Determination of Menbutone: Development and Validation of a Sensitive HPLC Assay according to the European Medicines Agency Guideline
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Animals and Experimental Procedures
2.3. Preparation of Stock, Calibration and Quality Control Working Solutions
2.4. Preparation of Analysis Samples
- Blank samples: Biological matrix without MB and IS (1 mL).
- Zero samples: Biological matrix (0.9 mL) with 0.1 mL IS (20 µg/mL).
- Calibration standards: 0.9 mL plasma was spiked with 100 µL of each calibration working solution to obtain calibration curves. Thus, concentration calibration samples were 0.2, 0.5, 1, 5, 10, 50 and 100 µg/mL for MB and 2 µg/mL for IS.
- Quality control samples were also prepared in plasma (0.9 mL) at concentrations of 0.2, 0.6, 30 and 75 µg/mL for MB (0.1 mL) and 2 µg/mL for IS (0.1 mL).
2.5. Extraction Method
2.6. HPLC System and Conditions
2.7. Method Validation Procedure
2.7.1. Selectivity
2.7.2. Carry-Over
2.7.3. LLOQ and Calibration Curve
2.7.4. Accuracy and Precision
2.7.5. Stability
2.8. Method Application
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
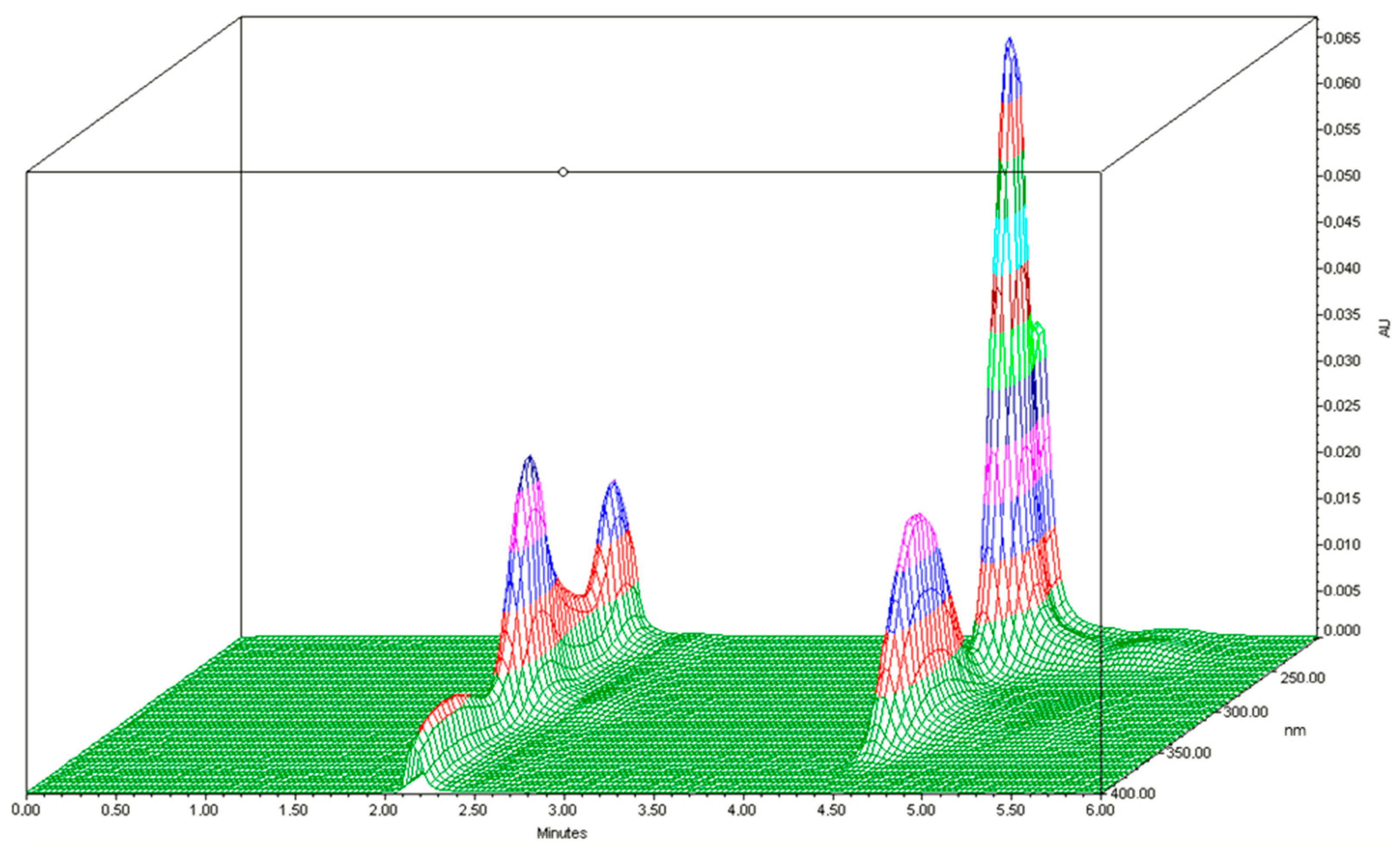
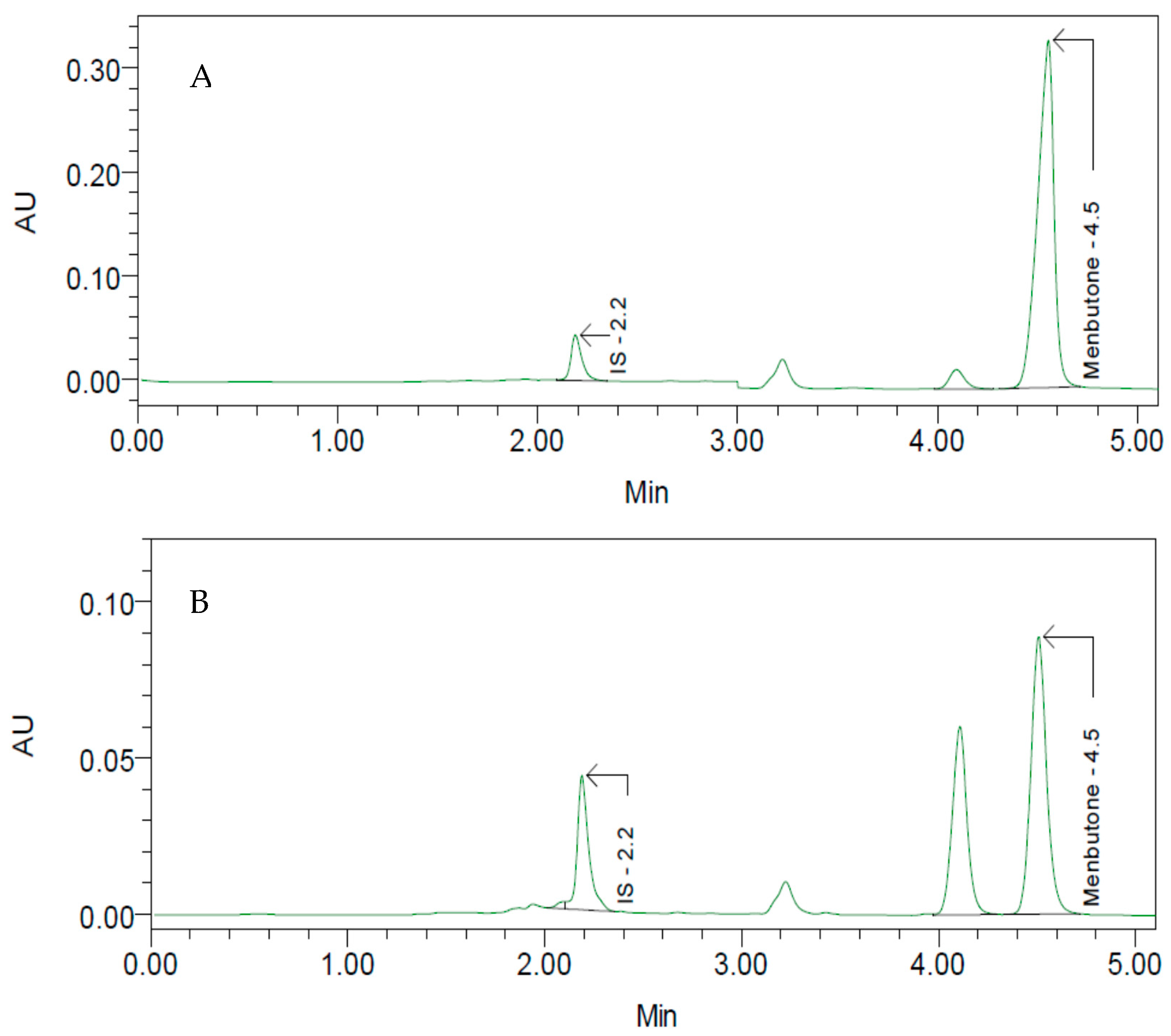
3.1. Selectivity
3.2. Carry-Over
3.3. Lower Limit of Quantification (LLOQ)
3.4. Calibration Curve
3.5. Accuracy and Precision
3.6. Stability
3.7. Method Application
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O´Neil, M. The Merck Index, 15th ed.; Royal Society Chemistry: Whitehouse Station, NJ, USA, 2013; ISBN 9781849736701. [Google Scholar]
- Symonds, H.W. The choleretic effect of menbutone and clanobutin sodium in steers. Vet. Rec. 1982, 110, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belal, F.; El-Razeq, S.A.-M.A.; Fouad, M.M.; Fouad, F.A. Spectrofluorimetric analysis of menbutone in veterinary formulations: Application to residue determination in bovine meat and milk. Eur. J. Chem. 2016, 7, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Bagary, R.I.; Elkady, E.F.; Ayoub, B.M. Spectrophotometric methods for the determination of sitagliptin and vildagliptin in bulk and dosage forms. Int. J. Biomed. Sci. 2011, 7, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heads of Medicines Agencies (EMA). VMRI (Veterinary Mutual Information Recognition). Product Index. Available online: https://www.hma.eu/vmriproductindex.html (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). CMDv/GUI/032 Guidance for Link to National Databases of Authorised Products. Available online: https://www.hma.eu/fileadmin/dateien/Veterinary_medicines/CMDv_Website/Procedural_guidance/General_info_on_applications/GUI-032-06_Link_to_national_databases_of_authorised_products.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Veterinary Medicines. Available online: https://www.medicinesinfo.eu/select-language?destination=/node/210934 (accessed on 7 March 2022).
- European Commission. Commission Regulation (EU) No 37/2010 of 22 December 2009 on pharmacologically active substances and their classification regarding maximum residue limits in foodstuffs of animal origin. Off. J. Eur. Union 2010, L15, 1–72. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, P.; Wu, L.; Wu, X.; Luo, L.; Xu, X.; Luo, Y. Determination of menbutone residuals in edible swine tissues based on solid-phase extraction and RP-HPLC. Lat. Am. J. Pharm. 2019, 38, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Wang, L.Z.; Luo, Y.H.; Wang, X. Improved Synthesis Method of Menbutone . CN Patent CN104370734A, 25 February 2015. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/CN104370734A/en (accessed on 17 January 2022).
- Hirosh, M.; Kouhei, F.; Toshiaki, T. Application to residue determination in bovine meat and milk. Kumamoto-Ken Hoken Kankyo Kagaku Kenkyushoho 2010, 39, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Belal, F.; El-Razeq, S.A.A.; Fouad, M.M.; Zayed, S.; Fouad, F.A. Determination of menbutone in bovine milk and meat using micellar liquid chromatography: Application to injectable dosage forms. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Guideline on Bioanalytical Method Validation (EMEA/CHMP/EWP/192217/2009). Available online: http://www.ema.europa.eu/ema/index.jsp?curl=pages/includes/document/document_detail.jsp?webContentId=WC500109686%26mid=WC0b01ac058009a3dc. (accessed on 15 January 2022).
- Spanish Agency of Medicines and Medical Devices (AEMPS). List of Laboratories Certified for Good Laboratory Practice Compliance [Listado de Laboratorios Certificados para el Cumplimiento de Buenas Prácticas de Laboratorio]. Available online: https://www.aemps.gob.es/industria-farmaceutica/buenas-practicas-de-laboratorio/listadolab-bpl/ (accessed on 7 March 2022).

| Nominal Concentration (µg/mL) | Intra-Day | Inter-Day | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Batch 1 | Batch 2 | Batch 3 | ||||||
| CV (%) | Accuracy (%) | CV (%) | Accuracy (%) | CV (%) | Accuracy (%) | CV (%) | Accuracy (%) | |
| 0.2 | 0.14 | 115.40 | 2.49 | 114.63 | 1.34 | 111.43 | 0.96 | 112.66 |
| 0.58 | 114.96 | 0.83 | 112.86 | 0.38 | 106.70 | |||
| Slope | Intercept | R2 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calibration curve 1 | 0.816 | 0.026 | 0.999 | < 0.001 |
| Calibration curve 2 | 0.730 | 0.013 | 1.000 | |
| Calibration curve 3 | 0.815 | 0.031 | 1.000 |
| Nominal Concentration (µg/mL) | Accuracy (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Calibration Curve 1 | Calibration Curve 2 | Calibration Curve 3 | |
| 0.2 | 115.18 | 113.75 | 109.06 |
| 0.5 | 94.09 | 96.70 | 104.19 |
| 1 | 90.61 | 96.37 | 102.59 |
| 5 | 110.68 | 102.78 | 96.32 |
| 10 | 103.85 | 98.81 | 103.48 |
| 50 | 96.97 | 100.00 | 99.21 |
| 100 | 100.69 | 100.01 | 100.17 |
| Nominal Concentration (µg/mL) | Sample Number | Intra-Day | Inter-Day | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Batch 1 | Batch 2 | Batch 3 | ||||||||
| CV (%) | Accuracy (%) | CV (%) | Accuracy (%) | CV (%) | Accuracy (%) | CV (%) | Accuracy (%) | |||
| QC1 | 0.2 | 1 | 2.64 | 109.05 | 3.34 | 111.17 | 2.13 | 105.99 | 2.68 | 109.09 ± 5.27 |
| 2 | 8.21 | 105.45 | 0.85 | 111.30 | 0.19 | 109.46 | ||||
| 3 | 6.35 | 104.18 | 0.47 | 117.67 | 2.71 | 103.56 | ||||
| 4 | 4.59 | 102.99 | 0.66 | 113.02 | 0.58 | 103.79 | ||||
| 5 | 6.01 | 119.52 | 0.99 | 113.99 | 0.45 | 105.29 | ||||
| QC2 | 0.6 | 1 | 0.71 | 88.03 | 0.48 | 95.19 | 1.45 | 95.67 | 1.34 | 92.91 ± 5.64 |
| 2 | 0.43 | 86.08 | 3.69 | 97.77 | 0.67 | 94.50 | ||||
| 3 | 1.09 | 86.79 | 4.17 | 105.61 | 0.12 | 93.24 | ||||
| 4 | 0.31 | 85.17 | 0.28 | 93.77 | 0.69 | 93.45 | ||||
| 5 | 0.88 | 85.84 | 0.42 | 94.97 | 4.77 | 97.63 | ||||
| QC3 | 30 | 1 | 0.36 | 85.68 | 0.19 | 93.22 | 2.88 | 105.39 | 0.84 | 95.48 ± 6.73 |
| 2 | 0.09 | 86.94 | 0.00 | 92.63 | 0.07 | 105.10 | ||||
| 3 | 0.18 | 88.18 | 0.07 | 93.52 | 3.35 | 103.80 | ||||
| 4 | 1.29 | 97.54 | 0.07 | 93.84 | 3.32 | 104.70 | ||||
| 5 | 0.29 | 89.39 | 0.11 | 94.61 | 0.29 | 97.70 | ||||
| QC4 | 75 | 1 | 0.03 | 87.95 | 0.03 | 93.55 | 2.91 | 104.92 | 0.28 | 97.86 ± 8.12 |
| 2 | 0.10 | 87.86 | 0.01 | 93.20 | 0.09 | 108.21 | ||||
| 3 | 0.10 | 88.00 | 0.03 | 94.24 | 0.02 | 107.97 | ||||
| 4 | 0.05 | 92.76 | 0.23 | 100.26 | 0.21 | 108.80 | ||||
| 5 | 0.01 | 92.94 | 0.10 | 97.52 | 0.26 | 109.67 | ||||
| Temperature (°C) | Time | QC2 | QC4 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CV (%) | Accuracy (%) | CV (%) | Accuracy (%) | ||
| −20 | 24 h | 0.44 | 85.40 | 1.99 | 87.06 |
| 48 h | 0.40 | 85.94 | 0.13 | 93.38 | |
| 72 h | 1.13 | 92.52 | 2.62 | 89.67 | |
| 4 | 24 h | 1.42 | 89.57 | 0.65 | 85.47 |
| 48 h | 1.89 | 87.56 | 0.10 | 94.90 | |
| 72 h | 1.07 | 89.54 | 4.02 | 91.35 | |
| 25 | 24 h | 3.40 | 93.95 | 1.81 | 87.75 |
| −20 | 7 days | 0.24 | 93.92 | 0.08 | 97.54 |
| 15 days | 3.69 | 86.96 | 0.06 | 93.36 | |
| 1 month | 1.13 | 88.31 | 1.45 | 89.54 | |
| 4 | 24 h after extraction | 0.30 | 87.82 | 0.14 | 104.35 |
| 48 h after extraction | 1.96 | 91.63 | 0.54 | 91.62 | |
| 25 | 24 h after extraction | 0.81 | 88.84 | 0.16 | 102.96 |
| 48 h after extraction | 1.56 | 94.45 | 3.98 | 89.87 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
López, C.; Díez, R.; Rodríguez, J.M.; Sierra, M.; García, J.J.; Fernández, N.; Diez, M.J.; Sahagún, A.M. Determination of Menbutone: Development and Validation of a Sensitive HPLC Assay according to the European Medicines Agency Guideline. Separations 2022, 9, 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9040084
López C, Díez R, Rodríguez JM, Sierra M, García JJ, Fernández N, Diez MJ, Sahagún AM. Determination of Menbutone: Development and Validation of a Sensitive HPLC Assay according to the European Medicines Agency Guideline. Separations. 2022; 9(4):84. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9040084
Chicago/Turabian StyleLópez, Cristina, Raquel Díez, José M. Rodríguez, Matilde Sierra, Juan J. García, Nélida Fernández, M. José Diez, and Ana M. Sahagún. 2022. "Determination of Menbutone: Development and Validation of a Sensitive HPLC Assay according to the European Medicines Agency Guideline" Separations 9, no. 4: 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9040084
APA StyleLópez, C., Díez, R., Rodríguez, J. M., Sierra, M., García, J. J., Fernández, N., Diez, M. J., & Sahagún, A. M. (2022). Determination of Menbutone: Development and Validation of a Sensitive HPLC Assay according to the European Medicines Agency Guideline. Separations, 9(4), 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9040084








