Abstract
Background: It is well-known that non-pathological axial myopic eyes present physiological and functional differences in comparison with emmetropic eyes due to altered retinal anatomy. Photostress tests have shown very significant capabilities to discriminate a normal retina from an abnormal retina. Accordingly, the aim of this work was to investigate the differences between myopic and emmetropic eyes in the measured photostress recovery time (PSRT) after retinal light-flashing in a population of young healthy subjects. Methods: A coaxial illumination total disability glare instrument was employed to measure the recovery time after photostress was induced by a 240 milliseconds flash-lighting (535 nm) exposure on 66 myopic and 66 emmetropic eyes. The measurements were carried out for different combinations of glare angles and contrasts of the visual stimuli. Results: In general terms, PSRT in myopic eyes was found at a statistically higher than in emmetropic eyes (Bonferroni correction). For both groups, the measured recovery strongly depends on the contrast of the test object used to measure baseline recovery function and markedly less on the source of glare angles explored. When the PSRTs obtained for different glare angles are averaged, the differences between PSRTs drastically increase with the reduction in the contrast of the stimuli between both groups of study. Conclusions: PSRT is higher for myopic than for young healthy emmetropic eyes (1.2 s and 0.2 s for 5% and 100% contrast test object, respectively). Though seemingly small, the magnitude of this finding can be relevant when flash-lighting happens while driving a car or while performing actions where the reaction time after a visual stimulus can be critical.
1. Introduction
Myopia is a very common vision condition in which central far vision is impaired due to a lack of concordance between the eye’s refractive power and axial length [1]. In a myopic eye, the image of a far vision object is formed before the retina, and so blurred vision is expected unless a proper refractive correction is used. The main myopia cause is related to an excessive axial globe elongation and, even in the absence of pathology, myopic eyes are associated with important retinal anatomic differences in relation to emmetropic eyes, including [2]: reduced photoreceptor density, thinning of scleral and choroidal layers at the posterior pole, peripapillary atrophy, and a reduced density of retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) [3,4,5,6].
Probably caused by this differential retinal anatomy, differential performances and/or deficits in visual function have been reported in myopic eyes, in comparison with emmetropic control groups, as: visual acuity [7,8], contrast sensitivity [9], altered electroretinograms (ERG) [10], altered first-class Stiles–Crawford effect (SCE) [11] or altered spatial summation (SS) [12].
For the same differential anatomic reasons and, in addition to that, static visual function differences, it can also be expected that myopic eyes will present different retinal temporal dynamics in comparison with emmetropic eyes. Photostress recovery time (PSRT) is the minimum time for the visual system to recover the baseline visual function, performed after retinal photobleaching by means of an intense light source. It has been traditionally measured by photostress tests including electrophysiological approaches [13], retinal ophthalmoscopic illuminators [14], scanning laser ophthalmoscopy [15] or, macular stressometers [16].
PSRT provides invaluable information to clinically assess visual functioning in age-related maculopathy eyes [17,18,19] and to differentiate retinal from some post-retinal diseases, via inconclusive eye fundus image [20] or screening, as diabetic retinopathy or glaucoma [21,22,23].
Out of retinal diseases, PSRT has been also successfully used as a nighttime driving performance predictor in disability glare conditions [24], as an indicator of aging [25], and to measure possible benefits of short wave-absorbing filters in pseudophakic eyes [26] and nutritional supplements as Lutein and Zeaxanthin [27] due to light and retinal physiology interaction.
One important and recognized drawback of PSRT measurement is the lack of a standardized technique for bleaching, as well as for measuring baseline and recovery visual function [28]. As a result, it is difficult to compare the PSRT results obtained in different studies. Nonetheless, according to the scientific literature, photostress is very useful to discriminate the ability to recover visual function between two different groups when it is suspected that a retinal cause might be involved in those PSRT differences.
In this work, taking into account myopic and emmetropic anatomical retinal differences, it was hypothesized that young non-pathological myopic eyes may present different PSRT values than non-pathological young emmetropic eyes.
To our knowledge, there are only two published studies [28,29] focused on finding PSRT differences due to the eye refraction condition, with apparent opposite results. On the one hand, the study reported by Magrain et al. [28] was focused on the comparison of different photostress test devices. However, with the suspicion that axial length can be a noticeable factor to achieve a smaller light density exposition, the authors also took advantage of the opportunity to study the relation between PSRT and myopia level in their sample study (range −1.50 D to −4.50 D). They hypothesized that PSRT should be smaller as myopia increases, establishing a non-significant relation between them.
On the other hand, Mashige’s study [29] was focused on finding differences between hypermetropic and myopic subject populations. A commercial glare tester (Night Sight Meter) was used to induce photostress and to measure baseline and recovery visual function. In this case, significant PSRT differences were found between hyperopic and myopic groups (male, black race), and a statistically significant PSRT increasing trend with myopia was found in opposition to the expectations of Magrain et al. [28]. Out of the specific racial and gender population study limitation exposed by the authors, we thought that glare source, test object, and methodology became additional important limitations for the results of the study. In Mashige’s study [29], the glare source of the tester was out of the line of sight and it was not possible to change their size or angular position or to control the time that the tested eye was illuminated. Regarding the test object, due to the methodology adopted to measure PSRT, contrast and mean luminance were not the same for all the observers. Finally, due to its normal retinal anatomy, the emmetropic sample was also considered to be the best reference sample to compare with.
In that sense, a custom-built optical system, previously developed to measure disability glare with variable glare source conditions [30], was adapted to measure PSRT in young non-pathologic emmetropic and myopic groups. According to other researchers who wanted to minimize patient collaboration requirements [31,32], retinal bleaching was achieved by means of a coaxial short-time exposition bright source of light (240 ms). In addition, the influence of the glare angle of the light source and the contrast of the object used to control the visual function on the PSRT difference between myopes and emmetropes was also researched.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
Sixty-six myopic (−2.77 ± 2.36 Diopters) and sixty-six emmetropic (spherical equivalent −0.75 D to +0.75 D) young adult subjects (25 ± 7 years old) with similar average ages were recruited from the Sciences Faculty of the University of Zaragoza (Spain). Exclusion criteria were any ocular pathology and/or visual acuity lower than 20/20 (Snellen) with the best spectacle correction.
All subjects were informed about the experimental procedures of the study and signed an informed consent. The study adhered to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Local Ethical Committee of the Health Sciences Institute of Aragon, reference: C.P.-C.I. PI20/377.
2.2. Experimental System
An optical system was designed (see Figure 1a) to allow both coaxial and optical conjugation of a variable disk glare source. Additionally, visual stimuli were used to induce total disability glare with photostress and measure baseline visual function (more details about the experimental system can be found elsewhere [30]). The glare source consisted of a bright, uniform disk centered at the fovea with a fixed exposure time of 240 milliseconds. The glare angle of the source was set by means of removable 3D printed masks with different aperture sizes. The wavelength of the disabling source was 535 nm. The reason for choosing this spectrum was due to the peak spectral sensitivity of the M-cone photoreceptors [33]. Table 1 shows the subtended angles of the glare source at the retina and the maximum illuminance of the disabling source at the entrance pupil plane for the 5 glare conditions tested in this work.
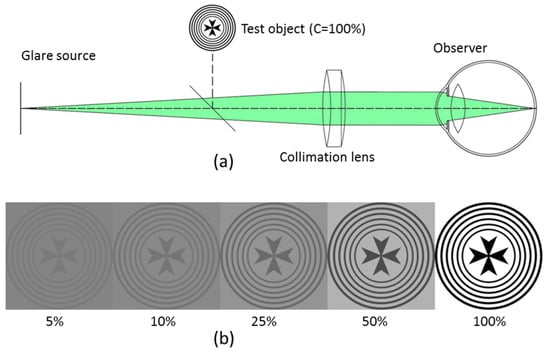
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic of the experimental optical bench. (b) Test visual stimulus for different Michelson contrast levels and constant spatially averaged luminance.

Table 1.
Maximum glare angle and illuminance entering the pupil of the eye.
2.3. Measurement Procedure
First, with the light room off, the participants were instructed by an experienced clinical optometrist to fix monocularly (right eye) on a single visual stimulus, with cross appearance (average illuminance of 170 lux) displayed at a Super 6.4 inches (1080 × 2400 pixels) AMOLED color display image at a far vision by means of a collimation lens (f′ = 100 mm). Figure 1b shows in grayscale the cross-like visual stimuli that subtended 14º degrees of angular field. The object does not present a differentiation between spatial frequencies but a visual stimuli with different Michelson contrast levels.
Second, the examiner ensures that the subject’s contrast sensitivity allows the perception of the stimulus that is considered the visual reference baseline.
Then, the glare source is triggered (240 milliseconds exposure time) to induce the retinal photobleaching of a particular glare angle.
The timing of the PSRT starts when the examiner triggers the disabling source and ends when the subject presses a stop bottom once the observer considers that the original baseline image is recovered. Five minutes were allowed for total disability glare recovery [34] before changing glare or contrast conditions to make the next measurement.
Finally, PSRT for each observer was measured for 5 glare incident angles (3°, 5°, 7°, 11°, and 14°) and 5 levels of Michelson’s contrast levels (5%, 10%, 25%, 50%, and 100%). For each observer, the entire measurement procedure was carried out in one single session lasting for approximately 35 min. Photometric measurements were carefully taken at the observer pupil plane using a lux meter (PCE-174 model) to ensure the same illumination conditions for all the participants of this study.
2.4. Graphical and Statistical Analysis
In order to obtain a quick overview of the experimental PSRT results for myopic and control groups, mean PSRT values were plotted together with their corresponding standard deviation error bars in three different groupings: (1) PSRT values for each glare angle depending on each corresponding object contrast (Figure 2a); (2) PSRT values for each glare angle depending on the object contrast for each corresponding glare angle (Figure 2b); and (3) PSRT variation between myopic and control groups for PSRT, averaged for all glare angles using the object contrast function.
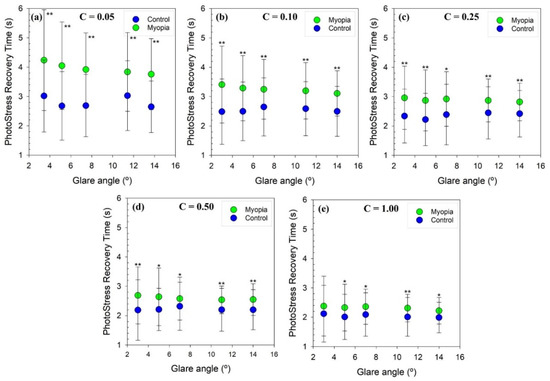
Figure 2.
PSRT as a function of the angle of the glare source for each stimulus contrast for myopic (green dots) and control groups (blue dots); (a): C = 0.05; (b): C = 0.10; (c): C = 0.25; (d): C = 0.50 and (e): C = 1.00. Error bars represent 1 standard deviation. A single asterisk sign (*) was plotted to indicate that statistically significant differences (p value < 0.05) for PSRT values between groups were found. A double asterisk (**) was plotted to point out the significant differences complying with Bonferroni’s correction (p value < 0.001).
To check if there are statistically significant differences between myopic and control groups, first, Shapiro–Wilk tests were performed to test for normal distribution. Then, depending on the result of the normality test, Bonferroni corrected (p value 0.05/5) Student’s t or Mann–Whitney rank sum tests were carried-out.
Furthermore, minimum squares regressions were applied to analyze the non-linear behavior of the recovery time as a function of the stimulus contrast for series (1) and (3).
Graphical representations and statistical tasks were fully performed using Sigmaplot software (Systat Software, Inc., Palo Alto, CA, USA).
3. Results
3.1. PSRT as a Function of the Stimuli Contrast and Glare Angle for Myopic and Emmetropic Groups
Figure 2 shows the averaged PSRT values for myopic (green dots) and control (blue dots) groups as a function of the glare angle for each contrast studied. The PSRT for a given object contrast remains almost constant for both groups despite changing the angle of the glare source.
Figure 3 shows the averaged PSRT values for myopic and emmetropic groups as a function of the stimuli contrast for a given glare angle (these are the same data used as in the previous figure, albeit represented differently). According to nonlinear regression analysis, both myopic and control groups show exponential decay behavior in PSRT values as a function of the stimulus contrast for all incident angles at the glare source.
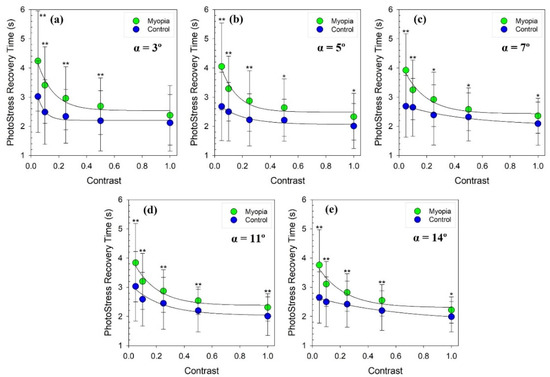
Figure 3.
PSRT as a function of the stimulus contrast for each incident angle of the glare source for myopic (green dots) and control groups (blue dots); (a): α = 3º; (b): α = 5º; (c): α = 7º; (d): α = 11º and (e): α = 14º. The black lines through the dots are non-linear exponential decay regressions fitted to the values. Error bars represent 1 standard deviation. A single asterisk sign (*) was plotted to indicate that statistically significant differences (p value < 0.05) for PSRT values between groups were found. A double asterisk sign (**) was plotted to point out the significant differences complying with Bonferroni’s correction (p value < 0.001).
Since the Shapiro–Wilk test showed that the PSRT in both groups did not follow a normal distribution in most of the cases studied, the non-parametric Mann–Whitney Sum Rank test was performed to test whether the differences between myopic and control groups were significant. Table 2 shows the mean PSRT values (mean ± std) obtained for the two groups for the different object contrasts and angles of the glare source studied, as well as the p value derived from the hypothesis testing. According to Bonferroni’s correction, the myopic group showed statistically higher PSRT values than the control group, especially when the stimulus contrast is low.

Table 2.
PSRT (mean ± 1 std) in seconds for the myopic and control group and the p value obtained in the Mann–Whitney test.
3.2. Myopia and Variation in PSRT
Finally, the PSRT values were averaged for all glare angles, after which the differences between both groups were calculated and shown in Figure 4. Results showed that the lower the contrast of the stimuli was, the higher the differences between the recovery time measured in myopic and emmetropic eyes in the presence of an external glare source would be. In addition, the Mann–Whitney test revealed that there were significant differences between the myopic group and the control group with the new regrouping of the data: the p value obtained in the five tests performed was less than 0.001.
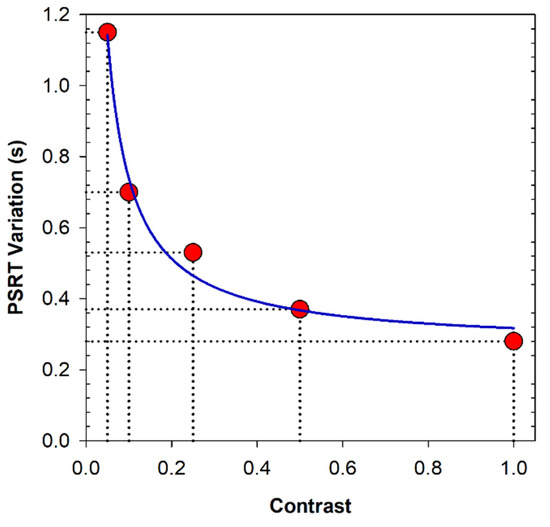
Figure 4.
PSRT variation (difference mean PSRT values for all glare angles between myopic and control eyes) as a function of the stimuli contrast. The blue line represents the non-linear regression of the plotted data.
A non-linear regression analysis revealed an inverse order correlation (R2 = 0.98, p = 0.047) between the difference in the variation in PSRT as a function of glare for each contrast value between myopic and control groups. That is, in the presence of a source of glare, the lower the contrast of the projected luminous stimulus was, the larger the differences between myopic and emmetropic eyes in PSRT values would be.
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Photo-stress recovery time has been reported during the last decades as a pragmatic simple test to distinguish between glaucoma and macular degeneration [24], allowing researchers to establish some correlations between the ophthalmoscopic findings and visual function assessments in central retinopathies [35]. Since then, PSRT has been widely employed to assess macular function [12], to distinguish between optical neuropathies and macular degeneration [16,17,18], or to assess the beneficial effects of antioxidant nutritional supplements [27].
In this work, a new instrument originally developed to measure disability glare [21] was adapted to measure if non-pathological young myopic eyes show greater systematic differences in PSRT values than a control group of young healthy emmetropic eyes. A major advantage of the instruments is the capability to control both the incident glare angle entering the eye (including the illuminance at the corneal plane) and the contrast of the projected visual stimuli. The study was designed to give answers to some uncontrolled experimental variables from, to our knowledge, the only published study (the contrast and luminance of test and source glare angle) devoted to finding if non-pathological myopia plays a role in PSRT values, and to compare myopic PSRT values with a more significant control group than the hyperopic control group used in Mashige’s study [28]: young healthy emmetropic eyes.
On the one hand, our results exposed in Figure 2 and Figure 3 and Table 2, revealed significant statistical differences (even with Bonferroni correction) between myopic and emmetropic eyes for almost all glare angles. The trend points out an exponential decay behavior of the recovery time as a function of the contrast of the stimuli. On the other hand, PSRT differences between myopic and emmetropic eyes were found to be very similar for the different glare angles used in this study.
Finally, Figure 4 supported the hypothesis that myopes have higher PSRT values than emmetropic eyes. Results showed that the lower the contrast of the stimuli was, the higher the differences between the recovery time measured in myopic and emmetropic eyes would be in the presence of an external glare source. According to our observers’ criteria, myopic eyes recover the baseline visual function near 1.2 s and 0.3 s average slower than emmetropic eyes when they are observing a low-(5%) and high-(100%) contrast object, respectively. It is important to note that even the smallest difference can make a large difference when flash-lighting occurs during a driving car task or while undertaking actions where the reaction time after seeing a visual stimulus can be critical. For instance, considering the above average differences and under the assumption of similar flashing conditions, a myopic driver driving at 100 km/h on a highway would travel 8.3 m more than an emmetropic subject after being dazzled before being able to see a high-contrast object (100%). For a 5% contrast object, the distance traveled after being dazzled would be 4 times greater (33.33 m).
4.1. Basics of Altered PSRT in Myopic Eyes
Trying to find an explanation for our results, it can be stated that there is anatomical difference between the retinas of myopic and emmetropic eyes as the main candidate to support the hypothesis of this work. Myopic choroidal and EPR layers are thinner in myopic than in emmetropic eyes so, due to physiological factors related to pigment photoreceptor renewal after bleaching, it is also expected that PSRT was higher in myopic eyes.
However, out of the significant anatomical differences between retinae and, taking into account our experimental paradigm, it is possible to speculate as to other plausible reasons explaining why to expect PSRT differences between emmetropic and myopic patients in two different argument blocks: (1) reasons caused by different retinal exposure to light and (2) reasons caused by different visual quality.
4.1.1. Factors Caused by a Different Retinal Exposure
As was argued by Margrain et al. [28], myopic eyes usually have elongated eye axial lengths and normal refractive power. Thus, because of the optical magnification, myopic retinal photoreceptors should be less illuminated by the glare source. Following this line, PSRTs should be shorter for the myopic compared to the emmetropic group. However, this argument does not apply in our experiment, since all myopic eyes were corrected with their spectacle correction during light exposition. In this way, an optical demagnification existed to compensate almost all the optical magnification caused by using elongated eye axial lengths. In this sense, as only myopic observers were wearing glasses during the flash-lighting, it is plausible to argue that they can be more protected from the glare exposition and therefore they would obtain smaller PSRT than emmetropic patients. On the basis of these results, it seems clear that ophthalmic lenses were not an effective tool to avoid glare.
In the opposite direction of the two previous considerations, iris anatomy could be responsible for the increased exposure for myopic eyes. Indeed, author visible found that: (1) if myopic eyes had bigger pupil diameters than emmetropic eyes as it was reported elsewhere [36,37,38], or (2) if the emmetropic eyes had smaller pupils due to an increased accommodation pupillary reflex [36,39]. Because pupil diameters were not controlled in this study and both groups had obviously different refraction characteristics, pupil constriction due to refractive causes cannot be discarded as the main cause of our finding. Nevertheless, in our study, the age mean was pretty similar for both groups participating in this study so pupillary changes related to age [37,38] were not a probable contributing factor to our results. Moreover, iris pigmentation was not controlled in this study so, it could be considered as another probable cause of getting different retinal exposure in both groups. However, some correlation between myopia and darker iris has been reported at [40], just in the opposite way that it can be expected to justify the higher PSRT values obtained for myopic eyes in this work.
4.1.2. Factors Caused by Different Visual Quality
As was discussed in [28] in reference to higher-order aberrations (HOA), it could be argued that PSRT would be smaller if the visual quality was better. This argument could be applied to our experimental paradigm, because it is expected that an observer with a good CSF reaches the recovery line faster than an observer with a bad CSF. In this sense, as some publications support myopic people have worse visual acuity [7,8] and CSF [9] than emmetropic people’s visual quality, this can be a factor to explain why myopic people achieve higher PSRT than emmetropic people According to this argument, the broad spatial-frequency content of the stimulus used in this study might have helped to remark this difference. More research would be performed to stablish the influence of the spatial–frequency content of the stimulus on the PSRT.
4.2. PSRT Comparison with Other Studies
It is important to note that as is usual in photostress studies, our PSRT values are hardly comparable with those of other studies. The main reason for that is the kind of illumination chosen to achieve retinal bleaching. In contrast with the flashlighting adopted in this work, the large majority of photostress studies work with continous light exposition trying to achieve a total retinal bleaching. As a consequence, our PSRT values (and PSRT differences) are quite smaller than those can be found in other scientific works. Curiously, the only comparable PSRT values that we have found with those obtained in this work comes from the only work devoted to measure PSRT difference in function of ammetropia [29], where PSRT myopic eyes marked 1.41 s comparison with our minimum 2.22 value obtained for maximum contrast and 14 degrees glare angle. We have no explanation for this because they reactions were performed in very different conditions.
4.3. Limitations and Conclusions
The main limitation of this study comes from the method it uses a to assess recovery function: the object was always the same and the criterium adopted in this study was open to the observer’s opinion and not based on an objective psychophysical threshold and it has been in other PSRT studies. This strategic decision let us perform a big quantity of trials in a comfortable amount of time for the participants of this study. However, due to the fact that our main result comes from a straightforward comparison between two different groups working with the same conditions, we are confident that the result cannot be invalidated by this fact. Another limitation can be considered that iris pigment and pupil diameter were not controlled to be present in both groups at the same proportion, as a consequence there could be a reasonable doubt as to whether these results are due to myopic retina or those other factors. Nevertheless, it is important to note that iris pigment has been controlled in [29], where significant differences were found also in PSRT.
To conclude, our results corroborated the capability of using our using our own instrument and experimental paradigm to find significant PSRT differences between myopic and emmetropic eyes after exposure to flash-lighting in natural conditions (no pupil control). According to our results, these differences are more evident the lower the contrast of the test object is, and they are independent of the glare source angle. Further studies will be needed to establish the origin of these differences.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.J.Á.; methodology, F.J.Á., J.A. and P.C.; validation, F.J.Á. and J.A.; formal analysis, F.J.Á., J.A. and P.C.; investigation, F.J.Á., J.A. and P.C.; data curation, F.J.Á., J.A. and P.C.; writing—original draft preparation, F.J.Á.; writing—review and editing, F.J.Á., J.A. and P.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Department of Industry and Innovation (Government of Aragon), research group R44-17R.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of the Health Sciences Institute of Aragon, Spain. (protocol code: C.P.-C.I. PI20/377, data of approval: 14 July 2020).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Excel dataset is available upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Pan, C.W.; Ramamurthy, D.; Saw, S.M. Worldwide prevalence and risk factors for myopia. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2012, 32, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonas, J.B.; Wang, Y.X.; Dong, L.; Guo, Y.; Panda-Jonas, S. Advances in myopia research anatomical findings in highly myopic eyes. Eye Vis. 2020, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heine, L. Beiträge zur Anatomie des myopischen Auges. Arch. Augenheilk 1899, 38, 277–290. [Google Scholar]
- Norman, R.E.; Flanagan, J.G.; Rausch, S.M.; Sigal, I.A.; Tertinegg, I.; Eilaghi, A.; Portnoy, S.; Sled, J.G.; Ethier, C.R. Dimensions of the human sclera: Thickness measurement and regional changes with axial length. Exp. Eye Res. 2010, 90, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vurgese, S.; Panda-Jonas, S.; Jonas, J.B. Scleral thickness in human eyes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonas, J.B.; Ohno-Matsui, K.; Holbach, L.; Panda-Jonas, S. Retinal pigment epithelium cell density in relationship to axial length in human eyes. Acta Ophthalmol. 2017, 95, e22–e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coletta, N.J.; Watson, T. Effect of myopia on visual acuity measured with laser interference fringes. Vis. Res. 2006, 46, 636–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strang, N.C.; Winn, B.; Bradley, A. The role of neural and optical factors in limiting visual resolution in myopia. Vis. Res. 1998, 38, 1713–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, S.-W.; Chiu, C.-J. Myopia and contrast sensitivity function. Curr. Eye Res. 2001, 22, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolsley, C.J.; Saunders, K.J.; Silvestri, G.; Anderson, R.S. Investigation of changes in the myopic retina using multifocal electroretinograms, optical coherence tomography and peripheral resolution acuity. Vis. Res. 2008, 48, 1554–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.S.; Garner, L.F.; Enoch, J.M. The relationship between the Stiles-Crawford effect of the first kind (SCE-I) and myopia. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2003, 23, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stapley, V.; Anderson, R.S.; Saunders, K.J.; Mulholland, P.J. Altered spatial summation optimizes visual function in axial myopia. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovasik, J.V. An electrophysiological investigation of the macular photostress test. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1983, 24, 437–441. [Google Scholar]
- Zabriskie, N.A.; Kardon, R.H. The pupil photostress test. Ophthalmology 1994, 101, 1122–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Horiguchi, M.; Miyake, Y.; Awaya, S. Extrafoveal photostress recovery testing with a scanning laser ophthalmoscope. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 1997, 41, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartlett, H.; Davies, L.N.; Eperjesi, F. Reliability, normative data, and the effect of age-related macular disease on the Eger Macular Stressometer photostress recovery time. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2004, 24, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, M.; Brown, B. Glare recovery and its relation to other clinical findings in age related maculopathy. Clin. Vis. Sci. 1989, 4, 155–163. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, M.; Brown, B. Glare recovery and age related maculopathy. Clin. Vis. Sci. 1989, 4, 145–153. [Google Scholar]
- Midena, E.; Degli Angeli, C.; Blarzino, M.C.; Valenti, M.; Segato, T. Macular function impairment in eyes with early age-related macular degeneration. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1997, 38, 469–477. [Google Scholar]
- Glaser, J.S.; Savino, P.J.; Sumers, K.D.; McDonald, S.A.; Knighton, R.W. The photostress recovery test in the clinical assessment of visual function. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1977, 83, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Weiter, J.J.; Santos, S.; Ginsburg, L.; Villalobos, R. The macular photostress test in diabetic retinopathy and age-related macular degeneration. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1990, 108, 1556–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherman, M.D.; Henkind, P. Photostress recovery in chronic open angle glaucoma. Br. J. Ophthal. 1988, 72, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baptista, A.M.G.; Sousa, R.; Rocha, F.A.S.Q.; Fernandes, P.S.; Macedo, A.F. The macular photostress test in diabetes, glaucoma, and cataract. Proc. SPIE 2013, 8785, 1740–1745. [Google Scholar]
- Boadi-Kusi, S.B.; Austin, E.; Abu Od, S.L.; Od, S.H.; Od, E.K.A.M. Disability glare and nighttime driving performance among commercial drivers in Ghana. J. Occup. Health 2021, 63, e12279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, J.D.; Wallstrom, G.; Narayanan, D.; Welch, D.; Abelson, M.B. An Alternative Psychophysical Diagnostic Indicator of the Aging Eye. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 2019, 2036192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, B.R. Attenuating photostress and glare disability in pseudophakic patients through the addition of a short-wave absorbing filter. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 2015, 60763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, B.R.; Fletcher, L.M.; Roos, F.; Wittwer, J.; Schalch, W. A double-blind, placebo-controlled study on the effects of lutein and zeaxanthin on photostress recovery, glare disability, and chromatic contrast. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 8583–8589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margrain, T.H.; Thomson, D. Sources of variability in the clinical photostress test. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2002, 22, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashige, K. Night vision and glare vision thresholds and recovery time in myopic and hyperopic eyes. S. Afr. Optom. 2010, 69, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, F.; Casado, P. Optical instrument for the study of time recovery from total disability glare vision. App. Opt. 2022, 61, 2438–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Ulla, F.; Louro, O.; Mosquera, M. Macular dazzling test on normal subjects. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1986, 70, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swan, E.; Schwiegerling, J.; Peyman, G.; Enikov, E. Photostress testing device for diagnosing retinal disease. Photonics 2014, 1, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, D.H. Chromatic function of the cone. In Encyclopedia of the Eye; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 266–274. [Google Scholar]
- Loughman, J.; Ratzlaff, M.; Foerg, B.; Connell, P. Suitability and repeatability of a photostress recovery test device, the macular degeneration detector (MDD-2), for diabetes and diabetic retinopathy assessment. Retina 2014, 34, 1006–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natsikos, V.E.; Hart, J.C. Photostress recovery times in case of central serous retinopathy. J. Royal. Soc. Med. 1980, 73, 793–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charman, W.N.; Radhakrishnan, H. Accommodation, pupil diameter and myopia. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2009, 29, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linke, S.J.; Baviera, J.; Munzer, G.; Fricke, O.H.; Richard, G.; Katz, T. Mesopic pupil size in a refractive surgery population (13,959 eyes). Optom. Vis. Sci. 2012, 89, 1156–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakmak, H.B.; Cagil, N.; Simavli, H.; Duzen, B.; Simsek, S. Refractive error may influence mesopic pupil size. Curr. Eye Res. 2010, 35, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, A.; Gehrmann, J.; Atchison, D.A. Influences of luminance and accommodation stimuli on pupil size and pupil center location. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 2166–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.-W.; Qiu, Q.-X.; Qian, D.-J.; Hu, D.-N.; Li, J.; Saw, S.-M.; Zhong, H. Iris colour in relation to myopia among Chinese school-aged children. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2018, 38, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).