Characteristics of the Zooplankton Community Structure in Shengjin Lake and Its Response to the Restored Aquatic Vegetation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Method
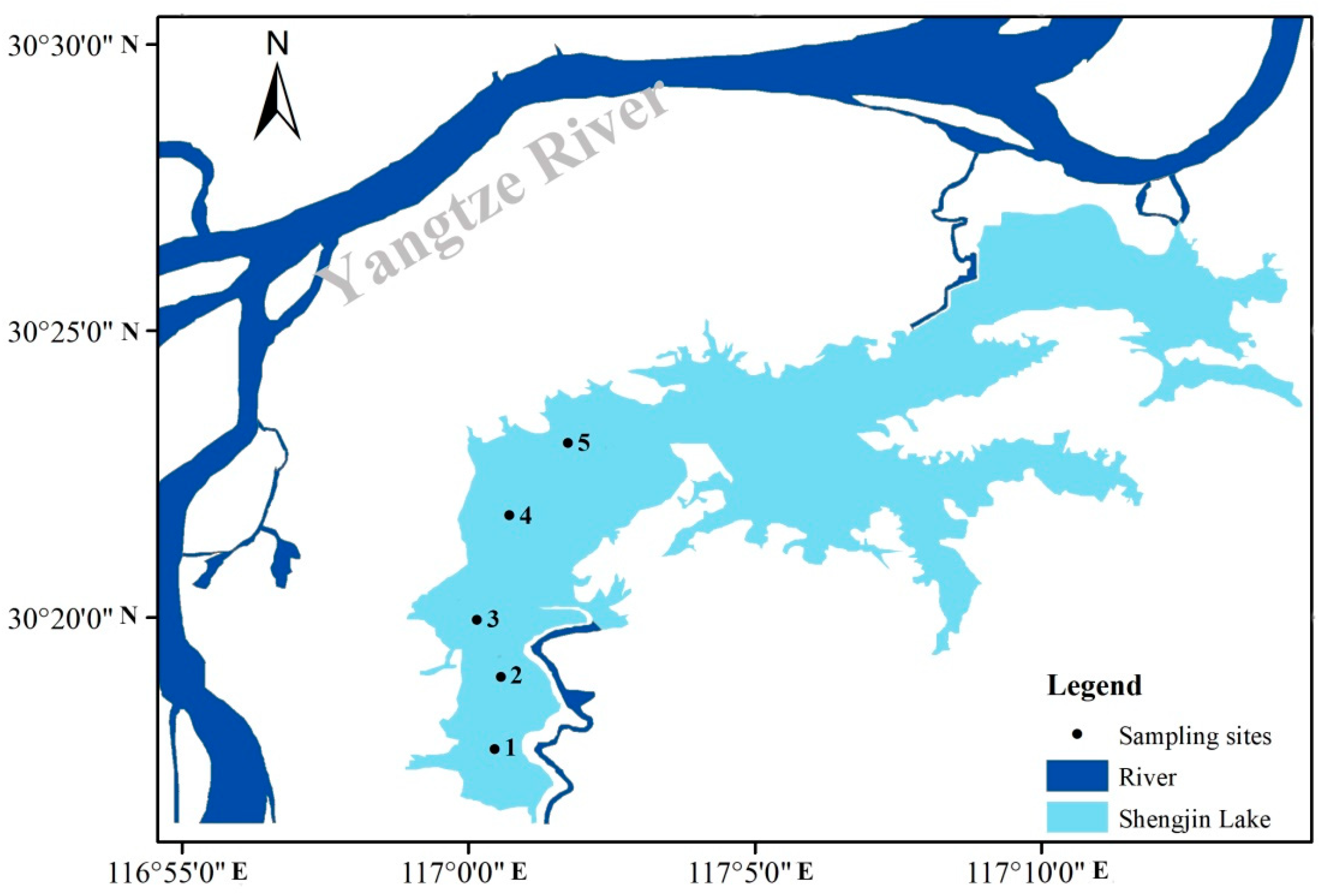
2.1. Study Area Description
2.2. Sampling Procedures and Experimental Design
| Sites | Common Name | Scientific Species Name | Dominant Macrophyte Taxa | Macrophyte Abundance | Ecological Life Forms |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site 1 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Site 2 | Foxnut | Euryale ferox. Salisb. | Euryale ferox Salisb. | Abundant | Freely floating |
| Water chestnut | Trapa bispinosa Roxb. | Spars | |||
| Site 3 | Yellow floating heart | Nymphoides peltatum (Gmel.) | Spars | Emergent | |
| Eelgrass | Vallisneria natans L. | Vallisneria natans L. | Abundant | submerged | |
| Site 4 | Coontail (rigid hornwort) | Ceratophyllum demersum Lenn. | Ceratophyllum demersum Lenn. | Abundant | submerged |
| Eurasian watermilfoil | Myriophyllum spicatum L. | Spars | |||
| Site 5 | Common reed | Phragmites australis | Phragmites australis | Abundant | Emergent |
| Wild rice | Zizania latifolia | Spars |
2.3. Limnological Variables and Zooplankton Data Collection
2.4. Statistical Treatment
3. Result
3.1. Environmental Parameters
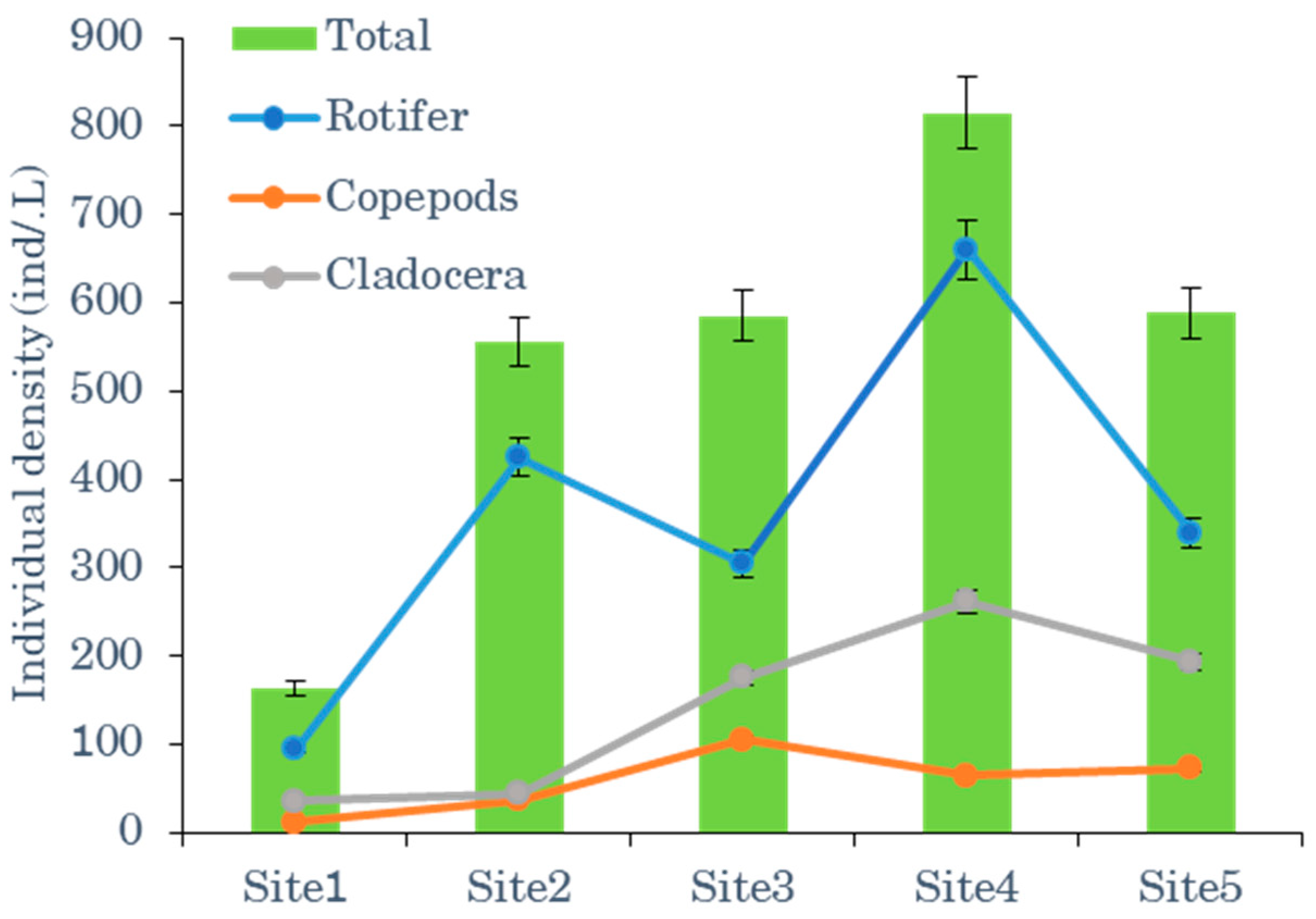
3.1.1. Zooplankton Distribution in Open Water and Vegetated Macrophyte Zones
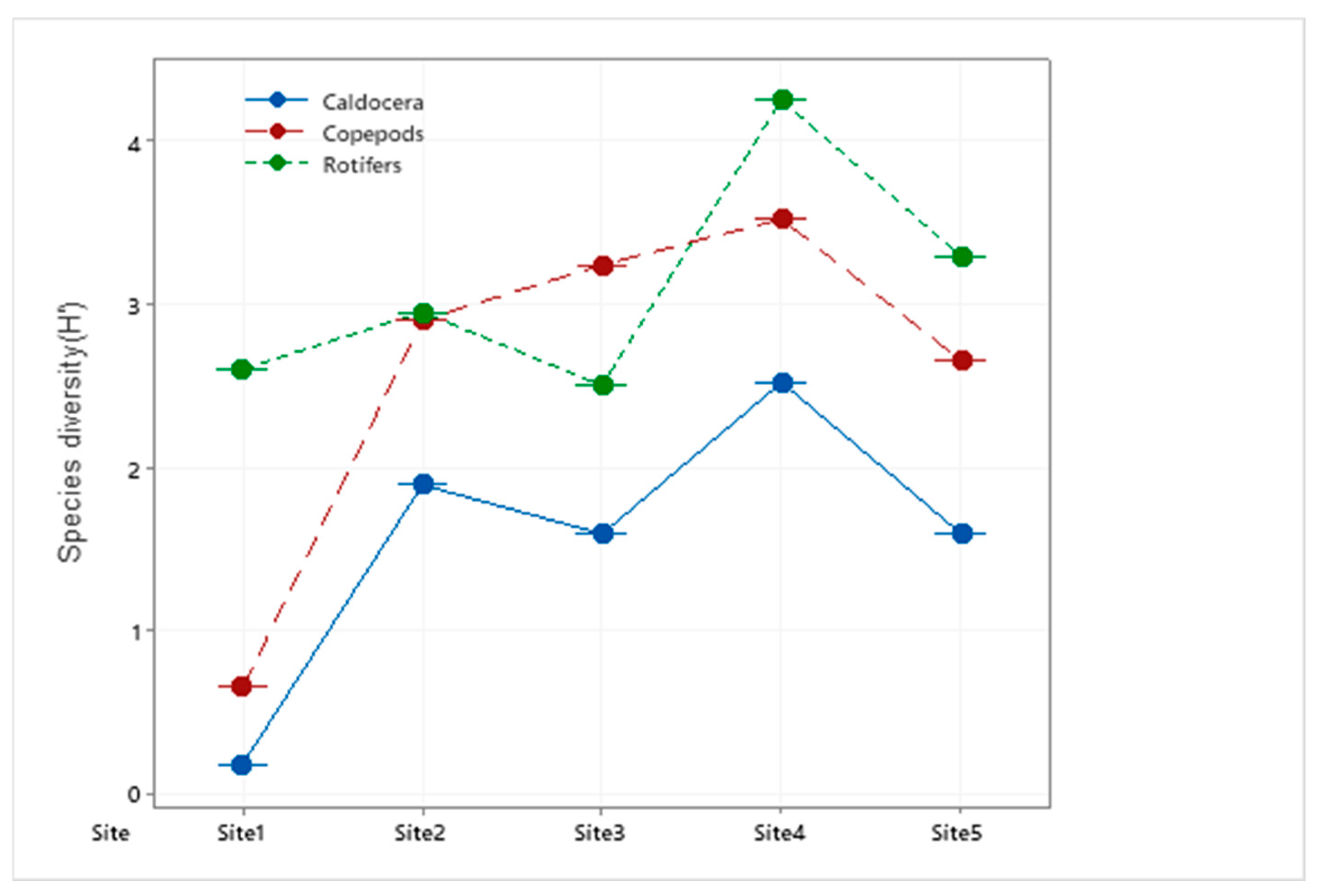
3.1.2. Species Diversity Index
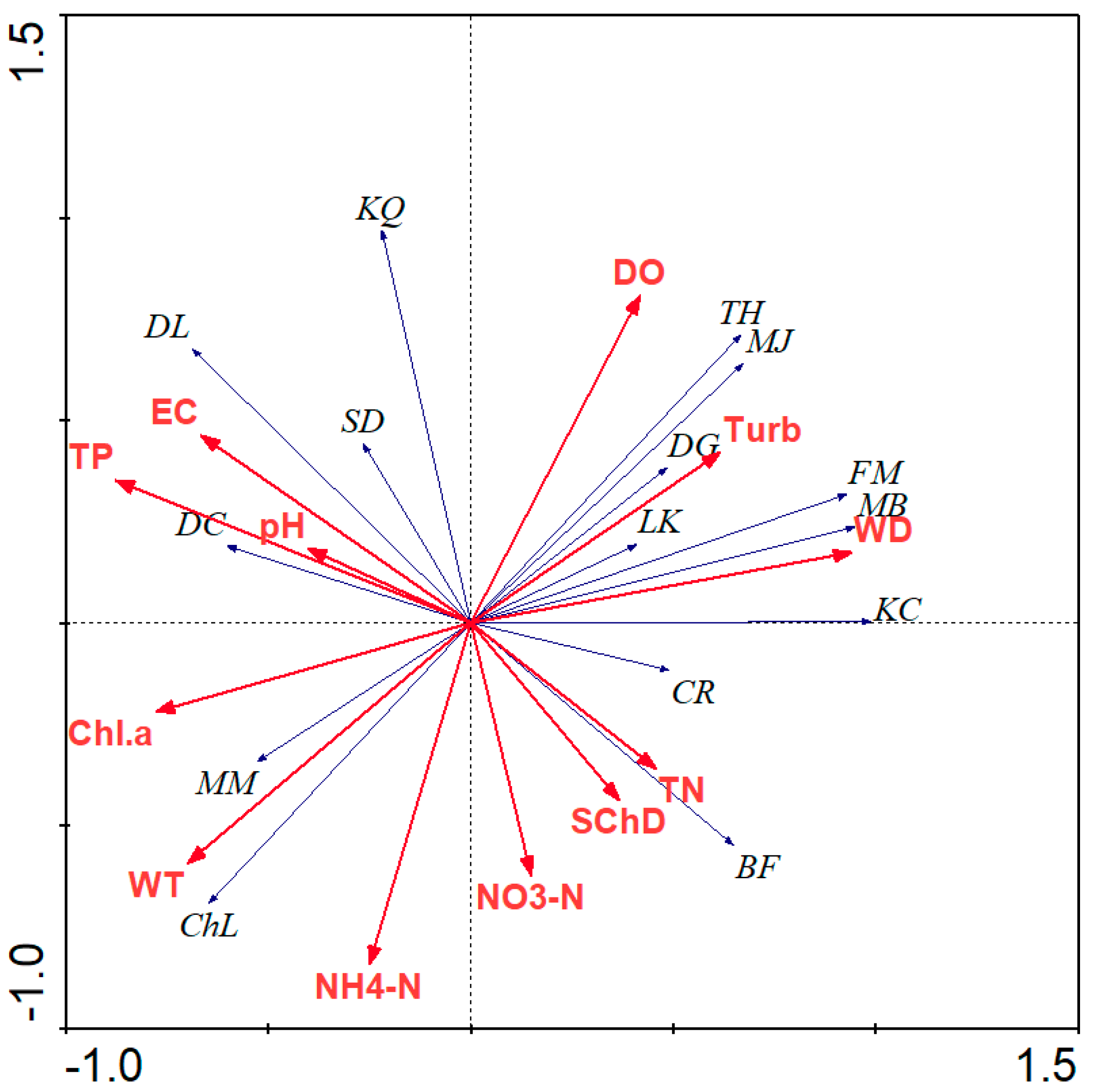
3.1.3. The Relationship Between Zooplankton Community and Environmental Variables
4. Discussion
4.1. Limnological Variables Along the Sampling Stations
4.2. The Relationship Between Environmental Variables and Zooplankton Communities
4.3. Zooplankton Spatial Variation, Distribution, and Species Composition
4.4. Macrophytes Restoration Practise and Management Strategies to Improve Zooplankton Taxa Diversity and Implication to Macrophyte Management
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Altshuler, I.; Demiri, B.; Xu, S.; Constantin, A.; Yan, N.D.; Cristescu, M.E. An integrated multi-disciplinary approach for studying multiple stressors in freshwater ecosystems: Daphnia as a model organism. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2011, 51, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudgeon, D.; Arthington, A.H.; Gessner, M.O.; Kawabata, Z.I.; Knowler, D.J.; Lévêque, C.; Naiman, R.J.; Prieur-Richard, A.H.; Soto, D.; Stiassny, M.L.J.; et al. Freshwater biodiversity: Importance, threats, status and conservation challenges. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2006, 81, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halpern, B.S.; Selkoe, K.A.; Micheli, F.; Kappel, C.V. Evaluating and ranking the vulnerability of global marine ecosystems to anthropogenic threats. Conserv. Biol. 2007, 21, 1301–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, B.; Hering, D.; Green, A.J.; Aidoud, A.; Becares, E.; Beklioglu, M.; Bennion, H.; Boix, D.; Brucet, S.; Carvalho, L.; et al. Climate change and the future of freshwater biodiversity in Europe: A primer for policy-makers. Freshw. Rev. 2009, 2, 103–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovaskainen, O.; Weigel, B.; Potyutko, O.; Buyvolov, Y. Long-term shifts in water quality show scale-dependent bioindicator responses across Russia—Insights from 40 year-long bioindicator monitoring program. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 98, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, J.; Mehra, N.K. Species diversity of planktonic and epiphytics in the Backwaters of the Delhi Segment of the Yamuna River, with remarks on new records from India. Zool. Stud. 2003, 42, 239–247. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, P.; Whitfield, M.; Biggs, J. How can we make new ponds biodiverse? A case study monitored over 7 years. Hydrobiologia 2008, 597, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, S.E. Application of ecological engineering principles in lake management. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 2006, 11, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagrario, M.A.G.; Jeppesen, E.; Gomàj, M.; Søndergaard, J.P.; Jensen, T.; Lauridsen, F. Landkildehus Does high nitrogen loading prevent clear-water conditions in shallow lakes at moderately high phosphorus concentrations? Freshw. Biol. 2005, 50, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arimoro, F.O.; Olisa, H.E.; Keke, U.N.; Ayanwale, A.V.; Chukwuemeka, V.I. Exploring spatio-temporal patterns of plankton diversity and community structure as correlates of water quality in a tropical stream. Ecol. Front. 2017, 38, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loick-Wilde, N.; Weber, S.C.; Conroy, B.J.; Capone, D.G.; Coles, V.J.; Medeiros, P.M.; Steinberg, D.K.; Montoya, J.P. Nitrogen sources and net growth efficiency of zooplankton in three Amazon River plume food webs. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2016, 61, 460–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shayestehfar, A.; Noori, M.; Shirazi, F. Environmental factor effects on the seasonally changes density in Parishan lake (Khajoo spring site). Iran Asian J. Exp. Biol. Sci. 2010, 1, 840–844. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Zhong, R.; Wang, Z.; Montaña, C.G.; Song, Y.; Pan, K.; Wu, Y. Intra-annual variation of zooplankton community structure and dynamics in response to the changing strength of bio-manipulation with two planktivorous fishes. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 101, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; You, W.H.; Yu, F.J.; Yu, Q.J.; Yu, H.G. Zooplankton Community structure and its relationships with environmental factors in Dishui Lake. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 23, 6918–6929. [Google Scholar]
- Estlander, S.; Nurminen, L.; Olin, M.; Vinni, M.; Horppila, J. Seasonal fluctuations in macrophyte cover and water transparency of four brown-water lakes: Implications for crustacean zooplankton in littoral and pelagic habitats. Hydrobiologia 2009, 620, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczyńska-Kippen, N.M.; Nagengast, B. The influence of the spatial structure of hydromacrophytes and differentiating habitat on the structure of cladoceran communities. Hydrobiologia 2006, 559, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Dyble, J.; Moisander, P.H.; Noble, R.T.; Piehler, M.F.; Pinckney, J.L.; Steppe, T.F.; Twomey, L.; Valdes, L.M. Microbial indicators of aquatic ecosystem change: Current applications to eutrophication studies. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2003, 46, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurminen, L.; Horppila, J.; Tallberg, P. Seasonal development of the Cladoceran assemblage in a turbid lake: The role of emergent macrophytes. Arch. Hydrobiol. 2001, 151, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurminen, L.; Horppila, J.; Pekcan-Hekim, Z. Effect of light and predator abundance on the habitat choice of plant attached zooplankton. Freshw. Biol. 2007, 52, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.Z.; Zhu, W.Z. Biodiversity and Conservation in Anqing Floodplain Wetlands; Hefei University of Technology Publishing House: Hefei, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- De Meester, L.S.; Declerck, R.; Stoks, G.; Louette, F.; van De Meutter, T.; De Bie, E.; Michels, L. Brendonck Ponds and pools as model systems in conservation biology, ecology and evolutionary biology. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2005, 15, 715–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodson, S.I.; Lillie, R.A. Zooplankton communities of restored depressional wetlands in Wisconsin, USA. Wetlands 2001, 21, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibar, D.T.; Zhang, K.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Ye, X. Ecological stoichiometric characteristics of Carbon (C), Nitrogen (N) and Phosphorus (P) in leaf, root, stem, and soil in four wetland plants communities in Shengjin Lake, China. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfield, D.E., Jr.; Shireman, J.V.; Colle, D.E.; Haller, W.T.; Watkins, C.E., II; Maceina, M.J. Prediction of Chlorophyll a concentrations in Florida Lakes importance of aquatic macrophytes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1984, 41, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomaz, S.M.; Carvalho, P.; Padial, A.A.; Kobayashi, J.T. Temporal and spatial patterns of aquatic macrophyte diversity in the Upper Paran_a River floodplain. Braz. J. Biol. 2009, 69, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Public Health Association (APHA). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; APHA, American Water Works Association, Water Environmental Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Marker, A.F.H.; Nusch, A.; Rai, H.; Riemann, B. The measurement of photosynthetic pigments in freshwater and standardization of methods: Conclusions and recommendations. Arch. Hydrobiol. Beihand Lung Ergeb. Limnol. 1980, 14, 91–106. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.B.; Xie, P.; Geng, H. The relative importance of physicochemical factors and crustacean zooplankton as determinants of density and species distribution in lakes adjacent to the Yangtze River, China. Limnologica 2010, 40, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isari, S.; Ramfos, A.; Somarakis, S.; Koutsikopoulos, C.; Kallianiotis, A.; Fragopoulu, N. Mesozooplankton distribution in relation to hydrology of the north-eastern aegean sea, eastern Mediterranean. J. Plankton Res. 2006, 28, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, L.; O’Hare, M. Changes in species composition and abundance along a trophic gradient in Loch Lomond, Scotland, UK. Hydrobiologia 2005, 546, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohman, M.D.; Lavaniegos, B.E. Comparative zooplankton sampling efficiency of a ring net and bongo net with comments on pooling of subsamples. CalCOFI Rep. 2002, 43, 162–173. [Google Scholar]
- Benzie, J.A.H. The genus Daphnia (including Daphniopsis). In Guides to the Identification of the Microinvertebrates of the Continental Waters of the World 21; Dumont, H.J.F., Ed.; Kenobi Productions: Ghent, Belgium; Backhuys Publishers: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Jongman, R.H.G.; Ter Braak, C.J.F.; Van Tongeren, O.F.R. Data Analysis in Community and Landscape Ecology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995; pp. 91–173. [Google Scholar]
- Ter Braak, C.J.F.; Smilauer, P. CANOCO Reference Manual and CanoDraw for Windows User’s Guide: Software for Canonical Community Ordination; Version 4.5; Microcomputer Power: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, M.O.; Gauch, H.G. Detrended correspondence analysis: An improved ordination technique. Vegetation 1980, 42, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, T.W.; Bullerjahn, G.S.; Tuttle, T.; McKay, R.M.; Watson, S.B. Effects of increasing nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations on phytoplankton community growth and toxicity during Planktonic blooms in Sandusky bay, Lake Erie. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 7197–7207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheffer, M.; Carpenter, S.R. Catastrophic regime shifts in ecosystems: Linking theory to observation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2003, 18, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozimek, T.; Gulati, R.D.; van Donk, E. Can macrophytes be useful in bio manipulation of lakes? The Lake Zwemlust example. Hydrobiologia 1990, 200, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, C.M. Nutrient concentration of aquatic plants: Patterns across species. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1992, 37, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkler Ferreira, T. The Role of Submerged Macrophytes on the Dynamics of Shallow Subtropical Lakes: The Importance for Restoration and Conservation of Lake Mangueira, Southern Brazil. Ph.D. Thesis, Instituto de Pesquisas Hidráulicas, Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Sul, Porto Alegre, Brazil, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter, S. Submersed vegetation: An internal factor in Lake Ecosystem succession. Am. Nat. 1981, 118, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudley, B.; Dunbar, M.; Penning, E.; Kolada, A.; Hellsten, S.; Oggioni, A.; Bertrin, V.; Ecke, F.; Søndergaard, M. Measurements of uncertainty in macrophytemetrics used to assess European lake water quality. Hydrobiologia 2013, 704, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Yu, Z.; Luo, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, X. Spatial and temporal variations in the relationship between lake water surface temperatures and water quality—A case study of Dianchi Lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 624, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolada, A. The effect of lake morphology on aquatic vegetation development and changes under the influence of eutrophication. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 38, 282–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.Z.; Song, X.L.; Hu, Y.H.; Liu, Z.W.; Qin, B.Q. Water quality improvement and response of the phytoplankton community at the ecological engineering area in the drinking water source in Meiliang Bay of Lake Taihu. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 1637–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilt, S.; Köhler, J.; Adrian, R.; Monaghan, M.T.; Sayer, C.D. Clear, crashing, turbid and back –long-term changes of macrophyte assemblages in a shallow lake. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 2027–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gürel, M.; Tanik, A.; Russo, R.C.; Gönenç, I.E. Biogeochemical cycles. In Coastal Lagoons: Ecosystem Processes and Modelling for Sustainable Use and Development; Gönenç, I.E., Woln, J.P., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Roton, FL, USA, 2005; pp. 79–192. [Google Scholar]
- Lacoul, P.; Freedman, B. Environmental influences on aquatic plants in freshwater ecosystems. Environ. Rev. 2006, 14, 89–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bando, F.M.; Michelan, T.S.; Cunha, E.R.; Figueiredo, B.R.S.; Thomaz, S.M. Macrophyte species richness and composition are correlated with canopy openness and water depth in tropical floodplain lakes. Braz. J. Bot. 2015, 38, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-Villamizar, E.A.; Piedade, M.T.F.; Da Costa, J.G.; Adeney, J.M.; Junk, W.J. Chemistry of different Amazonian water types for river classification: A preliminary review. WIT Trans. Ecol. Environ. 2013, 178, 17–28. [Google Scholar]
- Jakhar, P. Role of phytoplankton and zooplankton as health indicators of aquatic ecosystem (a review). Int. J. Innov. Res.Stud. 2013, 2, 490–500. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.S.; Uddin, S.; Haque, M.A. Abundance and composition of zooplankton at Sitakunda coast of Chittagong, Bangladesh. Res. Agric. Livest. Fish. 2015, 2, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Khanna, D.R.; Bhutiani, R.; Gagan, M.; Ginh, V.; Kumar, D.; Ahraf, J. A study of zooplankton with special reference to the concentration of River Ganga at Haridwar. Environ. Conserv. J. 2009, 10, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisan, G.V.; Forsberg, B.R. Relationships among nitrogen and total phosphorus, algal biomass and zooplankton density in the central Amazonia lakes. Hydrobiologia 2007, 586, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, M.; Mukherjee, J.; Banerjee, A.; Roy, M.; Bandyopdhyay, G.; Ray, S. Impact of environmental factors on maintaining water quality of Bakreswar reservoir, India. Comput. Ecol. Softw. 2015, 5, 239–253. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, B.S.R.V.; Srinivasu, P.D.N.; Varma, P.S.; Raman, A.V.; Ray, S. Dynamics of dissolved oxygen in relation to saturation and health of an aquatic body: A case for Chilka Lagoon. India. J. Ecosyst. 2014, 2014, 526245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, B.K.; Kalff, J.; Pinel-Alloul, B. The influence of macrophyte beds on plankton communities and their export from fluvial lakes in the St. Lawrence River. Freshw. Biol. 2000, 45, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norlin, J.I.; Bayley, S.S.E.; Rosa, L.C.M. Submerged macrophyte, zooplankton and the predominance of low-over high chlorophyll states in western boreal shallow water wetland. Freshw. Biol. 2005, 50, 868–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Lu, X.T.; Pei, H.Y.; Hu, W.R.; Xie, J. Seasonal dynamics of phytoplankton and its relationship with the environmental factors in Dongping Lake, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 2627–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeppesen, E.; Søndergaard, M.; Søndergaard, M.; Christoffersen, K. The Structuring Role of Submerged Macrophytes in Lakes; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.Y.; Jeong, K.S.; La, G.H.; Kim, S.K.; Goo, G.J. Sustainment of epiphytic microinvertebrates’ assemblage in relation with different aquatic plant microhabitats in freshwater wetlands (South Korea). J. Limnol. 2014, 73, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakkilainen, K.T.; Kairesalo, J.; Hietala, D.M.; Balaya, E.; Cares, W.J.; Van De Bund, E.V.; Donk, A.M.; Fernandez, M.; Gyllstrom, L.A.; Hansson, M.R.; et al. Response of zooplankton to nutrient enrichment and fish in shallow Lakes.Apan-European mesocosm experiment. Freshw. Biol. 2004, 49, 1619–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shabrawy, G.M.; Dumont, H.J. Spatial and seasonal variation of the zooplankton in the coastal zone and main khors of Lake Nasser (Egypt). Hydrobiologia 2003, 491, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Difonzo, C.D.; Campbell, J.M. Spatial partitioning of microhabitats in littoral cladoceran communities. J. Freshw. Ecol. 1988, 4, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolle, A.; Hallgren, P.; Von Einem, J.; Kritzberg, E.S.; Granéli, W.; Persson, A.; Brönmark, C.; Hansson, L. Predicted warming and browning affect timing and magnitude of plankton phenological events in lakes: A mesocosm study. Freshw. Biol. 2012, 57, 684–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazzanelli, M.; Warming, T.P.; Christoffersen, K.S. Emergent and floating-leaved macrophytes as refuge for zooplankton in a eutrophic temperate lake without submerged vegetation. Hydrobiologia 2008, 605, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radke, R.; Kald, U. Effects of a filter-feeding fish (silver carp, Hypophthalmicthys molitrix (Val.)) on phyto- and zooplankton in a mesotrophic reservoir: Results from an enclosure experiment. Freshw. Biol. 2002, 47, 2337–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, J. Associations of planktonic and periphytic in a tropical swamp, the Okavango Delta, Southern Africa. Hydrobiologia 2003, 490, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amundsen, P.A.; Siwertsson, A.; Primicerio, R.; Bøhn, T. Long-term responses of zooplankton to invasion by a planktivorous fish in a subarctic watercourse. Freshw. Biol. 2009, 54 (Suppl. S1), 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meerhoff, M.C.; Iglesias, F.T.; De Mello, J.M.; Clemente, E.; Jensen, T.L.; Lauridsen, E. Jeppesen Effects of habitat complexity on community structure and predator avoidance behaviour of littoral zooplankton in temperate versus subtropical shallow lakes. Freshw. Biol. 2007, 52, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, E.V.; Lópea, C.M. Zooplankton community composition and some limnological aspects of an oxbow lake of the Paraopeba River, São Francisco River Basin, Minas Gerais. Braz. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2000, 43, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Wu, L. Enhancement of Moina micrura by the filter-feeding silver and bighead carps in a subtropical Chinese lake. Arch. Hydrobiol. 2002, 154, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, C.; Goyenola, G.; Mazzeo, N.; Meerhoff, M.; Rodó, E.; Jeppesen, E. Horizontal dynamics of zooplankton in subtropical Lake Blanca (Uruguay) hosting multiple zooplankton predators and aquatic plant refuges. Hydrobiologia 2007, 584, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrantuono, L.; Mancinelli, T. Littoral invertebrates associated with aquatic plants and bioassessement of ecological status in Lake Bracciano (Central Italy). J. Limnol. 2005, 64, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burks, R.L.; Jeppesen, E.; Lodge, D.M. Littoral zone structures as Daphnia refuge against fish predators. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2001, 46, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hann, B.J. Invertebrates associations with submersed aquatic plants in a prairie wetland. USF (Delta Marsh) Annu. Rep. 1995, 30, 78–84. [Google Scholar]
- Sakuma, M.; Hanazato, T.; Nakazato, R. Methods for quantitative sampling of epiphytic microinvertebrates in lake vegetation. Limnology 2002, 3, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennie, M.D.; Jackson, L.J. The influence of habitat complexity on littoral invertebrate distributions: Patterns differ in shallow prairie lakes with and without fish. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2005, 62, 2088–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brucet, S.D.; Boix, S.; Gasco’n, J.; Sala, X.D.; Quintana, A.; Badosa, M.; Søndergaard, T.; Lauridsen, L.; Jeppesen, E. Species richness of crustacean zooplankton and trophic structure of brackish lagoons in contrasting climate zones: North temperate Denmark and Mediterranean Catalonia (Spain). Ecography 2009, 32, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, M.G.; Underwood, A.J.; Hochuli, D.F.; Coleman, R.A. Independent effects of patch size and structural complexity on diversity of benthic macroinvertebrates. Ecology 2010, 91, 1908–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rougier, C.; Pourriot, R.; Lam-Hoai, T.; Guiral, D. Ecological patterns of the communities in the Kaw River estuary (French Guiana). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2005, 63, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tews, J.; Brose, U.; Grimm, V.; Tielbörger, K.; Wichmann, M.C.; Schwager, M.; Jeltsch, F. Animal species diversity driven by habitat heterogeneity/diversity: The importance of keystone structures. J. Biogeogr. 2004, 31, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ailstock, M.S.; Norman, C.M.; Bushmann, P.J. Common reed Phragmites australis: Control and effects upon biodiversity in freshwater nontidal wetlands. Restor. Ecol. 2001, 9, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variables | Site 1 | Site 2 | Site 3 | Site 4 | Site 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TN (mg L−1) | 1.85 ± 0.49 * | 1.68 ± 0.67 * | 1.3 ± 0.29 * | 0.71 ± 0.55 * | 1.06 ± 0.84 * |
| NO3-N (mg L−1) | 1.32 ± 0.25 | 0.113 ± 0.32 * | 0.12 ± 0.015 * | 0.037 ± 0.031 * | 0.059 ± 0.03 ** |
| NH4-N ((mg L−1 | 0.718 ± 0.231 * | 0.077 ± 0.055 * | 0.0117 ± 0.12 * | 0.017 ± 0.156 * | 0.039 ± 0.03 * |
| TP (mg L−1) | 0.146 ± 0.145 * | 0.036 ± 0.033 * | 0.028 ± 0.035 * | 0.018 ± 0.002 * | 0.107 ± 0.015 * |
| WT (°C) | 31.7 ± 1.53 * | 28.6 ± 0.15 * | 25.4 ± 0.5 | 19.9 ± 1.762 ** | 22.13 ± 0.59 * |
| EC (µS cm−3) | 190 ± 0.53 ** | 164.9 ± 13.6 * | 128.5 ± 0.96 | 114.9 ± 0.31 ** | 185.3 ± 32.3 * |
| SD (m) | 0.417 ± 0.202 * | 27.9 ± 4.02 | 53. ± 3.05 * | 64.7 ± 10.02 * | 69 ± 9.8 * |
| Chl.a (µg L–l) | 14.08 ± 2.72 * | 4.24 ± 1.24 | 4.25 ± 0.69 ** | 2.56 ± 2.74 ** | 4.56 ± 1.49 * |
| Trub (NTU) | 66.87 ± 7.2 | 15.67 ± 2.8 * | 9.4 ± 1.72 * | 5.38 ± 0.8 * | 24.13 ± 1.06 |
| DO (mg L−1) | 4.67 ± 0.038 | 9.54 ± 1.42 * | 6.75 ± 2.4 ** | 8.24 ± 1.7 | 6.16 ± 0.051 ** |
| pH | 5.98 ± 1.54 * | 3.48 ± 0.42 | 7.31 ± 1.31 * | 7.62 ± 0.04 | 6.75 ± 0.19 |
| WD (m) | 0.92 ± 0.854 * | 3.97 ± 0.73 | 8.41 ± 0.50 * | 1.52 ± 0.05 * | 2.9 ± 0.035 |
| Site 1 | Site 2 | Site 3 | Site 4 | Site 5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rotifer | 40 | 30 | 45 | 76 | 39 |
| Copepods | 16 | 17 | 24 | 47 | 30 |
| Cladocera | 42 | 30 | 64 | 98 | 37 |
| Total zooplankton biomass | 102 | 128 | 335 | 385 | 341 |
| Axes | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | Total Variance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eigenvalues | 0.572 | 0.378 | 0.038 | 0.011 | 1.000 |
| Species–environment correlations | 0.962 | 0.902 | 0.952 | 0.867 | |
| Cumulative percentage variance of species data | 57.2 | 69.1 | 89.6 | ||
| Cumulative percentage variance of species–environment relation | 74.5 | 83.9 | 86.4 | 97.5 | |
| Sum of all eigenvalues | 1.000 | ||||
| Sum of all canonical eigenvalues | 0.879 |
| Phylum | Family | Genera | Species |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rotifer | Brachionidae | Anuraeopsis | Anuraeopsis fissa (Gosse, 1851) |
| Gastopodidae | Ascomorpha | Ascomorpha ecaudis (Perty, 1850) | |
| Ascomorpha ovalis (Bergendal, 1892) | |||
| Asphalnchnidae | Aspalnchna | Aspalnchna brightwellii (Gosse, 1850) | |
| Asplanchna girodi (Guerne, 1888) | |||
| Barchionidae | Barchionus | Barchionus angularis(Gosse, 1851) | |
| Barchionus forficula (Wierzejski, 1891) | |||
| Brachionus calyciflorus(Pallas, 1766) | |||
| Brachionus caudatus (Barrois & Daday, 1894) | |||
| Brachionus falcatus (Zacharias, 1898) | |||
| Brachionus forficula(Wierzejski, 1891) | |||
| Brachionus leydigi (Cohn, 1862) | |||
| Brachionus patulus (Müller, 1786) | |||
| Brachionus urceus (Pallas, 1766) | |||
| Notommatidae | Cephalodella | Cephalodella catellina (Müller, 1786) | |
| Collothecidae | Collotheca | Collotheca pelagica (Rousselet, 1893) | |
| Conochilidae | Conochilus | Conochilus unicornis (Rousselet, 1892) | |
| Euchlanidae | Euchlanis | Euchlanis dilatata (Ehrenberg, 1832) | |
| Filiniidae | Filinia | Filinia cornuta (Weisse 1847) | |
| Filina terminalis (Plate,1886) | |||
| Filinia longiseta (Ehrenberg, 1834) | |||
| Filinia passa (O.F. Muller, 1786) | |||
| Hexarthridae | Hexarthra | Hexarthra mira (Hudson, 1871) | |
| Brachionidae | Keratella | Keratella cochlearis (Gosse, 1851) | |
| Keratella quadrata (Müller, 1786) | |||
| Keratella serrulata (Ehrenberg, 1838) | |||
| Keratella tecta (Gosse, 1851) | |||
| Keratella valga(Ehrenberg, 1834) | |||
| Keratella tropica (Apstein, 1907) | |||
| Lapdellidae | Lapdella | Lapdella patella (Müller, 1773) | |
| Lecaniidae | Lecane Nitzsch | Lecane luna (Müller, 1776) | |
| Lecane closterocerca (Schmarda, 1859) | |||
| Lecane ludwigii (Eckstein, 1883) | |||
| Lecane ungulata (Gosse, 1887) | |||
| Lecane lunaris (Ehrenberg,1832) Lecane furcata (Murray, 1913) | |||
| Monostyla | Monostyla bulla (Gosse, 1851) | ||
| Monostyla copies (Harring & Myers, 1926) | |||
| Monostyla lunaris (Ehrenberg,1832) | |||
| Monostyla clostercerca (Schmarda, 1859) | |||
| Brachionidae | Notholca | Notholca accuminata (Ehrenberg,1832) | |
| Notholca caudate (Carlin, 1943) | |||
| Notholca labis (Gosse, 1886) | |||
| Notholca longispina (Kellicott, 1879) | |||
| Hexarthridae | Hexarthra Schmarda | Pedalia mira (Hudson, 1871) | |
| Synchaetidae | Ploesoma | Ploesoma hudsoni (Imhof, 1891) | |
| Ploesoma Herric | Ploesoma truncatum (Levander, 1894) | ||
| Polyarthra | Polyarthra euryptera (Wierzejski, 1891) | ||
| Testudinellidae | Pompholyx | Pompholyx sulcata (Hudson, 1885) | |
| Philodinidae | Rotaria Scopoli | Rotaria neptunia (Ehrenberg, 1832) | |
| Synchaetidae | Synchaeta Ehrenberg | Synchaeta stylata (Wierzejski, 1893) | |
| Synchaeta pectinata (Ehrenberg, 1832) | |||
| Trichocercidae | Trichocera | Trichocera pusilla (Jennings, 1903) | |
| Trichocercidae | Trichocera | Trichocerca longiseta (Schrank, 1802) | |
| Trichocerca similis (Wierzejski, 1893) | |||
| Trichocerca turnacata (Müller, 1776) | |||
| Trichocerca bicristata (Gosse, 1887) | |||
| Cyclopidae | Acanthocyclops Kiefer | Acanthocyclops robustus (Sars G.O., 1863) | |
| Macrothricidae | Acantholeberis Lillijborg | Acantholeberis curvirostris (O.F.Müller, 1776) | |
| Chydoridae | Alona | Alona affinis (Leydig, 1860) | |
| Cladocera | Alona baird | Alona bicolor (Frey, 1965) | |
| Alona costata (Sars, 1862) | |||
| Alona guttata (G.O. Sars, 1862) | |||
| Alona | Alona rectangular (G.O. Sars, 1862) | ||
| Alonella | Alonella exigua (Lilljeborg, 1853) | ||
| Alonella nana (Baird, 1843) | |||
| Alonopsis | Alonopsis americana (G.O. Sars, 1862) | ||
| Bosiminidae | Bosmina | Bosmina coregoni (Baird,1857) | |
| Bosmina fatalis (Burckhardt, 1924) | |||
| Bosmina longispina (Leydig, 1860) | |||
| Bosminopsis deitersi (Richard, 1895) | |||
| Bosmina longirostsis (O.F. Müller, 1785) | |||
| Daphniidae | Ceriodaphnia | Ceriodaphnia cornuta (G.O. Sars, 1885) | |
| Ceriodaphnia dubia (Richard, 1894) | |||
| Ceriodaphnia laticaudata (P.E.Müller, 1867) | |||
| Ceriodaphnia cornuta (G.O. Sars, 1885) | |||
| Ceriodaphnia longispina (O.F. Müller, 1776) | |||
| Ceriodaphnia quadrangula (O.F. Müller, 1785) | |||
| Chydoridae | Chydorus | Chydorus sphaericus (O.F. Müller, 1776) | |
| Chydrous latus (Sars, 1862) | |||
| Chydorus bicornutus (Doolitle, 1909) | |||
| Daphniidae | Daphnia | Daphnia cucculata (G.O. Sars, 1862) | |
| Daphnia duplex (Leydig, 1860) | |||
| Daphnia galeata (Sars, 1864) | |||
| Daphnia longispina (O.F. Müller, 1776) | |||
| Daphnia magna (Straus, 1820) | |||
| Daphnia Sarsi (O.F.Müller, 1785) | |||
| Daphnia dubia (Herrick, 1883) | |||
| Sididae | Daphinosoma | Diaphanosoma brachyurum (Liévin, 1848) | |
| Diaphniidae | Diaphnia | Diaphina pulex (Leydig, 1860) | |
| Daphnia carinata (King, 1853) | |||
| Eurycercidae | Eurycercus | Eurycercus lamellatus (O.F.Müller, 1776) | |
| Chydoridae | Kurzia | Kurzia latissima (Kurz, 1875) | |
| leptodoridae | leptodora | Leptodora kindtii (Focke, 1844) | |
| Chydoridae | Leydigia | Leydigia acanthocercoides (Fischer, 1854) | |
| Moinidae | Moina | Moina affinis (Birge, 1893) | |
| Moina micura (Kurz, 1875) | |||
| Chydoridae | Peluroxus | Pleuroxus trigonellus (O.F.Müller, 1776) | |
| Barchionidae | Platyias | Platyias quadricornis (Ehrenberg, 1832) | |
| Chydoridae | Pleuroxus | Picripleuroxus denticulatus (Birge, 1879) | |
| Pleuroxus hamulatus (Birge, 1879) | |||
| Pleuroxus striatus (Schödler, 1862) | |||
| Pleuroxus trigonellus (O.F.Müller, 1776) | |||
| Daphniidae | Scapholeberis | Scapholeberis mucronata (O.F.Müller, 1776) | |
| Sididae | Sida | Sida crystallina (O.F.Müller, 1776) | |
| Daphniidae | Simnocephalus | Simocephalus vetulus (O.F.Müller, 1776) | |
| Simocephalus serrulatus (Koch, 1841) | |||
| Cyclopidae | Acanthocyclops | Acanthocyclops vernalis (Fischer, 1853) | |
| Acanthocyclops formosanus (Harada, 1931) | |||
| Copepods | Canthocamptidae | Afrocamptus | Canthocamptus (Westwood, 1836) |
| Cyclopidae | Cyclops Müller | Cyclops strenuus (Fischer, 1851) | |
| Cyclops vicinus (Ulyanin, 1875) | |||
| Cyclops | Eucyclops elegans (Herrick, 1884) | ||
| Eucyclops serrulatus (Fischer, 1851) | |||
| Eucyclops agilisEucyclops agilis (Koch, 1838) | |||
| Eucyclops macruroides (Lilljeborg, 1901) | |||
| Temoridae | Eurythemora Giesbrecht | Eurytemora affinis (Poppe, 1880) | |
| Cyclopidae | Homocyclops Forbes | Homocyclops ater (Herrick,1882) | |
| Diaptomidae | Leptodiaptomus Light | Leptodiaptomus minutus (Lilljeborg, 1889) | |
| Centropagidae | Limnocalanus m | Limnocalanus macrurus (Sars G.O., 1863) | |
| Diaptomidae | Acanthodiaptomus Kiefer | Leptodiaptomus sicilis (Forbes S.A., 1882) | |
| Macrocyclops | Macrocyclops albidus (Jurine, 1820) | ||
| Macrocyclops distinctus (Richard, 1887) | |||
| Mesocyclops | Mesocyclops leuckarti (Claus, 1857) | ||
| Mesocyclops ogunnus (Sars G.O.1914) | |||
| Microcyclops javanus (Kiefer, 1930) | |||
| Microcyclops | Microcyclops vericanas (Sars G.O., 1863) | ||
| Nannopodidae | Nannopus | Nannopus palustris (Brady, 1880) | |
| Laophontidae | Onychocamotus | Onychocamptus mohammed (Blanchard & Richard, 1891) | |
| Cyclopidae | Orthocyclops | Orthocyclops modusta (Herrick, 1883) | |
| Paracyclops | Paracyclops affinis (Sars G.O., 1863) | ||
| Pseudodiaptomidae | Archiaptomus | Schmackeria inopinus (Burckhardt, 1913) | |
| Centropagidae | Sinocalanus | Sinocalanus doerrii (Berhm.1909) | |
| Diaptomidae | Sinodiaptomus | Sinodiaptomus sarsi (Rylov, 1923) | |
| Skistodiaptomus | Skistodiaptomus oregonensis (Lilljeborg in Guerne and Richard, 1889) | ||
| Mesocyclops | Thermocyclops brevifurcatus (Harada, 1931) | ||
| Cyclopidae | Thermocyclops | Thermocyclops minutus (Lowndes, 1934) | |
| Thermocyclops neglectus (Sars G.O., 1909) | |||
| Thermocyclops taihokuensis (Harada, 1931) | |||
| Cyclopidae | Thermocyclops | Thermocyclops vermifer (Lindberg, 1935) | |
| Thermodiaptomus | Thermodiaptomus galebi (Barrois, 1891) | ||
| Tropocyclops | Tropocyclops prasinus (Fischer, 1860) |
| Response Variables | Explanatory Variables | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | DO | EC | pH | Chla. | WD | SCh. | TN | NO3-N | NH4-N | TP | TUB | ||
| RoH | Coef. | 9.28 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | −42.7 | - |
| S.E. | 0.573 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 10 | - | |
| T-value | 17.14 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | −4.26 | - | |
| p-value | 0.037 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | −0.024 | - | |
| RoB | Coef. | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| S.E. | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| T-value | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| p-value | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| ClH | Coef. | - | - | - | - | - | −6.316 | - | - | 0.2514 | −9.366 | - | - |
| S.E. | - | - | - | - | - | 0.09 | - | - | 0.013 | 0.156 | - | - | |
| T-value | - | - | - | - | - | −70.18 | - | - | 22.17 | −60.17 | - | - | |
| p-value | - | - | - | - | - | 0.009 | - | - | 0.029 | 0.011 | - | - | |
| ClB | Coef. | - | - | 0.229 | - | 1.6613 | - | - | - | −16.588 | - | - | - |
| S.E. | - | - | 0.009 | - | 0.0205 | - | - | - | 0.0285 | - | - | - | |
| T-value | - | - | 238.8 | - | 81.01 | - | - | - | −581.36 | - | - | - | |
| p-value | - | - | 0.003 | - | 0.008 | - | - | - | 0.001 | - | - | - | |
| CoH | Coef. | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| S.E. | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| T-value | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| p-value | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| CoB | Coef. | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | −7.25 | - | - | - |
| S.E. | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 1.94 | - | - | - | |
| T-value | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | −3.74 | - | - | - | |
| p-value | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.033 | - | - | - | |
| TZH | Coef. | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| S.E. | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| T-value | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| p-value | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | ||
| TZB | Coef. | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | −7.609 | - | - | - |
| S.E. | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.0857 | - | - | - | ||
| T-value | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | −88.7 | - | - | - | |
| p-value | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.007 | - | - | - | |
| Zooplaknton Taxa | Environmental Variables | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | DO | EC | pH | Chla. | WD | SCh. | TN | NO3-N | NH4-N | TP | TUB | |
| Rotifer (ind L−1) | −0.836 | 0.439 * | −0.374 * | −0.825 ** | 0.415 * | −0.122 | 0.132 * | 0.510 * | −0.671 * | 0.185 * | −0.109 | 0.158 |
| Copepod (ind L−1) | 0.215 * | 0.763 ** | 0.89 | 0.131 * | 0.182 | 0.432 * | 0.289 ** | 0.99 ** | 0.428 ** | 0.569 | 0.116 * | −0.789 * |
| Cladocera (ind L−1) | 0.326 * | 0.75 * | 0.56 * | 0.78 * | −0.265 | −0.419 * | −0.218 | −0.329 * | 0.295 | −0.625 ** | 0.356 | −0.861 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dibar, D.T.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, Z. Characteristics of the Zooplankton Community Structure in Shengjin Lake and Its Response to the Restored Aquatic Vegetation. Limnol. Rev. 2025, 25, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/limnolrev25010005
Dibar DT, Zhang K, Zhou Z. Characteristics of the Zooplankton Community Structure in Shengjin Lake and Its Response to the Restored Aquatic Vegetation. Limnological Review. 2025; 25(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/limnolrev25010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleDibar, Dagne Tafa, Kun Zhang, and Zhongze Zhou. 2025. "Characteristics of the Zooplankton Community Structure in Shengjin Lake and Its Response to the Restored Aquatic Vegetation" Limnological Review 25, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/limnolrev25010005
APA StyleDibar, D. T., Zhang, K., & Zhou, Z. (2025). Characteristics of the Zooplankton Community Structure in Shengjin Lake and Its Response to the Restored Aquatic Vegetation. Limnological Review, 25(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/limnolrev25010005






