Dissimilar Laser Beam Welding of Titanium to Stainless Steel Using Pure Niobium as Filler Material in Lap Joint Configuration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
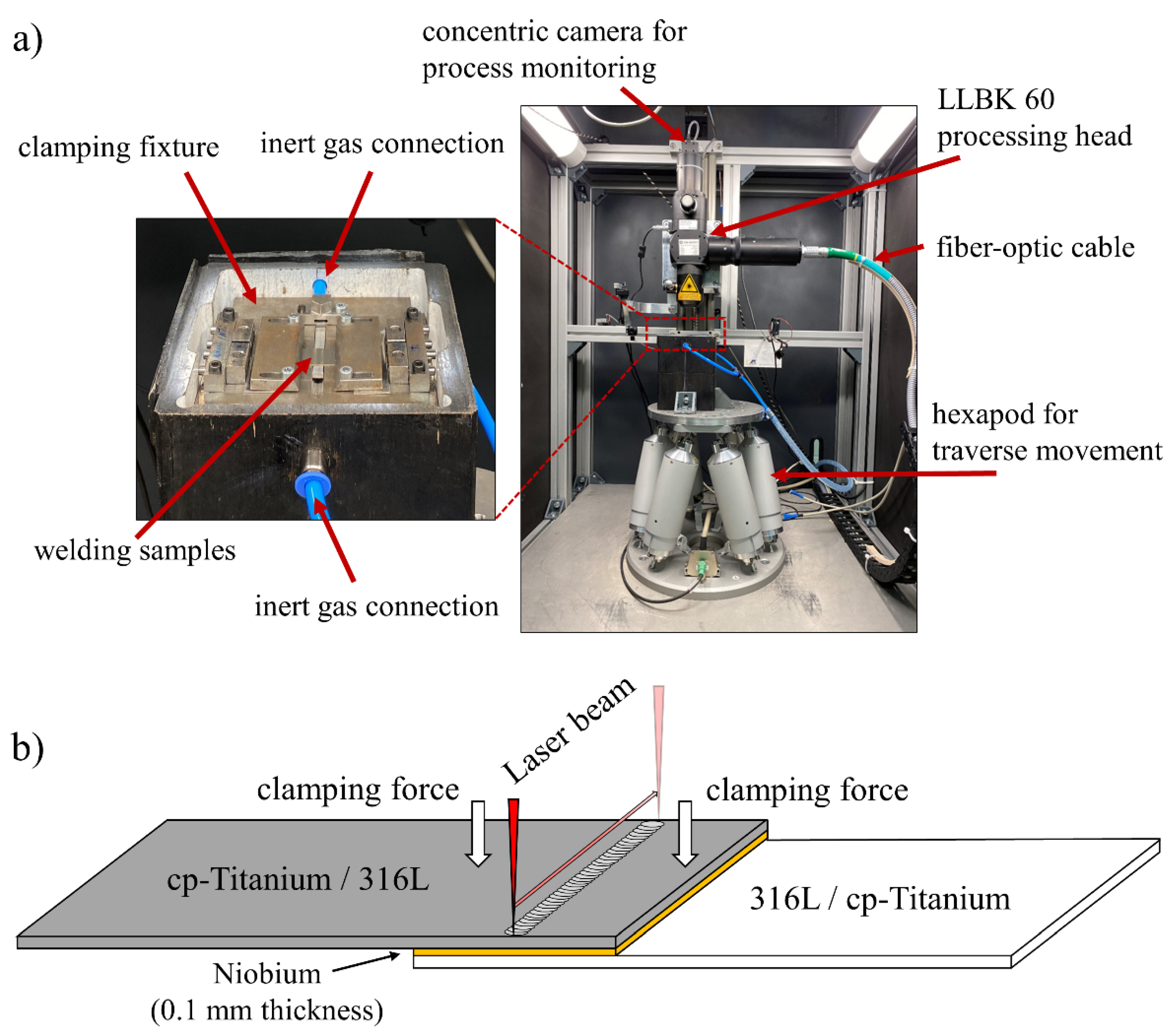
2. Materials and Methods
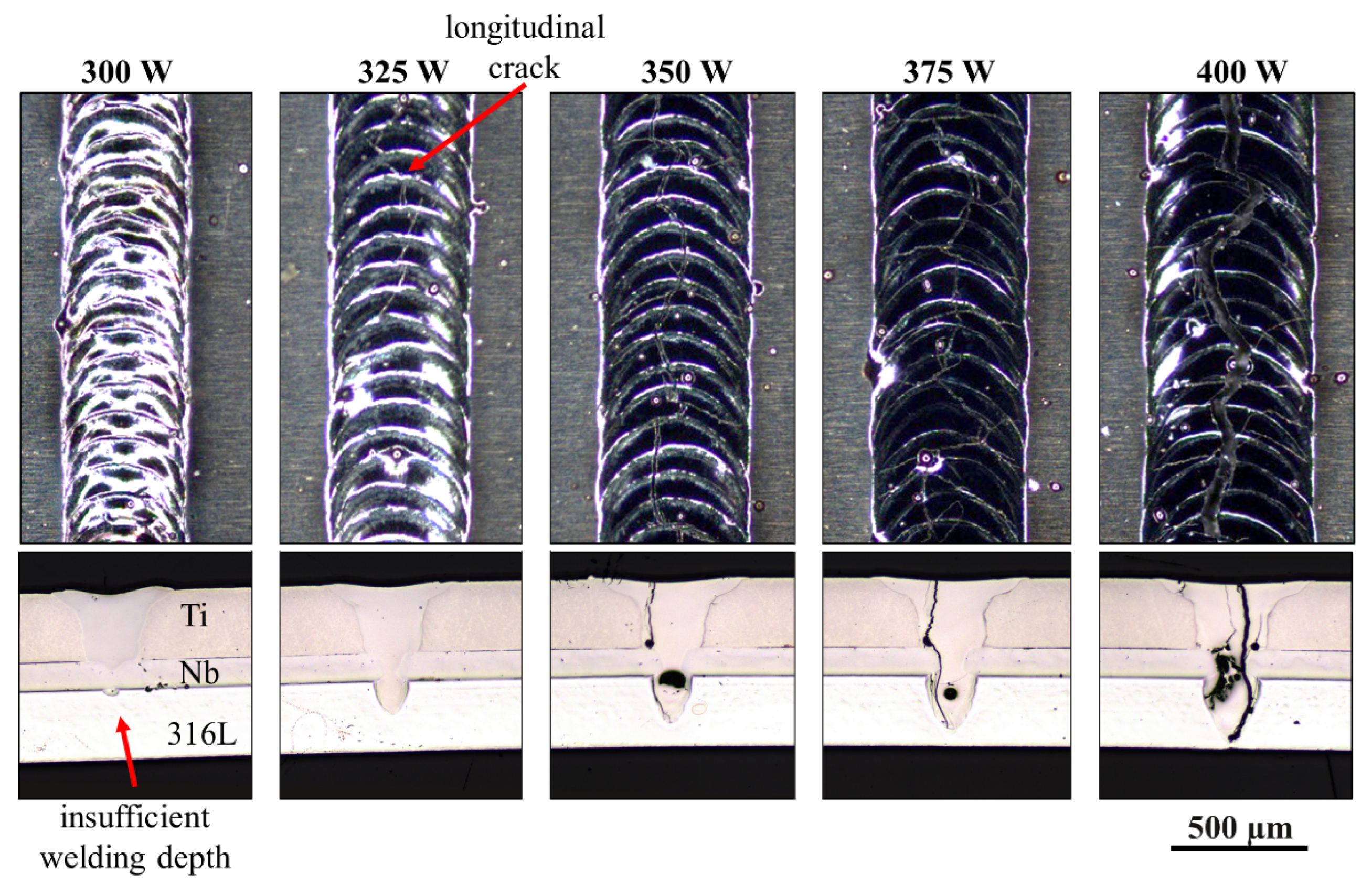
3. Results and Discussion
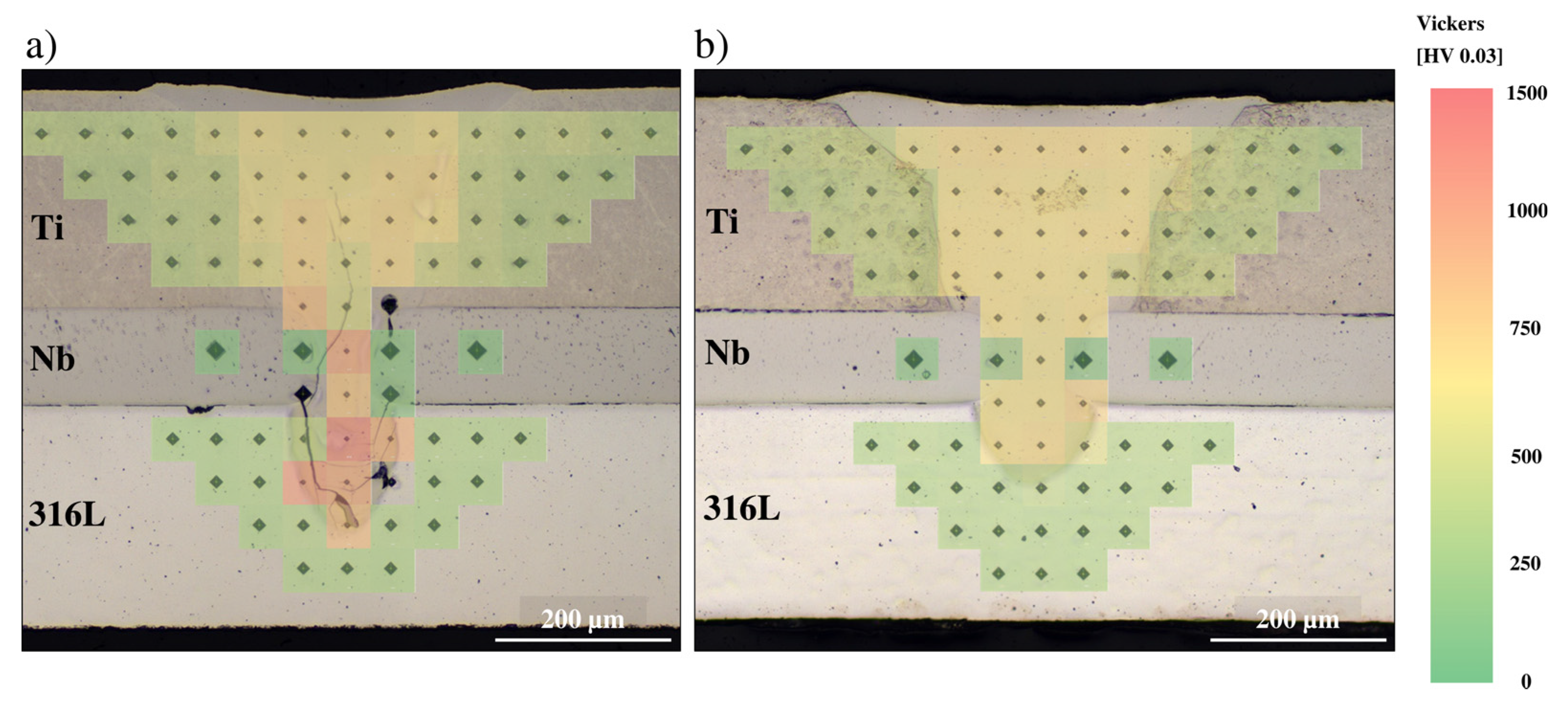
3.1. 316 L as Top Sheet/cp-Ti as Substrate Sheet
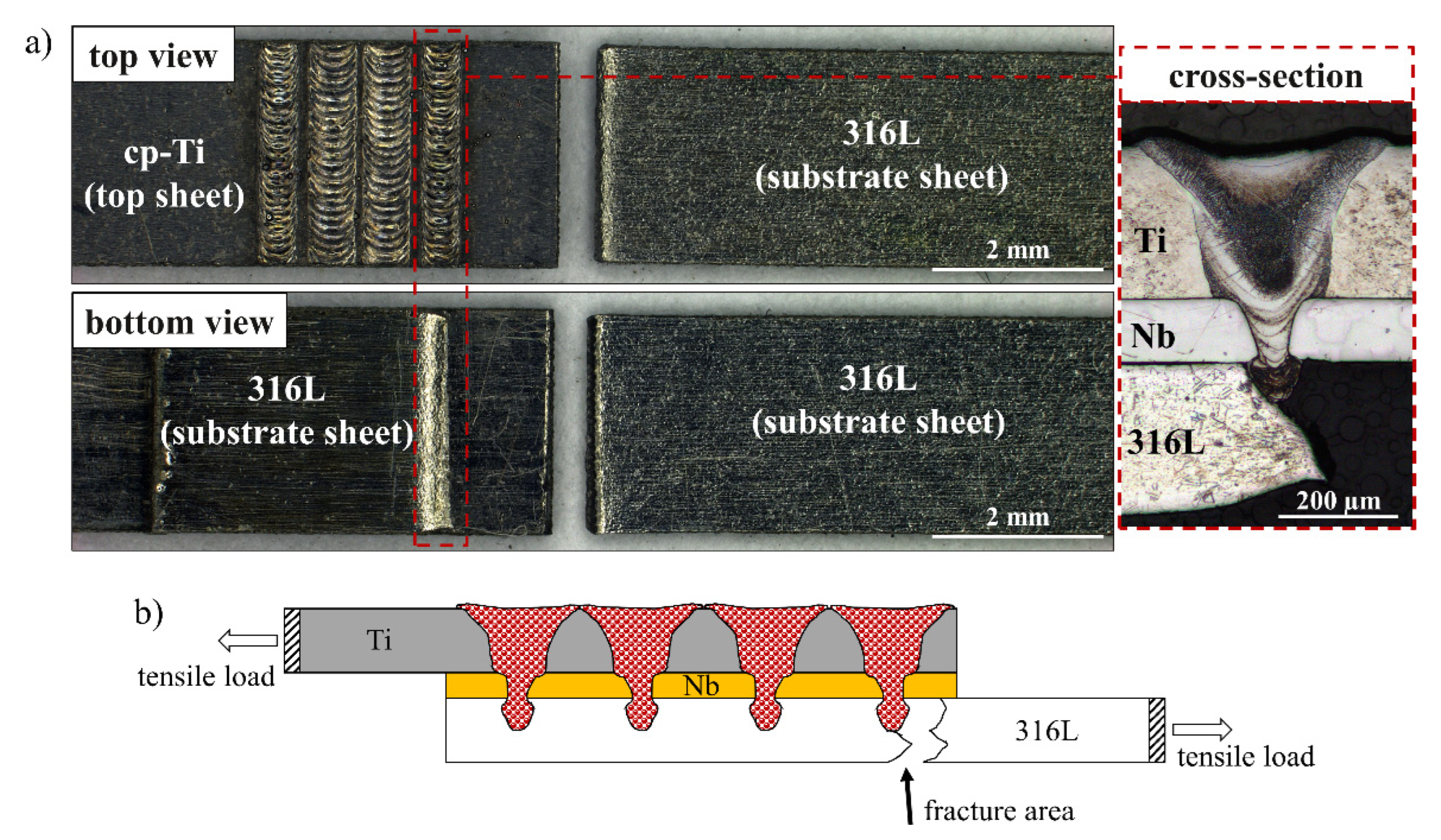
3.2. cp-Ti as Top Sheet/316L as Substrate Sheet
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Quazi, M.M.; Ishak, M.; Fazal, M.A.; Arslan, A.; Rubaiee, S.; Qaban, A.; Aiman, M.H.; Sultan, T.; Ali, M.M.; Manladan, S.M. Current research and development status of dissimilar materials laser welding of titanium and its alloys. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 126, 106090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegand, M.; Marks, L.; Sommer, N.; Böhm, S. Dissimilar micro beam welding of titanium to Nitinol and stainless steel using biocompatible filler materials for medical applications. Weld. World 2023, 67, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhang, M.; Huang, J.; Cui, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, X. Microstructures and mechanical property of laser butt welding of titanium alloy to stainless steel. Mater. Des. 2014, 53, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciamani, G.; de Keyzer, J.; Ferro, R.; Klotz, U.E.; Lacaze, J.; Wollants, P. Critical evaluation of the Fe–Ni, Fe–Ti and Fe–Ni–Ti alloy systems. Intermetallics 2006, 14, 1312–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, S.; Raza, M.S.; Kumar, S.; Saha, P. Exploring the possibility of dissimilar welding of NiTi to Ti using Yb-fiber laser. Adv. Mater. Process. Technol. 2018, 4, 614–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaei Zoeram, A.; Akbari Mousavi, S. Laser welding of Ti–6Al–4V to Nitinol. Mater. Des. 2014, 61, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satoh, G.; Yao, Y.L.; Qiu, C. Strength and microstructure of laser fusion-welded Ti–SS dissimilar material pair. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 66, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugarajan, B.; Padmanabham, G. Fusion welding studies using laser on Ti–SS dissimilar combination. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2012, 50, 1621–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, B.; Feng, J. Influences of different filler metals on electron beam welding of titanium alloy to stainless steel. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2014, 24, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannucci, A.; Tomashchuk, I.; Mathieu, A.; Cicala, E.; Boucheron, T.; Bolot, R.; Lafaye, S. Direct laser welding of pure titanium to austenitic stainless steel. Procedia CIRP 2018, 74, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, D.Q.; Gu, X.Y.; Liu, Y.J. Nd/YAG pulsed laser welding of TC4 titanium alloy to 301L stainless steel via pure copper interlayer. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 90, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannucci, A.; Tomashchuk, I.; Mathieu, A.; Bolot, R.; Cicala, E.; Lafaye, S.; Roudeix, C. Use of pure vanadium and niobium/copper inserts for laser welding of titanium to stainless steel. J. Adv. Join. Process. 2020, 1, 100022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Sun, D.; Li, H. Two pass laser welding of TC4 Titanium alloy to 301L stainless steel via pure V interlayer. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 1400–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Song, T.; Mo, D.; Luo, Z. Pulsed laser welding of Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy to AISI 316L stainless steel using Cu/Nb bilayer. Mater. Lett. 2019, 244, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Jin, P.; Sun, Q.; Feng, J. Benefits of interfacial regulation with interlayers in laser welding Ti6Al4V/316L steel. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 125, 106007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Sun, D.; Li, H. Three-pass laser welding of Ti alloy-stainless steel using Nb and Ni interlayers. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 1780–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, D.Q.; Gu, X.Y.; Duan, Z.Z.; Li, H.M. Nd:YAG pulsed laser welding of TC4 Ti alloy to 301L stainless steel using Ta/V/Fe composite interlayer. Mater. Lett. 2018, 212, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, N.; Stredak, F.; Wiegand, M.; Böhm, S. Grain growth and precipitation behaviour of AISI 430 ferritic stainless steel subjected to pulsed laser beam welding using free-form pulse shaping. Weld. World 2023, 67, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Ion, J.C. Laser welding of dissimilar metal combinations. J. Mater. Sci. 1995, 30, 4205–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- METALCOR GmbH. Datenblatt: Titan-Grade 4 (3.7065). Available online: http://www.metalcor.de/datenblatt/124/ (accessed on 22 August 2023).
- Deutsche Edelstahlwerke GmbH. Werkstoffdatenblatt 1.4404. Available online: https://www.dew-stahl.com/fileadmin/files/dew-stahl.com/documents/Publikationen/Werkstoffdatenblaetter/RSH/1.4404_de.pdf (accessed on 22 August 2023).
- WHS Sondermetalle GmbH & Co. KG. Datenblatt Niob (NB, NbZr1). Available online: https://www.whs-sondermetalle.de/images/pdf/Nb-Niob.pdf (accessed on 22 August 2023).
- Ge, F.; Peng, B.; Oliveira, J.P.; Ke, W.; Teshome, F.B.; Li, Y.; Zeng, Z. Dissimilar Laser Welding of a NiTi Shape Memory Alloy to Ti2AlNb. Metals 2021, 11, 1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yu, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, N. Laser welding/brazing of 5182 aluminium alloy to ZEK100 magnesium alloy using a nickel interlayer. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2018, 23, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Material | Melting Point [°C] | Ultimate Tensile Strength * [MPa] | Elongation at Break * [%] | Thermal Conductivity [Wm−1K−1] | Coefficient of Thermal Expansion [10−6 K−1] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cp-Titanium (grade 4) | 1660 | ~679 | ~23 | 18 | 8.6 |
| 316L (X2CrNiMo17-12-2, annealed) | ~1450 | ~656 | ~44 | 15 | 16 |
| Niobium (purity 99.9%) | 2468 | ~254 | ~42 | 52 | 7.1 |
| Pulse Duration [ms] | Pulse Peak Power [W] | Traverse Speed [mm/s] | Pulse Frequency [Hz] | Pulse interval [mm] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 700–800 | 0.15 | 3 | 0.05 |
| 3 | 400–500 | 0.3 | 0.1 | |
| 7 | 300–400 | 0.3 | 0.1 | |
| 10 | 250–350 | 0.3 | 0.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wiegand, M.; Kimm, A.; Sommer, N.; Marks, L.; Kahlmeyer, M.; Böhm, S. Dissimilar Laser Beam Welding of Titanium to Stainless Steel Using Pure Niobium as Filler Material in Lap Joint Configuration. Photonics 2023, 10, 1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10091063
Wiegand M, Kimm A, Sommer N, Marks L, Kahlmeyer M, Böhm S. Dissimilar Laser Beam Welding of Titanium to Stainless Steel Using Pure Niobium as Filler Material in Lap Joint Configuration. Photonics. 2023; 10(9):1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10091063
Chicago/Turabian StyleWiegand, Michael, Alexander Kimm, Niklas Sommer, Linda Marks, Martin Kahlmeyer, and Stefan Böhm. 2023. "Dissimilar Laser Beam Welding of Titanium to Stainless Steel Using Pure Niobium as Filler Material in Lap Joint Configuration" Photonics 10, no. 9: 1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10091063
APA StyleWiegand, M., Kimm, A., Sommer, N., Marks, L., Kahlmeyer, M., & Böhm, S. (2023). Dissimilar Laser Beam Welding of Titanium to Stainless Steel Using Pure Niobium as Filler Material in Lap Joint Configuration. Photonics, 10(9), 1063. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10091063






