A Two-Step Global Alignment Method for Feature-Based Image Mosaicing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
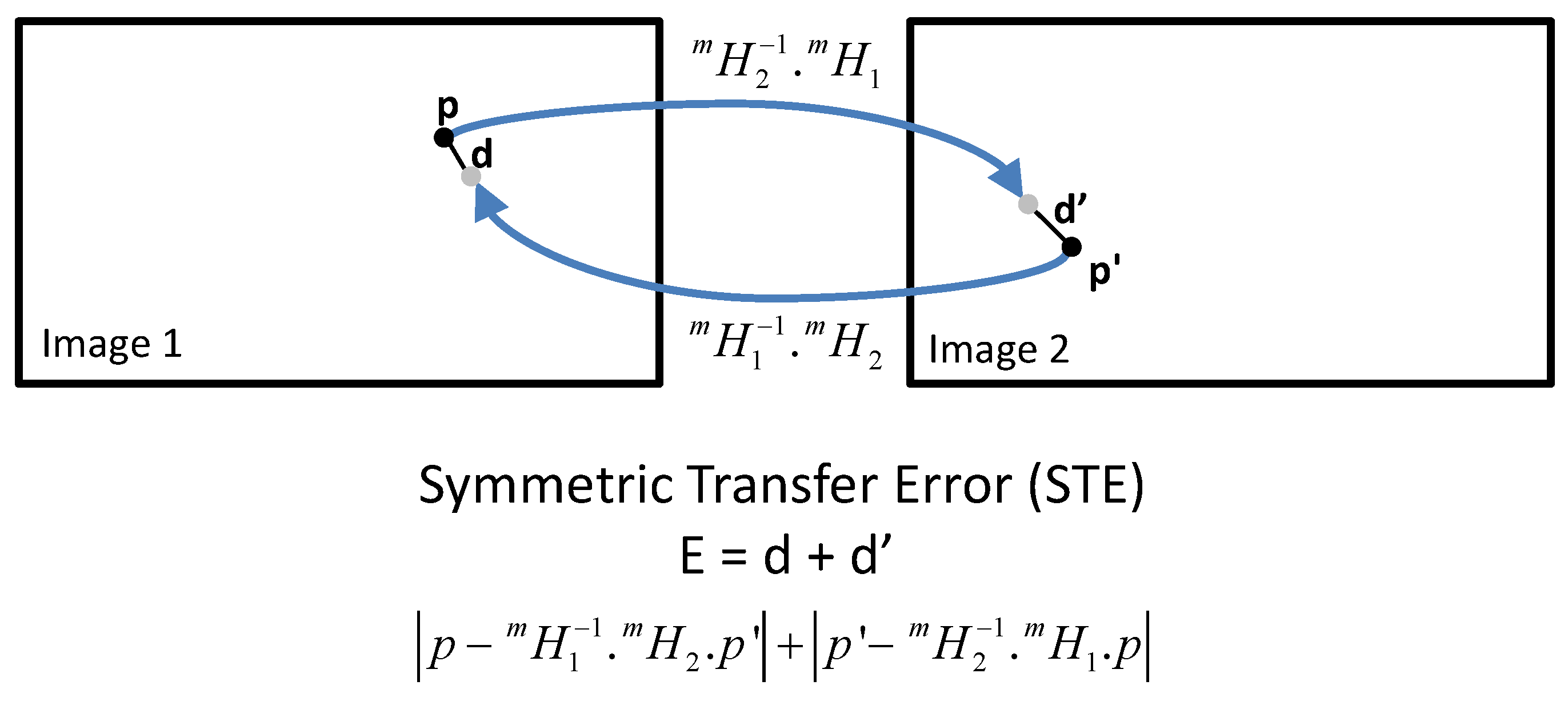
2. Nomenclature
- n is the total number of images.
- is the total number of correspondences between images i and j.
- represents the scale, rotation (in radians) and translation parameters (in pixels) of a similarity type planar transformation
- is the transformation relating image points represented in the coordinate frame image j to the coordinate frame of image i and it consists of parameters ().
- The transformation from image i to the global frame m is represented with . is composed of parameters () similarly above. For simplicity, m is dropped in the representation of parameters.
- The first image frame is selected as a mosaic frame. Therefore, is identity and m equals to 1. Parameters for the first image are not considered as unknown.
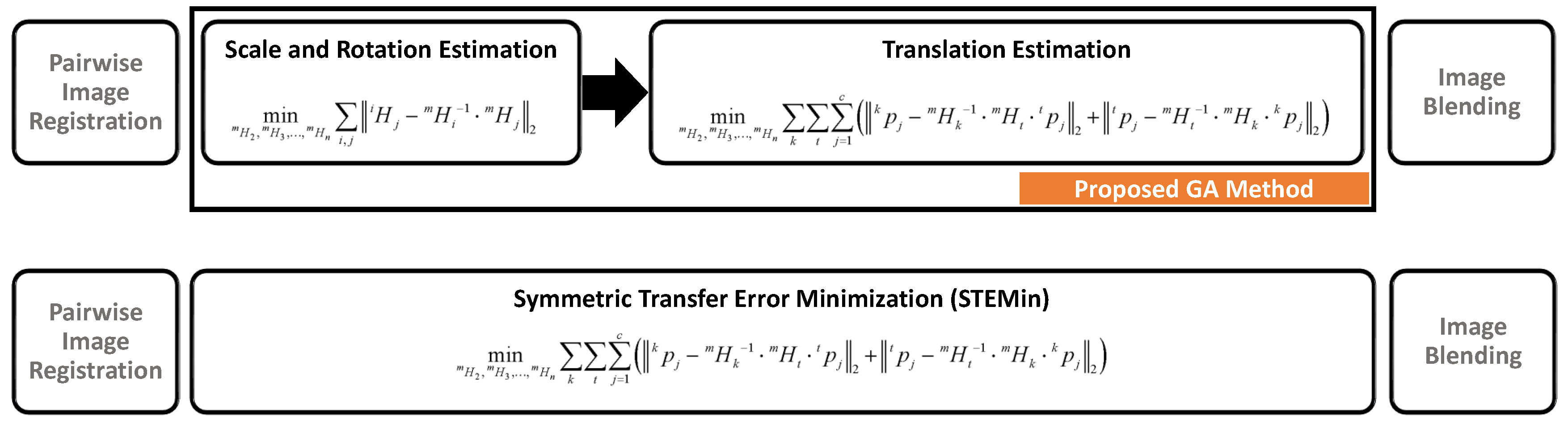
3. Two-Step Global Alignment for Feature-Based Image Mosaicing (FIM)
3.1. Scale and Rotation Estimation
3.2. Translation Estimation
4. Experimental Results
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Szeliski, R. Image alignment and stitching: A tutorial. Found. Trends® Comput. Graph. Vis. 2006, 2, 1–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Shi, R.; Shen, I.F.; Chen, W. Video Stabilization Using Scale-Invariant Features. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Information Visualization, Zurich, Switzerland, 4–6 July 2007; pp. 871–877.
- Turner, D.; Lucieer, A.; Watson, C. An automated technique for generating georectified mosaics from ultra-high resolution unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) imagery, based on structure from motion (SfM) point clouds. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 1392–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elibol, A.; Gracias, N.; Garcia, R.; Gleason, A.; Gintert, B.; Lirman, D.; Reid, P.R. Efficient autonomous image mosaicing with applications to coral reef monitoring. In Proceedings of the IROS 2011 Workshop on Robotics for Environmental Monitoring, San Francisco, SA, USA, 30 September 2011.
- Gledhill, D.; Tian, G.; Taylor, D.; Clarke, D. Panoramic imaging—A review. Comput. Graph. 2003, 27, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steedly, D.; Pal, C.; Szeliski, R. Efficiently registering video into panoramic mosaics. In Proceedings of the Tenth IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Beijing, China, 17–21 October 2005; Volume 2, pp. 1300–1307.
- Brown, M.; Lowe, D.G. Automatic Panoramic Image Stitching using Invariant Features. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2007, 74, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capel, D.P. Image Mosaicing and Super-Resolution; Springer Verlag: London, United Kingdom, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Fischler, M.A.; Bolles, R.C. Random sample consensus: A paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography. Commun. ACM 1981, 24, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, R.; Zisserman, A. Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Harlow, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Sawhney, H.; Hsu, S.; Kumar, R. Robust Video Mosaicing through Topology Inference and Local to Global Alignment. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Freiburg, Germany, 2–6 June 1998; Volume 2, pp. 103–119.
- Triggs, B.; McLauchlan, P.F.; Hartley, R.I.; Fitzgibbon, A.W. Bundle adjustmenta modern synthesis. In Vision Algorithms: Theory and Practice; Springer: Corfu, Greece, 1999; pp. 298–372. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z. Consistent image alignment for video mosaicing. Signal Image Video Process. 2013, 7, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kekec, T.; Yildirim, A.; Unel, M. A new approach to real-time mosaicing of aerial images. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2014, 62, 1755–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negahdaripour, S.; Firoozfam, P. Positioning and photo-mosaicking with long image sequences; comparison of selected methods. In Proceedings of the MTS/IEEE Conference and Exhibition OCEANS, 2001, Honolulu, HI, USA, 5–8 November 2001; Volume 4, pp. 2584–2592.
- Davis, J. Mosaics of Scenes with Moving Objects. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 23–25 June 1998; Volume 1, pp. 354–360.
- Ribas, D.; Palomeras, N.; Ridao, P.; Carreras, M.; Hernandez, E. ICTINEU AUV Wins the first SAUC-E competition. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Roma, Italy, 10–14 April 2007.
- Lirman, D.; Gracias, N.; Gintert, B.; Gleason, A.; Reid, R.P.; Negahdaripour, S.; Kramer, P. Development and Application of a Video–Mosaic Survey Technology to Document the Status of Coral Reef Communities. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 159, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribas, D.; Palomeras, N.; Ridao, P.; Carreras, M.; Mallios, A. Girona 500 AUV: From Survey to Intervention. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2012, 17, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 60, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Mierle, K. Ceres Solver. Available online: http://ceres-solver.org (accessed on 9 November 2015).
- Domke, J.; Aloimonos, Y. Deformation and Viewpoint Invariant Color Histograms. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference, Edinburgh, UK, 4–7 September 2006; pp. 509–518.
- Elibol, A.; Shim, H. Developing a Visual Stopping Criterion for Image Mosaicing Using Invariant Color Histograms. In Advances in Multimedia Information Processing PCM 2015; Springer: Gwangju, Republic of Korea, 2015; Volume 9315, Lecture Notes in Computer Science; pp. 350–359. [Google Scholar]
- Prados, R.; García, R.; Neumann, L. Image Blending Techniques and their Application in Underwater Mosaicing; Springer Briefs in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
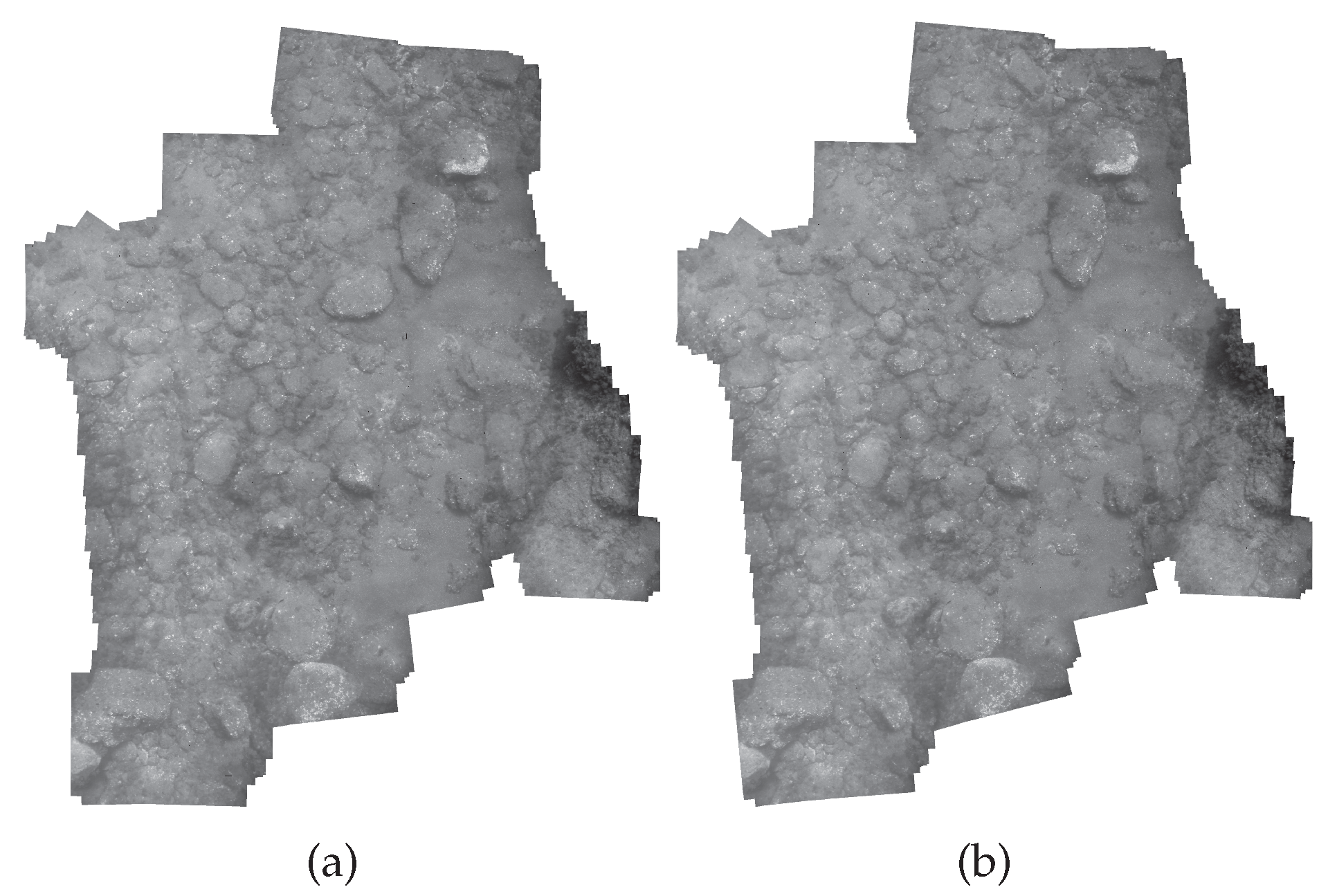
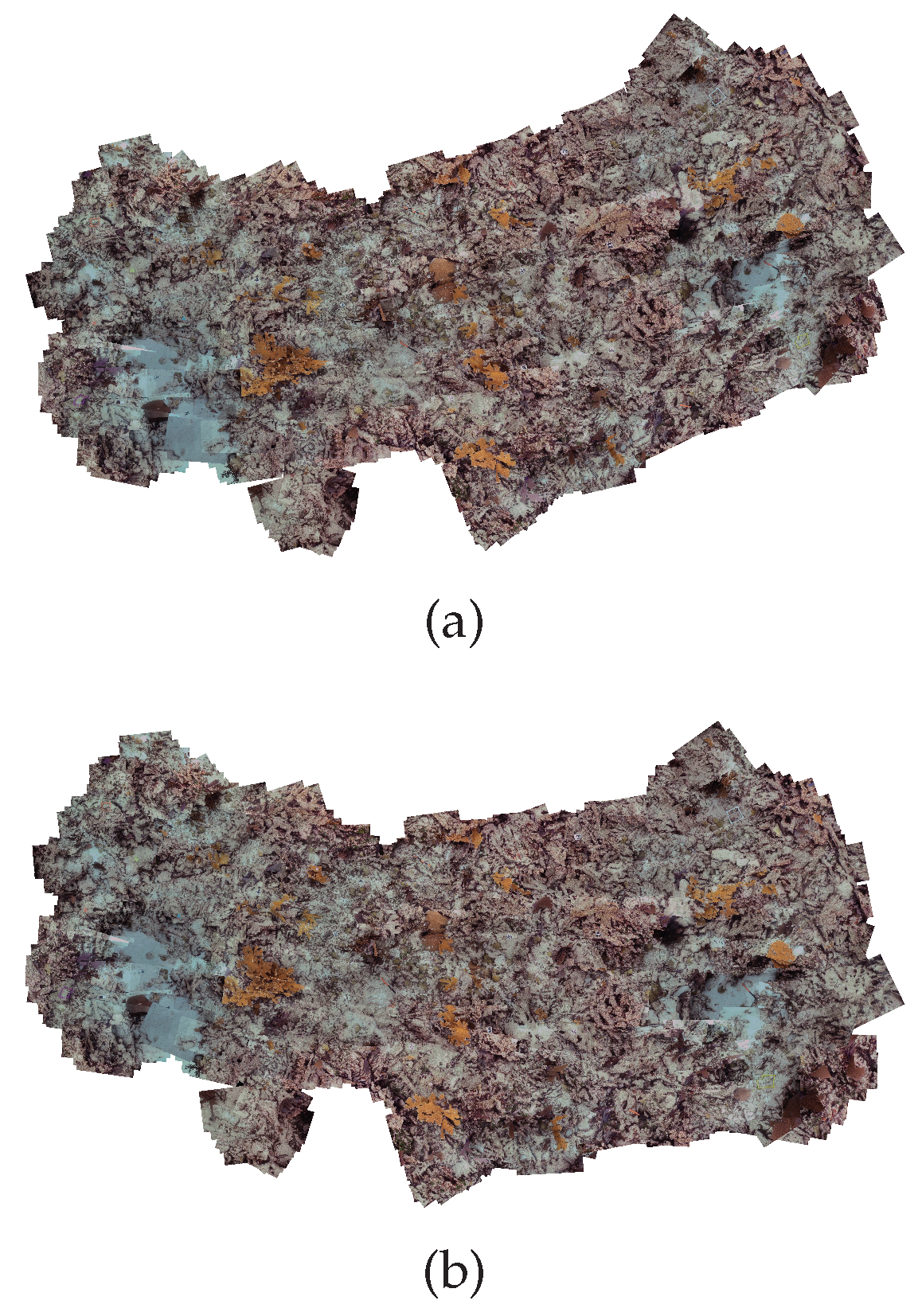
| Dataset | Image Size | Color | Total Number of | Scale | Angle in Degree | Overlapping Area 1 (in Percent) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Images | Overlapping Pairs | Correspondences | min. | max. | min. | max. | min. | mean | max. | |||
| Dataset I | RGB | 486 | 3225 | 360,262 | 0.73 | 1.33 | -45.07 | 52.51 | 15.91 | 64.28 | 97.65 | |
| Dataset II | RGB | 493 | 3686 | 259,443 | 0.62 | 1.74 | -40.33 | 51.54 | 13.93 | 62.03 | 96.64 | |
| Dataset III | RGB | 1136 | 3798 | 550,845 | 0.76 | 1.39 | -37.55 | 49.16 | 18.12 | 72.98 | 96.10 | |
| Dataset IV | Grayscale | 430 | 5412 | 930,898 | 0.78 | 1.26 | -31.70 | 72.31 | 22.57 | 64.18 | 99.04 | |
| Dataset V | RGB | 245 | 3311 | 2,218,502 | 0.74 | 1.44 | -0.77 | 0.78 | 1.06 | 38.82 | 97.35 | |
| Dataset VI | RGB | 3031 | 14,132 | 2,322,233 | 0.61 | 1.54 | -70.45 | 66.93 | 5.02 | 56.06 | 96.97 | |
| Dataset VII | RGB | 268 | 3688 | 1,425,402 | 0.85 | 1.19 | -179.84 | 179.85 | 6.13 | 40.98 | 96.42 | |
| Dataset | Strategy | Avg. Error | Std. Deviation | Max. Error | Final Mosaic Size | Time 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| in Pixels | in Pixels | in Pixels | in Pixels | in Seconds | ||
| Dataset I | Proposed method | 7.69 | 3.32 | 41.22 | 37432419 | 13.48 |
| STEMin | 6.08 | 2.70 | 36.68 | 35492284 | 104.16 | |
| Combined | 6.08 | 2.70 | 36.68 | 35492284 | 73.00 | |
| Dataset II | Proposed method | 24.72 | 12.10 | 181.47 | 60357134 | 10.69 |
| STEMin | 20.39 | 9.93 | 155.50 | 59497239 | 93.45 | |
| Combined | 20.39 | 9.93 | 155.50 | 59497239 | 47.89 | |
| Dataset III | Proposed method | 6.50 | 2.64 | 54.57 | 36112352 | 17.93 |
| STEMin | 5.54 | 2.37 | 40.50 | 36232346 | 141.31 | |
| Combined | 5.54 | 2.37 | 40.50 | 36232346 | 110.77 | |
| Dataset IV | Proposed method | 6.18 | 2.76 | 58.88 | 31872602 | 41.96 |
| STEMin | 5.80 | 2.54 | 61.20 | 32952674 | 292.86 | |
| Combined | 5.80 | 2.54 | 61.20 | 32952674 | 222.86 | |
| Dataset V | Proposed method | 5.55 | 2.86 | 44.14 | 55468475 | 75.30 |
| STEMin | 5.23 | 2.72 | 51.20 | 55358442 | 808.90 | |
| Combined | 5.23 | 2.72 | 51.20 | 55358442 | 352.54 | |
| Dataset VI | Proposed method | 33.82 | 15.86 | 266.94 | 18,93411,710 | 158.80 |
| STEMin | 24.78 | 11.38 | 223.32 | 20,46711,343 | 4590.39 | |
| Combined | 24.78 | 11.38 | 223.32 | 20,46711,343 | 835.39 | |
| Dataset VII | Proposed method | 2.81 | 1.06 | 16.96 | 22031727 | 80.09 |
| STEMin | 2.35 | 0.90 | 17.13 | 22011728 | 2885.82 | |
| Combined | 2.35 | 0.90 | 17.13 | 22011728 | 604.72 | |
| Sensor 4-DOFs | 2.85 | 1.18 | 23.96 | 21961721 | ||
| Sensor 8-DOFs | 1.56 | 0.82 | 21.00 | 19921589 |
| Dataset | Scale | Angle (in Degree) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Std. Deviation | Maximum | Mean | Std. Deviation | Maximum | |
| Dataset I | 0.0604 | 0.0559 | 0.2047 | 1.7991 | 1.2261 | 7.5344 |
| Dataset II | 0.0260 | 0.0205 | 0.1134 | 3.0023 | 2.4866 | 11.5737 |
| Dataset III | 0.0148 | 0.0117 | 0.0609 | 1.5241 | 0.9683 | 5.8098 |
| Dataset IV | 0.0390 | 0.0348 | 0.1733 | 1.8220 | 1.6750 | 8.1793 |
| Dataset V | 0.0035 | 0.0028 | 0.0147 | 0.0974 | 0.0745 | 0.4068 |
| Dataset VI | 0.0802 | 0.0619 | 0.4038 | 11.4706 | 3.6440 | 23.2907 |
| Dataset VII | 0.0067 | 0.0056 | 0.0263 | 0.5214 | 0.2992 | 1.2662 |
| Dataset | |
|---|---|
| Dataset I | 0.0223 |
| Dataset II | 0.0052 |
| Dataset III | 0.0038 |
| Dataset V | 0.0025 |
| Dataset VI | 0.0910 |
| Dataset VII | 0.0027 |
| Sensor 4-DOFs | 0.0034 |
| Sensor 8-DOFs | 0.0610 |
© 2016 by the author; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elibol, A. A Two-Step Global Alignment Method for Feature-Based Image Mosaicing. Math. Comput. Appl. 2016, 21, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/mca21030030
Elibol A. A Two-Step Global Alignment Method for Feature-Based Image Mosaicing. Mathematical and Computational Applications. 2016; 21(3):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/mca21030030
Chicago/Turabian StyleElibol, Armagan. 2016. "A Two-Step Global Alignment Method for Feature-Based Image Mosaicing" Mathematical and Computational Applications 21, no. 3: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/mca21030030
APA StyleElibol, A. (2016). A Two-Step Global Alignment Method for Feature-Based Image Mosaicing. Mathematical and Computational Applications, 21(3), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/mca21030030





