Abstract
Aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) is a common mycotoxin present in agricultural and food products. Therefore, rapid screening methods must be developed for AFB1 detection with high sensitivity and good selectivity. In this study, we developed an analytical method based on the combination of solid-phase microextraction (SPME) with carbon fiber ionization (CFI)-mass spectrometry (MS) to detect the presence of trace AFB1 from complex samples. A pencil lead (type 2B, length: ~2.5 cm) with a sharp end (diameter: ~150 μm) was used as the SPME fiber and the ionization emitter in CFI-MS analysis. Owing to the graphite structure of the pencil lead, AFB1 can be trapped on the pencil lead through π–π interactions. After adsorbing AFB1, the pencil lead was directly introduced in a pipette tip (length: ~0.7 cm; tip inner diameter: ~0.6 mm), placed close (~1 mm) to the inlet of the mass spectrometer, and applied with a high voltage (−4.5 kV) for in situ AFB1 elution and CFI-MS analysis. A direct electric contact on the SPME-CFI setup was not required. Followed by the introduction of an elution solvent (10 μL) (acetonitrile/ethanol/deionized water, 2:2:1 (v/v/v)) to the pipette tip, electrospray ionization was generated from the elution solvent containing AFB1 for CFI-MS analysis. A reactive SPME-CFI-MS strategy was employed to further identify AFB1 and improve elution capacity using our approach. Butylamine was added to the elution solvent, which was then introduced to the pipette tip inserted with the SPME fiber. Butylamine-derivatized AFB1 was readily generated and appeared in the resultant SPME-CFI mass spectrum. The lowest detectable concentration against AFB1 using our approach was ~1.25 nM. Our method can distinguish AFB1 from AFG1 in a mixture and can be used for the detection of trace AFB1 in complex peanut extract samples.
1. Introduction
Aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) is a well-known carcinogen that is generated from fungi, such as Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus parasiticus [1,2], and is the most toxic aflatoxin in the aflatoxin family [1,2]. AFB1 is produced by fungi that commonly contaminate agricultural crops and products [3,4,5]. Completely eliminating the presence of AFB1 in agricultural crops and products is impossible. Thus, many countries have regulated the maximum allowed AFB1 level in agricultural products [3,4,5], for example, 2–5 μg kg−1 in agricultural products such as cereals, and their derived products according to the European Union [5]. Different analytical methods have been developed for aflatoxin detection [6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36]. Supporting Information (SI) Table S1 lists the comparisons of these existing methods. For example, the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) has been used to detect AFB1 using antibodies as probes to recognize AFB1 [6]. Although this method is sensitive and selective toward AFB1, cross-reactions with other aflatoxin members, such as aflatoxin G1 (AFG1) [6], have been reported due to the similarity of chemical structures among aflatoxins. High-performance liquid chromatography equipped with an optical spectroscopic detector has been used to detect aflatoxins in complex samples [7]. Moreover, highly sensitive and selective mass spectrometry (MS) [10,11,12,13,14,15,16] is an effective detection tool for AFB1.
Owing to interference from complex matrices in real samples, sample pretreatment is usually required prior to sensitive analytical tools [22]. Liquid–liquid extraction [10,11,13,18,19], solid-phase extraction [12,13,14,15,20,21], liquid-phase microextraction [22] and solid-phase microextraction (SPME) [37,38,39,40,41] are commonly used in sample pretreatment for AFB1 analysis. SPME is solvent-free and has a high extraction efficiency, and thus, has gained considerable attention [37,38,39,40,41]. In this method, a small fiber functionalized with specific functional groups is used as a probe for the sampling, isolation, and concentration of trace target analytes from complex samples [37,38,39,40,41]. MS has been coupled with SPME because of its high sensitivity, selectivity, and speed [38,39,40]. The analytes trapped by the SPME fiber are desorbed by heating [42,43,44,45,46,47] or solvent elution [48,49,50,51] prior to detection by analysis tools such as MS. SPME coupled with gas chromatography (GC)-MS has been widely applied in the analysis of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) because VOCs trapped on the SPME fiber can be readily desorbed in the heating chamber at the injection port of GC-MS [43,44,45,46,47]. In addition, electrospray ionization (ESI) is commonly used as the interface to couple SPME with MS when polar molecules are the target analytes [48,49,50,51]. The main challenge in coupling SPME with ESI-MS online is to effectively elute analytes from SPME fibers using suitable solvents in situ for instantaneous MS detection. The elution means and compositions of the elution solvents play key roles in the coupling of SPME and ESI-MS.
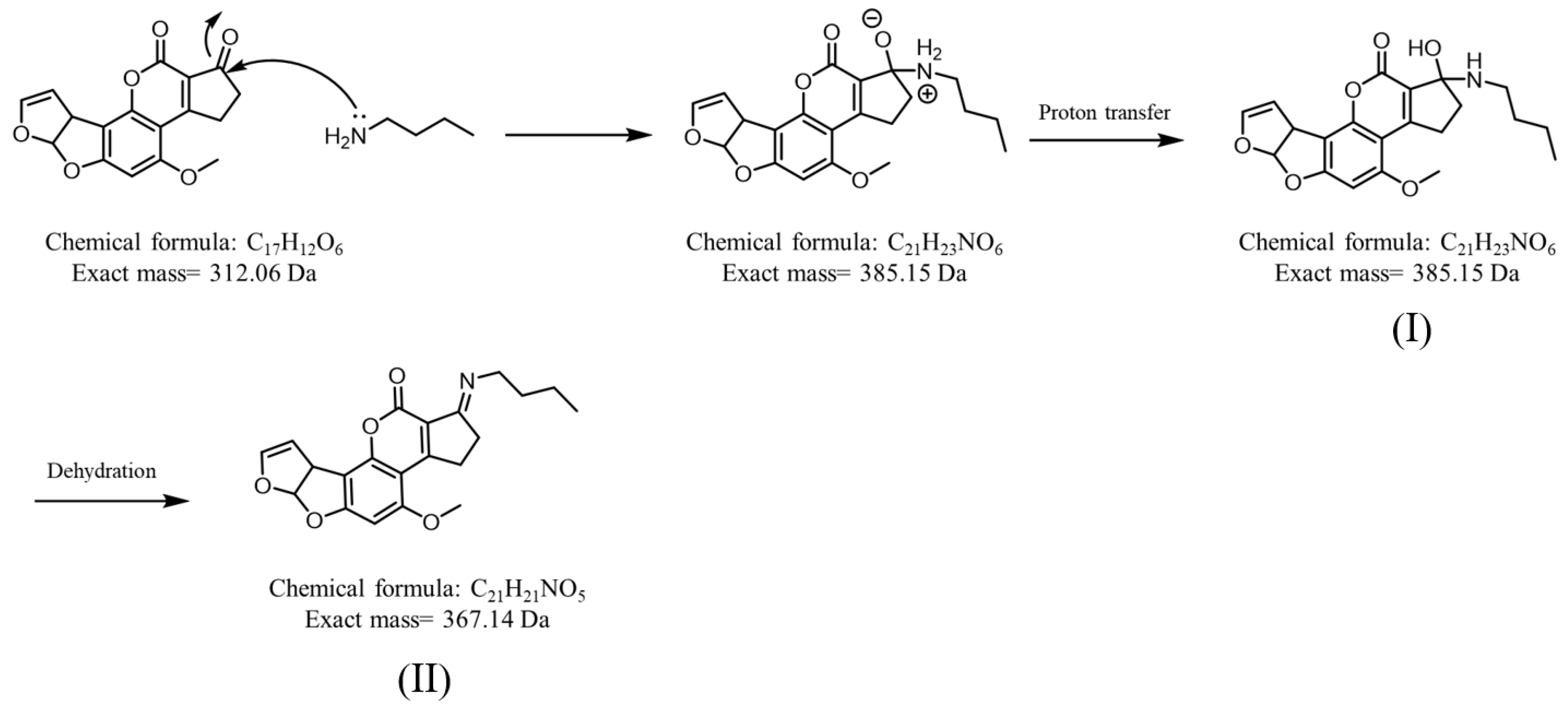
Graphene [52], graphene oxide [16,53], and magnetic graphene oxide [16] have good adsorption capacity with AFB1 because their graphite structures can strongly interact with the aromatic rings on AFB1 [16]. Pencil leads are mainly composed of graphite and a clay binder [54]. Pencil leads have several classifications depending on their blackness (B) and hardness (H), including H, B, HB, and 2B [54]. Carbon fiber ionization (CFI)-MS has been developed based on the use of pencil leads with sharp ends [55] or carbon fibers [55,56,57,58,59,60] as ionization emitters for the analysis of polar and nonpolar analytes. Contactless CFI setup is particularly simple because no direct electric contact is required during CFI-MS analysis [55,57,58,59,60]. Owing to its graphite structure, a sharp pencil lead was used as the SPME fiber for trapping AFB1 in this study. The resultant SPME fiber was directly used as the ionization emitter for CFI-MS analysis. Suitable solvents for the in situ elution of AFB1 from SPME fibers and the facilitating ionization of eluted AFB1 in CFI-MS analysis have also been investigated. Reactive SPME [61] and SPME combined with reactive desorption electrospray ionization MS [62] were used to improve the identification power against target analytes. In this study, an amine, e.g., butylamine, which can react with AFB1 through Schiff base reactions, was added to the elution solvent. In situ reactions that occurred between the AFB1 on the SPME fiber and the added amines (Figure 1) simultaneously occurred during AFB1 elution and CFI-MS analysis. The resulting AFB1 derivatives improved ionization efficiency due to the added amine group and could be used to confirm the presence of AFB1. Accordingly, the feasibility of our developed method for the detection of AFB1 from complex samples was verified in this work.
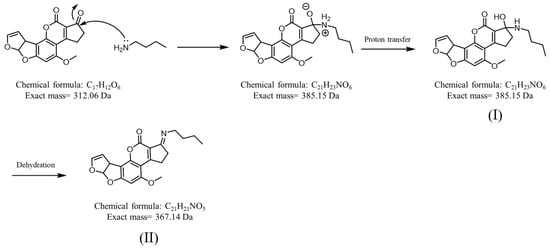
Figure 1.
Derivatization of AFB1 by butylamine via the Schiff base reaction. Structures (I) and (II) show the reaction intermediate and product, respectively.
2. Experimental Section
The details of reagents, materials, and instrumentations are provided in the SI.
2.1. Treatment of Pencil Leads
Pencil leads (length: ~2.5 cm; diameter: 0.3 mm) were sharpened with a box cutter to have diameters of ~150 μm. The surface polymer coating of the pencil leads was removed by using a piece of sandpaper. The resulting pencil leads were soaked in aqueous nitric acid (70%) for 2 h, which was followed by sonication with deionized water, acetone/deionized water (1:1, v/v), and deionized water in a sequence for 20 min to remove residues. The resulting pencil leads were dried in an oven at 60 °C for 2 h prior to use.
2.2. Examination of the Maximum Binding Capacity of Model Analytes on Pencil Leads
To examine the binding capacity of AFB1 (or AFG1) on the as-prepared pencil leads, we placed four pencil leads (length: 1 cm) obtained above in the sample (0.4 mL) containing AFB1 (10−5 M) (or AFG1 (10−5 M)) prepared in Tris buffer (pH 8). The binding capacity of AFB1 (or AFG1) to the pencil lead was estimated according to an absorption band at the wavelength of 365 nm (or 363 nm for AFG1) derived from the samples obtained before and after incubation with the pencil leads by ultraviolet–visible absorption spectroscopy. The maximum binding capacity of the pencil leads to AFB1 (or AFG1) was determined based on the optimal incubation time.
2.3. SPME-CFI-MS Setup
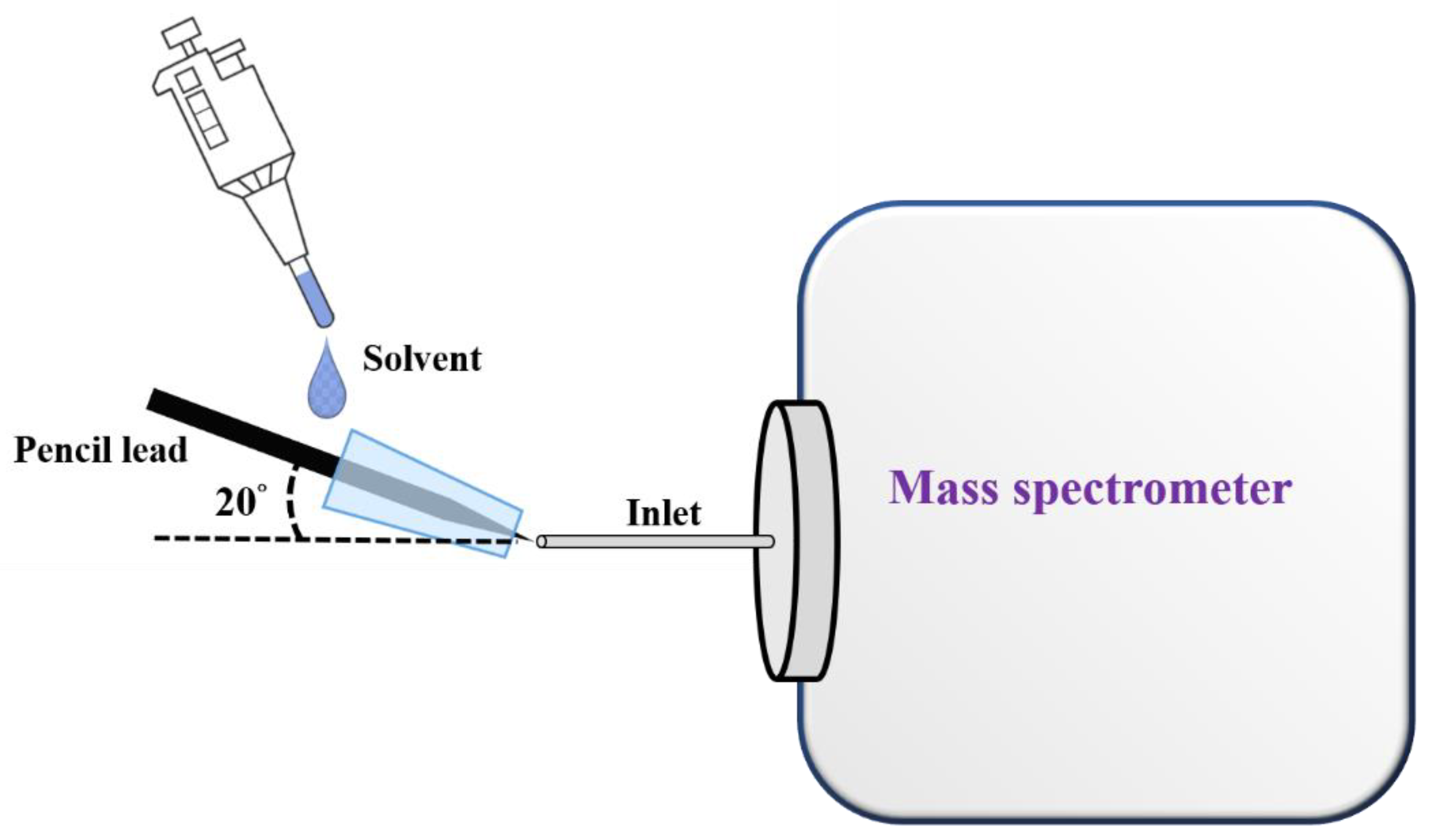
Figure 2 shows the cartoon illustration of our ionization setup. A sharp pencil lead (length: ~2.5 cm; diameter of the sharp tip: ~150 μm) was inserted into a pipette tip (inner diameter: ~0.6 mm in the smaller opening, length: ~0.7 cm), which was placed close to the inlet of the mass spectrometer with an angle of 20°. The mass spectrometer was first turned on prior to placing the pipette inserted with the sharp pencil lead close to the inlet of the mass spectrometer. The pipette tip inserted with a sharp pencil lead was placed in front of the inlet of the mass spectrometer with a distance of ~1 mm. Subsequently, the sample solution (or elution solvent) (10 µL) was injected from the large opening of the pipette tip using a pipette. Mass spectra were immediately recorded by the mass spectrometer upon introduction of the sample solution or elution solvents. When optimizing the distance between our ionization setup and the inlet of the mass spectrometer, AFB1 (10−6 M) was used as the model samples. The sample was serially diluted from an AFB1 stock solution (1 mM) prepared in methanol by ethanol/deionized water (4:1, v/v) with a dilution factor of 10.
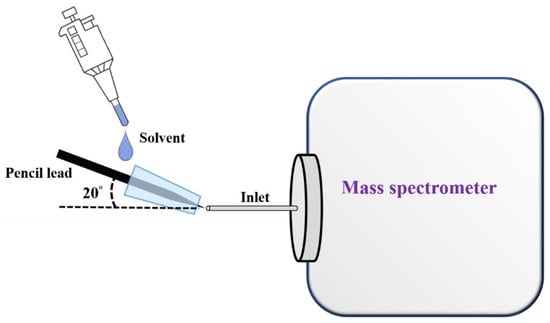
Figure 2.
Cartoon illustration of the setup of a SPME fiber online coupled with CFI-MS.
In addition, we also examined the angle effects between our ionization emitter and the inlet of the mass spectrometer. AFB1 (10−6 M) prepared in ethanol/deionized water (4:1, v/v) was used as a model sample. The mass spectrometer was first switched on prior to placing our ionization emitter. Our ionization setup was placed close to the inlet of the mass spectrometer with a distance of ~1 mm. The angle between the ionization setup with the inlet of the mass spectrometer was varied from 0 to 90°.
2.4. Analysis of Small and Large Biomolecules
To demonstrate the suitability of using our setup for the analysis of analytes with a wide mass range, ametryn (10−7 M) prepared in ethanol/deionized water (1:1, v/v), DK-10 with the sequence of DVFLGRGGGK (10−6 M) prepared in acetonitrile/deionized water (4:1, v/v) and myoglobin (10−6 M) prepared in acetonitrile/deionized water (4:1, v/v) containing 0.1% acetic acid were used as model samples. We placed the pipette tip inserted with a sharp pencil lead close to the inlet of the mass spectrometer with a distance of ~1 mm at an angle of ~20° to the inlet of the mass spectrometer (Figure 2). The mass spectrometer was switched on prior to the introduction of the sample solution. The sample solution (10 µL) was injected from the large opening of the pipette tip. Mass spectra were acquired immediately after the introduction of the sample solution.
2.5. Enrichment of AFB1 on the Pencil Lead for Online Elution and CFI-MS Analysis
The sharp end (2–3 mm) of a pencil lead was immersed in the sample solution containing AFB1 for a given time, stirring with a speed of 400 rpm. After enrichment, the pencil lead was rinsed with Tris buffer (10 mM, pH 8, 0.1 mL × 2), followed by inserting it into a pipette tip that was placed close (~1 mm) to the inlet of the mass spectrometer, which had been switched on. The solvents of ethanol/acetonitrile/deionized water (2:2:1, v/v/v) without and with butylamine were used as online elution solvents. The elution solvent (10 μL) was introduced to the large opening of the pipette (Figure 2), where the elution solvent immediately flowed to the outlet, mainly due to the capillary action. Mass spectra were acquired after the introduction of the elution solvent.
2.6. Examination of Selectivity
To examine the selectivity of our method towards AFB1, a mixture containing AFB1 (100 nM) and AFG1 (300 nM) prepared in Tris (pH 8) was used as a model sample. The sharp end (2 to 3 mm) of the pencil lead was immersed in the prepared mixture (7.5 mL), stirring at a speed of 400 rpm for 2 h. Subsequently, the pencil lead was rinsed with Tris buffer (10 mM, pH 8, 0.1 mL × 2). The resulting pencil lead was inserted into a pipette tip placed close (~1 mm) to the inlet of the mass spectrometer that had been switched on. Mass spectra were immediately recorded by the mass spectrometer after the elution solvent (10 µL) containing ethanol/acetonitrile/deionized water (2:2:1, v/v) spiked with butylamine (10−6 M) was introduced from the large opening of the pipette tip (Figure 2).
2.7. Detection of AFB1 from Peanut Extracts
The intact peanuts with shells (~2 g) prepared in Tris buffer (pH 8, 10 mL) were stirred at a speed of 400 rpm for 5 min. The supernatant of the sample was obtained after centrifugation at 17,000 rpm for 5 min. The resulting supernatant was 3-fold diluted by using Tris buffer (pH 8). The resulting supernatants (7.5 mL) spiked and not spiked with AFB1 (20 nM) were enriched with our SPME fiber. The enrichment steps, the composition of the elution solvent, and the operation of the MS analysis were the same as those stated above.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Examination of the Binding Capacity of AFB1 on the SPME Fiber
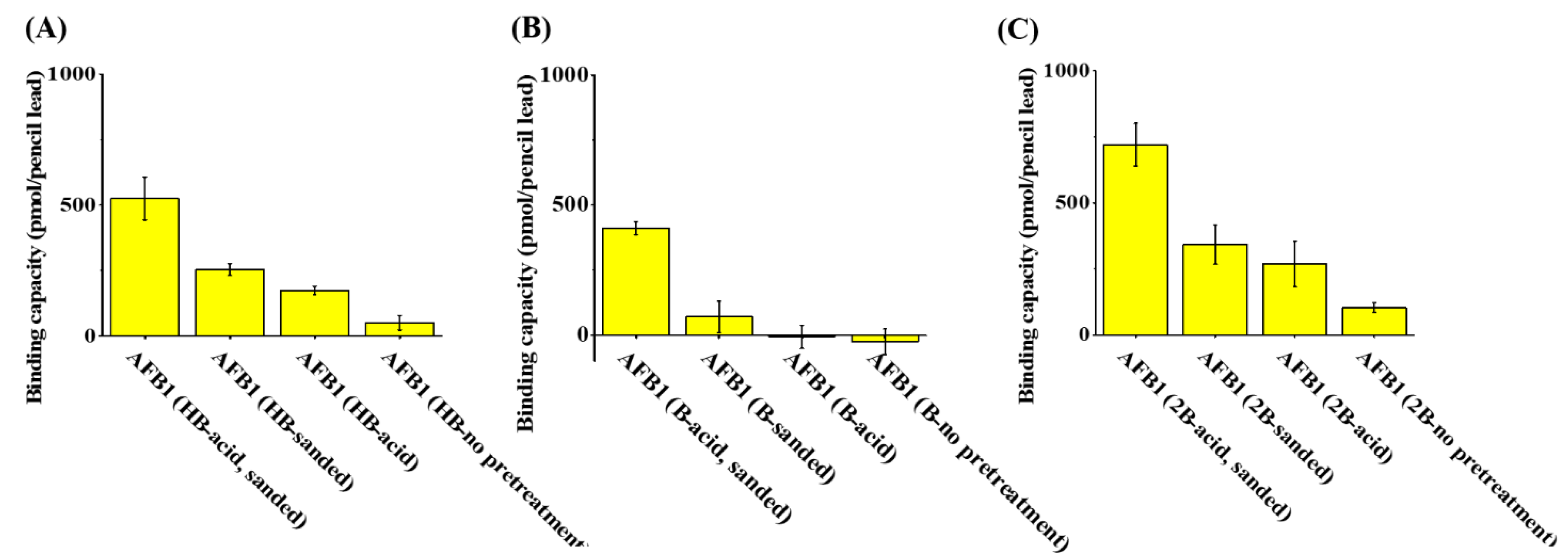
The binding capacities of pencil leads of different types (HB, 1B, and 2B) against AFB1 were examined to determine whether pencil leads can be used as adsorbents for AFB1. The pencil leads were treated with sandpaper and acid prior to extraction to reveal their graphite structures. Figure 3A–C show the binding capacity of HB, 1B, and 2B pencil leads (length: 1 cm), respectively, to AFB1 after being treated with sanding and subsequent soaking in acid, sanding only, soaking in acid only, or without pretreatment. The maximum binding capacity to AFB1 was recorded for the 2B pencil lead treated by sanding and subsequent soaking in an acid solution (Figure 3C). These results indicated that sanding and a subsequent acid treatment are required to effectively remove the surface coating and reveal the graphite structures on the surface of the pencil lead. The 2B pencil leads contain the highest amount of graphite structures among these three types of pencil leads and, therefore, have the highest binding capacity to AFB1. Thus, 2B pencil lead was selected as the SPME fibers for the enrichment of AFB1 from sample solutions in the following analyses.
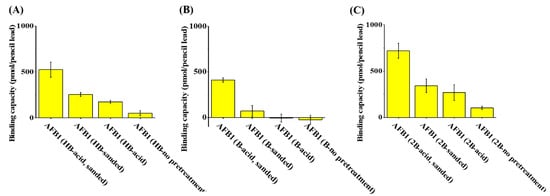
Figure 3.
Examination of the binding capacity of types (A) HB, (B) B, and (C) 2B pencil leads against AFB1.
Raman spectroscopy was employed to characterize the surface of the pencil lead and further confirm the presence of the graphite structure on the treated 2B pencil lead. SI Figure S1A–D show the Raman spectra of 2B pencil leads treated by sanding and soaking in acid, sanding alone, soaking in acid, and no treatment, respectively. Two main peaks at the wavenumbers appeared at ~1347 and ~1576 cm−1, corresponding to the D and G bands, respectively [63]. The G band indicated the presence of graphite structures on the 2B pencil lead, whereas the D band stood for the discorded graphite structure. The intensity of the G band was much higher than that of the D band, indicating that the pencil lead contained abundant graphite structures. Moreover, the pencil lead treated by sanding and soaking in an acid solution had the highest G band among the four Raman spectra shown in Figure S1, indicating the treatments could reveal abundant graphite structures. Thus, the pencil leads treated by sanding and soaking in acid were used as the SPME adsorbents in the following studies.
3.2. Examination of the Optimal Extraction and Recovery Parameters
The optimal binding pH conditions were further examined. SI Figure S2 shows the binding capacity of the SPME fiber (1 cm), i.e., a 2B pencil lead, to AFB1. The results indicated similar binding capacities at different pH conditions. This finding was expected because the binding of AFB1 on the SPME fiber was due to π–π interactions between the aromatic ring in the AFB1 structure and the graphite structures on the pencil lead. Thus, pH conditions should not affect such π–π interactions. However, the binding capacity was slightly improved at a pH above 7. Accordingly, pH 8 was selected as the binding condition in the following analyses.
The equilibrium time for binding of AFB1 to the SPME fiber and the optimal composition of the elution solution was further examined. SI Figure S3A shows the amount of AFB1 trapped by the SPME fiber with different incubation times. The amount of AFB1 on the SPME fiber reached the plateau after 120 min of incubation. Given the short online elution of AFB1 from the SPME fiber for MS analysis, the recovery efficiency after vortex-mixing the SPME fiber adsorbed with AFB1 in different elution solvents for 1 min was investigated. The elution solvents included acetonitrile/deionized water (4:1, v/v), ethanol/deionized water (4:1, v/v), acetonitrile/ethanol/deionized water (3:1:1, v/v/v), and acetonitrile/ethanol/deionized water (2:2:1, v/v/v). SI Figure S3B shows the recovery of AFB1 from AFB1-adsorbed SPME fibers using the solvents as the elution solvents (blue bars). The recovery reached more than 50% when the above elution solvents were employed. These results indicated that AFB1 can be effectively released with suitable solvents in 1 min. The solvent of acetonitrile/ethanol/deionized water (2:2:1, v/v/v) was finally selected as the elution solvent because the addition of ethanol to the elution solvent increased the ion signal of AFB1 during CFI-MS analysis. The yellow bars representing the addition of butylamine in the elution solvents are discussed later.
3.3. Analysis of Model Analytes Using Our Ionization Setup
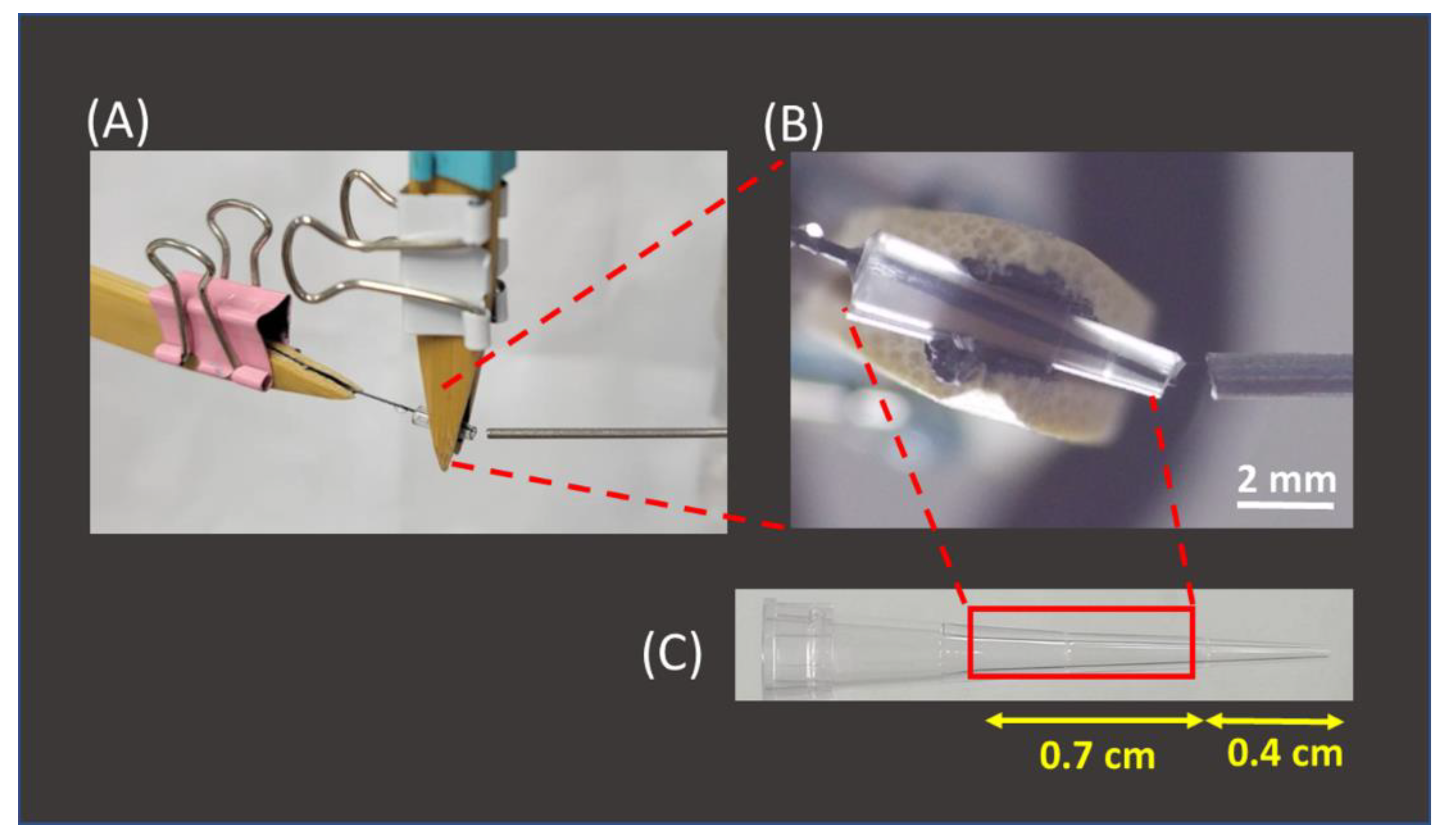
After the feasibility of using 2B pencil lead as SPME fibers for the enrichment of AFB1 from sample solutions was verified, the interface used to couple the SPME fiber and the mass spectrometer was established. Figure 4A shows the photograph of our setup. A pencil lead (length: ~2.5 cm) with a sharp end was inserted into a pipette tip, which was originally used to load a maximum volume of 10 μL (Figure 4B,C). The two ends of the tip were cut (Figure 4B,C) to fit the fiber and load it with the elution solvent. The squared part was used as the tip for fiber insertion (Figure 4C). The solvent or sample solution could be readily introduced to the inlet of the tip from the large opening of the tip during CFI-MS analysis. Furthermore, the angle of ~20° between the ionization tip and the inlet of the mass spectrometer was used to allow the sample solution to easily elute from the tip outlet. If the angle is too large, then the flow rate of the sample solution will become high due to the influence of gravity. An extremely high flow rate is not favorable to ionization. Standard analytes with a wide mass range were used as model samples to examine whether the analytes could be readily ionized using the current setup. SI Figure S4A–C show the mass spectra of ametryn, DK-10, and myoglobin. The protonated ametryn ion at m/z 228 dominated the mass spectrum in SI Figure S4A, and multiply charged ions derived from DK-10 and myoglobin dominated the mass spectra in SI Figure S4B,C. These results showed that our setup is a suitable ionization source and could be readily used to analyze these model samples with a wide mass range. ESI-like mass spectra were obtained. It should be noted that no direct electric contact was made in the SPME-CFI ionization setup. Ionization occurred, mainly resulting from the polarization-induced electrospray [55]. Eliminating the requirement of direct contact on the setup allowed one to easily operate this coupled tool.
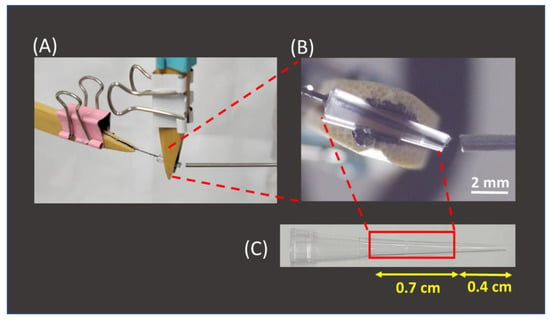
Figure 4.
(A) Photograph of the SPME-CFI interface setup, (B) the zoom-in photograph of the interface, and (C) photograph of the pipette tip.
3.4. Analysis of AFB1 by SPME-CFI-MS
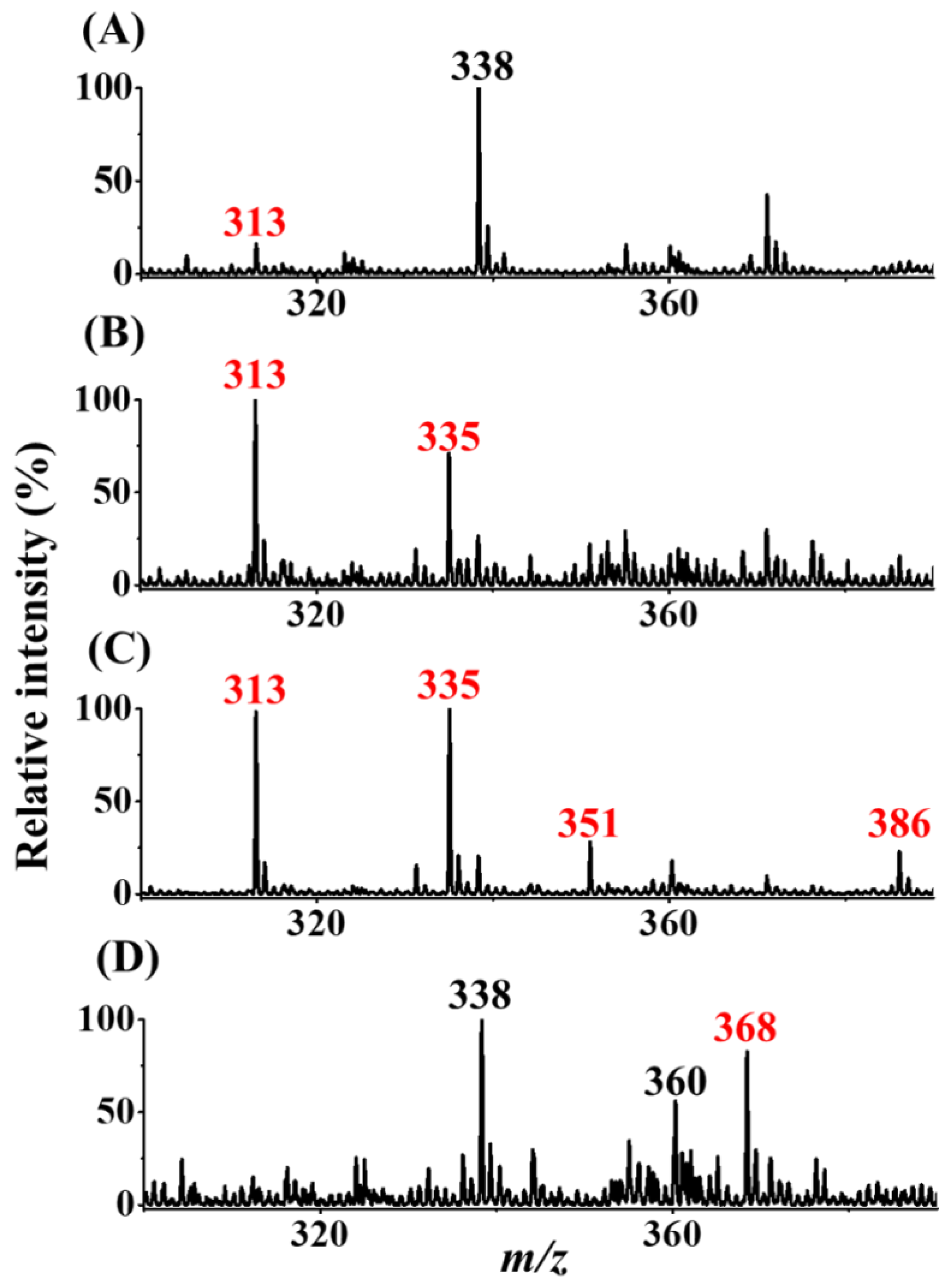
After our setup was verified as an ionization source, further examination was conducted to determine whether our SPME-CFI-MS could be used to detect trace AFB1 from the sample solution trapped by our SPME fiber and subsequent online elution for CFI-MS analysis. Figure 5A shows the direct CFI mass spectrum of the sample containing AFB1 (50 nM) obtained using our setup. A weak peak at m/z 313 corresponding to protonated AFB1 appeared in the mass spectrum. The peak at m/z 338 was attributed to the solvent background. After enrichment with the pencil lead and subsequent online elution for CFI-MS analysis, the peaks at m/z 313 and 335 were derived from protonated and sodiated AFB1, respectively, and improved intensity was observed in the same mass spectrum (Figure 5B). These results showed that our setup can be easily used to couple SPME and CFI-MS online using a sharp pencil lead inserted into a small pipette tip as the interface to effectively improve the intensity of the ions derived from AFB1. Butylamine was added to the elution solvent for online reactive SPME-CFI-MS analysis against AFB1 to further increase the peak intensity derived from AFB1 and confirm its identity. AFB1 was recovered from the SPME fiber using the elution solvent added with butylamine. SI Figure S3B shows the bar graphs (yellow bars) representing the recovery of AFB1 from the SPME fibers with elution by different elution solvents containing butylamine. The results indicated that the addition of butylamine in the elution solvents improved the recovery of AFB1 from the SPME fiber adsorbed with AFB1, except when using the solvent composed of ethanol/deionized water (4:1, v/v). Therefore, the solvent of acetonitrile/ethanol/deionized water (2:2:1, v/v/v) added to butylamine (10−7 M) was used as the online elution solvent for SPME-CFI-MS analysis. The sample was the same as that used in Figure 5B. Figure 5C shows the resultant mass spectrum. Peaks appeared at m/z 313, 335, and 351, which were attributed to protonated AFB1 and sodium and potassium adducts of AFB1, respectively. In addition, a new peak appeared at m/z 386 that corresponded to the protonated derivative of AFB1 (structure I in Figure 1). The appearance of the AFB1 derivative at m/z 386 can be used to further confirm the presence of AFB1 in the sample. Moreover, the signal-to-noise ratios of the peaks derived from AFB1 were improved when using the elution solvent containing additional butylamine. These findings were in agreement with the recovery results (yellow bars in Figure S3B) and verified the possibility of in situ derivatization of AFB1 by butylamine during SPME-CFI-MS analysis. Moreover, improved results were obtained. The reaction between butylamine and the aldehyde group on the AFB1 structure presumably weakened the binding between AFB1 and the SPME fiber. Therefore, the presence of butylamine in the elution solvent not only derivatized AFB1 through the Schiff base reaction in situ, but also improved the elution efficiency of AFB1 from the SPME fiber. The lowest detectable concentration using the current approach was further examined. Figure 5D shows the mass spectra obtained using our SPME fiber to enrich the trace AFB1 from the sample containing AFB1 (~1.25 nM). The peak at m/z 368 corresponding to the protonated derivative (structure II in Figure 1) was observed in the mass spectrum, but the ions derived from the protonated and sodium/potassium adducts of AFB1 were not observed. Nevertheless, the peak was possibly derived from the fragment of derivative I at m/z 386 by losing water, considering that water was not eliminated during reaction and ionization. The signal-to-noise level at the ion at m/z 368 was ~13. These results showed that the lowest detectable concentration of our approach against AFB1 was lower than the allowed level (2 μg kg−1 (=~6 nM))) regulated by most countries [5].
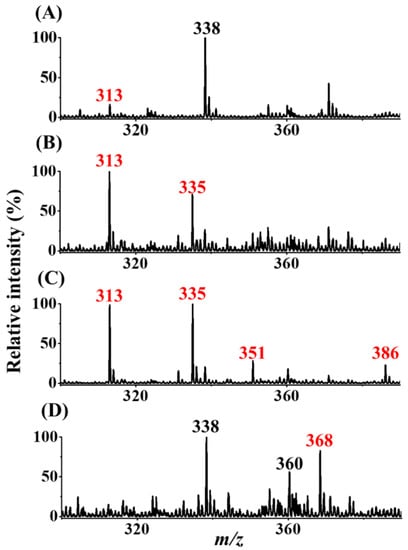
Figure 5.
Mass spectra obtained without and with the addition of butylamine in the elution solvent for online SPME-CFI-MS analysis. (A) Direct CFI-MS mass spectrum of the sample (10 μL) containing AFB1 (50 nM). SPME-CFI mass spectra of samples obtained from the SPME fiber adsorbed with AFB1 (B) without and (C) with the addition of butylamine (10 nM) in the elution solvent containing acetonitrile/ethanol/deionized water (2:2:1, v/v/v). A 2B pencil lead was used as the SPME fiber to enrich AFB1 (50 nM) from the sample solution (7.5 mL) prepared in Tris buffer (pH 8) under stirring for 2 h. (D) SPME-CFI mass spectrum obtained from the sample (7.5 mL) containing AFB1 (~1.25 nM) in Tris buffer (pH 8) after enrichment using our approach.
3.5. Examination of Selectivity
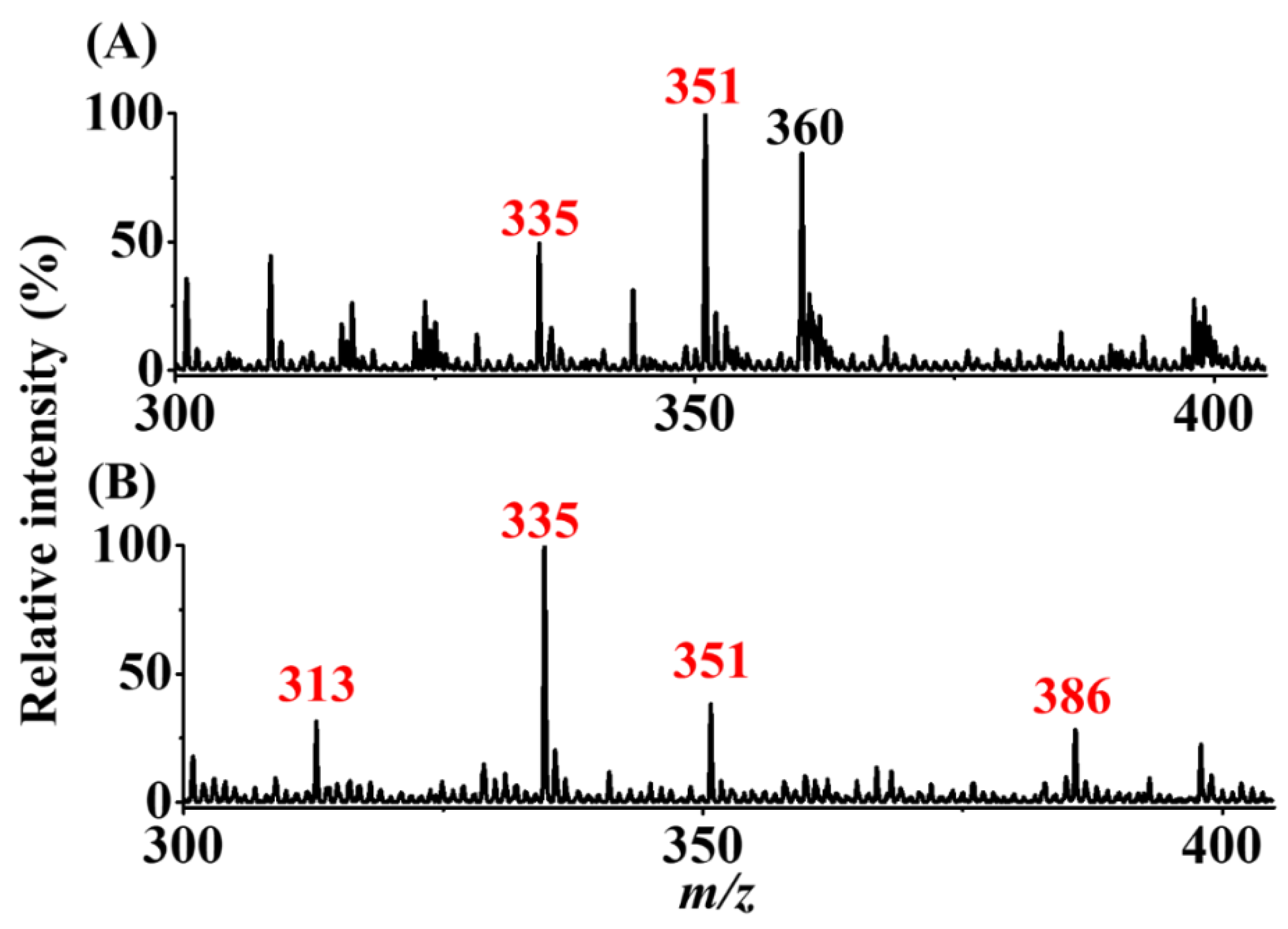
The mixture (7.5 mL) of AFB1 (100 nM) and AFG1 (300 nM) was used as the model sample to examine the selectivity of our method. The experimental steps and parameters were the same as those in Figure 5C,D. Figure 6A,B show the SPME-CFI-MS mass spectra obtained before and after enrichment, respectively. Before enrichment, the peak at m/z 335 corresponded to the sodium adduct of AFB1, and the peak at m/z 360 was attributed to the solvent background. In addition, the peak at m/z 351, possibly from the potassium adduct of AFB1 and the sodium adduct of AFG1, was observed in the mass spectrum. Whether the peak at m/z 351 was derived from AFB1 or AFG1 was impossible to confirm because the potassium adduct of AFB1 and the sodium adduct of AFG1 have indistinguishable nominal masses. After enrichment using our approach, the peak at m/z 313 corresponding to the protonated AFB1 was observed, and the intensity of the peak at m/z 335 was greatly improved. Moreover, the peak at m/z 351 with a decreased intensity was observed in the same mass spectrum, whereas the peak at m/z 386 derived from the protonated butylamine derivative of AFB1 (structure I in Figure 1) was observed in the same mass spectrum. The results showed that AFB1 from the mixture was selectively enriched. This finding was expected because our SPME fiber had a lower binding affinity to AFG1 than to AFB1. The binding capacities of AFB1 and AFG1 were ~720 and 138 pmol/pencil, respectively, according to our experimental results. Presumably, AFG1 has a higher polarity than AFB1 because of one additional oxygen atom in the structure of AFG1 (inset structures in Figure 6A), leading to a poorer binding affinity to the 2B pencil lead. Similar results were obtained when using graphene oxide as adsorbents against AFB1 and AFG1 [16]. Moreover, AFB1 could be easily identified after enrichment using our approach based on the appearance of the derivative peak at m/z 386. These results confirmed that the addition of butylamine to the elution solvent did not only improve enrichment efficiency, but also helped in identification of the presence of AFB1. Our approach can be used to distinguish AFB1 from AFG1.
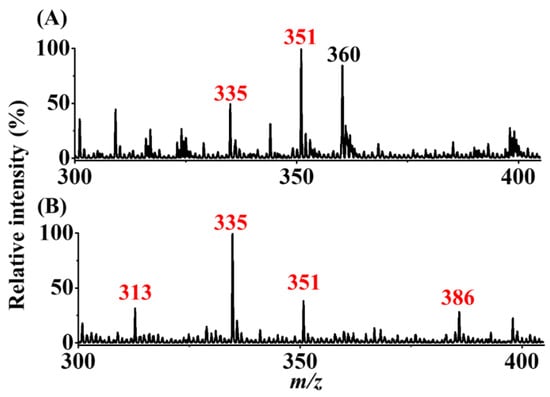
Figure 6.
Examination of selectivity. SPME-CFI mass spectra of the samples (7.5 mL) containing AFB1 (100 nM) and AFG1 (300 nM) obtained (A) before and (B) after enrichment. The elution solvent (10 μL) contained acetonitrile/ethanol/deionized water (2:2:1, v/v/v) with the addition of butylamine (1 μM).
3.6. Analysis of Simulated Real Samples
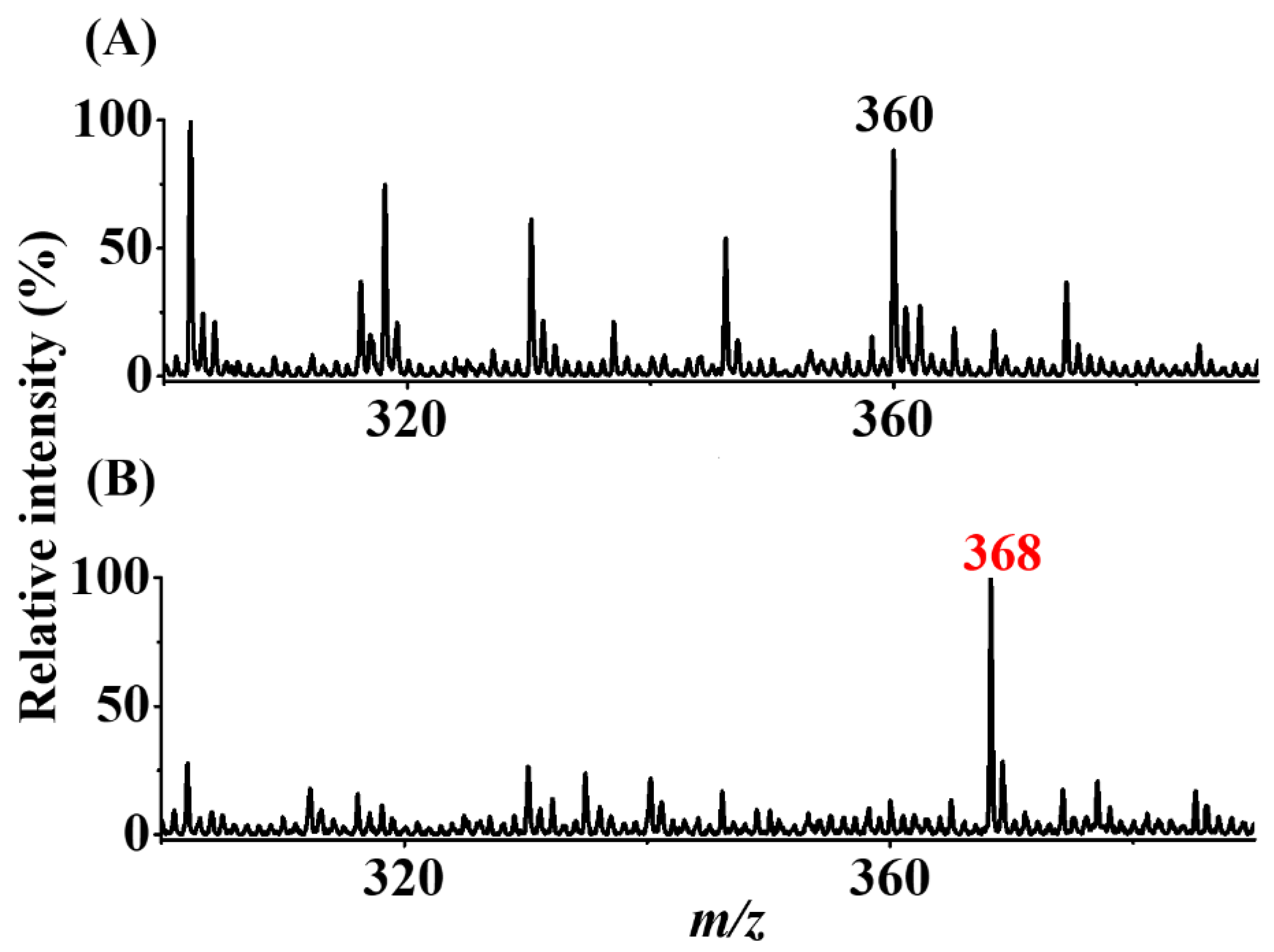
Peanuts obtained from a local store were also used as model samples to determine whether our approach can be used to detect the presence of trace AFB1 from real-world samples. The experimental details are provided in the Section 2. Figure 7A shows the direct CFI-MS mass spectrum of the sample containing peanut extract spiked with AFB1 (20 nM) obtained before enrichment. No AFB1-derived ions were observed, and only the solvent background ions at m/z 360 were observed in the mass spectrum. Figure 7B shows the SPME-CFI mass spectrum of the sample containing peanut extract spiked with AFB1 (20 nM) after enrichment. The ion at m/z 368 corresponding to the protonated AFB1 derivative with a loss of a water molecule (structure II in Figure 1) appeared in the mass spectrum. These results showed that our approach can be used to detect trace AFB1 from complex peanut extract samples.
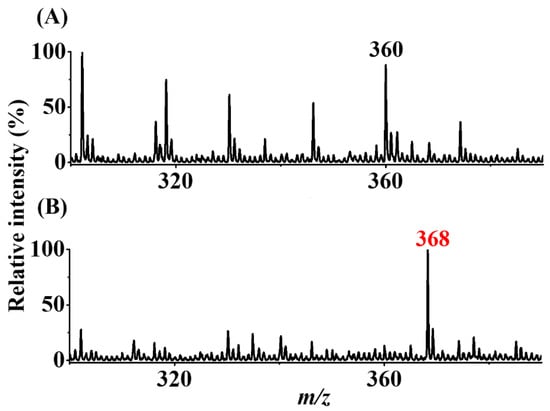
Figure 7.
Real sample analysis. SPME-CFI mass spectra of the samples (7.5 mL) containing peanut extract (A) without and (B) with additional AFB1 (20 nM) obtained after enrichment. The elution solvent (10 μL) contained acetonitrile/ethanol/deionized water (2:2:1, v/v/v) with the addition of butylamine (1 μM).
3.7. Comparison of Our Method with Those Existing Methods for Analysis of AFB1
SI Table S2 shows the comparison of our developed method with other methods reported lately [14,64,65,66,67,68,69,70]. The fabrication of the SPME fiber, i.e., 2B pencil leads, required a much shorter time to prepare than that of other SPME fibers. Although the extraction time in our current approach was longer than that required in other approaches, the elution time was shorter and the elution volume was much smaller than those required in the previous reports. In addition, the LOD obtained in our approach was not the lowest compared with other existing methods, but the analysis time only took 1 min, which was the shortest among these methods for the detection of AFB1.
4. Conclusions
We successfully developed a reactive SPME-CFI-MS coupled method for the detection of AFB1. Our results indicated that 2B pencil lead has good binding capacity to AFB1, and the AFB1 adsorbed on the pencil lead can be effectively eluted by suitable elution solvents. In situ reactive SPME-CFI-MS analysis of AFB1 can be readily carried out with the addition of butylamine in the elution solvent. Moreover, the elution efficiency of AFB1 from the SPME fiber with the elution solvent containing butylamine can be further improved. The derivatives of AFB1 from its reaction with butylamine can be used to further confirm the identity of AFB1. The interface, which only requires a sharp pencil lead as the SPME fiber and a 10 μL pipette tip to couple the SPME fiber and CFI-MS, can be easily configured. Direct electric contact on the interface is not necessary; thus, the setup can be easily established in front of the mass spectrometer. The lowest detectable concentration of AFB1 using our approach is lower than the regulated concentration by most countries, indicating that our strategy can be used to rapidly screen the presence of AFB1 in real-world samples. The main advantages of the developed method include speed, simplicity, and a low cost interface. Efforts are still required to develop strategies in demonstrating the feasibility of using the current method for quantitative analysis. To our knowledge, this work is the first report on reactive SPME-CFI-MS for AFB1 analysis. Furthermore, the derivative agent, i.e., butylamine, that can assist in AFB1 elution from the SPME fiber in addition to the in situ derivatization reaction, was demonstrated for the first time. Our results also indicated that 2B pencil lead is a useful SPME fiber for aromatic ring-containing molecules, e.g., AFB1. Thus, the possibility of using 2B pencil lead as the SPME fiber for trapping other analytes containing aromatic rings must be further investigated. The detection tool in the developed method is CFI-MS, which possesses good selectivity and confirmation power for analytes with different molecular weights. Thus, the identification of the analytes trapped by the SPME fiber can be readily carried out by the developed SPME-CFI-MS method. However, further investigation is required to examine this possibility.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/separations9080199/s1, Figure S1: Raman spectra of 2B pencil leads; Figure S2: Examination of pH effects; Figure S3: Examination of the optimal enrichment time and the recovery with different elution solvents; Figure S4. Analysis of standard samples using our ionization setup; Table S1: List of the existing methods for analysis of AFB1 and related mycotoxins; Table S2: List of the existing SPME approaches for the analysis of AFB1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.-J.T., Y.-T.L. and Y.-C.C.; Data curation, J.-J.T. and Y.-C.C.; Funding acquisition, Y.-C.C.; Investigation, J.-J.T. and Y.-T.L.; Methodology, J.-J.T., Y.-T.L. and Y.-C.C.; Resources, Y.-C.C.; Supervision, Y.-C.C.; Validation, J.-J.T. and Y.-C.C.; Visualization, J.-J.T.; Writing—original draft, J.-J.T. and Y.-C.C.; Writing—review & editing, Y.-C.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan (MOST 108–2113-M-009–018-MY3).
Acknowledgments
We are thankful for the financial support of this study from the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan (MOST 108–2113-M-009–018-MY3).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Moss, M.O. Risk assessment for aflatoxins in foodstuffs. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegradation 2002, 50, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kew, M.C. Aflatoxins as a cause of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastrointest. Liver Dis. 2013, 22, 305–310. [Google Scholar]
- Juan, C.; Zinedine, A.; Moltó, J.C.; Idrissi, L.; Mañes, J. Aflatoxins levels in dried fruits and nuts from Rabat-Sale’ area, Morocco. Food Control 2008, 19, 849–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, T. How to establish international limits for mycotoxins in food and feed? Food Control 2003, 14, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Regulation (EU) No 165/2010 of 26 February 2010 Amending Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 Setting Maximum Levels for Certain Contaminants in Foodstuffs as Regards Aflatoxins. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A32010R0165&qid=1643338579869 (accessed on 28 January 2022).
- Lee, N.A.; Wang, S.; Allan, R.D.; Kennedy, I.R. A rapid aflatoxin B1 ELISA: Development and validation with reduced matrix effects for peanuts, corn, pistachio, and Soybeans. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 2746–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, P.D.; Gomes da Silva, J.L.; Caldas, E.D. Simultaneous analysis of aflatoxins B1, B2, G1, G2, M1 and ochratoxin A in breast milk by high-performance liquid chromatography/fluorescence after liquid-liquid extraction with low temperature purification (LLE-LTP). J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1304, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Ding, F.; Yin, W.; Ma, J.; Wang, B.; Nie, A.; Han, H. From electrochemistry to electroluminescence: Development and application in a ratiometric aptasensor for aflatoxin B1. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 7578–7585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Zhao, Y.; Li, C.; Jie, G. Versatile Electrochemiluminescence and electrochemical “on–off” assays of methyltransferases and aflatoxin b1 based on a novel multifunctional dna nanotube. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 3546–3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorensen, L.K.; Elbæk, T.H. Determination of mycotoxins in bovine milk by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2005, 820, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.Q.; Zou, B.; Zhao, X.Y.; Liu, S.; Xu, W.W.; Huang, T.T.; Zong, Q.; Wang, S.W. Rapid qualitative and quantitative analysis of aflatoxin B1 in Pu-erh tea by liquid chromatography-isotope dilution tandem mass spectrometry coupled with the QuEChERS purification method. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 4776–4783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Li, C.; Moezzi, B. Simultaneous determination of bisphenol A, aflatoxin B1, ochratoxin A, and patulin in food matrices by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2013, 27, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, H.L.; Su, X.G.; Wang, H.B. Simultaneous determination of aflatoxin B1, bisphenol A, and 4-nonylphenol in peanut oils by liquid-liquid extraction combined with solid-phase extraction and ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 1303–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Wang, S.; Huang, J.; Chu, C.; Li, R.; Li, Q.; Wang, Q.; Hu, Y.; Cao, J.; Chen, Y.; et al. Determination of aflatoxin M1 and B1 in milk and jujube by miniaturized solid-phase extraction coupled with ultra high performance liquid chromatography and quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 3677–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCoy, L.F.; Scholl, P.F.; Schleicher, R.L.; Groopman, J.D.; Powers, C.D.; Pfeiffer, C.M. Analysis of aflatoxin B1-lysine adduct in serum using isotope-dilution liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 19, 2203–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.-T.; Kandasamy, K.; Chen, Y.-C. Magnetic graphene oxide-based affinity surface-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry for screening of aflatoxin B1 from complex samples. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 7310–7316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josselin, L.; De Clerck, C.; De Boevre, M.; Moretti, A.; Jijakli, M.H.; Soyeurt, H.; Fauconnier, M.L. Volatile organic compounds emitted by aspergillus flavus strains producing or not aflatoxin B1. Toxins 2021, 13, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheijooni-Fumani, N.; Hassan, J.; Yousefi, S.R. Determination of aflatoxin B1 in cereals by homogeneous liquid-liquid extraction coupled to high performance liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection. J. Sep. Sci. 2011, 34, 1333–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corcuera, L.-A.; Ibáñez-Vea, M.; Vettorazzi, A.; Gonzalez-Penas, E.; de Cerain, A.L. Validation of a UHPLC-FLD analytical method for the simultaneous quantification of aflatoxin B1 and ochratoxin a in rat plasma, liver and kidney. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2011, 879, 2733–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-X.; Zhang, P.; Fu, X.-F.; Zhou, Y.-X.; Peng, X.-T. Rapid and sensitive detection of aflatoxin B1, B2, G1 and G2 in vegetable oils using bare Fe3O4 as magnetic sorbents coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2020, 58, 678–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Tian, M.; Yan, X.; Xiao, W. Isolation of Aflatoxin B1 from Moldy Foods by Solid-Phase Extraction Combined with Bifunctional Ionic Liquid-Based Silicas. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2018, 2018, 8427580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexovic, M.; Horstkotte, B.; Solich, P.; Sab, J. Automation of static and dynamic non-dispersive liquid phase microextraction. Part 2: Approaches based on impregnated membranes and porous supports. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 907, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Survey, A.T. Global Mycotoxin Occurrence in Feed: A ten-year survey. Toxins 2019, 11, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, L.A.M.; Pereyra, M.L.G.; Keller, K.M.; Alonso, V.A.; Oliveira, A.A.; Almeida, T.X.; Barbosa, T.S.; Nunes, L.M.T.; Cavaglieri, L.R.; Rosa, C.A.R. Fungal and mycotoxins contamination in corn silage: Monitoring risk before and after fermentation Fungal and mycotoxins contamination in corn silage: Monitoring risk before and after fermentation. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2013, 52, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, Y.; Tatnell, J.; Krosch, S.; Karanja, J.; Gnonlonfin, B.; Wanjuki, I.; Wainaina, J.; Harvey, J. An improved simulation model to predict pre-harvest aflatoxin risk in maize. Food Crop. Res. 2015, 178, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Chang, P.K.; Ehrlich, K.C.; Cary, J.W.; Bhatnagar, D.; Cleveland, T.E.; Payne, G.A.; Linz, J.E.; Woloshuk, C.P.; Bennett, J.W. Clustered Pathway Genes in Aflatoxin Biosynthesis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klich, M.A. Aspergillus flavus: The major producer of aflatoxin. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2007, 8, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrenk, D.; Bignami, M.; Bodin, L.; Chipman, J.K.; Grasl-kraupp, B.; Hogstrand, C.; Hoogenboom, L.R.; Leblanc, J.; Nebbia, C.S.; Nielsen, E.; et al. Risk assessment of aflatoxins in food. EFSA J. 2020, 18, 6040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food, E.; Authority, S. Outcome of a Public Consultation on the Draft Risk Assessment of Aflatoxins in Food; European Food Safety Authority (EFSA): Parma, Italy, 2020; Volume 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matabaro, E.; Ishimwe, N.; Uwimbabazi, E.; Lee, B.H. Current immunoassay methods for the rapid detection of aflatoxin in milk and dairy products. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 808–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, P.A.; Hendrich, S.; Landgren, C.; Bryant, C.M. Food mycotoxins: An update. J. Food Sci. 2006, 71, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, L.; Sant’Ana, A.S. Modified mycotoxins: An updated review on their formation, detection, occurrence, and toxic effects. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 111, 189–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthiller, F.; Cramer, B.; Iha, M.H.; Krska, R.; Lattanzio, V.M.T.; MacDonald, S.; Malone, R.J.; Maragos, C.; Solfrizzo, M.; Stranska- Zachariasova, M.; et al. Developments in mycotoxin analysis: An update for 2016–2017. World Mycotoxin J. 2018, 10, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelderblom, W.C.; Shephard, G.S.; African, S.; Vismer, H. Mycotoxins detection methods, management. In Mycotoxins: Detection Methods, Management, Public Health and Agricultural Trade; CABI Publishing: Manhattan, KS, USA, 2008; pp. 29–39. ISBN 9781845930820. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, J.W.; Inamdar, A.A. Are some fungal volatile organic compounds (VOCs) mycotoxins? Toxins 2015, 7, 3785–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inamdar, A.A.; Morath, S.; Bennett, J.W. Fungal volatile organic compounds: More than just a funky smell? Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 74, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, H.; Lord, H.L.; Pawliszyn, J. Applications of solid-phase microextraction in food analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 880, 35–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Garcés, N.; Gionfriddo, E.; Gómez-Ríos, G.A.; Alam, M.N.; Boyacı, E.; Bojko, B.; Singh, V.; Grandy, J.; Pawliszyn, J. Advances in solid phase microextraction and perspective on future directions. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 302–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Ouyang, G.F. In situ solid phase microextraction sampling of analytes from living human objects for mass spectrometry analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 143, 116368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vas, G.; Vekey, K. Solid-phase microextraction: A powerful sample preparation tool prior to mass spectrometric analysis. J. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 39, 233–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.W.; Yang, Y.Y.; Wang, X.W.; Luan, T.G. Strategies for coupling solid-phase microextraction with mass spectrometry. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 55, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Deng, J.W.; Yang, Y.Y.; Wang, X.W.; Chen, B.W.; Liu, H.T.; Zhou, H.Y.; Ouyang, G.F.; Luan, T.G. Coupling solid-phase microextraction with ambient mass spectrometry: Strategies and applications. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 85, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochalski, P.; King, J.; Unterkofler, K.; Hinterhuber, H.; Amann, A. Emission rates of selected volatile organic compounds from skin of healthy volunteers. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. 2014, 959, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucero, M.; Estell, R.; Tellez, M.; Fredrickson, E. A retention index calculator simplifies identification of plant volatile organic compounds. Phytochem. Anal. 2009, 20, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farag, M.A.; Rasheed, D.M.; Kamal, I.M. Volatiles and primary metabolites profiling in two Hibiscus sabdariffa (roselle) cultivars via headspace SPME-GC-MS and chemometrics. Food Res. Int. 2015, 78, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- San, A.T.; Joyce, D.C.; Hofman, P.J.; Macnish, A.J.; Webb, R.I.; Matovic, N.J.; Williams, C.; De Voss, J.J.; Wong, S.H.; Smyth, H.E. Stable isotope dilution assay (SIDA) and HS-SPME-GCMS quantification of key aroma volatiles for fruit and sap of Australian mango cultivars. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conde, F.J.; Afonso, A.M.; Gonzalez, V.; Ayala, J.H. Optimization of an analytical methodology for the determination of alkyl- and methoxy-phenolic compounds by HS-SPME in biomass smoke. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2006, 385, 1162–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzo, A.; Panseri, S.; Vagge, I.; Giorgi, A. Volatile fingerprint of italian populations of orchids using solid phase microextraction and gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry. Molecules 2014, 19, 7913–7936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Fonslow, B.R.; Wong, C.C.L.; Nakorchevsky, A.; Yates, I.J.R. Improving the comprehensiveness and sensitivity of sheathless capillary electrophoresis–tandem mass spectrometry for proteomic analysis. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 8505–8513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, M.T.; Saraji, M.; Yousefi, S. Negative electrospray ionization ion mobility spectrometry combined with microextraction in packed syringe for direct analysis of phenoxyacid herbicides in environmental waters. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1249, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Zheng, B.; Rickert, D.; Gomez-Rios, G.A.; Bojko, B.; Pawliszyn, J.; Yao, Z.P. Direct coupling of solid phase microextraction with electrospray ionization mass spectrometry: A Case study for detection of ketamine in urine. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1075, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feizy, J.; Jahani, M.; Beigbabaei, A. Graphene adsorbent-based solid-phase extraction for aflatoxins clean-up in food samples. Chromatographia 2019, 82, 917–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geleta, G.S.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, Z. A novel reduced graphene oxide/molybdenum disulfide/polyaniline nanocomposite-based electrochemical aptasensor for detection of aflatoxin B1. Analyst 2018, 143, 1644–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pencil. Available online: http://www.fact-index.com/p/pe/pencil.html (accessed on 24 February 2022).
- Wu, M.-X.; Wang, H.-Y.; Zhang, J.-T.; Guo, Y.L. Multifunctional Carbon Fiber Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 9547–9553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.-L.; Chen, T.-Y.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.-C. Carbon fiber ionization mass spectrometry for the analysis of analytes in vapor, liquid, and solid phases. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 13458–13465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.-L.; Chen, T.-Y.; Chen, W.-J.; Faha Baig, M.M.; Wu, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.-C. Carbon fiber ionization mass spectrometry coupled with solid phase microextraction for analysis of Benzo[a]pyrene. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1049, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.-L.; Wu, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.-C. Detection of pesticide residues on intact tomatoes by carbon fiber ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 1095–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Xi, H.; Wu, L.; Zhang, J.; Peng, G.; Su, Y. Direct analysis of volatile components from intact jujube by carbon fiber ionization mass spectrometry. BMC Chem. 2019, 13, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.-C. Reactive carbon fiber ionization-mass spectrometry for characterization of unsaturated hydrocarbons from plant aroma. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 5489–5497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, J.J.; Grandy, J.J.; Gomez-Rios, G.A.; Gionfriddo, E.; Pawliszyn, J. Solid phase microextraction on-fiber derivatization using a stable, portable, and reusable pentafluorophenyl hydrazine standard gas generating vial. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 6859–6866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Chen, H.; Zhang, X.; Cooks, R.G.; Ouyang, Z. Rapid screening of anabolic steroids in urine by reactive desorption electrospray ionization. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 8327–8332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenta, M.A.; Dresselhaus, G.; Dresselhaus, M.S.; Cançado, L.G.; Jorio, A.; Saito, R. Studying disorder in graphite-based systems by Raman spectroscopy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2007, 9, 1276–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Es’haghi, Z.; Sorayaei, H.; Samadi, F.; Masrournia, M.; Bakherad, Z. Fabrication of a novel nanocomposite based on sol-gel process for hollow fiber-solid phase microextraction of aflatoxins: B1 and B2, in cereals combined with high performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2011, 879, 3034–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinto, M.; Spadaccino, G.; Palermo, C.; Centonze, D. Determination of aflatoxins in cereal flours by solid-phase microextraction coupled with liquid chromatography and post-column photochemical derivatization-fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 8636–8641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nonaka, Y.; Saito, K.; Hanioka, N.; Narimatsu, S.; Kataoka, H. Determination of aflatoxins in food samples by automated on-line in-tube solid-phase microextraction coupled with liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 4416–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chmangui, A.; Jayasinghe, G.; Driss, M.R.; Touil, S.; Bermejo-Barrera, P.; Bouabdallah, S.; Moreda-Piñeiro, A. Assessment of trace levels of aflatoxins AFB1 and AFB2 in non-dairy beverages by molecularly imprinted polymer based micro solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Methods 2021, 13, 3433–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasinghe, G.T.M.; Domínguez-González, R.; Bermejo-Barrera, P.; Moreda-Piñeiro, A. Ultrasound assisted combined molecularly imprinted polymer for the selective micro-solid phase extraction and determination of aflatoxins in fish feed using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1609, 460431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amde, M.; Temsgen, A.; Dechassa, N. Ionic liquid functionalized zinc oxide nanorods for solid-phase microextraction of aflatoxins in food products. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2020, 91, 103528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Xu, C.; Jiang, N.; Wang, J.; Ding, C.F. Poly (methacrylic acid-co-diethenyl-benzene) monolithic microextraction column and its application to simultaneous enrichment and analysis of mycotoxins. Talanta 2018, 178, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).