Physicochemical and Microbial Quality of Water from the Ugandan Stretch of the Kagera Transboundary River
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
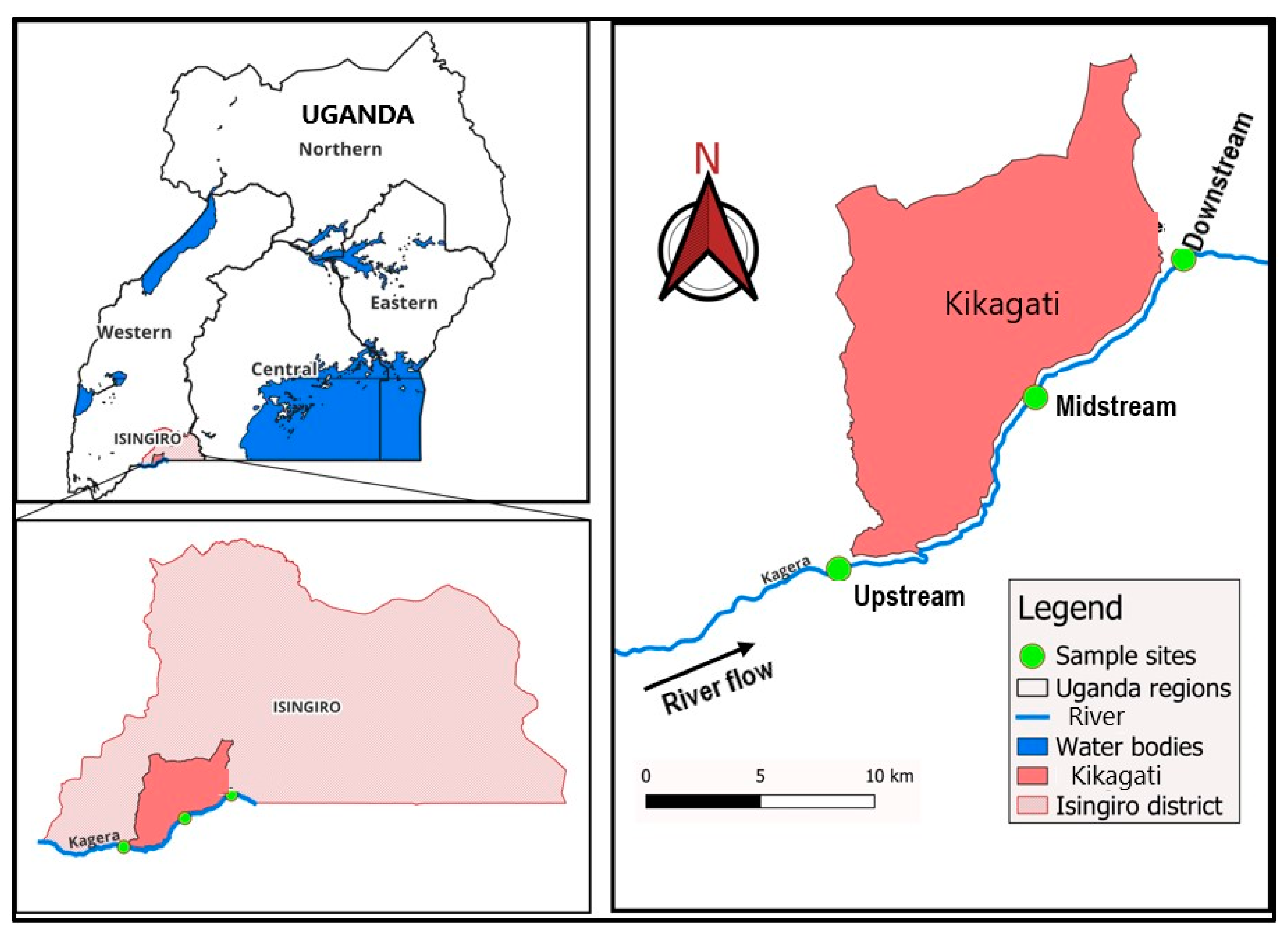
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Collection and Preparation of Samples
2.3. Measurement of Physicochemical Parameters of Water Samples
2.3.1. Temperature, Total Dissolved Solids, pH, Conductivity and Colour
2.3.2. Dissolved Oxygen and Biochemical Oxygen Demand
2.3.3. Total Alkalinity and Hardness
2.3.4. Chlorides
2.3.5. Total Phosphorous
2.3.6. Nitrates
2.3.7. Sulphates
2.4. Heavy Metal Analysis
2.5. Microbial Quality of the Water Samples
2.6. Analytical Quality Assurance and Quality Control
2.7. Statistical Analysis of Results
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Spatial Variations in the Physicochemical and Microbiological Quality of Surface Water from the Kagera River
3.1.1. pH
3.1.2. Electrical Conductivity
3.1.3. Temperature
3.1.4. Colour
3.1.5. Total Dissolved Solids and Turbidity
3.1.6. Dissolved Oxygen and Biochemical Oxygen Demand
3.1.7. Total Alkalinity
3.1.8. Total, Calcium and Magnesium Hardness
3.1.9. Nutrients (Nitrates and Phosphorous)
3.1.10. Chlorides and Sulphates Content
3.1.11. Microbial Profile of the Samples
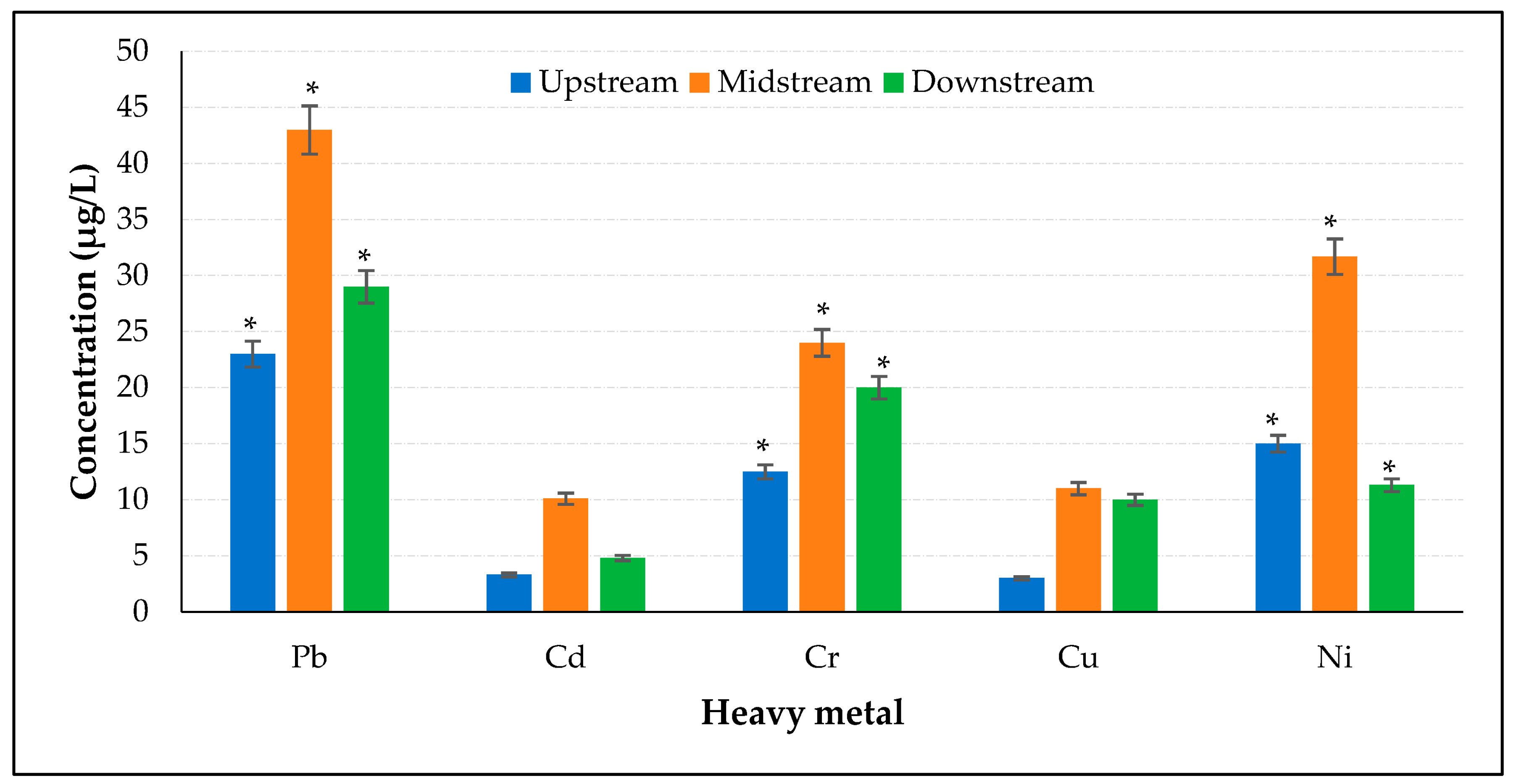
3.2. Spatial Variations in the Heavy Metal Content of the Surface Water Samples
3.2.1. Lead
3.2.2. Cadmium
3.2.3. Chromium
3.2.4. Copper
3.2.5. Nickel
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mugagga, F.; Nabaasa, B.B. The centrality of water resources to the realization of Sustainable Development Goals (SDG). A review of potentials and constraints on the African continent. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2016, 4, 215–223. [Google Scholar]
- International Science Council. UN 2023 Water Conference: ISC Policy Brief. 2023. Available online: https://council.science/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/ISC-Water-Policy-Brief.pdf (accessed on 16 October 2023).
- Fantini, E. An introduction to the human right to water: Law, politics, and beyond. WIREs Water 2020, 7, e1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogryzek, M. The Sustainable Development Paradigm. Geomat. Environ. Eng. 2023, 17, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boretti, A.; Rosa, L. Reassessing the projections of the World Water Development Report. npj Clean Water 2019, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, M.; Ma, Z.; Fang, W.; Bi, J. Quality matters: Pollution exacerbates water scarcity and sectoral output risks in China. Water Res. 2022, 224, 119059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcal, J.; Antizar-Ladislao, B.; Hofman, J. Addressing Water Security: An Overview. Sustainability 2021, 13, 13702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lürling, M.; Mucci, M. Mitigating eutrophication nuisance: In-lake measures are becoming inevitable in eutrophic waters in the Netherlands. Hydrobiologia 2020, 847, 4447–4467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN Water. Blueprint for Acceleration: Sustainable Development Goal 6 Synthesis Report on Water and Sanitation 2023. Available online: https://www.unwater.org/sites/default/files/2023-08/UN-Water_SDG6_SynthesisReport_2023.pdf (accessed on 16 October 2023).
- IUCN. Navigating Transboundary Waters in Eastern and Southern Africa. 2023. Available online: https://www.iucn.org/story/202306/navigating-transboundary-waters-eastern-and-southern-africa (accessed on 16 October 2023).
- Springuel, I.; Ali, O. The River Nile basin. In The World’s Largest Wetlands: Ecology and Conservation; Fraser, L., Keddy, P., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005; pp. 347–392. [Google Scholar]
- Semyalo, R. Deterioration of Lake Victoria: The Price of Inaction. 2021. Available online: https://ideas4development.org/en/lake-victoria-ecosystem/ (accessed on 16 October 2023).
- Okechi, J.K.; Peoples, N.; Nyamweya, C.S.; Glaser, S.; Kaufman, L. The ecological health of Lake Victoria (Kenya) in the face of growing cage aquaculture. Conserv. Sci. Pract. 2022, 4, e12826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosnjakovic, B. UN/ECE Strategies for Protecting the Environment with Respect to International Watercourses. The Helsinki and Espoo Conventions. 2001, pp. 47–50. Available online: https://unece.org/DAM/env/water/cwc/legal/UNECEstrategies_bosnjakovic.pdf (accessed on 16 October 2023).
- Nshimiyimana, F.; Nhapi, I.; Wali, U.G.; Nsengimana, H.; Banadda, N.; Nansubuga, I.; Kansiime, F. Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution in a Trans-Boundary River: The Case of the Akagera River. Int. J. Math. Comput. 2010, 9, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Wali, U.G.; Nhapi, I.; Ngombwa, A.; Banadda, N.; Nsengimana, H.; Kimwaga, R.J.; Nansubuga, I. Modelling of Nonpoint Source Pollution in Akagera Transboundary River in Rwanda. Open Environ. Eng. J. 2011, 4, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munyaneza, O.; Ndayisaba, C.; Wali, U.G.; Mulungu, D.M.M.; Dulo, S.O. Integrated Flood and Drought Management for Sustainable Development in the Kagera River Basin. Nile Basin Water Sci. Eng. J. 2011, 4, 60–70. [Google Scholar]
- Stanley, H.M. Through the Dark Continent; G. Newnes: London, UK, 1899; 566p. [Google Scholar]
- Nteziyaremye, P.; Omara, T. Bioaccumulation of priority trace metals in edible muscles of West African lungfish (Protopterus annectens Owen, 1839) from Nyabarongo River, Rwanda. Cogent Environ. Sci. 2020, 6, 1779557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demhardt, I.J. German contributions to the cartography of South West and East Africa from Mid-19th Century to World War I. In Proceedings of the 21st International Cartographic Conference (ICC), Durban, South Africa, 10–16 August 2003; Available online: https://icaci.org/files/documents/ICC_proceedings/ICC2003/Papers/110.pdf (accessed on 15 October 2023).
- Mbabazi, J.; Kwetegyeka, J.; Ntale, M.; Wasswa, J. Ineffectiveness of Nakivubo wetland in filtering out heavy metals from untreated Kampala urban effluent prior to discharge into Lake Victoria, Uganda. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2010, 5, 3431–3439. [Google Scholar]
- Bungane, B. Uganda: $270m Approved for Kikagati Hydropower Plant. 2019. Available online: https://www.esi-africa.com/industry-sectors/generation/uganda-27m-approved-for-kikagati-hydropower-plant/ (accessed on 17 May 2023).
- FMO. Kikagati Power Company Ltd. 2017. Available online: https://www.fmo.nl/project-detail/52073 (accessed on 14 October 2023).
- Kushaba, A. Isingiro Historical Cave in RuinsIsingiro Historical Cave in Ruins. Available online: https://ugandaradionetwork.net/story/isingiro-historical-cave-in-ruins-?districtId=545 (accessed on 28 September 2023).
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Waste Water, 22nd ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA; American Water Works Association: Denver, CO, USA; Water Environment Federation: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kanadhia, K.C.; Ramavataram, D.V.; Nilakhe, S.P.; Patel, S. A study of water hardness and the prevalence of hypomagnesaemia and hypocalcaemia in healthy subjects of Surat district (Gujarat). Magnes. Res. 2014, 27, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangiah, A.S. Spectrophotometric determination of sulphate and nitrate in drinking water at Asia-Pacific International University Campus, Muak Lek, Thailand. Rasayan J. Chem. 2019, 12, 1503–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; Incorporating the 1st Addendum; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- UNBS. US EAS 12:2014. Potable Water—Specification. Available online: https://webstore.unbs.go.ug/store.php?src=10&preview (accessed on 17 May 2023).
- Hussner, A.; Mettler-Altmann, T.; Weber, A.P.M.; Sand-Jensen, K. Acclimation of photosynthesis to supersaturated CO2 in aquatic plant bicarbonate users. Freshw. Biol. 2016, 61, 1720–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yartsev, A. Neutrality and the Influence of Temperature and Pressure on pH. 2015. Available online: https://derangedphysiology.com/main/cicm-primary-exam/required-reading/acid-base-physiology/Chapter%20114/neutrality-and-influence-temperature-and-pressure-ph (accessed on 17 May 2023).
- Matta, G. A study on physico-chemical Characteristics to assess the pollution status of river Ganga in Uttarakhand. J. Health Pop. Nutr. 2014, 7, 210–217. [Google Scholar]
- Mukisa, W.; Yatuha, J.; Andama, M.; Aventino, K. Heavy metal pollution in the main rivers of Rwenzori region, Kasese district South-western Uganda. Octa J. Environ. Res. 2020, 8, 078–090. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, O.; Wasswa, J.; Nakiguli, C.K.; Ntambi, E. Spatial Variation in Physicochemical Surface Water Quality in River Rwizi, Western Uganda. J. Water Res. Protect. 2019, 4, 1427–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lema, M.W.J.; Mwegoha, W.J.S. Assessment of surface water quality near municipal Solid Waste dumping facility in Bukoba, Kagera Region, Tanzania. Environ. Qual. Manag. 2023, 32, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikuku, M. Association of Heavy Metal Tolerance with Multiple Antibiotic Resistance in Bacteria Isolated from Wetlands of Lake Victoria Basin Kenya. Master’sThesis, Kenyatta University, Nairobi, Kenya, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Omara, T.; Nteziyaremye, P.; Akaganyira, S.; Opio, D.W.; Karanja, L.N.; Nyangena, D.M.; Kiptui, B.J.; Ogwang, R.; Epiaka, S.M.; Jepchirchir, A.; et al. Physicochemical quality of water and health risks associated with consumption of African lung fish (Protopterus annectens) from Nyabarongo and Nyabugogo rivers, Rwanda. BMC Res. Notes 2020, 13, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatanga, P.; Ntuli, V.; Mugomeri, E.; Keketsi, T.; Chikowore, N.V.T. Situational analysis of physico-chemical, biochemical and microbiological quality of water along Mohokare River, Lesotho. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2019, 45, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochieng, H.; Dong, R.O.; Okot-Okumu, J. Comparison of temperate and tropical versions of Biological Monitoring Working Party (BMWP) index for assessing water quality of River Aturukuku in Eastern Uganda. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 23, e01183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busulwa, H.S.; Bailey, R.G. Aspects of the physico-chemical environment of the Rwenzori rivers, Uganda. Afr. J. Ecol. 2004, 42, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masereka, J.; Byamugisha, D.; Adaku, C. Physicochemical Quality and Health Risks Associated with Use of Water from Nyamwamba River, Kasese, Western Uganda. Asian J. Appl. Chem. Res. 2022, 12, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 3rd ed.; Volume 1—Recommendations Incorporating the First and Second Addenda; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008; Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241547611 (accessed on 13 October 2023).
- Butu, A.W.; Emeribe, C.N.; Muoka, I.O.; Emeribe, O.F.; Ogbomida, E.T. Downstream Effects of Industrial Effluents Discharge on Some Physicochemical Parameters and Water Quality Index of River Rido, Kaduna State, Nigeria. Trop. Aqua. Soil Pollut. 2022, 2, 90–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bwire, G.; Sack, D.A.; Kagirita, A.; Obala, T.; Debes, A.K.; Ram, M.; Komakech, H.; George, C.M.; Orach, C.G. The quality of drinking and domestic water from the surface water sources (lakes, rivers, irrigation canals and ponds) and springs in cholera prone communities of Uganda: An analysis of vital physicochemical parameters. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turinayo, Y.K. Physicochemical Properties of Sugar Industry and Molasses Based Distillery Effluent and its Effect on Water Quality of River Musamya in Uganda. Int. J. Environ. Agric. Biotechnol. 2017, 2, 1064–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.S.; Kimirei, I.A.; Yu, C.; Shen, Q.; Gao, Q. Assessment of urban river water pollution with urbanization in East Africa. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 40812–40825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkurunziza, G.; Omara, T.; Nakiguli, C.K.; Mukasa, P.; Byamugisha, D.; Ntambi, E. Physicochemical Quality of Water from Chuho Springs, Kisoro District, Uganda. Fr.-Ukr. J. Chem. 2021, 09, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olajire, A.A.; Imeokparia, F.E. Water Quality Assessment of Osun River: Studies on Inorganic Nutrients. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2001, 69, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palamuleni, L.; Akoth, M. Physico-Chemical and Microbial Analysis of Selected Borehole Water in Mahikeng, South Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 8619–8630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reda, A.H. Physico-Chemical Analysis of Drinking Water Quality of Arbaminch Town. J. Environ. Anal. Toxicol. 2016, 6, 356. [Google Scholar]
- Opolot, M.; Omara, T.; Adaku, C.; Ntambi, E. Spatio-temporal Variations and Potential Health Risks of Heavy Metals in Water from River Manafwa, Uganda. Lett. Appl. NanoBioSci. 2024, 13, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Amare, G.; Dobo, B.; Haile, E. The Effect of Wet Coffee Processing Plant Effluent on Physicochemical and Bacteriological Quality of Receiving Rivers Used by Local Community: Case of Aroresa District, Sidama, Ethiopia. Environ. Health Insights 2023, 17, 11786302231165186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhateria, R.; Jain, D. Water quality assessment of lake water: A review. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2016, 2, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saalidong, B.M.; Aram, S.A.; Otu, S.; Lartey, P.O. Examining the dynamics of the relationship between water pH and other water quality parameters in ground and surface water systems. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0262117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, N.H. Water Quality Parameters. In Water Quality—Science, Assessments and Policy; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Water Stewardship Information Series. 2007. Hardness in Groundwater. Available online: https://www.rdn.bc.ca/cms/wpattachments/wpID2284atID3802.pdf (accessed on 16 October 2023).
- Egor, M.; Mbabazi, J.; Ntale, M. Heavy metal and nutrient loading of River Rwizi by effluents from Mbarara Municipality, Western Uganda. Int. J. Chem. Mater. Res. 2014, 2, 36–47. [Google Scholar]
- Crawford, M.D. Hardness of drinking-water and cardiovascular disease. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 1972, 31, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, D.; Dini, F.L.; Azzarelli, A.; Giaconi, A.; Volterrani, C.; Lunardi, M. Sudden cardiac death rate in an area characterized by high incidence of coronary artery disease and low hardness of drinking water. Angiology 1995, 46, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vincenzo, F.; Puca, P.; Lopetuso, L.R.; Petito, V.; Masi, L.; Bartocci, B.; Murgiano, M.; De Felice, M.; Petronio, L.; Gasbarrini, A.; et al. Bile Acid-Related Regulation of Mucosal Inflammation and Intestinal Motility: From Pathogenesis to Therapeutic Application in IBD and Microscopic Colitis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Hardness in Drinking-Water: Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kabenge, M.; Wang, H.; Li, F. Urban eutrophication and its spurring conditions in the Murchison Bay of Lake Victoria. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzan, L.W.; Shimizu, K. Metabolic regulation of Escherichia coli and its phoB and phoR genes knockout mutants under phosphate and nitrogen limitations as well as at acidic condition. Microb. Cell Factories 2011, 10, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A. Effects of Wastewater Discharge on Fresh Water Quality in Dar es Salaam: A Case of Msimbazi River. Master’s Dissertation, The Open University of Tanzania, Dar es Salaam, Tanzania, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Businge, F.; Kagoya, S.; Omara, T.; Angiro, C. Pollution of Mpanga River by Kabundaire Abattoir Effluents, Fort Portal Tourism City, Uganda. Asian J. Fish. Aquat. Res. 2021, 11, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angiro, C.; Abila, P.P.; Omara, T. Effects of industrial effluents on the quality of water in Namanve stream, Kampala Industrial and Business Park, Uganda. BMC Res. Notes 2020, 13, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juhna, T.; Birzniece, D.; Rubulis, J. Effect of Phosphorus on survival of Escherichia coli in drinking water biofilms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 3755–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. E. coli . 2018. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/e-coli (accessed on 16 October 2023).
- Uganda Investment Authority. Mineral Sector Profile. Available online: https://www.ugandainvest.go.ug/uia/images/Download_Center/SECTOR_PROFILE/Mining_Sector_Profile.pdf (accessed on 28 September 2023).
- Nalubwama, B. New Road Opens Up Kikagati’s Tin to the Outside World. Available online: https://sunrise.ug/news/201909/new-road-opens-up-kikagatis-tin-to-the-outside-world.html (accessed on 28 September 2023).
- Turyahabwa, S.; Jurua, E.; Oriada, R.; Mugaiga, A.; Ben Enjiku, D.D. Determination of natural radioactivity levels due to mine tailings from selected mines in Southwestern Uganda. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 6, 154–163. [Google Scholar]
- Ahabwe, C. Gender Effect on Banana Production in Kikagati subcounty Isingiro district. Bachelor’s Thesis, Makerere University, Kampala, Uganda, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Badr, A.M.; Mahana, N.A.; Eissa, A. Assessment of Heavy Metal Levels in Water and Their Toxicity in Some Tissues of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in River Nile Basin at Greater Cairo, Egypt. Glob. Vet. 2014, 13, 432–443. [Google Scholar]
- Nhapi, I.; Wali, U.G.; Uwonkunda, B.K.; Nsengimana, H.; Banadda, N.; Kimwaga, R. Assessment of water pollution levels in the Nyabugogo catchment, Rwanda. Open Environ. Eng. J. 2011, 4, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mvungi, A.; Hranova, R.K.; Love, D. Impact of home industries on water quality in a tributary of the Marimba River, Harare: Implications for urban water management. Phys. Chem. Earth 2003, 28, 1131–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okonkwo, J.O.; Mothiba, M. Physico-chemical characteristics and pollution levels of heavy metals in the rivers in Thohoyandou, South Africa. J. Hydrol. 2005, 308, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omara, T.; Ogwang, R.; Ndyamuhaki, S.; Kagoya, S.; Kigenyi, E.; Musau, B.; Adupa, E. Spectroscopic analysis of selected priority trace metals in the extant East African gilled lungfish (Protopterus amphibius) in Lira municipal lagoon and its edibility health risk. Sci. J. Anal. Chem. 2018, 6, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Luo, D.; Zhao, D.; Li, N.; Xiao, T.; Liu, J.; Wei, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, G. Distribution, Source and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metal(oid)s in Water, Sediments, and Corbicula Fluminea of Xijiang River, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algül, F.; Beyhan, M. Concentrations and sources of heavy metals in shallow sediments in Lake Bafa, Turkey. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onen, P.; Akemkwene, R.; Nakiguli, C.K.; Nimusiima, D.; Ruma, D.H.; Khanakwa, A.V.; Angiro, C.; Bamanya, G.; Opio, B.; Gonzaga, A.; et al. Health Risks from Intake and Contact with Toxic Metal-Contaminated Water from Pager River, Uganda. J. Xenobiot. 2023, 13, 544–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mwesigye, A.R.; Tumwebaze, S.B. Water contamination with heavy metals and trace elements from Kilembe copper mine and tailing sites in Western Uganda; implications for domestic water quality. Chemosphere 2017, 169, 281–287. [Google Scholar]
- Amadi, E.K. Nutrient loads and heavy metals assessment along Sosiani River, Kenya. Chem. Mater. Res. 2013, 3, 14–20. [Google Scholar]
- Kihampa, C.; Wenaty, A. Impact of mining and farming activities on water and sediment quality of the Mara river basin, Tanzania. Res. J. Chem. Sci. 2013, 3, 15–24. [Google Scholar]
- Afzaal, M.; Hameed, S.; Liaqat, I.; Khan, A.A.A.; Manan, H.A.; Shahid, R.; Altaf, M. Heavy metals contamination in water, sediments and fish of freshwater ecosystems in Pakistan. Water Pract. Technol. 2022, 17, 253–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Rao, J.; Jia, Q. Heavy metal pollution and environmental risks in the water of Rongna River caused by natural AMD around Tiegelongnan copper deposit, Northern Tibet, China. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0266700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Kumar, D.; Dwivedi, A.; Vishwakarma, U.; Malik, D.S.; Paroha, S.; Mohan, N.; Gupta, N. Heavy metal contamination in river water, sediment, groundwater and human blood, from Kanpur, Uttar Pradesh, India. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 1807–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.S.; Rahman, A.K.M.L.; Sarkar, M.; Islam, J.B.; Jahan, I.A.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Saha, B.; Bhoumi, N.C. Assessment on the level of contamination of Turag river at Tongi area in Dhaka. Bangladesh J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2016, 51, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leventeli, Y.; Yalcin, F. Data analysis of heavy metal content in riverwater: Multivariate statistical analysis and inequality expressions. J. Inequal. Appl. 2021, 2021, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dippong, T.; Mihali, C.; Marian, M.; Rosca, O.M.; Resz, M.-A. Correlations between chemical, hydrological and biotic factors in rivers from the protected area of Tisa Superioară, Romania. Process Saf. Environ. Protect. 2023, 176, 40–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokarram, M.; Saber, A.; Sheykhi, V. Effects of heavy metal contamination on river water quality due to release of industrial effluents. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 123380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrees, N.; Tabassum, B.; Abd Allah, E.F.; Hashem, A.; Sarah, R.; Hashim, M. Groundwater contamination with cadmium concentrations in some West U.P. Regions, India. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 25, 1365–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lung, S.; Li, H.; Bondy, S.C.; Campbell, A. Low concentrations of copper in drinking water increase AP-1 binding in the brain. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2015, 13, 1178–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, F.; Irfan, M.; Ahmad, T.; Iqbal, J.; Butt, M.T.; Sadef, Y.; Umbreen, M.; Shaikh, I.A.; Moniruzzaman, M. Efficient utilization of low cost agro materials for incorporation of copper nanoparticles to scrutinize their antibacterial properties in drinking water. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 21, 101228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, W.; Rai, S.; Banerjee, S.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Mondal, M.H.; Bhattarai, A.; Saha, B. A comprehensive review on the sources, essentiality and toxicological profile of nickel. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 9139–9153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Upstream | Midstream | Downstream | WHO Guidelines [28] | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 5.80 ± 0.49 | 6.01 ± 0.54 | 6.00 ± 0.56 | 6.5–8.5 | 0.7876 |
| Electrical conductivity (µS/cm) | 133.38 ± 7.87 | 144.91 ± 7.42 | 135.11 ± 8.43 | 1500 | 0.0853 |
| Temperature (°C) | 23.38 ± 0.53 | 23.43 ±0.18 | 23.41 ± 0.31 | — | 0.5822 |
| Colour (Pt-co units) | 118.00 ± 8.9 | 145.2 ± 30.58 | 122.51 ± 10.68 | 15 | 0.0979 |
| Total dissolved solids (mg/L) | 61.27 ± 6.96 | 69.46 ± 6.02 | 62.08 ± 8.01 | 1000 | 0.1714 |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 24.77 ± 5.59 | 43.99 ± 6.87 | 31.11 ± 4.91 | 5 | 0.0007 * |
| Dissolved oxygen (mg/L) | 5.26 ± 0.64 | 3.85 ± 0.47 | 4.55 ± 0.48 | 4 | 0.0048 * |
| Biochemical oxygen demand (mg/L) | 0.95 ± 0.17 | 2.10 ± 0.29 | 1.74 ± 0.17 | 5 | 0.0000 * |
| Alkalinity (mg/L) | 32.54 ± 18.86 | 43.69 ± 23.26 | 32.95 ± 15.44 | 200 | 0.6008 |
| Chlorides (mg/L) | 8.79 ± 1.29 | 11.19 ± 1.69 | 9.47 ± 2.53 | 250 | 0.1646 |
| Total hardness (mg/L) | 40.32 ± 8.84 | 53.25 ± 10.64 | 44.23 ± 9.74 | 500 | 0.1423 |
| Calcium (mg/L) | 6.36 ± 1.17 | 9.54 ± 2.17 | 8.38 ± 2.12 | 150 | 0.0577 |
| Magnesium (mg/L) | 34.19 ± 7.55 | 43.97 ±10. 45 | 35.88 ± 8.56 | 250 | 0.2221 |
| Nitrates (mg/L) | 0.200 ± 0.05 | 0.36 ± 0.12 | 0.29 ± 0.09 | 45 | 0.0658 |
| Total phosphorous (mg/L) | 0.205 ± 0.45 | 0.53 ± 0.79 | 0.30 ± 0.39 | 2.2 | 0.3800 |
| Sulphates (mg/L) | 1.41 ± 0.17 | 0.41 ± 1.09 | 3.31 ± 0.93 | 250 | 0.0004 * |
| Parameter | pH | EC | TDS | DO | BOD5 | Chlorides | TH | Mg | Nitrates | TP | Colour | Sulphates | Turbidity | E. coli | Pb | Cu | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| EC | 0.38 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| Temperature | 0.823 ** | 0.087 | |||||||||||||||
| DO | 0.231 | −0.658 ** | −0.238 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| BOD5 | 0.206 | 0.506 | 0.337 | −0.670 ** | 1 | ||||||||||||
| Alkalinity | 0.696 ** | 0.412 | −0.519 * | −0.09 | 0.349 | ||||||||||||
| TH | −0.169 | 0.631 * | 0.525 * | 0.531 * | 0.486 | 0.675 ** | 1 | ||||||||||
| Ca | 0.071 | 0.634 * | 0.356 | −0.513 | 0.793 ** | 0.525 * | 0.733 ** | ||||||||||
| Mg | −0.199 | 0.555 * | 0.536 * | −0.472 | 0.359 | 0.648 ** | 0.982 ** | 1 | |||||||||
| Nitrates | −0.187 | 0.065 | 0.847 * | −0.435 | 0.526 * | 0.582 * | 0.607 * | 0.642 * | 1 | ||||||||
| Colour | −0.133 | 0.466 | 0.590 * | −0.501 | 0.334 | 0.670 ** | 0.828 ** | 0.852 ** | 0.684 ** | 0.265 | 1 | ||||||
| Sulphates | 0.115 | 0.173 | 0.620 * | 0.543 * | 0.853 ** | 0.635 * | 0.473 | 0.402 | 0.625 * | 0.191 | 0.457 | 1 | |||||
| Turbidity | 0 | 0.311 | 0.491 | 0.561 * | 0.635 * | 0.555 * | 0.432 | 0.406 | 0.645 ** | 0.495 | 0.690 ** | 0.707 ** | 1 | ||||
| E. coli | 0.092 | 0.613 * | 0.138 | −0.408 | 0.396 | 0.313 | 0.486 | 0.448 | 0.201 | 0.862 ** | 0.605 * | 0.232 | 0.654 ** | 1 | |||
| Pb | −0.092 | 0.0708 ** | −0.042 | −0.629 * | 0.336 | 0.271 | 0.374 | 0.341 | 0.193 | 0.485 | 0.42 | 0.134 | 0.468 | 0.616 * | 1 | ||
| Cd | −0.428 | 0.197 | 0.198 | −0.452 | 0.261 | 0.376 | 0.095 | 0.054 | 0.324 | 0.037 | 0.201 | 0.218 | 0.396 | 0.036 | 0.592 | ||
| Cu | −0.154 | −0.217 | 0.343 | −0.216 | 0.524 * | 0.386 | 0.028 | 0.021 | 0.543 * | 0.168 | 0.034 | 0.685 ** | 0.398 | −0.23 | −0.055 | 1 | |
| Ni | 0.128 | 0.224 | 0.582 * | −0.315 | 0.238 | 0.398 | 0.516 * | 0.581 * | 0.603 * | 0.317 | 0.787 ** | 0.442 | 0.696 ** | 0.592 * | 0.285 | 0.012 | 1 |
| River (Country) | Pb | Cd | Cr | Cu | Ni | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kagera River (Uganda) | 20.0–60.0 | 2.1–10.1 | BDL–35.0 | BDL–80.0 | 11.3–31.7 | This study |
| Pager River (Uganda) | 296–576 | 278–524 | – | – | – | [80] |
| Kagera River and tributaries (Rwanda) | 45.0 | 965.0 | 15.0 | – | – | [15] |
| River Nyamwamba (Uganda) | 400–8210 | 50–1400 | 790–13,470 | 210–10,740 | – | [41] |
| 270–400 | – | – | 1900–61,000 | 670–12,000 | [81] | |
| 470 | – | – | 740 | – | [33] | |
| River Mubuku (Uganda) | 53 | – | – | 25 | – | |
| River Rwimi (Uganda) | 67 | – | – | 10 | – | |
| River Manafwa (Uganda) | 20–100 | 10–20 | 3–11 | 3–60 | 1.5–9.5 | [51] |
| Nyabarongo River (Rwanda) | 500–750 | BDL–106 | BDL–60 | BDL–240 | – | [19,37] |
| Nyabugogo River (Rwanda) | 590 | BDL | 150 | 290 | – | [37] |
| Sosiani River (Kenya) | 20–1890 | – | 3.0–50 | 1–275 | – | [82] |
| Mara River (Tanzania) | 10–710 | BDL–110 | BDL–310 | BDL–20 | – | [83] |
| Marimba River (Zimbabwe) | 213–544 | – | – | 130–140 | 210–330 | [76] |
| Dzindi, Madanzhe and Mvudi rivers (South Africa) | 10.5–20.1 | 1.6–9.3 | – | 2–3 | – | [75] |
| River Kabul (Pakistan) | 337–810 | 150–380 | 157–480 | – | 368–2120 | [84] |
| Bolong River (China) | 0.34–0.64 | 0.11–0.54 | 1.74–3.08 | 5.42–7.37 | 10.7–18.2 | [85] |
| Rongna River (China) | 0.49–2.41 | 0.12–0.64 | 1.56–6.37 | 1.89–806 | 7.45–60.1 | |
| River Ganga (India) | 37–163 | 10–59 | 19–725 | 32–125 | – | [86] |
| Turag River (Bangladesh) | – | 6.8–17.0 | 33.9–633.4 | 14.8–170.3 | 128.2–620.7 | [87] |
| Akcay River (Turkey) | BDL–0.36 | – | 3.63–12.44 | BDL–6.34 | 10.17–90.42 | [88] |
| Tisa River (Romania) | 1.6–5.14 | 0.11–2.06 | 1.38–59 | 3.07–18.9 | 2.9–31 | [89] |
| Kor River (Iran) | – | 200–17,360 | 740–55,500 | 80–22,710 | 1100–25,280 | [90] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nimusiima, D.; Byamugisha, D.; Omara, T.; Ntambi, E. Physicochemical and Microbial Quality of Water from the Ugandan Stretch of the Kagera Transboundary River. Limnol. Rev. 2023, 23, 157-176. https://doi.org/10.3390/limnolrev23030010
Nimusiima D, Byamugisha D, Omara T, Ntambi E. Physicochemical and Microbial Quality of Water from the Ugandan Stretch of the Kagera Transboundary River. Limnological Review. 2023; 23(3):157-176. https://doi.org/10.3390/limnolrev23030010
Chicago/Turabian StyleNimusiima, Daniel, Denis Byamugisha, Timothy Omara, and Emmanuel Ntambi. 2023. "Physicochemical and Microbial Quality of Water from the Ugandan Stretch of the Kagera Transboundary River" Limnological Review 23, no. 3: 157-176. https://doi.org/10.3390/limnolrev23030010
APA StyleNimusiima, D., Byamugisha, D., Omara, T., & Ntambi, E. (2023). Physicochemical and Microbial Quality of Water from the Ugandan Stretch of the Kagera Transboundary River. Limnological Review, 23(3), 157-176. https://doi.org/10.3390/limnolrev23030010







