A Novel Demodulation Algorithm Based on the Spatial-Domain Carrier Frequency Fringes Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
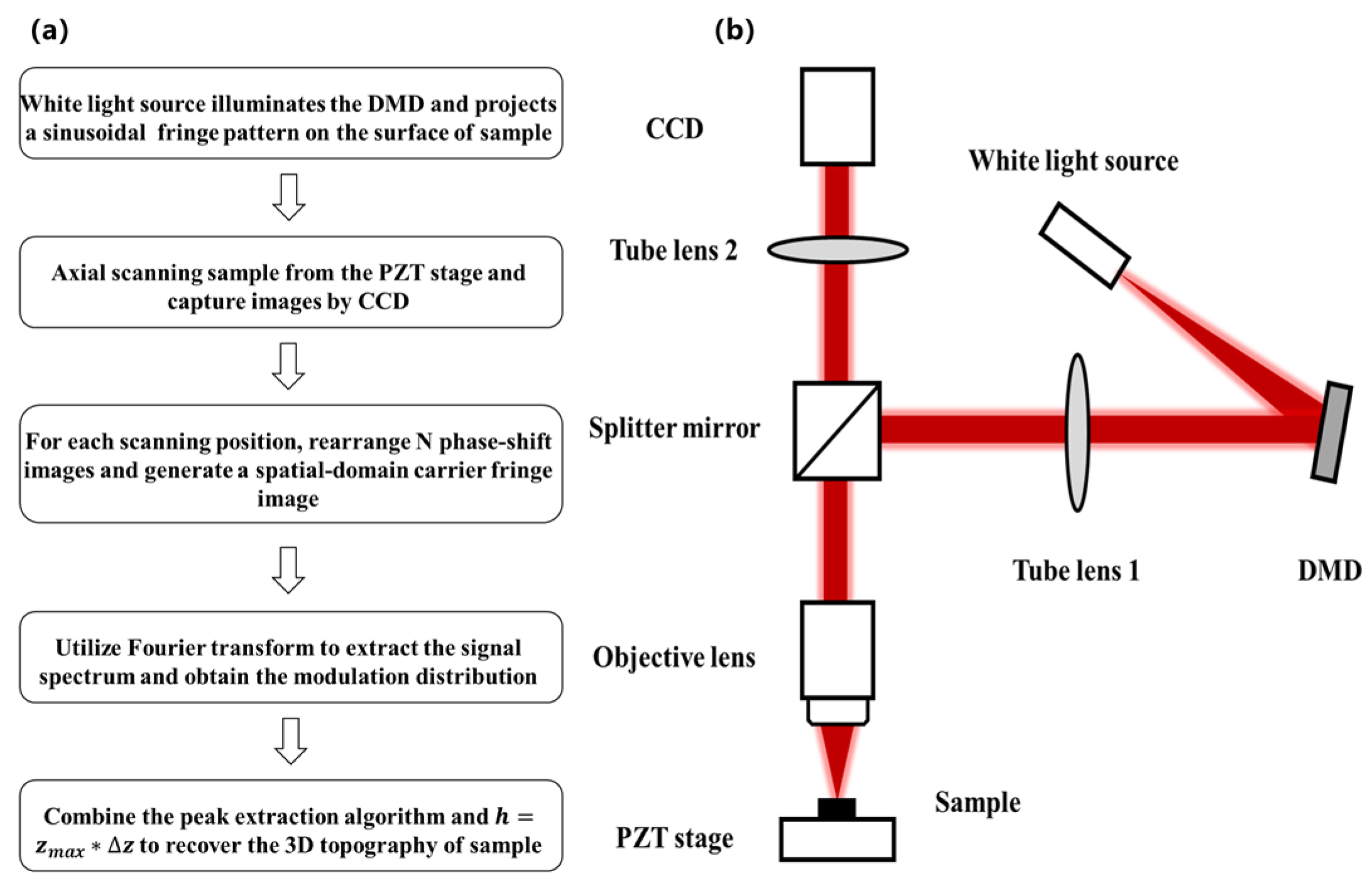
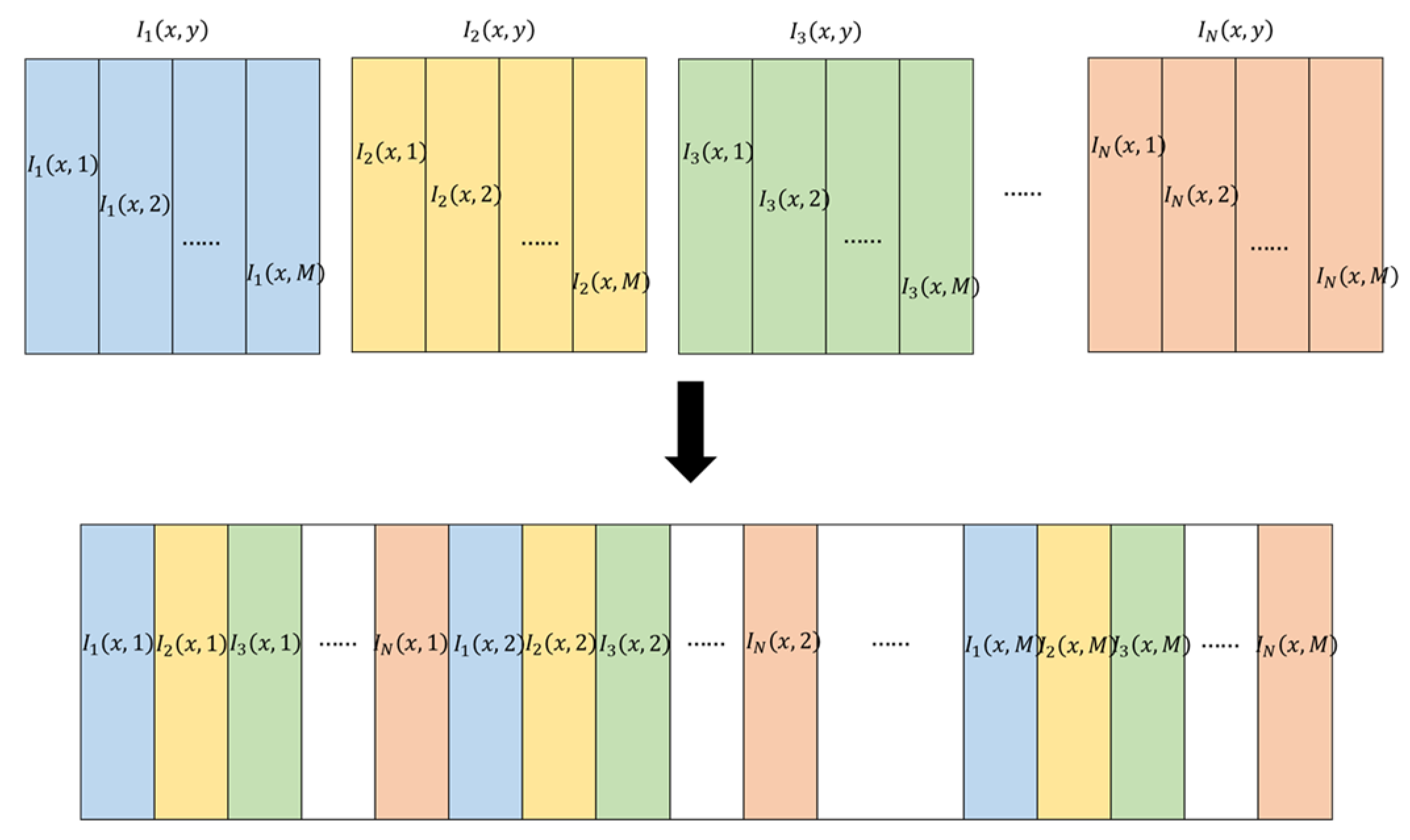
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
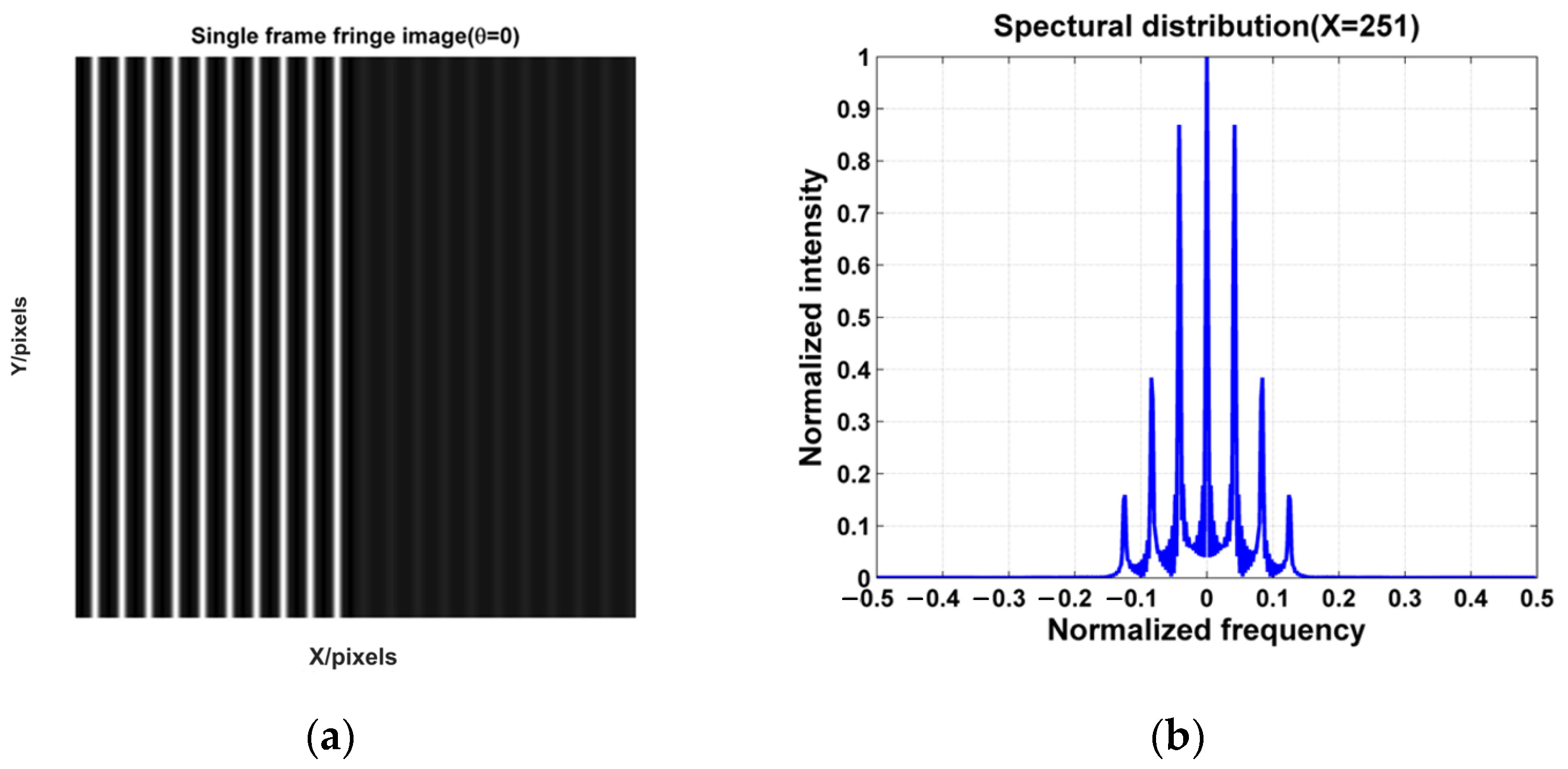
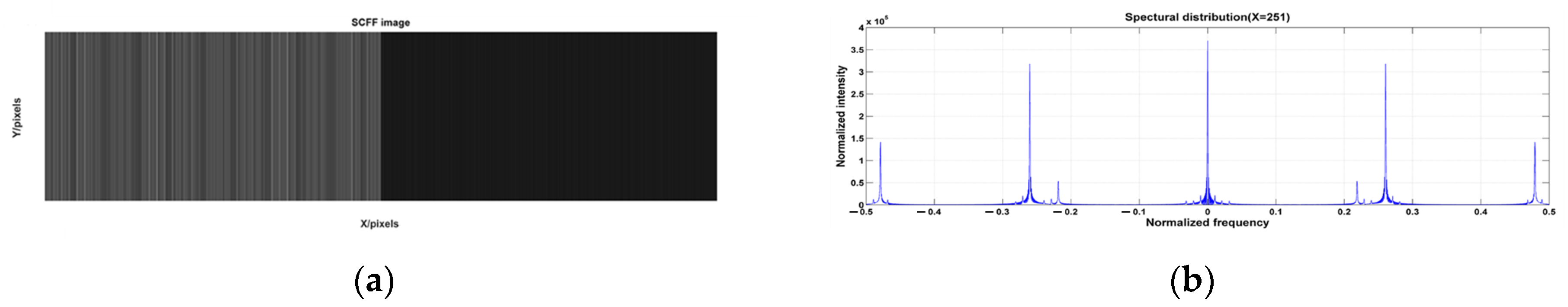
3.1. Simulation
3.2. Experiments
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- König, M. Literature Review of Microstructure Formation in Compacted Graphite Iron. Int. J. Cast Met. Res. 2010, 23, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Liu, X.; Liang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xie, J.; Wang, X. Recent Advancements in Optical Microstructure Fabrication through Glass Molding Process. Front. Mech. Eng. 2017, 12, 46–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smalyukh, I.I.; Lansac, Y.; Clark, N.A.; Trivedi, R.P. Three-Dimensional Structure and Multistable Optical Switching of Triple-Twisted Particle-like Excitations in Anisotropic Fluids. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuche, E.; Bevilacqua, F.; Depeursinge, C. Digital Holography for Quantitative Phase-Contrast Imaging. Opt. Lett. 1999, 24, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, M.; Yang, Z.; Kessel, A.; Kranitzky, C.; Faber, C.; Häusler, G. Structured-Illumination Microscopy on Technical Surfaces: 3D Metrology with Nanometer Sensitivity; Lehmann, P.H., Osten, W., Gastinger, K., Eds.; SPIE: Munich, Germany, 2011; p. 80820S. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.W.; Kim, D.-H.; Han, S.-H.; Lee, J.-C.; Kim, P.-G. Three-Dimensional Surface Topography of the Needle Stomatal Complexes of Pinus Rigida and Its Hybrid Species by Complementary Microscopy. Micron 2010, 41, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paddock, S.W. Principles and Practices of Laser Scanning Confocal Microscopy. Mol. Biotechnol. 2000, 16, 127–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neil, M.A.A.; Juškaitis, R.; Wilson, T. Method of Obtaining Optical Sectioning by Using Structured Light in a Conventional Microscope. Opt. Lett. 1997, 22, 1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, C.; Feng, S.; Huang, L.; Tao, T.; Yin, W.; Chen, Q. Phase Shifting Algorithms for Fringe Projection Profilometry: A Review. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2018, 109, 23–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, M.; Eluru, G.; Gorthi, S.S. Structured Illumination Microscopy. Adv. Opt. Photonics 2015, 7, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, P.J.; Schmidt, A.D.; Santella, A.; Khairy, K.; Bao, Z.; Wittbrodt, J.; Stelzer, E.H.K. Fast, High-Contrast Imaging of Animal Development with Scanned Light Sheet–Based Structured-Illumination Microscopy. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, J.; Dang, S.-P.; Zhou, X.; Dan, D.; Wang, Z.-J.; Zhao, T.-Y.; Liang, Y.-S.; Yao, B.-L.; Lei, M. Fast Structured Illumination Three-Dimensional Color Microscopic Imaging Method Based on Hilbert-Transform. Acta Phys. Sin. 2020, 69, 128701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z.; Chen, J.; Liu, G.; Chen, S.-C. Single-Shot Optical Sectioning Microscopy Based on Structured Illumination. Opt. Lett. 2022, 47, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, T.; Qi, Y.; Zhu, C.; Tang, Y.; Wu, B. Three-Dimensional Microscopic Image Reconstruction Based on Structured Light Illumination. Sensors 2021, 21, 6097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Hu, Z.; Liu, W.; Li, F.; Li, X. Two-Step Phase-Shifting Sectioning Structured Illumination Microscopy. In Second Target Recognition and Artificial Intelligence Summit Forum; Wang, T., Chai, T., Fan, H., Yu, Q., Eds.; SPIE: Changchun, China, 2020; p. 46. [Google Scholar]
- Su, X.-Y.; Zhou, W.-S. Automated Phase-Measuring Profilometry Using Defocused Projection of a Ronchi Grating. Opt. Commun. 1992, 94, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S. Comparative Study on Passive and Active Projector Nonlinear Gamma Calibration. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; He, H.; Chen, M. Gamma Correction for Digital Fringe Projection Profilometry. Appl. Opt. 2004, 43, 2906–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Wang, Y.; Lau, D.L.; Hao, Q.; Hassebrook, L.G. Gamma Model and Its Analysis for Phase Measuring Profilometry. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2010, 27, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Li, Y. Gamma-Distorted Fringe Image Modeling and Accurate Gamma Correction for Fast Phase Measuring Profilometry. Opt. Lett. 2011, 36, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, T.; Pan, B.; Nguyen, D.; Wang, Z. Generic Gamma Correction for Accuracy Enhancement in Fringe-Projection Profilometry. Opt. Lett. 2010, 35, 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Yau, S.-T. Generic Nonsinusoidal Phase Error Correction for Three-Dimensional Shape Measurement Using a Digital Video Projector. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.S. High-Speed 3-D Shape Measurement Based on Digital Fringe Projection. Opt. Eng. 2003, 42, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, S. Optimal Pulse Width Modulation for Sinusoidal Fringe Generation with Projector Defocusing. Opt. Lett. 2010, 35, 4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, B.; Kemao, Q.; Huang, L.; Asundi, A. Phase Error Analysis and Compensation for Nonsinusoidal Waveforms in Phase-Shifting Digital Fringe Projection Profilometry. Opt. Lett. 2009, 34, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, S. Three-Dimensional Shape Measurement with Binary Dithered Patterns. Appl. Opt. 2012, 51, 6631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

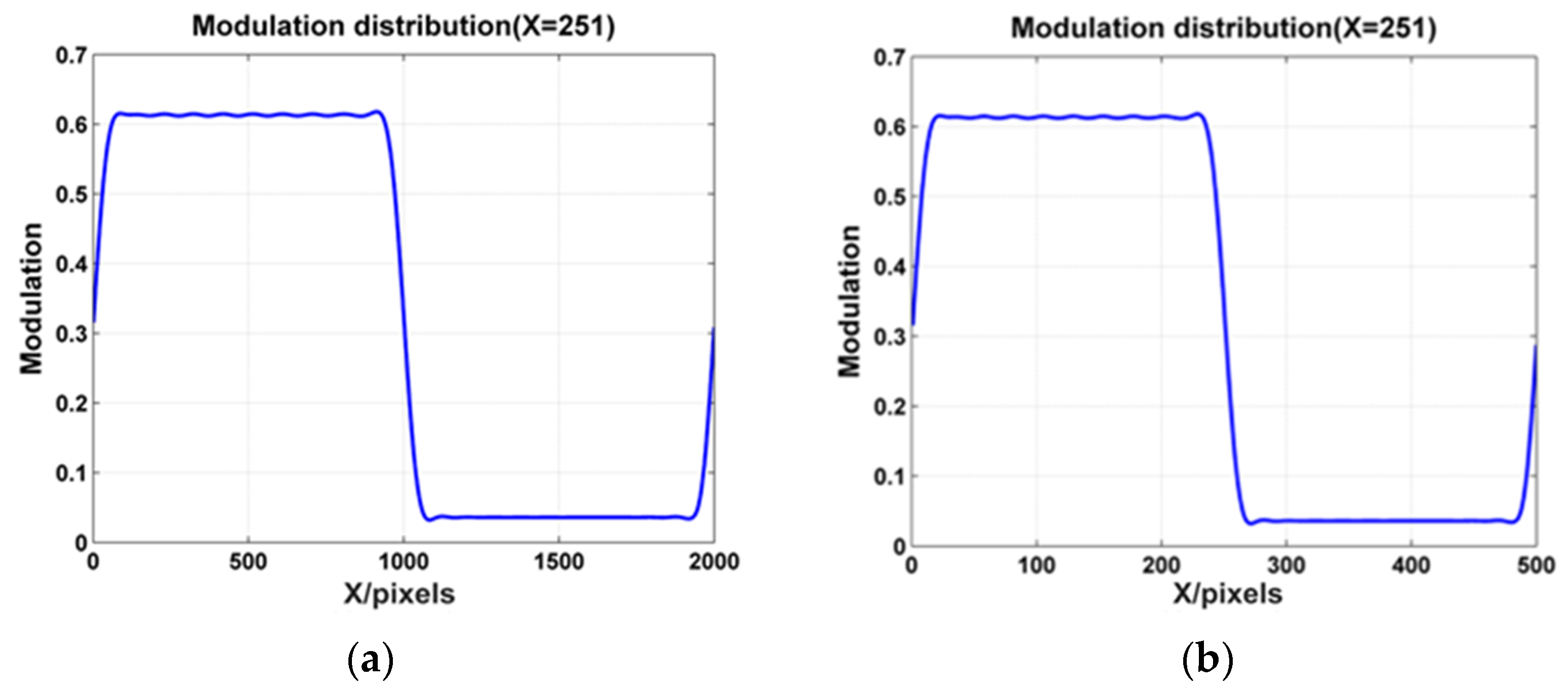
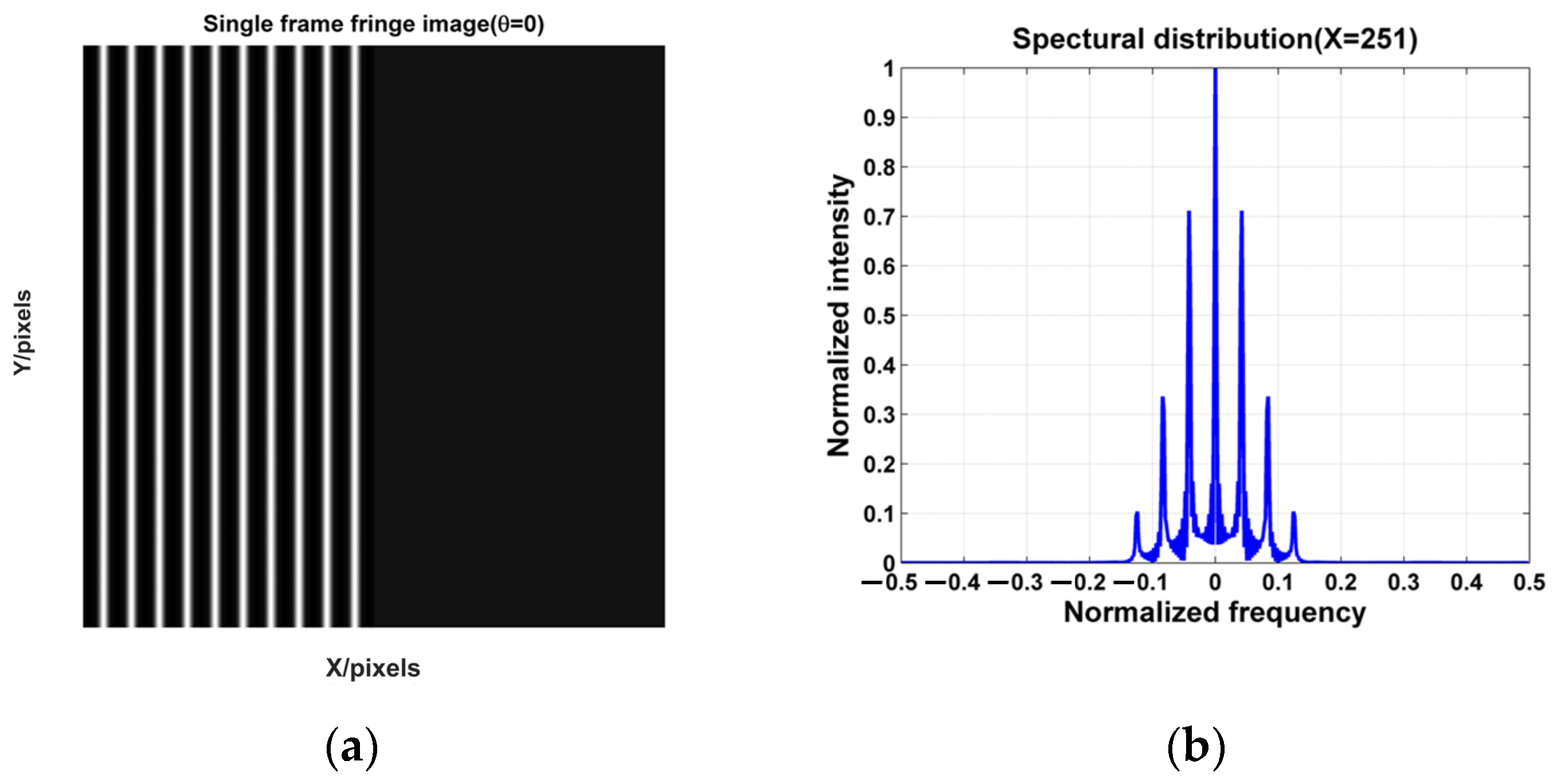
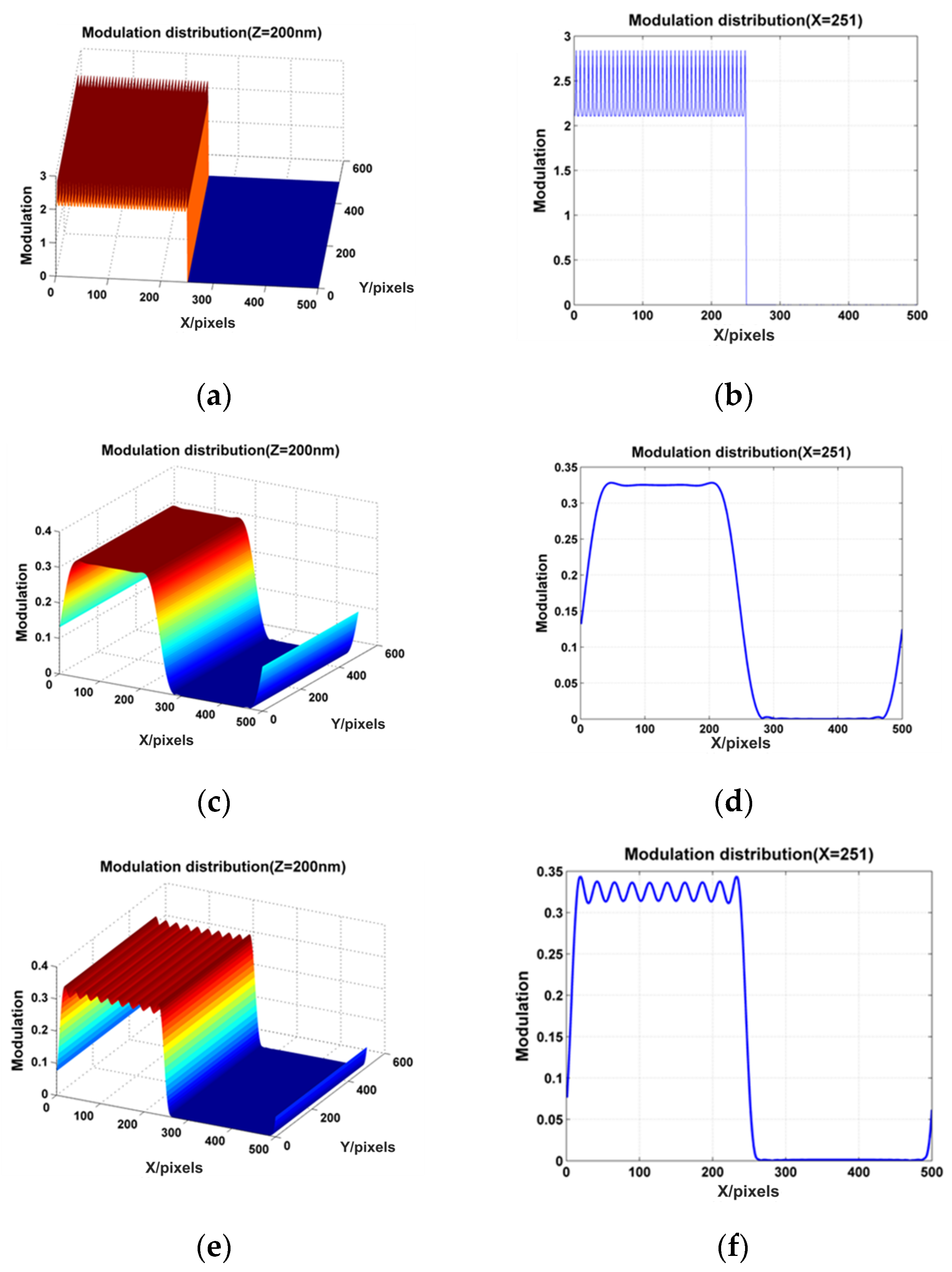
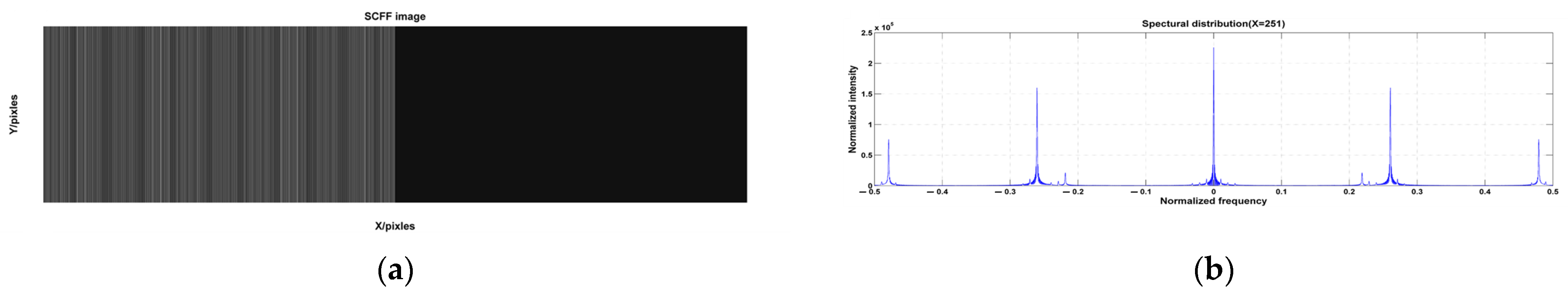
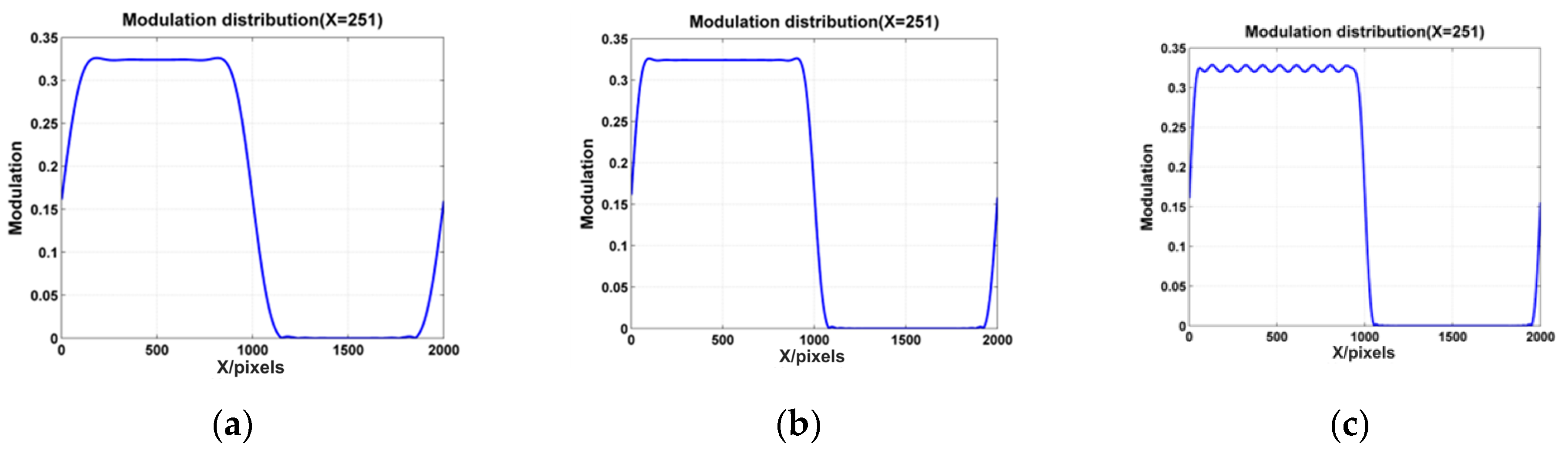

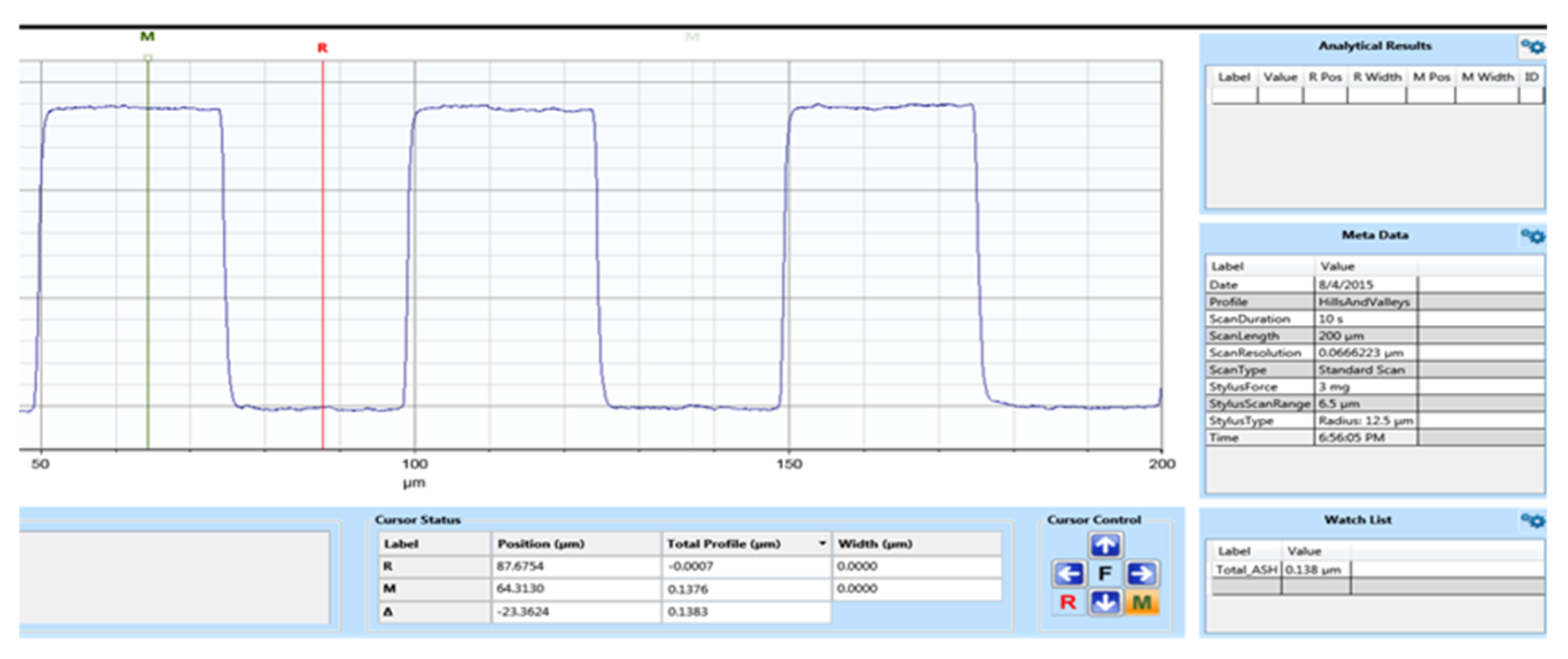
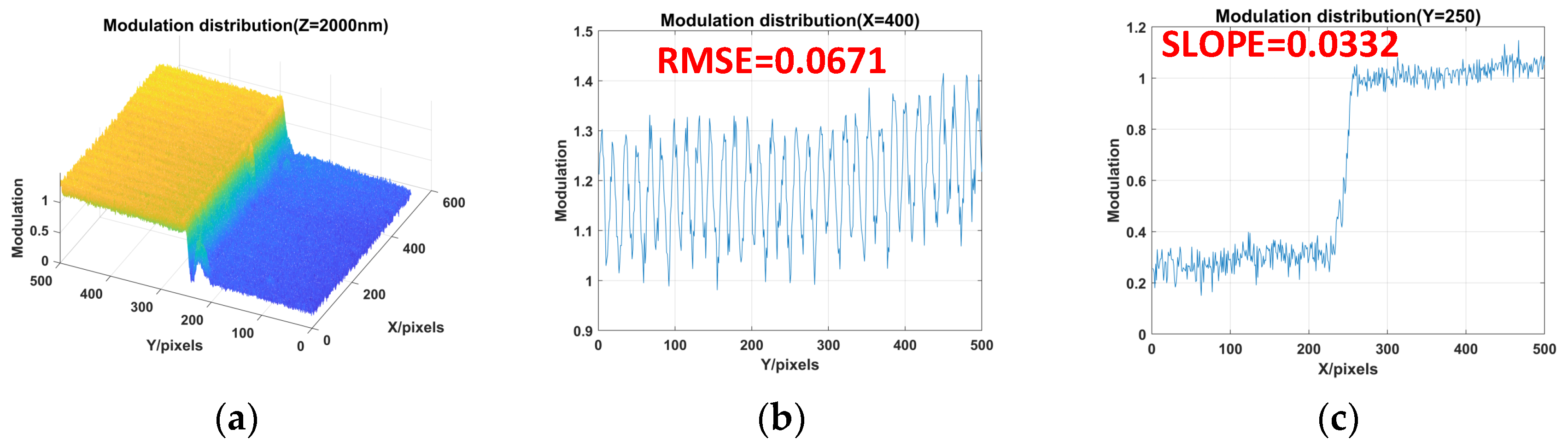
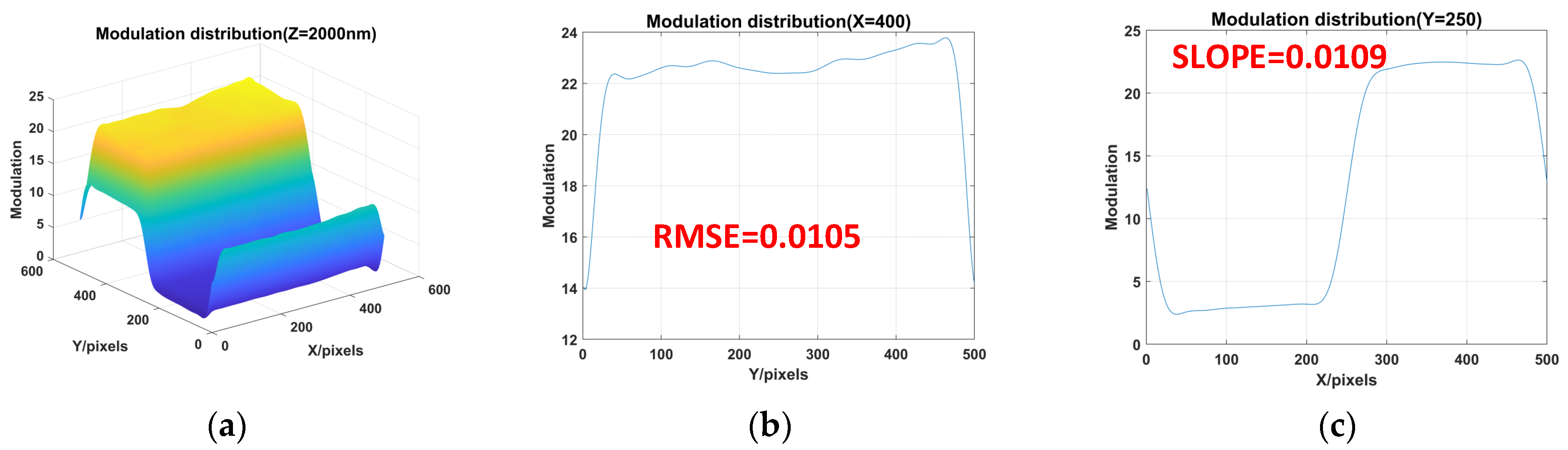
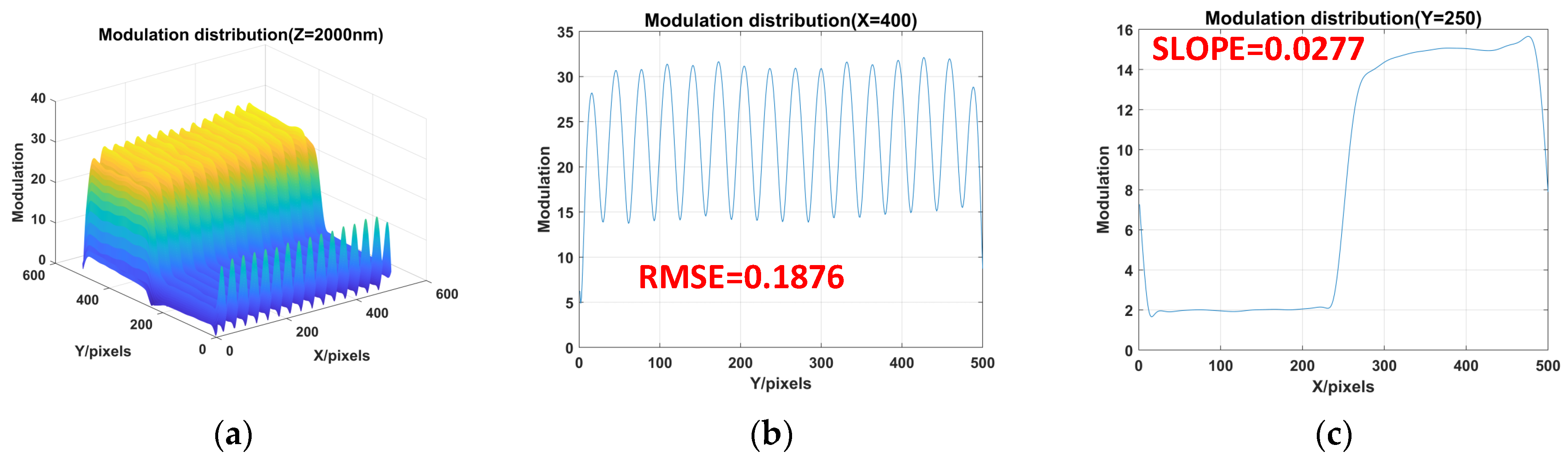

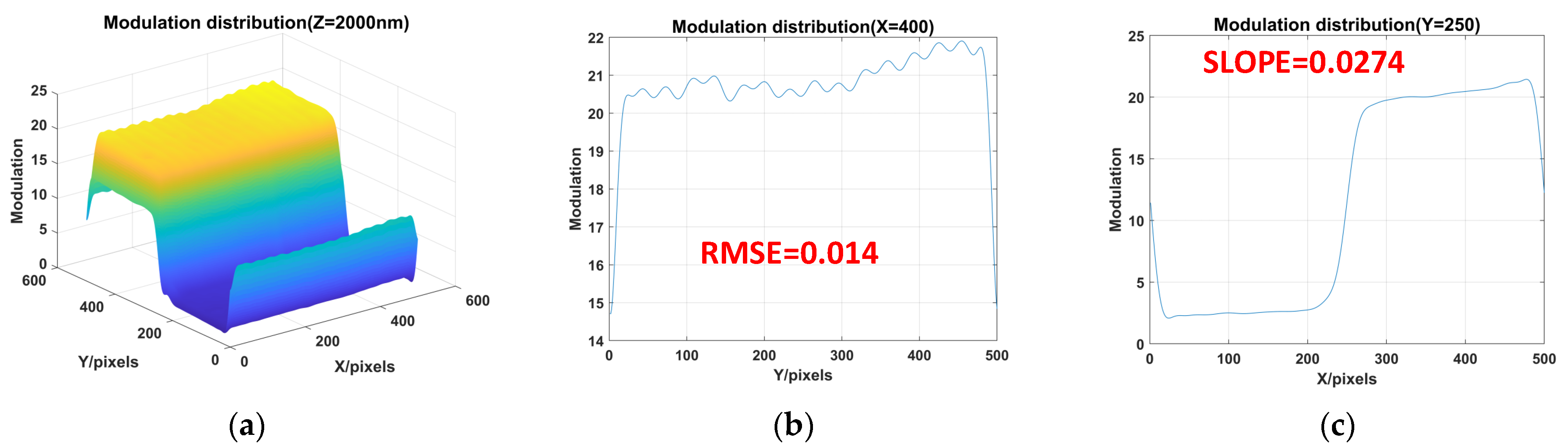
| Methods | RMSE | SLOPE |
|---|---|---|
| Phase-shifting | 0.0671 | 0.0332 |
| Fourier transform filter window 15 × 15 | 0.0105 | 0.0109 |
| Fourier transform filter window 18 × 18 | 0.1876 | 0.0277 |
| Proposed method filter window 18 × 18 | 0.0132 | 0.0256 |
| Proposed method filter window 20 × 20 | 0.014 | 0.0274 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, C.; Ju, Y.; Zhao, Z.; He, Y.; Tang, Z. A Novel Demodulation Algorithm Based on the Spatial-Domain Carrier Frequency Fringes Method. Photonics 2024, 11, 1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11121125
Han C, Ju Y, Zhao Z, He Y, Tang Z. A Novel Demodulation Algorithm Based on the Spatial-Domain Carrier Frequency Fringes Method. Photonics. 2024; 11(12):1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11121125
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Chenhaolei, Yuan Ju, Zongxu Zhao, Yuni He, and Zhan Tang. 2024. "A Novel Demodulation Algorithm Based on the Spatial-Domain Carrier Frequency Fringes Method" Photonics 11, no. 12: 1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11121125
APA StyleHan, C., Ju, Y., Zhao, Z., He, Y., & Tang, Z. (2024). A Novel Demodulation Algorithm Based on the Spatial-Domain Carrier Frequency Fringes Method. Photonics, 11(12), 1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11121125




