Reduction in Temperature-Dependent Fiber-Optic Gyroscope Bias Drift by Using Multifunctional Integrated Optical Chip Fabricated on Pre-Annealed LiNbO3
Abstract
1. Introduction
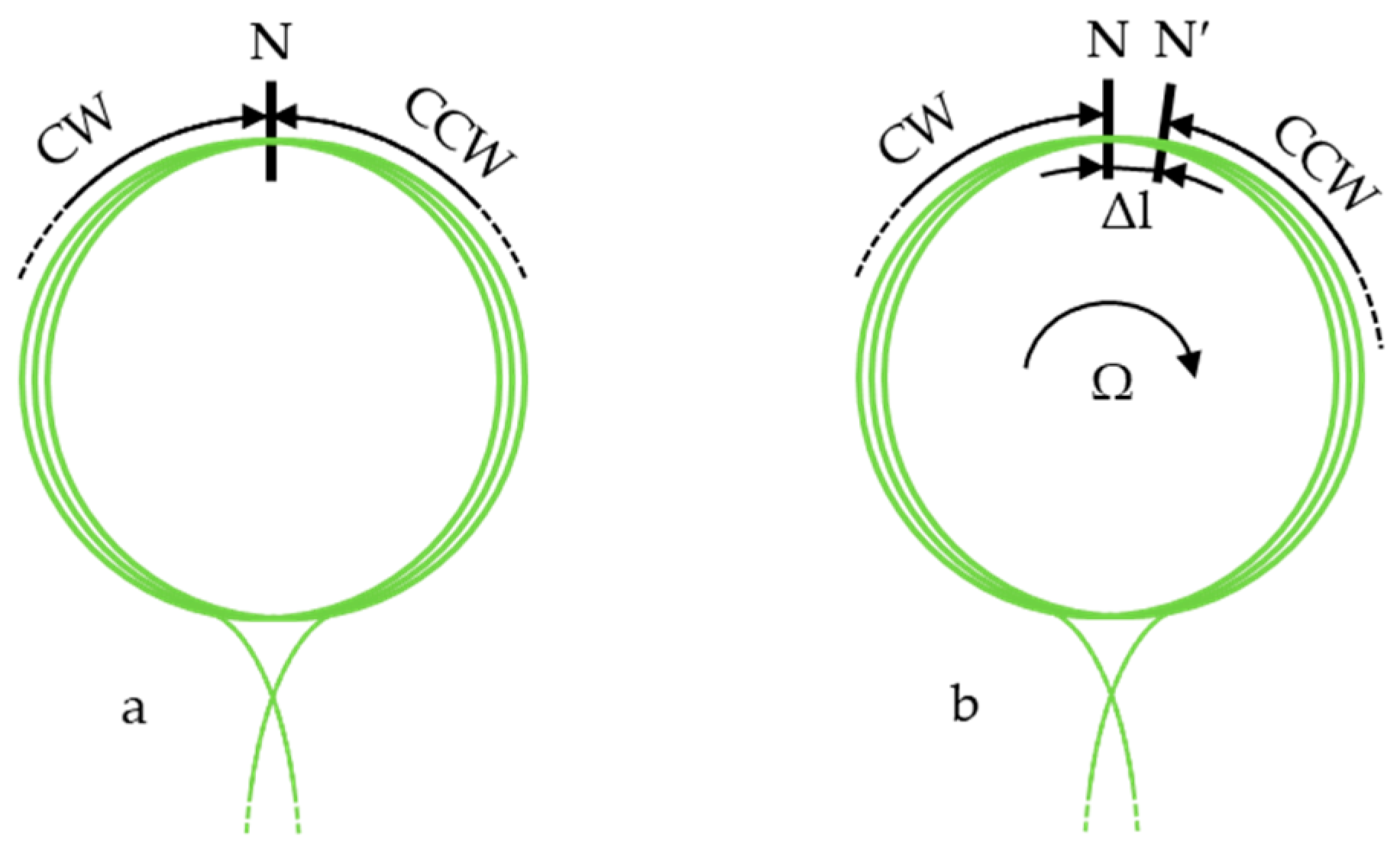
1.1. Interferometric Fiber-Optic Gyroscopes
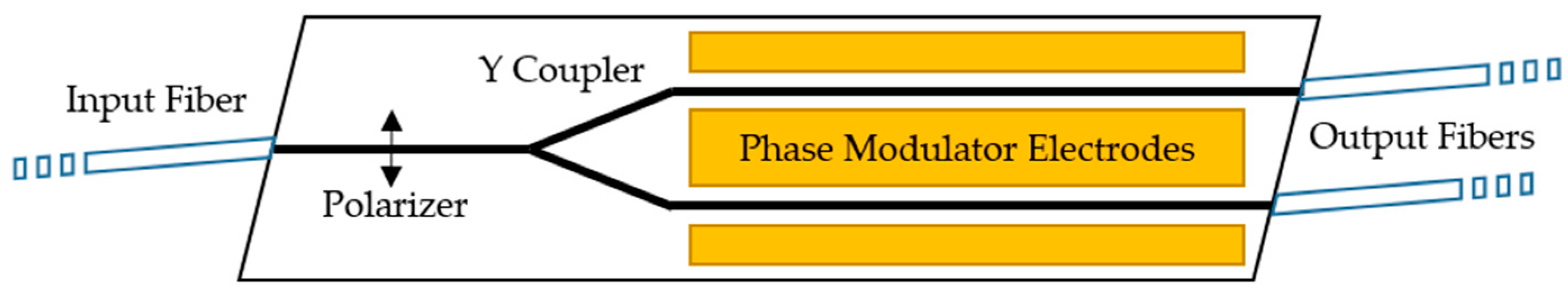
1.2. Multifunctional Integrated Optical Chip
2. Fabrication, Test, and Results
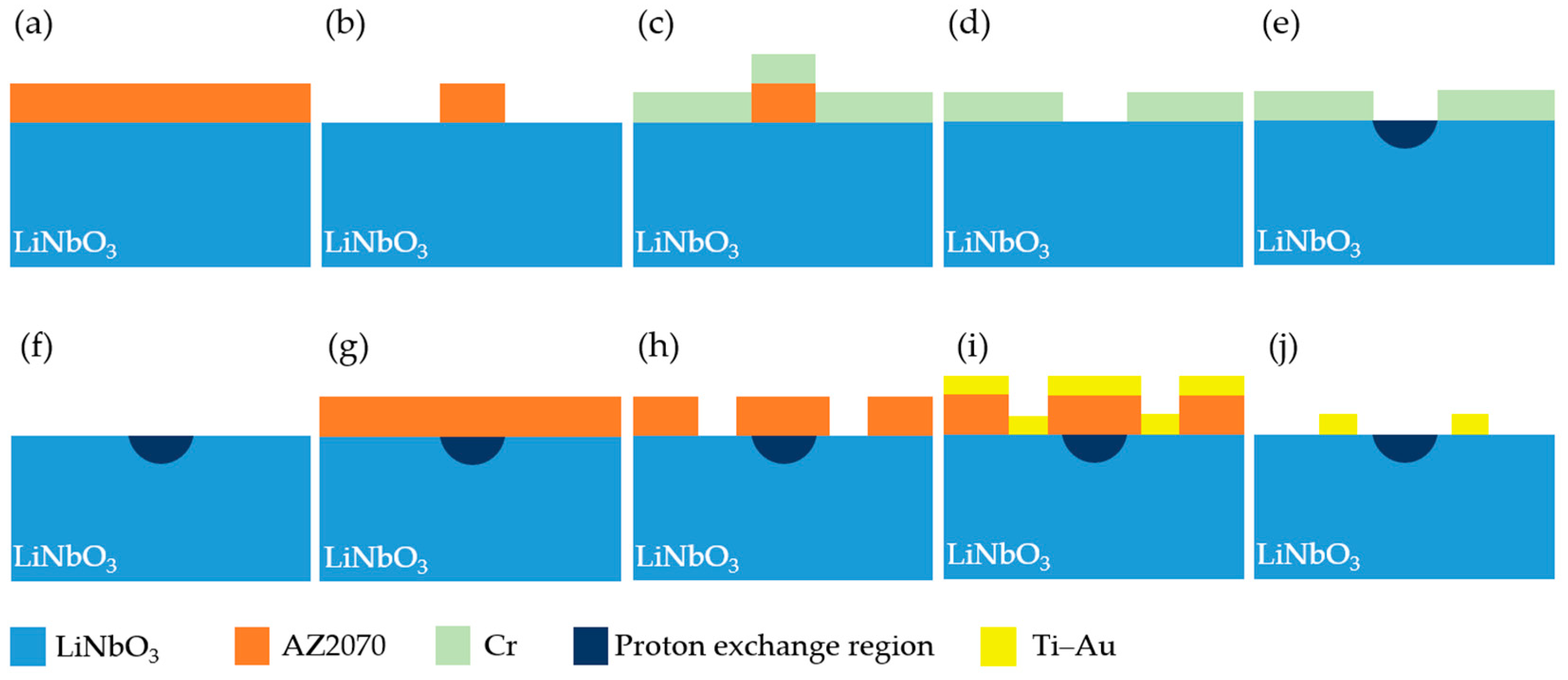
2.1. MIOC Fabrication
2.2. MIOC Throughput Measurements
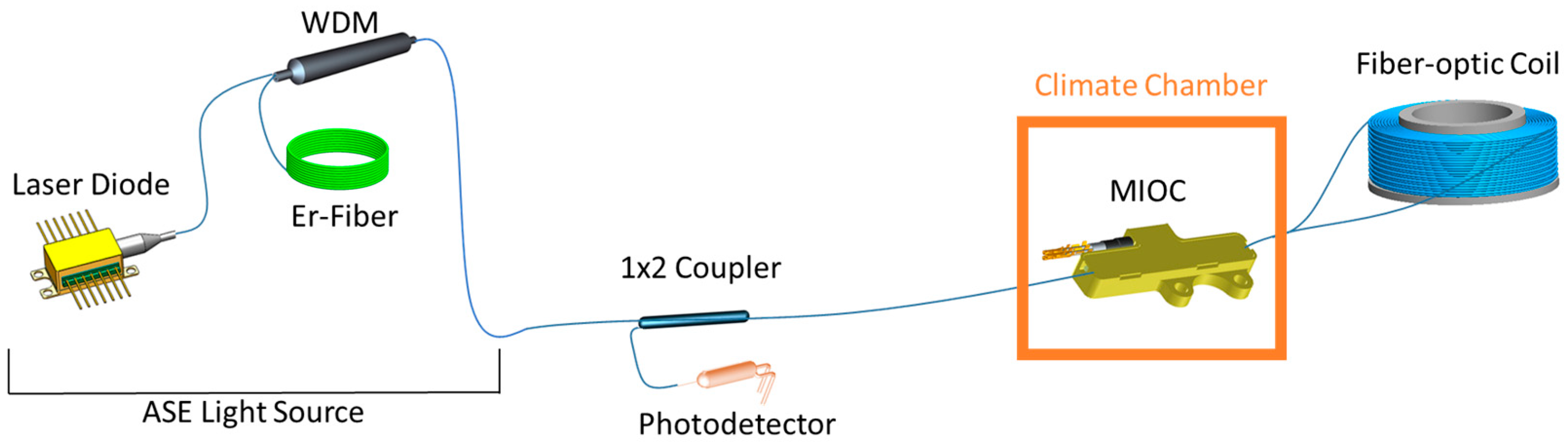
2.3. IFOG Bias Test Setup Configuration
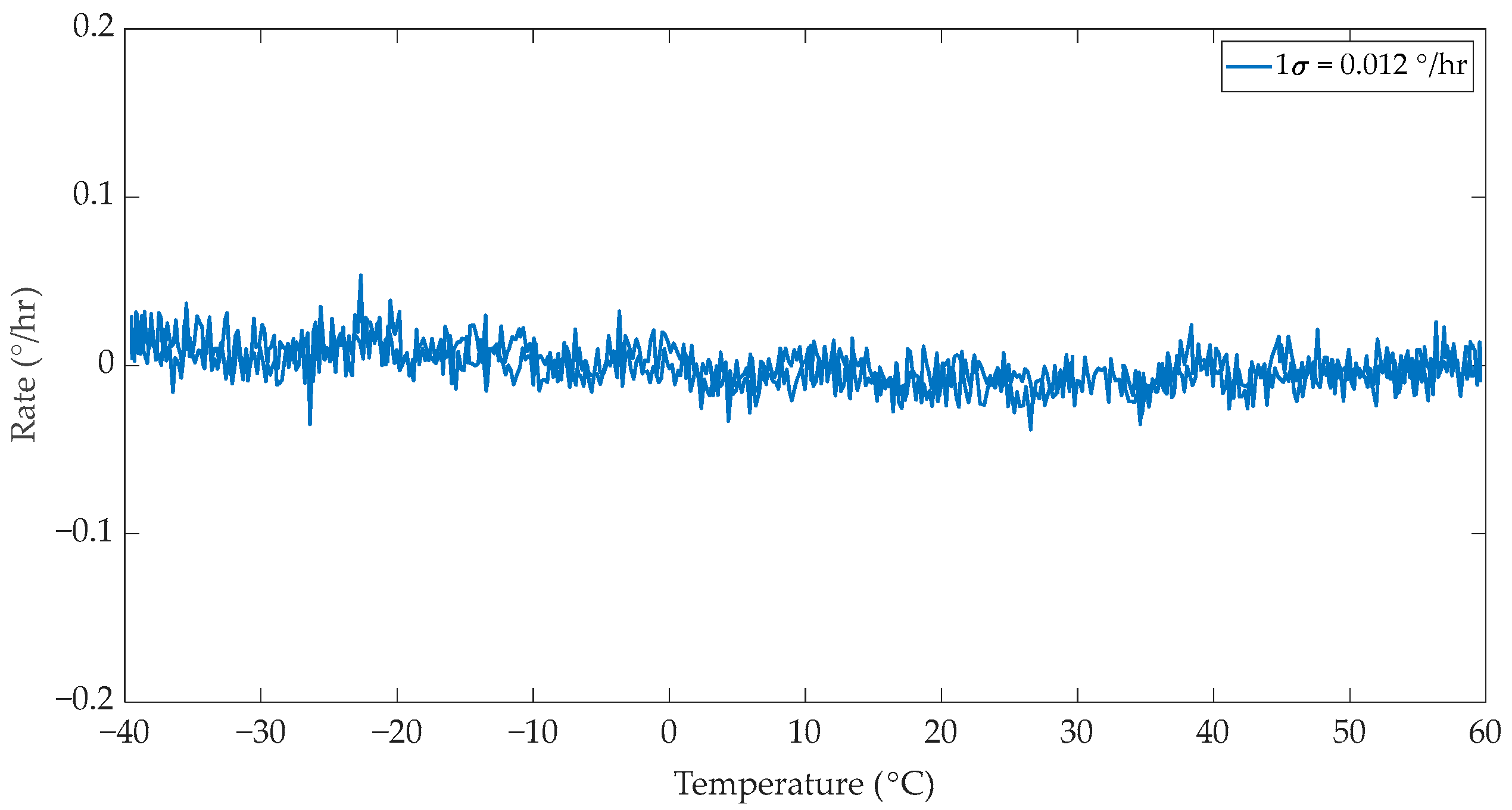
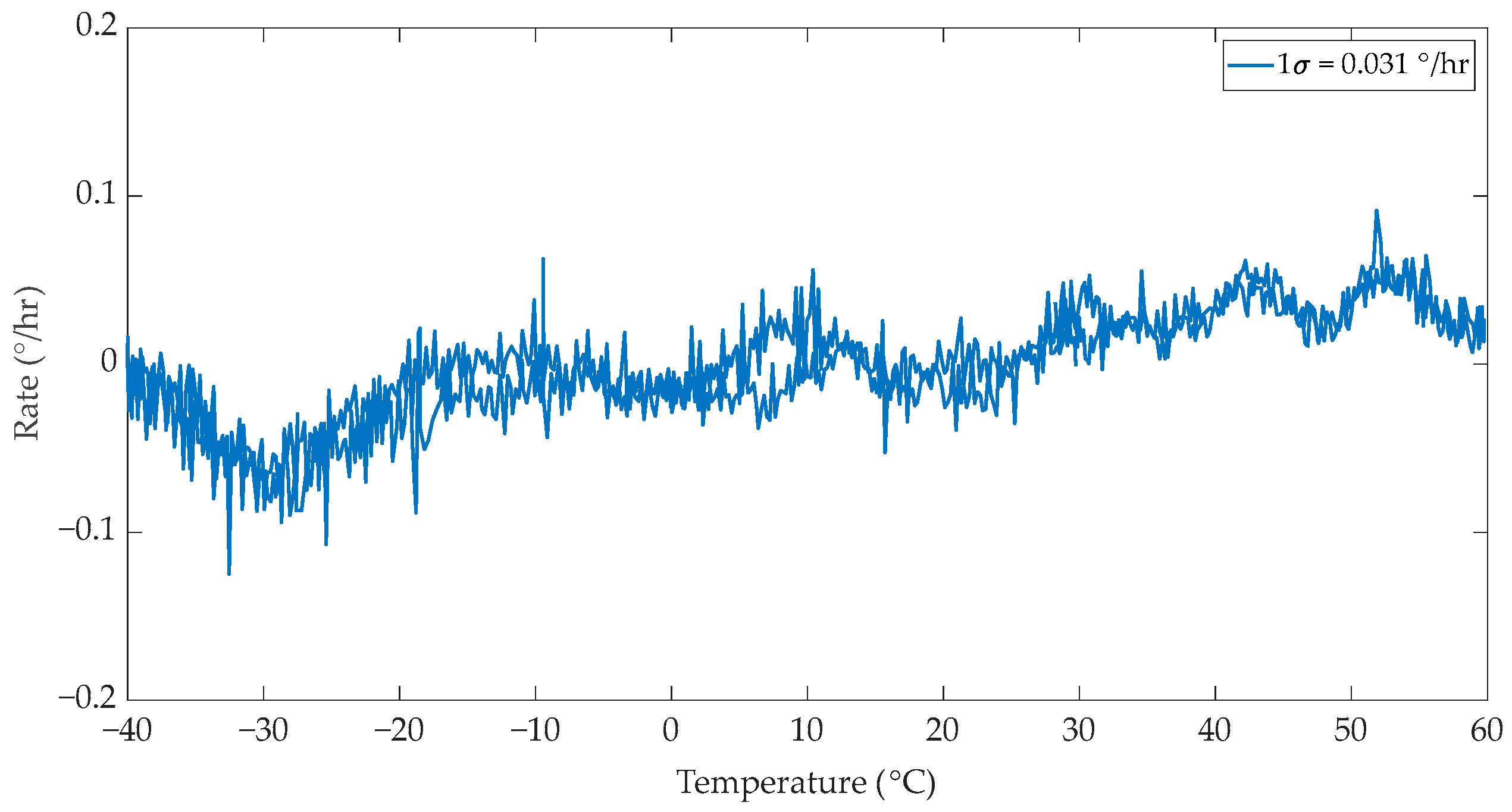
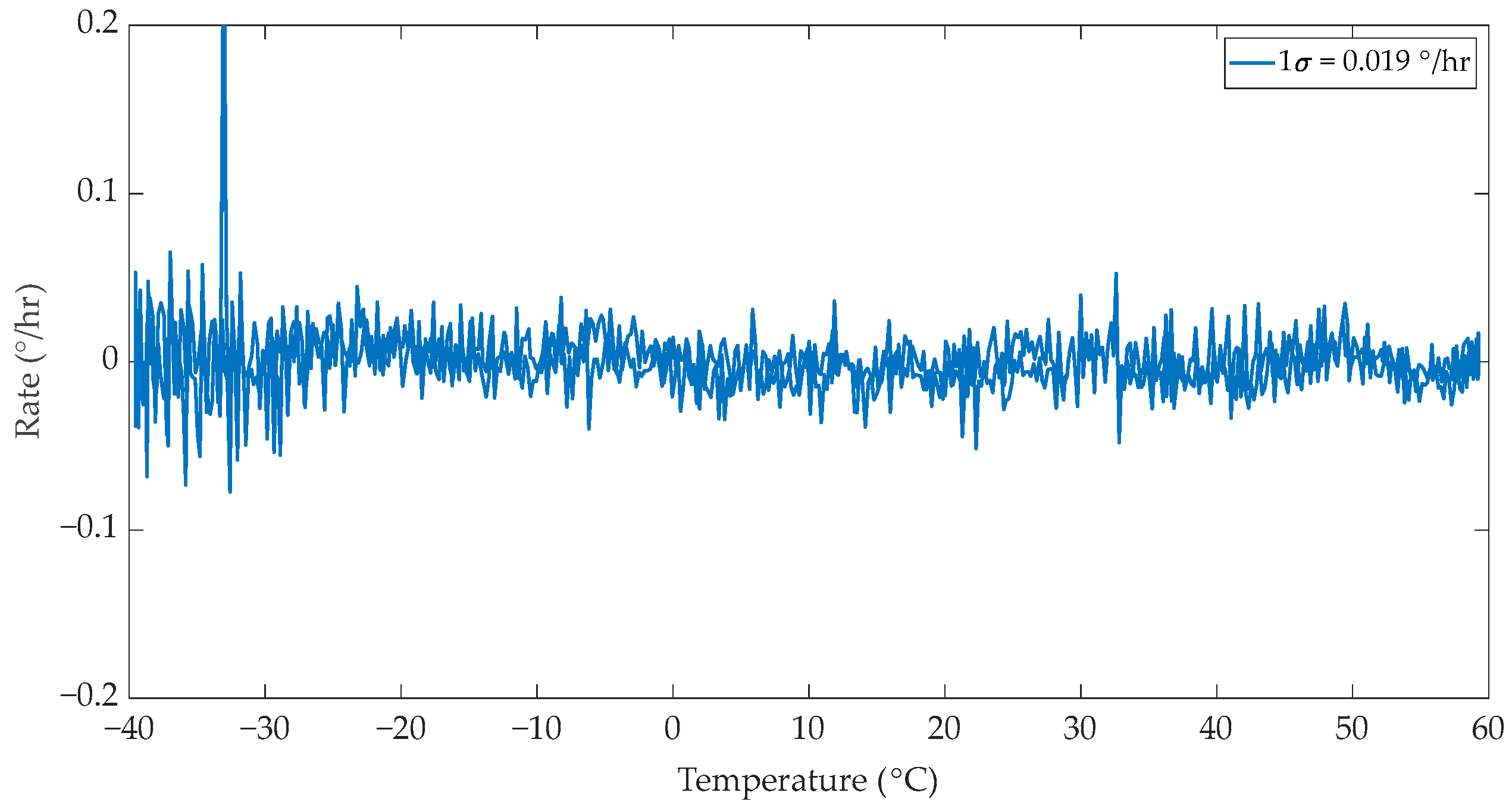
2.4. IFOG Bias Measurement Under Temperature Variations
3. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Passaro, V.M.N.; Cuccovillo, A.; Vaiani, L.; De Carlo, M.; Campanella, C.E. Gyroscope Technology and Applications: A Review in the Industrial Perspective. Sensors 2017, 17, 2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozelle, D.M. The Hemispherical Resonator Gyro: From Wineglass to the Planets. In Proceedings of the 19th AAS/AIAA Space Flight Mechanics Meeting, Savannah, Georgia, 8–12 February 2009; Volume 134, pp. 1157–1178. [Google Scholar]
- Merlo, S.; Norgia, M.; Donati, S. Fiber Gyroscope Principles. In Handbook of Fibre Optic Sensing Technology; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Grattan, K.T.V.; Sun, T. Fiber Optic Sensor Technology: An Overview. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2000, 82, 40–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, W.W.; Gea-Banacloche, J.; Pedrotti, L.M.; Sanders, V.E.; Schleich, W.; Scully, M.O. The Ring Laser Gyro. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1985, 57, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefevre, H.C. The Fiber-Optic Gyroscope; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2014; ISBN 1608076962. [Google Scholar]
- Sanders, G.A.; Szafraniec, B.; Liu, R.-Y.; Laskoskie, C.L.; Strandjord, L.K.; Weed, G. Fiber Optic Gyros for Space, Marine, and Aviation Applications. In Proceedings of the Fiber Optic Gyros: 20th Anniversary Conference, Denver, CO, USA, 4–9 August 1996; Volume 2837, pp. 61–71. [Google Scholar]
- Sanders, G.A.; Szafraniec, B.; Liu, R.-Y.; Bielas, M.S.; Strandjord, L.K. Fiber-Optic Gyro Development for a Broad Range of Applications. In Proceedings of the Fiber Optic and Laser Sensors XIII, Munich, Germany, 20–21 June 1995; Volume 2510, pp. 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Song, N.; Jin, J.; He, J.; Zio, E. Configuration Optimization in Miniature Interferometric Fiber-Optic Gyroscopes for Space Application. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 7107–7117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-C.; Lu, S.-Y.; Yen, T.-H.; Wei, C.-C.; Chiu, Y.-J.; Liu, R.-Y.; Hung, Y.-J. Silicon Photonics Multi-Function Integrated Optical Circuit for Miniaturized Fiber Optic Gyroscope. J. Light. Technol. 2023, 41, 6324–6332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhang, W.; Chen, W.; Li, K.; Dai, F.; Cui, F.; Wu, X.; Ma, G.; Xiao, Q. The Development of Micro-Gyroscope Technology. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2009, 19, 113001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogue, R. MEMS Sensors: Past, Present and Future. Sens. Rev. 2007, 27, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L. Applications and Prospects of Mems Sensors in Automotive. Proc. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1884, 12010. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, A.K. Gps/Ins Uses Low-Cost Mems Imu. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2005, 20, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhanshe, G.; Fucheng, C.; Boyu, L.; Le, C.; Chao, L.; Ke, S. Research Development of Silicon MEMS Gyroscopes: A Review. Microsyst. Technol. 2015, 21, 2053–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.-H.; Suh, M.-G.; Lu, Y.-K.; Shen, B.; Yang, Q.-F.; Wang, H.; Li, J.; Lee, S.H.; Yang, K.Y.; Vahala, K. Earth Rotation Measured by a Chip-Scale Ring Laser Gyroscope. Nat. Photonics 2020, 14, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.; Mahmoud, A.; Cai, L.; Khan, M.; Mukherjee, T.; Bain, J.; Piazza, G. Novel on Chip Rotation Detection Based on the Acousto-Optic Effect in Surface Acoustic Wave Gyroscopes. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 25060–25075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, J. Fiber-Optic Gyroscopes: From Design to Production. Appl. Opt. 2011, 50, E152–E161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajioka, H.; Kumagai, T.; Nakai, H.; Dohsho, T.; Soekawa, H.; Yuhara, T. Commercial Applications of Mass-Produced Fiber Optic Gyros. In Proceedings of the Fiber Optic Gyros: 20th Anniversary Conference, Denver, CO, USA, 4–9 August 1996; Volume 2837, pp. 18–32. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, G.; Kumar, S.; Marques, C.; Min, R.; Li, X. Recent Advancements in Resonant Fiber Optic Gyro—A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 18240–18252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotate, K. Future Evolution of Fiber Optic Gyros. Opt. Rev. 1997, 4, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Chang, X.; Mao, H.; Jin, Z. Laser Frequency Noise Limited Sensitivity in a Resonator Optic Gyroscope. In Proceedings of the OECC 2010 Technical Digest, Sapporo, Japan, 5–9 July 2010; pp. 706–707. [Google Scholar]
- Sanders, G.A. Critical Review of Resonator Fiber Optic Gyroscope Technology. In Proceedings of the Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers (SPIE) Conference Series, Boston, MA, USA, 8-11 September 19921993; Volume 10266, p. 102660A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, F.; Wang, X. Advanced Interferometric Fiber Optic Gyroscope for Inertial Sensing: A Review. J. Light. Technol. 2023, 41, 4023–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajulapati, R.M.; Nayak, J.; Naseema, S. Modeling and Simulation of Signal Processing for a Closed Loop Fiber Optic Gyro’s Using FPGA. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Techn. 2012, 4, 947–959. [Google Scholar]
- Lefevre, H.C.; Bettini, J.P.; Vatoux, S.; Papuchon, M. Progress in Optical Fiber Gyroscopes Using Integrated Optics. In AGARD Guided Optical Structures in the Military Environment; National Aerospace Library: Farnborough, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Korkishko, Y.N.; Fedorov, V.A.; Kostritskii, S.M.; Alkaev, A.N.; Paderin, E.M.; Maslennikov, E.I.; Apraksin, D.V. Multifunctional Integrated Optical Chip for Fiber Optical Gyroscope Fabricated by High-Temperature Proton Exchange. In Integrated Optical Devices: Fabrication and Testing; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bruges, Belgium 2002, 2003; Volume 4944, pp. 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooten, E.L.; Kissa, K.M.; Yi-Yan, A.; Murphy, E.J.; Lafaw, D.A.; Hallemeier, P.F.; Maack, D.; Attanasio, D.V.; Fritz, D.J.; McBrien, G.J.; et al. Review of Lithium Niobate Modulators for Fiber-Optic Communications Systems. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2000, 6, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkishko, Y.N.; Fedorov, V.A.; Feoktistova, O.Y. LiNbO3 Optical Waveguide Fabrication by High-Temperature Proton Exchange. J. Light. Technol. 2000, 18, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.V.; Kaminow, I.P. Metal-diffused Optical Waveguides in LiNbO3. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1974, 25, 458–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchoski, P.G.; Findakly, T.K.; Leonberger, F.J. LiNbO3 Integrated Optical Components for Fiber Optic Gyroscopes. In Proceedings of the Integrated Optical Circuit Engineering VI, Boston, MA, USA, 7–9 September 1988; Volume 993, pp. 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Il’ichev, I.V.; Kozlov, A.S.; Gaenko, P.V.; Shamray, A.V. Optimisation of the Proton-Exchange Technology for Fabricating Channel Waveguides in Lithium Niobate Crystals. Quantum Electron. 2009, 39, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosunov, A.V.; Petukhov, I.V.; Zhuravlev, A.A.; Ponomarev, R.S.; Mololkin, A.A.; Kuneva, M. Influence of Thermal Pretreatment of Lithium Niobate Plates on the Characteristics of Proton-Exchange Waveguides. Crystallogr. Rep. 2022, 67, 980–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosunov, A.V.; Ponomarev, R.S.; Mushinsky, S.S.; Volyntsev, A.B.; Mololkin, A.A.; Maléjacq, V. Effect of the Structure of the Lithium Niobate Surface Layer on the Characteristics of Optical Waveguides. Crystallogr. Rep. 2020, 65, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosunov, A.; Ponomarev, R.; Semenova, O.; Petukhov, I.; Volyntsev, A. Effect of Pre-Annealing of Lithium Niobate on the Structure and Optical Characteristics of Proton-Exchanged Waveguides. Opt. Mater. 2019, 88, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosunov, A.; Ponomarev, R.; Zhuravlev, A.; Mushinsky, S.; Kuneva, M. Reduction in Dc-Drift in LiNbO3-Based Electro-Optical Modulator. Photonics 2021, 8, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, G.; Barnett, N.; Insley, L.; Vajda, S. Evolution of Precision IFOG. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of The Institute of Navigation, Albuquerque, NM, USA, 11–13 June 2001; pp. 200–204. [Google Scholar]
- Celikel, O.; San, S.E. Establishment of All Digital Closed-Loop Interferometric Fiber-Optic Gyroscope and Scale Factor Comparison for Open-Loop and All Digital Closed-Loop Configurations. IEEE Sens. J. 2009, 9, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papuchon, M.; Puech, C. Integrated Optics-A Possible Solution for the Fiber Gyroscope. In Proceedings of the Laser Inertial Rotation Sensors, SPIE, San Diego, CA, USA, 30–31 August 1978; Volume 157, pp. 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkishko, Y.N.; Fedorov, V.A.; Prilutskii, V.E.; Ponomarev, V.G.; Morev, I.V.; Skripnikov, S.F.; Khmelevskaya, M.I.; Buravlev, A.S.; Kostritskii, S.M.; Fedorov, I. V Strapdown Inertial Navigation Systems Based on Fiber-Optic Gyroscopes. Gyroscopy Navig. 2014, 5, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, R.; She, X.; Huang, T.; Shu, X. Temperature Modeling of Modulation Phase Error in the Integrated Optical Chip for Closed-Loop Interferometric Fiber Optic Gyroscope. Opt. Eng. 2019, 58, 67104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefèvre, H.C. The Fiber-Optic Gyroscope: Challenges to Become the Ultimate Rotation-Sensing Technology. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2013, 19, 828–832. [Google Scholar]
- Guattari, F.; Moluçon, C.; Bigueur, A.; Ducloux, E.; De Toldi, E.; Honthaas, J.; Lefèvre, H. Touching the Limit of FOG Angular Random Walk: Challenges and Applications. In Proceedings of the 2016 DGON Intertial Sensors and Systems (ISS), Karlsruhe, Germany, 20–21 September 2016; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Chen, X. Analysis and Modeling for Fiber-Optic Gyroscope Scale Factor Based on Environment Temperature. Appl. Opt. 2012, 51, 2541–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurbatov, A.M.; Kurbatov, R.A.; Goryachkin, A.M. Fiber-Optic Gyroscope Accuracy Improvement by Suppressing the Parasitic Effects in Integrated Optic Phase Modulators. Gyroscopy Navig. 2019, 10, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda, M.; Takei, N.; Miyazawa, Y.; Kozuma, M. Multi-Harmonic Modulation in a Fiber-Optic Gyroscope. Sensors 2023, 23, 4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvestrini, J.P.; Guilbert, L.; Fontana, M.; Abarkan, M.; Gille, S. Analysis and Control of the Dc Drift in LiNbO3-Based Mach-Zehnder Modulators. J. Light. Technol. 2011, 29, 1522–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weis, R.S.; Gaylord, T.K. Lithium Niobate: Summary of Physical Properties and Crystal Structure. Appl. Phys. A 1985, 37, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Wang, Z.; Luo, R.; Zhao, D.; Peng, C.; Li, Z. Polarization Nonreciprocity Suppression of Dual-Polarization Fiber-Optic Gyroscope under Temperature Variation. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 1826–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackel, J.L.; Rice, C.E.; Veselka, J.J. Proton Exchange for High-index Waveguides in LiNbO3. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1982, 41, 607–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchoski, P.; Findakly, T.K.; Leonberger, F.J. Stable Low-Loss Proton-Exchanged LiNbO3 Waveguide Devices with No Electro-Optic Degradation. Opt. Lett. 1988, 13, 1050–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasemin Aşık, F.; Gökkavas, M.; Öztekin, E.; Karagöz, E.; Ceylan, A.; Özbay, E. Optimization of the Annealed Proton Exchange Method with Controlled Annealing for Multifunctional Integrated Optical Chip Production. Appl. Opt. 2022, 61, 8898–8903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dönertaş, S.; Gökkavas, M.; Özbay, E.; Orhan, E.Ö. Determining Thermo-Mechanical Stress Sources of an Integrated Optical Device. Optik 2021, 242, 167281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dönertaş, S.; Gökkavas, M.; Özbay, E.; Orhan, E. Case Study for Thermo Mechanical Performance of an Integrated Optic Device via Equation-Based Modelling. Gazi Univ. J. Sci. Part A Eng. Innov. 2021, 8, 135–145. [Google Scholar]
- Kanlı, Y.; Öztekin, E.; Dönertaş, S.; Gökkavas, M.; Ozbay, E. Ti-Indiffused Waveguide Polarizers on Lithium Niobate for Fiber Optic Gyroscope. In Proceedings of the Optical Fiber Sensors, Lausanne, Switzerland, 24–28 September 2018; p. WF51. [Google Scholar]
- Yertutanol, A.; Akçaalan, Ö.; Öğüt, S.; Özbay, E.; Ceylan, A. Fiber-Optic Gyroscope for the Suppression of a Faraday-Effect-Induced Bias Error. Opt. Lett. 2021, 46, 4328–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbaş, E.E.; Yertutanol, A.; Andaç, T.; Özbay, E.; Azizian-Kalandaragh, Y. Optimization of ASE Light Source Design for Enhancement of Wavelength Stability. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE SENSORS, Vienna, Austria, 29 October–1 November 2023; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Andac Senol, T.; Akcaalan, O.; Yertutanol, A.; Ozbay, E. A Novel Method to Eliminate the Symmetry Dependence of Fiber Coils for Shupe Mitigation. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 9076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osunluk, B.; Ogut, S.; Ozbay, E. Thermally Induced Bias Error Due to Strain Inhomogeneity through the Fiber Optic Gyroscope Coil. Appl. Opt. 2020, 59, 10416–10421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogut, S.; Osunluk, B.; Ozbay, E. Modeling of Thermal Sensitivity of a Fiber Optic Gyroscope Coil with Practical Quadrupole Winding. In Proceedings of the Fiber Optic Sensors and Applications XIV, Anaheim, CA, USA, 11–12 April 2017; Volume 10208, pp. 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, C.W.; Fang, Y.-H.; Chen, Y.-J.; Weng, Z.-Y.; Chu, J.-Y.; Chen, R.-Y.; Dong, C.-H.; Lin, W.; Chiu, Y.-J. Fabrication of Superluminescent Diode (SLD) for Gyro Light Source with Broadband, High Power, and Large Polarization-Extinction Ratio Performance. In Proceedings of the 2020 Opto-Electronics and Communications Conference (OECC), IEEE, Taipei, Taiwan, 4–8 October 2020; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shupe, D.M. Thermally Induced Nonreciprocity in the Fiber-Optic Interferometer. Appl. Opt. 1980, 19, 654–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, W.; Hu, X.; Zang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Lou, S.; Huang, B.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M. Accurate Measurement and Enhancement of Fiber Coil Symmetry. Appl. Opt. 2023, 62, E109–E118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Non-Pre-Annealed (NPA) Wafers | Pre-Annealed (PA) Wafers | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wafer Name | NPA-1 | NPA-2 | NPA-3 | NPA-4 | PA-1 | PA-2 | PA-3 | PA-4 |
| Total throughput MIOC #1 (%) | 29.10 | 33.70 | 37.80 | 35.60 | 52.50 | 48.10 | 49.40 | 51.20 |
| Total throughput MIOC #2 (%) | 30.00 | 36.30 | 31.40 | 35.80 | 51.90 | 46.10 | 49.60 | 52.10 |
| Total throughput MIOC #3 (%) | 36.30 | 32.60 | 35.20 | 37.10 | 53.90 | 44.00 | 52.10 | 53.60 |
| Total throughput MIOC #4 (%) | 32.40 | 29.30 | 32.80 | 37.00 | 54.30 | 47.90 | 51.70 | 54.20 |
| Mean (per wafer) (%) | 31.95 | 32.98 | 34.30 | 36.38 | 53.15 | 46.53 | 50.70 | 52.78 |
| Standard deviation (per wafer) | 3.22 | 2.90 | 2.81 | 0.78 | 1.14 | 1.91 | 1.40 | 1.37 |
| Mean (%) | 33.90 | 50.79 | ||||||
| Standard deviation | 2.89 | 3.02 | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karagöz, E.; Aşık, F.Y.; Gökkavas, M.; Akbaş, E.E.; Yertutanol, A.; Özbay, E.; Özcan, Ş. Reduction in Temperature-Dependent Fiber-Optic Gyroscope Bias Drift by Using Multifunctional Integrated Optical Chip Fabricated on Pre-Annealed LiNbO3. Photonics 2024, 11, 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11111057
Karagöz E, Aşık FY, Gökkavas M, Akbaş EE, Yertutanol A, Özbay E, Özcan Ş. Reduction in Temperature-Dependent Fiber-Optic Gyroscope Bias Drift by Using Multifunctional Integrated Optical Chip Fabricated on Pre-Annealed LiNbO3. Photonics. 2024; 11(11):1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11111057
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaragöz, Ercan, Fatma Yasemin Aşık, Mutlu Gökkavas, Erkut Emin Akbaş, Aylin Yertutanol, Ekmel Özbay, and Şadan Özcan. 2024. "Reduction in Temperature-Dependent Fiber-Optic Gyroscope Bias Drift by Using Multifunctional Integrated Optical Chip Fabricated on Pre-Annealed LiNbO3" Photonics 11, no. 11: 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11111057
APA StyleKaragöz, E., Aşık, F. Y., Gökkavas, M., Akbaş, E. E., Yertutanol, A., Özbay, E., & Özcan, Ş. (2024). Reduction in Temperature-Dependent Fiber-Optic Gyroscope Bias Drift by Using Multifunctional Integrated Optical Chip Fabricated on Pre-Annealed LiNbO3. Photonics, 11(11), 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11111057





