Optimal Orientation Angle Configuration of Polarizers Exists in a 3 × 3 Mueller Matrix Polarimeter
Abstract
:1. Introduction
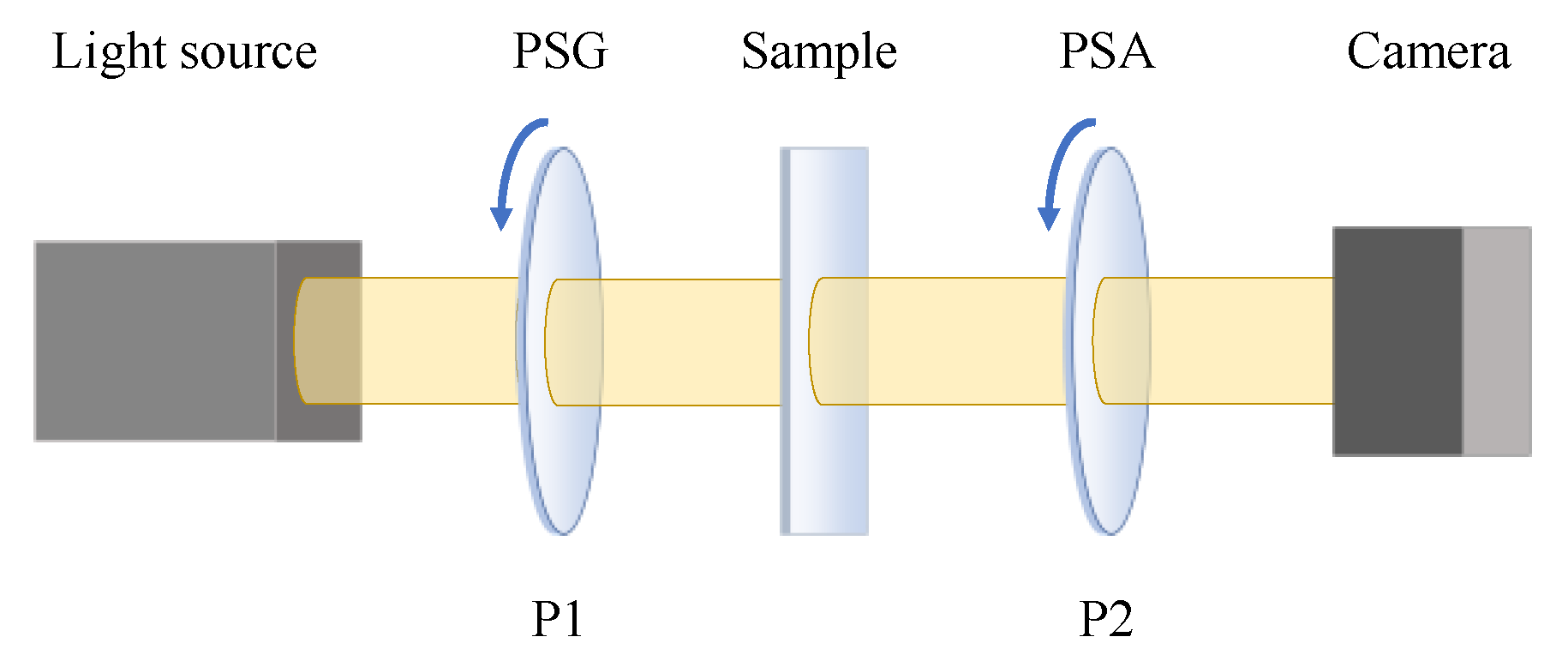
2. Principle of a 3 × 3 MM Polarimeter
2.1. The 3 × 3. MMs of Polarizers
2.2. Principle of 3 × 3 MM Polarimeter
3. Error Analysis of the MM Polarimeter
3.1. Measurement Errors in MM Polarimeter
3.2. Error Analysis of the System Composed of the PSA and the Camera
3.3. Error Analysis of the PSG
3.4. Error Estimation of the MM Polarimeter
4. Optimal Design of Polarizers in MM Polarimeter
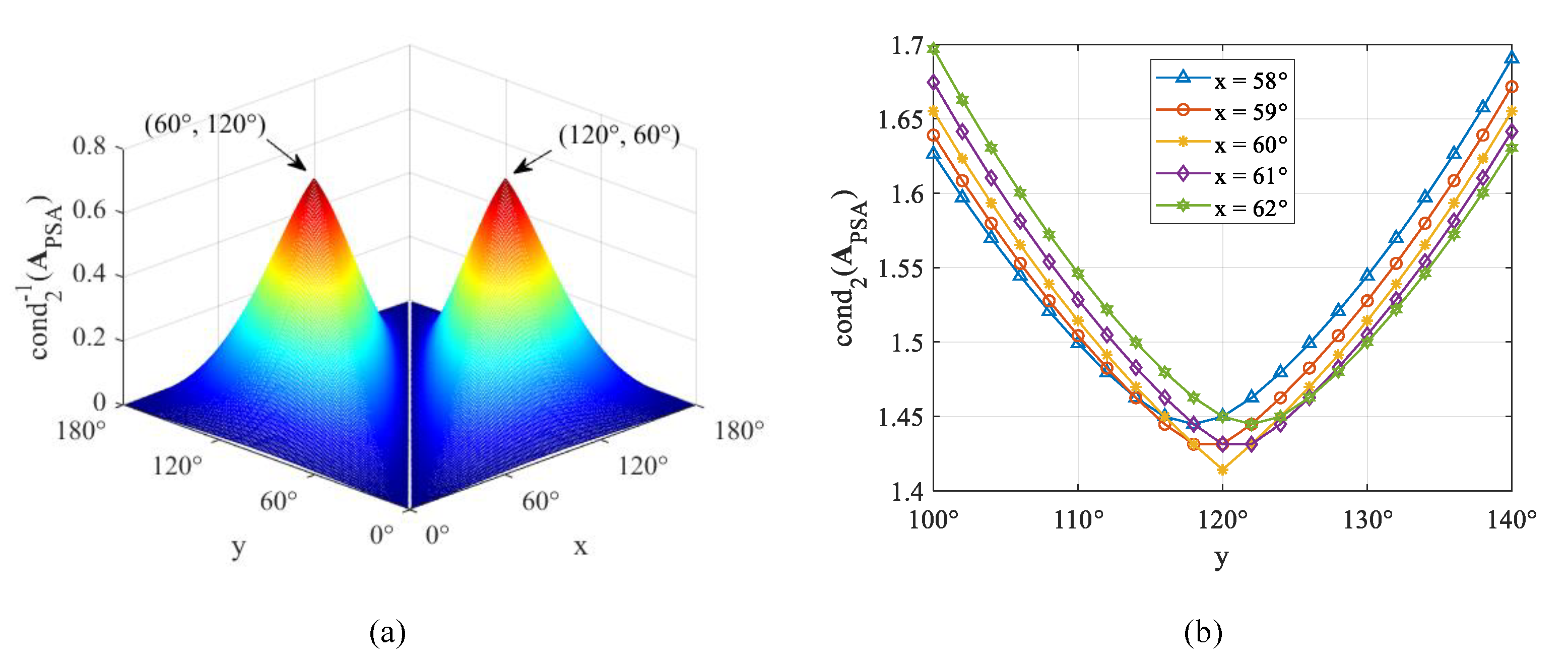
- Partial derivatives of cond2(APSA) with respect to x and y at (x, y) = (60°, 120°) are always zeros for arbitrary DPSA ≠ 0.
- Values of cond2(APSA) at (x, y) = (60°, 120°) equal to .
- The orientation angle configurations of the PSA and the PSG, i.e., (, , ) and (, , ), need to both satisfy the form of (c°, c° + 60°, c° + 120°), where c is an arbitrary real constant.
- Extinction ratios of the PSA and the PSG need to be as large as possible.
5. Discussion
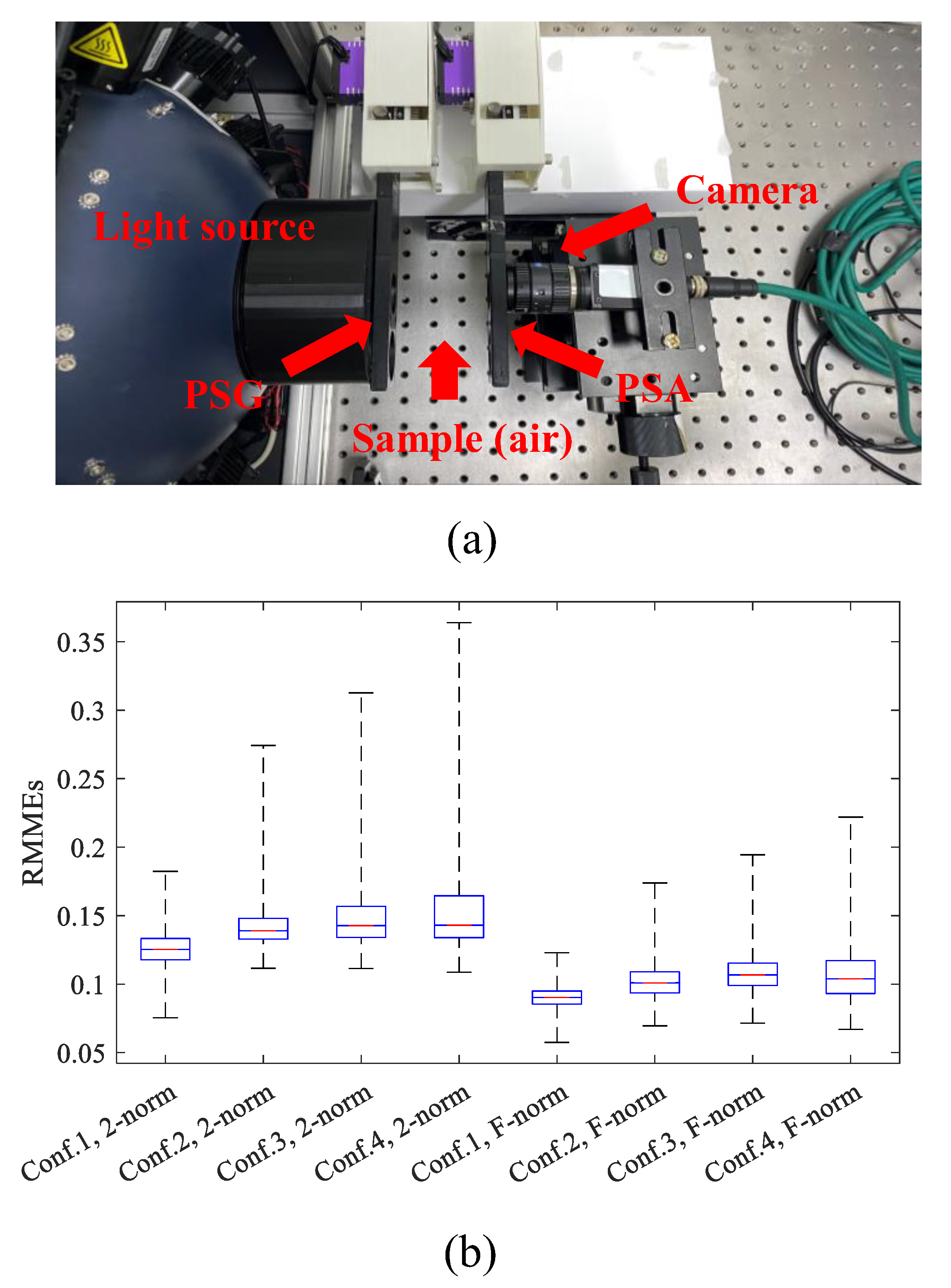
5.1. Effectiveness of the Error Analysis: A Simulation
5.2. Effectiveness of the Optimal Criterion: A Practical Experiment
5.3. Three States vs. Four States
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Meng, J. Detection of non-small cell lung cancer cells based on microfluidic polarization microscopic image analysis. Electrophoresis 2019, 40, 1202–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Xiong, J.; Liu, J. Polarization multi-parametric imaging method for the inspection of cervix cell. Opt. Commun. 2021, 488, 126846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Chang, J.; Salter, P.S. Revealing complex optical phenomena through vectorial metrics. Adv. Photonics 2022, 4, 026001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Wan, J.; Si, L. Deriving polarimetry feature parameters to characterize microstructural features in histological sections of breast tissues. IEEE Trans. Bio. Med. Eng. 2020, 68, 881–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Khaliq, A.; Iqbal, M. Mueller matrix polarimetry for characterization of skin tissue samples: A review. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2020, 30, 101708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, N.; Vitkin, I.A. Tissue polarimetry: Concepts, challenges, applications, and outlook. J. Biomed. Opt. 2011, 16, 110801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wu, L. Polarization microwave-induced thermoacoustic imaging for quantitative characterization of deep biological tissue microstructures. Photonics Res. 2022, 10, 1297–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, B.M.; Goasmat, F.; Sohn, M.Y. Enhancing 9 nm node dense patterned defect optical inspection using polarization, angle, and focus. Proc. SPIE 2013, 8681, 134–141. [Google Scholar]
- Kazama, A.; Oshige, T. A defect inspection technique using polarized images for steel strip surface. Proc. SPIE 2008, 7072, 153–161. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.Y.; Chipman, R.A. Interpretation of Mueller matrices based on polar decomposition. JOSA A 1996, 13, 1106–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swami, M.K.; Manhas, S.; Buddhiwant, P. Polar decomposition of 3 × 3 Mueller matrix: A tool for quantitative tissue polarimetry. Opt. Express 2006, 14, 9324–9337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.; Ye, M.; Singh, M. Narrow band 3×3 Mueller polarimetric endoscopy. Biomed. Opt. Express 2013, 4, 2433–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Huang, Z.; He, H. Flexible 3 × 3 Mueller matrix endoscope prototype for cancer detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2018, 67, 1700–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyo, J.S. Design of optimal polarimeters: Maximization of signal-to-noise ratio and minimization of systematic error. Appl. Opt. 2002, 41, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twietmeyer, K.M. Mueller matrix retinal imager with optimized polarization conditions. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 21339–21354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambirajan, A.; Lock, D.C., Jr. Optimum angles for a Mueller matrix polarimeter. Proc. SPIE 1994, 2265, 314–326. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, J.; Elson, D.S.; Stoyanov, D. Eigenvalue calibration method for 3 × 3 Mueller polarimeters. Opt. Lett. 2019, 44, 2362–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramella-Roman, J.C.; Duncan, D.D. A new approach to Mueller matrix reconstruction of skin cancer lesions using a dual rotating retarder polarimeter. Proc. SPIE 2006, 6080, 107–113. [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein, D.H. Mueller matrix dual-rotating retarder polarimeter. Appl. Opt. 1992, 31, 6676–6683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.X.; Wu, G.B.; Chan, K.F. Demonstration of a terahertz multi-spectral 3 × 3 Mueller matrix polarimetry system for 2D and 3D imaging. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 14853–14867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Hoyo, J.; Sanchez-Brea, L.M.; Gomez-Pedrero, J.A. High precision calibration method for a four-axis Mueller matrix polarimeter. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2020, 132, 106112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, J.M. Polarimetry using liquid-crystal variable retarders: Theory and calibration. J. Opt. A Pure Appl. Op. 2000, 2, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J. Development of Optical Polarisation Resolved Endoscopy. Ph.D. Thesis, Imperial College London, London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]



| (x, y) | Extinction Ratio | cond2(APSA) and cond2(APSG) | condF(APSA) and condF(APSG) |
|---|---|---|---|
| (60°, 120°) | ∞ | 1.4142 | 3.1623 |
| (60°, 120°) | 100:1 | 1.4428 | 3.1818 |
| (60°, 120°) | 10:1 | 1.7285 | 3.4124 |
| (45°, 90°) | ∞ | 2.4142 | 3.8730 |
| (45°, 90°) | 100:1 | 2.4489 | 3.8969 |
| (45°, 90°) | 10:1 | 2.8162 | 4.1794 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, H.; Zhou, Y.; Ren, L.; Ma, F. Optimal Orientation Angle Configuration of Polarizers Exists in a 3 × 3 Mueller Matrix Polarimeter. Photonics 2023, 10, 1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10101087
Wei H, Zhou Y, Ren L, Ma F. Optimal Orientation Angle Configuration of Polarizers Exists in a 3 × 3 Mueller Matrix Polarimeter. Photonics. 2023; 10(10):1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10101087
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Hanyue, Yifu Zhou, Liyong Ren, and Feiya Ma. 2023. "Optimal Orientation Angle Configuration of Polarizers Exists in a 3 × 3 Mueller Matrix Polarimeter" Photonics 10, no. 10: 1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10101087
APA StyleWei, H., Zhou, Y., Ren, L., & Ma, F. (2023). Optimal Orientation Angle Configuration of Polarizers Exists in a 3 × 3 Mueller Matrix Polarimeter. Photonics, 10(10), 1087. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10101087





