Quantitative Phase Contrast Microscopy with Optimized Partially Coherent Illumination
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
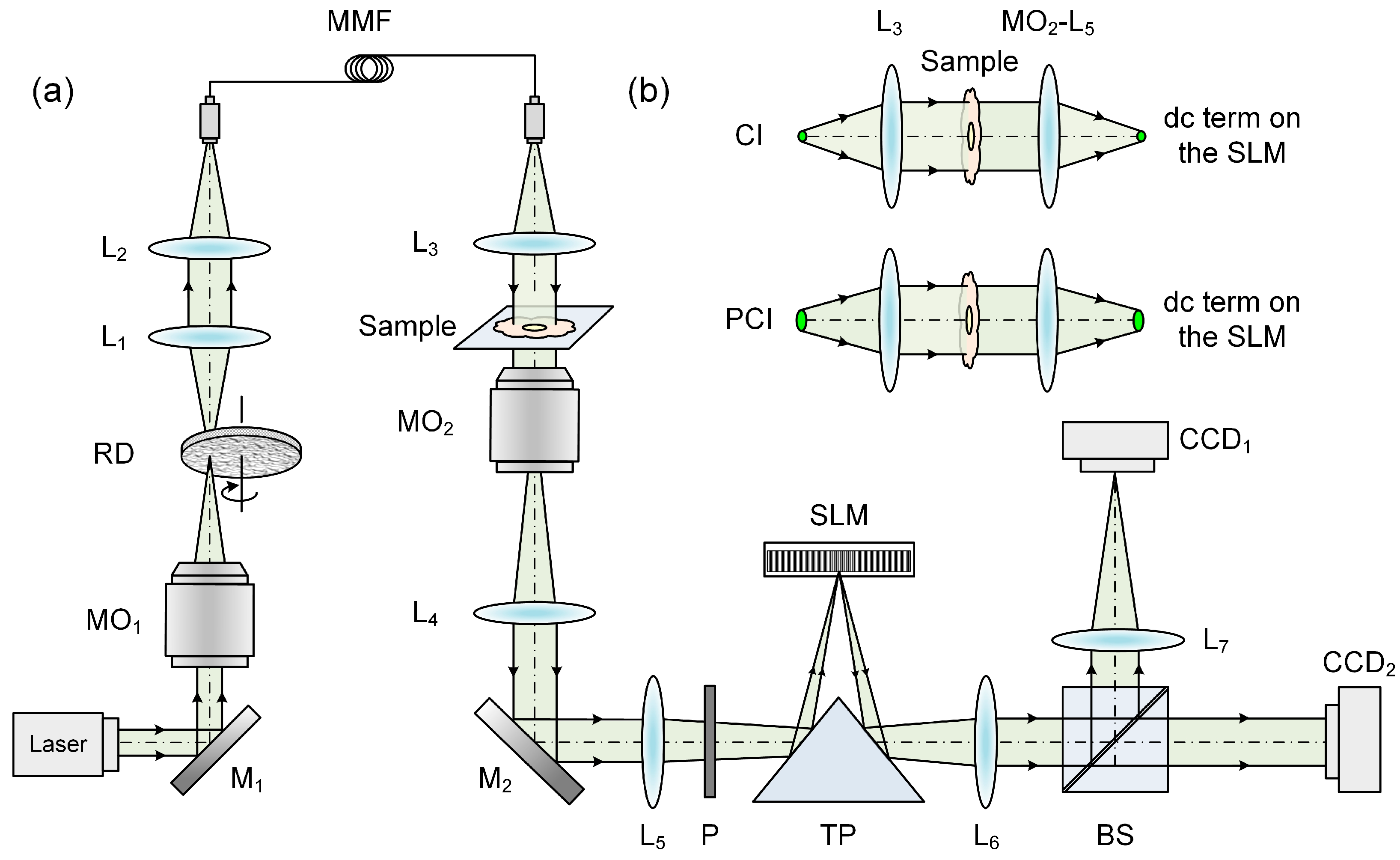
2.1. Experimental Setup of PCI-QPCM
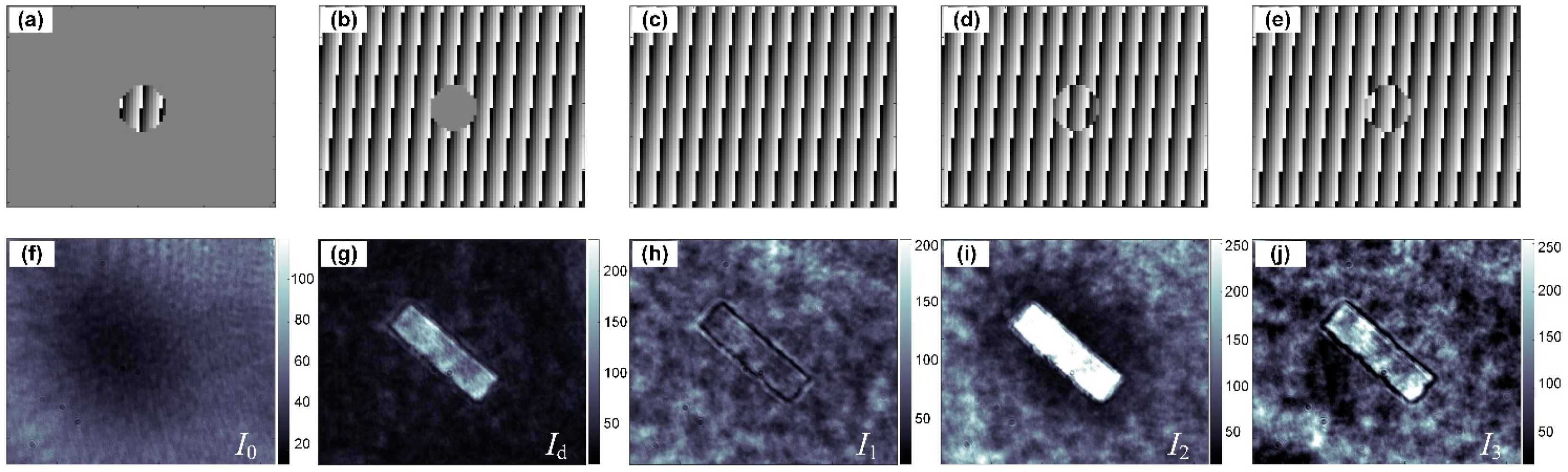
2.2. Numerical Reconstruction of PCI-QPCM
3. Results
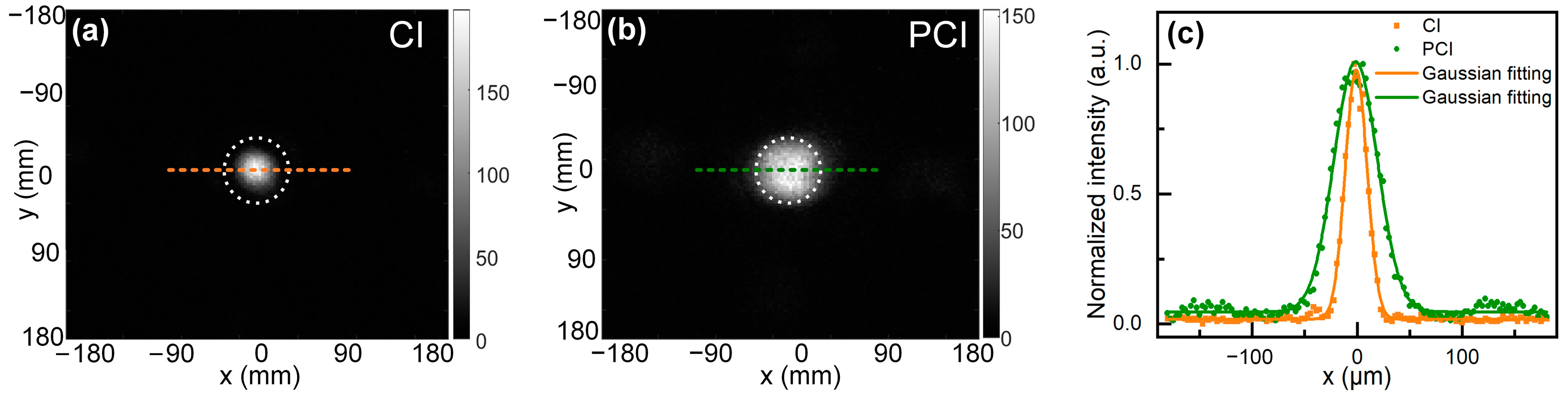
3.1. Imaging of Phase-Step Sample Using PCI-QPCM
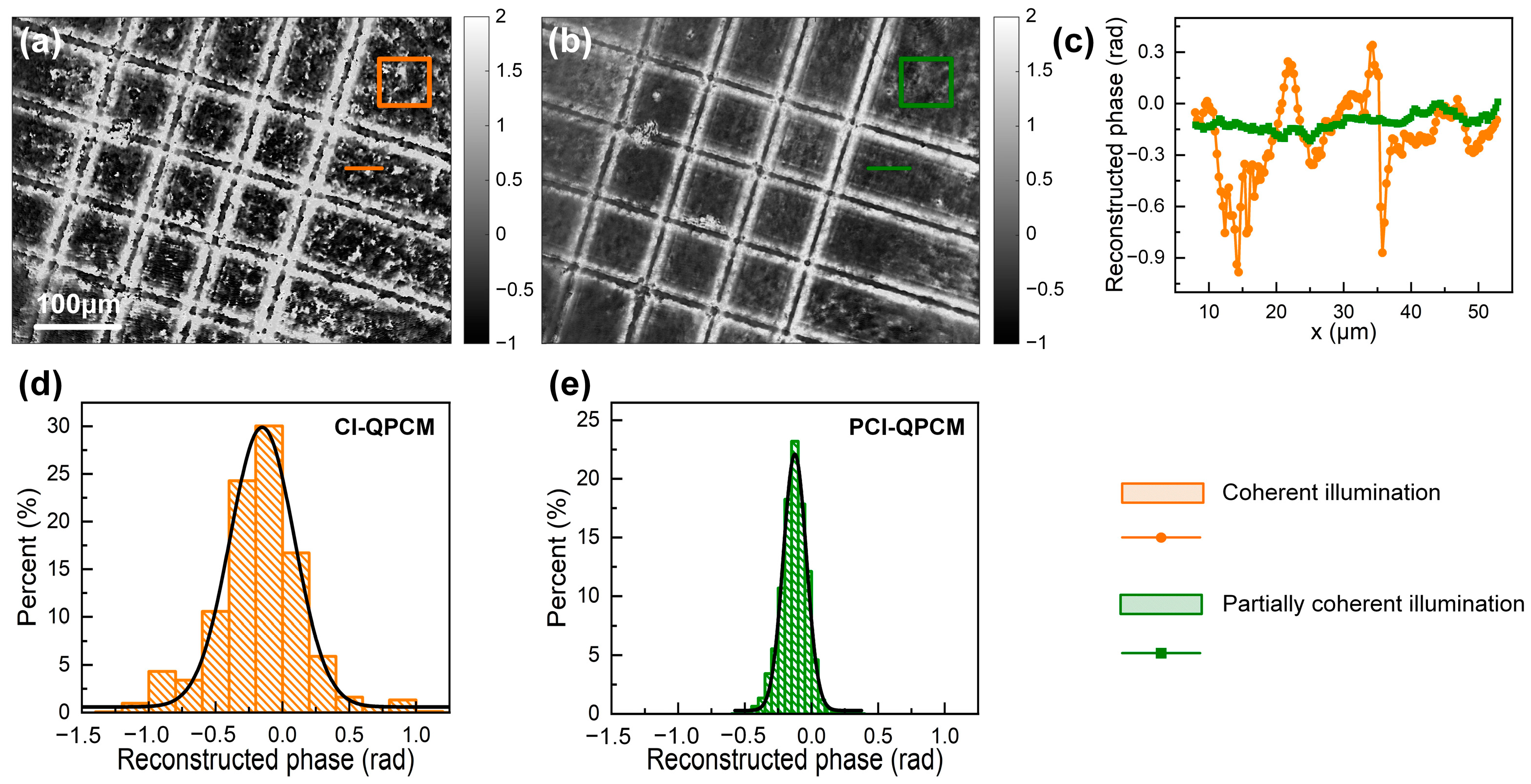
3.2. Comparison of Speckle Noise between CI-QPCM and PCI-QPCM
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, Y.; Depeursinge, C.; Popescu, G. Quantitative phase imaging in biomedicine. Nat. Photonics 2018, 12, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barty, A.; Nugent, K.A.; Paganin, D.; Roberts, A. Quantitative optical phase microscopy. Opt. Lett. 1998, 23, 817–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wen, K.; Zheng, J.; Liu, L.; Gao, P. Polarization grating based on diffraction phase microscopy for quantitative phase imaging of paramecia. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 29775–29787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, K.; Ma, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, J.; Zalevsky, Z.; Zheng, J. Transmission structured illumination microscopy for quantitative phase and scattering imaging. Front. Phys. 2021, 8, 630350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micó, V.; Zheng, J.; Garcia, J.; Zalevsky, Z.; Gao, P. Resolution enhancement in quantitative phase microscopy. Adv. Opt. Photonics 2019, 11, 135–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abregana, T.J.; Almoro, P.F. Phase retrieval by amplitude modulation using digital micromirror device. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2022, 150, 106851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Min, J.; Yuan, X.; Xue, Y.; Bai, C.; Yao, B. Triple-wavelength quantitative phase imaging with refractive index measurement. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2022, 156, 107110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osten, W.; Faridian, A.; Gao, P.; KöRner, K.; Naik, D.; Pedrini, G.; Singh, A.K.; Takeda, M.; Wilke, M. Recent advances in digital holography [Invited]. Appl. Opt. 2014, 53, 44–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Pedrini, G.; Osten, W. Structured illumination for resolution enhancement and autofocusing in digital holographic microscopy. Opt. Lett. 2013, 38, 1328–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wen, K.; Liu, M.; Ma, Y.; Zheng, J.; Gao, P. Partially coherent illumination based point-diffraction digital holographic microscopy study dynamics of live cells. Front. Phy. 2021, 9, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Wen, K.; Zhuo, K.; Guo, R.; Gao, P. Partially coherent illumination-based digital holographic microscopy and its applications. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2021, 58, 1811005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery, Y.; Cuche, E.; Colomb, T.; Depeursinge, C.; Rappaz, B.; Marquet, P.; Magistretti, P. DHM (Digital Holography Microscope) for imaging cells. In Proceedings of the Journal of Physics: Conference Series, Basel, Switzerland, 30 July–4 August 2007; pp. 1317–1321. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Dai, S.; Ma, C.; Xi, T.; Di, J.; Zhao, J. A review of common-path off-axis digital holography: Towards high stable optical instrument manufacturing. Light Adv. Manuf. 2021, 2, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Miller, E.D.; Weiss, L.E.; Campbell, P.G.; Kanade, T. Online Tracking of Migrating and Proliferating Cells Imaged with Phase-Contrast Microscopy. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshop (CVPRW’06), New York, NY, USA, 17–22 June 2006; p. 65. [Google Scholar]
- Bhaduri, B.; Pham, H.; Mir, M.; Popescu, G. Diffraction phase microscopy with white light (wDPM). Opt. Lett. 2012, 37, 1094–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobiny, A.; Lu, H.; Nguyen, H.V.; Roysam, B.; Varadarajan, N. Automated Classification of Apoptosis in Phase Contrast Microscopy Using Capsule Network. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2019, 39, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theriault, D.H.; Walker, M.L.; Wong, J.Y.; Betke, M. Cell morphology classification and clutter mitigation in phase-contrast microscopy images using machine learning. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2012, 23, 659–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debeir, O.; Van Ham, P.; Kiss, R.; Decaestecker, C. Tracking of migrating cells under phase-contrast video microscopy with combined mean-shift processes. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2005, 24, 697–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, L.; Zheng, J.; Liu, M.; Gao, P. Reflectional quantitative phase-contrast microscopy (RQPCM) with annular epi-illumination. Appl. Opt. 2022, 61, 3641–3647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Shao, M.; Yang, X.; Si, L.; Jiang, M.; Wang, T.; Ke, Z.; Peng, T.; Fang, S.; Zhang, S. Morphology analysis of unlabeled red blood cells based on quantitative differential phase contrast microscopy. Cytom. A 2022, 101, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadono, H.; Ogusu, M.; Toyooka, S. Phase shifting common path interferometer using a liquid-crystal phase modulator. Opt. Commun. 1994, 110, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lue, N.; Choi, W.; Popescu, G.; Ikeda, T.; Feld, M.S. Quantitative phase imaging of live cells using fast Fourier phase microscopy. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 1836–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsheerali, P.T.; Das, B.; Joseph, J. Quantitative phase contrast imaging using common-path in-line digital holography. Opt. Commun. 2012, 285, 1062–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.K.; He, Y.R.; Sobh, N.; Popescu, G. Label-free colorectal cancer screening using deep learning and spatial light interference microscopy (SLIM). APL Photonics 2020, 5, 040805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Kandel, M.E.; Popescu, G. Spatial light interference microscopy (SLIM): Principle and applications to biomedicine. Adv. Opt. Photonics 2020, 13, 353–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Guo, S.; Pan, Y.; Fan, R.; Smith, Z.J.; Lane, S.; Chu, K. Quantitative phase microscopy with enhanced contrast and improved resolution through ultra-oblique illumination (UO-QPM). J. Biophotonics 2019, 12, e201900011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Ma, Y.; Pan, Y.; Smith, Z.J.; Chu, K. Organelle-specific phase contrast microscopy enables gentle monitoring and analysis of mitochondrial network dynamics. Biomed. Opt. Express 2021, 12, 4363–4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Dai, T.; Lei, Y.; Zheng, J.; Liu, M.; Sui, B.; Smith, Z.J.; Chu, K.; Kong, L.; Gao, P. Label-free imaging of intracellular organelle dynamics using flat-fielding quantitative phase contrast microscopy (FF-QPCM). Opt. Express 2022, 30, 9505–9520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, S.; Dashtdar, M.; Sánchez-Ortiga, E.; Martínez-Corral, M.; Javidi, B. Stable and simple quantitative phase-contrast imaging by Fresnel biprism. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 112, 113701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernet, S.; Jesacher, A.; Fürhapter, S.; Maurer, C.; Ritsch-Marte, M. Quantitative imaging of complex samples by spiral phase contrast microscopy. Opt. Express 2006, 14, 3792–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Yao, B.; Gao, P.; Ye, T. Phase contrast microscopy with fringe contrast adjustable by using grating-based phase-shifter. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 16077–16082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kandel, M.E.; Fanous, M.J.; Hu, C.; Chen, H.; Lu, X.; Popescu, G. Harmonically decoupled gradient light interference microscopy (HD-GLIM). Opt. Lett. 2020, 45, 1487–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Sam, R.; Shan, M.; Nastasa, V.; Wang, M.; Kim, T.; Gillette, M.; Sengupta, P.; Popescu, G. Optical excitation and detection of neuronal activity. J. Biophotonics 2019, 12, e201800269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joglekar, M.; Trivedi, V.; Chhaniwal, V.; Claus, D.; Javidi, B.; Anand, A. LED based large field of view off-axis quantitative phase contrast microscopy by hologram multiplexing. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 29234–29245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stangner, T.; Zhang, H.; Dahlberg, T.; Wiklund, K.; Andersson, M. Step-by-step guide to reduce spatial coherence of laser light using a rotating ground glass diffuser. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 5427–5435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfling, S.; Lanzmann, E.; Israeli, M.; Ben-Yosef, N.; Arieli, Y. Spatial phase-shift interferometry—A wavefront analysis technique for three-dimensional topometry. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 2005, 22, 2498–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhuo, K.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; An, S.; Zalevsky, Z.; Zheng, J.; Gao, P. Quantitative Phase Contrast Microscopy with Optimized Partially Coherent Illumination. Photonics 2023, 10, 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10040391
Zhuo K, Wang Y, Ma Y, An S, Zalevsky Z, Zheng J, Gao P. Quantitative Phase Contrast Microscopy with Optimized Partially Coherent Illumination. Photonics. 2023; 10(4):391. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10040391
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhuo, Kequn, Yang Wang, Ying Ma, Sha An, Zeev Zalevsky, Juanjuan Zheng, and Peng Gao. 2023. "Quantitative Phase Contrast Microscopy with Optimized Partially Coherent Illumination" Photonics 10, no. 4: 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10040391
APA StyleZhuo, K., Wang, Y., Ma, Y., An, S., Zalevsky, Z., Zheng, J., & Gao, P. (2023). Quantitative Phase Contrast Microscopy with Optimized Partially Coherent Illumination. Photonics, 10(4), 391. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10040391








