Abstract
Ozone near the surface of the atmosphere directly stimulates the human respiratory tract and affects human health. In recent years, ozone pollution in China has become a serious problem, so controlling ozone pollution is an urgent task. Differential absorption lidar is a useful tool for detecting ozone concentration, but it cannot receive complete signals in the lower hundreds of meters because of the overlap factor. CCD imaging lidar technology can effectively solve this problem. A fitting method of inverting the ozone concentration profile using ultraviolet differential CCD imaging lidar is proposed in this paper. The effect of three different types of aerosol extinction coefficient, three different types of ozone concentration, and five different types of aerosol wavelength index on retrieving ozone concentrations was analyzed using simulation. For clean aerosol, the relative error of the retrieved ozone concentration is less than 5%. As to polluted aerosol, the relative error of the retrieved ozone concentration is less than 10%. As to heavily polluted aerosol, the relative error of the retrieved ozone concentration is less than 25%. The results show that the larger the value of the aerosol extinction coefficient, the larger the relative error of the retrieved ozone concentration; meanwhile, the lower the ozone concentration, the larger the relative error of the retrieved ozone concentration; at the same time, the further the aerosol wavelength index deviates from 1, the larger the relative error of the retrieved ozone concentration. The relative error of the retrieved ozone concentration in this case was about 4%. It is shown that this fitting method of retrieving ozone concentrations is reasonable and feasible.
1. Introduction
Ozone is one of the important trace gases in the atmosphere [], and it is mainly distributed in the stratosphere. Although ozone has a relatively low content in the atmosphere, it has an important effect on the earth’s total radiation, temperature profile, atmospheric circulation, human health [,,], and plant growth. Specifically, the ozone layer in the stratosphere not only absorbs ultraviolet radiation, which is harmful to human beings and other creatures, but it is also the heat source of the stratosphere atmosphere, which plays an important role in the heat balance of the stratosphere atmosphere. So, the temperature and circulation of the stratosphere change with the ozone layer. The ozone in the troposphere has a greenhouse effect, and its change affects the global climate. The ozone near the surface damages human health by directly irritating the human respiratory tract. The ozone near the surface causes plant leaves to turn yellow or even wither and leads to reduced production and economic benefits of agricultural and forestry plants. Meanwhile, ozone is also the main intermediate product of secondary pollution caused by photochemical smog [,,,].
The sources of ozone are mainly divided into natural and anthropogenic sources. The natural source of ozone is mainly transmitted downwards in the stratosphere. The anthropogenic ozone is mainly generated by photochemical reactions of pollutants, such as NOx and VOCs emitted by humans. The ozone concentration near the ground changes over time and space, and its formation mechanism, source analysis, and migration patterns are extremely complex and have not been fully understood till now.
At present, atmospheric ozone pollution is gradually emerging in China, especially in Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei, the Yangtze River Delta, and the Pearl River Delta [,,]. In response to this increasingly prominent ozone pollution, China’s Environmental Air Quality Standards (GB3095-2012) published in February 2012 limited the 8-h average concentration for ozone. The standard for ozone is that the daily averages of 8-h ozone concentration are less than 100 μg∙m−3 for the first level and 160 μg∙m−3 for the second level. So, the prevention and control of ozone pollution is an urgent task. The first step is to monitor the vertical distribution of ozone concentration. Therefore, the formation mechanism, source analysis, and migration law of ozone were analyzed, and the columnar content of ozone was calculated. There are many international active and passive ozone observation methods and instruments, such as ozone analyzers, Dobson spectrometers, radiosondes, satellite passive sensors, and lidar. Because of the advantages of large distance and high spatial resolution [,,,], differential absorption lidar has become a powerful tool to detect the profiles of ozone concentration in the atmosphere. So far, many researchers have developed a variety of lidar methods to detect ozone concentration in the atmosphere [,,,,].
The detector is a photo multiplier in traditional differential absorption lidar, and the transmitter is a pulse laser. The signal detected by traditional differential absorption lidar is not complete in the low hundreds of meters because of the overlap factor. Imaging lidar uses a charge-coupled device (CCD) as its detector; the CCD camera and emission device are placed separately in two places so that the lidar based on CCD can avoid the overlap factor and has a higher spatial resolution near the ground, which makes it suitable for detecting the aerosol optical parameter profiles near the surface [,,]. Liang Mei proposed a method to detect oxygen in the atmosphere using continuous differential absorption lidar []. Guangqiang Fan proposed a new tropospheric ozone concentration inversion algorithm based on differential absorption lidar []. Shaolin Liang designed a hyperspectral total ozone detector based on a CCD imaging system []. Our group, for the first time, proposes a new method to detect ozone concentration profiles using ultraviolet differential CCD imaging lidar []. The retrieval method of ozone concentration profile using ultraviolet differential CCD imaging lidar will be introduced in this paper.
2. Instrument
The ultraviolet differential CCD imaging lidar system consists of three parts: emission, detection and control part. The system includes two continuous ultraviolet lasers, an ultraviolet CCD and a computer.The schematic diagram of this lidar system is shown in Figure 1, where θ represents the scattering angle.
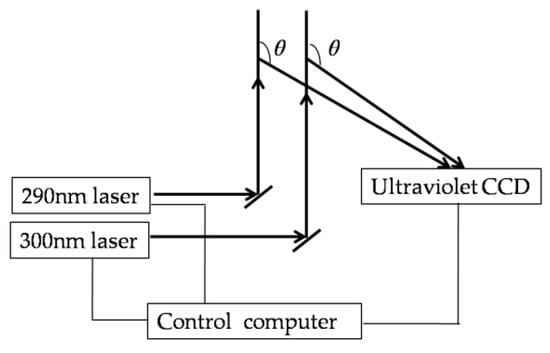
Figure 1.
Diagram of the ultraviolet differential CCD imaging lidar system.
According to the principle of differential lidar absorption and the absorption cross-section curve of ozone in the ultraviolet spectrum, two similar lasers with wavelengths of 290 nm and 300 nm were selected. Two continuous ultraviolet lasers emit two laser beams into the atmosphere, which interact with atmospheric molecules and aerosols and emit scattered light in various directions. The CCD receives side-scattering echo signals at wavelengths of 290 nm and 300 nm from different altitudes and directions. How to retrieve ozone concentration profiles from these side-scattering echo signals will be introduced in the following section.
3. Principle and Method
Compared with the traditional differential absorption lidar equation, there are three main differences in the ultraviolet CCD imaging lidar equation. First, echo signals have no range square dependence; second, the range resolution is not constant; third, the scattering term includes the aerosol side-scattering coefficient. Therefore, the retrieval method of traditional differential absorption lidar is not suitable for ultraviolet differential CCD imaging lidar. In addition, the detection altitude of ultraviolet CCD imaging lidar is relatively low, generally within the range of 3 km, so it is difficult to retrieve the aerosol optical parameters from the ultraviolet signal. As a result, it is not suitable to correct the aerosol interference using the traditional retrieval method. According to the characteristics of the ultraviolet CCD imaging lidar equation, such as the aerosol side-scattering coefficient, non-constant range resolution, and low detection range, a fitting method for retrieving ozone concentration profiles is proposed.
3.1. Principle
The CCD imaging lidar receives a side-scattering signal, and different altitudes correspond to different scattering angles. Therefore, the CCD imaging lidar equation contains the atmospheric (aerosol and molecule) side-scattering coefficient with different scatter angles as shown in Equations (1) and (2):
where θ is the scattering angle; dθ is the field of view (FOV) of one pixel; P(λ, z) is the received photoelectron number at the altitude z by one pixel; Con and Coff are two lidar constants; βα(λ,θ), βm(λ, θ) are the side-scattering coefficients of aerosol and atmospheric molecule, respectively; αg(λ, z)=αa(λ, z)+αm(λ, z) is the atmospheric extinction coefficient except ozone (including aerosol extinction coefficient αa(λ, z) and atmospheric molecule extinction coefficient αm(λ, z)); σ(λ) is the absorption cross section of ozone molecule; NO3(z) is the ozone concentration; and the subscripts on and off represent the strong absorption and weak absorption of ozone, respectively.
By introducing the phase function and relative phase function of aerosol and atmospheric molecule, the side-scattering coefficient can be expressed as the product of backscattering coefficient and relative phase function []. The relative phase function of atmospheric molecule was obtained using Rayleigh scattering theory, and the relative phase function of aerosol was obtained using the experimental method in []. When the relative phase functions of aerosol and atmospheric molecule are substituted into Equations (1) and (2) as known quantities, the side-scattering coefficients of aerosol and atmospheric molecule are eliminated from the CCD imaging lidar equation, and Equations (1) and (2) become Equations (3) and (4), which contain the backscattering coefficient of aerosol and atmospheric molecule.
Here, fa(θ) and fm(θ) represent the relative phase function of aerosol and atmospheric molecule, respectively. Equations (3) and (4) contain extinction coefficients and backscattering coefficients of aerosol and atmospheric molecule, which are the same as the backscattering lidar equation.
It is difficult to directly retrieve the optical parameters of aerosol from the ultraviolet differential CCD imaging lidar because ozone is strongly absorbed in the ultraviolet spectrum and the detection altitude of ultraviolet lidar is lower. A 532 nm lidar is added to retrieve the aerosol backscattering coefficient and extinction coefficient at 532 nm, and then, it is converted to βα(λon, π), βα(λoff, π), αa(λon, z), and αa(λoff, z) to correct the aerosol interference using the relationship between the aerosol backscattering coefficient and extinction coefficient with the wavelength in Equations (5) and (6). Here, v and w are the aerosol backscattering coefficient wavelength index and extinction coefficient wavelength index, respectively.
In view of the characteristic mentioned above that the spatial resolution is not constant, a fitting method is proposed. Based on and an assumed ozone concentration profile, an array of simulated signals corresponding to λon can be obtained by changing the assumed ozone concentration profile value within a certain range. The simulated signal corresponding to λon is marked as . By comparing with one by one, the assumed ozone concentration profile will be the final solution for ozone concentration profile when the difference between and is small enough (i.e., less than the threshold).
3.2. Method
The main difference between the fitting method proposed in this paper and the traditional method is whether to make full use of the lidar detection data. As shown in Equations (3) and (4), the echo signals at different altitudes are received by ultraviolet differential CCD imaging lidar. In the fitting method, it is assumed that n+1 lidar detection data are included in the interval of Δz (n > 1, for example, n = 5), so, there are 2(n + 1) lidar detection data for λon and λoff in the interval from z to z + Δz. Because the detection device is a CCD camera and receives side-scattering echo signals, it can be seen in Figure 1 that the spatial resolution is higher near the ground and is not constant. However, in the fitting method, the spatial resolution is taken as a certain value. The smaller the Δz, the greater the spatial resolution. On the other hand, the smaller the Δz, the larger the random error. Therefore, the selection of Δz takes into account these two factors and generally selects several tens of meters. In the traditional method, only four lidar detection data at z and z + Δz are used, while other data are discarded. The fitting method proposed in this paper improves the data utilization rate.
The main steps of inverting the ozone concentration profile from Equations (3) and (4) are as follows:
Step 1. It is assumed that the ozone concentration NO3 (z) is uniform from z to z + Δz, and the ozone concentration NO3 (z) = lC0, where l is a variable natural number and C0 is the minimum detectable ozone concentration, such as 1ppb. NO3 (z) changes with l.
Step 2. The aerosol extinction coefficient and backscattering coefficient retrieved from 532 nm lidar are converted into aerosol extinction coefficient and backscattering coefficient at λon and λoff according to Equations (5) and (6). Let w = v = 1.0 and
Step 3. Based on P(λoff, z), simulated signals P′(λon, z+Δzn) ( n= 1, 2, 3…) are constructed according to the principle of lidar receiving signals in the range of z to z + Δz, and the construction formula is as follows:
Step 4. The sum of squares of the difference between the simulated signals P′(λon, z + Δzn) and the measured signal P(λon, z + Δzn) at the corresponding altitude is calculated in the range of z to z + Δz. Namely,
Obviously, Sum (l) is a function of l in step 1.
Step 5. Let l take 1, 2… Nt in sequence (NtC0 is the maximum ozone concentration that may occur, which depends on the situation of the detection location). Then, repeat steps 2 and 3 to obtain Nt different Sum (l).
Step 6. Select the minimum Sum (l). The l corresponding to the minimum Sum (l) is denoted as lfit. When NO3 (z) is taken as lfitC0, the constructed simulated signal is closest to the measured signal. Thus, the value of ozone concentration NO3 (z) is lfitC0 in the range of z to z + Δz.
Step 7. The altitude z increases gradually from 0 to ztop. Repeat step 3 to step 6 for each Δz. Finally, a fitting ozone concentration profile is obtained.
4. Validation and Case
4.1. Validation
In order to test the proposed fitting method in this paper, a simulation method was used. The aerosol extinction coefficient profile and backscattering coefficient profile at 532 nm were assumed and converted into the ones at 290 nm and 300 nm using Equations (5) and (6). The atmospheric molecule extinction coefficient and backscattering coefficient at 290 nm and 300 nm were obtained using Rayleigh scattering theory. The relative phase function of aerosol was obtained using the HG formula (or CCD detection). Then, assuming the ozone concentration profile in the atmosphere, the stimulated signals of the CCD imaging lidar at 290 nm and 300 nm can be calculated using Equations (3) and (4). Lastly, the simulated signals were inverted to verify the feasibility and reliability of the method for retrieving ozone concentration profiles.
The values of the aerosol extinction coefficient, ozone concentration, and aerosol wavelength index have a certain influence on the error of the retrieved ozone concentration. Therefore, it is assumed that the aerosol extinction coefficient profile was divided into three types in the simulation experiments, which are shown in Figure 2: clean aerosol, polluted aerosol, and heavily polluted aerosol.
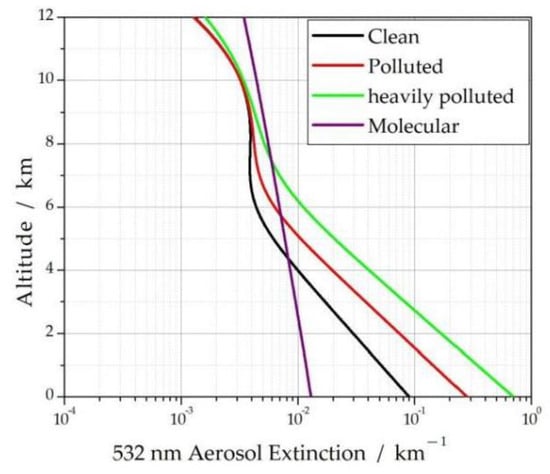
Figure 2.
Three kinds of assumed aerosol extinction coefficient profiles.
It is assumed that the ozone concentration is also divided into three types: low concentration, middle concentration, and high concentration, as shown in Figure 3. It is also assumed that w = v = k, and k can be taken as 0.5, 0.8, 1.0, 1.2, and 1.5.
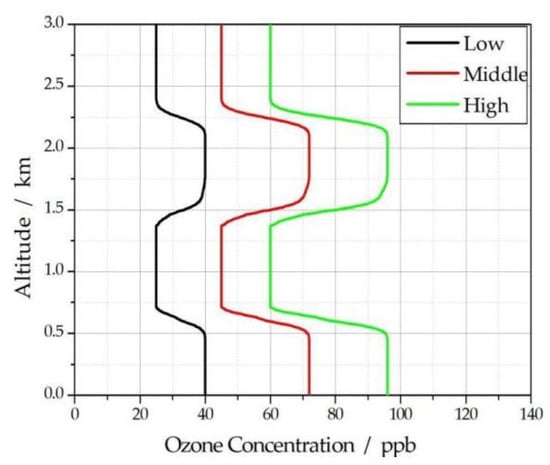
Figure 3.
Three kinds of assumed ozone concentration profiles.
For clean aerosol, five simulation signal profiles can be obtained by taking five different values of k for each assumed ozone concentration profile. During the inversion process, k is always taken as 1; the retrieved ozone concentration and the corresponding relative error are shown in Figure 4.
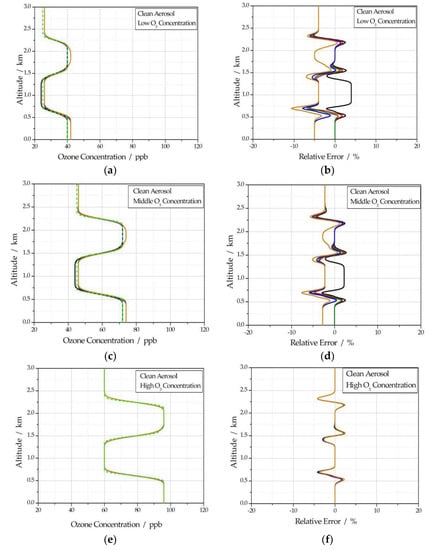
Figure 4.
(a) Retrieval ozone concentration profile of clean aerosol at low ozone concentration; (b) the corresponding relative error of clean aerosol at low ozone concentration; (c) retrieval ozone concentration profile of clean aerosol at middle ozone concentration; (d) the corresponding relative error of clean aerosol at middle ozone concentration; (e) retrieval ozone concentration profile of clean aerosol at high ozone concentration; (f) the corresponding relative error of clean aerosol at high ozone concentration.
In Figure 4, the black solid line represents k = 0.5, the red solid line represents k = 0.8, the olive solid line represents k = 1, the blue solid line represents k = 1.2, and the orange solid line represents k = 1.5. In Figure 4a,c,e, the green short dashed line represents the original O3 concentration.
As shown in Figure 2, the extinction coefficient of clean aerosol at 532 nm is less than 0.1 km−1, so the atmospheric visibility is greater than 30 km, and the atmosphere is clean. In this case, it can be seen from Figure 4 that the retrieval accuracy of the ozone concentration profile is very high within the altitude of 3 km. The maximum relative error is less than 5%. The higher the ozone concentration, the smaller the relative error.
For polluted aerosol, five simulation signal profiles can be obtained by taking five different values of k for each assumed ozone concentration profile. During the inversion process, k is always taken as 1, and the retrieved ozone concentration and the corresponding relative error are shown in Figure 5. In Figure 5, all lines have the same meanings as in Figure 4.
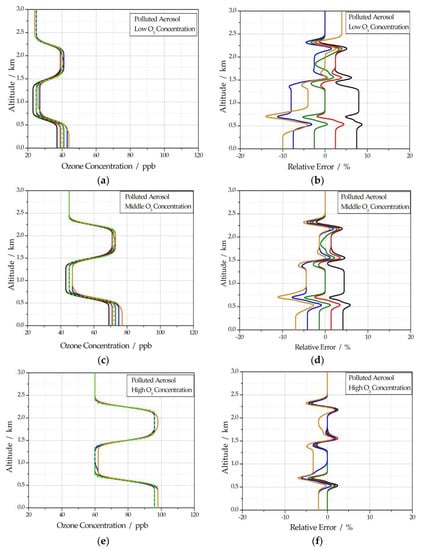
Figure 5.
(a) Retrieval ozone concentration profile of polluted aerosol at low ozone concentration; (b) the corresponding relative error of polluted aerosol at low ozone concentration; (c) retrieval ozone concentration profile of polluted aerosol at middle ozone concentration; (d) the corresponding relative error of polluted aerosol at middle ozone concentration; (e) retrieval ozone concentration profile of polluted aerosol at high ozone concentration; (f) the corresponding relative error of polluted aerosol at high ozone concentration.
As shown in Figure 2, the extinction coefficient of polluted aerosol at 532 nm is less than 0.3 km−1, so atmospheric visibility is about 13 km. In this case, it can be seen from Figure 5 that the retrieval accuracy of the ozone concentration profile for the high ozone concentration is still very high, and the maximum relative error is less than 2%; for the middle ozone concentration, the maximum relative error of the retrieval ozone concentration profile is about 7%; for the low ozone concentration, the maximum relative error of the retrieval ozone concentration profile is about 10%. The lower the ozone concentration, the larger the relative error.
For heavily polluted aerosol, five simulation signal profiles can be obtained by taking five different values of k for each assumed ozone concentration profile using the same method. During the inversion process, k is always taken as 1, and the retrieved ozone concentration and the corresponding relative error are shown in Figure 6. In Figure 6, all lines have the same meanings as in Figure 4.
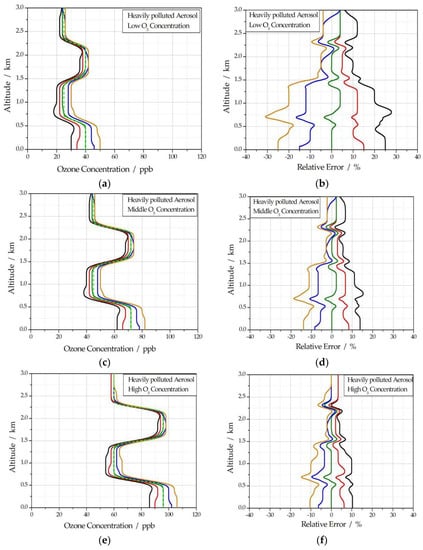
Figure 6.
(a) Retrieval ozone concentration profile of heavily polluted aerosol at low ozone concentration; (b) the corresponding relative error of heavily polluted aerosol at low ozone concentration; (c) retrieval ozone concentration profile of heavily polluted aerosol at middle ozone concentration; (d) the corresponding relative error of heavily polluted aerosol at middle ozone concentration; (e) retrieval ozone concentration profile of heavily polluted aerosol at high ozone concentration; (f) the corresponding relative error of heavily polluted aerosol at high ozone concentration.
As shown in Figure 2, the extinction coefficient of heavily polluted aerosol at 532 nm is less than 0. 7 km−1, so atmospheric visibility is about 5.5 km. In this case, it can be seen from Figure 6 that the retrieval accuracy of the ozone concentration profile is still very high for the high ozone concentration, and the maximum relative error is less than 10%; for the middle ozone concentration, the maximum relative error of the retrieval ozone concentration profile is about 14%; for the low ozone concentration, the maximum relative error of the retrieval ozone concentration profile is about 25%. The lower the ozone concentration, the larger the relative error.
To sum up, the greater the aerosol extinction coefficient, the larger the relative error; the higher the ozone concentration, the smaller the relative error. The further the aerosol wavelength index is from 1, the larger the relative error.
4.2. Case
On the evening of 1 October 2021, it was sunny in Hefei. Our research group detected the echo signals at 290 nm and 300 nm using ultraviolet differential CCD imaging lidar, as shown in Figure 7. As can be seen, 290 nm is the stronger ozone absorption cross-section and 300 nm is the weaker ozone absorption cross-section.
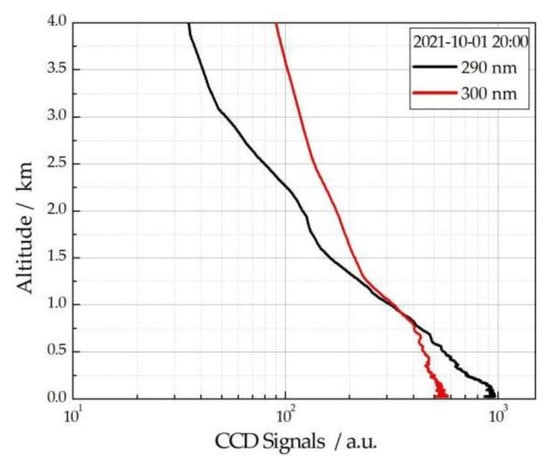
Figure 7.
Echo signal profiles using ultraviolet differential CCD imaging lidar.
Using the echo signal of ultraviolet differential CCD imaging lidar, the real-time ozone concentration profile was retrieved using the fitting inversion method proposed in this paper, as shown in Figure 8. From Figure 8, it can be seen that the ozone concentration varies with altitude, and there is a hierarchical structure. The ozone concentration shows a nonlinear change with altitude. The ultraviolet differential lidar system proposed by Jiangfeng Shao also has similar results in detecting the ozone concentration profile []. The maximum ozone concentration at ground level is 58.7 ppb. The ozone concentration is the lowest at 1.68 km, with a minimum value of 50.0 ppb. In order to test the reliability of the inversion results, the ozone concentration detected by the Sanli’an National Control Station in Shushan District, Hefei City, three kilometers away from the location of the experimental system, was compared. The ozone concentration detector at Sanli’an National Control Station is an ozone analyzer. The detection altitude is 250 m. The ozone concentration was 108 μg∙m−3, detected at the same time. For ozone molecules, 1 μg∙m−3 is equal to 0.518 ppb. The 108 μg∙m−3 measured by the ground station is equal to 55.9 ppb, while the ozone concentration corresponding to the altitude is 58.2 ppb, as shown in Figure 8, with a relative error of about 4%. Multiple experiments have been conducted at different times, the retrieved ozone concentration was compared with the ozone concentration detected by the national control station, and the results show that the relative errors are all less than 5%.
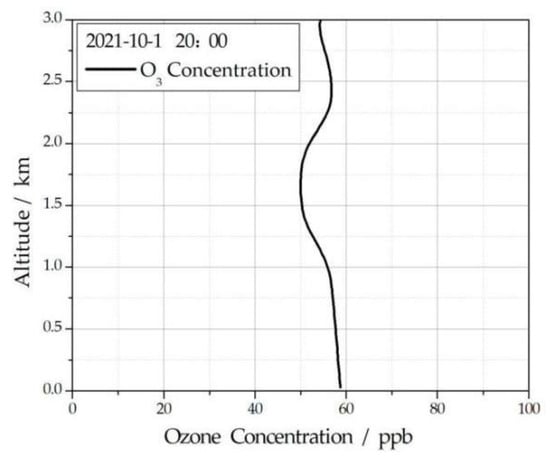
Figure 8.
Retrieved ozone concentration profile.
5. Conclusions
In view of the characteristics that the spatial resolution of the ultraviolet differential CCD imaging lidar is not constant, the spatial resolution is high near the ground, and the detection altitude in the ultraviolet spectrum is relatively low. The 532 nm lidar channel was added to retrieve the aerosol optical parameters at 532 nm, which were converted to the ones at two ultraviolet wavelengths using the wavelength index. Then, in this study, a fitting method has been proposed to retrieve the ozone concentration profile.
The ultraviolet CCD imaging lidar signals at λon and λoff were simulated in the case of three types of aerosol extinction coefficient, three types of ozone concentration profiles, and five different wavelength indexes. The ozone concentration profiles were retrieved, which show that the greater the aerosol extinction coefficient, the larger the relative error of the ozone concentration; the lower the ozone concentration, the larger the relative error of the ozone concentration; the further the wavelength index of the aerosol optical parameter is away from 1, the larger the relative error of the ozone concentration. For clean aerosol, the relative error is within 5%; for polluted aerosol, the relative error is within 10%; and for heavily polluted aerosol, the relative error can reach 25% with a low ozone concentration, but the relative error is also within 15% in other cases. The simulation results show that the fitting method proposed in this paper is feasible and reliable, and the observational case also supports this point of view.
Author Contributions
Methodology, H.S. and Z.T.; validation, H.Z. and X.M.; formal analysis, J.H. and S.W.; investigation, K.C.; resources, C.J.; data curation, S.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, H.S.; writing—review and editing, J.Q. and X.M.; visualization, Z.W.; supervision, D.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41975026), the Key Research and Development Program of Anhui Province (2022h11020008), and the HFIPS director’s Fund (2021YZGH01).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Li, Z.; Lin, W.; Xu, X. Characteristics of surface ozone at Shangri La region atmospheric background stations. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2015, 24, 1412–1417. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G. Atmospheric Ozone Layer and Ozone Hole; Meteorological Press: Beijing, China, 2003; pp. 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Guan, M.; Chen, L. Analysis on the spatial and temporal distribution of O3 and it’s effect on emergency dispatches in Shijiazhuang, 2013–2015. J. Med. Pest Control 2017, 33, 859–862. [Google Scholar]
- Fleming, Z.L.; Doherty, R.M.; von Schneidemesser, E.; Malley, C.S.; Cooper, O.R.; Pinto, J.P.; Colette, A.; Xu, X.; Simpson, D.; Schultz, M.G.; et al. Tropospheric Ozone Assessment Report: Present-day ozone distribution and trends relevant to human health. Elem. Sci. Anthr. 2018, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Sun, H.; Chen, L. Acute health impacts of ozone exposure on daily mortality in Nanjing. Jiangsu J. Prev. Med. 2017, 28, 366–368. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Xiao, C. Ozone distribution and effect on respiratory system. Chin. J. Micro Ecol. 2018, 30, 853–857. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Liu, M.; Song, J. Spatiotemporal Variations and Influent Factors of Tropospheric Ozone Concentration over China Based on OMI Data. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Russo, A.; Du, H.; Xiang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, C. Impact of meteorological conditions at multiple scales on ozone concentration in the Yangtze River Delta. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 791, 148044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Sheng, S. Spatial Patterns in the Extreme Dependence of Ozone Pollution between Cities in China’s BTH Region. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, X. Ozone Spatial-temporal Distribution and Trend over China Since 2013: Insight from Satellite and Surface Observation. Environ. Sci. 2019, 40, 1132–1142. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X.; Gong, Z.; Zhang, X. Pollution Characteristics of Ozone in China and Key Regions. Environ. Monit. China 2017, 33, 17–25. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Li, A.; Chen, H.; Sun, J.; Lu, Z. Scale-adaptive three-dimensional imaging using Risley-prism-based coherent lidar. Opt. Lett. 2023, 48, 2587–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duma, V.-F.; Dimb, A.-L. Exact Scan Patterns of Rotational Risley Prisms Obtained with a Graphical Method: Multi-Parameter Analysis and Design. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Liu, X.; Sun, J.; Lu, Z. Risley-prism-based multi-beam scanning LiDAR for high-resolution three-dimensional imaging. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2022, 150, 106836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C. MEMS mirror based omnidirectional scanning for lidar optical systems. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2022, 158, 107178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schotland, R.M. Errors in the lidar measurement of atmospheric gases by differential absorption. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1974, 13, 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- McGee, T.J.; Gross, M.R.; Singh, U.N.; Butler, J.J.; Kimvilakani, P.E. Improved stratospheric ozone lidar. Opt. Eng. 1995, 34, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar]
- Kovalev, A.V.; James, L.M. Differential absorption lidar measurement of vertical ozone profile in the troposphere that contains aerosol layer with strong backscattering gradients: A simplified version. Appl. Opt. 1994, 33, 8393–8401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Nakane, H.; Hu, H.; Zhou, J. Three-wavelength dual differential absorption lidar method for stratospheric ozone measurements in the presence of volcanic aerosols. Appl. Opt. 1997, 36, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Tomasi, F.; Perrone, M.R.; Protopapa, M.L. Monitoring O3 with solar-blind Raman lidar. Appl. Opt. 2001, 40, 1314–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, J.E.; Sharma, N.P.; Kaplan, T.B. Atmospheric aerosol profiling with a bistatic imaging lidar system. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 2922–2929. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, Z.; Liu, D.; Wang, Z.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Q.; Xie, C.; Bo, G.; Hu, S.; Wang, Y. Measurements of aerosol phase function and vertical backscattering coefficient using a charge-coupled device side-scatter lidar. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 1127–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Z.; Liu, D.; Ma, X.; Shi, B.; Shan, H.; Zhao, M.; Xie, C.; Wang, Y. Vertical distribution of near-ground aerosol backscattering coefficient measured by a CCD side-scattering lidar. Appl. Phys. B 2015, 120, 631–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, L.; Brydegaard, M. Continuous-wave differential absorption lidar. Laser Photonics Rev. 2015, 9, 2014000419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.-Q.; Liu, J.; Liu, W.-Q.; Lu, Y.-H.; Zhang, T.-S.; Dong, Y.-S.; Zhao, X.-S. A new retrieval method for Ozone concentration at the troposphere based on differential absorption lidar. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2012, 32, 3304–3308. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, S. Design and Test of CCD Imaging System for Hyperspectral Total Ozone Unit. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, Z.; Liu, D. Design and simulation of CCD laser beam imaging technique in detecting ozone concentration profile. Infrared Laser Eng. 2021, 49, 20200383. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, Z.; Liu, D. A numerical inversion method for CCD side-scatter lidar, in Proceedings of International Conference on Remote Sensing. Environ. Transp. Eng. 2013, 31, 350–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Hua, D. Development of ultraviolet dual-wavelength lidar and analysis of its signal-to-noise ratio. Acta Opt. Sin. 2020, 40, 1201004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).