Abstract
The extensive use of pesticides represents a risk to human health. Consequently, legal frameworks have been established to ensure food safety, including control programs for pesticide residues. In this context, the performance of analytical methods acquires special relevance. Such methods are expected to be able to determine the largest number of compounds at trace concentration levels in complex food matrices, which represents a great analytical challenge. Technical advances in mass spectrometry (MS) have led to the development of more efficient analytical methods for the determination of pesticides. This review provides an overview of current analytical strategies applied in pesticide analysis, with a special focus on MS methods. Current targeted MS methods allow the simultaneous determination of hundreds of pesticides, whereas non-targeted MS methods are now applicable to the identification of pesticide metabolites and transformation products. New trends in pesticide analysis are also presented, including approaches for the simultaneous determination of pesticide residues and other food contaminants (i.e., mega-methods), or the recent application of techniques such as ion mobility–mass spectrometry (IM–MS) for this purpose.
1. Introduction
Today, there is a growing interest in the consumption of organic food by part of the population, most of whom largely associate these products with food free of pesticides and mineral fertilizers [1]. However, the use of pesticides is still relevant in agricultural production to prevent disease and infestation of crops. The consumption of agro-food products is the main source of exposure to pesticides [2]. In 2019, around 403,569.6 tons of pesticides were sold in the European Union (EU) [3], which is an indicator of the risk that these substances represent to today’s society. There are currently up to 448 active ingredients that can be used in the EU as pesticides, while up to 934 compounds have been banned for this purpose [4]. These substances are regulated by Regulation (EC) No. 1107/2009 [5]. The Codex Alimentarius Commission, the EU, and many countries around the world have established maximum residue levels (MRLs) for active substances in food to protect consumers’ health, since exposure to higher concentrations poses a health risk [6,7]. Likewise, prohibited active substances must not be found in foodstuffs. A default MRL of 0.01 mg/kg has been established for pesticides in plant and animal commodities when not otherwise indicated.
Control plans are currently carried out under Regulation (EC) No 396/2005 to examine the levels of pesticide residues in food on the European market [6]. In 2019, 1.0% of the 12,579 food samples that were investigated under the EU-coordinated control program were declared non-compliant, since they exceeded the MRLs established for specific pesticide compounds [8]. A total of 182 pesticides was included in this monitoring program. Several pesticides not approved in the EU—such as carbofuran, acephate, and fipronil, among others—were found in samples of products grown in the EU or in imported samples. This highlights the importance of efficient control plans that involve the application of reliable analytical methods, which are not only essential to comply with current legislation, but ultimately are also necessary to protect the health of citizens in accordance with current knowledge on the toxicity of pesticides.
The HBM4EU initiative has recently identified a list of substances of very high concern due to their potential adverse effects on humans, including several classes of pesticides (i.e., pyrethroids, organophosphates, glyphosate, polyethoxylated tallow amine (POEA), or fipronil) [9]. However, the simultaneous monitoring of these substances and other pesticide residues in food represents an analytical challenge. Pesticides consist of different chemical classes with different psychochemical properties, and are present at low concentrations in complex food matrices [10]. Food samples can contain highly polar and non-polar pesticides, making it impossible to achieve good recovery through the application of a specific sample treatment or their chromatographic separation by a single analytical method. Moreover, today, the monitoring of pesticides per se does not seem sufficient, and the analysis of their transformation products also seems necessary. Pesticide transformation products are a consequence of their degradation in the environment through hydrolysis, photolysis, oxidation, and biodegradation processes and, in certain cases, their toxicity is greater than that of their chemical precursors [11]. Despite this, the toxicity of these transformation products is not taken into account for pesticide marketing approval [12]. The analysis of pesticide transformation products in food can be analytically difficult and cumbersome. Information on these compounds is limited, and chemical standards that allow their identification are not always available [13].
In this framework, the EU guidelines on analytical quality control and method validation procedures for the analysis of pesticide residues in food indicate that, although other detection systems are possible, mass spectrometry (MS) is the preferred detection technique for this purpose [14]. The main reason for this is that MS provides more confidence in the identification of compounds. Gas chromatography (GC) coupled with MS has traditionally been applied for the determination of pesticides, but liquid chromatography LC–MS is now more widely used for this purpose. LC–MS is more suitable for the analysis of a broader range of compounds, especially for more polar pesticides and pesticide metabolites, as well as for non-volatile analytes [15]. In this sense, there is also a clear tendency to go beyond traditional targeted methods focused on the determination of specific pesticide residues, such as those methods used in official control plans. Currently, there is a trend towards the development of suspect screening and non-targeted methods aimed at the detection of initially expected pesticide residues and the identification of unknown pesticide-related substances (e.g., transformation products) [16].
This review discusses the current role of MS in pesticide analysis workflows, including the evolution from single-residue methods to multiclass methods and, more recently, to mega-methods aimed at the simultaneous analysis of chemical residues and contaminants. Furthermore, although targeted methods are commonly used in pesticide residue monitoring, recent approaches focused on the development of suspect screening and non-targeted methods for this purpose are also presented. A brief discussion of the sample treatments and chromatographic separations currently applied in the determination of pesticides is also included. They are of great importance in the matrix effect observed in MS-based methods and in the quality of the mass spectra obtained. This is not a comprehensive review, and only a few of the most relevant studies have been selected to illustrate the current analytical strategies in pesticide analysis.
2. From Single-Residue Methods to “Mega-Methods”
Pesticide residue monitoring programs are generally restricted to a reduced number of selected pesticides and metabolites. Therefore, the scope and capabilities of these multiresidue methods are limited and, among other issues, the presence of less common or misused pesticides and/or their transformation products may go unnoticed [17]. Although the development of analytical methods for the determination of a reduced number of pesticides belonging to the same chemical family is still reported [18,19,20], current selective analytical approaches are largely limited to the determination of challenging pesticides. In general, multiresidue methods must be applied for pesticide analysis according to SANTE/2020/12830 [14]. If multiresidue methods are not applicable for a specific pesticide, data and/or justification explaining why must be provided. Single-residue methods are intended for selected pesticides that, due to their particular physicochemical properties (e.g., usually high polarity), require specific protocols for their determination [21]. The main drawbacks that prevent the simultaneous determination of these compounds with other pesticides are their low or close-to-zero affinity for the organic solvents commonly used as the extraction phase in sample treatments, and their low retention in conventional reversed-phase columns used in pesticide analysis [22]. To overcome these problems, the EU Reference Laboratories have proposed up to 11 different main single-residue methods for the determination of up to 55 polar pesticides [23].
Despite the different physicochemical properties of pesticides, which are especially crucial for the efficient extraction of analytes from complex food samples, the development of large-scale multiresidue methods based on generic conditions has been the main goal in recent decades. Multiresidue methods are typically called multiclass methods because they cover two or more families of pesticides. The development of these methods to determine most of the pesticides on the market in a single analysis is of great interest for reducing time and economic costs. Both issues are critical in pesticide residue monitoring because almost 800 compounds must be investigated, and the application of various methods to routinely monitor them presents serious limitations for food control laboratories [24]. Initial attempts have been made to implement multiresidue methods for highly polar pesticides, but in general these methods do not achieve the determination of 20 compounds in total [22,25,26]. In this sense, large-scale multiresidue methods refer to those capable of covering at least 80 analytes [27]. Multiresidue methods for less-polar pesticides can cover the determination of hundreds to thousands of pesticides and metabolites, using either GC–MS methods [28,29,30] or LC–MS methods [31,32].
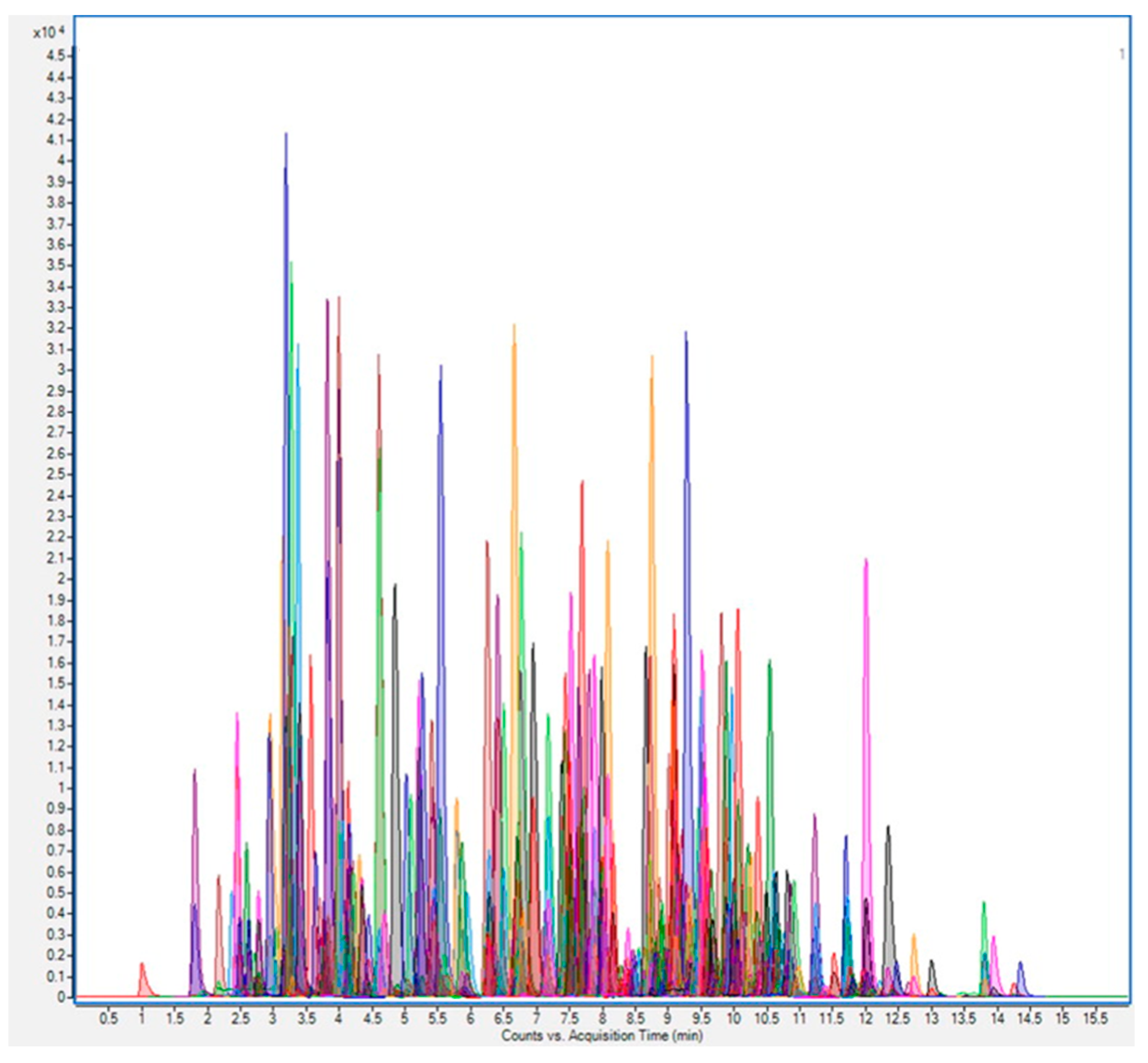
Advances in LC–MS and GC–MS instrumentation have contributed to the implementation of multiresidue pesticide methods as they provide higher sensitivity and selectivity. Furthermore, the replacement of classical sample preparation methods with QuEChERS (Quick, Easy, Cheap, Effective, Rugged and Safe) procedures has allowed us to reach the current situation, where hundreds of pesticides can be analyzed simultaneously in a large variety of different samples (Figure 1) [33,34]. Multiresidue or multiclass methods involve both low-resolution mass spectrometry (LRMS) and high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS) instruments. In addition, new analytical strategies for data acquisition, based mainly on suspect screening or non-targeted analysis, have contributed to a step towards multiresidue methods capable of a more comprehensive monitoring of pesticides, metabolites, and transformation products—even when there is a lack of information about them or they are totally unknown [35,36]. LRMS is already widely implemented in official control laboratories for the targeted analysis of pesticide residues. However, HRMS brings new possibilities for unexpected findings, as this technology is used for non-targeted analysis. Furthermore, retrospective analysis is possible. Consequently, MS data can be explored over time to identify metabolites and transformation products [37].
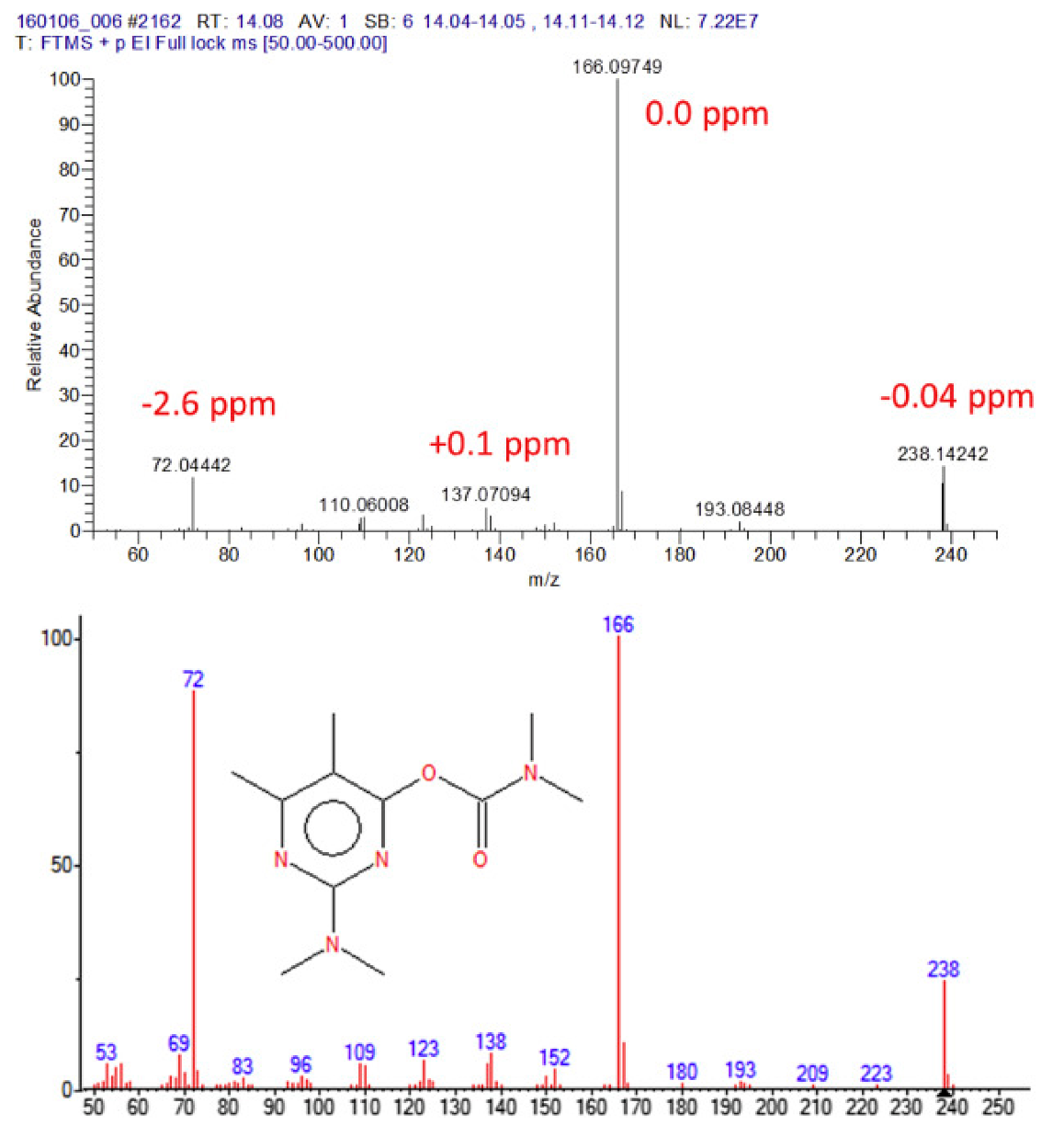
Figure 1.
Chromatogram obtained from the simultaneous analysis of a mixture of 250 pesticide residues, each at 0.01 mg/kg, in grape extract, using ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC)–tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) on a triple-quadrupole (QqQ) instrument in selected reaction monitoring (SRM) mode with rapid polarity switching. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [34]. Copyright (2014) Elsevier.
Analytical advances in data acquisition and sample preparation have also led to the development of generic analytical workflows applicable to the simultaneous determination of a wide range of pesticides and other substances. These methods are of great value in routine monitoring programs as chemical contaminants, such as mycotoxins, may be present in food and feed samples in addition to pesticides. The simultaneous determination of all of these chemical hazards provides more complete information to ensure food safety, and reduces costs and analysis time. In 2008, Mol et al. reported the first comprehensive method for the simultaneous determination of 136 pesticides, 86 veterinary drugs, and 36 natural toxins—including plant toxins and mycotoxins—in different feed and food matrices (i.e., maize, honey, meat, egg, and milk) [38]. Since then, the number of reported methods for the analysis of various categories of residues and contaminants has increased [39]. The main characteristic of these methods is that they focus more on how analytical techniques are best suited to the detection and identification of compounds based on their chemical properties, rather than on how they reach the food supply chain (i.e., environmental contaminants, residues, etc.). Although these types of methods covering multiple classes of residues and contaminants are also called multiresidue or multiclass methods, they can be described as mega-methods [40].
3. Sample Preparation in MS-Based Methods
A proper selection of the sample treatment is crucial to achieve good analytical results in the control of pesticide residues in food [41,42], and could be considered the bottleneck of the whole analytical process. Sample preparation requires a systematic approach to answer the question: How do we get the analytes from the sample to extract? This is not a trivial issue, since the main objectives of sample preparation are the removal of possible matrix interferences, the pre-concentration of the analytes, and the obtaining of a final extract compatible with the chromatographic system [43]. Analytical methods for the determination of pesticides are generally based on UHPLC–MS/MS using electrospray ionization (ESI) and reversed-phase chromatographic separations. However, one of the main drawbacks of ESI for quantitative purposes is the well-known matrix effect. The matrix effect is due to the presence of co-eluting interfering species in the final extract. Therefore, these species can cause signal suppression of the analytes of interest. The matrix effect hampers the accuracy and trueness of the results, and reduces laboratory throughput, because external calibration with standards in pure solvent for accurate quantification is not possible [44]. Various approaches have been developed to overcome, minimize, or compensate for the matrix effect observed in MS methods. These strategies include the improvement of chromatographic performance [45,46], the use of isotope dilution mass spectrometry [47], the matrix dilution or “dilute-and-shoot” approach [48], and the application of specific dedicated clean-up protocols [49].
Regarding the latter strategy, various sample treatments ranging from traditional liquid–liquid extraction (LLE) and solid–liquid extraction (SLE) methods to solid-phase extraction (SPE) have been applied for sample preparation in the determination of pesticide residues in food [50]. The most suitable sample treatment for analyte extraction and matrix removal ultimately depends on the complexity of the sample. In this sense, food products (not feed) are currently divided into nine main commodity groups (e.g., foods with high content of oils, high content of water, etc.) according to the SANTE/2020/12830 guideline [14]. It is expected that samples of food products belonging to the same commodity group can be prepared following the same sample treatment protocol for the determination of the same pesticide mixture. In this sense, SANTE/2020/12830 claims that analytical methods for pesticide analysis must be validated for at least one representative commodity from each commodity group.
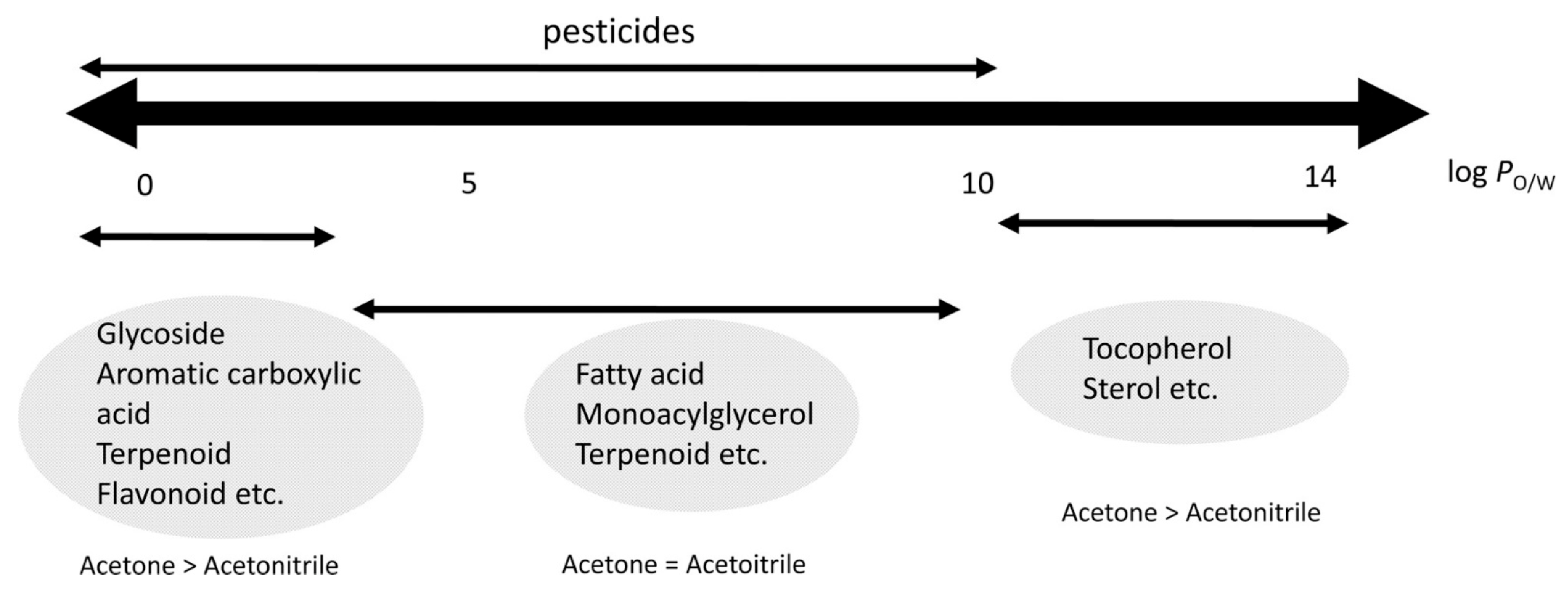
One of the main handicaps of applying exclusively LLE or SLE is the excessive number of endogenous sample compounds co-extracted, which may cause the matrix effect. Therefore, the current trend is to apply LLE or SLE as the first step of sample treatment, followed by clean-up procedures—usually based on SPE purification [51,52] or dispersive SPE (dSPE) [53,54]. Sugitate et al. studied the relationships between the co-extracted compounds depending on the nature of the solvent extract [55]. As shown in Figure 2, the use of acetonitrile (MeCN) allowed the determination of pesticides with a wide range of polarities, reducing the number of co-extracted matrix components compared with acetone. Therefore, a key aspect is the proper selection of the extraction solvent, taking into account the octanol/water partition coefficient (log PO/W) of the pesticide. Organic solvents such as MeCN, ethyl acetate, acetone, or hexane are used to isolate the analytes of interest from the matrix [56]. Other binary extraction solutions—such as dichloromethane/acetone [57] and ethyl acetate/cyclohexane [58]—have also been used for this purpose. In this sense, the Quick Polar Pesticides (QuPPe) method has become very popular for the analysis of highly polar pesticides that are not amenable to common multiresidue methods (e.g., QuEChERS). This method mainly consists of the adjustment of the sample water and extraction with acidified methanol, followed by LC–MS analysis [59]. Two different protocols have been reported for the analysis of pesticides by the QuPPe method, which are related to the sample matrix: a protocol for the determination of pesticides in products of plant origin and honey [23], and another protocol for their analysis in products of animal origin, excluding honey [60].
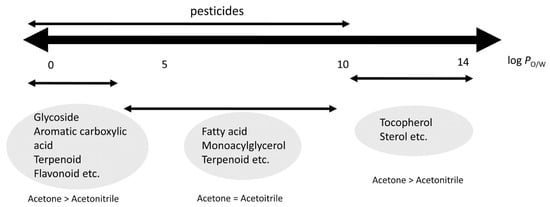
Figure 2.
Relationship between matrix co-extracts, pesticides, and log PO/W. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [55]. Copyright (2012) American Chemical Society.
The combination of SLE with dSPE, widely known as the QuEChERS approach, has revolutionized the way multiresidue pesticide analyses are carried out [50,61,62]. In general, this sample preparation method consists of an extraction with MeCN, which is caused by partitioning between the aqueous phase of the sample and that of MeCN by adding magnesium sulfate and sodium chloride salts. Finally, a dSPE step is carried out to remove most of the remaining matrix interference [63]. Initially, QuEChERS was developed for the determination of pesticides in vegetables using PSA as a dSPE sorbent [64]. The most commonly used dSPE sorbents are primary secondary amine (PSA), bonded octadecyl silica (C18), and graphitized carbon black (GCB). New sorbents have also been commercialized for the analysis of pesticides in fatty samples such as avocado, nuts, or salmon. Among them, Z-Sep (i.e., a zirconia-based sorbent) and Enhanced Matrix Removal-Lipid (EMR-Lipid) have been developed for selective clean-up of lipids from fatty matrices, providing good results in terms of the matrix effect [65,66,67]. The rapid implementation of QuEChERS in routine laboratories has been due to its excellent performance, including high extraction efficiency (recoveries > 85%), high reproducibility, high sample throughput of around 30 samples per hour, low waste generation, low cost of the reagents used in the method, the small number of devices needed to carry out sample preparation, and its application in the simultaneous extraction of a large number of analytes. For example, as a consequence of the application of QuEChERS extraction, 400 pesticide residues in tea leaves [68] or 248 pesticide residues in seeds [69] can currently be monitored in a single analysis.
Furthermore, the application of QuEChERS procedures is gaining significant popularity in the analysis of a wide spectrum of analytes (e.g., antibiotics, mycotoxins, hormones) in different types of complex samples. In this regard, Lehotay et al. have recently updated the QuEChERS approach with the QuEChESER mega-method (“Quick, Easy, Cheap, Effective, Rugged, Safe, Efficient, Robust”), which broadens the range of polarity of the compounds for which mega-methods are applicable [70]. In this improved version of the QuEChERS protocol, a small volume of the initial extract is taken for the determination of pesticides, veterinary drugs, and other LC-amenable analytes by LC–MS. The remaining extracted portion is submitted to MeCN–water partitioning and further sample clean-up with an automated SPE system. Subsequently, GC-amenable pesticides and environmental contaminants are determined by fast, low-pressure (LP)-GC–MS [71,72]. This sample treatment tailored for both LC–MS and GC–MS analyses extends the analytical scope of mega-methods to cover a broader range of chemical residues and contaminants that may be present together in food samples. Today, mega-methods are capable of covering the determination of more than 1200 residues and contaminants in feed, including around 500 pesticides [73].
In addition to QuEChERS, “dilute-and-shoot” approaches are very efficient for simple sample preparation in multiresidue analysis [37]. “Dilute-and-shoot” procedures involve diluting the sample before “shooting” it into an analytical instrument for analysis. Such methods have become increasingly popular in the last 10–15 years because they significantly improve sample throughput. They are now used in many types of multiresidue LC–MS analyses [74]. Considering the definition described, it seems that “dilute-and-shoot” is limited to liquid samples. However, a previous SPE and subsequent dilution of the organic extract could also be considered as a “dilute-and-shoot” approach. Dilution of the sample or the organic extract is an excellent approach to simplify sample treatment and overcome the matrix effect. It should be noted that “dilute-and-shoot” approaches have been made possible by the improvement of LC–MS/MS instrumentation in terms of concentration sensitivity [56]. To estimate which dilution factor(s) can be applied, it is necessary to take into account several variables, such as the expected concentration of the analytes, the sample matrix, and the selectivity and sensitivity of the MS platform used. Dilution factors typically range from 1:1 up to 1:100. Advantages of this methodology include its simplicity, minimal analyte losses, high sample throughput, and the number of analyte classes included [75].
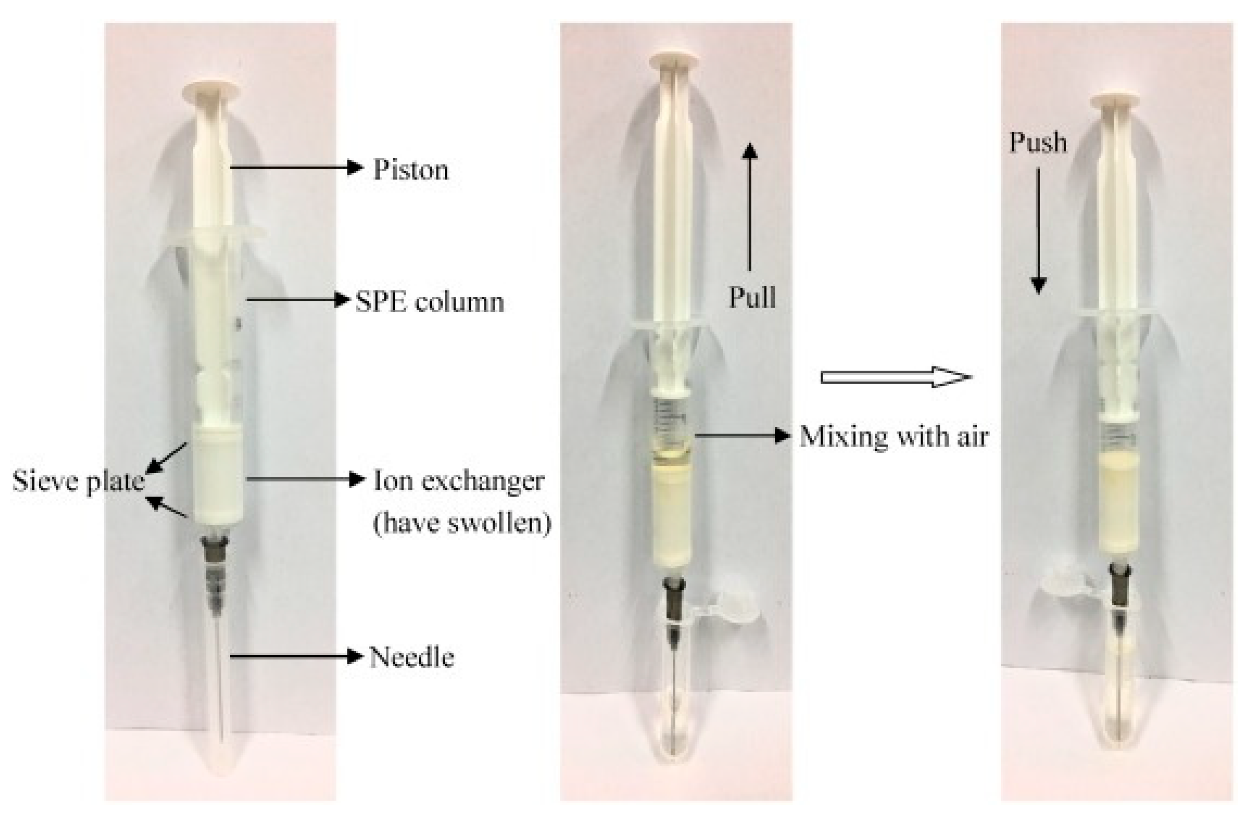
Although QuEChERS and “dilute-and-shoot” approaches provide high sample throughput, and are simple and low-cost sample preparation strategies, more intensive sample treatments—such as traditional SPE—are required to remove matrix interference and reduce the matrix effect. SPE is one of the most widely used sample treatments for multiresidue analysis [76], mainly because it provides high extraction efficiency, moderate solvent consumption, and high reproducibility. Today, there is a wide variety of SPE sorbents available on the market, and these stationary phases are generally available in cartridge or disk forms. Selection of the most suitable SPE sorbent is based on the characteristics of the analyte and the sample. There is a plethora of SPE sorbents, and the most widely used are Florisil (magnesium silicate), C18, alumina (Al2O3), diol (diol-bonded silica), SAX (strong anion exchange), Extrelut™ (SiO2·n H2O), PSA, ENVI-Carb™ (GCB), and Oasis HLB (hydrophilic/lipophilic balanced copolymer of N-vinylpyrrolidone and divinylbenzene) [77]. Moreover, the well-known mixed-mode SPE is a practical approach for the analysis of pesticides with different properties, because this type of SPE sorbent is able to retain compounds through two modes of interaction. Likewise, different combinations of SPE sorbents have also been used, such as dual-layer GCB–PSA for removing lipids from fatty matrices [78], C18 combined with PSA [79], or GCB with PSA [80]. Despite its advantages in reducing the matrix effect, traditional SPE involves many time-consuming and tedious steps, including cartridge conditioning, sample loading, cartridge washing, and sample elution. Consequently, several approaches have been proposed to increase the laboratory throughput when using SPE sorbents. In this sense, there are commercially available SPE cartridges based on pass-through, in which traditional SPE steps such as conditioning, equilibration, and washing are not required. Oasis PRiME HLB and Captiva EMR-Lipid are clear examples of this trend [81]. Aside from the traditional SPE formats, disposable pipette extraction (DPX) has been increasing in use in recent years. DPX is a type of SPE in which the sorbent is placed into a disposable pipette tip instead of a cartridge (Figure 3). The sorbent is then mixed with the sample, and the analytes are eluted with small amounts of solvent [82]. As in traditional SPE, there is a wide variety of sorbents for DPX, and it is a rapid, efficient, and reproducible approach for the development of multiresidue methods in food analysis.
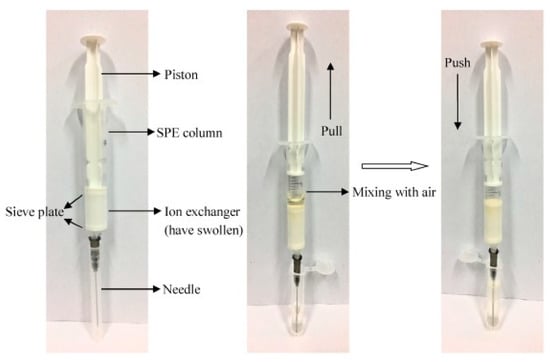
Figure 3.
Step-by-step working of the DPX column. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [82]. Copyright (2018) Elsevier.
In addition to the abovementioned sample treatments, other sample preparation strategies have been proposed for the analysis of pesticide residues in food. However, they have been implemented less or not at all in routine laboratories for the control of pesticide residues. In general, the main objective of these approaches has been to decrease the solvent consumption, which has led to the miniaturization of traditional sample treatments [83]. Solid-phase microextraction (SPME) is the most popular of these microextraction techniques, and involves the extraction of target analytes with a thin fiber made of fused silica coated with a suitable stationary phase. Then, the analytes are released at high temperatures in GC–MS analysis, or by solvent desorption when applying LC–MS methods [84]. SPME has been show to provide efficient clean-up and minimize the matrix effect that typically occurs in ESI-MS analyses [85]. In recent years, other miniaturized approaches have been developed, such as stir bar sorptive extraction (SBSE), magnetic solid-phase extraction (MSPE), molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction (MISPE), single-drop microextraction (SDME), hollow-fiber liquid-phase microextraction (HF-LPME), and dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction, among others [86,87].
4. Chromatographic Separations in MS-Based Methods
Chromatographic separation is generally carried out prior to MS analysis of pesticides in food. In general, it contributes to reducing the matrix effect [88]. It also decreases the probability of false positive results, and simplifies mass spectra when working in HRMS; therefore, it improves method selectivity. In general, LC–MS and GC–MS are the techniques most widely applied to the analysis of pesticides in food [49,56,89]. GC has been widely used for the determination of pesticides in the field of food analysis for decades. However, GC is limited to the determination of volatile and semi-volatile compounds. Although non-volatile compounds can be analyzed after carrying out a derivatization process, this process is considered laborious and time-consuming. Consequently, these pesticides are usually analyzed by LC [90]. Nevertheless, it should not be considered that LC has totally replaced GC in the analysis of pesticides, as both are complementary techniques. Indeed LC–MS has been shown to be more sensitive in the determination of almost all pesticides, but not for pyrethrins and organochlorines [91].
Performance enhancement of GC–MS methods has recently focused on reducing analysis time to improve sample throughput without losing sensitivity and analytical quality [92]. While many parameters can be optimized to reduce the runtime (e.g., use of short columns, fast oven temperature ramps, or higher carrier-gas linear velocities), changing these parameters can lead to a loss of chromatographic resolution [93]. In this sense, low-pressure gas chromatography (LPGC)–MS has also been evaluated as an alternative to modifying the parameters of the method, avoiding the aforementioned disadvantages [94,95]. LPGC–MS is the most practical and beneficial fast GC technique available to achieve chromatographic separations in less than 10 min for applications that typically involve analysis times between 20 and 40 min [96]. For example, the determination of 244 pesticides in an 11 min run has been achieved using LPGC–QqQ-MS. This means a 50% decrease in analysis time compared to a traditional GC separation using a 30 m column [94]. Furthermore, the development and application of multidimensional GC has undoubtedly been a major trend in GC–MS methods in recent years, as it is a powerful tool to increase resolving power [97].
In addition, the growing interest in the application of GC in pesticide analysis is related to the development of soft ionization sources for GC–MS coupling, as discussed in more detailed in Section 5. It is well known that ionization sources commonly employed under vacuum conditions in GC–MS methods—such as electron impact (EI) ionization or chemical ionization (CI)—provide an excessive fragmentation pattern, especially for labile compounds. This hard ionization is due to the universally established ionization energy of 70 eV in EI ionization [91]. To overcome this issue, the use of “milder” EI conditions is a promising alternative [98]. This term refers to the application of an ionization energy of around 20 eV. Therefore, it is possible to obtain mass spectra with a higher relative abundance of the parent ion and reduce fragmentation at lower mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) values at the same time. Recently, other soft ionization sources have been developed, such as atmospheric-pressure ionization (API) or plasma-based ion sources. The ionization mechanisms of atmospheric-pressure chemical ionization (APCI) have been shown to involve less fragmentation than EI [99]. APCI enables the acquisition of spectral data typically rich in molecular or quasi-molecular ion information [100]. However, the main disadvantage of the APCI source is that the matrix effect could be remarkable [101]. In this sense, dielectric barrier discharge ionization (DBDI), which could be considered the most representative plasma-based ionization source, could overcome this problem while allowing soft ionization [102].
It is well-known that LC is applied as a separation technique in the analysis of highly polar and non-volatile and/or thermally labile pesticides. In recent years, in food analysis, the major contribution to advances in LC separation has been the introduction of columns packed with sub-2 μm particles. These columns have led to the emergence of UHPLC, which has greatly improved chromatographic efficiency [103]. Mass transfer is improved with small particles, and high mobile-phase flow rates can be applied. Consequently, laboratory throughput is increased, and analysis costs are decreased. Other advantages of UHPLC–MS methods over traditional LC–MS methods include an increased resolving power and minimized matrix effect, because co-elution of matrix interferences can be avoided. Furthermore, UHPLC–MS enables methods with lower limits of quantification (LOQs) in comparison to conventional LC methods. For all of these reasons, its use has increased exponentially in the last decade, and has been widely employed in research and routine laboratories [104]. In addition, the use of two-dimensional liquid chromatography (2D-LC) has grown in recent years [105]. It has been demonstrated that if the number of components exceeds 37% of the peak capacity of the method, the peak resolution is clearly reduced [106]. 2D-LC allows the number of compounds in a single run to be increased compared to single-dimension chromatography. In this sense, two independent and complementary separation mechanisms could be employed in each dimension to obtain efficient results.
Although C18 columns are still the most widely used in LC separations of pesticides, new stationary phases have been developed to expand LC applications, such as hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC) and ion-exchange phases. The use of HILIC columns is the best option for the chromatographic separation of highly polar pesticides, as opposed to other approaches such as ion-pair chromatography. However, most HILIC methods are single-residue methods because it is very difficult to compromise between the many variables involved in HILIC separation (i.e., the type of buffer and its concentration, pH, sample solvent composition). Thus, multiresidue-based HILIC methods are not yet common [107]. Among others, LC–MS methods for the determination of glyphosate and its main degradation product—aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA)—can be highlighted as examples of currently used single-residue HILIC methods. Glyphosate and AMPA are highly polar and ionic molecules, and have minimal solubility in organic solvents. Consequently, their determination is more challenging than for most pesticides on the market today, and none of these compounds are included in typical multiresidue pesticide monitoring methods [108]. Although reversed-phase columns can be used to achieve the separation of these compounds if they are previously derivatized to modify their polarity [109], ion-exchange chromatography (IEC)–MS and HILIC–MS are the main analytical techniques used to separate and detect this type of pesticides [25,110]. The use of mixed-mode LC columns involving HILIC and IEC interactions has recently been proposed as an attractive tool to improve the performance of analytical methods for the determination of these compounds [111]. In general, special separation conditions must be applied in single-residue methods. In the case of glyphosate and AMPA, their determination is challenging not only because of their high polarity, but also because they have a phosphate group that makes them sensitive to metals. As a consequence, poor-quality chromatographic peaks can be observed for these analytes. Additives such as medronic acid or pyrophosphoric acid can be added to the mobile phase to improve the peak shape, and without observing the significant signal suppression caused by the addition of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) as a metal chelator [112]. This strategy helps to overcome the poor peak shapes commonly observed for polar-charged analytes.
5. Mass Spectrometry
In accordance with guidance documents for the analytical quality control and method validation procedures for pesticide residue analysis, MS is the detection technique recommended for use in pesticide analysis, as other selective detectors for GC and LC offer limited specificity [14,113]. Despite this fact, the use of these detection systems instead of MS is possible in pesticide analysis, and can be considered in monitoring methods. However, it is essential to note that MS provides more confidence for compound identification, and has been the gold standard for pesticide determination for the last 20 years [114]. The number and type of ions that must be observed for the correct identification of the analytes of interest by MS is indicated by the SANTE/2020/12830 guideline, and varies between 2 and 3 ions when using LRMS, or requires 2 ions with a mass accuracy lower than 5 ppm when applying HRMS [14].
In addition to selectivity and specificity, concentration sensitivity is one of the main analytical parameters to be taken into account in a method for the determination of pesticides. These substances are usually present in food samples at concentration levels of µg/kg, or even ng/kg. Therefore, analytical methods must provide low limits of detection (LODs) to detect such a concentration of residues. In monitoring methods for pesticide residues in food commodities, the validated LOQ is generally at the default MRL of 0.01 mg/kg [14]. In MS-based methods, the sensitivity is highly dependent on the ionization source used for LC (or GC)-MS coupling, as well as the type of mass spectrometer used. This section discusses the most commonly used ionization techniques in pesticide analysis when applying LC–MS or GC–MS workflows, as well as the analytical strategies followed for data acquisition, depending on the type of mass spectrometer used. In addition, new trends in MS for pesticide analysis are covered, such as IM–MS hyphenation and ambient (desorption/ionization) mass spectrometry (AMS).
5.1. Ionization Sources
ESI is the most commonly applied ionization technique in LC–MS. The ESI technique is characterized by high ionization efficiency (i.e., the effectiveness of producing gas-phase ions from analytes in solution) and high transmission efficiency (i.e., the ability to transfer the ions from atmospheric pressure to the low-pressure zone of the MS system); therefore, high sensitivity is generally observed in LC–ESI-MS methods [115]. ESI is a soft ionization technique that not only provides high concentration sensitivity under properly optimized source conditions, but also often provides information on the protonated or deprotonated ions of pesticides. This information is of great relevance for the identification of unknown molecules in non-targeted analysis (e.g., pesticide transformation products), as this feature is advantageous to identify the molecular mass of the analytes. In contrast, the mass spectra resulting from ESI-MS analyses provide little information about the structure of the analytes, making structural elucidation difficult [116]. This fact also hampers the simultaneous determination of a large number of analytes in a single run [27]. Therefore, fragmentation experiments are required to overcome these problems, as well as to comply with current legislation and recommendations regarding the number of ions to be observed [14]. However, this does not represent a technical limitation at present. In-source fragmentation can be investigated to collect the ions required for identification, but can lead to complex mass spectra due to background interference that complicates the identification process. Therefore, MS/MS (or MS2) is preferred to clearly obtain sufficient characteristic fragment ions for increased confidence in pesticide identification [117], whether in targeted or non-targeted analyses.
Furthermore, although almost all current LC–MS methods for pesticide analysis involve ESI as the ionization mode, other soft ionization techniques—such as atmospheric-pressure photoionization (APPI) and APCI—can also be used. ESI has been shown to be more universal than APCI for the ionization of many pesticides, whereas photoionization of pesticides has rarely been reported [90]. A large number of multiresidue methods and mega-methods have been proposed for the determination of pesticide residues by LC–ESI-MS in a wide variety of feed [73] and food products, such as vegetables and fruits [118] or honey [119].
EI ionization has been the most predominant ionization technique in GC–MS. In this framework, GC–EI-MS methods were commonly applied in the control of pesticide residues in food until the widespread implementation of LC–ESI-MS methods for pesticide analysis. However, LC–ESI-MS has been shown to achieve higher concentration sensitivity compared to GC–EI-MS for most classes of pesticides, except for pyrethrins and organochlorines [91]. This better performance could be one of the reasons that explains the shift from GC–EI-MS to LC–ESI-MS methods for pesticide determination. In this sense, the higher sensitivity observed in the LC–ESI-MS methods may be related to the larger sample volumes that are injected into LC columns than into GC columns, and to the lower fragmentation observed in ESI sources compared to EI ionization [90].
Recently, the implementation of the APCI source in GC–MS instruments has significantly improved the sensitivity typically observed in GC–EI-MS systems [91]. For example, a 1–8-fold increase in sensitivity has been observed for the determination of organophosphorus pesticides when an APCI source is used instead of an EI source [120]. APCI is a much softer ionization technique compared to EI. Therefore, in-source fragmentation is reduced, and the protonated or deprotonated ions of the compounds can be observed in satisfactory abundance [121]. Due to the ionization mechanisms that occur in APCI (i.e., charge transfer and proton transfer), both the molecular ion (M+) and the protonated ion ([M + H]+) can be observed simultaneously. In this sense, water or methanol can be added as a modifier in the source chamber to promote the exclusive formation of protonated ions, thus increasing the sensitivity [100,122]. Currently, although it is a promising technique, GC–APCI-MS has rarely been applied to the determination of pesticides in food [123]. Among the studies focused on the analysis of pesticide residues in food by GC–APCI-MS, a screening method validated for 130 pesticides can be highlighted as an example of a multiresidue method applied to the determination of pesticides in a wide range of fruits and vegetables (i.e., strawberries, oranges, apples, carrots, lettuces, zucchini, red peppers, and tomatoes) [124]. The strength of the reported method is that it was also applied to the retrospective analysis of other 286 pesticides, which was facilitated by the presence of the molecular ion/protonated molecule in the APCI spectra.
5.2. Matrix Effect
Regardless of the analytical approach, a similar drawback is observed in LC–MS and GC–MS methods—the so-called matrix effect. The matrix effect refers to the observed enhancement or suppression of the analytical signal for a specific analyte when determined in real samples, and compared to the analysis of its analytical standard. In the determination of pesticides, the matrix effect is calculated according to Equation (1). It is considered significant if it exceeds ±20% [14].
In the case of LC–MS methods, the matrix effect is associated with phenomena that occur in the ESI source. The ionization of analytes is reduced or favored by the presence of matrix components [125]. However, in the case of GC–MS methods, the matrix effect is usually caused by the retention/decomposition of analytes at the active sites (i.e., free silanol groups) in the injector, column, or detector. This is observed when standards are injected in pure solvents, but not when real samples are injected. In the latter case, matrix components can block the active sites; therefore, there are fewer active sites available to adsorb the analytes. Consequently, an enhancement in their signals is observed [126]. The determination of 341 and 315 pesticides in rice by LC–MS and GC–MS, respectively, represents a clear example of how signal suppression is usually observed in LC–ESI-MS, while signal enhancement is observed in GC–MS [127]. If the sample treatment proves ineffective in avoiding the matrix effect, it can be compensated for by applying two main strategies: (1) by using matrix-matched calibration curves (i.e., calibration curves of standards prepared in blank matrix extracts), or (2) by using isotopically labeled internal standards (IL-ISs). Both strategies are commonly applied for either LC–MS [25,128] or GC–MS methods [129,130]. It should be noted that although only one or a few IL-ISs are selected for the IL-IS approach, the quantitative performance of multiresidue methods increases when multiple IL-ISs covering different families of pesticides are used [131,132]. Other strategies to reduce the matrix effect include the possibility of applying standard addition or procedural calibration; however, matrix-matched calibration is still the preferred approach according to SANTE/2020/12830 [14]. The main challenge of using matrix-matched calibration is to find blank samples. In addition, this approach also implies the assumption that the matrix effect for a given product is the same for different samples, which is not necessarily true [133].
In GC–MS methods, the use of analyte protectants or coated inlet liners also reduces the matrix effect [126]. For example, a mixture of analyte protectants consisting of ethylglycerol, gulonolactone, D-sorbitol, and shikimic acid prepared in 4/1 (%, v/v) MeCN/water containing 0.05% (v/v) formic acid has been used for the analysis of 35 pesticides (i.e., organophosphorus pesticides, organochlorine pesticides, triazines, triazoles, carbamates, imidazoles, etc.) in tropical fruits [134]. In general, the matrix effect was significantly reduced when the analyte protectants were used. A reduction of more than three times was observed in the case of the compounds that showed a more significant matrix effect. Nevertheless, although the use of analyte protectants reduces the matrix effect and improves peak shape [135,136], these compounds must be dissolved in polar solvents such as water and MeCN. The injection of these solvents in GC systems has several drawbacks (i.e., limitations on injection volumes due to their high expansion coefficient, and poor focusing of chromatographic peaks due to their high polarity), which represents the main disadvantage of this strategy for reducing the matrix effect [69,126].
5.3. Targeted MS-Based Methods
Current developments in mass spectrometers and data analysis have led to a growing interest in non-targeted methods for pesticide analysis; however, targeted methods are more established in routine food testing laboratories [137]. GC–MS-based targeted methods were the technique of choice for pesticide analysis until the late 1990s [91]. GC–MS methods were initially limited to the determination of volatile and thermostable analytes, but the implementation of derivatization strategies also allowed the analysis of non-volatile compounds. In general, early GC–MS methods involved the use of a single quadrupole (Q) operating in selected ion monitoring (SIM). Nevertheless, the development of hybrid mass spectrometers made GC–QqQ-MS, in addition to GC–Q-linear ion trap (LIT)-MS, the preferred tool for pesticide residue control. GC–MS/MS works in SRM or multiple reaction monitoring (MRM). This acquisition mode is very selective, because it allows monitoring of at least two fragmentation transitions per analyte (one transition corresponds to a precursor/fragment ion pair), minimizing or avoiding matrix interference, and meeting current guidelines for proper pesticide identification [138]. It is also very sensitive, because it reduces the chemical noise in the chromatogram, allowing lower LODs to be achieved [139]. Current GC–QqQ-MS-based methods allow the simultaneous determination of hundreds of pesticides, as has been shown in the analysis of 220 pesticides in sesame seeds with a separation run of 22 min [140], or in the determination of 365 pesticides in grain, beans, fruits, and vegetables with a separation time of 36 min [141].
Although LC separations have partially replaced GC separations in pesticide analysis in recent decades, QqQ-MS and QLIT-MS remain the gold standard detection tools used in analytical workflows for pesticide determination [15]. As in GC–MS/MS methods, SRM/MRM is applied as acquisition mode in LC–MS methods. Two or even three fragmentation transitions per pesticide are recorded to reduce the risk of false positives [142]. Recent multiresidue methods based on LC–MS workflows tend to cover the simultaneous analysis of a wide range of pesticides [143,144], which requires monitoring of a large number of fragmentation transitions. This is a real challenge for QqQ-MS instruments due to their slow acquisition rates. To ensure a minimum of 15 data points per chromatographic peak for satisfactory analysis reproducibility, transitions related to each analyte are only monitored within a time-limited window that covers the retention time of the compound. However, any unexpected shift in the retention time can partially or completely exclude an analyte from its detection window, resulting in truncated or undetected peaks [142]. Advanced targeted acquisition approaches for pesticide analysis should be explored to overcome this drawback following applications in other research fields [145]. For example, “Scout MRM” represents one of these advanced acquisition strategies that has already been applied to pesticide determination [142]. “Scout molecules” are compounds spiked in the samples and detected along the chromatographic separation. Once one of the “scout molecules” is detected, it triggers the monitoring of a transition group (i.e., a group of transitions from various analytes of interest). It stops upon detection of the next “scout molecule” and activation of the subsequent transition group acquisition.
Other recent improvements in LC–MS/MS methods for pesticide determination include performing MS experiments complementary to MRM transitions, such as acquisition of the full MS/MS spectrum. Recent advances in QqQ-MS technology have made it possible to decrease the dwell time required per MRM transition and to trigger such additional MS experiments. This strategy has been shown to increase confidence in pesticide identification compared to classical identification based on two MRM transitions [32].
5.4. Non-Targeted MS-Based Methods
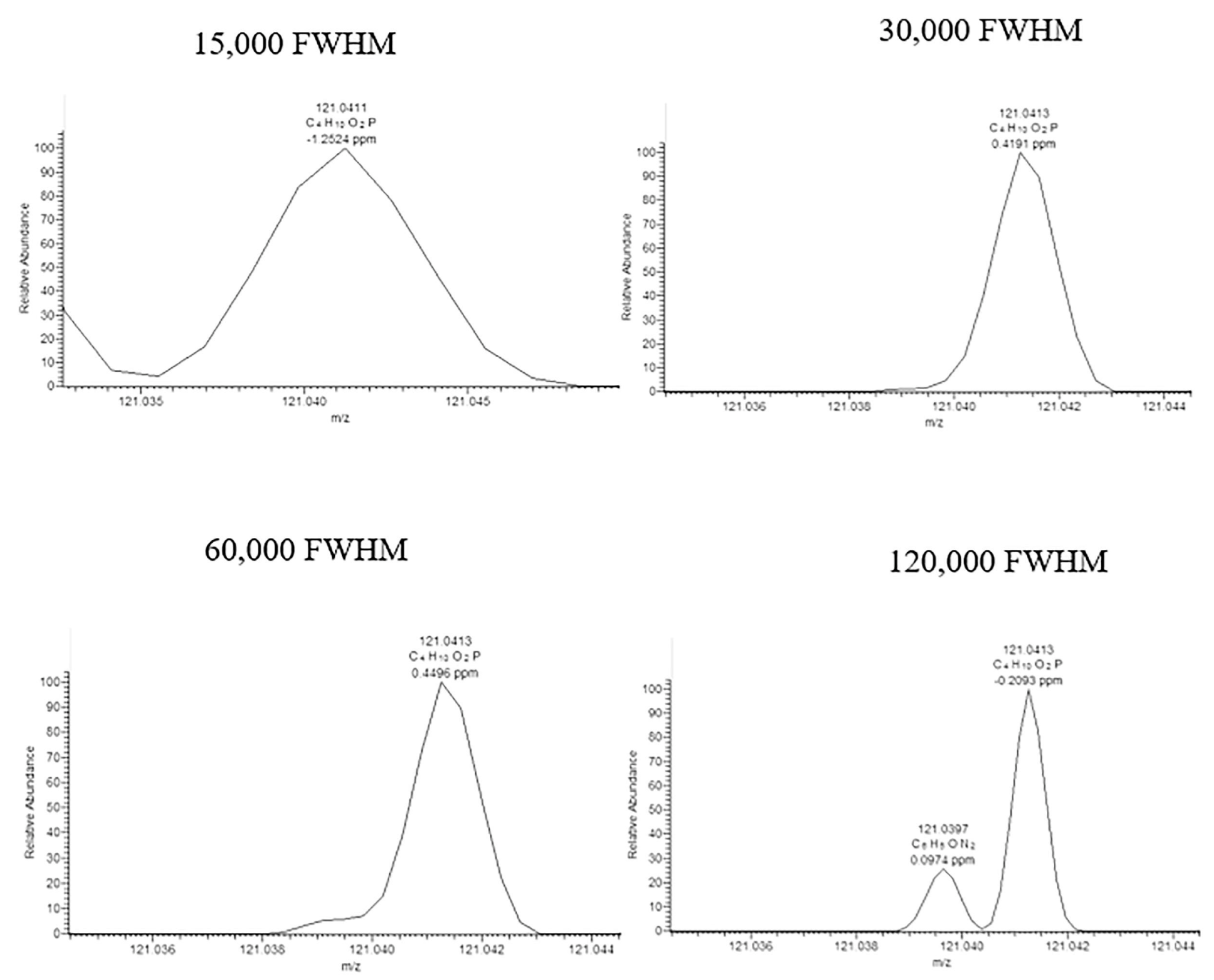
Quadrupole instruments today are very robust, and probably provide the highest concentration sensitivity compared to other mass spectrometers, but only allow unit mass resolution. Consequently, their use is limited to targeted applications. The development of HRMS instruments has opened up new possibilities allowing semi-targeted (i.e., suspect screening) and non-targeted analysis of pesticide residues. Furthermore, high mass resolution is of great interest to avoid overestimating the amount of the target compound due to co-elution of the analyte with isobaric compounds in the matrix (Figure 4) [146]. Depending on the HRMS technology, high mass accuracy (±0.001 Da), high mass resolution (ratio of mass to mass difference ≥ 20,000), and wide mass range (simultaneous acquisition of ions up to 2000 Da) can be obtained [147]. Mass resolving power of up to 1,000,000 can be achieved in routine analyses, specifically when using Fourier-transform ion cyclotron resonance (FT-ICR) mass spectrometers [148]. The term “resolving power” describes the ability to distinguish between ions that differ in the m/z by a small increment, and is equal to the full width at half-maximum (FWHM). FWHM is defined as , where m represents the mass of the ion being measured, and Δm is the full width of the spectral peak at half-maximum peak height [149].
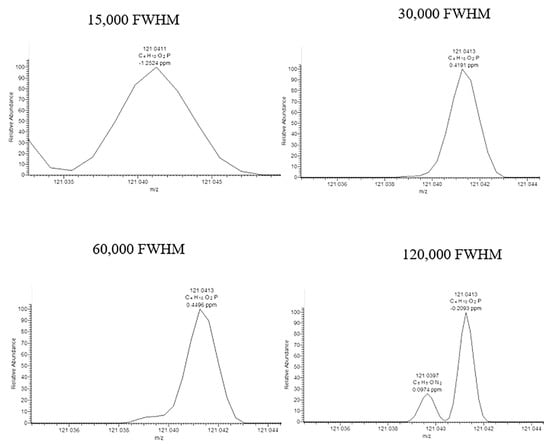
Figure 4.
Mass spectra zoomed in at m/z 121.0418 ± 5 ppm (C4H10O2P+) for chlormephos in wheat spiked at 10 µg/kg, with a resolving power setting of 15,000 FWHM, 30,000 FWHM, 60,000 FWHM, and 120,000 FWHM at m/z 200. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [146]. Copyright (2021) Elsevier.
Due to the analytical performance and instrumentation cost, time-of-flight (ToF) and Orbitrap spectrometers, as well as hybrid Q-ToF and Q-Orbitrap instruments, are mainly used for pesticide determination in applications in which high mass accuracy is required [49]. More information on the capabilities of high-resolution mass spectrometers can be found in the literature [150,151]. One of the main reasons that have limited the implementation of HRMS in official pesticide controls has been the lower concentration sensitivity shown by high-resolution mass spectrometers compared to the low-resolution mass spectrometers traditionally used for this purpose. Despite QqQ-MS having been shown to be more sensitive and robust for pesticide determination at trace levels, Q-Orbitrap-MS operating in full scan can provide equal or even higher sensitivity for certain applications [146]. In fact, Orbitrap-MS has been shown to be applicable as an analytical tool in routine pesticide monitoring. Up to 210 pesticides have been determined simultaneously in fruits and vegetables under routine conditions (i.e., 102 samples), demonstrating these devices to be robust and efficient in terms of sensitivity (LOQs ≤ 10 µg/kg for the majority of pesticides and commodities) and mass accuracy (±1 mDa) [152]. Regarding high-resolution mass spectrometers, Orbitrap-MS (140,000 FWHM, m/z 200) and ToF-MS (30,000 FWHM, m/z 556), both operating in full scan, have been compared for the quantification of pesticide residues (n = 146) in tea samples [153]. In general, similar results were observed for both mass spectrometers, but Orbitrap-MS was found to provide slightly better sensitivity and selectivity than ToF-MS at lower concentration levels (10 µg/kg), due to its higher mass resolution. Nevertheless, both mass spectrometers were demonstrated to be suitable for routine pesticide monitoring, not only because of the LODs achieved (i.e., detectable responses between 0.01 and 0.1 mg/kg, depending on the pesticide and the detector), but also in terms of intra- and inter-day precision (RSDs < 20%).
In the context of routine pesticide monitoring programs, LRMS-based methods operating in SIM or SRM/MRM have traditionally been applied to the simultaneous determination of 100–200 pesticides in a single run. However, as discussed in Section 2, analytical methods are evolving to cover a larger number of compounds. In this framework, HRMS-based methods have significantly expanded the testing scope of pesticides, monitoring almost 1000 analytes in less than 15 min [118]. Despite the fact that targeted analysis of pesticides can also be addressed by HRMS [22,154], HRMS-based workflows are primarily intended for non-targeted analysis of pesticides, including suspect screening approaches. The main objective of such methods is to determine pesticide residues in food products beyond a predefined scope of target pesticides. At the same time, these methods also make the identification of pesticide metabolites or (bio)transformation products feasible [155]. LC (or GC)–HRMS methods are mainly applied in two different contexts:
- Determination of “known unknowns” (i.e., pesticides with known chemical structure and suspected presence in the food sample, but without available reference standards). Suspect screening approaches are based on screening of large lists of priority compounds using their exact mass, and subsequent tentative identification by comparing MS/MS spectra against mass spectral databases [156]. For example, Bauer et al. developed a UPLC–Q-ToF-MS method for the suspect screening of pesticide metabolites in fruit and vegetables [35]. A database of 684 metabolites of 58 active compounds was created based on relevant pesticide metabolites reported in scientific literature and approval documents. This database was subsequently applied to the tentative identification of 47 pesticide metabolites in 96 representative fruit and vegetable samples selected from a daily routine pesticide analysis. This strategy is of high interest, since the detection of metabolites in the absence of the parent pesticide may provide evidence of its illegal use.
- Identification of “unknown unknown pesticides” without any a priori criteria, which requires a solid basic knowledge of chemistry and biochemistry to achieve an unambiguous structural elucidation of the relevant analytical signals [157]. Non-targeted analysis involves the detection of a large number of peaks, of which a significant number remain unidentified [155]. Since this analytical approach has several limitations, and does not always lead to satisfactory results to compensate for the time and effort involved in its execution, suspect screening approaches are the most commonly followed in applications related to pesticide analysis in food. In this regard, most HRMS methods for pesticide determination directly involve a list of high-interest pesticides. Consequently, they should be classified as suspect screening approaches rather than non-targeted approaches, as is often reported by many authors. Nevertheless, great efforts are currently being made to develop suitable non-targeted methods based on HRMS to detect unexpected contaminants and chemical residues in food, such as in the case of fipronil in Dutch eggs spread in Europe in 2017, much earlier [158].
In addition, HRMS has another important advantage over LRMS. Full-scan HRMS analyses provide complete information on the content of the sample, being limited only by the satisfactory ionization and detection of the molecules under the conditions of the analytical method carried out. Therefore, raw mass spectra can be retrospectively exploited to search for a specific substance if a specific concern arises. This approach is also applicable to the determination of pesticide metabolites or (bio)transformation products whose detection was not part of the primary study objective of the original analyses. A retrospective analysis of HRMS data has been carried out for the identification of pesticides in infant milk formulas. Pesticides are not the main contaminants or chemical residues expected in this type of matrix, but they were reported to be present in 33.3% of the samples [159]. In addition, retrospective data analysis has also been carried out for the identification of pesticide transformation products in food products (i.e., honey, meat, feed, and nutraceutical products such as ginkgo, soya, green tea, and royal jelly) that were previously found to content pesticide residues. One substance—3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol—was identified as transformation product of alachlor and chlorpyrifos [160]. Although retrospective analysis opens up new possibilities for wide-scope screening and reuse of raw mass data, it is not without limitations. Its application in routine analysis may be ineffective due to the necessity of high experience of the operators and the time required for compound identification, as well as for extracting information of interest from HRMS data generated without a previous hypothesis.
Most reported HRMS methods for pesticide analysis involve LC separation [49] and data acquisition in one of the following main MS modes: full scan, data-dependent acquisition (DDA), or data-independent acquisition (DIA) [161]. Full-scan acquisition involves only monitoring the accurate mass and isotopic distribution of ions reaching the detector, so full-scan data may not be sufficient for complete compound identification. Therefore, full-scan acquisition may be suitable for targeted analysis of pesticides when using HRMS [146,153], but it is not the most appropriate for suspect screening and non-targeted analysis. In these cases, product ion scan (MS2) data are needed for molecular structure identification. HRMS offers DDA and DIA modes as two data acquisition possibilities to simultaneously acquire information on the precursor ion and related fragmentation ions [162].
In DDA mode, data acquisition is carried out in full scan (MS1), and when precursor ions meet predefined criteria such as a specific m/z or an intensity threshold, they are selected as candidates for fragmentation (MS2). Conversely, in DIA mode, all precursor ions are fragmented without applying any criteria, so maximum MS2 is obtained. To date, various DIA strategies have been implemented [163], although the most commonly applied in pesticide analysis are those integrated into MS vendor software, including all-ion fragmentation (AIF) employed in Orbitrap instruments, or “all-in-one” analysis (MSE) developed by Waters. Regardless of the applied DDA or DIA mode, the collected MS2 is compared against mass spectral libraries for compound identification. DIA can potentially generate more MS2 matches, resulting in a higher chance of identifying pesticides or related compounds of interest, but without the high selectivity of DDA that provides cleaner mass spectra [161,162]. The application of DDA mode can be recommended for pesticide residue determination, since most of these compounds are known and can be effectively identified by DDA [164]. On the other hand, DIA should be implemented in those workflows aimed at the discovery of pesticide metabolites and (bio)transformation products, since these are usually unknown compounds [165]. However, recent work has shown that pesticide identification rates can be increased when the DDA and DIA modes are combined, while also providing fewer false results for the target pesticides [166,167].
Although GC–HRMS methods have been reported for the analysis of pesticides in food, they represent a lower percentage than the LC–HRMS methods developed for this purpose. GC–HRMS workflows are not yet well defined, and the possibilities of this technique have not been fully explored [91]. The commercialization of hyphenated GC–Orbitrap-MS platforms is recent (2015) and, as previously mentioned, LC–MS methods cover a wide range of applications traditionally addressed by GC–MS without requiring derivatization, and involving soft ionization (ESI vs. EI). In this sense, the ionization source for GC–HRMS coupling can also raise several questions, as occurs in GC–LRMS methods. APCI produces molecular ions that facilitate compound identification in pesticide screening [124], and is a fairly generic ionization technique for GC-amenable compounds, but is not as generic as EI [168]. In addition, generic spectral libraries for APCI-MS are still lacking, while several mass spectral libraries exist for EI-MS (e.g., NIST spectral database), which are crucial for compound identification in non-targeted analyses. Although the latter refer to nominal spectral libraries (i.e., based on EI-LRMS measurements), they are instrument-independent, and can be used for library matching if the standard ionization energy of 70 eV is used. Minor differences between EI-LRMS and EI-HRMS spectra can be observed, such as a reduced relative abundance of ions < 90 m/z when working with GC–EI-Orbitrap-MS operated in full scan compared to the NIST library [168]. However, such differences do not prevent the observation of a high match for pesticide mass spectra, thus providing high confidence in compound identification (Figure 5). For example, non-targeted analysis of different food commodities—such as mushrooms and peppers, among others—by GC–EI-Q-Orbitrap-MS, along with further comparison of data against libraries containing more than 200,000 spectra, allowed the detection of several pesticides (i.e., lambda-cyhalothrin, triadimenol, imazalil, pyrimethanil, and tebuconazol as the most common compounds) without any prior hypothesis [169].
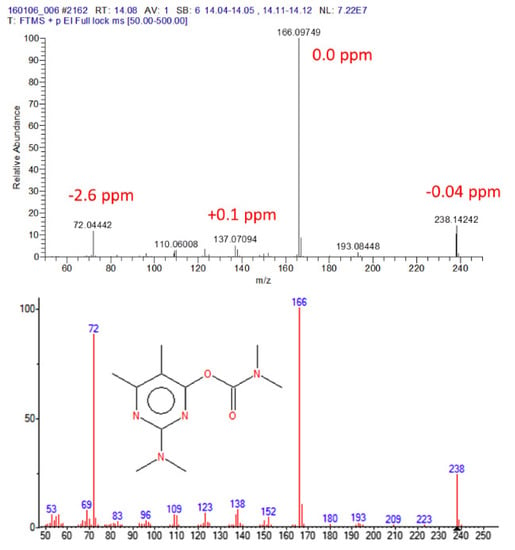
Figure 5.
Accurate GC–EI-Orbitrap mass spectrum for pirimicarb (upper spectrum); 250 pg on-column, resolving power 60 K. Lower spectrum: GC–EI-MS nominal mass spectrum for pirimicarb from NIST. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [168]. Copyright (2016) Elsevier.
5.5. IM–MS Hyphenation
The recent commercialization of ion mobility–mass spectrometry (IM–MS) instruments has brought new possibilities to food analysis, and specifically to pesticide residue analysis in the field of food safety [170,171]. The IMS dimension is located after the ionization source, so this analytical technique is applied to the separation of charged molecules based on their mass, charge, and shape under an electric field and in the presence of a neutral gas (e.g., typically N2, He, or CO2). In addition, chromatographic techniques (either LC or GC), ion-mobility spectrometry (IMS), and MS can be coupled, since the separation in these three dimensions occurs on different time scales (i.e., minutes/seconds, milliseconds, and microseconds, respectively). There are different IMS technologies coupled with MS on the market, including drift-tube ion-mobility spectrometry (DTIMS), traveling-wave ion-mobility spectrometry (TWIMS), trapped ion-mobility spectrometry (TIMS), high-field asymmetric-waveform ion-mobility spectrometry (FAIMS), and differential ion-mobility spectrometry (DIMS). To date, pesticide analysis has only been addressed by DTIMS–MS [172], TWIMS–MS [173,174,175], and DMS–MS [176]. Commercial DTIMS–MS and TWIMS–MS systems typically involve TOF mass spectrometers, because these types of analyzers offer a high acquisition rate. This instrumentation has been developed primarily for non-targeted analysis purposes. In contrast, DMS–MS systems involve QqQ-MS technology. Unlike DTIMS and TWIMS cells—where all ions entering the mobility cell are likely to reach the exit and, subsequently, be detected by MS—DMS cells act as filters of the analytes of interest [103,177]. Therefore, DMS–MS is mainly applied for targeted analysis purposes.
The high selectivity of DMS contributes to the removal of matrix compounds that co-elute in the LC dimension with target pesticides, as shown for the determination of phosphonic acid in samples that naturally contain a high concentration of phosphoric acid [23]. When applying LC–MS methods, the chromatographic separation of both substances can be compromised, while the most important qualifier mass transition of phosphonic acid is also the minor transition of phosphoric acid. Therefore, phosphoric acid can exert interference with phosphonic acid, leading to false positives. This can be avoided by integrating DMS into the LC–QqQ-MS workflow. In addition, the removal of interferences and matrix compounds in the DMS dimension not only improves method selectivity, but also improves method sensitivity by reducing chemical noise and removing adjacent chromatographic peaks from the matrix compounds. This improvement has been observed for the analysis of triazole fungicides at 0.01 mg/kg in different samples of plant origin (e.g., turnip and soy bean), which were barely identified as chromatographic peaks when applying an LC–MS method, but which could be integrated perfectly when using an LC–DMS–MS method [178].
The integration of DTMIS or TWIMS into non-targeted LC–MS workflows enhances the analytical performance of the method from three standpoints: selectivity, sensitivity, and confidence in compound identification [171]. This last aspect is of special importance for reducing the number of false positives reported in residue analysis. Both DTIMS and TWIMS (also TIMS) provide an additional identification parameter to chromatographic retention indices and mass spectra—the so-called collision cross-section (CCS). CCS is a molecular characteristic related to the spatial conformation of the ions in the gas phase. Although the drift time (i.e., the time required for ions to traverse the IMS cell) has also been used as an identification parameter in the analysis of pesticides in different fruits and vegetables [173], this parameter is instrument-dependent, and varies depending on the applied instrument settings. Nevertheless, CCS values have been shown to be reproducible between different IM–MS platforms when using the same IMS technology [179,180]. Consequently, it is possible to rely on CCS databases reported by different laboratories to use this information for identification purposes in pesticide analysis.
Several CCS databases for pesticides have been already reported [181,182]. They are also expected to be improved with CCS values for more pesticides, including transformation products and metabolites, due to the increasing implementation of LC–IM–MS instrumentation in residue analysis laboratories. In this context, the number of false positives in the screening analysis of pesticides is drastically reduced when the CCS is included in the identification criteria (i.e., threshold of ±2% from values in databases) [182]. This fact has been shown for the screening of 110 pesticides in cocoa beans at three different concentration levels (10, 50, and 150 µg/kg) [183], and for the screening of 156 pesticides at 10, 50, and 200 µg/kg in salmon feed (n = 20) [174]. In this last case, the number of false positives was reduced from 42 to 1 when the CCS was also selected as an identification criterion. Furthermore, the use of CCS values as identification criteria in the determination of pesticides by screening analysis has been shown to lead to a higher detection rate than the identification of at least one fragment ion, as this criterion is compromised for pesticides at low concentration levels [175].
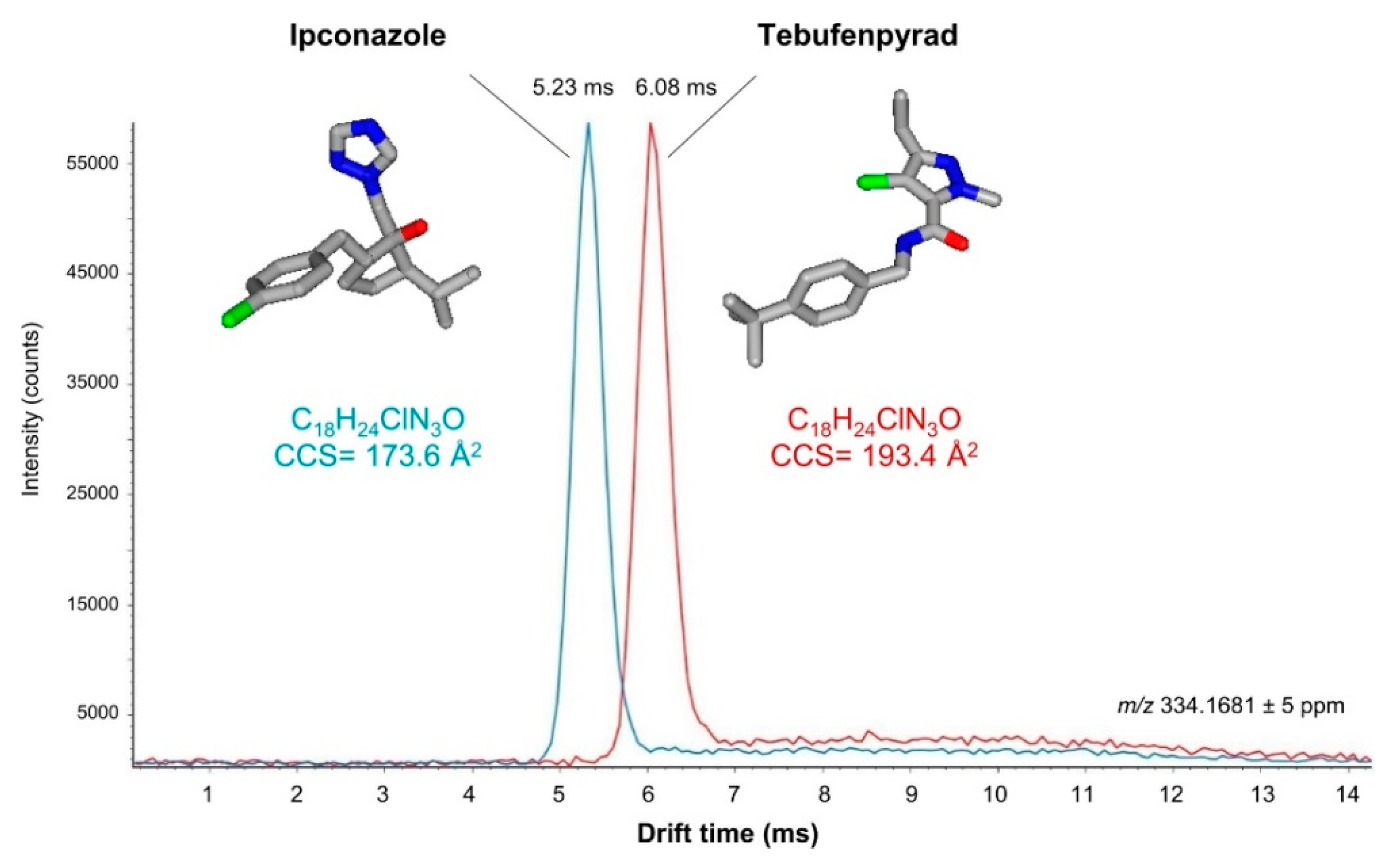
The selectivity improvement provided by DTIMS or TWIMS in LC–IM–MS methods is directly related to their resolving power, which obviously depends on the IMS technology. In general, it has been estimated that the resolving power is still very limited in the LC–IM–MS instrumentation used in multiresidue analysis [103]. However, IMS has already been shown to be effective for the separation of isomeric pesticides, such as the protonated ions of ipconazole and tebufenpyrad (C18H24ClN3O) (Figure 6) [181]. The use of current IMS technology with increased resolving power, such as cyclic-TWIMS, also allows the separation of charged isomers (e.g., protomers). This helps to understand why the relative abundance of characteristic product ions of a pesticide can vary depending on whether they are produced from analytical standards or chemical residues in food matrices [184]. Although according to SANTE 11312/2021 it is not necessary to take into account the ion ratio for pesticide identification when using HRMS, the ion ratio is a parameter to consider for this purpose when using LRMS [138]. Information on the formation of promoters for different pesticides could justify non-detected compounds present in the sample in targeted analyses when using unit mass spectrometers—due to a missing quantifier/qualifier ion, or to the alteration of their ion ratio [175]. Therefore, it could be useful to avoid false negatives when the ion ratio criterion is not fulfilled but pesticide residues are present in the sample.
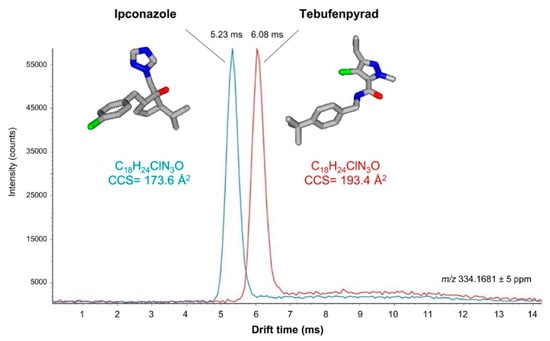
Figure 6.
Extracted ion-mobility spectra obtained for the [M + H]+ ions of the structural isomers ipconazole and tebufenpyrad. Conditions: trap bias, 40 V; IMS wave velocity, 250 m/s; IMS wave height, 45 V. Reprinted with permission from Ref. [181]. Copyright (2016) American Chemical Society.
Finally, DTIMS and TWIMS in LC–IM–MS workflows also isolate targeted compounds from background noise, providing cleaner mass spectra, facilitating mass spectral interpretation, and improving confidence in pesticide identification [172]. This effect also provides extracted ion chromatograms of greater quality, resulting in increased concentration sensitivity due to the improvement of the signal-to-noise ratio (S/N). Although this effect has not been extensively explored for the determination of pesticides in complex food matrices, improvements of S/N from 2- to 7-fold have been reported for the determination of small molecules when TWIMS has been integrated into an LC–MS method [185].
5.6. Ambient Mass Spectrometry
Ambient-ionization mass spectrometry (AIMS) is an emerging technology in the field of pesticide analysis. Compared to traditional analytical techniques used in this field, AIMS provides higher sample throughput as it involves direct, real-time, in situ analysis with minimal or no sample preparation. However, although the performance of AIMS has been studied with great interest by many routine food safety laboratories, the applications evaluated so far have not met the monitoring demands in field trials for pesticide screening. The main limitations of AIMS observed in the initial trials for routine implementation are related to the narrow analytical scope and the high rate of false positives and negatives [186]. AIMS can be considered as a promising approach for application in pesticide analysis—especially as an initial strategy to decide which samples should be sent to the laboratory for further testing. However, technical advances are still required to improve the poor reproducibility currently observed in sample analysis due to the sample heterogeneity and ion collection. These advances should also increase the concentration sensitivity, which is crucial in residue analysis but is quite limited due to the high matrix effect attributed to AIMS [76].
There is a wide range of AIMS techniques currently available for pesticide analysis, but these are mainly classified into ESI-related and APCI-related techniques. Although different AIMS approaches have been evaluated for the determination of pesticides [187], desorption electrospray ionization (DESI) and direct analysis in real time (DART) represent the most commonly used AIMS techniques in residue analysis. DESI is based on the spraying of charged solvent microdroplets at the sample surface, desorbing and ionizing the analytes that subsequently enter into the mass spectrometer [188]. The high irreproducibility of the analytical results provided by DESI is mainly associated with instrument setup and operation [189], as well as the fact that only a part of the sample surface is examined even when the pesticide residues are not homogeneously distributed on it. In this sense, the use of IL-ISs improves the reproducibility of DESI methods, and (semi)-quantification of pesticide residue levels is feasible [190]. On the other hand, DART involves the generation of plasma via the ionization of gas molecules (i.e., He, Ar, or N2), which can be consequently heated, and are impinged on the sample to cause desorption and ionization of the analytes [191]. Despite AIMS having generally been applied to the qualitative determination of pesticides in food, DART in combination with the QuPPe extraction method has been shown to be efficient for quantification purposes in the analysis of highly polar pesticides in lettuce and celery [192].
6. Conclusions
The determination of pesticide residues in food has greatly evolved in recent decades, mainly due to technological advances in MS instrumentation. This has allowed the shift from the analysis of a limited number of pesticides (single-residue methods) to the determination of hundreds of pesticide residues in a single run (multiresidue methods). The new trends in the analysis of residues and contaminants in food go further. Mega-methods are being developed to achieve the simultaneous determination of a wide variety of chemical agents such as pesticides, mycotoxins, and environmental contaminants, among others, increasing the capabilities of routine laboratories. However, the analysis of polar pesticides remains challenging, and they still require single-residue methods for their determination.
As multiresidue and mega-methods pursue the analysis of a large number of compounds with different physicochemical properties, sample preparations have become more generic, and provide higher sample throughput. In this sense, QuEChERS has been become the gold standard of sample treatments in the determination of pesticide residues. However, simple sample treatments such as QuEChERS protocols also involve less exhaustive sample clean-up, and higher matrix effect can be expected for pesticide analysis in complex samples. Reducing or avoiding the matrix effect, without renouncing the application of simple sample preparations, is currently one of the main challenges of LC–ESI-MS methods for the control of pesticide residues.
In general, LC–ESI-MS has largely replaced GC–EI-MS for pesticide analysis, mainly because softer ionization occurs and (de)protonated ions are observed. However, the development of APCI sources for GC–MS coupling has revived interest in this analytical technique. The development of HRMS is also revolutionizing LC–MS and GC–MS methods for pesticide analysis, as it provides the measurement of the accurate mass of ions, and data acquisition is no longer limited to target pesticides. It also allows the determination of both target pesticides and pesticides suspected of being present in the sample, as well as the detection and subsequent identification of other pesticides, metabolites, or transformation products whose presence in the sample was unexpected, or which were previously unknown compounds.
Finally, advances in analytical techniques such as IMS and AIMS are also impacting pesticide determination. IMS adds an extra separation dimension to LC–MS and GC–MS workflows, allowing the separation of isobaric and isomeric pesticides, and providing additional information for compound identification (i.e., the CCS parameter). In contrast, AIMS avoids the need for any chromatographic separation, giving it great potential to be implemented as a first step for rapid pesticide screening.
Author Contributions
M.H.-M. conceptualized the manuscript. M.H.-M. and D.M.-G. wrote, reviewed, and edited the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Grant IJC2019-040989-I funded by MCIN/AEI/ 10.13039/501100011033. D.M.-G. acknowledges funding from the Research Program of the University of Jaen (Plan 2021-2023, “Acción 9”).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Von Meyer-Höfer, M.; Nitzko, S.; Spiller, A. Is there an expectation gap? Consumers’ expectations towards organic: An exploratory survey in mature and emerging european organic food markets. Br. Food J. 2015, 117, 1527–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyabina, V.P.; Esimbekova, E.N.; Kopylova, K.V.; Kratasyuk, V.A. Pesticides: Formulants, distribution pathways and effects on human health—A review. Toxicol. Rep. 2021, 8, 1179–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eurostat. Pesticide Sales in the European Union. Available online: http://appsso.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/nui/show.do?dataset=aei_fm_salpest09&lang=en (accessed on 9 February 2022).
- European Commission. EU Pesticides Database. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/food/plants/pesticides/eu-pesticides-database_en (accessed on 9 February 2022).
- European Commission. Regulation (EC) No 1107. Off. J. Eur. Union 2009, 309, 1–50. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Regulation (EC) No 396/2005, Maximum residue levels of pesticides in/on food and feed of plant and animal. Off. J. Eur. Union 2005, L70, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- FAO/WHO. Codex Alimentarius Commision—Procedural Manual, 21st ed.; Joint FAO/WHO Food Standards Programme: FAO, Rome, Italy, 2013; Volume 21, ISBN 9789251064931. [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco Cabrera, L.; Medina Pastor, P. The 2019 European Union report on pesticide residues in food. EFSA J. 2021, 19, 6491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HBM4EU Initiative. European Human Biomonitoring Initiative. Available online: https://www.hbm4eu.eu/ (accessed on 9 February 2022).
- Correia, M.; Rodrigues, M.; Paíga, P.; Delerue-Matos, C. Fungicides. In Encyclopedia of Food and Health; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenner, K.; Canonica, S.; Wackett, L.P.; Elsner, M. Evaluating pesticide degradation in the environment: Blind spots and emerging opportunities. Science 2013, 341, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ji, C.; Song, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, P.; Liu, J.; Sun, Z.; Zhao, M. The potential endocrine disruption of pesticide transformation products (TPs): The blind spot of pesticide risk assessment. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostopoulou, K.; Nannou, C.; Evgenidou, E.; Lambropoulou, D. Overarching issues on relevant pesticide transformation products in the aquatic environment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 815, 152863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SANTE/2020/12830; Guidance Document on Pesticide Analytical Methods for Risk Assessment and Post-Approval Control and Monitoring Purposes. European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2021; pp. 1–50.
- Stachniuk, A.; Fornal, E. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry in the analysis of pesticide residues in food. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 1654–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernández, F.; Ibáñez, M. Multiresidue methods for pesticides and related contaminants in food. In Liquid Chromatography: Applications; Fanali, S., Haddad, P., Poole, C., Schoenmakers, P., Lloyd, D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 319–336. ISBN 9780124158061. [Google Scholar]
- García-Reyes, J.F.; Molina-Díaz, A.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. Identification of pesticide transformation products in food by liquid chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry via “fragmentation- degradation” relationships. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, H.; Ma, W.; Guo, Z.; Li, X.; Song, S.; Tang, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q. Development of precise GC-EI-MS method to determine the residual fipronil and its metabolites in chicken egg. Food Chem. 2019, 281, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murcia-Morales, M.; Cutillas, V.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. Supercritical fluid chromatography and gas chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry for the analysis of pyrethroids in vegetable matrices: A comparative study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 12626–12632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Mesa, M.; García-Campaña, A.M. Determination of sulfonylurea pesticide residues in edible seeds used as nutraceuticals by QuEChERS in combination with ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1617, 460831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nortes-Méndez, R.; Robles-Molina, J.; López-Blanco, R.; Vass, A.; Molina-Díaz, A.; Garcia-Reyes, J.F. Determination of polar pesticides in olive oil and olives by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry and high resolution mass spectrometry. Talanta 2016, 158, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzano-Sánchez, L.; Martínez-Martínez, J.A.; Domínguez, I.; Vidal, J.L.M.; Frenich, A.G.; Romero-González, R. Development and application of a novel pluri-residue method to determine polar pesticides in fruits and vegetables through liquid chromatography high resolution mass spectrometry. Foods 2020, 9, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastassiades, M.; Kolberg, D.I.; Eichhorn, E.; Wachtler, A.-K.; Benkenstein, A.; Zechmann, S.; Mack, D.; Wildgrube, C.; Barth, A.; Sigalov, I.; et al. Quick method for the analysis of numerous highly polar pesticides in food involving extraction with acidified methanol and LC-MS/MS measurement. I. Food of plant origin (QuPPe-PO-Method) Version. Eurl-Srm 2020, 11, 1–101. [Google Scholar]
- García-Reyes, J.F.; Hernando, M.D.; Ferrer, C.; Molina-Díaz, A.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. Large scale pesticide multiresidue methods in food combining liquid chromatography-time-of-flight mass spectrometry and tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 7308–7323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera López, S.; Scholten, J.; Kiedrowska, B.; de Kok, A. Method validation and application of a selective multiresidue analysis of highly polar pesticides in food matrices using hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1594, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melton, L.M.; Taylor, M.J.; Flynn, E.E. The utilisation of ion chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry (IC-MS/MS) for the multi-residue simultaneous determination of highly polar anionic pesticides in fruit and vegetables. Food Chem. 2019, 298, 125028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Alba, A.R.; García-Reyes, J.F. Large-scale multi-residue methods for pesticides and their degradation products in food by advanced LC-MS. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2008, 27, 973–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.X.; Li, X.Y.; Chang, Q.Y.; Li, Y.; Jin, L.H.; Pang, G.F.; Fan, C.L. Screening of 439 pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables by gas chromatography-quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry based on TOF accurate mass database and Q-TOF spectrum library. J. AOAC Int. 2018, 101, 1631–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahammed Shabeer, T.P.; Girame, R.; Utture, S.; Oulkar, D.; Banerjee, K.; Ajay, D.; Arimboor, R.; Menon, K.R.K. Optimization of multi-residue method for targeted screening and quantitation of 243 pesticide residues in cardamom (Elettaria cardamomum) by gas chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (GC-MS/MS) analysis. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wylie, P.L.; Westland, J.; Wang, M.; Radwan, M.M.; Majumdar, C.G.; ElSohly, M.A. Screening for more than 1000 pesticides and environmental contaminants in cannabis by GC/Q-TOF. Med. Cannabis Cannabinoids 2020, 3, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ortega, P.; Lara-Ortega, F.J.; García-Reyes, J.F.; Beneito-Cambra, M.; Gilbert-López, B.; Martos, N.R.; Molina-Díaz, A. Determination of over 350 multiclass pesticides in jams by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UHPLC-TOFMS). Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 1939–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonoli, D.; Staub Spörri, A.; Blanco, M.; Jan, P.; Larcinese, J.P.; Schmidt-Millasson, P.; Ortelli, D.; Edder, P. Performance enhancement and sample throughput increase of a multiresidue pesticides method in fruits and vegetables using Data-Dependent MS acquisition. Food Addit. Contam.-Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo Risk Assess. 2020, 37, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pszczolińska, K.; Kociołek, B. The pesticide residue analysis in commodities with high content of chlorophyll based on the quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged, and safe method: A review. J. Sep. Sci. 2022, 45, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hird, S.J.; Lau, B.P.Y.; Schuhmacher, R.; Krska, R. Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry for the determination of chemical contaminants in food. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 59, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bauer, A.; Luetjohann, J.; Rohn, S.; Jantzen, E.; Kuballa, J. Development of a suspect screening strategy for pesticide metabolites in fruit and vegetables by UPLC-Q-Tof-MS. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 1591–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiefer, K.; Müller, A.; Singer, H.; Hollender, J. New relevant pesticide transformation products in groundwater detected using target and suspect screening for agricultural and urban micropollutants with LC-HRMS. Water Res. 2019, 165, 114972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Steiner, D.; Malachová, A.; Sulyok, M.; Krska, R. Challenges and future directions in LC-MS-based multiclass method development for the quantification of food contaminants. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mol, H.G.J.; Plaza-Bolaños, P.; Zomer, P.; De Rijk, T.C.; Stolker, A.A.M.; Mulder, P.P.J. Toward a generic extraction method for simultaneous determination of pesticides, mycotoxins, plant toxins, and veterinary drugs in feed and food matrixes. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 9450–9459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnipseed, S.B.; Jayasuriya, H. Analytical methods for mixed organic chemical residues and contaminants in food. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 5969–5980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapozhnikova, Y. Rapid sample preparation and fast GC-MS-MS for the analysis of pesticides and environmental contaminants in fish. LC-GC N. Am. 2014, 32, 878–886. [Google Scholar]
- Frenich, A.G.; Romero-González, R.; del Mar Aguilera-Luiz, M. Comprehensive analysis of toxics (pesticides, veterinary drugs and mycotoxins) in food by UHPLC-MS. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 63, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsidar, A.; Siddiquee, S.; Shaarani, S.M. A review of extraction, analytical and advanced methods for determination of pesticides in environment and foodstuffs. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 71, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, J.; Liu, D.; Chen, L. Recent advances in solid-phase sorbents for sample preparation prior to chromatographic analysis. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 59, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-González, D.; Pérez-Ortega, P.; Gilbert-López, B.; Molina-Díaz, A.; García-Reyes, J.F.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. Evaluation of nanoflow liquid chromatography high resolution mass spectrometry for pesticide residue analysis in food. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1512, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churchwell, M.I.; Twaddle, N.C.; Meeker, L.R.; Doerge, D.R. Improving LC-MS sensitivity through increases in chromatographic performance: Comparisons of UPLC-ES/MS/MS to HPLC-ES/MS/MS. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2005, 825, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreno-González, D.; Alcántara-Durán, J.; Gilbert-López, B.; García-Reyes, J.F.; Molina-Díaz, A. Matrix-effect free quantitative liquid chromatography mass spectrometry analysis in complex matrices using nanoflow liquid chromatography with integrated emitter tip and high dilution factors. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1519, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Antuña, A.; Domínguez-Romero, J.C.; García-Reyes, J.F.; Rodríguez-González, P.; Centineo, G.; García Alonso, J.I.; Molina-Díaz, A. Overcoming matrix effects in electrospray: Quantitation of β-agonists in complex matrices by isotope dilution liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry using singly 13C-labeled analogues. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1288, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, C.; Lozano, A.; Agüera, A.; Girón, A.J.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. Overcoming matrix effects using the dilution approach in multiresidue methods for fruits and vegetables. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 7634–7639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masiá, A.; Suarez-Varela, M.M.; Llopis-Gonzalez, A.; Picó, Y. Determination of pesticides and veterinary drug residues in food by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 936, 40–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picó, Y.; Blasco, C.; Font, G. Environmental and food applications of LC-tandem mass spectrometry in pesticide-residue analysis: An overview. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2004, 23, 45–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuzimski, T.; Rejczak, T. Application of HPLC-DAD after SPE/QuEChERS with ZrO2-based sorbent in d-SPE clean-up step for pesticide analysis in edible oils. Food Chem. 2016, 190, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallegrave, A.; Pizzolato, T.M.; Barreto, F.; Eljarrat, E.; Barceló, D. Methodology for trace analysis of 17 pyrethroids and chlorpyrifos in foodstuff by gas chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 7689–7697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-González, D.; Huertas-Pérez, J.F.; García-Campaña, A.M.; Gámiz-Gracia, L. Determination of carbamates in edible vegetable oils by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry using a new clean-up based on zirconia for QuEChERS methodology. Talanta 2014, 128, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Matarrita, J.; Sapozhnikova, Y.; Lehotay, S.J. Evaluation of a recent product to remove lipids and other matrix co-extractives in the analysis of pesticide residues and environmental contaminants in foods. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1449, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugitate, K.; Saka, M.; Serino, T.; Nakamura, S.; Toriba, A.; Hayakawa, K. Matrix behavior during sample preparation using metabolomics analysis approach for pesticide residue analysis by GC-MS in agricultural products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 10226–10234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madej, K.; Kalenik, T.K.; Piekoszewski, W. Sample preparation and determination of pesticides in fat-containing foods. Food Chem. 2018, 269, 527–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pose-Juan, E.; Cancho-Grande, B.; Rial-Otero, R.; Simal-Gándara, J. The dissipation rates of cyprodinil, fludioxonil, procymidone and vinclozoline during storage of grape juice. Food Control 2006, 17, 1012–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannino, A.; Bolzoni, L.; Bandini, M. Application of liquid chromatography with electrospray tandem mass spectrometry to the determination of a new generation of pesticides in processed fruits and vegetables. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1036, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golge, O. Validation of Quick Polar Pesticides (QuPPe) method for determination of eight polar pesticides in cherries by LC-MS/MS. Food Anal. Methods 2021, 14, 1432–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastassiades, M.; Wachtler, A.-K.; Kolberg, D.I.; Eichhorn, E.; Benkenstein, A.; Zechmann, S.; Mack, D.; Barth, A. EU Reference Laboratory for pesticides requiring Single Residue Methods (EURL-SRM). Quick method for the analysis of numerous highly polar pesticides in food involving extraction with acidified methanol and LC-MS/MS measurement. II. Food of animal origin (QuPPe-PO-Method) Version. Eurl-Srm 2019, 2, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, E. Review of sample preparation methods for chromatographic analysis of neonicotinoids in agricultural and environmental matrices: From classical to state-of-the-art methods. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1643, 462042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejczak, T.; Tuzimski, T. Recent trends in sample preparation and liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry for pesticide residue analysis in food and related matrixes. J. AOAC Int. 2015, 98, 1143–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejczak, T.; Tuzimski, T. A review of recent developments and trends in the QuEChERS sample preparation approach. Open Chem. 2015, 13, 980–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastassiades, M.; Lehotay, S.J.; Štajnbaher, D.; Schenck, F.J. Fast and easy multiresidue method employing acetonitrile extraction/partitioning and “dispersive solid-phase extraction” for the determination of pesticide residues in produce. J. AOAC Int. 2003, 86, 412–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parrilla Vázquez, P.; Hakme, E.; Uclés, S.; Cutillas, V.; Martínez Galera, M.; Mughari, A.R.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. Large multiresidue analysis of pesticides in edible vegetable oils by using efficient solid-phase extraction sorbents based on quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged and safe methodology followed by gas chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1463, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Blanco, R.; Nortes-Méndez, R.; Robles-Molina, J.; Moreno-González, D.; Gilbert-López, B.; García-Reyes, J.F.; Molina-Díaz, A. Evaluation of different cleanup sorbents for multiresidue pesticide analysis in fatty vegetable matrices by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1456, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilla-Fernández, D.; Moreno-González, D.; Bouza, M.; Saez-Gómez, A.; Ballesteros, E.; García-Reyes, J.F.; Molina-Díaz, A. Assessment of a specific sample cleanup for the multiresidue determination of veterinary drugs and pesticides in salmon using liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry. Food Control 2021, 130, 108311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly, T.K.; Ho, T.D.; Behra, P.; Nhu-Trang, T.T. Determination of 400 pesticide residues in green tea leaves by UPLC-MS/MS and GC-MS/MS combined with QuEChERS extraction and mixed-mode SPE clean-up method. Food Chem. 2020, 326, 126928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutkowska, E.; Łozowicka, B.; Kaczyński, P. Compensation of matrix effects in seed matrices followed by gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry analysis of pesticide residues. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1614, 460738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehotay, S.J. The QuEChERSER Mega-Method. LC-GC N. Am. 2022, 40, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro, S.H.; Lehotay, S.J.; Sapozhnikova, Y.; Ninga, E.; Lightfield, A.R. High-throughput mega-method for the analysis of pesticides, veterinary drugs, and environmental contaminants by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and robotic mini-solid-phase extraction cleanup + low-pressure gas chromatography−tandem mass spectrometry, Part 1: Beef. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michlig, N.; Lehotay, S.J.; Lightfield, A.R.; Beldoménico, H.; Repetti, M.R. Validation of a high-throughput method for analysis of pesticide residues in hemp and hemp products. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1645, 462097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, D.; Sulyok, M.; Malachová, A.; Mueller, A.; Krska, R. Realizing the simultaneous liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry based quantification of >1200 biotoxins, pesticides and veterinary drugs in complex feed. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1629, 461502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malachová, A.; Stránská, M.; Václavíková, M.; Elliott, C.T.; Black, C.; Meneely, J.; Hajšlová, J.; Ezekiel, C.N.; Schuhmacher, R.; Krska, R. Advanced LC–MS-based methods to study the co-occurrence and metabolization of multiple mycotoxins in cereals and cereal-based food. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 801–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greer, B.; Chevallier, O.; Quinn, B.; Botana, L.M.; Elliott, C.T. Redefining dilute and shoot: The evolution of the technique and its application in the analysis of foods and biological matrices by liquid chromatography mass spectrometry. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 141, 116284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Mesa, M.; Lara, F.J.; Moreno-González, D.; Olmo-Iruela, M.; García-Campaña, A.M. Trends in Multiresidue Analysis; Meyers, R.A., Ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; ISBN 9780470027318. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade-Eiroa, A.; Canle, M.; Leroy-Cancellieri, V.; Cerdà, V. Solid-phase extraction of organic compounds: A critical review (Part I). TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 80, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimelis, O.; Yang, Y.; Stenerson, K.; Kaneko, T.; Ye, M. Evaluation of a solid-phase extraction dual-layer carbon/primary secondary amine for clean-up of fatty acid matrix components from food extracts in multiresidue pesticide analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1165, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walorczyk, S.; Drodyński, D.; Gnusowski, B. Multiresidue determination of 160 pesticides in wines employing mixed-mode dispersive-solid phase extraction and gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 2011, 85, 1856–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaperumal, P.; Anand, P.; Riddhi, L. Rapid determination of pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables, using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2015, 168, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakme, E.; Lozano, A.; Uclés, S.; Gómez-Ramos, M.M.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. High-throughput gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis of pesticide residues in spices by using the enhanced matrix removal-lipid and the sample dilution approach. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1573, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Z.; He, F.; Wei, J.; Tan, H.; Li, X. Simultaneous determination of neonicotinoid insecticides and insect growth regulators residues in honey using LC–MS/MS with anion exchanger-disposable pipette extraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1557, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagirani, M.S.; Ozalp, O.; Soylak, M. New trend in the extraction of pesticides from the environmental and food samples applying microextraction based green chemistry scenario: A review. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2021, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spietelun, A.; Kloskowski, A.; Chrzanowski, W.; Namieśnik, J. Understanding solid-phase microextraction: Key factors influencing the extraction process and trends in improving the technique. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 1667–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza Silva, E.A.; Risticevic, S.; Pawliszyn, J. Recent trends in SPME concerning sorbent materials, configurations and in vivo applications. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 43, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Płotka-Wasylka, J.; Szczepańska, N.; de la Guardia, M.; Namieśnik, J. Miniaturized solid-phase extraction techniques. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2015, 73, 19–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarafraz-Yazdi, A.; Amiri, A. Liquid-phase microextraction. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2010, 29, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desfontaine, V.; Capetti, F.; Nicoli, R.; Kuuranne, T.; Veuthey, J.L.; Guillarme, D. Systematic evaluation of matrix effects in supercritical fluid chromatography versus liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry for biological samples. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2018, 1079, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murcia-Morales, M.; Heinzen, H.; Parrilla-Vázquez, P.; del Gómez-Ramos, M.M.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. Presence and distribution of pesticides in apicultural products: A critical appraisal. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2022, 146, 116506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alder, L.; Greulich, K.; Kempe, G.; Vieth, B. Residue analysis of 500 high priority pesticides: Better by GC-MS or LC-MS/MS? Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2006, 25, 838–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pico, Y.; Alfarhan, A.H.; Barcelo, D. How recent innovations in gas chromatography-mass spectrometry have improved pesticide residue determination: An alternative technique to be in your radar. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 122, 115720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, B.; David, F.; Sandra, P. Capillary gas chromatography-mass spectrometry: Current trends and perspectives. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 124, 115475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakme, E.; Lozano, A.; Uclés, S.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. Further improvements in pesticide residue analysis in food by applying gas chromatography triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (GC-QqQ-MS/MS) technologies. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 5491–5506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, K.R.; Dane, A.J.; Cody, R.B. Fast pesticide analysis using low-pressure gas chromatography paired with a triple quadrupole mass spectrometer equipped with short collision cell technology. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2022, 36, e9258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninga, E.; Sapozhnikova, Y.; Lehotay, S.J.; Lightfield, A.R.; Monteiro, S.H. High-throughput mega-method for the analysis of pesticides, veterinary drugs, and environmental contaminants by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and robotic mini-solid-phase extraction cleanup + low-pressure gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry, Part 2: Catfish. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 1169–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehotay, S.J.; de Zeeuw, J.; Sapozhnikova, Y.; Michlig, N.; Hepner, J.R.; Konschnik, J.D. There is no time to waste: Low-pressure gas chromatography–mass spectrometry is a proven solution for fast, sensitive, and robust GC–MS analysis. LC-GC N. Am. 2020, 38, 457–466. [Google Scholar]
- Gruber, B.; Weggler, B.A.; Jaramillo, R.; Murrell, K.A.; Piotrowski, P.K.; Dorman, F.L. Comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography in forensic science: A critical review of recent trends. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2018, 105, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tranchida, P.Q.; Aloisi, I.; Giocastro, B.; Zoccali, M.; Mondello, L. Comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography-mass spectrometry using milder electron ionization conditions: A preliminary evaluation. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1589, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Dong, F.; Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Wu, X.; Chen, Z.; Pan, X.; Zheng, Y. Atmospheric pressure gas chromatography quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry for simultaneous determination of fifteen organochlorine pesticides in soil and water. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1435, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portolés, T.; Mol, J.G.J.; Sancho, J.V.; Hernández, F. Advantages of atmospheric pressure chemical ionization in gas chromatography tandem mass spectrometry: Pyrethroid insecticides as a case study. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 9802–9810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Geng, X.; Organtini, K.L.; Dong, F.; Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Wu, X.; Zheng, Y. A target screening method for detection of organic pollutants in fruits and vegetables by atmospheric pressure gas chromatography quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry combined with informatics platform. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1577, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirabelli, M.F.; Wolf, J.C.; Zenobi, R. Atmospheric pressure soft ionization for gas chromatography with dielectric barrier discharge ionization-mass spectrometry (GC-DBDI-MS). Analyst 2017, 142, 1909–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaufmann, A. The use of UHPLC, IMS, and HRMS in multiresidue analytical methods: A critical review. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2020, 1158, 122369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Ruiz, R.; Romero-González, R.; Garrido Frenich, A. Ultrahigh-pressure liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry: An overview of the last decade. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, K.; Mandolfino, F.; Cacciola, F.; Dugo, P.; Mondello, L. Multidimensional liquid chromatography approaches for analysis of food contaminants. J. Sep. Sci. 2021, 44, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Schmitz, O.J. Comprehensive two-dimensional liquid chromatography tandem diode array detector (DAD) and accurate mass QTOF-MS for the analysis of flavonoids and iridoid glycosides in Hedyotis diffusa. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Molina, J.; Gilbert-López, B.; García-Reyes, J.F.; Molina-Díaz, A. Simultaneous liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry determination of both polar and “multiresidue” pesticides in food using parallel hydrophilic interaction/reversed-phase liquid chromatography and a hybrid sample preparation approach. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1517, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicini, J.L.; Jensen, P.K.; Young, B.M.; Swarthout, J.T. Residues of glyphosate in food and dietary exposure. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 5226–5257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansons, M.; Pugajeva, I.; Bartkevics, V.; Karkee, H.B. LC-MS/MS characterisation and determination of dansyl chloride derivatised glyphosate, aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA), and glufosinate in foods of plant and animal origin. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2021, 1177, 122779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Mayán, L.; Castro, G.; Ramil, M.; Cela, R.; Rodríguez, I. Approaches to liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry assessment of glyphosate residues in wine. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 1445–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutillas, V.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. Analysis by LC-MS/MS of polar pesticides in fruits and vegetables using new hybrid stationary phase. MethodsX 2021, 8, 101306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, J.J.; Potter, O.G.; Chu, T.W.; Yin, H. Improved LC/MS methods for the analysis of metal-sensitive analytes using medronic acid as a mobile phase additive. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 9457–9464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SANTE/12682/2019; Guidance Document on Analytical Quality Control and Method Validation for Pesticide Residues Analysis in Food and Feed. Safety of the Food Chain Pesticides and Biocides. European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2019; pp. 1–48.
- Parrilla Vázquez, P.; Ferrer, C.; Martínez Bueno, M.J.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. Pesticide residues in spices and herbs: Sample preparation methods and determination by chromatographic techniques. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 115, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupo, S. LC-MS sensitivity: Practical strategies to boost your signal and lower your noise. LC-GC N. Am. 2018, 36, 652–661. [Google Scholar]
- De Vijlder, T.; Valkenborg, D.; Lemière, F.; Romijn, E.P.; Laukens, K.; Cuyckens, F. A tutorial in small molecule identification via electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry: The practical art of structural elucidation. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2018, 37, 607–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wong, J.W.; Yang, P.; Hayward, D.G.; Sakuma, T.; Zou, Y.; Schreiber, A.; Borton, C.; Nguyen, T.V.; Kaushik, B.; et al. Protocol for an electrospray ionization tandem mass spectral product ion library: Development and application for identification of 240 pesticides in foods. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 5677–5684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chow, W.; Wong, J.W.; Chang, J. Applications of nDATA for screening, quantitation, and identification of pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables using UHPLC/ESI Q-Orbitrap all ion fragmentation and data independent acquisition. J. Mass Spectrom. 2021, 56, e4783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrynko, I.; Łozowicka, B.; Kaczyński, P. Liquid chromatographic MS/MS analysis of a large group of insecticides in honey by modified QuEChERS. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 2307–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Z.; Dong, F.; Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Wu, X.; Chen, Z.; Pan, X.; Gan, J.; Zheng, Y. Simultaneous determination of organophosphorus pesticides in fruits and vegetables using atmospheric pressure gas chromatography quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2017, 231, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, M.; Cai, Z. Atmospheric pressure chemical ionization in gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for the analysis of persistent organic pollutants. Trends Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 25, e00076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, K.H.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.H. Development of a quantitative screening method for pesticide multiresidues in orange, chili pepper, and brown rice using gas chromatography-quadrupole time of flight mass spectrometry with dopant-assisted atmospheric pressure chemical ionization. Food Chem. 2022, 374, 131626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito-Shida, S.; Nagata, M.; Nemoto, S.; Akiyama, H. Quantitative analysis of pesticide residues in tea by gas chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry with atmospheric pressure chemical ionization. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2020, 1143, 122057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervera, M.I.; Portolés, T.; López, F.J.; Beltrán, J.; Hernández, F. Screening and quantification of pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables making use of gas chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry with atmospheric pressure chemical ionization. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 6843–6855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigano, F.; Tranchida, P.Q.; Dugo, P.; Mondello, L. High-performance liquid chromatography combined with electron ionization mass spectrometry: A review. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 118, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutkowska, E.; Łozowicka, B.; Kaczyński, P. Three approaches to minimize matrix effects in residue analysis of multiclass pesticides in dried complex matrices using gas chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2019, 279, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran-Lam, T.-T.; Bui, M.Q.; Nguyen, H.Q.; Dao, Y.H.; Le, G.T. A combination of chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry systems (UPLC-MS/MS and GC-MS/MS), modified QuEChERS extraction and mixed-mode SPE clean-up method for the analysis of 656 pesticide residues in rice. Foods 2021, 10, 2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.E.; Lee, J.Y.; Mansur, A.R.; Jang, H.W.; Lim, M.C.; Lee, Y.; Yoo, M.; Nam, T.G. Determination of 60 pesticides in hen eggs using the QuEChERS procedure followed by LC-MS/MS and GC-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2019, 298, 125050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacinti, G.; Raynaud, C.; Capblancq, S.; Simon, V. Matrix-matching as an improvement strategy for the detection of pesticide residues. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, T1342–T1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsuchiyama, T.; Katsuhara, M.; Sugiura, J.; Nakajima, M.; Yamamoto, A. Combined use of a modifier gas generator, analyte protectants and multiple internal standards for effective and robust compensation of matrix effects in gas chromatographic analysis of pesticides. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1589, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchiyama, T.; Katsuhara, M.; Nakajima, M. Compensation of matrix effects in gas chromatography–mass spectrometry analysis of pesticides using a combination of matrix matching and multiple isotopically labeled internal standards. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1524, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colazzo, M.; Alonso, B.; Ernst, F.; Cesio, M.V.; Perez-Parada, A.; Heinzen, H.; Pareja, L. Determination of multiclass, semi-polar pesticide residues in fatty fish muscle tissue by gas and liquid chromatography mass spectrometry. MethodsX 2019, 6, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabregat-Cabello, N.; Zomer, P.; Sancho, J.V.; Roig-Navarro, A.F.; Mol, H.G.J. Comparison of approaches to deal with matrix effects in LC-MS/MS based determinations of mycotoxins in food and feed. World Mycotoxin J. 2016, 9, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varela-Martínez, D.A.; González-Curbelo, M.Á.; González-Sálamo, J.; Hernández-Borges, J. High-throughput analysis of pesticides in minor tropical fruits from Colombia. Food Chem. 2019, 280, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastassiades, M.; Maštovská, K.; Lehotay, S.J. Evaluation of analyte protectants to improve gas chromatographic analysis of pesticides. J. Chromatogr. A 2003, 1015, 163–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, M.; Khorshid, M.A.; Abo-Aly, M.M. Combination of analyte protectants and sandwich injection to compensate for matrix effect of pesticides residue in GC–MS/MS. Microchem. J. 2020, 156, 104852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.W.; Wang, J.; Chow, W.; Carlson, R.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, K.; Hayward, D.G.; Chang, J.S. Perspectives on Liquid Chromatography—High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry for Pesticide Screening in Foods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 9573–9581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sante/11312/2021; Guidance Document on Analytical Quality Control and Method Validation for Pesticide Residues Analysis in Food and Feed. European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2021; pp. 1–57.
- Grimalt, S.; Dehouck, P. Review of analytical methods for the determination of pesticide residues in grapes. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1433, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, R.; Pardeshi, A.; Dhanshetty, M.; Anastassiades, M.; Banerjee, K. Development and validation of an analytical method for the multiresidue analysis of pesticides in sesame seeds using liquid- and gas chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1652, 462346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.S.; Kim, M.K.; Kim, E.J. High-throughput simultaneous analysis of multiple pesticides in grain, fruit, and vegetables by GC-MS/MS. Food Addit. Contam.-Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2020, 37, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, A.; Carrière, R.; Ayciriex, S.; Margoum, C.; Leblanc, Y.; Lemoine, J. Scout-multiple reaction monitoring: A liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry approach for multi-residue pesticide analysis without time scheduling. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1621, 461046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiljanek, T.; Niewiadowska, A.; Małysiak, M.; Posyniak, A. Miniaturized multiresidue method for determination of 267 pesticides, their metabolites and polychlorinated biphenyls in low mass beebread samples by liquid and gas chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 2021, 235, 122721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Végh, R.; Sörös, C.; Majercsik, N.; Sipos, L. Determination of Pesticides in Bee Pollen: Validation of a multiresidue high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry/mass spectrometry method and testing pollen samples of selected botanical origin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 1507–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Bentum, M.; Selbach, M. An introduction to advanced targeted acquisition methods. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2021, 20, 100165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belarbi, S.; Vivier, M.; Zaghouani, W.; De Sloovere, A.; Agasse-Peulon, V.; Cardinael, P. Comparison of new approach of GC-HRMS (Q-Orbitrap) to GC–MS/MS (triple-quadrupole) in analyzing the pesticide residues and contaminants in complex food matrices. Food Chem. 2021, 359, 129932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollender, J.; Schymanski, E.L.; Singer, H.P.; Ferguson, P.L. Nontarget screening with high resolution mass spectrometry in the environment: Ready to go? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 11505–11512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bowman, A.P.; Blakney, G.T.; Hendrickson, C.L.; Ellis, S.R.; Heeren, R.M.A.; Smith, D.F. Ultra-high mass resolving power, mass accuracy, and dynamic range MALDI mass spectrometry imaging by 21-T FT-ICR MS. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 3133–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urban, J.; Afseth, N.K.; Štys, D. Fundamental definitions and confusions in mass spectrometry about mass assignment, centroiding and resolution. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 53, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Špánik, I.; Machyňáková, A. Recent applications of gas chromatography with high-resolution mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 163–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Reyes, J.F.; Moreno-González, D.; Nortes-Méndez, R.; Gilbert-López, B.; Molina Díaz, A. HRMS: Hardware and Software. In Applications in High Resolution Mass Spectrometry; Romero-González, R., Garrido, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; ISBN 9780128096482. [Google Scholar]
- Uclés, S.; Uclés, A.; Lozano, A.; Martínez Bueno, M.J.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. Shifting the paradigm in gas chromatography mass spectrometry pesticide analysis using high resolution accurate mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1501, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito-Shida, S.; Hamasaka, T.; Nemoto, S.; Akiyama, H. Multiresidue determination of pesticides in tea by liquid chromatography-high-resolution mass spectrometry: Comparison between Orbitrap and time-of-flight mass analyzers. Food Chem. 2018, 256, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ortega, P.; Lara-Ortega, F.J.; Gilbert-López, B.; Moreno-González, D.; García-Reyes, J.F.; Molina-Díaz, A. Screening of over 600 pesticides, veterinary drugs, food-packaging contaminants, mycotoxins, and other chemicals in food by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UHPLC-QTOFMS). Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 1216–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Huang, S.; Wang, J. Non-targeted screening of pesticides for food analysis using liquid chromatography high-resolution mass spectrometry-a review. Food Addit. Contam.-Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2020, 37, 1180–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollender, J.; van Bavel, B.; Dulio, V.; Farmen, E.; Furtmann, K.; Koschorreck, J.; Kunkel, U.; Krauss, M.; Munthe, J.; Schlabach, M.; et al. High resolution mass spectrometry-based non-target screening can support regulatory environmental monitoring and chemicals management. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2019, 31, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pourchet, M.; Debrauwer, L.; Klanova, J.; Price, E.J.; Covaci, A.; Caballero-Casero, N.; Oberacher, H.; Lamoree, M.; Damont, A.; Fenaille, F.; et al. Suspect and non-targeted screening of chemicals of emerging concern for human biomonitoring, environmental health studies and support to risk assessment: From promises to challenges and harmonisation issues. Environ. Int. 2020, 139, 105545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunzelmann, M.; Winter, M.; Åberg, M.; Hellenäs, K.E.; Rosén, J. Non-targeted analysis of unexpected food contaminants using LC-HRMS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 5593–5602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Izzo, L.; Narváez, A.; Castaldo, L.; Gaspari, A.; Rodríguez-Carrasco, Y.; Grosso, M.; Ritieni, A. Multiclass and multi-residue screening of mycotoxins, pharmacologically active substances, and pesticides in infant milk formulas through ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with high-resolution mass spectrometry analysis. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 2948–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Pérez, M.L.; Romero-González, R.; Vidal, J.L.M.; Frenich, A.G. Identification of transformation products of pesticides and veterinary drugs in food and related matrices: Use of retrospective analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1389, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, C.M.; Croley, T.R.; Knolhoff, A.M. Data processing strategies for non-targeted analysis of foods using liquid chromatography/high-resolution mass spectrometry. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 136, 116188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liang, W.; Feng, X.; Ruan, T.; Jiang, G. Recent advances in data-mining techniques for measuring transformation products by high-resolution mass spectrometry. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 143, 116409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Ge, W.; Ruan, G.; Cai, X.; Guo, T. Data-Independent Acquisition mass spectrometry-based proteomics and software tools: A glimpse in 2020. Proteomics 2020, 20, 1900276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Cao, Y.M.; Miao, S.; Lan, L.; Chen, M.; Li, W.T.; Mao, X.H.; Ji, S. Qualitative screening and quantitative determination of 569 pesticide residues in honeysuckle using ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography coupled to quadrupole-Orbitrap high resolution mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1606, 460374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschet, C.; Lew, B.M.; Hasenbein, S.; Anumol, T.; Young, T.M. LC- and GC-QTOF-MS as complementary tools for a comprehensive micropollutant analysis in aquatic systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 1553–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajski, Ł.; Petromelidou, S.; Díaz-Galiano, F.J.; Ferrer, C.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. Improving the simultaneous target and non-target analysis LC-amenable pesticide residues using high speed Orbitrap mass spectrometry with combined multiple acquisition modes. Talanta 2021, 228, 122241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Tan, H.; Li, Y.; De Boevre, M.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, S. An integrated data-dependent and data-independent acquisition method for hazardous compounds screening in foods using a single UHPLC-Q-Orbitrap run. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mol, H.G.J.; Tienstra, M.; Zomer, P. Evaluation of gas chromatography-electron ionization-full scan high resolution Orbitrap mass spectrometry for pesticide residue analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 935, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Pérez, M.; Domínguez, I.; González, F.J.E.; Frenich, A.G. Application of full scan gas chromatography high resolution mass spectrometry data to quantify targeted-pesticide residues and to screen for additional substances of concern in fresh-food commodities. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1622, 461118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Mesa, M.; Escourrou, A.; Monteau, F.; Le Bizec, B.; Dervilly-Pinel, G. Current applications and perspectives of ion mobility spectrometry to answer chemical food safety issues. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 94, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Mesa, M.; Ropartz, D.; García-Campaña, A.M.; Rogniaux, H.; Dervilly-Pinel, G.; Le Bizec, B. Ion mobility spectrometry in food analysis: Principles, current applications and future trends. Molecules 2019, 24, 2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.P.; Zhang, F.; Guo, Y.L. Validating an ion mobility spectrometry-quadrupole time of flight mass spectrometry method for high-throughput pesticide screening. Analyst 2019, 144, 4835–4840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goscinny, S.; Joly, L.; De Pauw, E.; Hanot, V.; Eppe, G. Travelling-wave ion mobility time-of-flight mass spectrometry as an alternative strategy for screening of multi-class pesticides in fruits and vegetables. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1405, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regueiro, J.; Negreira, N.; Hannisdal, R.; Berntssen, M.H.G. Targeted approach for qualitative screening of pesticides in salmon feed by liquid chromatography coupled to traveling-wave ion mobility/quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Food Control 2017, 78, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, A.; Kuballa, J.; Rohn, S.; Jantzen, E.; Luetjohann, J. Evaluation and validation of an ion mobility quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry pesticide screening approach. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 2178–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolberg, D.I.S.; Zechmann, S.; Wildgrube, C.; Sigalov, I.; Scherbaum, E.; Anastassiades, M. Determination of triazole derivative metabolites (TDMs) in fruit and vegetables using the QuPPe method and differential mobility spectrometry (DMS) and survey of the residue situation in organic and conventional produce. Asp. Food Control Anim. Health 2016, 2, 2196–3460. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, B.B.; Nazarov, E.G.; Londry, F.; Vouros, P.; Covey, T.R. Differential mobility spectrometry/mass spectrometry history, theory, design optimization, simulations, and applications. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2016, 35, 687–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasak, J.; Le Blanc, Y.; Speer, K.; Billian, P.; Schoening, R.M. Analysis of triazole-based metabolites in plant materials using differential mobility spectrometry to improve LC/MS/MS selectivity. J. AOAC Int. 2012, 95, 1768–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stow, S.M.; Causon, T.J.; Zheng, X.; Kurulugama, R.T.; Mairinger, T.; May, J.C.; Rennie, E.E.; Baker, E.S.; Smith, R.D.; McLean, J.A.; et al. An interlaboratory evaluation of drift tube ion mobility-mass spectrometry collision cross section measurements. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 9048–9055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hernández-Mesa, M.; D’Atri, V.; Barknowitz, G.; Fanuel, M.; Pezzatti, J.; Dreolin, N.; Ropartz, D.; Monteau, F.; Vigneau, E.; Rudaz, S.; et al. Interlaboratory and interplatform study of steroids collision cross section by traveling wave ion mobility spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 5013–5022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regueiro, J.; Negreira, N.; Berntssen, M.H.G. Ion-mobility-derived collision cross section as an additional identification point for multiresidue screening of pesticides in fish feed. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 11169–11177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goscinny, S.; McCullagh, M.; Far, J.; De Pauw, E.; Eppe, G. Towards the use of ion mobility mass spectrometry derivedcollision cross section as a screening approach for unambiguousidentification of targeted pesticides in food. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2019, 33, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zainudin, B.H.; Salleh, S.; Yaakob, A.S.; Mohamed, R. Comprehensive strategy for pesticide residue analysis in cocoa beans through qualitative and quantitative approach. Food Chem. 2022, 368, 130778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCullagh, M.; Goscinny, S.; Palmer, M.; Ujma, J. Investigations into pesticide charge site isomers using conventional IM and cIM systems. Talanta 2021, 234, 122604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Mesa, M.; Monteau, F.; Le Bizec, B.; Dervilly-Pinel, G. Potential of ion mobility-mass spectrometry for both targeted and non-targeted analysis of phase II steroid metabolites in urine. Anal. Chim. Acta X 2019, 1, 100006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehotay, S.J.; Chen, Y. Hits and misses in research trends to monitor contaminants in foods. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 5331–5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beneito-Cambra, M.; Gilbert-López, B.; Moreno-González, D.; Bouza, M.; Franzke, J.; García-Reyes, J.F.; Molina-Díaz, A. Ambient (desorption/ionization) mass spectrometry methods for pesticide testing in food: A review. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 4831–4852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentili, A.; Fanali, S.; Mainero Rocca, L. Desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry for food analysis. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 115, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelley, J.T.; Badal, S.P.; Engelhard, C.; Hayen, H. Ambient desorption/ionization mass spectrometry: Evolution from rapid qualitative screening to accurate quantification tool. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 4061–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerbig, S.; Stern, G.; Brunn, H.E.; Düring, R.A.; Spengler, B.; Schulz, S. Method development towards qualitative and semi-quantitative analysis of multiple pesticides from food surfaces and extracts by desorption electrospray ionization mass spectrometry as a preselective tool for food control. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 2107–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajslova, J.; Cajka, T.; Vaclavik, L. Challenging applications offered by direct analysis in real time (DART) in food-quality and safety analysis. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2011, 30, 204–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, F.J.; Chan, D.; Dickinson, M.; Lloyd, A.S.; Adams, S.J. Evaluation of direct analysis in real time for the determination of highly polar pesticides in lettuce and celery using modified Quick Polar Pesticides Extraction method. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1496, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).