Steroid Hormone Pollution and Life History Strategies of Freshwater Planarians and Snails in a Mesocosm Experiment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Mesocosm Experiment
2.2. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
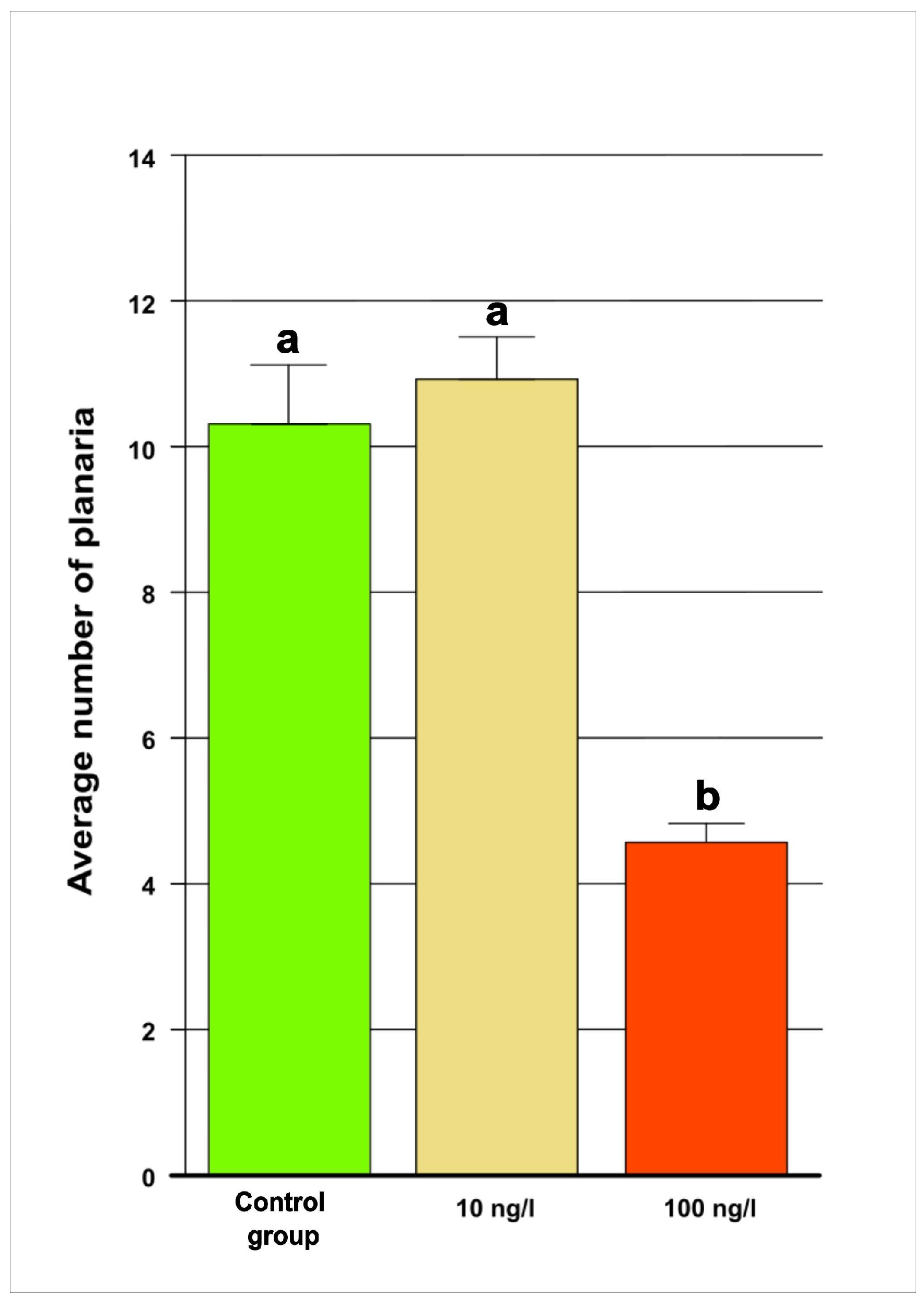
3.1. Behavior and Growth of Studied Organisms
3.2. Changes in Reproductive Effort
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Q.-Q.; Xing, C.; Cai, Y.Y.; Yan, X.T.; Ying, G.G. How Much Do Human and Livestock Actually Contribute to Steroids Emission and Surface Water Pollution from Past to the Future: A Global Research. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 145558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes-Alonso, R.; Montesdeoca-Esponda, S.; Pacheco-Juárez, J.; Sosa-Ferrera, Z.; Santana-Rodríguez, J.J. A Survey of the Presence of Pharmaceutical Residues in Wastewaters. Evaluation of Their Removal Using Conventional and Natural Treatment Procedures. Molecules 2020, 25, 1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GlobeNewswire. Drugs for Hormonal Replacement Therapy Global Market Report. 20 February 2023. Available online: https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2023/02/20/2611529/0/en/Drugs-For-Hormonal-Replacement-Therapy-Global-Market-Report-2023.html (accessed on 23 October 2025).
- O’Malley, B.W.; Schrader, W.T. The Receptors of Steroid Hormones. Sci. Am. 1976, 234, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beato, M.; Klug, J. Steroid hormone receptors: An update. Hum. Reprod. Update 2000, 6, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Johnson, A.C.; Trubiroha, A.; Tumová, J.; Ihara, M.; Grabic, R.; Kloas, W.; Tanaka, H.; Kroupová, H.K. The challenge presented by progestins in ecotoxicological research: A critical review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 2625–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stout, E.P.; La Clair, J.J.; Snell, T.W.; Shearer, T.L.; Kubanek, J. Conservation of progesterone hormone function in invertebrate reproduction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 11859–11864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moschet, C.; Hollender, J. Microbial degradation of steroid hormones in the environment and technical systems. Inst. Biogeochem. Pollut. 2009, 1, 1–20. Available online: https://www.thermopileproject.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/06/Microbial-Degradation-of-Steroid-Hormones-in-the-Environment-and-Technical-Systems.pdf (accessed on 23 October 2025).
- Oropesa, A.L.; Guimarães, L. Occurrence of Levonorgestrel in Water Systems and Its Effects on Aquatic Organisms: A Review. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; De Voogt, P., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, M.J.; Rocha, E. Synthetic progestins in waste and surface waters: Concentrations, impacts and ecological risk. Toxics 2022, 10, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skałba, P.H. Gestageny in Endokrynologia Ginekologiczna; Żakowska, Z., Głodowska, J., Eds.; Wydawnictwo Lekarskie PZWL: Warsaw, Poland, 2008; pp. 208–240. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Hohmann, H.; Creinin, M.D. The contraceptive implant. Clin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2007, 50, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runnalls, T.J.; Beresford, N.; Losty, E.; Scott, A.P.; Sumpter, J.P. Several synthetic progestins with different potencies adversely affect reproduction of fish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 2077–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, H. Food selection by freshwater snails in the Gezira irrigation canals, Sudan. Hydrobiologia 1992, 228, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolaji, D.A.; Edokpayi, C.A.; Samuel, O.B.; Akinnigbagbe, R.O.; Ajulo, A.A. Morphological characteristics and salinity tolerance of Melanoides tuberculatus (Muller, 1774). World J. Biol. Res. 2011, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Maciaszek, R.; Sosnowski, W.; Wilk, S. Tropical snail Melanoides tuberculata Müller, 1774 (Thiaridae) found in thermally polluted canal in Central Poland. World Sci. News 2019, 122, 249–254. [Google Scholar]
- Van Bocxlaer, B.; Clewing, C.; Mongindo Etimosundja, J.P.; Kankonda, A.; Wembo Ndeo, O.; Albrecht, C. Recurrent camouflaged invasions and dispersal of an Asian freshwater gastropod in tropical Africa. BMC Evol. Biol. 2015, 15, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, A.J.; Kadri, A.B.H. Reproduction in the Malayan freshwater cerithiacean gastropod Melanoides tuberculata. J. Zool. 1974, 172, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Ami, F.; Hodgson, A.N. Ovoviviparity and the structure of the brood pouch in Melanoides tuberculata (Gastropoda: Prosobranchia: Thiaridae). J. Morphol. 2005, 263, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rompolas, P.; Patel-King, R.S.; King, S.M. Schmidtea mediterranea: A model system for analysis of motile cilia. In Methods in Cell Biology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009; Volume 93, pp. 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svigruha, R.; Fodor, I.; Padisak, J.; Pirger, Z. Progestogen-induced alterations and their ecological relevance in different embryonic and adult behaviours of an invertebrate model species, the great pond snail (Lymnaea stagnalis). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 59391–59402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Säfholm, M.; Ribbenstedt, A.; Fick, J.; Berg, C. Risks of hormonally active pharmaceuticals to amphibians: A growing concern regarding progestagens. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 2014, 369, 20130577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, W.B., Jr.; Rodgers, J.H., Jr.; Crossland, N.O. Effects of a nonionic surfactant (C14–15AE-7) on aquatic invertebrates in outdoor stream mesocosms. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1996, 15, 1418–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crossland, N.O.; La Point, T.W. The Design of Mesocosm Experiments. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1992, 11, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitina, S.M.; Polunina, J.J. Complex of Steroid Hormones in Invertebrate Hydrobionts. Inland Water Biol. 2024, 17, 669–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermakov, A.; Kudykina, N.; Bykova, A.; Tkacheva, U. Morphogenic Effect of Exogenous Glucocorticoid Hormones in the Girardia tigrina Planarian (Turbellaria, Tricladida). Biology 2023, 12, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.H. Acute toxicity of industrial endocrine-disrupting chemicals, natural and synthetic sex hormones to the freshwater planarian, Dugesia japonica. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2013, 95, 984–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janer Gual, G. Steroid Levels, Steroid Metabolic Pathways and Their Modulation by Endocrine Disruptors in Invertebrates; Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona: Barcelona, Spain, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Croll, R.P. Effects of Sex Steroids on Spawning in the Sea Scallop, Placopecten magellanicus. Aquaculture 2006, 256, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudikina, N.P.; Ermakov, A.M.; Omelnitskaya, E.A.; Skorobogatykh, I.A. The morphogenetic effects of exogenous sex steroid hormones in the planarian Girardia tigrina (Turbellaria, Tricladida). Biophysics 2019, 64, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharp, M.E.; Collins, J.J., III; Newmark, P.A. A lophotrochozoan-specific nuclear hormone receptor is required for reproductive system development in the planarian. Dev. Biol. 2014, 396, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macaulay, S.J.; Jeppesen, E.; Riebesell, U.; Nejstgaard, J.C.; Berger, S.A.; Lewandowska, A.M.; Rico, A.; Kefford, B.J.; Vad, C.F.; Costello, D.M.; et al. Addressing grand ecological challenges in aquatic ecosystems: How can mesocosms be used to advance solutions? Oikos 2025, 2025, e11020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semlitsch, R.D.; Boone, M.D.; Dodd, C.K., Jr. Aquatic mesocosms. Amphibian ecology and conservation. In A Handbook of Techniques; Techniques in Ecology & Conservation Series; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2010; pp. 87–104. [Google Scholar]
- Abd El-Atti, M.S.; Desouky, M.A.; Elsheakh, A.A.; Elgohary, W.S. Control of Theba pisana land snails using pharmaceutical mono-hormonal contraceptive drug at Sharkia Governorate. Bull. Fac. Sci. Zagazig Univ. 2023, 2023, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garba Djirmay, A.; Yadav, R.S.; Guo, J.; Rollinson, D.; Madsen, H. Chemical control of snail vectors as an integrated part of a strategy for the elimination of schistosomiasis—A review of the state of knowledge and future needs. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2024, 9, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weselak, M.; Kaliszewicz, A. Steroid Hormone Pollution and Life History Strategies of Freshwater Planarians and Snails in a Mesocosm Experiment. Limnol. Rev. 2025, 25, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/limnolrev25040054
Weselak M, Kaliszewicz A. Steroid Hormone Pollution and Life History Strategies of Freshwater Planarians and Snails in a Mesocosm Experiment. Limnological Review. 2025; 25(4):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/limnolrev25040054
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeselak, Marcin, and Anita Kaliszewicz. 2025. "Steroid Hormone Pollution and Life History Strategies of Freshwater Planarians and Snails in a Mesocosm Experiment" Limnological Review 25, no. 4: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/limnolrev25040054
APA StyleWeselak, M., & Kaliszewicz, A. (2025). Steroid Hormone Pollution and Life History Strategies of Freshwater Planarians and Snails in a Mesocosm Experiment. Limnological Review, 25(4), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/limnolrev25040054





