Abstract
Salvia rosmarinus (Lamiaceae), previously known as Rosmarinus officinalis, is a plant cultivated worldwide, native to the Mediterranean region. Its leaves are traditionally used for cooking. This species possesses numerous biological activities, including antioxidant, antimicrobial, anticancer, anti-inflammatory, and hepatoprotective properties. These biological properties are due to the presence of phenolic compounds, including rosmarinic acid and phenolic diterpenoids, such as carnosic acid and carnosol. In this study, we investigated the chemical composition of a green extract obtained by maceration with ethyl lactate for the first time. Seventy-five compounds were tentatively identified by UHPLC–ESI–MS/MS, including six organic acids, six cinnamic acid derivatives, five fatty acids, eighteen flavonoids, and thirty-eight terpenoids. Thus, abietane-type diterpenoids from the ethyl lactate extract were the predominant diterpenoids in the Chilean S. rosmarinus species, in contrast to the Chinese species, in which labdane and isopimarane-type diterpenoids were found for the first time. Finally, our study confirms that the extraction of S. rosmarinus with green ethyl lactate as a solvent is efficient and sustainable for the identification of flavonoids, phenols, and terpenoids from leaves.
Keywords:
abietane; environment; ethyl lactate; green chemistry; phenolic compounds; rosemary; terpenoids 1. Introduction
Organic solvents are widely used for dissolving, diluting, and dispersing water-insoluble substances, and as a medium for organic synthesis and extraction in natural product chemistry [1]. Despite the warnings against their use due to exposure and environmental pollution, their continued use is inevitable. In recent decades, many researchers have focused on reducing the use of volatile organic solvents by introducing green solvents into their processes [2]. Green solvents have shown to be promising candidates and good alternatives to petrochemical solvents because they are derived from crops and are environmentally friendly [3]. Ethyl lactate (EL) is considered to be a green solvent derived from corn. Chemically, it is the ester of lactic acid. EL is biodegradable, non-corrosive, non-carcinogenic, and non-ozone depleting. It is mainly used in the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries. Therefore, if it is not possible to replace volatile organic solvents, their use should be optimized, and one should try to recycle them [4,5,6,7]. However, to our knowledge, there are very few studies on the use of ethyl lactate as an extracting solvent in natural product chemistry. Therefore, we decided to use ethyl lactate for the extraction of secondary metabolites.
S. rosmarinus is commonly known as “rosemary”, whose distinctive feature is its aroma, culinary use, and wide application in traditional medicine, including the treatment of colds, body aches, postpartum pain, varicose veins, discolored teeth, rheumatism, kidney infections, mental disorders, and even cancer. Additionally, it is used by the local people as a lucky charm [8,9]. The current scientific name of Salvia rosmarinus was previously known as Rosmarinus officinalis. This change was made in 2017 based on phylogenetic evidence. In addition, although the plant is cultivated worldwide, it is native to the Mediterranean region [10]. The phytochemistry of R. officinalis includes the presence of 1,8-cineole, α-pinene, camphor, limonene, and trans-caryophyllene as the main volatile terpenes in its essential oil [11,12,13]. In addition, terpenoids (carnosic acid, carnosol, and ursolic acid), flavonoids, phenolic compounds (caffeic acid, rosmarinic acid), vitamins, and minerals have been detected [14,15,16]. Their main biological activities include antioxidant, antibacterial, analgesic, anti-ulcerogenic, neuroprotective, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antiobesity, antiviral, antidepressant, antidiabetic, and anticancer properties [14,17,18,19].
UHPLC, coupled with orbitrap technology as a mass analyzer, provides high resolution, sensitivity, high mass accuracy, and a powerful separation of metabolites in natural extracts; therefore, it is the most commonly used form in metabolomic studies. It can also determine the elemental composition of parent and daughter ions in the structural elucidation of organic compounds [20,21]. For R. officinalis, some LC–MS/MS reports have previously been published, showing the presence of flavonoids and their glycosides, phenols, phenolic diterpenoids, and pentacyclic triterpenoids (Table 1).

Table 1.
Metabolomic profiles of R. officinalis samples by using LC–MS reported.
This study aims to determine and evaluate the chemical composition of an S. rosmarinus extract, obtained by maceration in the green solvent ethyl lactate using UHPLC–ES–MS/MS to initiate the transition from toxic organic solvents to green solvents.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
The green solvent used in this work was ethyl lactate (CAS 687-47-8), purchased from Sigma Aldrich (Santiago, Chile). UHPL–MS/MS solvents were purchased from Merck (Santiago, Chile).
2.2. Plant Material
Salvia rosmarinus L., was collected in Talca, VII Region, Chile. Leaves were dried at room temperature in darkness. S. rosmarinus was identified by Prof. O. Garcia, and a voucher specimen (N° RO-2015/1215) was preserved in the Laboratory of Herbarium of Extreme Natural Products of the University of Chile.
2.3. Extract Preparation
An extract (80 mg) of S. rosmarinus was obtained by maceration from 1 g of dried and powdered leaves using 10 mL of ethyl lactate (three times, 10 mL each time, 3d/extraction) as an alternative food-grade solvent (Sigma-Aldrich, CAS 687-47-8, (-)-Ethyl (S)-2-hydroxypropionate). The extract was obtained by evaporation of the solvent in vacuum (2 mbar).
2.4. UHPLC–ESI–MS/MS Conditions for Analysis
The Ultimate 3000 UHPLC system (Thermo Scientific Dionex), equipped with a quaternary pump and Ultimate 3000 series TCC-3000RS column compartments, with a Ultimate 3000 series WPS-3000RS autosampler and a PDA detector controlled by Chromeleon 7.2 software (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA, and Dionex Softron GmbH Part of Thermo Fisher Scientific, Bremen, Germany), coupled with a high-resolution Thermo Q Exactive focus mass spectrometer (Thermo, Bremen, Germany) were employed for analysis. The chromatographic unit was coupled with the MS with a heated electrospray ionization source II (HESI II). Nitrogen (purity > 99.999%) was used as both a collision and damping gas. Mass calibration was performed once a week, in both negative and positive modes, to ensure a working mass accuracy of 5 ppm or less. Caffeine and N-butylamine (Sigma Aldrich, Saint Louis, MO, USA) were the calibration standards for positive ions and buspirone hydrochloride, while sodium dodecyl sulfate and taurocholic acid sodium salt (Sigma Aldrich, Saint Louis, MO, USA) were used for mass-spectrometer calibration. These chemicals were dissolved in a mixture of acetic acid, acetonitrile, water, and methanol (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) and were infused using a Chemyx Fusion 100 syringe pump (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Bremen, Germany). XCalibur 3.0 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Bremen, Germany) and Trace Finder 3.2 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, San José, CA, USA) software were used for UHPLC control and data processing, respectively. Q Exactive 2.0 SP 2, from Thermo Fisher Scientific, was used to control the mass spectrometer.
Chromatography separations were performed using a UHPLC C18 column (Acclaim, 150 mm × 4.6 mm ID, 2.5 µm, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Bremen, Germany) at 25 °C. Analysis was monitored at 254, 280, 330, and 354 nm using a DAD range of 200 to 800 nm for peak characterization. Mobile phases A (0.1 % formic aqueous solution) and B (acetonitrile) were pumped at a flow rate of 1.00 mL min−1, according to the following gradient pattern: (0.00, 5% B); (5.00, 5% B); (10.00, 30% B); (15.00, 30% B); (20.00, 70% B); (25.00, 70% B); (35.00, 5% B) for 12 min for column equilibration before each injection. For this study, 2 mg of an ethyl lactate extract was dissolved in 10 mL of ethanol and filtered (PTFE filter, Merck), and the injection volume was 10 µL. Then, the solutions were kept at 10 °C during storage in an autosampler.
The HESI parameters included a sheath gas flow rate of 75 units, an auxiliary gas flow rate of 20, a capillary temperature of 400 °C, an auxiliary gas heater temperature of 500 °C, a spray voltage of 2500 V (for ESI), and an S-lens at RF stage 30. Full scan data in the positive and negative regions were acquired at a resolving power of 70,000 FWHM (full width at half maximum) at m/z 200. A scan range of m/z 100–1000 was chosen for the compounds of interest: the automatic gain control (AGC) was set at 3 × 106 and the injection time to 200 ms. The scan rate was set to 2 scans s−1. External calibration was obtained with a calibration solution in positive and negative polarity. For confirmation, a targeted MS/MS analysis was performed using the mass inclusion list with a time window of 30 s, with the Orbitrap spectrometer operating in both positive and negative modes at 17,500 FWHM (m/z 200). The AGC target was set to 2 × 105, and the maximum injection time was 20 ms. The precursor ions were filtered through the quadrupole, which operated with an isolation window of m/z 2. The pre-vacuum, high vacuum, and ultra-high vacuum were maintained at about 2 mbar, from 105 and below 1010 mbar, respectively. The higher energy collisional dissociation (HCD) cell was operated at 30 kV. Detection was based on the calculated exact mass and the retention time of the compounds. The mass tolerance window was set at 5 ppm for both modes.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Metabolomic Profiling Using UHPLC–ESI–MS/MS
Ethyl lactate was chosen because there is little information on an environmentally friendly extraction agent and to reduce the negative effects of the toxic organic solvents used. The high-resolution, accurate mass via Orbitrap used in this study yielded the identification and preliminary characterization of seventy-five compounds (Figure 1; Table 2), including organic acids, cinnamic acids, flavonoids, and terpenoids. As shown in Table 1, the solvents previously used in LC/MS studies are methanol, or their mixtures. Here, ethyl lactate was used for the first time for S. rosmarinus.
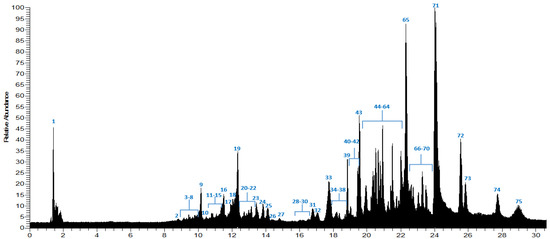
Figure 1.
Chromatogram of S. rosmarinus (Ethyl lactate extract).

Table 2.
Metabolomic profiles of ethyl lactate extract from S. rosmarinus.
3.1.1. Organic Acids
Peak 1 was identified as quinic acid (C7H11O6-) [23], and peaks 2 and 10 as hydroxybenzoic acid (C7H5O3-) [27] and benzoic acid (C7H5O2-), respectively. Peaks 7 and 9 with an [M-H]- ion at m/z: 387.1655 were assigned to tuberonic acid glucoside and their isomer (C18H27O9-) [33], while its aglycone at peak 12 was identified as tuberonic acid (C12H17O4-).
3.1.2. Cinnamic Acid Derivatives
Peaks 3 and 6 with an [M-H]- ion at m/z: 341.0873 were assigned to isomers of caffeic acid hexoside (C15H17O9-), peak 8 to chlorogenic acid (C16H17O9-), and peaks 17 and 19 to rosmarinic acid and its isomer [25,27]. Peak 13 was tentatively assigned to methyl dihydro-p-coumaric acid with an [M-H]- ion at m/z: 179.0708.
3.1.3. Flavonoids
Many flavonoid glycosides and their aglycones were tentatively identified using UV and HRMS. Peaks 11, 14, 15, 25, and 32 were identified as hydroxyluteolin-7-O-glucoside (C21H19O12-), luteolin-7-O-glucoside (C21H19O11-), luteolin-3-O-glucuronide (C21H17O12-), Luteolin (C15H9O6-), and methyl luteolin (C16H11O6-), respectively. Peaks 21, 22 and 23 at m/z: 503.0829 ([M-H]-) were assigned to luteolin acetyl-O-glucuronide isomers (C23H19O13-) [25,26,27]. Peak 18 was identified as hispidulin-7-glucoside (C22H21O11-) [26], and peaks 16 and 20 were assigned to nepitrin (C22H21O12-), previously isolated by Karim et al. [34], and its derivative feruloylnepitrin (C32H29O15-), which was also isolated by Bai et al. [35]. Peaks 26 and 34 were isorhamnetin (C16H11O7-) and methyl isorhamnetin (C17H13O7-), respectively, while peaks 29, 31, and 42 represented the flavonoid aglycones pectolinarigenin (C17H13O6-), apigenin (C15H9O5-), and cirsimaritin (C17H13O6-), respectively [25,27,36]. Finally, peaks 48 and 49 were identified as the isomers acacetin [27,36] and genkwanin [25,26,37], respectively, both with an [M-H]- ion at m/z: 283.0611 (C16H11O5-). A proposed biosynthetic relationship between luteolin (peak 25) and its derivatives detected by UHPLC–ESI–MS/MS is shown in Figure 2.
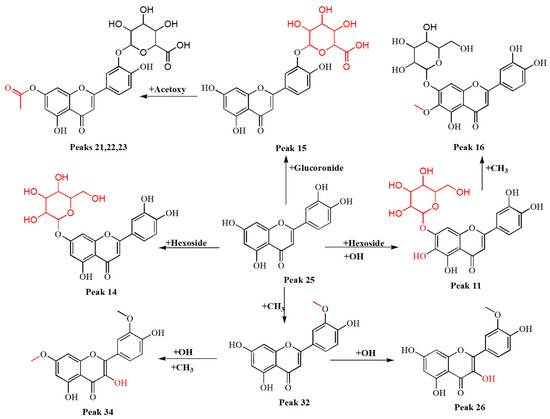
Figure 2.
Proposed biosynthetic connection for the luteolin derivatives.
3.1.4. Terpenes and Their Derivatives
It is known that numerous phenolic diterpenoids have been isolated from R. officinalis. Among them, carnosic acid, carnosol, rosmanol, and epirosmanol have been reported. Peaks 43, 45, and 53 were tentatively identified as epirosmanol and its isomers (C20H25O5-) [25,27]. Peaks 33, 54, and 62 were assigned to rosmanol and its isomers (C20H25O5-) [23]. Peak 27 was considered to be a new rosmanol derivative and it tentatively designated as nor rosmanol (C19H23O5-). Acetylated hydroxyrosmanol was assigned to two other peaks, namely 40 and 41 (C22H27O7-), peak 63 was considered to be rosmanol methyl ether (C21H27O5-) [26] and peaks 24 and 37 were considered to be the hydroxy rosmanol isomers [38]. Rosmadial and its isomers (C20H23O5-) were detected and tentatively identified in peaks 47, 67, and 68 [37], while peaks 35 and 69 were identified as hydroxyrosmadial (C20H23O6-) and rosmaridiphenol (C20H27O3-), respectively [38].
The known phenolic diterpenoid carnosic acid and its isomer (C20H27O4-) were assigned to peaks 44 and 71 [25,26,27,37]. In addition, some carnosic acid derivatives were detected at peaks 56, 57, and 72, which were identified as dihydroxy methylcarnosic acid (C21H29O6-), acetoxycarnosic acid (C22H29O6-), and methyl carnosate (C21H29O4-), respectively [25,27,38]. Peaks 39 (C20H27O5-), 55 (C25H37O6-) and 58 (C25H37O6-) were assigned to hydroxycarnosic acid [38] and prenylated dihydroxycarnosic acid and its isomer, while peaks 73 and 74 were assigned to desoxy carnosic acid isomers (C20H29O3-) and considered as new diterpenoids. Peaks 65 and 66 corresponded to diterpenoid carnosol and its isomer (C20H25O4-), respectively [25,26,27,37]. Peak 59 was assigned to methoxycarnosol (C21H27O5-) and peak 64 to 16-hydroxy-20-deoxocarnosol (C20H27O4) [38], while peaks 52, 46, and 61 were assigned to hydroxyacetylcarnosol (C22H27O6-) and desoxy norcarnosol isomers (C19H23O3-), respectively, which could be considered as the first time diterpenoids have been detected in this species. Finally, peaks 50 (C20H27O5-), 60 (C20H27O5-), 70 (C19H25O3-), and 75 (C30H45O3-) were tentatively assigned to salvicanaric acid methyl isomer [39], 5,6,7,10-tetrahydro-7-hydroxyrosmariquinone [36], and the triterpenoid micromeric acid [25]. A proposed biosynthetic pathway for the carnosic acid derivatives detected by UHPLC–ESI–MS/MS is shown in Figure 3.
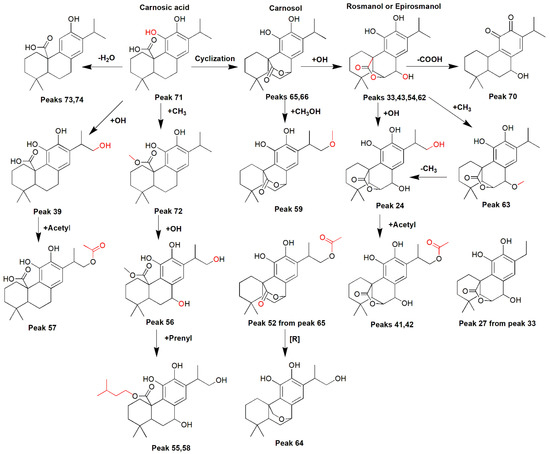
Figure 3.
Proposed formation of the phenolic diterpenes from carnosic acid (peak 71) detected by UHPLC–ESI–MS/MS.
3.1.5. Fatty Acids
Five fatty acids were detected and tentatively identified. Peaks 28 and 36 were assigned to trihydroxyoleic acid and its isomer (C18H33O5-). Peaks 36, 38, and 51 were identified as trihydroxyoctadecadienoic acid (C18H31O5-), hydroxyhexadecanedioic acid (C16H29O5-), and dihydroxyoctadecadienoic acid (C18H31O4-), respectively.
3.1.6. Unidentified Compounds
Peak 4 (C25H19O7-) and peak 5 (C23H19O7-) were not identified.
Many toxic organic solvents have been identified as causing negative environmental impacts, pollution, and potential harm to humans. Fortunately, natural product extraction processes consider environmental safety by using a combination of environmentally friendly technology and solvents. The use of ethyl lactate as a solvent in the extraction of natural products for the untargeted analysis of extracts is not widely used, but it is considered to be a potential green solvent for the extraction of hydrophilic and lipophilic phytonutrients [40]. In some studies, ethyl lactate was used as a solvent for the decaffeination of green tea, preserving the content of catechins [41,42]. In addition, it has shown a higher extraction capacity of α-mangotin in Garcinia mangostana [43], carotenoids in dried tomatoes, luteolin, and β-carotene from powders of white corn and carrots [44]. Other studies have shown that ethyl lactate is an efficient solvent for the extraction of polyphenols, such as caffeic acid, protocatechuic acid, kaempferol, quercetin, chrysin, orientin, and apigenin, as well as the alkaloid lupamine, which has high antioxidant and antibacterial activity [45].
As shown in Table 1, the analysis of LC/MS/MS, previously performed on methanolic extracts of R. officinalis leaves, showed the presence of the following: organic acids, including quinic acid, syringic acid, vanillic acid, gallic acid, protocatechuic acid, and hydroxybenzoic acid with their hexosides [22,23,24,25,27,28]; cinnamic acid derivatives, such as caffeic acid and its derivatives, chlorogenic acids, p-coumaric acid, salvianolic acid B, and rosmarinic acid and its hexoside [22,23,24,25,26,27,30,31,32]; flavonoids, such as luteolin and its derivatives, nepitrin, apigenin and its hexosides, acacetin, quercetin and its derivatives, eriodictyol, and kaempferol and its hexosides [22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32]; some phenolic diterpenes or their derivatives, including carnosic acid, rosmanol and its derivatives, epirosmanol, rosmadial, and carnosol [22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29]; and triterpenes, such as oleanolic acid, ursolic acid, betulinic acid, asiatic acid, and micromeric acid [22,23,30,31,32]. In this study, the qualitative analysis of the green ethyl lactate extract revealed the presence of 6 organic acids, 6 cinnamic acid derivatives, 19 flavonoids, 37 phenolic diterpenes, and 1 triterpene. One group of abundant secondary metabolites were diterpenoids, including abietane skeletons, especially carnosol and carnosic acid, and polyphenolic compounds, such as luteolin and rosmarinic acid. Although the secondary metabolites in S. rosmarinus from different sites were almost similar, the profiles of flavonoids, phenolic compounds, and terpenoids showed great differences. Therefore, the use of a green solvent, such as ethyl lactate proved to be efficient for qualitative analysis, as the 75 metabolites were tentatively identified in negative mode.
It has been reported that phenolic diterpenoids with abietane skeleton possess several biological activities, including diterpenoids, such as methyl carnosate with antibacterial and antioxidant properties [46,47], carnosol with anticancer, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and gastroprotective activities [48,49,50,51], and carnosic acid with antioxidant, antimicrobial, antitumor, and anti-SARS-CoV-2 properties [47,50,52,53,54]. On the other hand, rosmarinic acid, a well-known phenolic acid found in many Lamiaceae species, has shown a wide range of biological activities, such as anti-SARS-CoV-2, anti-inflammatory, anti-ageing, antidepressant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, antidiabetic, antioxidant, and antimicrobial properties, as well as the inhibition of tau protein fibrillization [50,52,54,55,56].
Some studies based on green strategies have been applied to R. officinalis. Wang et al. [57] studied ultrasound-assisted extraction coupled with high-speed countercurrent chromatography (HSCCC) separation using hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents (DESs). They found that, among the studied DESs, D,L-menthol: D,L-lactic acid, 1:2 was the best extraction agent, but not as a HSCCC solvent. Similarly, Vladimir-Knezevic et al. [58] showed that DESs, such as choline chloride (ChCl): ethylene glycol (EG), 1:3 at 50% water, gave the same yields as 70% ethanol for phenolic acid extraction. Meanwhile, 70% ethanol was most effective for flavonoid extraction from R. officinalis compared to water, 70% ChCl: EG and 50% ChCl: EG. Kessler et al. [59] compared two extraction methods from Portuguese R. officinalis: hydrodistillation (HD) and supercritical fluid extraction (SFE)-CO2. They demonstrated and confirmed that the essential oils from the SFE-CO2 extraction were higher than those obtained from the HD extraction and, after defining the safety profile, they can be used to improve bread odor with these green extracts. Finally, Chen et al. [60] reported that they used SFE-CO2 as the first step of the purification of R. officinalis. Then, the remaining solid was subjected to an isolation process, which revealed the presence of labdane (six) and isopimarane (five) diterpenoids for the first time. Among them, seven diterpenoids were identified as new diterpenoids after nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and MS/MS analyses. In addition, rosmarinusin J; M; O; labda-8(14), 12E, 15-triene-18-acid and (E)-geranylferulic acid showed cytoprotective activity against H2O2-induced oxidative damage to SH-SY5Y cells. In this study, neither labdane nor isopimarane diterpenoids were found in the Chilean species.
Our study confirms that the extraction of S. rosmarinus with the green solvent ethyl lactate is efficient and sustainable for the identification of flavonoids, phenols and terpenoids from the leaves.
4. Conclusions
Green solvents are a good alternative to toxic organic solvents because they are environmentally friendly. Among them, ethyl lactate, which is considered a green solvent, is biodegradable, non-corrosive, non-carcinogenic, and non-ozone depleting. In this work, a green extract of the plant Salvia rosmarinus, formerly known as Rosmarinus officinalis, was prepared by maceration as a conventional technique, in combination with ethyl lactate Then, the chemical composition of this extract was investigated for the first time by UHPLC–ESI–MS/MS. The obtained results showed that seventy-five compounds were tentatively identified by untargeted metabolomics study, including six organic acids, six cinnamic acid derivatives, five fatty acids, eighteen flavonoids, one triterpene, and thirty-seven phenolic diterpenes. This result shows that the extraction of phenolic diterpenoids with ethyl lactate is better than that with toxic organic solvents (Table 1). Many diterpenoids, such as hydroxyrosmanol, hydroxyrosmadial, hydroxyepirosmanol, hydroxycarnosic acid, salvicanaric acid methyl ester, acetoxycarnosic acid, hydroxydeoxocarnosol, desoxycarnosic acid, and prenylated dihydroxycarnosic acid, were detected for the first time in this species. Further isolation efforts should be made to confirm the molecular structures of these diterpenoids. Finally, ethyl lactate could be used for the extraction of secondary compounds as an alternative to toxic solvents to enable more sustainable extraction processes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.A.; methodology, C.A., G.C., N.C., B.S. and G.C.; formal analysis, J.C. and D.B.-P.; Investigation C.A., G.C., N.C. and B.S.; Data curation, C.A., G.C., N.C., B.S., D.B.-P. and J.C.; Writing—Original draft preparation, C.A.; Writing—Review and editing, J.C. and D.B.-P.; Supervision, C.A.; Funding acquisition, C.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by FONDECYT Regular, grant number 1190314 (ANID).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bruckner, J.V.; Anand, S.S.; Warren, D.A. Toxic effects of solvents and vapors. In Casarette and Doull’s Essential of Toxicology: The Basic Science of Poison; Klaass, E., Ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 981–1051. [Google Scholar]
- Chemat, F.; Abert, M.A.; Ravi, H.K. Toward petroleum-free with plant-based chemistry. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 28, 100450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capello, C.; Fischer, U.; Hungerbuhler, K. What is a green solvent? A comprehensive framework for the environmental assessment of solvents. Green Chem. 2007, 9, 927–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvjetko-Bubalo, M.; Vidović, S.; Radojčić-Redovniković, I.; Jokić, S. Green solvents for green technologies. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2015, 90, 1631–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio, S.; Alcalde, R. The green solvent ethyl lactate: An experimental and theoretical characterization. Green Chem. 2009, 11, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, C.S.M.; Silva, V.M.T.M.; Rodrigues, A.E. Ethyl lactate as a solvent: Properties, applications and production processes—A review. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 2658–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, C.S.; Rodrigues, A.E. Ethyl lactate main properties, production processes, and applications. In Alternative Solvents for Natural Products Extraction; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 107–125. [Google Scholar]
- Bussmann, R.W.; Paniagua-Zambrana, N.Y.; Moya-Huanca, L.A.; Hart, R. Changing markets—Medicinal plants in the markets of La Paz and El Alto, Bolivia. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 193, 76–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macía, M.J.; García, E.; Vidaurre, P.J. An ethnobotanical survey of medicinal plants commercialized in the markets of la Paz and El Alto, Bolivia. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 97, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drew, B.T.; González-Gallegos, J.G.; Xiang, C.L.; Kriebel, R.; Drummond, C.P.; Walker, J.B.; Sytsma, K.J. Salvia united: The greatest good for the greatest number. Taxon 2017, 66, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celiktas, O.Y.; Kocabas, E.E.H.; Bedir, E.; Sukan, F.V.; Ozek, T.; Baser, K.H.C. Antimicrobial activities of methanol extracts and essential oils of Rosmarinus officinalis, depending on location and seasonal variations. Food Chem. 2007, 100, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leporini, M.; Bonesi, M.; Loizzo, M.R.; Passalacqua, N.G.; Tundis, R. The essential oil of Salvia rosmarinus spenn. From Italy as a source of health-promoting compounds: Chemical profile and antioxidant and cholinesterase inhibitory activity. Plants 2020, 9, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, R.S.; Lima, E.S.; Keita, H.; Ferreira, I.M.; Fernandes, C.P.; Cruz, R.A.S.; Duarte, J.L.; Velázquez-Moyado, J.; Ortiz, B.L.S.; Castro, A.N.; et al. Anti-inflammatory and antialgic actions of a nanoemulsion of Rosmarinus officinalis L. essential oil and a molecular docking study of its major chemical constituents. Inflammopharmacology 2017, 26, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro-Santos, R.; Carvalho-Costa, D.; Cavaleiro, C.; Costa, H.S.; Albuquerque, T.G.; Castilho, M.C.; Ramos, F.; Melo, N.R.; Sanches-Silva, A. A novel insight on an ancient aromatic plant: The rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.). Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Vallinas, M.; Reglero, G.; Ramírez de Molina, A. Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) Extract as a Potential Complementary Agent in Anticancer Therapy. Nutr. Cancer 2015, 67, 1223–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, A.; Sandhya, S.; Ali, S.S.; Vinod, K.R.; Reddy, S.; Banji, D. An in-depth review on the medicinal flora Rosmarinus officinalis (lamiaceae). Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2013, 12, 61–73. [Google Scholar]
- Hamidpour, R.; Hamidpour, S.; Elias, G. Rosmarinus Officinalis (Rosemary): A Novel Therapeutic Agent for Antioxidant, Antimicrobial, Anticancer, Antidiabetic, Antidepressant, Neuroprotective, Anti-Inflammatory, and Anti-Obesity Treatment. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2017, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvezzi De Macedo, L.; Mendes dos Santos, É.; Militao, L.; Lacalendola Tundisi, L.; Artem Ataide, J.; Barbosa Souto, E.; Gava Mazzola, P. Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L., syn Salvia rosmarinus Spenn.) A Review. Plants 2020, 9, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, J.M.; Faustino, C.; García, C.; Ladeiras, D.; Reis, C.P.; Rijo, P. Rosmarinus officinalisL.: An update review of its phytochemistry and biological activity. Futur. Sci. OA 2018, 4, FSO283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halket, J.M.; Waterman, D.; Przyborowska, A.M.; Patel, R.K.P.; Fraser, P.D. Chemical derivatization and mass spectral libraries in metabolic profiling by GC/MS and LC/MS/MS. J. Exp. Bot. 2005, 56, 219–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaleckis, R.; Meister, I.; Zhang, P.; Wheelock, C.E. Challenges, progress and promises of metabolite annotation for LC—MS-based metabolomics. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2019, 55, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, Y.; Velamuri, R.; Fagan, J.; Schaefer, J. Full-Spectrum Analysis of Bioactive Compounds in Rosemary ( Rosmarinus officinalis L.) as Influenced by Different Extraction Methods. Molecules 2020, 25, 4599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achour, M.; Mateos, R.; Fredj, B.; Mtiraoui, A.; Bravo, L.; Saguem, S. A Comprehensive Characterisation of Rosemary tea Obtained from Rosmarinus officinalis L. Collected in a sub-Humid Area of Tunisia. Phytochem. Anal. 2017, 29, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Mendoza, M.B.; Llorens-escobar, L.; Vanegas, P.E.; Cifuentes, A.; Ibañez, E.; Villar-Martínez, A.A. Chemical characterization of leaves and calli extracts of Rosmarinus officinalis by UHPLC-MS. Electrophoresis 2019, 41, 1776–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velamuri, R.; Sharma, Y.; Fagan, J.; Schaefer, J. Application of UHPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS in Phytochemical Profiling of Sage (Salvia officinalis) and Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis). Planta Medica Int. Open 2020, 7, e133–e144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brindisi, M.; Bouzidi, C.; Frattaruolo, L.; Loizzo, M.R.; Tundis, R.; Dugay, A.; Deguin, B.; Cappello, A.R.; Cappello, M.S. Chemical Profile, Antioxidant, Anti-inflammatory, and Anti-cancer Effects of Italian Salvia rosmarinus spenn. Methanol Leaves Extracts. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.; Rai, D.; Brunton, N.; Martin-Diana, A.B.; Barry-Ryan, C. Characterization of Phenolics Composition in Lamiaceae Spices by LC-ESI-MS/MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 10576–10581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrás-Linares, I.; Stojanović, Z.; Quirantes-Piné, R.; Arráez-Román, D.; Švarc-Gajić, J.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, A.; Segura-Carretero, A. Rosmarinus Officinalis Leaves as a Natural Source of Bioactive Compounds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 20585–20606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana-Méridas, O.; Polissiou, M.; Izquierdo-Melero, M.E.; Astraka, K.; Tarantilis, P.A.; Herraiz-Peñalver, D.; Sánchez-Vioque, R. Polyphenol composition, antioxidant and bioplaguicide activities of the solid residue from hydrodistillation of Rosmarinus officinalis L. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 59, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontogianni, V.G.; Tomic, G.; Nikolic, I.; Nerantzaki, A.A.; Sayyad, N.; Stosic-Grujicic, S.; Stojanovic, I.; Gerothanassis, I.P.; Tzakos, A.G. Phytochemical profile of Rosmarinus officinalis and Salvia officinalis extracts and correlation to their antioxidant and anti-proliferative activity. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mena, P.; Cirlini, M.; Tassotti, M.; Herrlinger, K.A.; Dall’Asta, C.; Del-Rio, D. Phytochemical Profiling of Flavonoids, Phenolic Acids, Terpenoids and Volatile Fraction of a Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) Extract. Molecules 2016, 21, 1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Camargo, A.D.P.; García-Cañas, V.; Herrero, M.; Cifuentes, A.; Ibáñez, E. Comparative study of green sub- and supercritical processes to obtain carnosic acid and carnosol-enriched rosemary extracts with in vitro anti-proliferative activity on colon cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Alford, A.R.; Niemeyer, E.D. Variation in phenolic profiles and antioxidant properties among medicinal and culinary herbs of the Lamiaceae family. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2020, 14, 1720–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, N.; Khan, I.; Abdelhalim, A.; Abdel-Halim, H.; Hanrahan, J.R. Molecular docking and antiamnesic effects of nepitrin isolated from Rosmarinus officinalis on scopolamine-induced memory impairment in mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 96, 700–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, N.; He, K.; Roller, M.; Lai, C.S.; Shao, X.; Pan, M.H.; Ho, C.T. Flavonoids and phenolic compounds from Rosmarinus officinalis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 5363–5367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Smuts, J.P.; Dodbiba, E.; Rangarajan, R.; Lang, J.C.; Armstrong, D.W. Degradation study of carnosic acid, carnosol, rosmarinic acid, and rosemary extract (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) assessed using HPLC. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 9305–9314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Fons, L.; Aranda, F.J.; Guillén, J.; Villalaín, J.; Micol, V. Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis) diterpenes affect lipid polymorphism and fluidity in phospholipid membranes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2006, 453, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luis, J.G.; San Andrés, L. C-16 Hydroxylated Abietane Diterpenes From Salvia mellifera. Phytochemistry 1993, 33, 635–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, A.G.; Herrera, J.R.; Luis, J.G.; Ravelo, A.G. Salvicanaric acid, a new diterpene from Salvia canariensis. J. Nat. Prod. 1987, 50, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kua, Y.L.; Gan, S.; Morris, A.; Ng, H.K. Ethyl lactate as a potential green solvent to extract hydrophilic (polar) and lipophilic (non-polar) phytonutrients simultaneously from fruit and vegetable by-products. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2016, 4, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermejo, D.V.; Luna, P.; Manic, M.S.; Najdanovic-Visak, V.; Reglero, G.; Fornari, T. Extraction of caffeine from natural matter using a bio-renewable agrochemical solvent. Food Bioprod. Process. 2013, 91, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermejo, D.V.; Mendiola, J.A.; Ibáñez, E.; Reglero, G.; Fornari, T. Pressurized liquid extraction of caffeine and catechins from green tea leaves using ethyl lactate, water and ethyl lactate + water mixtures. Food Bioprod. Process. 2015, 96, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundeesomchok, K.; Filly, A.; Rakotomanomana, N.; Panichayupakaranant, P.; Chemat, F. Extraction of α-mangostin from Garcinia mangostana L. using alternative solvents: Computational predictive and experimental studies. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 65, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, B.K.; Chapman, M.H. Carotenoid extraction from plants using a novel, environmentally friendly solvent. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lores, M.; Pájaro, M.; Álvarez-casas, M.; Domínguez, J.; García-jares, C. Use of ethyl lactate to extract bioactive compounds from Cytisus scoparius: Comparison of pressurized liquid extraction and medium scale ambient temperature systems. Talanta 2015, 140, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Climati, E.; Mastrogiovanni, F.; Valeri, M.; Salvini, L.; Bonechi, C.; Mamadalieva, N.Z.; Egamberdieva, D.; Taddei, A.R.; Tiezzi, A. Methyl carnosate, an antibacterial diterpene isolated from Salvia officinalis leaves. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2013, 8, 429–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.W.; Frankel, E.N.; Schwarz, K.; Aeschbach, R.; German, J.B. Antioxidant Activity of Carnosic Acid and Methyl Carnosate in Bulk Oils and Oil-in-Water Emulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1996, 44, 2951–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.J. Carnosol: A promising anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory agent. Cancer Lett. 2011, 305, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.A.; Charles, H.P. Antimicrobial activity of Carnosol and Ursolic acid: Two anti-oxidant constituents of Rosmarinus officinalis L. Food Microbiol. 1987, 4, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordán, M.J.; Lax, V.; Rota, M.C.; Lorán, S.; Sotomayor, J.A. Relevance of carnosic acid, carnosol, and rosmarinic acid concentrations in the in vitro antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Rosmarinus officinalis (L.) methanolic extracts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 9603–9608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Areche, C.; Schmeda-Hirschmann, G.; Theoduloz, C.; Rodríguez, J.A. Gastroprotective effect and cytotoxicity of abietane diterpenes from the Chilean Lamiaceae Sphacele chamaedryoides (Balbis) Briq. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2009, 61, 1689–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkan, N.; Ayranci, G.; Ayranci, E. Antioxidant activities of rosemary (Rosmarinus Officinalis L.) extract, blackseed (Nigella sativa L.) essential oil, carnosic acid, rosmarinic acid and sesamol. Food Chem. 2008, 110, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.I.; Lin, C.C.; Kuo, S.M.; Lai, J.C.; Wang, Y.Q.; You, H.L.; Hsu, M.L.; Chen, C.H.; Shiu, L.Y. Carnosic acid impedes cell growth and enhances anticancer effects of carmustine and lomustine in melanoma. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, BSR20180005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elebeedy, D.; Elkhatib, W.F.; Kandeil, A.; Ghanem, A.; Kutkat, O.; Alnajjar, R.; Saleh, M.A.; Abd El Maksoud, A.I.; Badawy, I.; Al-Karmalawy, A.A. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 activities of tanshinone IIA, carnosic acid, rosmarinic acid, salvianolic acid, baicalein, and glycyrrhetinic acid between computational and in vitro insights. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 29267–29286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadeem, M.; Imran, M.; Gondal, T.A.; Imran, A.; Shahbaz, M.; Amir, R.M.; Sajid, M.W.; Qaisrani, T.B.; Atif, M.; Hussain, G.; et al. Therapeutic potential of rosmarinic acid: A comprehensive review. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornejo, A.; Sandoval, F.A.; Caballero, L.; Machuca, L.; Muñoz, P.; Caballero, J.; Perry, G.; Ardiles, A.; Areche, C.; Melo, F. Rosmarinic acid prevents fibrillization and diminishes vibrational modes associated to β sheet in tau protein linked to Alzheimer’s disease. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2017, 32, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, Q.; Guo, Q.; Li, P.; Yang, H. A hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents-based integrated method for efficient and green extraction and recovery of natural products from Rosmarinus officinalis leaves, Ginkgo biloba leaves and Salvia miltiorrhiza roots. Food Chem. 2021, 363, 130282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladimir-Knežević, S.; Perković, M.; Zagajski Kučan, K.; Mervić, M.; Rogošić, M. Green extraction of flavonoids and phenolic acids from elderberry (Sambucus nigra L.) and rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) using deep eutectic solvents. Chem. Pap. 2022, 76, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, J.C.; Vieira, V.; Martins, I.M.; Manrique, Y.A.; Ferreira, P.; Calhelha, R.C.; Afonso, A.; Barros, L.; Rodrigues, A.E.; Dias, M.M. Chemical and organoleptic properties of bread enriched with Rosmarinus officinalis L.: The potential of natural extracts obtained through green extraction methodologies as food ingredients. Food Chem. 2022, 384, 132514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Luo, Q.; Hu, W.; Chen, J.; Zhang, R. Labdane and isopimarane diterpenoids from Rosmarinus officinalis solid wastes: MS/MS spectrometric fragmentations and neuroprotective effect. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 177, 114441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).