Total Differential Photometric Mesh Refinement with Self-Adapted Mesh Denoising
Abstract
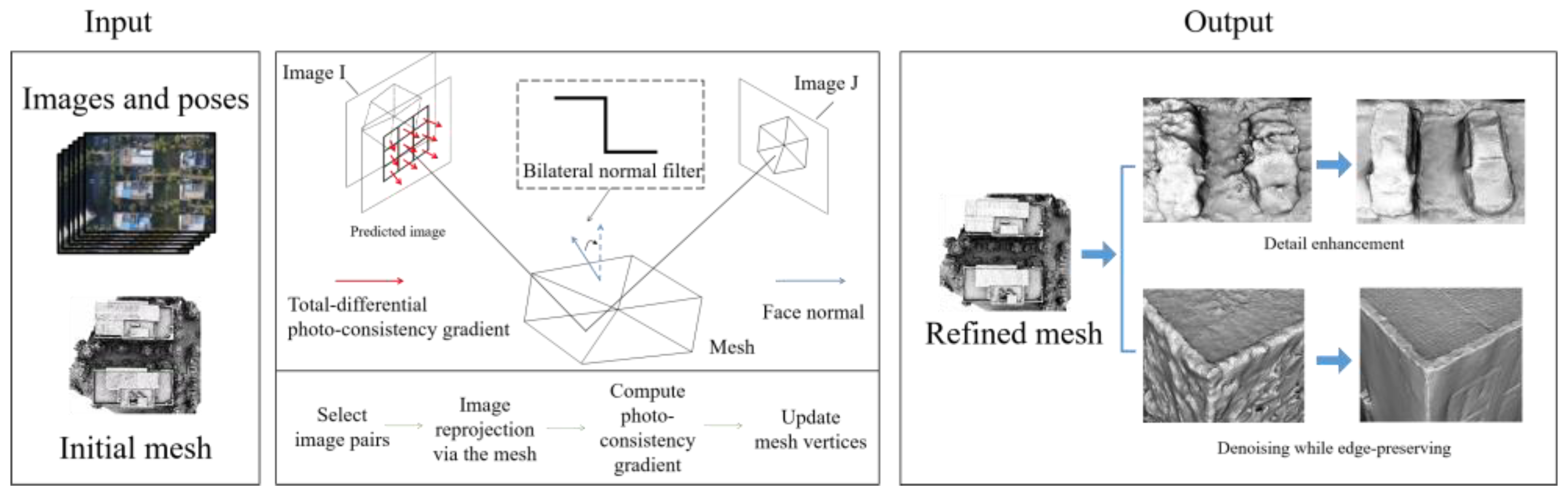
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Preliminaries on Variational Mesh Refinement
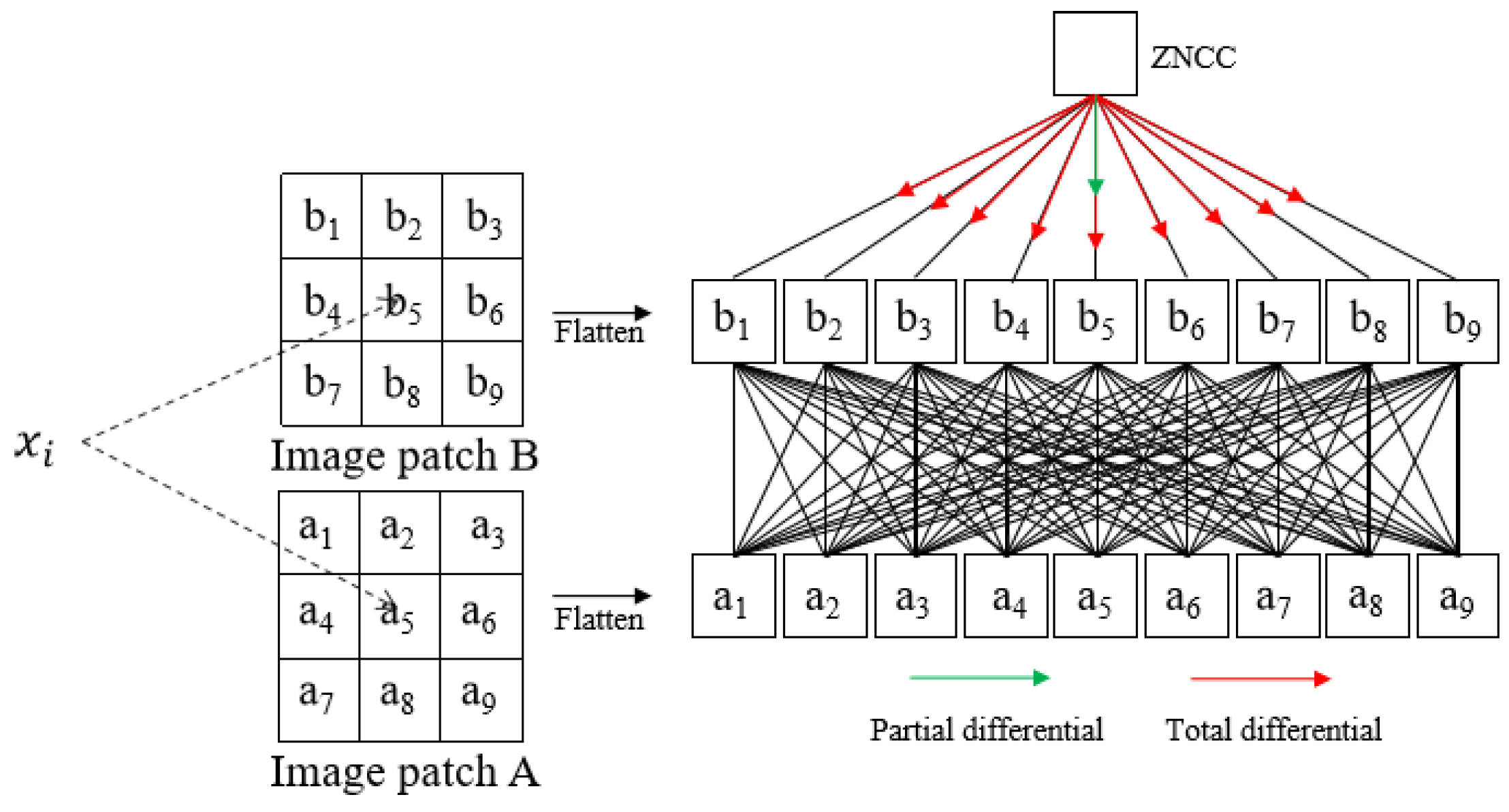
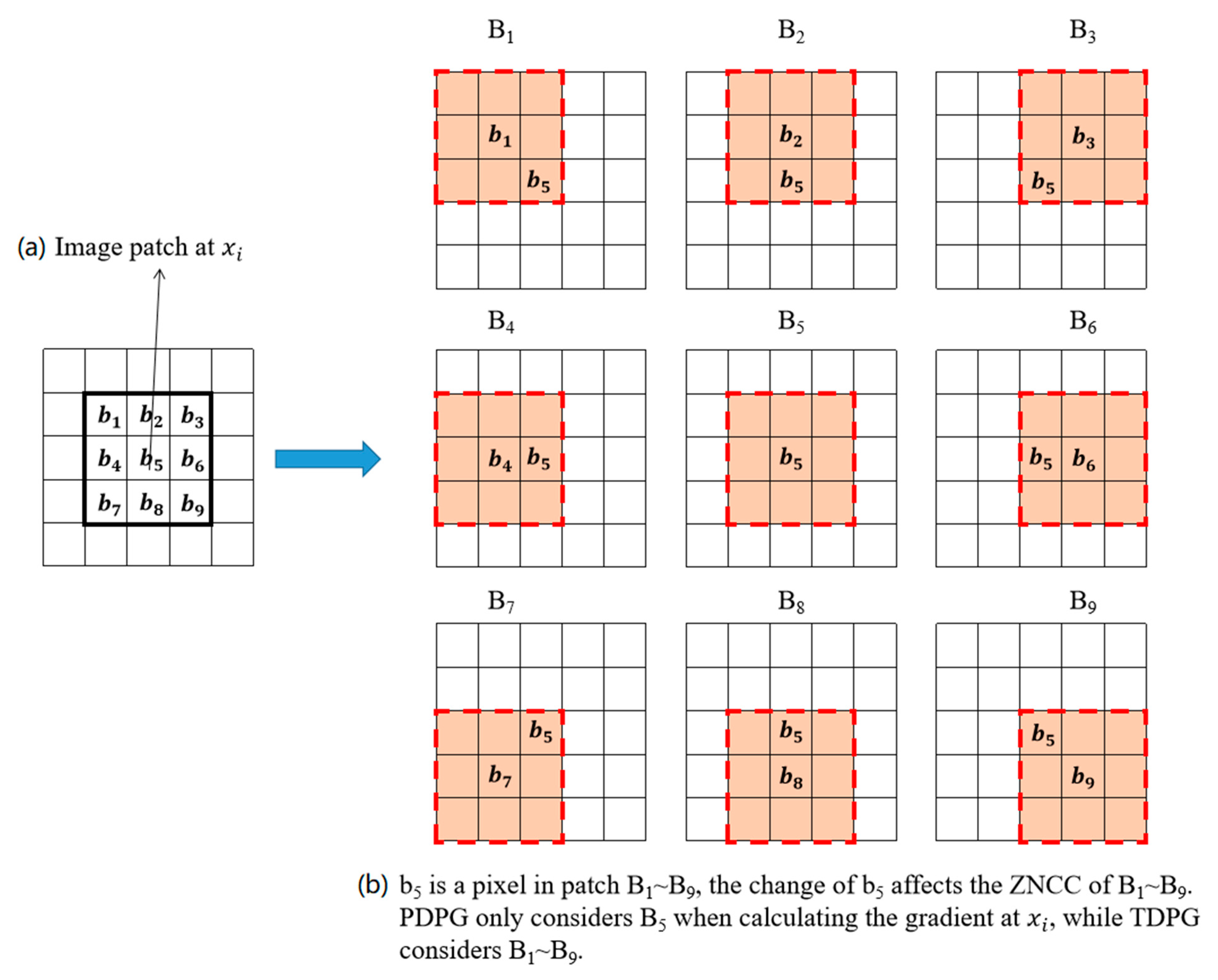
2.2. Total-Differential Photo-Consistency Gradient Calculation
2.3. Self-Adaptive Mesh Denoising
2.4. Initialization and Implementation Details
3. Experiments
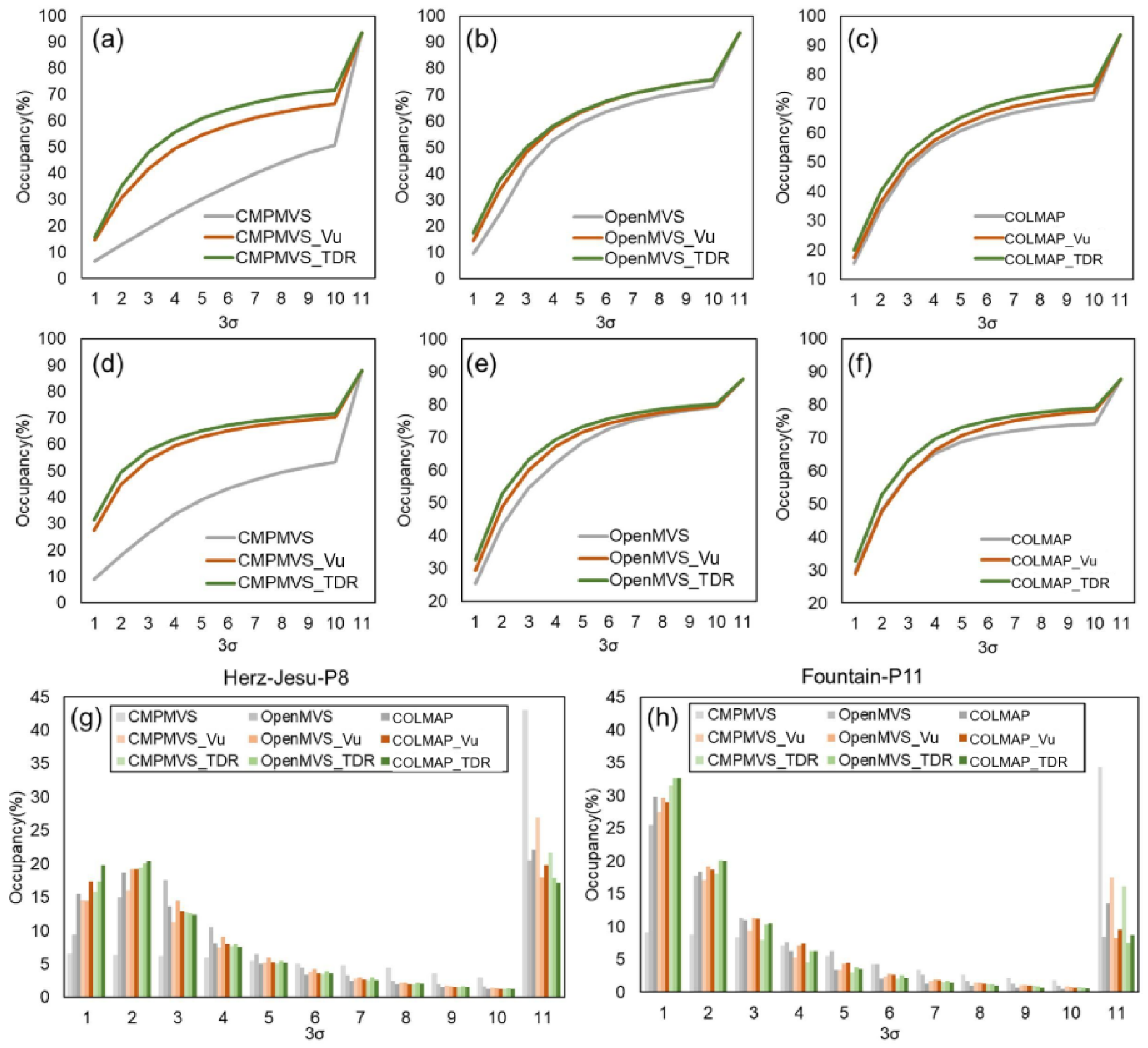
3.1. Dataset and Evaluation Metrics
- (1)
- Tanks And Temples [22] is a benchmark for image-based 3D reconstruction. The image sequences come from video streams. We picked the Family, Francis, Horse, and Panther data for close-range scene evaluation.
- (2)
- ETH3D [23] is a benchmark for multiview stereo (MVS) evaluation. It provides ultrahigh-resolution images registered to the 3D laser scan point clouds. We picked its facade, delivery_area, relief, and relief_2 data for close-range scene evaluation.
- (3)
- BlendedMVS [24] is a large-scale simulation MVS dataset. It provides ground-truth meshes and rendered images. We selected four outdoor scenes captured by UAVs, namely, UAV_Scene1, UAV_Scene2, and UAV_Scene3, for UAV scene evaluation.
- (4)
- (5)
- The EPFL dataset [27] provides two ground-truth meshes captured by LIDAR sensors, namely, Herz-Jesu-P8 and Fountain-P11, and provides the images registered with the meshes.
- (6)
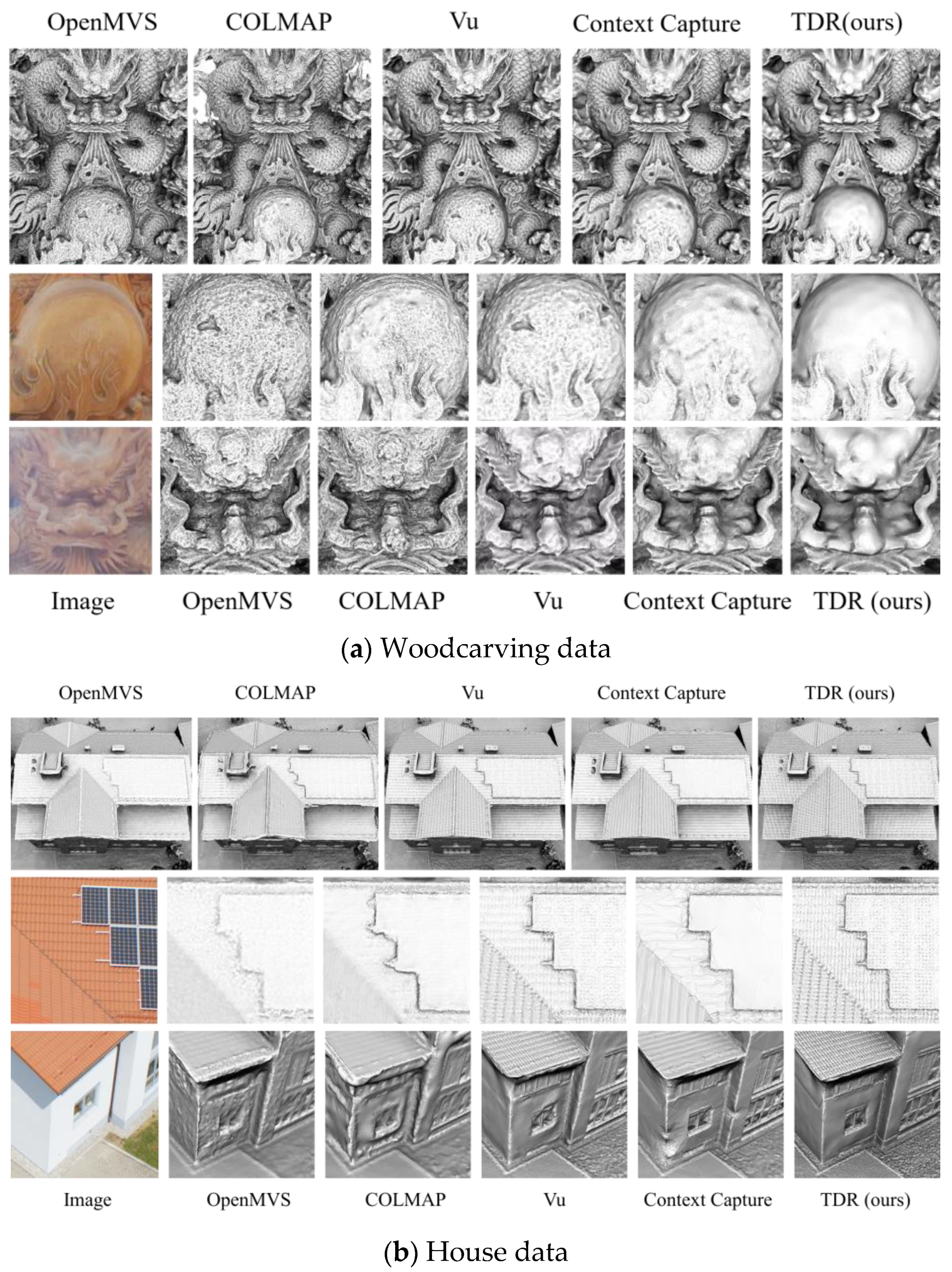
- Personal Collection Dataset. We collected multiview images from the internet and natural scenes for qualitative evaluation.
3.2. Comparison with the Baseline Method
3.2.1. Performance on the UAV Dataset
3.2.2. Performance on the Close-Range Dataset
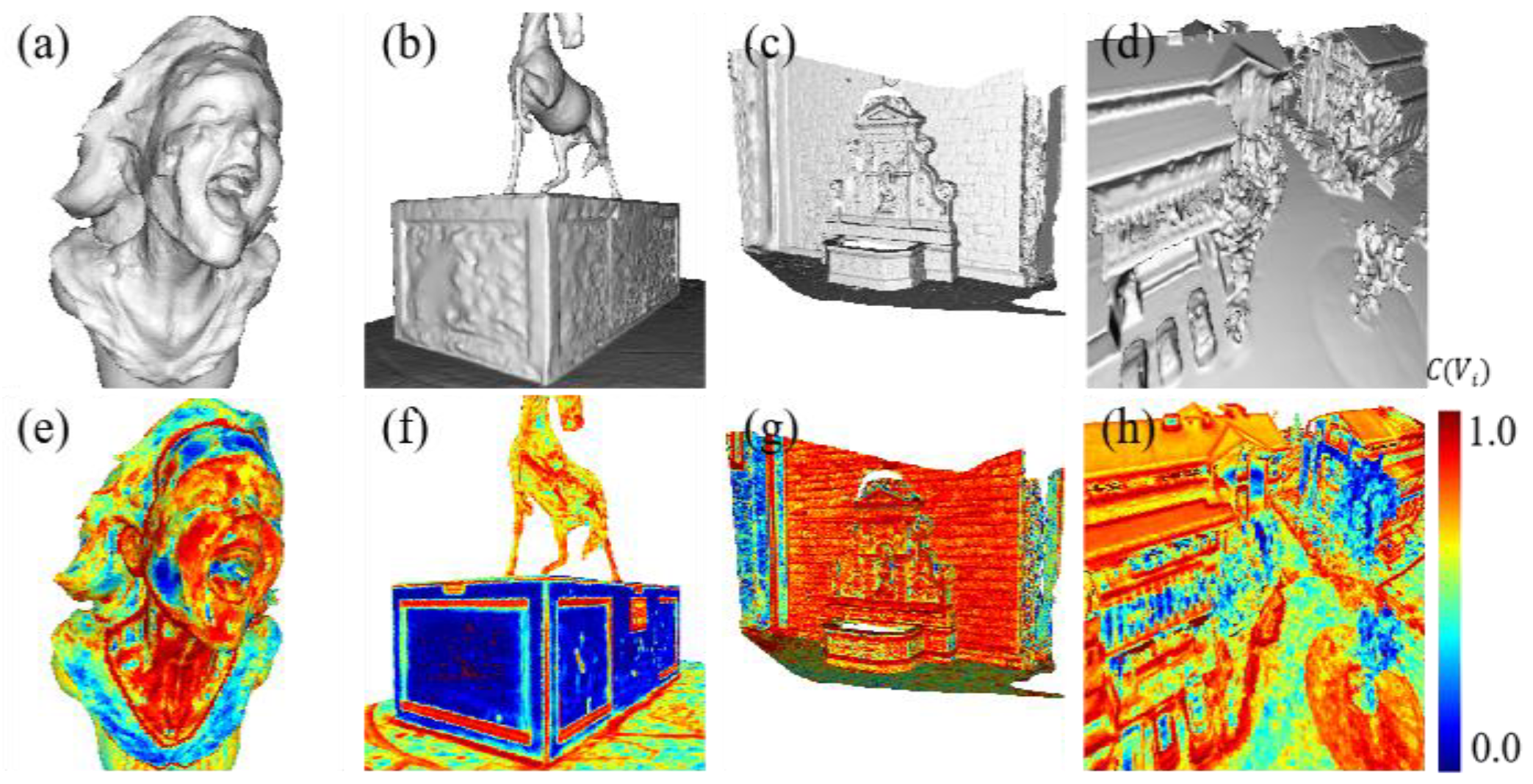
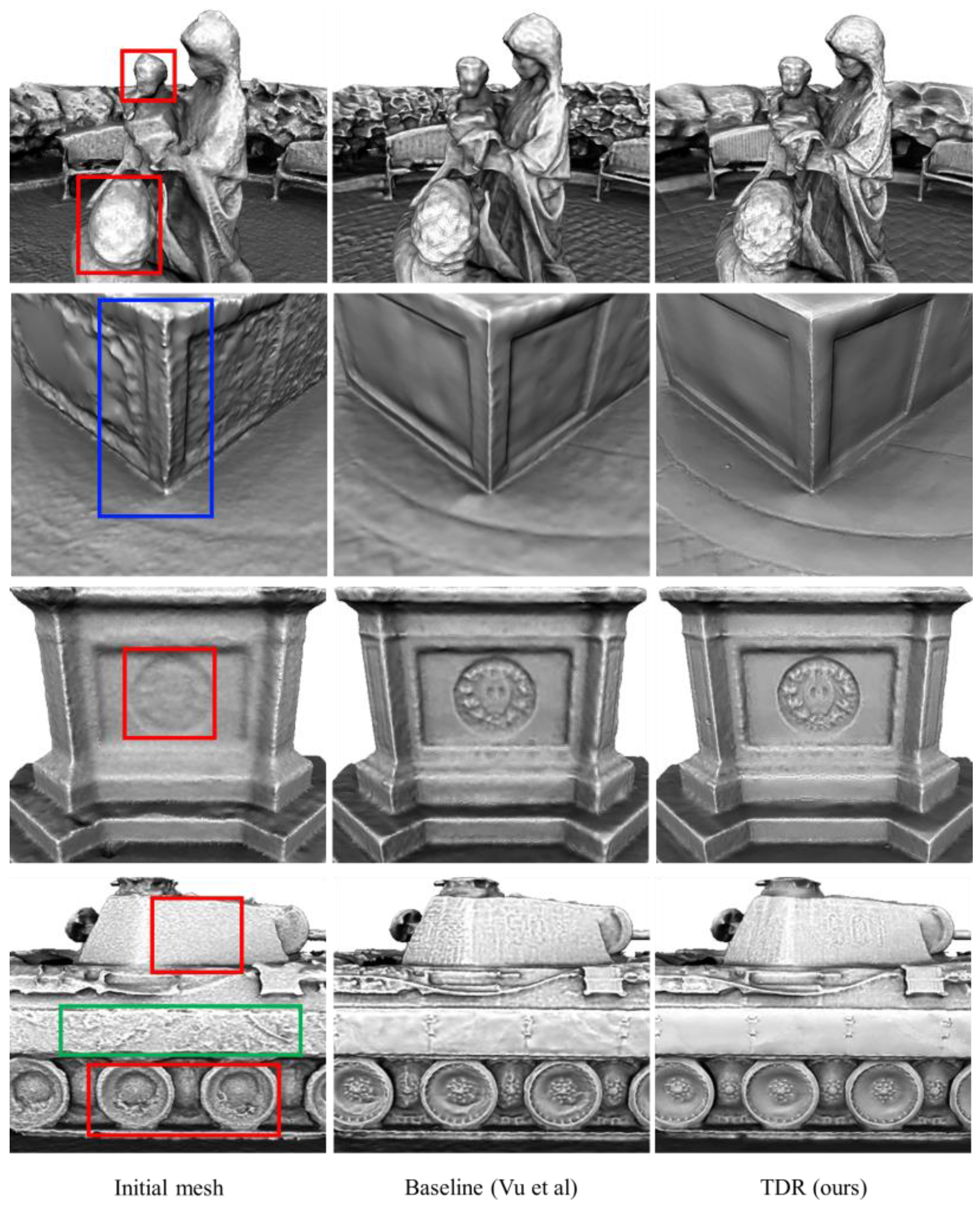
3.3. Discussion
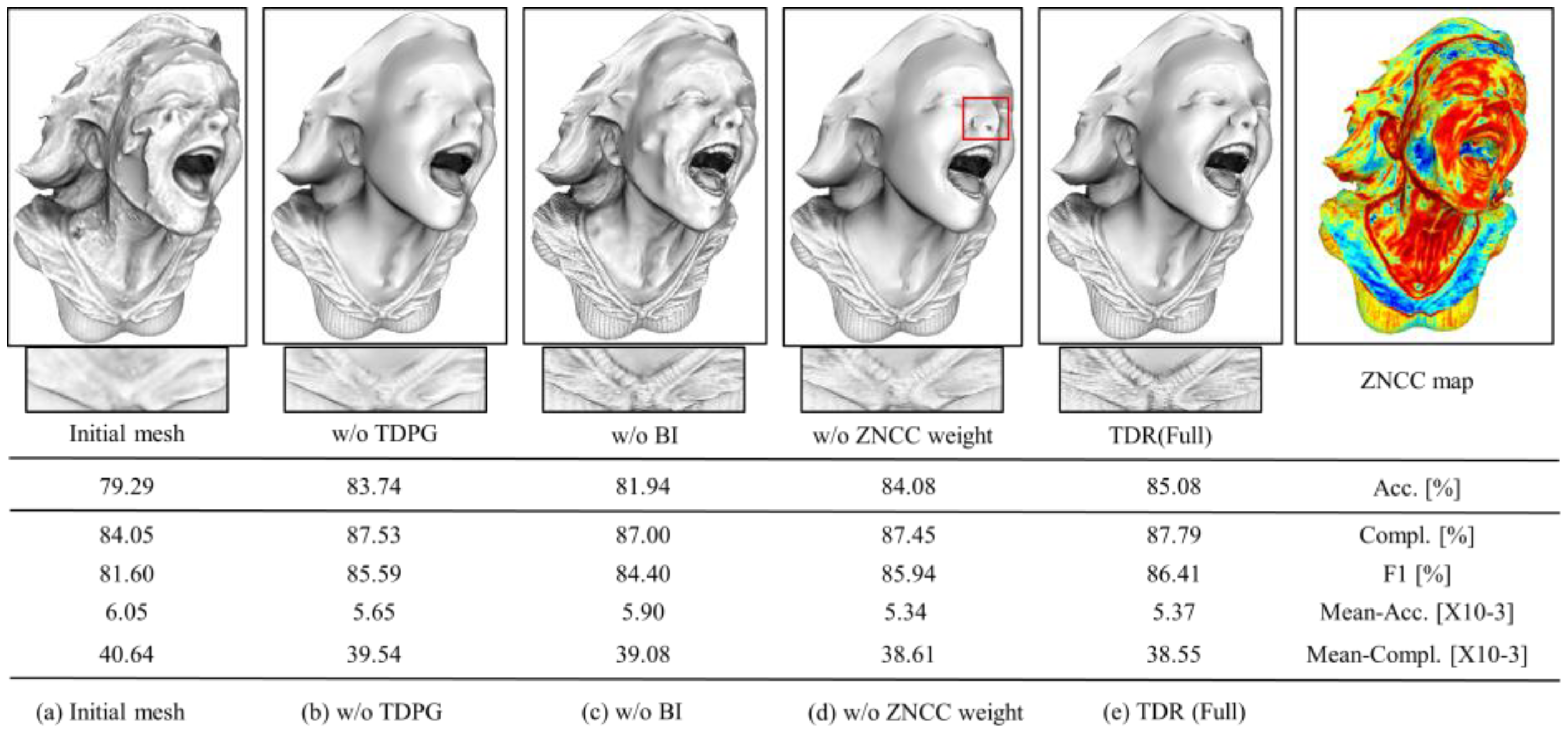
3.3.1. Ablation Experiment
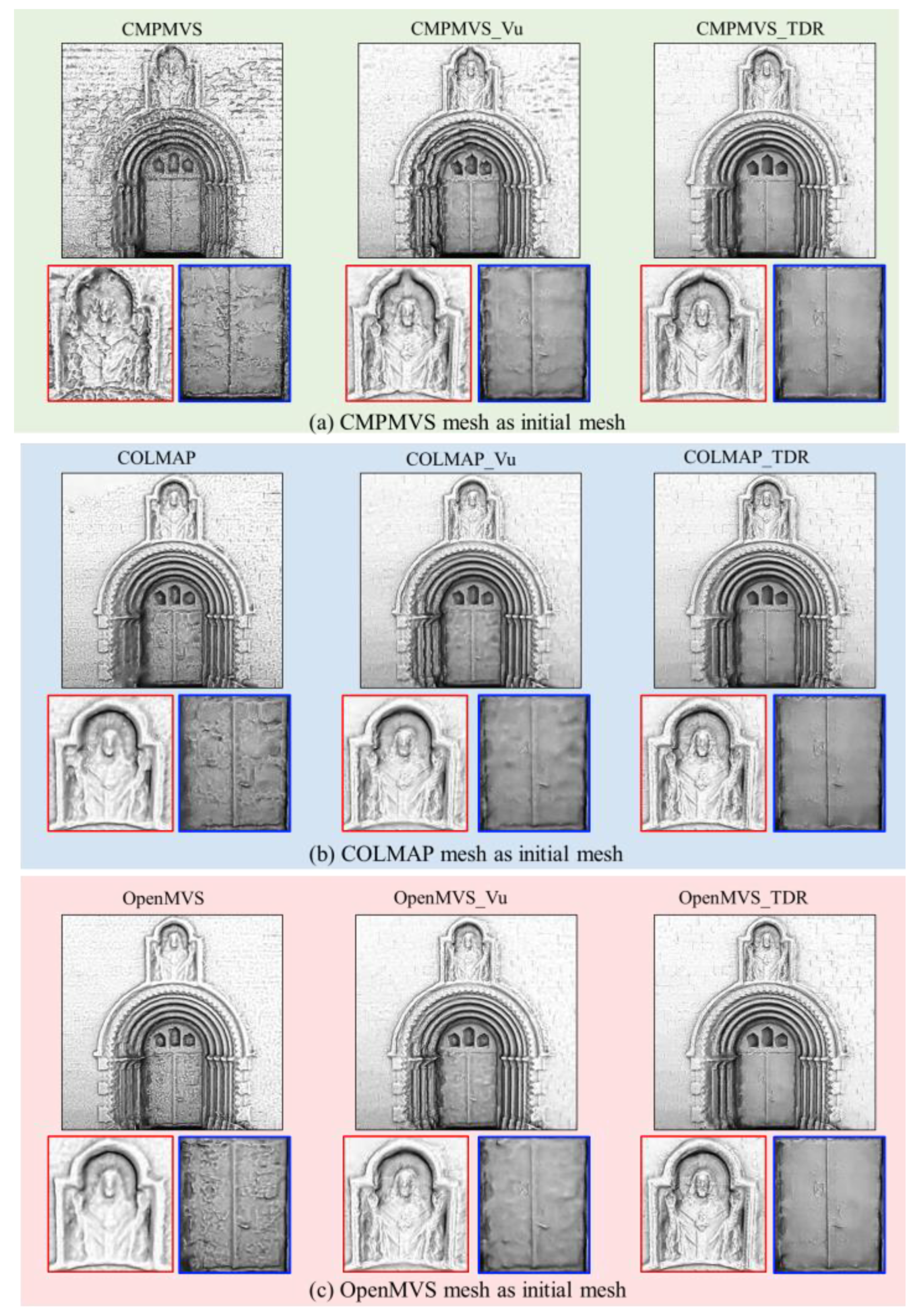
3.3.2. The Influence of Initial Meshes
3.3.3. Running Times Evaluation
3.4. Comparison with Open Source and Commercial Software
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ju, Y.; Shi, B.; Jian, M.; Qi, L.; Dong, J.; Lam, K.-M. NormAttention-PSN: A High-frequency Region Enhanced Photometric Stereo Network with Normalized Attention. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2022, 130, 3014–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ding, B.; He, Z.; Pan, G.; Cao, Y.; Cao, Y.; Zheng, Q. ReDDLE-Net: Reflectance Decomposition for Directional Light Estimation. Photonics 2022, 9, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.; Jian, M.; Guo, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Dong, J. Incorporating lambertian priors into surface normals measurement. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.; Peng, Y.; Jian, M.; Gao, F.; Dong, J. Learning conditional photometric stereo with high-resolution features. Comput. Vis. Media 2022, 8, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ju, Y.; Jian, M.; Gao, F.; Rao, Y.; Hu, Y.; Dong, J. A deep-shallow and global–local multi-feature fusion network for photometric stereo. Image Vis. Comput. 2022, 118, 104368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanoni, A.; Matteucci, M. Facetwise Mesh Refinement for Multi-View Stereo. In Proceedings of the 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Milan, Italy, 10–15 January 2021; pp. 6794–6801. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Wang, K.; Zuo, W.; Meng, D.; Zhang, L. Detail-Preserving and Content-Aware Variational Multi-View Stereo Reconstruction. Ieee Trans. Image Process. 2016, 25, 864–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanoni, A.; Matteucci, M. Mesh-based camera pairs selection and occlusion-aware masking for mesh refinement. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2019, 125, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaha, M.; Rothermel, M.; Oswald, M.R.; Sattler, T.; Richard, A.; Wegner, J.D.; Pollefeys, M.; Schindler, K. Semantically Informed Multiview Surface Refinement. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 3839–3847. [Google Scholar]
- Romanoni, A.; Ciccone, M.; Visin, F.; Matteucci, M. Multi-view Stereo with Single-View Semantic Mesh Refinement. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 706–715. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Fu, H.; Au, O.K.; Tai, C.L. Bilateral normal filtering for mesh denoising. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph 2011, 17, 1521–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pons, J.-P.; Keriven, R.; Faugeras, O. Multi-view stereo reconstruction and scene flow estimation with a global image-based matching score. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2007, 72, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, H.H.; Labatut, P.; Pons, J.P.; Keriven, R. High accuracy and visibility-consistent dense multiview stereo. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 34, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Siu, S.Y.; Fang, T.; Quan, L. Efficient multi-view surface refinement with adaptive resolution control. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 349–364. [Google Scholar]
- Kobbelt, L.; Campagna, S.; Vorsatz, J.; Seidel, H.-P. Interactive multi-resolution modeling on arbitrary meshes. In Proceedings of the 25th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, Orlando, FL, USA, 19–24 July 1998; pp. 105–114. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, C.; Zhang, J.; Deng, J. Variational mesh denoising using total variation and piecewise constant function space. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2015, 21, 873–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrd, R.H.; Lu, P.H.; Nocedal, J.; Zhu, C.Y. A Limited Memory Algorithm for Bound Constrained Optimization. Siam J. Sci. Comput. 1995, 16, 1190–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.Y.; Byrd, R.H.; Lu, P.H.; Nocedal, J. Algorithm 778: L-BFGS-B: Fortran subroutines for large-scale bound-constrained optimization. Acm Trans. Math. Softw. 1997, 23, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cernea, D. OpenMVS: Open Multiple View Stereovision. Available online: https://github.com/cdcseacave/openMVS/ (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Schonberger, J.L.; Frahm, J.-M. Structure-from-motion revisited. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 4104–4113. [Google Scholar]
- Jancosek, M.; Pajdla, T. Multi-View Reconstruction Preserving Weakly-Supported Surfaces. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Knapitsch, A.; Park, J.; Zhou, Q.-Y.; Koltun, V. Tanks and temples: Benchmarking large-scale scene reconstruction. ACM Trans. Graph. ToG 2017, 36, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schps, T.; Schnberger, J.L.; Galliani, S.; Sattler, T.; Schindler, K.; Pollefeys, M.; Geiger, A. A Multi-View Stereo Benchmark with High-Resolution Images and Multi-Camera Videos. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Y.; Luo, Z.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Ren, Y.; Zhou, L.; Fang, T.; Quan, L. Blendedmvs: A large-scale dataset for generalized multi-view stereo networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 1790–1799. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.; Torii, A.; Okutomi, M. Multi-View Inverse Rendering under Arbitrary Illumination and Albedo. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 750–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blender. Version v2.93.4 (Software). Available online: https://www.blender.org/ (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Strecha, C.; Von Hansen, W.; Van Gool, L.; Fua, P.; Thoennessen, U. On benchmarking camera calibration and multi-view stereo for high resolution imagery. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, AK, USA, 24–26 June 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kazhdan, M.; Chuang, M.; Rusinkiewicz, S.; Hoppe, H. Poisson surface reconstruction with envelope constraints. In Computer Graphics Forum; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; Volume 39, pp. 173–182. [Google Scholar]
- Facciolo, G.; Limare, N.; Meinhardt-Llopis, E. Integral images for block matching. Image Process. Line 2014, 4, 344–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ContextCapture. Version v4.4.9.516 (Software). 2020. Available online: https://www.bentley.com/en/products/brands/contextcapture (accessed on 20 December 2022).


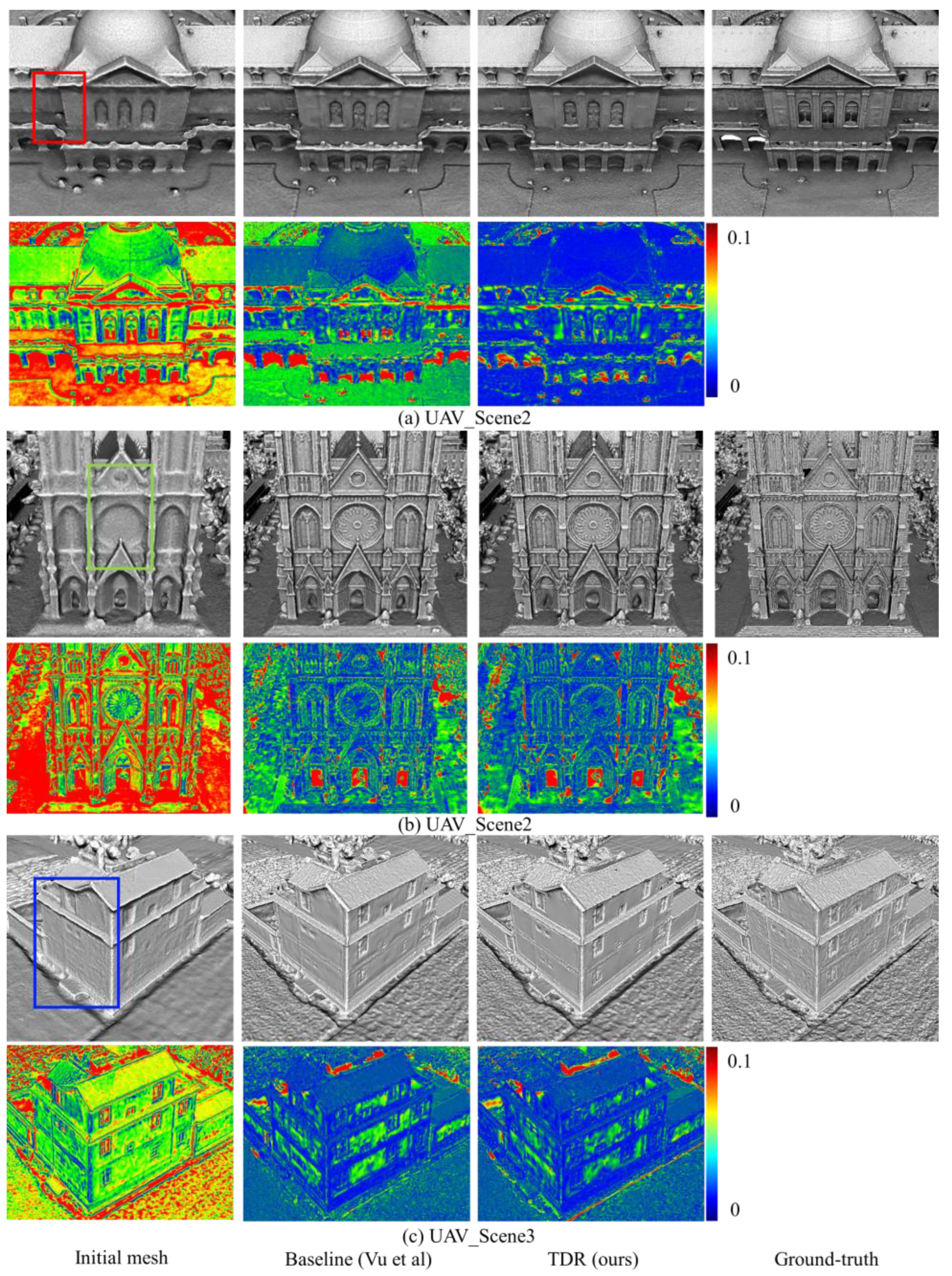
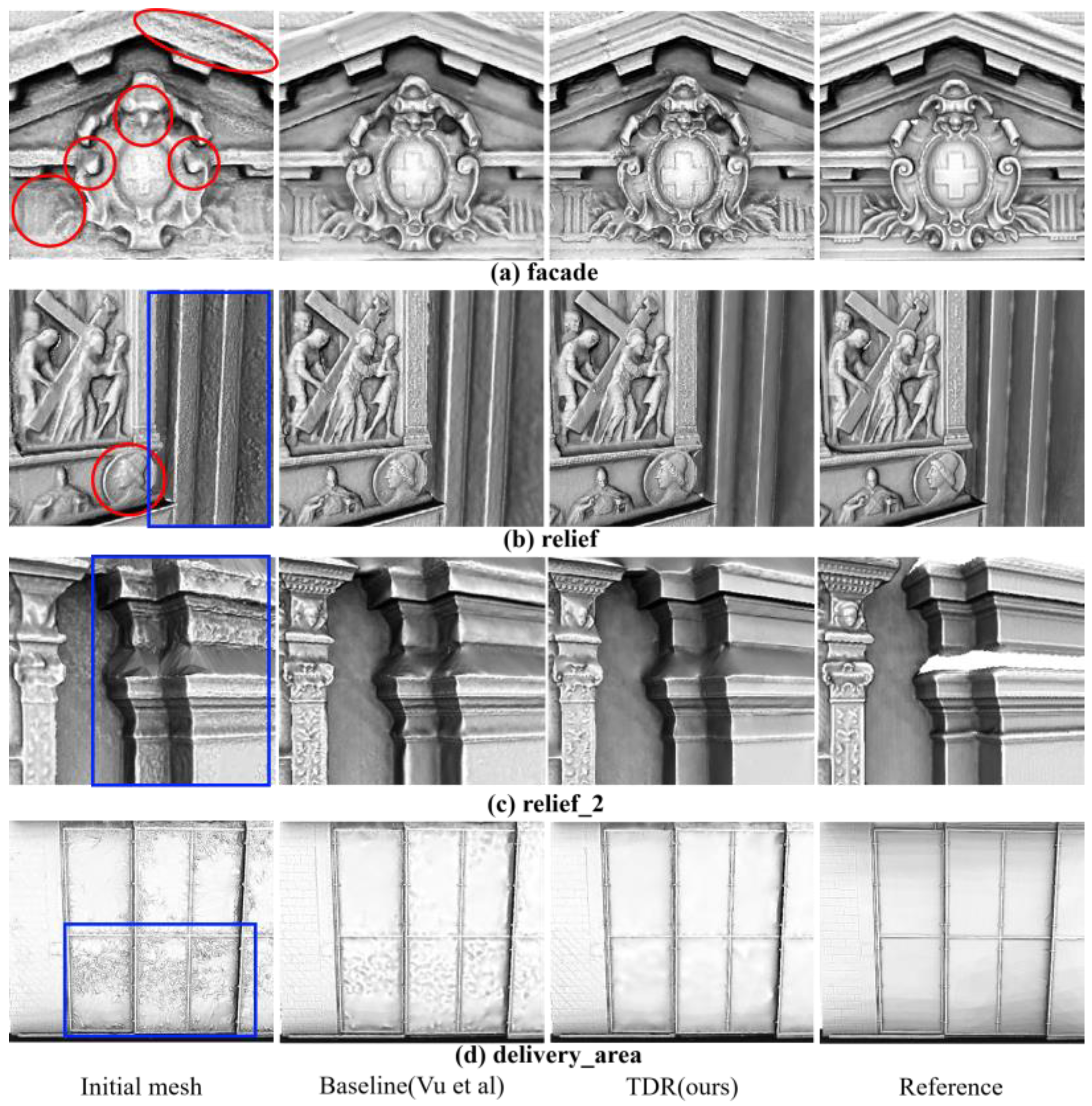


| Dataset | Name | Image Size | Number of Images | Initial Mesh | Image Acquisition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tanks And Temples | Family | 1920 × 1080 | 153 | OpenMVS | Handheld |
| Francis | 1920 × 1080 | 302 | OpenMVS | Handheld | |
| Horse | 1920 × 1080 | 151 | OpenMVS | Handheld | |
| Panther | 1920 × 1080 | 314 | OpenMVS | Handheld | |
| ETH3D | delivery area | 6048 × 4032 | 44 | OpenMVS | Handheld |
| facade | 6048 × 4032 | 76 | OpenMVS | Handheld | |
| relief | 6048 × 4032 | 31 | OpenMVS | Handheld | |
| relief 2 | 6048 × 4032 | 31 | OpenMVS | Handheld | |
| BlendedMVS | UAV_ Scene1 | 2048 × 1536 | 77 | OpenMVS | Rendered |
| UAV_ Scene2 | 2048 × 1536 | 125 | OpenMVS | Rendered | |
| UAV_ Scene3 | 2048 × 1536 | 75 | OpenMVS | Rendered | |
| EPFL | Herz- Jesu-P8 | 3072 × 2048 | 8 | OpenMVS /COLMAP/ CMPMVS | Handheld |
| Fountain-P11 | 3072 × 2048 | 11 | OpenMVS/ COLMAP/ CMPMVS | Handheld | |
| CG Simulation Dataset | Joyful | 1920 × 1080 | 70 | OpenMVS | Rendered |
| Personal Collection Dataset | House | 4592 × 3056 | 36 | OpenMVS | UAV |
| Woodcarving | 2016 × 4032 | 146 | OpenMVS | Handheld |
| Initial Mesh | Baseline | TDR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UAV_ Scene1 | Acc. [%] | 28.11 | 77.00 | 81.67 |
| Compl. [%] | 20.30 | 61.37 | 63.16 | |
| F1 [%] | 23.57 | 68.30 | 71.23 | |
| Mean-Acc. [X10-2] | 10.89 | 6.71 | 5.09 | |
| Mean-Compl. [X10-2] | 24.13 | 15.03 | 14.13 | |
| UAV_ Scene2 | Acc. [%] | 31.90 | 72.79 | 77.71 |
| Compl. [%] | 29.80 | 90.20 | 90.77 | |
| F1 [%] | 30.81 | 80.57 | 83.73 | |
| Mean-Acc. [X10-2] | 12.80 | 8.00 | 6.70 | |
| Mean-Compl. [X10-2] | 42.40 | 28.30 | 27.30 | |
| UAV_ Scene3 | Acc. [%] | 29.53 | 83.98 | 85.79 |
| Compl. [%] | 28.90 | 66.85 | 67.95 | |
| F1 [%] | 29.21 | 74.44 | 75.84 | |
| Mean-Acc. [X10-2] | 10.27 | 5.37 | 4.94 | |
| Mean-Compl. [X10-2] | 26.80 | 17.55 | 17.44 |
| Initial Mesh | Baseline | TDR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| delivery_area | Acc. [%] | 53.18 | 53.33 | 56.98 |
| Compl. [%] | 37.65 | 41.85 | 42.95 | |
| F1 [%] | 44.09 | 46.89 | 48.98 | |
| Mean-Acc. [X10-3] | 7.89 | 7.80 | 7.24 | |
| Mean-Compl. [X10-3] | 51.24 | 50.90 | 50.84 | |
| facade | Acc. [%] | 24.25 | 34.35 | 42.78 |
| Compl. [%] | 27.07 | 38.22 | 45.15 | |
| F1 [%] | 25.58 | 36.18 | 43.93 | |
| Mean-Acc. [X10-3] | 34.89 | 30.67 | 26.76 | |
| Mean-Compl. [X10-3] | 15.35 | 13.91 | 13.22 | |
| relief | Acc. [%] | 95.45 | 95.87 | 95.97 |
| Compl. [%] | 94.09 | 95.63 | 96.79 | |
| F1 [%] | 94.77 | 95.75 | 96.38 | |
| Mean-Acc. [X10-3] | 1.79 | 16.25 | 13.51 | |
| Mean-Compl. [X10-3] | 2.15 | 1.76 | 13.17 | |
| relief_2 | Acc. [%] | 90.48 | 90.34 | 92.58 |
| Compl. [%] | 86.72 | 89.74 | 90.72 | |
| F1 [%] | 88.56 | 90.04 | 91.64 | |
| Mean-Acc. [X10-3] | 1.94 | 2.16 | 1.93 | |
| Mean-Compl. [X10-3] | 2.66 | 2.19 | 2.13 |
| Herz-Jesu-P8 | Fountain-P11 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #faces [M] | Acc. [3σ] | Compl. [%] | #faces [M] | Acc. [3σ] | Compl. [%] | |
| CMPMVS | 2.76 | 6.25 | 50.57 | 2.47 | 5.08 | 53.42 |
| CMPMVS_Vu | 1.25 | 4.30 | 66.55 | 1.55 | 2.90 | 70.34 |
| CMPMVS_TDR | 1.25 | 3.77 | 71.83 | 1.55 | 2.64 | 71.70 |
| OpenMVS | 1.54 | 4.04 | 72.96 | 1.89 | 2.42 | 79.37 |
| OpenMVS_Vu | 1.26 | 3.59 | 75.62 | 1.52 | 2.15 | 79.52 |
| OpenMVS_TDR | 1.26 | 3.49 | 75.72 | 1.53 | 1.95 | 80.29 |
| COLMAP | 1.14 | 3.80 | 71.45 | 1.51 | 2.42 | 74.33 |
| COLMAP_Vu | 1.23 | 3.60 | 73.77 | 1.39 | 2.24 | 78.25 |
| COLMAP_TDR | 1.22 | 3.32 | 76.41 | 1.40 | 1.99 | 79.12 |
| Herz-Jesu-P8 | Fountain-P11 | Family | Francis | Horse | Panther | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (s) | Ratio (%) | Time (s) | Ratio (%) | Time (s) | Ratio (%) | Time (s) | Ratio (%) | Time (s) | Ratio (%) | Time (s) | Ratio (%) | |
| SFM | - | - | - | - | 472 | 12 | 925 | 19 | 276 | 12 | 1388 | 22 |
| MVS | 120 | 35 | 196 | 38 | 1009 | 25 | 1313 | 27 | 575 | 24 | 1545 | 24 |
| Mesh reconstruction | 60 | 18 | 86 | 17 | 222 | 6 | 131 | 3 | 91 | 4 | 331 | 5 |
| Mesh refinement | 159 | 47 | 233 | 45 | 2335 | 58 | 2455 | 51 | 1427 | 60 | 3149 | 49 |
| Herz-Jesu-P8 | Fountain-P11 | Family | Francis | Horse | Panther | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vu | TDR | Vu | TDR | Vu | TDR | Vu | TDR | Vu | TDR | Vu | TDR | |
| #Vertices (K) | 754 | 754 | 944 | 944 | 895 | 895 | 672 | 672 | 527 | 527 | 1897 | 1897 |
| #Images pixels (M) | 50 | 50 | 69 | 69 | 317 | 317 | 626 | 626 | 313 | 313 | 651 | 651 |
| Ray tracing (s) | 30 | 32 | 43 | 45 | 561 | 389 | 624 | 524 | 416 | 291 | 850 | 810 |
| Compute (s) | 7 | 85 | 10 | 129 | 231 | 1391 | 285 | 1271 | 184 | 759 | 198 | 1626 |
| Compute (s) | 17 | 16 | 26 | 23 | 371 | 257 | 277 | 245 | 211 | 151 | 339 | 316 |
| Compute (s) | 0 | 3 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 10 |
| Others (s) | 22 | 24 | 30 | 32 | 435 | 290 | 504 | 410 | 331 | 221 | 433 | 387 |
| Total (s) | 76 | 159 | 109 | 233 | 1597 | 2335 | 1690 | 2455 | 1142 | 1427 | 1819 | 3149 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qu, Y.; Yan, Q.; Yang, J.; Xiao, T.; Deng, F. Total Differential Photometric Mesh Refinement with Self-Adapted Mesh Denoising. Photonics 2023, 10, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10010020
Qu Y, Yan Q, Yang J, Xiao T, Deng F. Total Differential Photometric Mesh Refinement with Self-Adapted Mesh Denoising. Photonics. 2023; 10(1):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10010020
Chicago/Turabian StyleQu, Yingjie, Qingsong Yan, Junxing Yang, Teng Xiao, and Fei Deng. 2023. "Total Differential Photometric Mesh Refinement with Self-Adapted Mesh Denoising" Photonics 10, no. 1: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10010020
APA StyleQu, Y., Yan, Q., Yang, J., Xiao, T., & Deng, F. (2023). Total Differential Photometric Mesh Refinement with Self-Adapted Mesh Denoising. Photonics, 10(1), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10010020





