A Model Proposal for a Multi-Objective and Multi-Criteria Vehicle Assignment Problem: An Application for a Security Organization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Survey
2.1. Studies about the Assignment Model
2.1.1. Model with at Most One Task per Agent
2.1.2. Models with Multiple Tasks per Agent
2.1.3. Multi-Dimensional Assignment Problem
2.2. Studies Using Multi-Objective Assignment Models
2.3. Studies Using Mathematical Modeling with the MCDM Techniques
2.4. Studies about Vehicle Selection
2.5. Studies about the Quality of Security Service
3. Methods
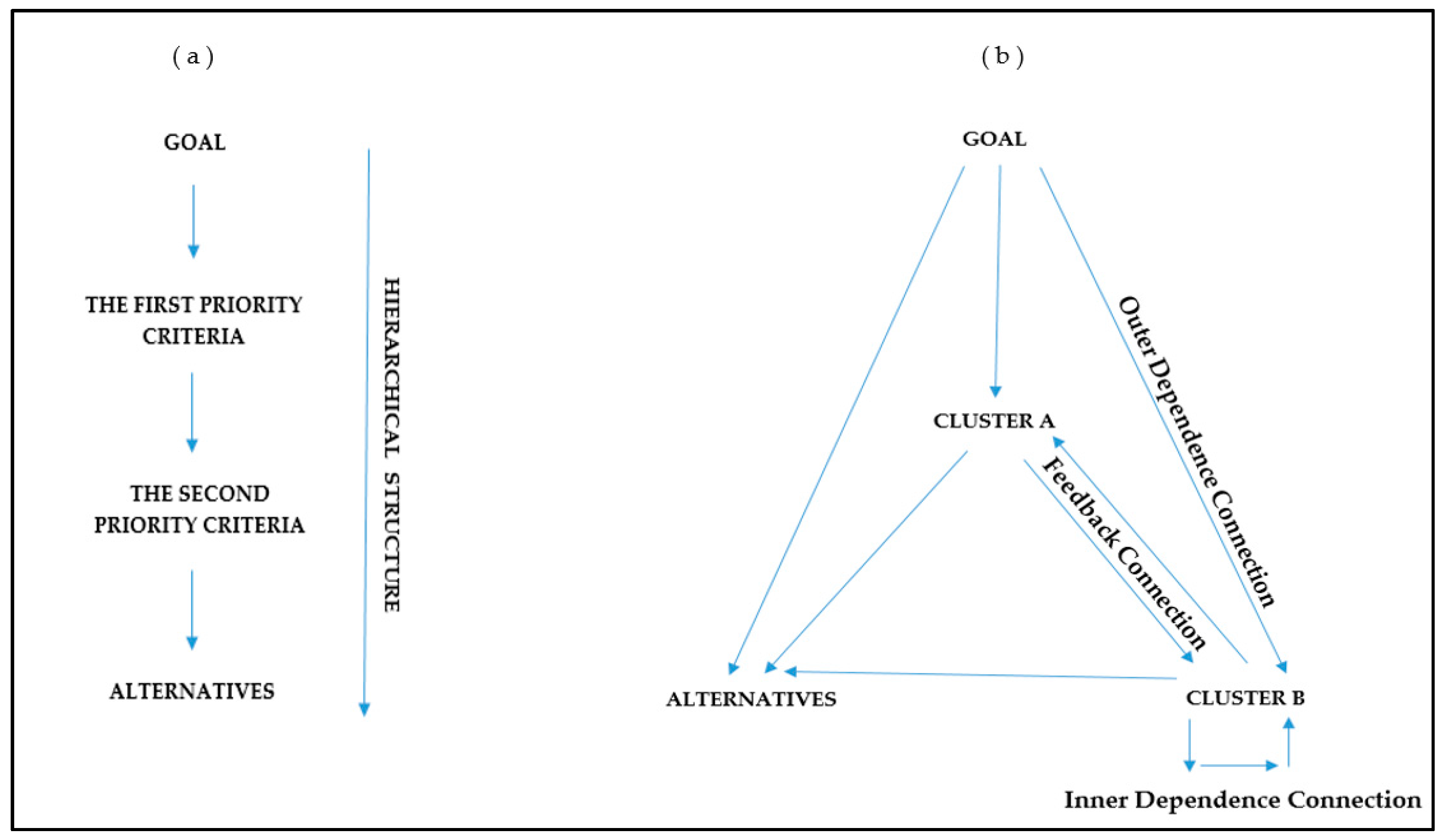
3.1. Analytic Network Process
3.2. The General Assignment Model in Linear Programming
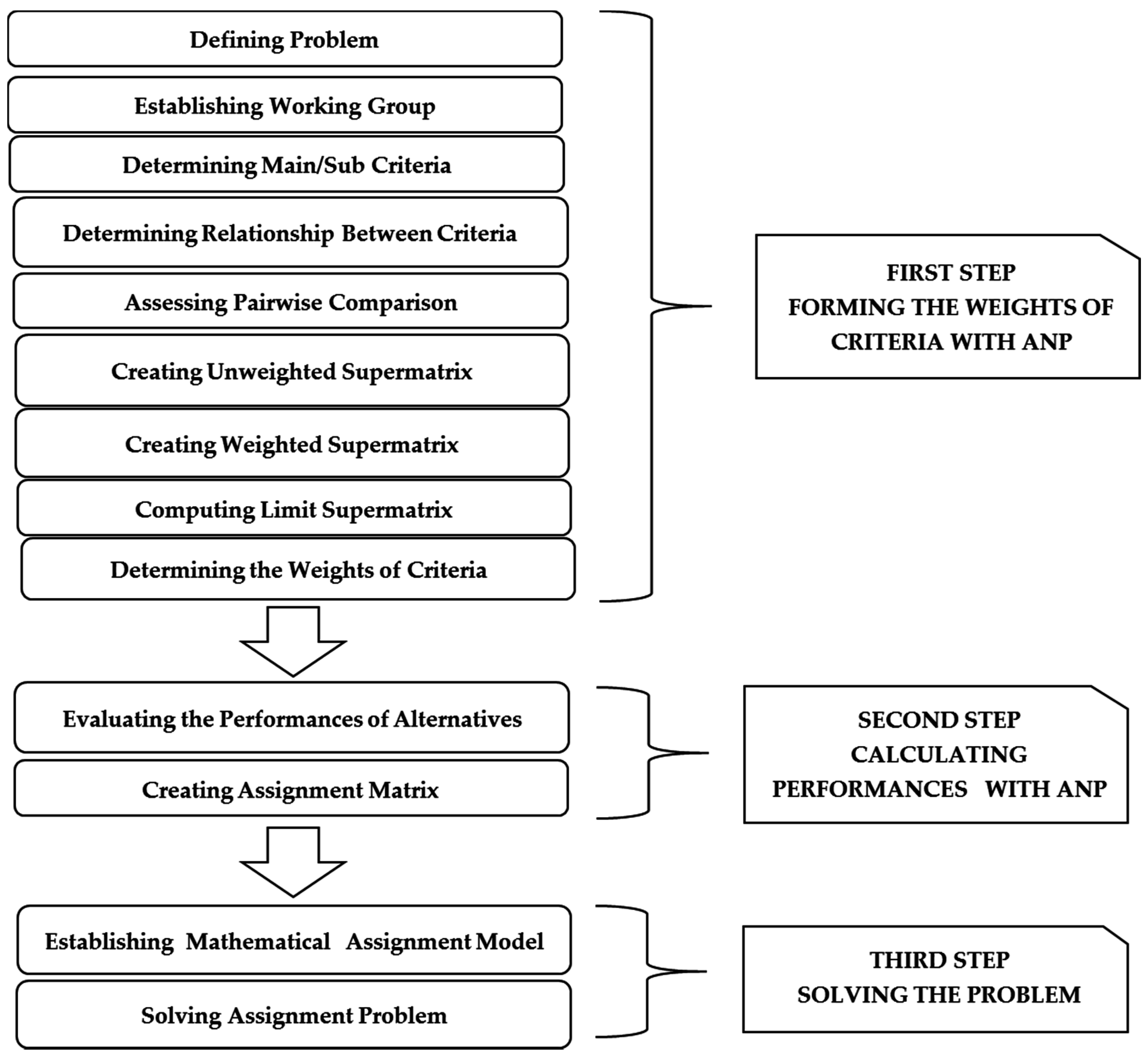
4. Proposed Multi-Criteria and Multi Objective Assignment Hybrid Methodology
- First step: using the ANP method for the calculation of the main/sub-criteria weight,
- Second step: evaluating the performance values of assigned vehicles for each district,
- Third step: modeling the assignment and realizing the vehicle assignment.
5. Illustrative Example
5.1. Forming the Weights of the Criteria with ANP (First Step)
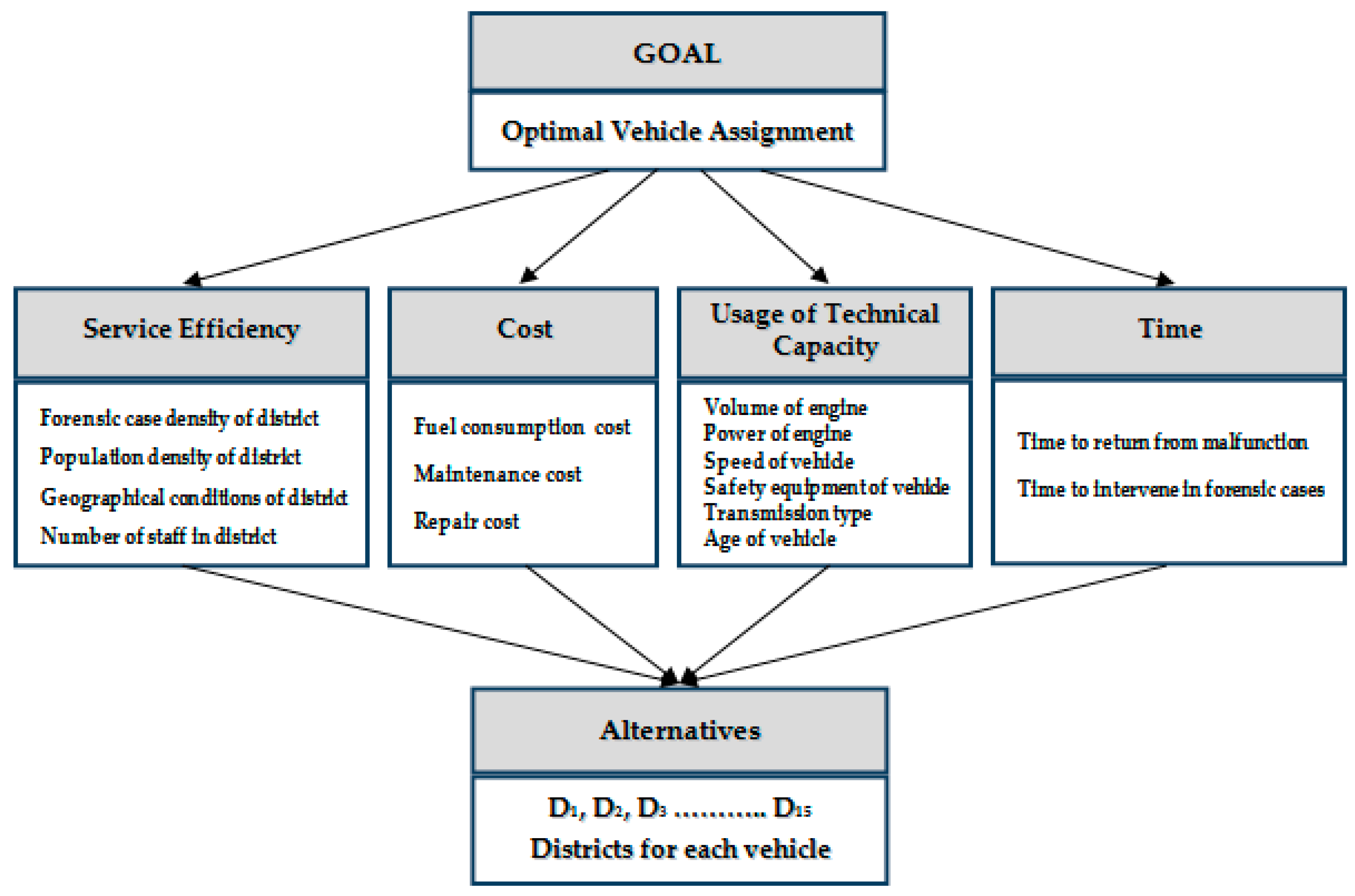
5.1.1. Problem Formulation
- Assigning large-capacity vehicles to populous district
- Assigning large-capacity vehicles to districts with a high density of forensic cases
- Assigning large-capacity vehicles to districts that have many policing personnel
- Assigning 4 × 4 type vehicles to high altitude districts.
- Assigning high-speed vehicles to districts that have plain terrain
- Assigning vehicles that have an adequate level of safety equipment, to the district where the accidents occur more frequently
- Using vehicles with high motor power in high altitudes
- Using vehicle with high motor volume in high altitudes
- Assigning relatively new vehicles to districts with a high density of desired purposes
- Assigning vehicles to district which will have minimum fuel consumption cost
- Minimizing maintenance cost and repair, which can change from district to district
5.1.2. Creating Working Group
5.1.3. Determining Main and Sub-Criteria
5.1.4. Determining the Relationship between Criteria
5.1.5. Making Pair-Wise Comparisons
5.1.6. Creating Unweighted Supermatrix
5.1.7. Creating the Weighted Supermatrix
5.1.8. Computing the Limit Supermatrix
5.1.9. Determining the Weight of Criteria
5.2. Finding the Performance Value of Each Vehicle for Each District (Second Step)
5.2.1. Evaluating the Performances of Alternatives
5.2.2. Creating Assignment Matrix
5.3. Establishing the Assignment Model and Performing the Assignment of Vehicles (Third Step)
5.3.1. Establishing the Mathematical Assignment Model
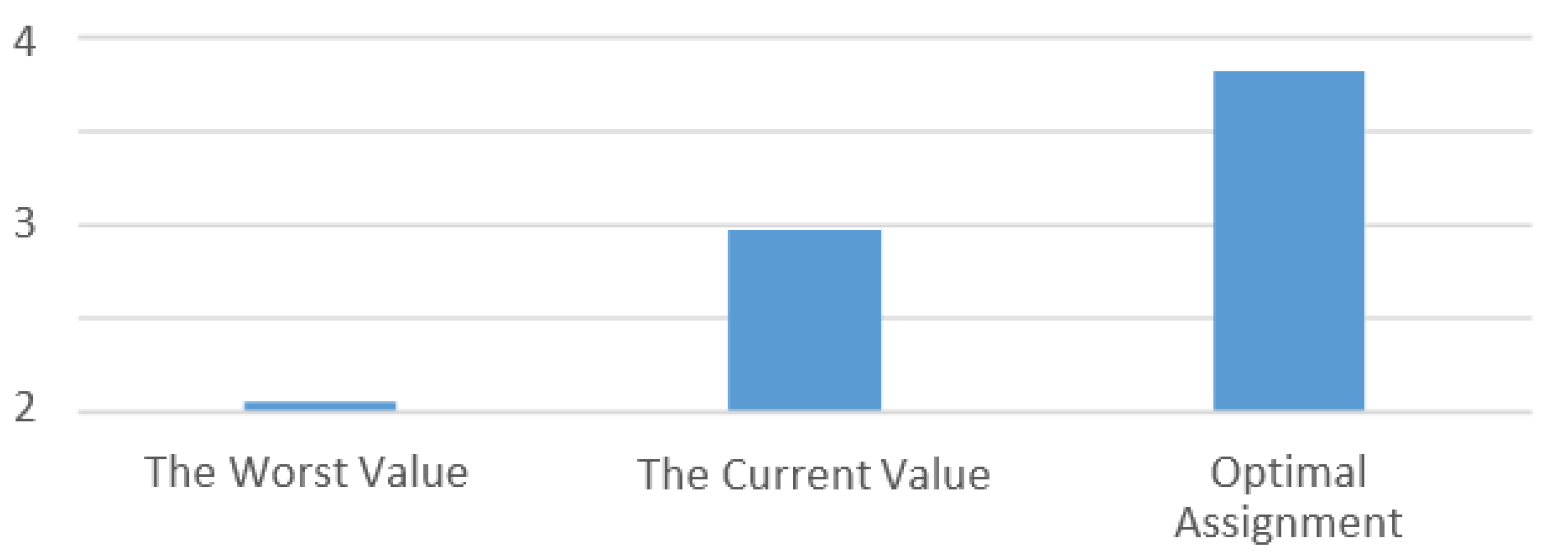
5.3.2. Solving the Assignment Problem and Evaluating the Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hyunseok, J.; Joongyeup, L.; Jennifer, C.G. The influence of the national government on confidence in the police: A focus on corruption. Int. J. Law Crime Justice 2015, 43, 553–568. [Google Scholar]
- Saaty, T.L. Fundamentals of the Analytic Network Process. In Proceedings of the ISAHP, Kobe, Japan, 12–14 August 1999.
- Pentico, D.W. Assignment Problems: A golden anniversary survey. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2007, 176, 774–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, G.; Hansen, P.; Jaumard, B. The Assignment Problem with Seniority and Job Priority Constraints. Oper. Res. 1999, 47, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, A.; Ramaswami, V. On the Bottleneck Assignment Problem. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 1977, 21, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del’Amico, M.; Martello, S. The k-cardinality assignment problem. Discret. Appl. Math. 1997, 76, 103–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martello, S.; Pulleyblank, W.R.; Toth, P.; de Werra, D. Balanced Optimization Problems. Oper. Res. Lett. 1984, 3, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattrysse, D.G.; Wassenhove, L.N.V. A Survey of Algorithms for the Generalized Assignment Problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1992, 60, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martello, S.; Toth, P. The Bottleneck Generalized Assignment Problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1995, 83, 621–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblanc, L.J.; Shtub, A.; Anandalingam, G. Formulating and Solving Production Planning Problems. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1999, 112, 54–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aora, S.; Puri, M.C. A variant of time minimizing assignment problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1998, 110, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, K.C.; Hofstra, R.B.; Bisgrove, R. An algorithm for a class of three-dimensional assignment problems arising in scheduling operations. Inst. Ind. Eng. Trans. 1987, 19, 29–33. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, K.C.; Hofstra, R.B. Multidimensional assignment problems. Decis. Sci. 1989, 19, 306–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, R.; Bhatia, H.L.; Puri, M.C. The three dimensional bottleneck assignment problem and its variants. Optimization 1985, 16, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, L.S.; Miller, J.L. Scheduling medical resident to rotations: Solving the large-scale multi period staff assignment. Oper. Res. 1993, 41, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, I.T.; Chou, J.S. Multi-objective optimization for manpower assignment in consulting engineering firms. Appl. Soft Comput. 2011, 11, 1183–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehlawat, M.K. A multi-choice goal programming approach for cots products selection of modular software systems. Int. J. Reliab. Qual. Saf. Eng. 2013, 20, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingman, D.; Phillips, N.V. Topological and Computational Aspects of Preemptive Multicriteria Millitary Personnel Assignment Problems. Manag. Sci. 1984, 30, 1362–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adiche, C.; Aider, M. A Hybrid Method for Solving the Multi-objective Assignment Problem. J. Math. Model. Algorithm 2010, 9, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.K.; Yeh, C.T. A Two-stage Approach for a Multi-objective Component Assignment Problem for a Stochastic-flow Network. Eng. Optim. 2013, 45, 265–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Jiang, B. Multi-objective Fleet Assignment Problem Based on Self-adaptive Genetic Algorithm. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 694–697, 2895–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachlaus, M.; Tiwari, M.K.; Chan, F.T.S. Multi-objective Resource Assignment Problem in a Product-driven Supply Chain Using a Taguchi-based DNA Algorithm. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2009, 47, 2345–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.K.; Chiu, H.N.; Yeh, R.H.; Chang, J.H. A Fuzzy Multi-criteria Decision Making Approach for Solving a Bi-objective Personnel Assignment Problem. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2009, 56, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybylski, A.; Gandibleux, X.; Ehrgott, M. A Two Phase Method for Multi-objective Integer Programming and Its Application to the Assignment Problem with Three Objective. Discret. Optim. 2010, 7, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schniederjans, M.J.; Garvin, T. Using The Analytic Hierarchy Process and Multi-Objective Programming for the Selection of Cost Drivers in Activity-Based Costing. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 1997, 100, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badri, M.A. Combining the Analytic Hierarchy Process and Goal Programming for Global Facility Location-Allocation Problem. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 1999, 62, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Kim, S.H. Using Analytic Network Process and Goal Programming For Interdependent Information System Project Selection. Comput. Oper. Res. 2000, 27, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karsak, E.E.; Sözer, S.; Alptekin, S.E. Product Planning in Quality Function Deployment Using a Combined Analytic Network Process and Goal Programming Approach. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2002, 44, 171–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.H.; Wey, W.M.; Tseng, H.Y. Using ANP Priorities with Goal Programming for Revitalization Strategies in Historic Transport: A Case Study of the Alishan Forest Railway. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 8682–8690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.B.; Huynh, V.N.; Nakamori, Y.; Murai, T. On Prioritized Weighted Aggregation in Multi-criteria Decision Making. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 812–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wey, W.M.; Wu, K.Y. Using ANP Priorities with Goal Programming in Resource Allocation in Transportation. Math. Comput. Model. 2007, 46, 985–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagır, M.; Ozturk, Z.K. Exam Scheduling: Mathematical Modeling and Parameter Estimation with the Analytic Network Process Approach. Math. Comput. Model. 2010, 52, 930–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aplak, H.S.; Turkbey, O. Fuzzy Logic Based Game Theory Applications in Multi-criteria Decision Making Process. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2013, 25, 359–371. [Google Scholar]
- Mehlawat, M.K.; Kumar, S. A Goal Programming Approach for a Multi-Objective Multi-Choice Assignment Problem. Optimization 2014, 63, 1549–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismayilova, N.A.; Sagır, M.; Gasimov, R.N. A Multiobjective Faculty–Course–Time Slot Assignment Problem with Preferences. Math. Comput. Model. 2007, 46, 1017–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, D. The AHP Approach for Selecting an Automobile Purchase Model. Inf. Manag. 2001, 38, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zak, J.; Jazkiewickz, A.; Redmer, A. Multiple Criteria Optimization Method for the Vehicle Assignment Problem in a Bus Transportation Company. J. Adv. Transp. 2009, 43, 203–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apak, S.; Gogus, G.G.; Karakadılar, İ.S. An Analytic Hierarchy Process Approach with a Novel Framework for Luxury Car Selection. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 58, 1301–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gungor, I.; Isler, D.B. Automobile Selection with Analytic Hierarchy Process Approach. ZKÜ Sosyal Bilimler Dergisi 2005, 1, 21–33. [Google Scholar]
- Soba, M. Selecting the best panelvan autocar by using promethee method and an application. J. Yasar Univ. 2012, 7, 4708–4721. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, K. Influence of Internal Service Quality on Job Performance: A Case Study of Royal Police Department. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2016, 224, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.M.; Lee, H.T.; Chen, S.H.; Tsai, T.H. The police service quality in rural Taiwan a comparative analysis of perceptions and satisfaction between police staff and citizens. Polic. Int. J. Police Strateg. Manag. 2014, 37, 521–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherghina, L. Strategies of the Quality of Local Police Public Service in the Municipalities from Romania’s Western Region Based on Marketing Research, Law of Local Police; Official Gazette: Resita, Romania, 2010; Part I; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Tari, J.J. Improving Service Quality in a Spanish Police Service. Total Qual. Manag. 2006, 17, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.N.; Kushwaha, S.; Hamid, F. Analytic Network Process—A Review of Application Areas. In Proceedings of the 1st IEEE International Conference on Logistics Operations Management, Le Havre, France, 17–19 October 2012; p. 14.
- Saaty, T.L.; Vargas, L.G. Decision Making with the Analytic Network Process: Economic, Political, Social and Technological Applications with Benefits, Opportunities, Costs and Risks; Springer Science + Business Media LLC: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka, A.; Nemery, P. Multi Criteria Decision Analysis: Methods and Software; John Wiley & Son: West Sussex, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gencer, C.; Gurpınar, D. Analytic Network Process in Supplier Selection: A Case Study in An Electronic Farm. Appl. Math. Model. 2007, 31, 2475–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khademi, N.; Behnia, K.; Saedi, R. Using Analytic Hierarchy/Network Process, (AHP/ANP) in Developing Countries: Shortcomings and Suggestions. Eng. Econ. 2014, 59, 2–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambroggi, M.D.; Trucco, P. Modelling and assessment of dependent performance shaping factors through Analytic Network Process. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2011, 96, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meade, L.M.; Sarkis, J. Analyzing organizational project alternatives for agile manufacturing processes: An analytic network approach. Int. J. Prod. Res. 1999, 37, 241–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, V.; Shankar, R.; Tiwari, M.K. Analyzing alternatives in reverse logistics for end-of-life computers: ANP and balanced scorecard approach. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2005, 48, 327–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Dawal, S.Z.; Nukman, Y.; Aoyama, H. A hybrid approach for fuzzy multi-attribute decision making in machine tool selection with consideration of the interactions of attributes. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 3078–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, V.F.; Hu, K.J.; Chang, A.Y. An interactive approach for the multi-objective transportation problem with interval parameters. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2015, 53, 1051–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitchcock, F.L. The Distribution of a Product from Several Sources to Numerous Localities. J. Math. Phys. 1941, 20, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, A.H. Operations Research: An Introduction, 8th ed.; PEARSON Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ignizio, P.J.; Cavalier, M.T. Linear Programming; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.J. Assignment Problem for Team Performance Promotion under Fuzzy Environment. Math. Probl. Eng. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bank, J. The Essence of Total Quality Management; Prentice Hall International: Hemel Hempstead, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, K.; Zhang, Q. Study on the Organizational Structured Problem Solving on Total Quality Management. Int. J. Bus. Manag. 2010, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satty, T.L.; Kearns, K.P. Analytical Planning: The Organization of Systems; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Yucenur, G.N.; Vayvay, O.; Demirel, N.C. Supplier selection problem in global supply chains by AHP and ANP approaches under fuzzy environment. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2011, 56, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Criteria | Local Weights | Total | Global Weights | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forensic Case Density of the District (FCDD) | 0.39353 | 1 | 0.23000 | 1 |
| Geographical Conditions of the District (GCD) | 0.30940 | 0.18083 | ||
| Population Density of the District (PDD) | 0.18427 | 0.10770 | ||
| Number of Law Enforcement Staff in the District (LESD) | 0.11280 | 0.06593 | ||
| Maintenance Cost (MC) | 0.25218 | 1 | 0.03289 | |
| Repair Cost (RC) | 0.15565 | 0.02030 | ||
| Fuel Consumption Cost (FCC) | 0.59216 | 0.07723 | ||
| Safety Equipment of Vehicle (SEV) | 0.03330 | 1 | 0.00464 | |
| Speed of Vehicle (SV) | 0.09306 | 0.01296 | ||
| Age of Vehicle (AV) | 0.23671 | 0.03296 | ||
| Power of Engine (PE) | 0.25387 | 0.03535 | ||
| Volume of Engine (VE) | 0.20404 | 0.02841 | ||
| Transmission Type (TT) | 0.17902 | 0.02493 | ||
| Time to Return from Malfunction to Use (TRMU) | 0.07367 | 1 | 0.01075 | |
| Time to Intervene in Forensic Cases (TIFC) | 0.92633 | 0.13513 |
| Districts | Priorities | FCDD | GCD | PDD | LESD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | 0.087359 | 1st Priority | 2nd Priority | 2nd Priority | 1st Priority |
| D2 | 0.043439 | 3rd Priority | 1st Priority | 4th Priority | 4th Priority |
| D3 | 0.066101 | 3rd Priority | 1st Priority | 1st Priority | 3rd Priority |
| D4 | 0.087359 | 1st Priority | 2nd Priority | 2nd Priority | 1st Priority |
| D5 | 0.111102 | 1st Priority | 1st Priority | 1st Priority | 2nd Priority |
| D6 | 0.051921 | 2nd Priority | 2nd Priority | 2nd Priority | 3rd Priority |
| D7 | 0.072010 | 2nd Priority | 1st Priority | 2nd Priority | 3rd Priority |
| D8 | 0.023351 | 3rd Priority | 2nd Priority | 4th Priority | 4th Priority |
| D9 | 0.046818 | 2nd Priority | 3rd Priority | 1st Priority | 4th Priority |
| D10 | 0.075306 | 1st Priority | 3rd Priority | 2nd Priority | 1st Priority |
| D11 | 0.054069 | 3rd Priority | 1st Priority | 3rd Priority | 2nd Priority |
| D12 | 0.066101 | 3rd Priority | 1st Priority | 1st Priority | 3rd Priority |
| D13 | 0.075306 | 1st Priority | 3rd Priority | 2nd Priority | 1st Priority |
| D14 | 0.076129 | 2nd Priority | 1st Priority | 2nd Priority | 2nd Priority |
| D15 | 0.063629 | 3rd Priority | 1st Priority | 1st Priority | 4th Priority |
| Annual Maintenance Costs ($) | ||
|---|---|---|
| District | Real Costs | Normalized Costs |
| D1 | 900 | 0.072 |
| D2 | 1,100 | 0.088 |
| D3 | 850 | 0.068 |
| D4 | 980 | 0.078 |
| D5 | 700 | 0.056 |
| D6 | 750 | 0.060 |
| D7 | 740 | 0.059 |
| D8 | 880 | 0.070 |
| D9 | 790 | 0.063 |
| D10 | 700 | 0.056 |
| D11 | 720 | 0.057 |
| D12 | 780 | 0.062 |
| D13 | 710 | 0.057 |
| D14 | 840 | 0.067 |
| D15 | 1,120 | 0.089 |
| Total | 12,560 | 1 |
| Current Assignment | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vehicle Types | Vehicle | D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | D5 | D6 | D7 | D8 | D9 | D10 | D11 | D12 | D13 | D14 | D15 | Capacity of Vehicles | |
| Administrative Veh. | V1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 10 | 15 | |||||
| V2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | ||||||||||||
| Traffic Vehicles | V3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 8 | 30 | ||||||||||
| V4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 13 | |||||||
| V5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | |||||||||||||
| V6 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 5 | ||||||||||||||
| Tactical Vehicles | V7 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 6 | 39 | ||||||||||||
| V8 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 33 | |||||
| Patrol Vehicles (T-I) | V9 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 27 | 90 |
| V10 | 1 | 1 | 2 | |||||||||||||||
| V11 | 1 | 11 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 8 | 7 | 2 | 4 | 10 | 61 | ||||
| Patrol Vehicles (T-II) | V12 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 12 | 22 | ||||||
| V13 | 22 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 10 | ||||||||||
| Capacity of Districts | 8 | 30 | 7 | 4 | 8 | 7 | 12 | 20 | 14 | 6 | 16 | 19 | 11 | 8 | 26 | 196 | ||
| Assignment Results | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vehicle Types | Vehicle | D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | D5 | D6 | D7 | D8 | D9 | D10 | D11 | D12 | D13 | D14 | D15 | Capacity of Vehicles | |
| Administrative Veh. | V1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 10 | 15 | |||||
| V2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | ||||||||||||
| Traffic Vehicles | V3 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | 30 | |||||||||
| V4 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 13 | ||||||||||||
| V5 | 4 | 4 | ||||||||||||||||
| V6 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | |||||||||||||
| Tactical Vehicles | V7 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 39 | ||||||||||||
| V8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 10 | 10 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 33 | ||||
| Patrol Vehicles (T-I) | V9 | 3 | 3 | 12 | 9 | 27 | 90 | |||||||||||
| V10 | 2 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
| V11 | 26 | 7 | 15 | 13 | 61 | |||||||||||||
| Patrol Vehicles (T-II) | V12 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 12 | 22 | |||||
| V13 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 10 | |||||||||||
| Capacity of Districts | 8 | 30 | 7 | 4 | 8 | 7 | 12 | 20 | 14 | 6 | 16 | 19 | 11 | 8 | 26 | 196 | ||
| wp: 0.584455 wc: 0.130425 wt: 0.145881 wu: 0.13924 | wp: weight of service efficiency objective wc: weight of cost objective wt: weight of time objective wu: weight of the usage of technical capacity objective | |||||||||||||||||
| Assignment Results | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vehicle Types | Vehicle | D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | D5 | D6 | D7 | D8 | D9 | D10 | D11 | D12 | D13 | D14 | D15 | Capacity of Vehicles | |
| Administrative Veh. | V1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 10 | 15 | |||||
| V2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | ||||||||||||
| Traffic Vehicles | V3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 8 | 30 | ||||||||||
| V4 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 13 | ||||||||||
| V5 | 3 | 1 | 4 | |||||||||||||||
| V6 | 1 | 4 | 5 | |||||||||||||||
| Tactical Vehicles | V7 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 39 | ||||||||||||
| V8 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 8 | 5 | 1 | 33 | ||||
| Patrol Vehicles (T-I) | V9 | 1 | 26 | 27 | 90 | |||||||||||||
| V10 | 2 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
| V11 | 3 | 6 | 3 | 12 | 15 | 22 | 61 | |||||||||||
| Patrol Vehicles (T-II) | V12 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 12 | 22 | ||||||
| V13 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 10 | |||||||||||
| Capacity of Districts | 8 | 30 | 7 | 4 | 8 | 7 | 12 | 20 | 14 | 6 | 16 | 19 | 11 | 8 | 26 | 196 | ||
| wp: 0.1 wc: 0.7 wt: 0.1 wu: 0.1 | wp: weight of service efficiency objective wc: weight of cost objective wt: weight of time objective wu: weight of the usage of technical capacity objective | |||||||||||||||||
| Assignment Results | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vehicle Types | Vehicle | D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | D5 | D6 | D7 | D8 | D9 | D10 | D11 | D12 | D13 | D14 | D15 | Capacity of Vehicles | |
| Administrative Veh. | V1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 10 | 15 | |||||
| V2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | ||||||||||||
| Traffic Vehicles | V3 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 8 | 30 | |||||||||||
| V4 | 9 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 13 | ||||||||||||
| V5 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 4 | ||||||||||||||
| V6 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 5 | |||||||||||||
| Tactical Vehicles | V7 | 4 | 2 | 6 | 39 | |||||||||||||
| V8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | 1 | 9 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 1 | 33 | |||
| Patrol Vehicles (T-I) | V9 | 4 | 11 | 12 | 27 | 90 | ||||||||||||
| V10 | 2 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
| V11 | 18 | 16 | 2 | 15 | 10 | 61 | ||||||||||||
| Patrol Vehicles (T-II) | V12 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | 12 | 22 | ||||||||||
| V13 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 10 | |||||||
| Capacity of Districts | 8 | 30 | 7 | 4 | 8 | 7 | 12 | 20 | 14 | 6 | 16 | 19 | 11 | 8 | 26 | 196 | ||
| wp: 0.1 wc: 0.1 wt: 0.7 wu: 0.1 | wp: weight of service efficiency objective wc: weight of cost objective wt: weight of time objective wu: weight of the usage of technical capacity objective | |||||||||||||||||
| Assignment Results | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vehicle Types | Vehicle | D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | D5 | D6 | D7 | D8 | D9 | D10 | D11 | D12 | D13 | D14 | D15 | Capacity of Vehicles | |
| Administrative Veh. | V1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 10 | 15 | |||||
| V2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | ||||||||||||
| Traffic Vehicles | V3 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | 30 | ||||||||||
| V4 | 9 | 1 | 3 | 13 | ||||||||||||||
| V5 | 1 | 3 | 4 | |||||||||||||||
| V6 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | ||||||||||||
| Tactical Vehicles | V7 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 6 | 39 | ||||||||||||
| V8 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 11 | 1 | 1 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 33 | ||||
| Patrol Vehicles (T-I) | V9 | 11 | 12 | 4 | 27 | 90 | ||||||||||||
| V10 | 2 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
| V11 | 26 | 15 | 2 | 18 | 61 | |||||||||||||
| Patrol Vehicles (T-II) | V12 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 12 | 22 | ||||||||
| V13 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 10 | |||||||||
| Capacity of Districts | 8 | 30 | 7 | 4 | 8 | 7 | 12 | 20 | 14 | 6 | 16 | 19 | 11 | 8 | 26 | 196 | ||
| wp: 0.1 wc: 0.1 wt: 0.1 wu: 0.7 | wp: weight of service efficiency objective wc: weight of cost objective wt: weight of time objective wu: weight of the usage of technical capacity objective | |||||||||||||||||
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Acar, E.; Aplak, H.S. A Model Proposal for a Multi-Objective and Multi-Criteria Vehicle Assignment Problem: An Application for a Security Organization. Math. Comput. Appl. 2016, 21, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/mca21040039
Acar E, Aplak HS. A Model Proposal for a Multi-Objective and Multi-Criteria Vehicle Assignment Problem: An Application for a Security Organization. Mathematical and Computational Applications. 2016; 21(4):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/mca21040039
Chicago/Turabian StyleAcar, Engin, and Hakan Soner Aplak. 2016. "A Model Proposal for a Multi-Objective and Multi-Criteria Vehicle Assignment Problem: An Application for a Security Organization" Mathematical and Computational Applications 21, no. 4: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/mca21040039
APA StyleAcar, E., & Aplak, H. S. (2016). A Model Proposal for a Multi-Objective and Multi-Criteria Vehicle Assignment Problem: An Application for a Security Organization. Mathematical and Computational Applications, 21(4), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/mca21040039





