Research on Monocular Depth Sensing Method Based on Liquid Zoom Imaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Principles and Methods
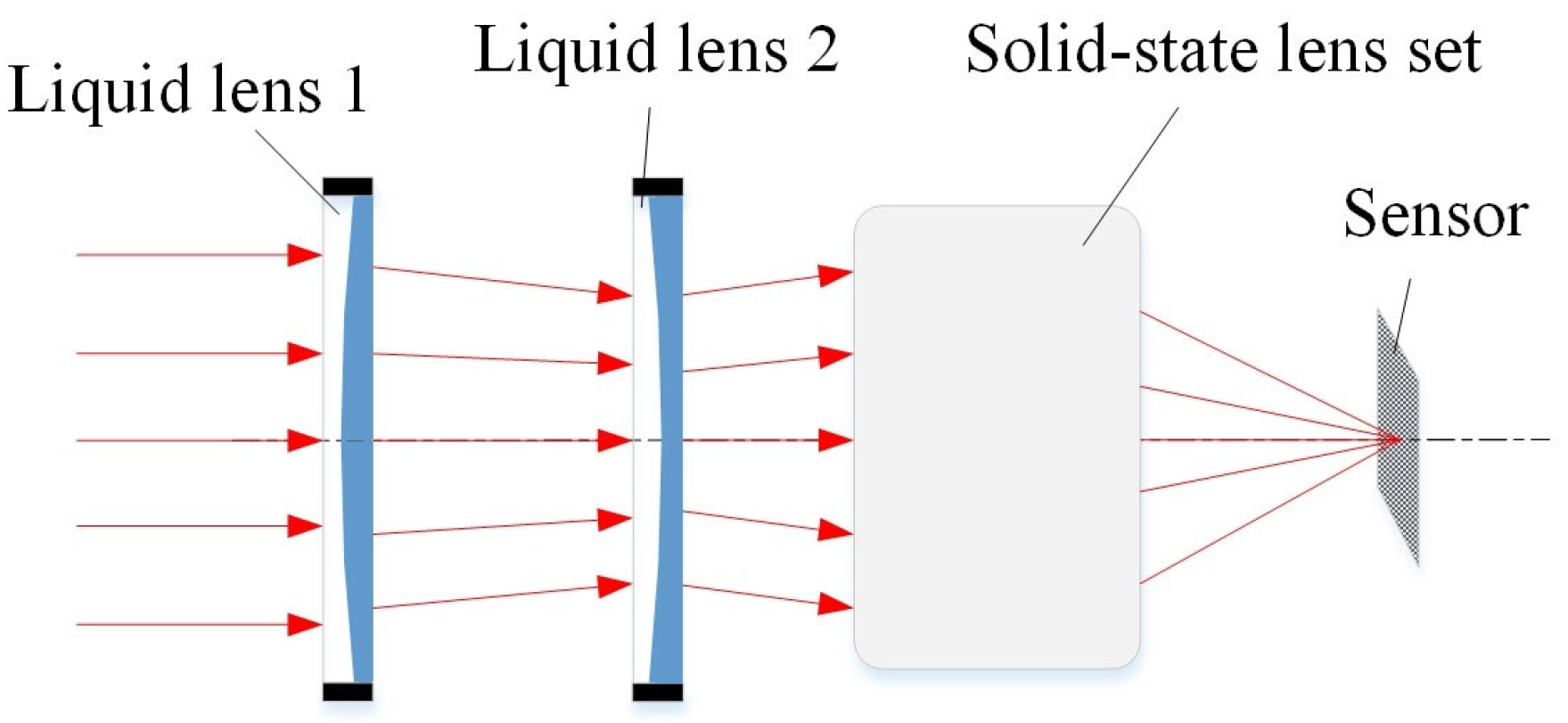
2.1. System Components
2.2. Depth Measurement Method
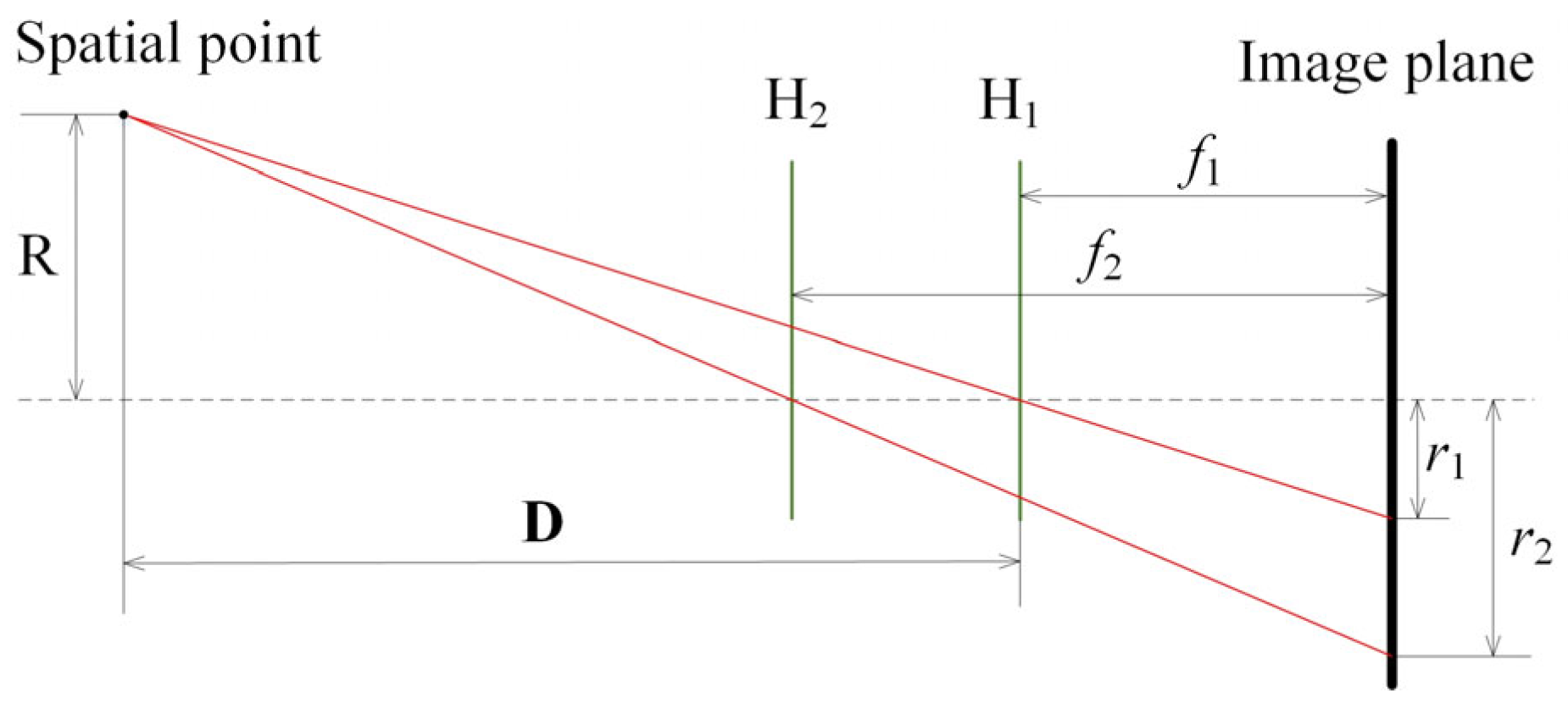
2.2.1. Theoretical Basis
2.2.2. Algorithm Analysis
2.3. Error Analysis and Optimization
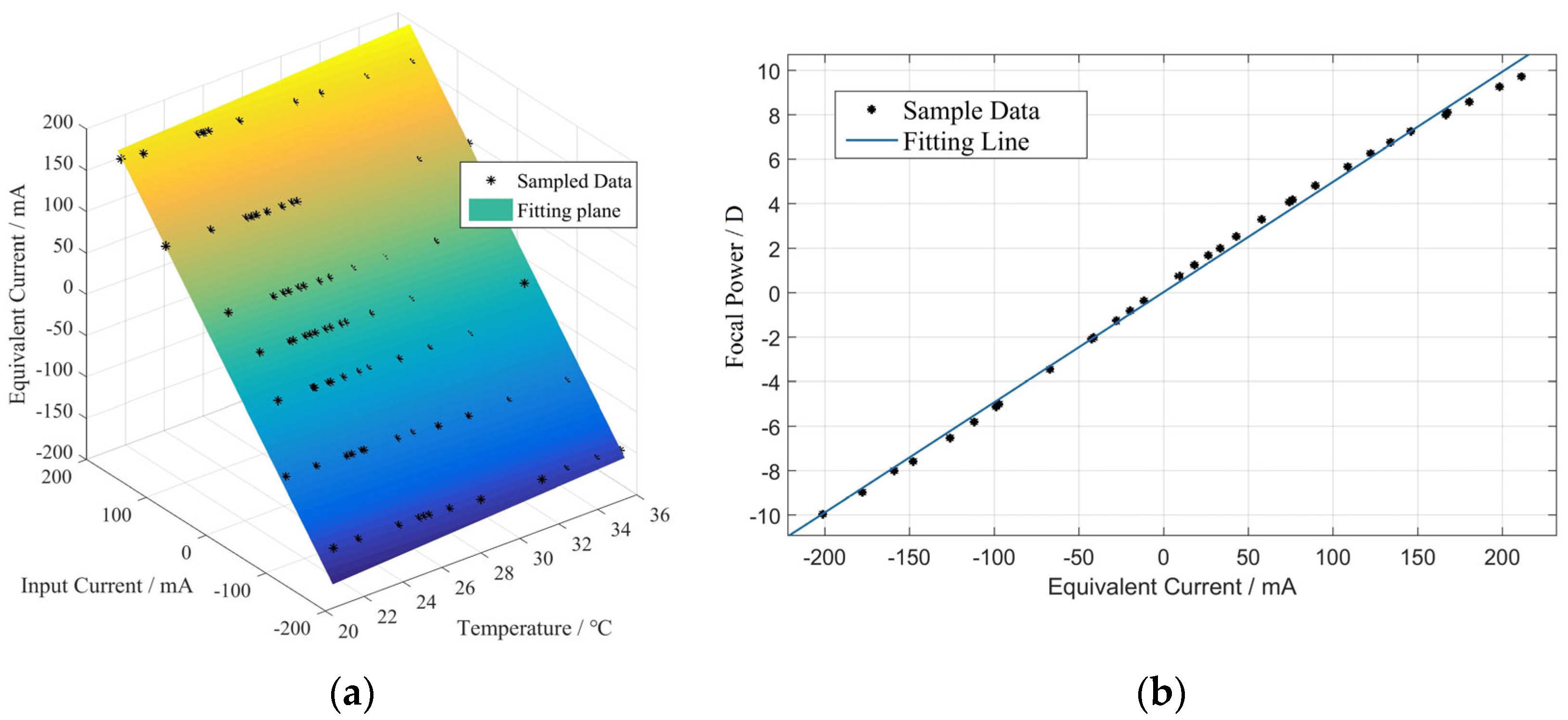
2.3.1. Temperature Drift and Compensation
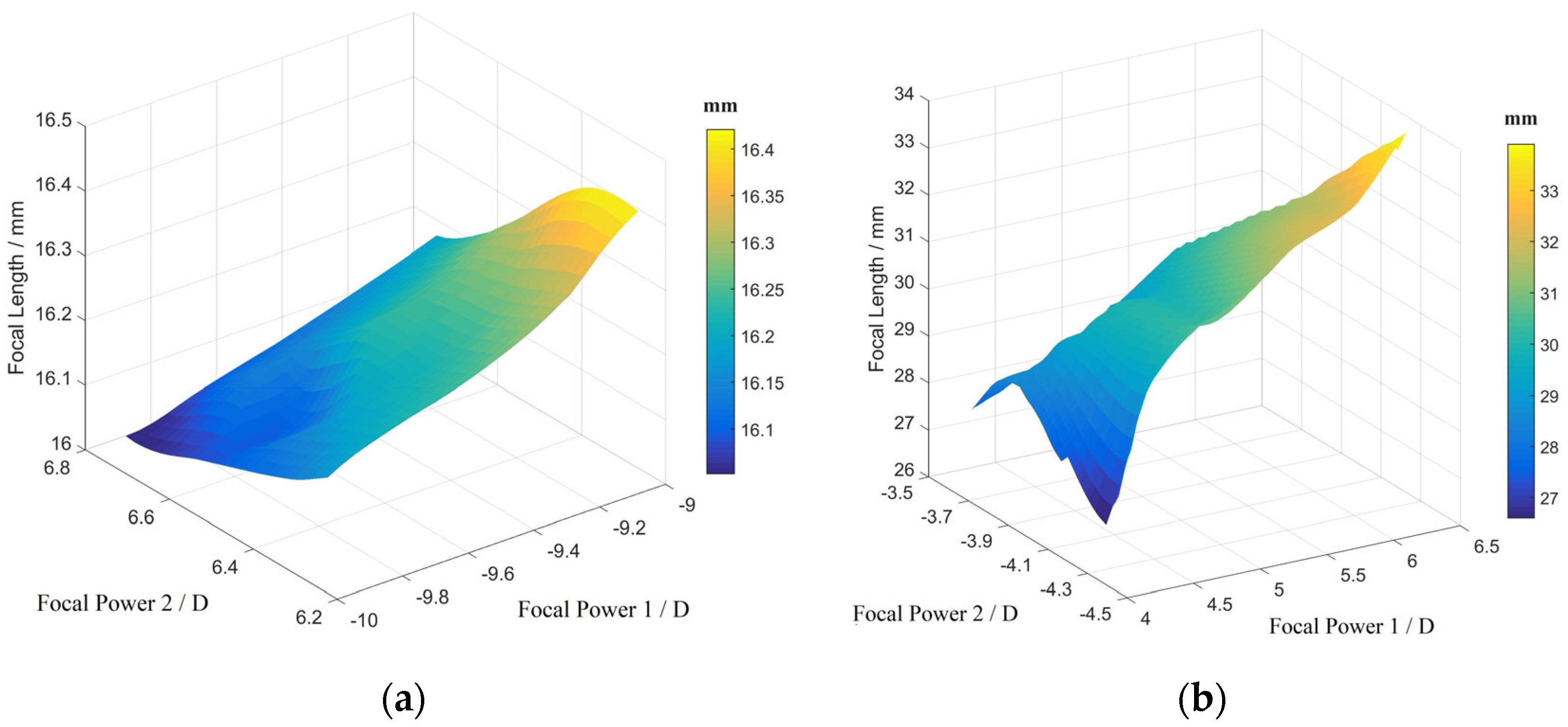
2.3.2. Parameter Model Optimization
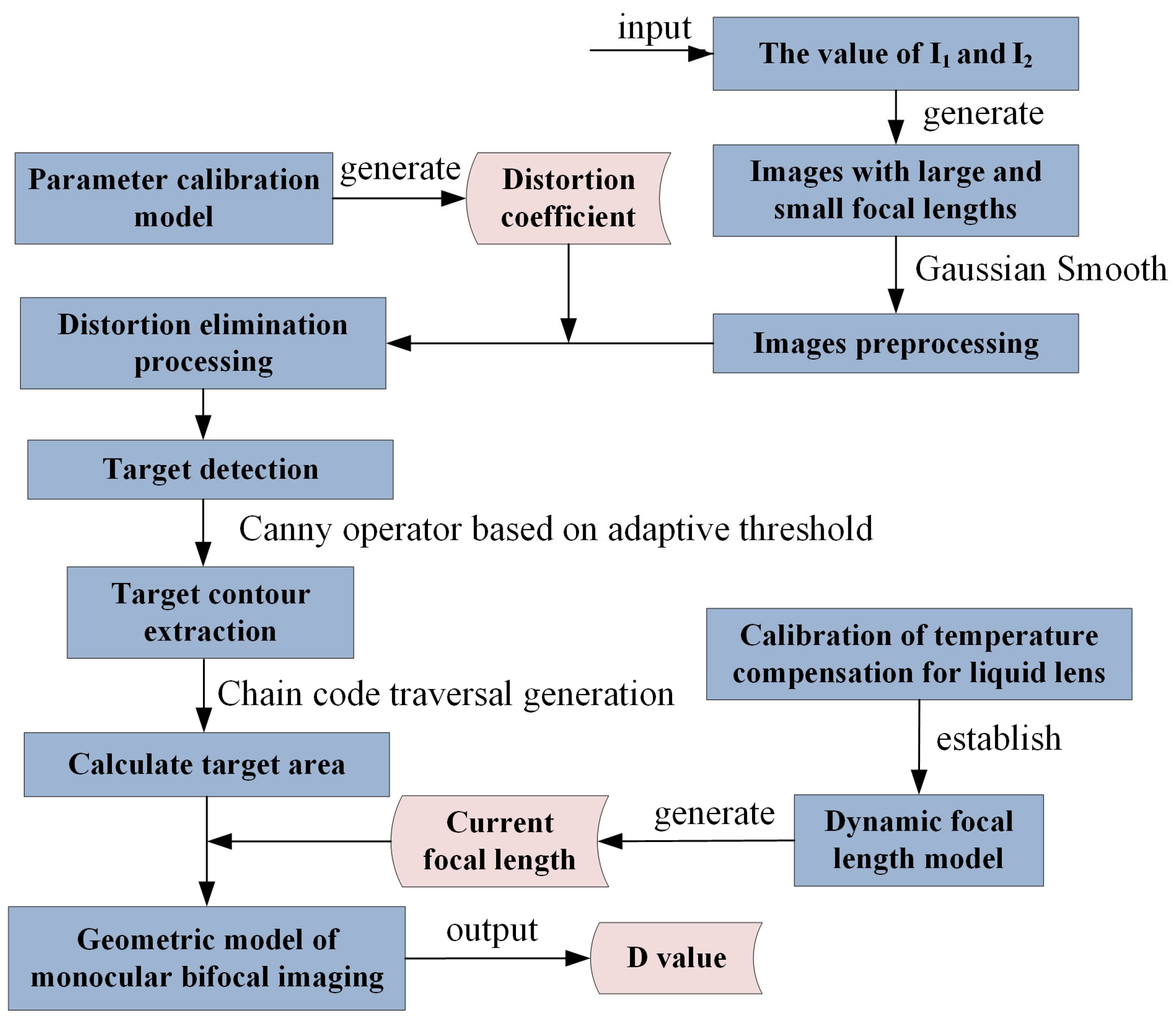
2.3.3. Process of Liquid Monocular Sensing Algorithm
3. Experiment and Discussion
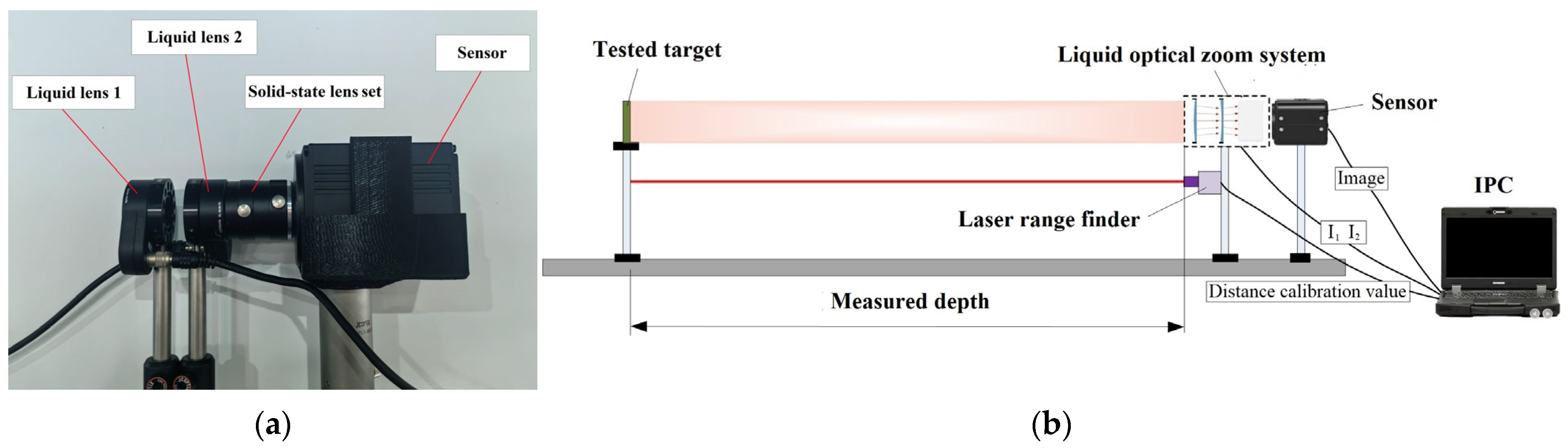
3.1. Experimental Method
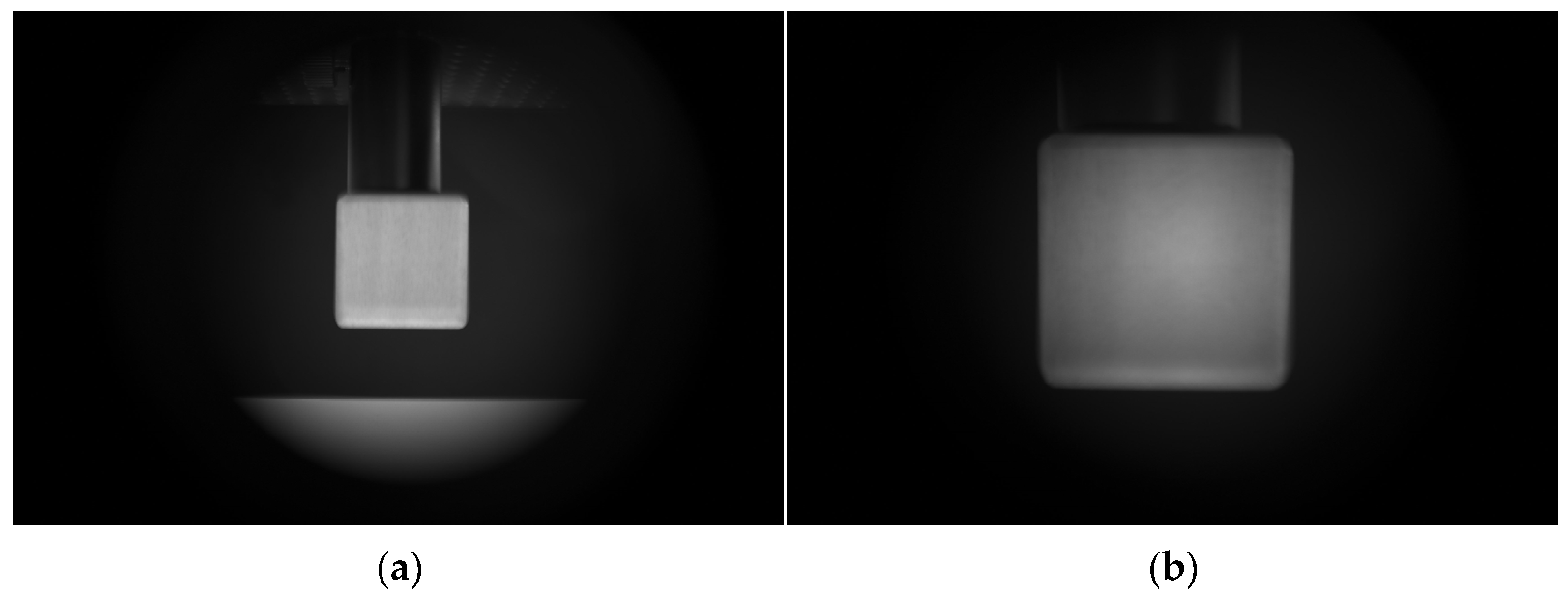
3.2. Liquid lens calibration
3.3. System Parameter Determination
3.4. Target Depth Measurement
3.4.1. Verification of Measurement Accuracy and Efficiency
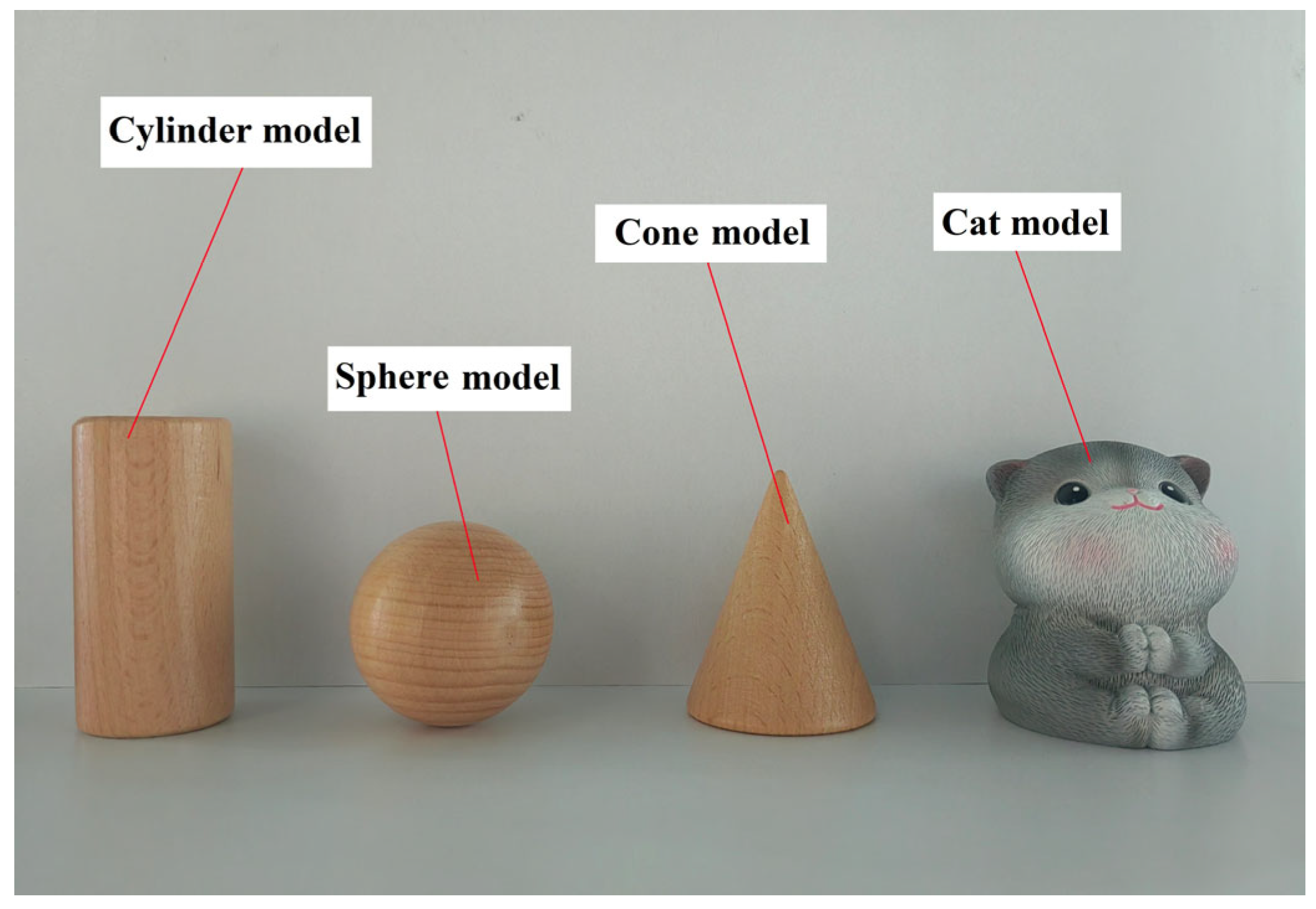
3.4.2. Validation of Generalization Ability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, Y.; Li, Q.; Chu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, C. Real-time detection and spatial localization of insulators for UAV inspection based on binocular stereo vision. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.L.; Ao, L.; Zheng, J.; Sun, Z.B. Reconstructing depth images for time-of-flight cameras based on second-order correlation functions. Photonics 2023, 10, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Liu, C.; Liu, P.; Zhang, G. Study on monocular distance measurement based on auto focus. Mach. Des. Manuf. 2019, 4, 146–149. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, H.; Yadav, A.S.; Gupta, S.; Venkatesh, K.S. Depth map estimation using defocus and motion cues. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2018, 29, 1365–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alenya, G.; Alberich, M.; Torras, C. Depth from the visual motion of a planar target induced by zooming. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics & Automation, Rome, Italy, 10–14 April 2007; pp. 4727–4732. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Olsen, S.I. Depth from zooming. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1990, 7, 1883–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, M.; Oda, A.; Asada, N.; Yamashita, H. Depth from defocus by zooming using thin lens-based zoom model. Electron. Commun. Jpn. 2006, 89, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z. 3D reconstruction from bifocus imaging. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Audio, Language and Image Processing, Shanghai, China, 23–25 November 2010; pp. 1479–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.; Chen, D.; Li, H.; Tang, D.; Yu, B.; Li, J.; Qu, J. Three-dimensional tracking of multiple particles in large depth of field using dual-objective bifocal plane imaging. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2020, 18, 071701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Hong, H.; Gan, Z.; Xing, K.; Chen, Y. Flexible Zoom Telescopic Optical System Design Based on Genetic Algorithm. Photonics 2022, 9, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, N.J.; Kim, W.S.; Jo, J.H.; Ryu, J.M.; Lee, H.J.; Kang, G.M. Numerical calculation method for paraxial zoom loci of complicated zoom lenses with infinite object distance by using Gaussian bracket method. Korean J. Opt. Photonics 2007, 18, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zheng, Y.; Yuan, R.Y.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, J.B.; Zhao, Y.R.; Wang, X.; Li, X.W.; Xing, Y.; Wang, Q.H. Tunable liquid lenses: Emerging technologies and future perspectives. Laser Photonics Rev. 2023, 17, 2300274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Song, W.; Zhao, X.; Zheng, R.; Qingge, L. An improved Otsu threshold segmentation algorithm. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2020, 22, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annapurna, P.; Kothuri, S.; Lukka, S. Digit recognition using freeman chain code. Int. J. Appl. Innov. Eng. Manag. 2013, 2, 362–365. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Hong, H.; Gan, Z.; Xing, K. Bionic vision autofocus method based on a liquid lens. Appl. Opt. 2022, 61, 7692–7705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Zhou, W.; Dong, D. Calibration method of liquid lens focusing system for machine vision measurement. Infrared Laser Eng. 2022, 51, 20210472. [Google Scholar]
- Ricolfe-Viala, C.; Sanchez-Salmeron, A.J. Lens distortion models evaluation. Appl. Opt. 2010, 49, 5914–5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, B.K.; Yoo, W.S.; Lee, C.S. Matrix representation for NURB curves and surfaces. Comput. Aided Des. 1990, 22, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, C.H.; Vickers, G.W. Free-form surface reconstruction for machine vision rapid prototyping. Opt. Eng. 1993, 32, 2191–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Previous Chain Code | Latter Chain Code | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | |
| 0 | LR | LR | LR | LR | R | R | R | R |
| 1 | L | L | L | L | LR | O | O | O |
| 2 | L | L | L | L | LR | LR | O | O |
| 3 | L | L | L | L | LR | LR | LR | O |
| 4 | L | L | L | L | LR | LR | LR | LR |
| 5 | LR | O | O | O | R | R | R | R |
| 6 | LR | LR | O | O | R | R | R | R |
| 7 | LR | LR | LR | O | R | R | R | R |
| Imaging Status Conditions | k1 | k2 | p1 | p2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wide field of view | −0.3017 | 0.3448 | −0.0236 | −0.000281 |
| Narrow field of view | −0.1829 | 0.2731 | −0.0151 | −0.000334 |
| Group Number | Adjusting Parameters for the Wide Field of View (mA/ °C) | Adjusting Parameters for the Narrow Field of View (mA/ °C) | f1 (mm) | f2 (mm) | S1/S2 | Measurement Value D (mm) | True Value D (mm) | Measure Relative Error (%) | Measure Time (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | I1: −197.73/27.5 I2: 122.86/31.75 | I1: 110.56/27.5 I2: −86.82/31.75 | 16.15 | 30.58 | 0.25555 | 337.18 | 350 | 3.66 | 120 ms |
| 2 | I1: −197.73/26.75 I2: 122.86/30.75 | I1: 106.63/26.75 I2: −86.82/30.75 | 16.15 | 30.21 | 0.26675 | 414.88 | 400 | 3.72 | 120 ms |
| 3 | I1: −197.73/27.25 I2: 122.86/30.5 | I1: 95.18/27.25 I2: −86.82/30.5 | 16.18 | 30.01 | 0.27586 | 535.25 | 500 | 7.05 | 33 ms |
| 4 | I1: −197.73/27 I2: 122.86/31.5 | I1: 95.18/27 I2: −86.82/31.5 | 16.14 | 29.86 | 0.27834 | 572.86 | 550 | 4.16 | 33 ms |
| 5 | I1: −197.73/27.25 I2: 122.86/31.5 | I1: 95.18/27.25 I2: −86.82/31.5 | 16.15 | 29.88 | 0.27929 | 617.37 | 600 | 2.90 | 33 ms |
| Group Number | Target Type | Adjusting Parameters for the Wide Field of View (mA/°C) | Adjusting Parameters for the Narrow Field of View (mA/°C) | Measurement Value D (mm) | Measure Relative Error (%) | Measure Time (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cylinder model | I1: −197.73/29 I2: 122.86/30.5 | I1: 95.18/29 I2: −86.82/30.5 | 529.90 | 5.98 | 33 ms |
| 2 | Sphere model | I1: −197.73/29 I2: 122.86/30.75 | I1: 95.18/29 I2: −86.82/30.75 | 470.77 | 5.85 | 33 ms |
| 3 | Cone model | I1: −197.73/28.75 I2: 122.86/31.75 | I1: 95.18/28.75 I2: −86.82/31.75 | 524.53 | 4.91 | 33 ms |
| 4 | Cat model | I1: −197.73/28.5 I2: 122.86/31.75 | I1: 95.18/28.5 I2: −86.82/31.75 | 527.90 | 5.58 | 33 ms |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gan, Z.; Liu, Z.; Liu, B.; Lv, J.; Zhang, M.; Hong, H. Research on Monocular Depth Sensing Method Based on Liquid Zoom Imaging. Photonics 2024, 11, 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11040353
Gan Z, Liu Z, Liu B, Lv J, Zhang M, Hong H. Research on Monocular Depth Sensing Method Based on Liquid Zoom Imaging. Photonics. 2024; 11(4):353. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11040353
Chicago/Turabian StyleGan, Zihao, Zhaoyang Liu, Bin Liu, Jianming Lv, Meng Zhang, and Huajie Hong. 2024. "Research on Monocular Depth Sensing Method Based on Liquid Zoom Imaging" Photonics 11, no. 4: 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11040353
APA StyleGan, Z., Liu, Z., Liu, B., Lv, J., Zhang, M., & Hong, H. (2024). Research on Monocular Depth Sensing Method Based on Liquid Zoom Imaging. Photonics, 11(4), 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11040353





