Natural Flexible and Responsive 2D Photonic Materials with Micro-Sandwich Structure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Analysis
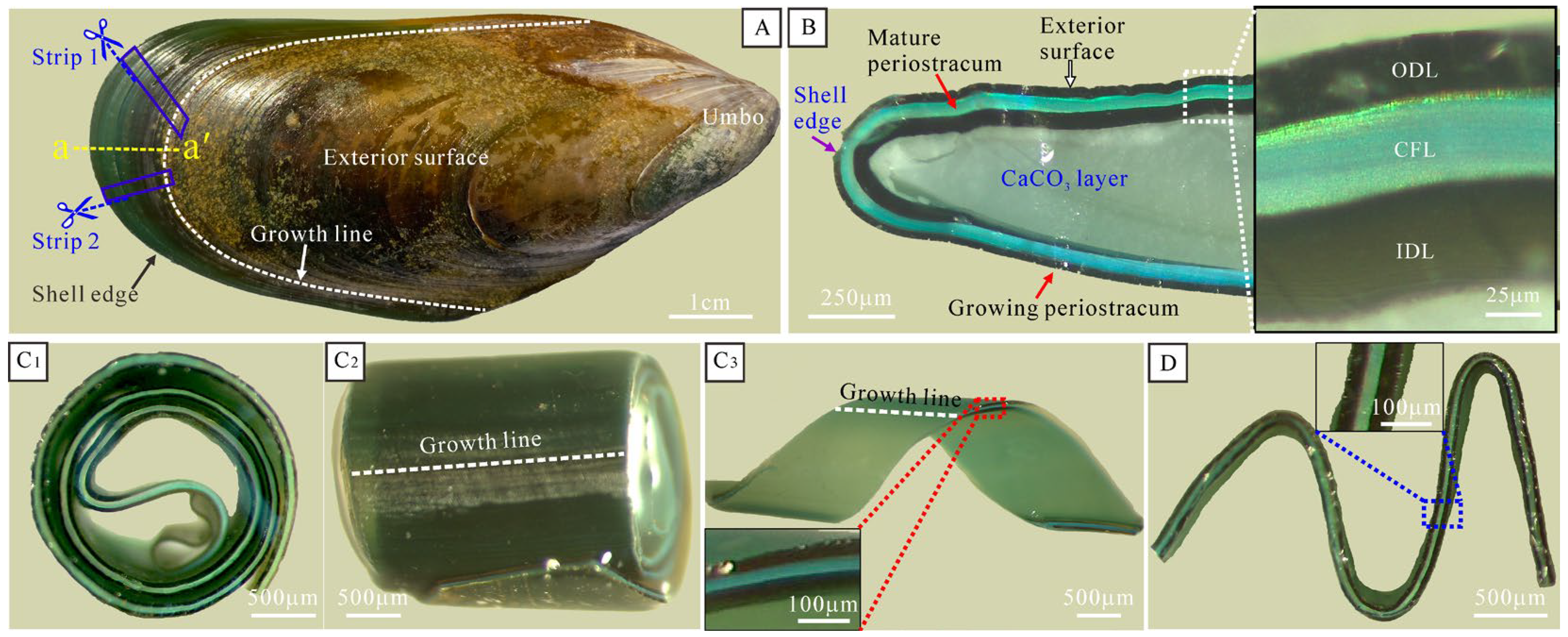
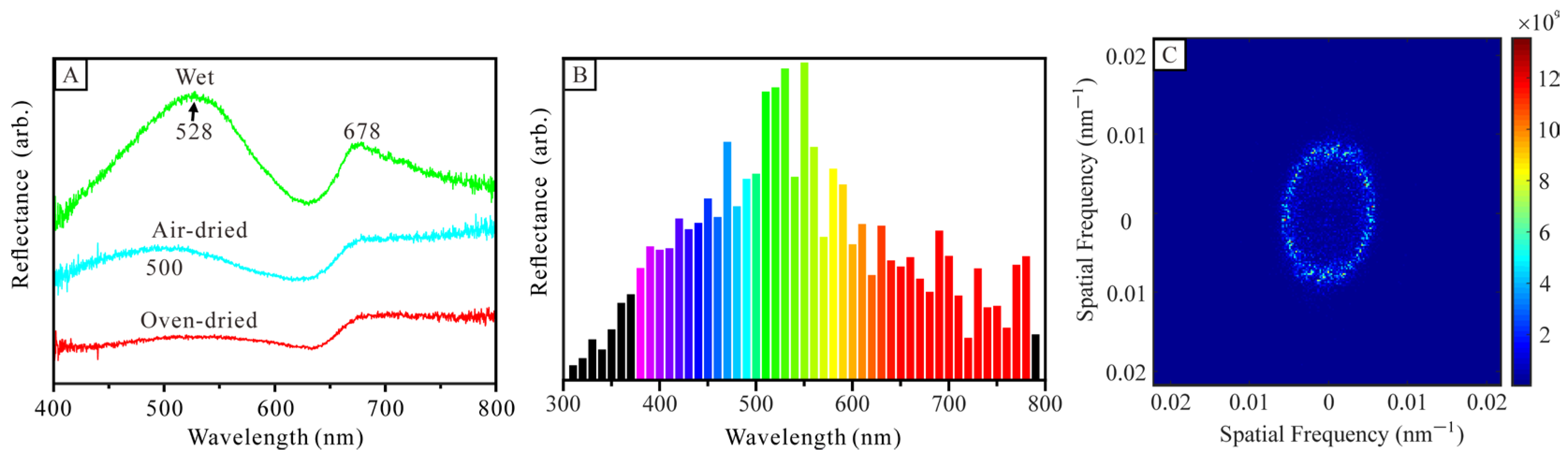
3.1. Optical Observation and Analysis
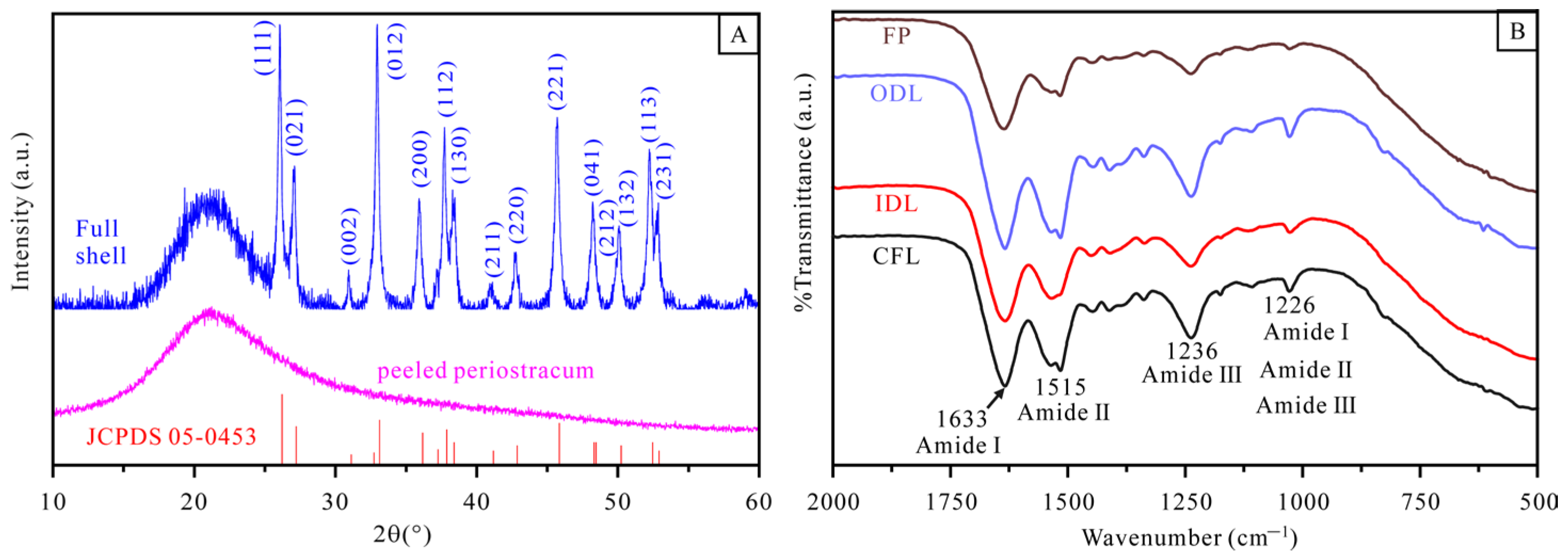
3.2. XRD and FTIR Analysis
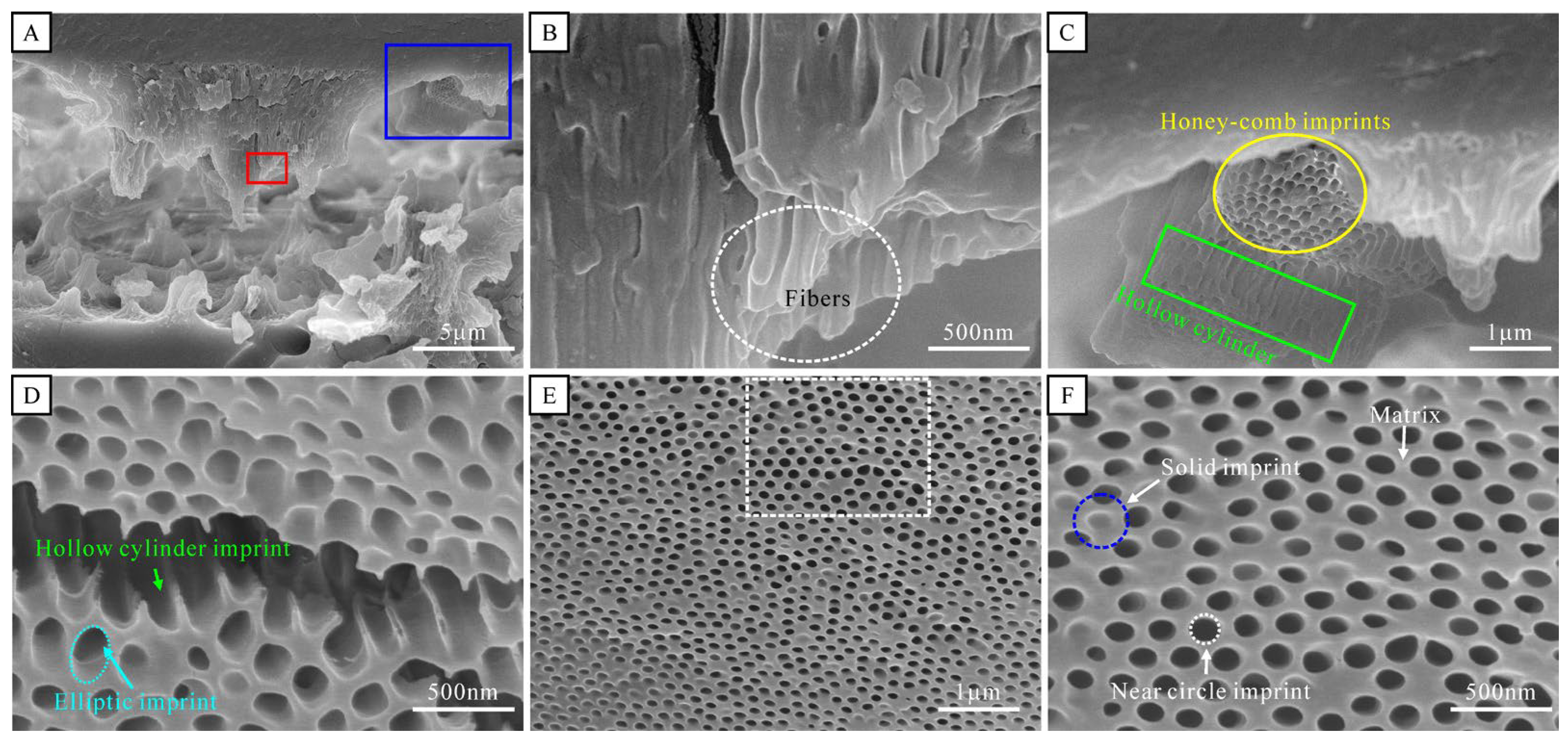
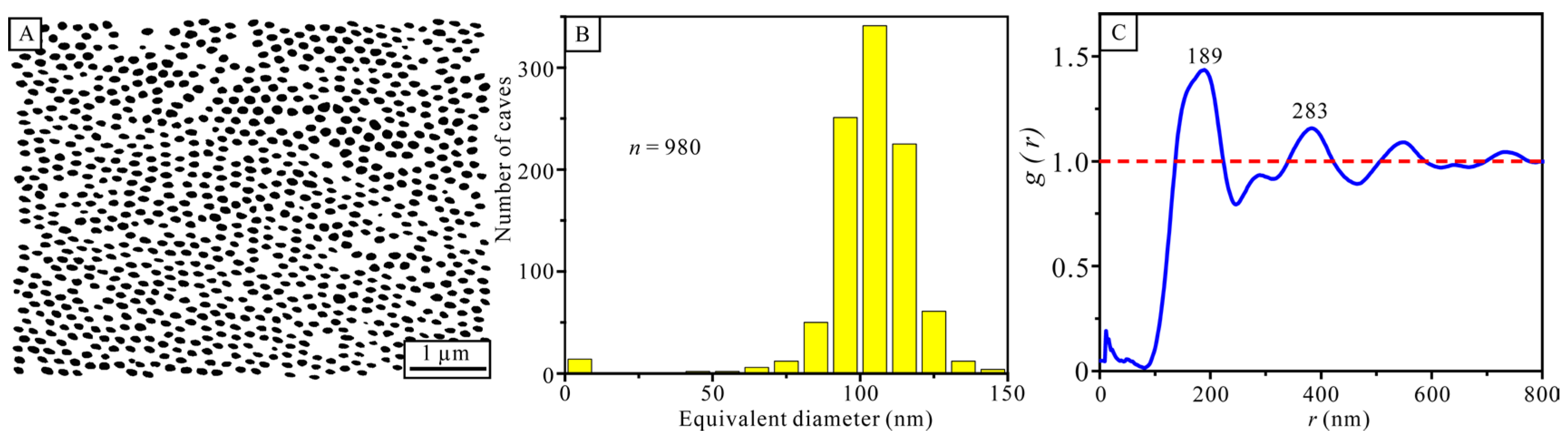
3.3. Structural Analysis
3.4. Spectral Analysis and Theoretical Predictions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, H.; Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, D.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, D.; Fan, T. Bio-Inspired Photonic Materials: Prototypes and Structural Effect Designs for Applications in Solar Energy Manipulation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1705309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouchet, S.R.; Deparis, O. Natural Photonics and Bioinspiration; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2021; ISBN 9781630817978. [Google Scholar]
- Ganter, P.; Lotsch, B.V. Photonic Nanoarchitectonics with Stimuli-Responsive 2D Materials. Mol. Syst. Des. Eng. 2019, 4, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Li, C.; Li, H.; Li, M.; Song, Y. Designable Structural Coloration by Colloidal Particle Assembly: From Nature to Artificial Manufacturing. iScience 2021, 24, 102121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, Q.; Yi, F.; Wang, S.; Lu, W. Artificial Structural Colors and Applications. Innovation 2021, 2, 100081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, S.; Yoshioka, S. Structural Colors in Nature: The Role of Regularity and Irregularity in the Structure. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2005, 6, 1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Bhushan, B.; Tong, J. Structural Coloration in Nature. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 14862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Shang, L.; Zhao, Y. Structural Color Materials from Natural Polymers. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2021, 6, 2100296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greanya, V. Bioinspired Photonics: Optical Structures and Systems Inspired by Nature, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, A.R.; McPhedran, R.C.; McKenzie, D.R.; Botten, L.C.; Nicorovici, N.-A.P. Aphrodite’s Iridescence. Nature 2001, 409, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayeb, G.; Gralak, B.; Enoch, S. Structural Colors in Nature and Butterfly-Wing Modeling. Opt. Photon- N. 2003, 14, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zi, J.; Yu, X.; Li, Y.; Hu, X.; Xu, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Fu, R. Coloration Strategies in Peacock Feathers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 12576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pol Vigneron, J.; Colomer, J.-F.; Rassart, M.; Ingram, A.L.; Lousse, V. Structural Origin of the Colored Reflections from the Black-Billed Magpie Feathers. Phys. Rev. E 2006, 73, 021914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Miyazaki, J.; Yoshioka, S.; Lee, H.; Sugita, S. The Weak Iridescent Feather Color in the Jungle Crow Corvus Macrorhynchos. Ornithol. Sci. 2012, 11, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prum, R.O.; Torres, R. Structural Colouration of Avian Skin: Convergent Evolution of Coherently Scattering Dermal Collagen Arrays. J. Exp. Biol. 2003, 206, 2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prum, R.O.; Torres, R.H. Structural Colouration of Mammalian Skin: Convergent Evolution of Coherently Scattering Dermal Collagen Arrays. J. Exp. Biol. 2004, 207, 2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, V.; Vigneron, J.P.; Lousse, V.; Parker, A. Optical Properties of the Iridescent Organ of the Comb-Jellyfish Beroë Cucumis (Ctenophora). Phys. Rev. E 2006, 73, 41916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G. Photonic Crystal Type Structure in Bivalve Ligament of Pinctada Maxima. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2007, 52, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.S.; Huang, Z.Q. Two-Dimensional Amorphous Photonic Structure in the Ligament of Bivalve Lutraria Maximum. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 13361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, G. A Humidity Sensitive Two-Dimensional Tunable Amorphous Photonic Structure in the Outer Layer of Bivalve Ligament from Sunset Siliqua. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 52, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Bhushan, B. Hierarchical Structure and Mechanical Properties of Nacre: A Review. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 7617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Checa, A.; Salas, C. Treatise Online No. 93: Part N, Revised, Volume 1, Chapter 3: Periostracum and Shell Formation in the Bivalvia. Treatise Online 2017, 84–100, 93:1-51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meenakshi, V.R.; Donnay, G.; Blackwelder, P.L.; Wilbur, K.M. The Influence of Substrata on Calcification Patterns in Molluscan Shell. Calcif. Tissue Res. 1974, 15, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosling, E. Marine Bivalve Molluscs, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2015; ISBN 9781119045212. [Google Scholar]
- Harper, E.M. The Molluscan Periostracum: An Important Constraint in Bivalve Evolution. J. Paleontol. 1997, 40, 71. [Google Scholar]
- Wählisch, F.C.; Peter, N.J.; Abad, O.T.; Oliveira, M.V.G.; Schneider, A.S.; Schmahl, W.; Griesshaber, E.; Bennewitz, R. Surviving the Surf: The Tribomechanical Properties of the Periostracum of Mytilus Sp. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waite, J.H.; Andersen, S.O. 3, 4-Dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA) and Sclerotization of Periostracum in Mytilus edulis. Biol. Bull. 1980, 158, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prum, R.O.; Torres, R.H. Fourier Blues: Structural Coloration of Biological Tissues. In Excursions in Harmonic Analysis; Birkhäuser: Boston, MA, USA, 2013; Volume 2, p. 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zengqiong, H.; Gangsheng, Z. A New Structural Model of Bivalve Ligament from Solen Grandis. Micron 2011, 42, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meek, K.M.; Dennis, S.; Khan, S. Changes in the Refractive Index of the Stroma and Its Extrafibrillar Matrix When the Cornea Swells. Biophys. J. 2003, 85, 2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, M.F. The Physics and Biology of Animal Reflectors. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 1972, 24, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prum, R.O.; Torres, R.; Williamson, S.; Dyck, J. Two-Dimensional Fourier Analysis of the Spongy Medullary Keratin of Structurally Coloured Feather Barbs. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 1999, 266, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.L.; Wong, D.; Lee, P. Iridescence of a Shell of Mollusk Haliotis Glabra. Opt. Express 2004, 12, 4847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlayson, C.E.; Goddard, C.; Papachristodoulou, E.; Snoswell, D.R.; Kontogeorgos, A.; Spahn, P.; Hellmann, G.; Hess, O.; Baumberg, J.J. Ordering in stretch-tunable polymeric opal fibers. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolle, M.; Lee, S. Progress and opportunities in soft photonics and biologically inspired optics. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1702669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waite, J.H. Quinone-tanned scleroproteins. In Metabolic Biochemistry and Molecular Biomechanics; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1983; p. 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Wang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fei, X.; Qi, P.; Lin, S.; Kaplan, D.L.; Buehler, M.J.; Ling, S. Biological material interfaces as inspiration for mechanical and optical material designs. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 12279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lertvachirapaiboon, C.; Jirapisitkul, T.; Pienpinijtham, P.; Wongravee, K.; Thammacharoen, C.; Ekgasit, S. Air-gap-enhanced pearlescent effect in periodic stratified bilayers of Perna viridis shell. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 6282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, A.L.; Sweeney, A.M.; Johnsen, S.; Morse, D.E. A highly distributed Bragg stack with unique geometry provides effective camouflage for Loliginid squid eyes. J. R. Soc. Interface 2011, 8, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, X.; Chi, H.; Zhang, G. Natural Flexible and Responsive 2D Photonic Materials with Micro-Sandwich Structure. Photonics 2023, 10, 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10030245
Pan X, Chi H, Zhang G. Natural Flexible and Responsive 2D Photonic Materials with Micro-Sandwich Structure. Photonics. 2023; 10(3):245. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10030245
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Xijin, Haoyang Chi, and Gangsheng Zhang. 2023. "Natural Flexible and Responsive 2D Photonic Materials with Micro-Sandwich Structure" Photonics 10, no. 3: 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10030245
APA StylePan, X., Chi, H., & Zhang, G. (2023). Natural Flexible and Responsive 2D Photonic Materials with Micro-Sandwich Structure. Photonics, 10(3), 245. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10030245





