, A.; Leppänen, I.; Kammiovirta, K.; Kapulainen, M.; Harlin, A. Optical Cellulose Fiber Made from Regenerated Cellulose and Cellulose Acetate for Water Sensor Applications. Cellulose 2020, 27, 1543–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierej, A.; Vagenende, M.; Filipkowski, A.; Siwicki, B.; Buczynski, R.; Thienpont, H.; Van Vlierberghe, S.; Geernaert, T.; Dubruel, P.; Berghmans, F.; et al. Poly(D,L-Lactic Acid) (PDLLA) Biodegradable and Biocompatible Polymer Optical Fiber. J. Light. Technol. 2019, 37, 1916–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodosiou, A.; Kalli, K. Recent Trends and Advances of Fibre Bragg Grating Sensors in CYTOP Polymer Optical Fibres. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2020, 54, 102079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TOPAS® COC Cyclic Olefin Copolymer. Available online: https://topas.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/TOPAS_Product-Brochure.pdf (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- Zeonex Product Information. Available online: https://www.zeon.co.jp/en/business/enterprise/resin/pdf/200323391.pdf (accessed on 7 February 2024).
- Stajanca, P.; Markos, C.; Nielsen, K.; Bang, O.; Stefani, A.; Krebber, K.; Fasano, A.; Woyessa, G.; Rasmussen, H.K. Fabrication and Characterization of Polycarbonate Microstructured Polymer Optical Fibers for High-Temperature-Resistant Fiber Bragg Grating Strain Sensors. Opt. Mater. 2016, 6, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cennamo, N.; Arcadio, F.; Marletta, V.; Baglio, S.; Zeni, L.; Ando, B. A Magnetic Field Sensor Based on SPR-POF Platforms and Ferrofluids. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statkiewicz-Barabach, G.; Mergo, P.; Urbanczyk, W. Bragg Grating-Based Fabry–Perot Interferometer Fabricated in a Polymer Fiber for Sensing with Improved Resolution. J. Opt. 2016, 19, 015609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Chen, Y.; Gao, S.; Min, R.; Woyessa, G.; Bang, O.; Qu, H.; Wang, H.; Caucheteur, C. Direct Bragg Grating Inscription in Single Mode Step-Index TOPAS/ZEONEX Polymer Optical Fiber Using 520 Nm Femtosecond Pulses. Citation 2022, 14, 1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dengler, S.A.; Roseeu, R.V.; Luber, G.M.; Ziemann, O.; Engelbrecht, R.; Schmauss, B. Performance Evaluation of Reference Reflections in Polymer Optical Fibers for Strain Sensing. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Optical Fiber Sensors; Optica Publishing Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Karpienko, K.; Wróbel, M.S.; Jędrzejewska-Szczerska, M. Determination of Refractive Index Dispersion Using Fiber-Optic Low-Coherence Fabry–Perot Interferometer: Implementation and Validation. Opt. Eng. 2014, 53, 077103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, R. Optical Fibers. Introduction to Fiber-Optic Communications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 19–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, B.E.A.; Teich, M.C. Fundamentals of Photonics 3rd Edition Part I: Optics Part II: Photonics; Wiley Series in Pure and Applied Optics; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; p. 1520. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, J.J.; Ghosh, A. Intensity Modulation Based U Shaped Plastic Optical Fiber Refractive Index Sensor. In Proceedings of the 2022 6th International Conference on Trends in Electronics and Informatics, ICOEI, Tirunelveli, India, 28–30 April 2022; pp. 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beres, C.; de Nazaré, F.V.B.; de Souza, N.C.C.; Miguel, M.A.L.; Werneck, M.M. Tapered Plastic Optical Fiber-Based Biosensor—Tests and Application. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 30, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomer, M.; Galindez, C.A.; Quintela, M.A.; Quintela, A.; Mirapeix, J.; Lopez-Higuera, J.M. Refractometric Sensor Based on Induced Losses in the Region of Transition from a Curved Side-Polished POF Fiber. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Optical Fibre Sensors, Perth, WA, Australia, 16 May 2008; Volume 7004, p. 70045H. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Listewnik, P.; Hirsch, M.; Struk, P.; Weber, M.; Bechelany, M.; Jędrzejewska-Szczerska, M. Preparation and Characterization of Microsphere ZnO ALD Coating Dedicated for the Fiber-Optic Refractive Index Sensor. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, M.; Listewnik, P.; Struk, P.; Weber, M.; Bechelany, M.; Szczerska, M. ZnO Coated Fiber Optic Microsphere Sensor for the Enhanced Refractive Index Sensing. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2019, 298, 111594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsen, L.B. Evanescent waves. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1976, 66, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, A.J.Y.; Ng, S.M.; Stoddart, P.R.; Chua, H.S. Theoretical Model and Design Considerations of U-Shaped Fiber Optic Sensors: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 14578–14589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.-C.; Li, Y.-L.; Wu, C.-W.; Chiang, C.-C. Glucose Sensor Using U-Shaped Optical Fiber Probe with Gold Nanoparticles and Glucose Oxidase. Sensors 2018, 18, 1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memon, S.F.; Wang, R.; Strunz, B.; Chowdhry, B.S.; Pembroke, J.T.; Lewis, E. Novel Corrugated Long Period Grating Surface Balloon-Shaped Heterocore-Structured Plastic Optical Fibre Sensor for Microalgal Bioethanol Production. Sensors 2023, 23, 1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, D.; Xu, Y.; Sun, S.; Sun, X. Refractive Index Sensor Based on Double Side-Polished U-Shaped Plastic Optical Fiber. Sensors 2020, 20, 5253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viegas, D.; Abad, S.; Santos, J.L.; Ferreira, L.A.; Araújo, F.M. Non-Terminal Miniature Fiber Bragg Grating Temperature Probe Based in a u-Shape Lossless Taper. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2010, 21, 094002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Leffers, L.; Locmelis, J.; Bremer, K.; Roth, B.; Overmeyer, L. Polymer Optical Fibre Bend Sensor Based on Eccentrical Bragg Gratings. In Proceedings of the 2021 Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics (CLEO), San Jose, CA, USA, 9–14 May 2021; p. STu2F.8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, A.J.Y.; Ng, S.M.; Stoddart, P.R.; Chua, H.S. Trends and Applications of U-Shaped Fiber Optic Sensors: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; M Granville, A. Polymer Fiber Optic Sensors—A Mini Review of Their Synthesis and Applications. J. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandemur, G.; Rodrigues, D.; Allil, R.; Queiroz, V.; Peixoto, R.; Werneck, M.; Miguel, M. Plastic Optical Fiber-Based Biosensor Platform for Rapid Cell Detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 54, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, C.; Shao, P.; Li, S.; Li, S.; Liu, H.; Deng, H.; Chen, M.; Yuan, L.; Deng, S. Double-Side Polished U-Shape Plastic Optical Fiber Based SPR Sensor for the Simultaneous Measurement of Refractive Index and Temperature. Opt. Commun. 2022, 525, 128844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johari, S.H.; Cheak, T.Z.; Abdul Rahim, H.R.; Jali, M.H.; Mohd Yusof, H.H.; Md Johari, M.A.; Yasin, M.; Harun, S.W. ZnO Nanorods Coated Tapered U-Shape Plastic Optical Fiber for Relative Humidity Detection. Photonics 2022, 9, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Gomez, D.; He, C.; Korposh, S.; Morgan, S.P.; Correia, R.; Hayes-Gill, B.; Setchfield, K.; Liu, L. A U-Shape Fibre-Optic pH Sensor Based on Hydrogen Bonding of Ethyl Cellulose with a Sol-Gel Matrix. J. Light. Technol. 2021, 39, 1557–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yetisen, A.K.; Jiang, N.; Fallahi, A.; Montelongo, Y.; Ruiz-Esparza, G.U.; Tamayol, A.; Zhang, Y.S.; Mahmood, I.; Yang, S.A.; Kim, K.S.; et al. Glucose-Sensitive Hydrogel Optical Fibers Functionalized with Phenylboronic Acid. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1606380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupar, D.Z.; Bajić, J.S.; Joža, A.V.; Dakić, B.M.; Slankamenac, M.P.; Živanov, M.B.; Cibula, E. Remote Monitoring of Water Salinity by Using Side-Polished Fiber-Optic U-Shaped Sensor. In Proceedings of the 15th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference and Exposition, EPE-PEMC 2012 ECCE Europe, Novi Sad, Serbia, 4–6 September 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johari, S.H.; Cheak, T.Z.; Rahim, H.R.A.; Jali, M.H.; Yusof, H.H.M.; Johari, M.A.M.; Harun, S.W. Formaldehyde Sensing Using Tapered U-Shape Plastic Optical Fiber Coated with Zinc Oxide Nanorods. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 91445–91451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaiswal, A.K.; Hokkanen, A.; Kapulainen, M.; Khakalo, A.; Nonappa; Ikkala, O.; Orelma, H. Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC) Optical Fibers for Environment Sensing and Short-Range Optical Signal Transmission. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 3315–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee Tan, A.J.; Seng Ung, K.; Ng, S.M.; Stoddart, P.R.; Chua, H.S. Refractive Index, Temperature, and Heat Source Origin Sensing with Dual U-Shaped Fiber Probes. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Sensors and Nanotechnology, Port Dickson, Malaysia, 22–24 September 2021; pp. 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Z.; Ren, Z.; Yang, X.; Wang, Q. Triangular Silver Nanoparticle U-Bent Fiber Sensor Based on Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance. AIP Adv. 2019, 9, 085307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Dhawangale, A.; Mukherji, S. Hand-Held Optical Sensor Using Denatured Antibody Coated Electro-Active Polymer for Ultra-Trace Detection of Copper in Blood Serum and Environmental Samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 110, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, A.; Amrutha, M.S.; Srivastava, P.; Sunil, S.; Sai, V.V.R.; Srinivasan, R. Development of a U-Bent Plastic Optical Fiber Biosensor with Plasmonic Labels for the Detection of Chikungunya Non-Structural Protein 3. Analyst 2021, 146, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.C.J. Discrete Multitone Modulation for Short-Range Optical Communications. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universiteit Eindhoven, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moslan, M.S.; Othman, M.H.D.; Samavati, A.; Salim, M.A.M.; Rahman, M.A.; Ismail, A.F.; Bakhtiar, H. Fabrication of Polycarbonate Polymer Optical Fibre Core via Extrusion Method: The Role of Temperature Gradient and Collector Speed on Its Characteristics. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2020, 55, 102162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckers, M.; Schlüter, T.; Vad, T.; Gries, T.; Bunge, C.A. An Overview on Fabrication Methods for Polymer Optical Fibers. Polym. Int. 2015, 64, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESKA Polymer Optical Fiber Technical Data. Available online: https://www.pofeska.com/pofeskae/download/02.html (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- Zubel, M.G.; Fasano, A.; Woyessa, G.; Sugden, K.; Rasmussen, H.K.; Bang, O. 3D-Printed PMMA Preform for Hollow-Core POF Drawing. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Plastic Optical Fibers, Birmingham, UK, 13–15 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ziemann, O.; Krauser, J.; Zamzow, P.E.; Daum, W. POF Handbook: Optical Short Range Transmission Systems; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 1–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pituru, S.M.; Greabu, M.; Totan, A.; Imre, M.; Pantea, M.; Spinu, T.; Tancu, A.M.C.; Popoviciu, N.O.; Stanescu, I.I.; Ionescu, E. A Review on the Biocompatibility of PMMA-Based Dental Materials for Interim Prosthetic Restorations with a Glimpse into Their Modern Manufacturing Techniques. Materials 2020, 13, 2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, U.; Karim, K.J.B.A.; Buang, N.A. A Review of the Properties and Applications of Poly (Methyl Methacrylate) (PMMA). Polym. Rev. 2015, 55, 678–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Castro Monsores, K.G.; Da Silva, A.O.; Oliveira, S.D.S.A.; Rodrigues, J.G.P.; Weber, R.P. Influence of Ultraviolet Radiation on Polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA). J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 3713–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierej, A.; Filipkowski, A.; Pysz, D.; Buczynski, R.; Vagenende, M.; Dubruel, P.; Thienpont, H.; Geernaert, T.; Berghmans, F. On the Characterization of Novel Step-Index Biocompatible and Biodegradable Poly(D,L-Lactic Acid) Based Optical Fiber. J. Light. Technol. 2020, 38, 1905–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omenetto, F.G.; Kaplan, D.L. A New Route for Silk. Nat. Photonics 2008, 2, 641–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, N.; Jansson, R.; Widhe, M.; Benselfelt, T.; Håkansson, K.M.O.; Lundell, F.; Hedhammar, M.; Söderberg, L.D. Ultrastrong and Bioactive Nanostructured Bio-Based Composites. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 5148–5159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CYTOPTM Technical Information—AGC Chemicals Europe. Available online: https://www.agcce.com/cytop-technical-information/ (accessed on 13 December 2023).
- CYTOP®|Product Information|Fluoroproducts Business|AGC Chemicals Company. Available online: https://www.agc-chemicals.com/jp/en/fluorine/products/detail/index.html?pCode=JP-EN-F019 (accessed on 13 December 2023).
- Koike, Y.; Koike, K. Optical Fibers. In Polymer Science: A Comprehensive Reference; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 283–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, Y. Fundamentals of Plastic Optical Fibers; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH 7 Co.: Weinheim, Germany, 2014; pp. 139–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Junior, A.G.; Theodosiou, A.; Díaz, C.R.; Marques, C.; Pontes, M.J.; Kalli, K.; Frizera, A. Simultaneous Measurement of Axial Strain, Bending and Torsion with a Single Fiber Bragg Grating in CYTOP Fiber. J. Light. Technol. 2019, 37, 971–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, Y.-G.; Yazd, N.S.; Chapalo, I.; Chah, K.; Hu, X.; Mégret, P. Properties of Fiber Bragg Grating in CYTOP Fiber Response to Temperature, Humidity, and Strain Using Factorial Design. Sensors 2022, 22, 1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evertz, A.; Schrein, D.; Olsen, E.; Hoffmann, G.; Overmeyer, L. Dip coating of thin polymer optical fibers. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2021, 66, 102638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Tian, F.; Yang, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, X.; Yang, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, T.; et al. Optical Fibers with Special Shaped Cores Drawn from 3D Printed Preforms. Optik 2017, 133, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.; Humar, M.; Kim, S.; Yun, S.H. Step-Index Optical Fiber Made of Biocompatible Hydrogels. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 4081–4086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Hou, K.; Yu, N.; Wei, P.; Chen, T.; Zhang, C.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Cao, R.; Zhu, L.; et al. Temperature-Adaptive Hydrogel Optical Waveguide with Soft Tissue-Affinity for Thermal Regulated Interventional Photomedicine. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, S.T.; Domachuk, P.; Amsden, J.; Bressner, J.; Lewis, J.A.; Kaplan, D.L.; Omenetto, F.C. Biocompatible Silk Printed Optical Waveguides. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2411–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woyessa, G.; Rasmussen, H.K.; Bang, O. Zeonex—A Route towards Low Loss Humidity Insensitive Single-Mode Step-Index Polymer Optical Fibre. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2020, 57, 102231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoetex Chemical Resistance. Available online: https://www.zeonex.com/pharmaceuticals.aspx.html (accessed on 7 February 2023).
- Woyessa, G.; Fasano, A.; Markos, C.; Rasmussen, H.K.; Bang, O. Zeonex Microstructured Polymer Optical Fibre Bragg Grating Sensor. In Photonics and Fiber Technology 2016 (ACOFT, BGPP, NP); Optica Publishing Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2016; p. AW3C.4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woliński, T.R.; Mileńko, K.; Tefelska, M.M.; Rutkowska, K.A.; Domański, A.W.; Ertman, S.; Orzechowski, K.; Sierakowski, M.; Chojnowska, O.; Dąbrowski, R. Liquid Crystals and Polymer-Based Photonic Crystal Fibers. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2014, 594, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglev, R.; Møller, E.; Højgaard, J.; Bang, O.; Janting, J. Optimization of All-Polymer Optical Fiber Oxygen Sensors with Antenna Dyes and Improved Solvent Selection Using Hansen Solubility Parameters. Sensors 2021, 21, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pires, R.A.; Pashkuleva, I.; Reis, R.L. Multifunctional Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Reimer, M.; Van Opdenbosch, D.; Zollfrank, C. Fabrication of Cellulose-Based Biopolymer Optical Fibers and Their Theoretical Attenuation Limit. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 3297–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woyessa, G.; Fasano, A.; Stefani, A.; Markos, C.; Nielsen, K.; Rasmussen, H.K.; Bang, O.; Dobb, H.; Webb, D.J.; Kalli, K.; et al. Single Mode Step-Index Polymer Optical Fiber for Humidity Insensitive High Temperature Fiber Bragg Grating Sensors. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Ali, M.; Elsherif, M.; Butt, H. UV polymerization fabrication method for polymer composite based optical fiber sensors. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 10823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimer, M.; Mayer, K.; Van Opdenbosch, D.; Scheibel, T.; Zollfrank, C. Biocompatible Optical Fibers Made of Regenerated Cellulose and Recombinant Cellulose-Binding Spider Silk. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MatWeb Material Property Data. Available online: https://www.matweb.com/search/DataSheet.aspx?MatGUID=632572aeef2a4224b5ac8fbd4f1b6f77&ckck=1 (accessed on 5 January 2025).
- He, R.; Teng, C.; Kumar, S.; Marques, C.; Min, R. Polymer Optical Fiber Liquid Level Sensor: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 1081–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcas, A.D.S.; Dutra, F.D.S.; Allil, R.C.S.B.; Werneck, M.M. Surface Plasmon Resonance and Bending Loss-Based U-Shaped Plastic Optical Fiber Biosensors. Sensors 2018, 18, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, A.R.A.; Hakim, A.A.N.; Yahaya, N.; Surani, A.H. U-Bent Polymer Optical Fiber (POF) for Escherichia Coli Detection. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. Rapid Commun. 2020, 14, 118–122. [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki, T.; Kamio, H.; Yoshioka, M.; Ueda, A.; Kuramitz, H.; Watanabe, T. U-Shaped Plastic Optical Fiber Sensor for Scale Deposition in Hot Spring Water. Anal. Sci. 2022, 38, 1549–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimer, M.; Zollfrank, C. Cellulose for Light Manipulation: Methods, Applications, and Prospects. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2003866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godbout, N.; Guo, N.; Gao, Y.; Dubois, C.; Dupuis, A.; Skorobogatiy, M.; Lacroix, S. Prospective for Biodegradable Microstructured Optical Fibers. Opt. Lett. 2007, 32, 109–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Peng, Y.; Chen, M.-Q.; Xia, F.; Tong, R.-J. U-Shaped Microfiber Coupler Coated with Polyvinyl Alcohol Film for Highly Sensitive Humidity Detection. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2019, 285, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.Y.; Hsu, H.C.; Tsai, Y.T.; Feng, W.K.; Lin, C.L.; Chiang, C.C. U-Shaped Optical Fiber Probes Coated with Electrically Doped GQDs for Humidity Measurements. Polymers 2021, 13, 2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dante, A.; Silva, P.H.; Lopes, R.; Allil, A.; Sbano, A.; Esteves, M.E.; Silva, M.; Werneck, M.; Allil, R. Development of an Escherichia Coli Optical Biosensor with Computational Validation. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2407, 012029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Du, F.; Jariyavidyanont, K.; Zhuravlev, E.; Schick, C.; Androsch, R. Glass Transition Temperature of Poly(D,L-Lactic Acid) of Different Molar Mass. Thermochim. Acta 2022, 718, 179387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsherif, M.; Umair Hassan, M.; Yetisen, A.K.; Butt, H. Hydrogel Optical Fibers for Continuous Glucose Monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 137, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekowska, N.; Arbeiter, D.; Konasch, J.; Riess, A.; Mau, R.; Eickner, T.; Seitz, H.; Grabow, N.; Teske, M. Thermomechanical properties of PEGDA and its co-polymers. Curr. Dir. Biomed. Eng. 2018, 4, 669–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczerska, M. Temperature Sensors Based on Polymer Fiber Optic Interferometer. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Application | Metrological Parameter | Material | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical | Temperature | Temp. range: 30–80 °C Sensitivity: 0.596 nm/°C | PMMA coated with PDMS | [38] |
| Humidity | Range: 35–90% RH Sensitivity: 0.0194 V/%RH | PMMA coated with ZnO | [39] | |
| RI | Range: 1.34–1.37 RIU Sensitivity: 1258 nm/RIU | PMMA coated with PDMS | [38] | |
| Chemical | pH | Range: 4.5 to 12.5 Resolution: 0.02 pH within the pH range: 7.5–12.5 | n.r. * | [40] |
| Glucose | Lowest detected concentration: 1.2 mmol L−1 | p (AM-co-PEGDA) coated with Ca-alginate | [41] | |
| Water salinity | Concentration: 0–25% v/v | PMMA | [42] | |
| Ethanol | Concentration: 0.00633 to 80% v/v LOD of 9.7 × 10−6 RIU | PMMA | [31] | |
| Formaldehyde Vapor | Concentration: 5% to 20% Sensitivity: 0.00543 V/% | PMMA coated with ZnO | [43] | |
| Biomedical | E. coli | 104–108 CFU/ml | PMMA | [37] |
| Respiratory rate sensor | Breaths per minute | CMC | [44] | |
| Conventional Polymer Optic Fibers (POFs) | Hydrogel Optical Fibers (HOFs) | Biopolymer Optic Fibers (BIOPOFs) | High-Performance Polymers (HPPs) | UV Acrylics, Polymers, Urethanes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poly (methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) [48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57] | The poly (D,L-Lactic Acid) (PDLLA) [11,58] | Spider silk [59,60] | CYTOP [49,61,62,63,64,65,66] | UV-curable methacrylates [67] |
| Polycarbonate (PC) [50,54,68] | Poly (ethylene glycol) (PEG) [69,70] | Silkworm silk [59,71] | ZEONEX [72,73,74,75] | Methacrylate set with luminophores [76] |
| Polystyrene (PS) [54] | Polyethylene glycol diacrylate (PEGDA) [77] | Cellulose [78] | TOPAS [13,79] | UV polymer composite [80] |
| Natural polymers (agarose, gelatin, cellulose derivatives) [77,78,81] | Rubbers, urethanes, silicones [77] | |||
| Polyacrylamide (PAAm) [77] |
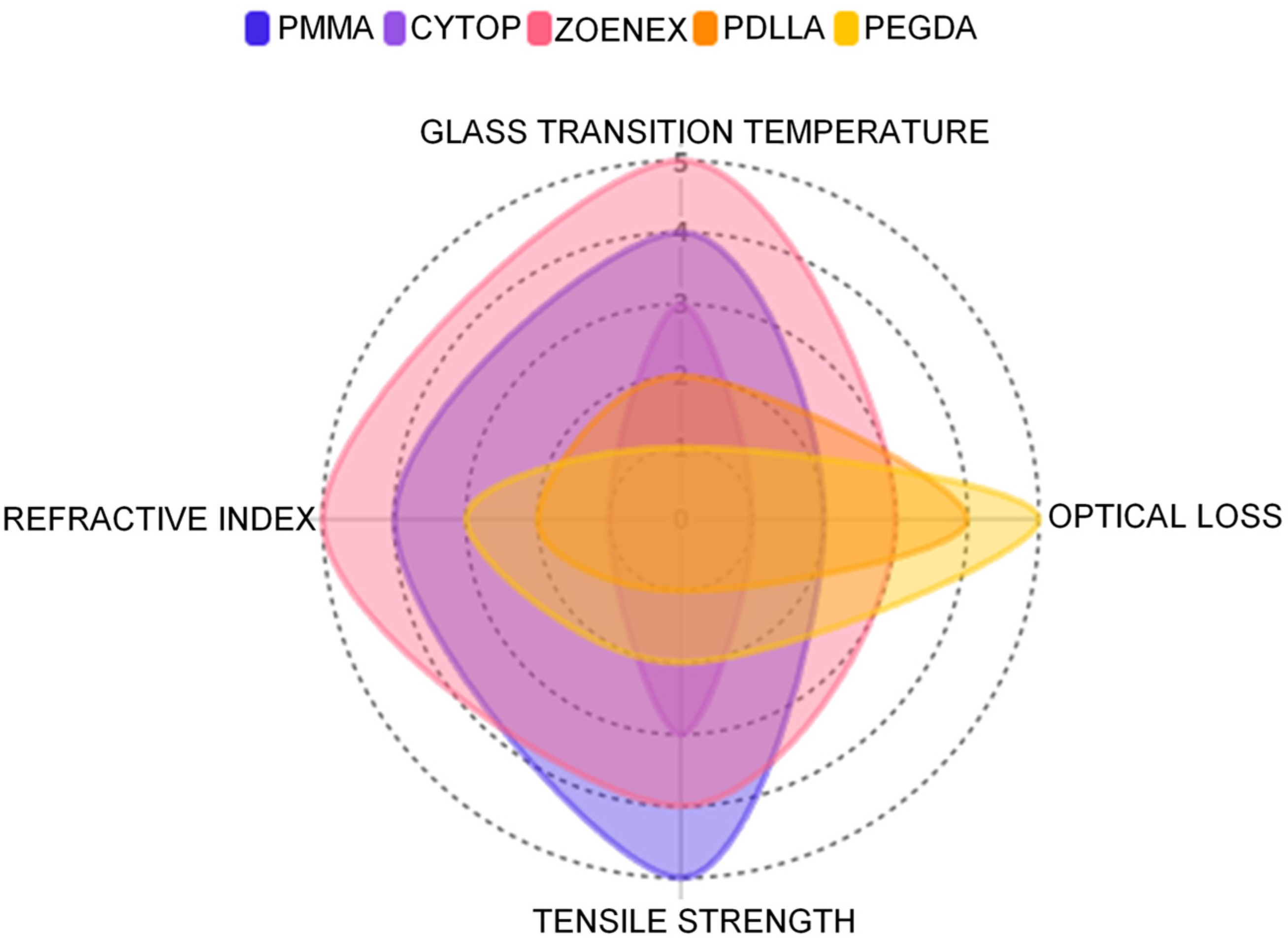
| Material | Refractive Index of Core | Optical Loss [dB/m] | Tensile Strength [MPa] | Glass Trans. Temp. [°C] | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PMMA | 1.49 @850 nm | 0.2 @650 nm | 76 | 105–120 | [51,52,53] |
| CYTOP | 1.34 @589 nm | 0.06 @850 nm | 41–49 | 108 | [61,62] |
| ZOENEX | 1.52 @589 nm | 2.34 @690 nm | 63–70 | 139 | [72,73,74,75,82] |
| PDLLA | 1.45 @656 nm | 11 @772 nm | n.r. * | 58 | [11,92] |
| PEGDA | 1.46 @532 nm | 40 @532 nm | 2.8–9.5 | 26.3–51 | [41,93,94] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sokołowski, P.; Łubiński, J.; Wierzba, P.; Czubek, J.; Miluski, P.; Janiak, F.; Guan, S.; Szczerska, M. Polymer Materials for U-Shaped Optic Fiber Sensors: A Review. Photonics 2025, 12, 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12010056
Sokołowski P, Łubiński J, Wierzba P, Czubek J, Miluski P, Janiak F, Guan S, Szczerska M. Polymer Materials for U-Shaped Optic Fiber Sensors: A Review. Photonics. 2025; 12(1):56. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12010056
Chicago/Turabian StyleSokołowski, Patryk, Jacek Łubiński, Paweł Wierzba, Jakub Czubek, Piotr Miluski, Filip Janiak, Shanyue Guan, and Małgorzata Szczerska. 2025. "Polymer Materials for U-Shaped Optic Fiber Sensors: A Review" Photonics 12, no. 1: 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12010056
APA StyleSokołowski, P., Łubiński, J., Wierzba, P., Czubek, J., Miluski, P., Janiak, F., Guan, S., & Szczerska, M. (2025). Polymer Materials for U-Shaped Optic Fiber Sensors: A Review. Photonics, 12(1), 56. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12010056






