Targeted Expression of TGFBIp Peptides in Mouse and Human Tissue by MALDI-Mass Spectrometry Imaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
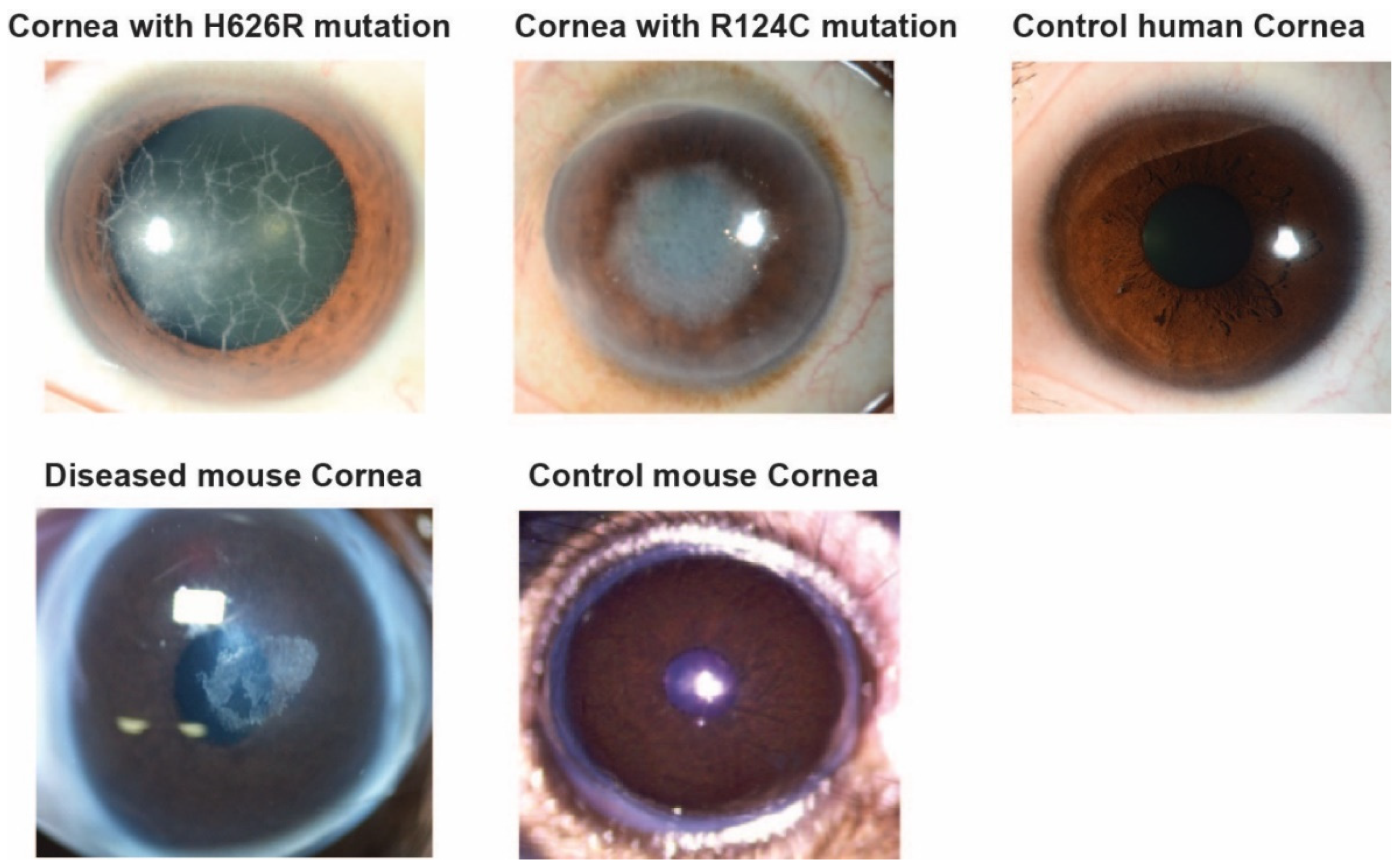
2.1. Details on the Mouse and Human Samples
2.2. Chemicals and Reagents
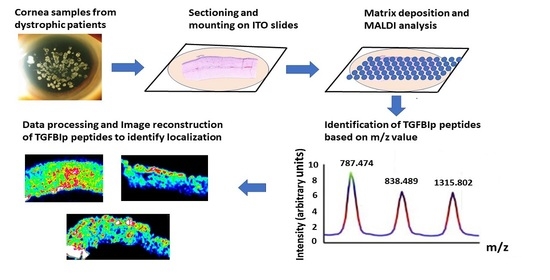
2.3. Sample Preparation
Sectioning of the Cornea
2.4. Washing of the Sections
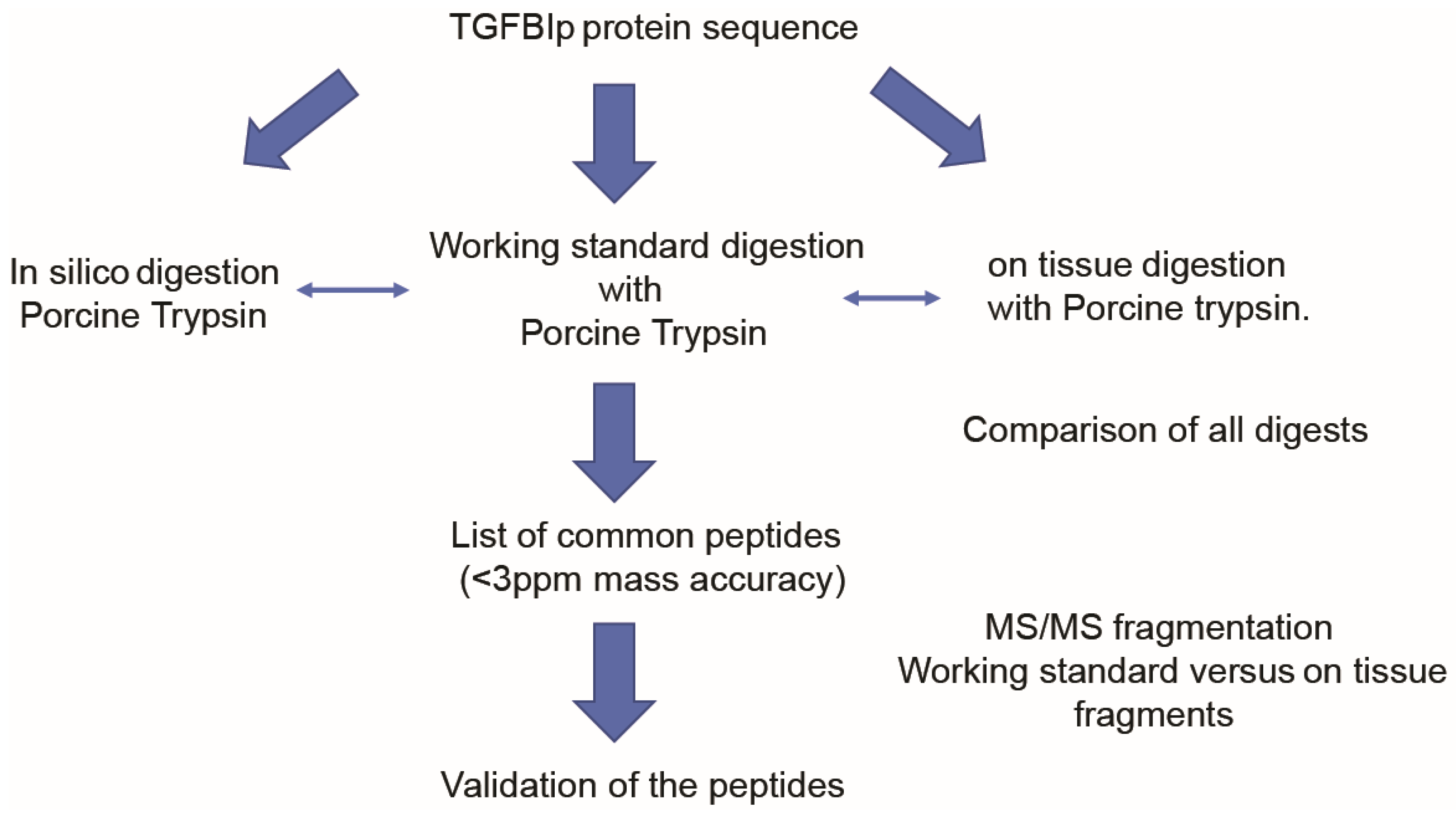
2.5. Digestion
2.6. MALDI Matrix Deposit
2.7. Congo Red and Hematoxylin and Eosin
2.8. MALDI-FTICR Acquisitions and Data Analysis
Mass Spectrometry Method
2.9. Software
2.10. Immunohistochemistry
3. Results
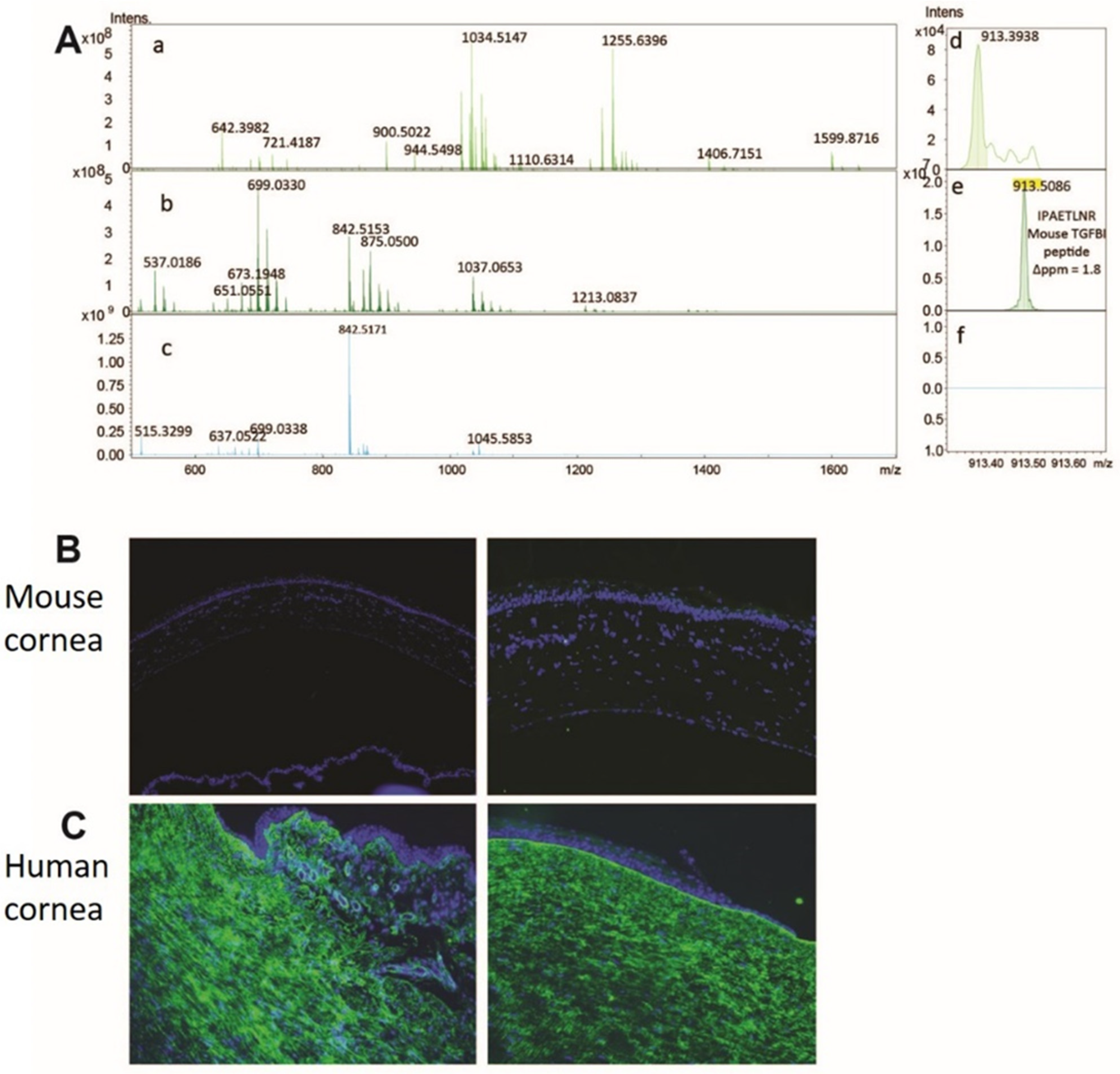
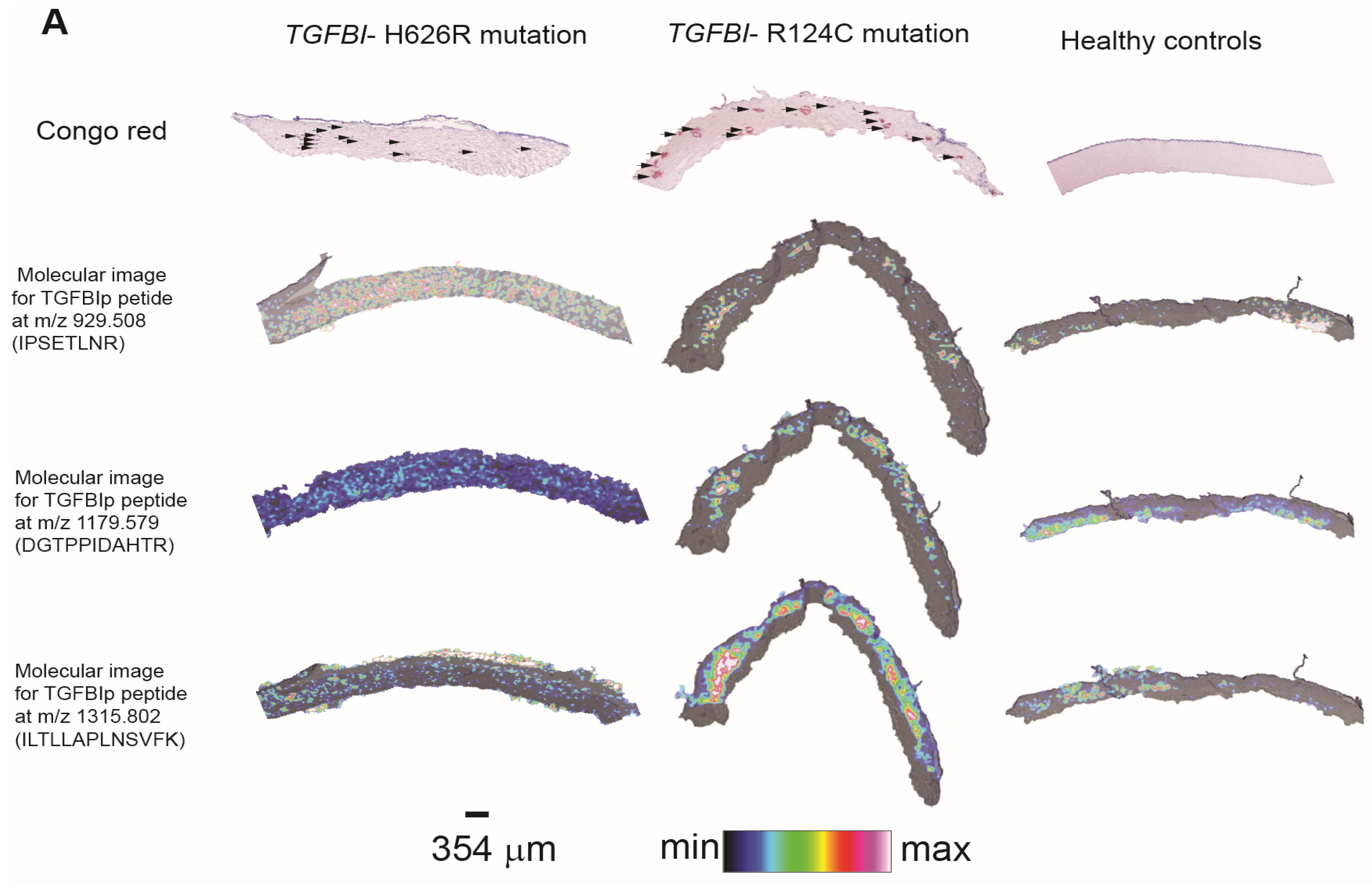
3.1. Evaluation by Microscopy and Histological Staining
3.2. Method Development to Detect TGFBIp in Control Mouse and Human Corneal Tissue
3.3. Method Development to Detect TGFBIp in Human Samples
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviation
| α CHCA | α-Cyano-4-hydroxycinnamic acid |
| CD | Corneal Dystrophy |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| FAS1 | Fasciclin like Domain 1 |
| GCD | Granular Corneal Dystrophy |
| ITO | Indium-tin-oxide |
| KDa | Kilodalton |
| LC | Liquid Chromatography |
| LCD | Lattice Corneal Dystrophy |
| MALDI | Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization |
| MS | Mass Spectrometry |
| MSI | Mass Spectrometry Imaging |
| PBS | Phosphate Buffered Saline |
| PMF | Peptide Mass Fingerprinting |
| qCID | Quadrupole Collision Induced Dissociation |
| TGFBI | Transforming Growth Factor Beta Induced gene |
| TGFBIp | Transforming Growth Factor Beta Induced protein |
| WT | Wild Type |
| 3D | 3 Dimensional |
References
- Hassell, J.R.; Birk, D.E. The molecular basis of corneal transparency. Exp. Eye Res. 2010, 91, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, M.F.; Fernald, R.D. The Evolution of Eyes. Ann. Rev. Neurosci. 1992, 15, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jue, B.; Maurice, D.M. The mechanical properties of the rabbit and human cornea. J. Biomech. 1986, 19, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyrlund, T.F.; Poulsen, E.T.; Scavenius, C.; Nikolajsen, C.L.; Thøgersen, I.B.; Vorum, H.; Enghild, J.J. Human Cornea Proteome: Identification and Quantitation of the Proteins of the Three Main Layers Including Epithelium, Stroma, and Endothelium. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 4231–4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, R.; Klinngam, W.; Heur, M.; Edman, M.C.; Hamm-Alvarez, S.F. Tear Proteases and Protease Inhibitors: Potential Biomarkers and Disease Drivers in Ocular Surface Disease. Eye Contact Lens 2020, 46, S70–S83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, M.-T.; Fang, P.-C.; Chao, T.-L.; Chen, A.; Lai, Y.-H.; Huang, Y.-T.; Tseng, C.-Y. Tear Proteomics Approach to Monitoring Sjögren Syndrome or Dry Eye Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-I.; Kim, T.-I.; Kim, K.S.; Kim, B.-Y.; Ahn, S.-Y.; Cho, H.-J.; Lee, H.K.; Kim, E.K. Decreased Catalase Expression and Increased Susceptibility to Oxidative Stress in Primary Cultured Corneal Fibroblasts from Patients with Granular Corneal Dystrophy Type II. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 175, 248–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohenstein-Blaul, N.V.T.U.; Kunst, S.; Pfeiffer, N.; Grus, F.H. Biomarkers for glaucoma: From the lab to the clinic. Eye 2017, 31, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauwen, S.; De Jong, E.K.; Lefeber, D.J.; Hollander, A.I.D. Omics Biomarkers in Ophthalmology. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, Bio88–Bio98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klintworth, G.K. Corneal dystrophies. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2009, 4, 7–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldave, A.J.; Sonmez, B.; Forstot, S.L.; Rayner, S.A.; Yellore, V.S.; Glasgow, B.J. A Clinical and Histopathologic Examination of Accelerated TGFBIp Deposition After LASIK in Combined Granular-Lattice Corneal Dystrophy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2007, 143, 416–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skonier, J.; Neubauer, M.; Madisen, L.; Bennett, K.; Plowman, G.D.; Purchio, A. cDNA Cloning and Sequence Analysis of βig-h3, a Novel Gene Induced in a Human Adenocarcinoma Cell Line after Treatment with Transforming Growth Factor-β. DNA Cell Biol. 1992, 11, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klintworth, G.K. The molecular genetics of the corneal dystrophies—Current status. Front. Biosci. 2003, 8, d687–d713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klintworth, G.K.; Valnickova, Z.; Enghild, J.J. Accumulation of beta ig-h3 gene product in corneas with granular dystrophy. Am. J. Pathol. 1998, 152, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Korvatska, E.; Henry, H.; Mashima, Y.; Yamada, M.; Bachmann, C.; Munier, F.L.; Schorderet, D.F. Amyloid and Non-amyloid Forms of 5q31-linked Corneal Dystrophy Resulting from Kerato-epithelin Mutations at Arg-124 Are Associated with Abnormal Turnover of the Protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 11465–11469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karring, H.; Runager, K.; Valnickova, Z.; Thøgersen, I.B.; Møller-Pedersen, T.; Klintworth, G.K.; Enghild, J.J. Differential expression and processing of transforming growth factor beta induced protein (TGFBIp) in the normal human cornea during postnatal development and aging. Exp. Eye Res. 2010, 90, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escribano, J. cDNA from human ocular ciliary epithelium homologous to beta ig-h3 is preferentially expressed as an extracellular protein in the corneal epithelium. J. Cell. Phys. 1994, 160, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, R.B.; Karring, H.; Møller-Pedersen, T.; Valnickova, Z.; Thøgersen, I.B.; Hedegaard, C.J.; Kristensen, T.; Klintworth, G.K.; Enghild, J.J. Purification and Structural Characterization of Transforming Growth Factor Beta Induced Protein (TGFBIp) from Porcine and Human Corneas. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 16374–16384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukassen, M.V.; Scavenius, C.; Thøgersen, I.B.; Enghild, J.J. Disulfide Bond Pattern of Transforming Growth Factor beta-Induced Protein. Biochemistry 2016, 55, 5610–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kheir, V.; Cortés-González, V.; Zenteno, J.C.; Schorderet, D.F. Mutation update: TGFBI pathogenic and likely pathogenic variants in corneal dystrophies. Hum. Mutat. 2019, 40, 675–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshminarayanan, R.; Vithana, E.N.; Chai, S.-M.; Chaurasia, S.S.; Saraswathi, P.; Venkatraman, A.; Rojare, C.; Venkataraman, D.; Tan, D.; Aung, T. A novel mutation in transforming growth factor-beta induced protein (TGFβIp) reveals secondary structure perturbation in lattice corneal dystrophy. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2011, 95, 1457–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karring, H.; Runager, K.; Thøgersen, I.B.; Klintworth, G.K.; Højrup, P.; Enghild, J.J. Composition and proteolytic processing of corneal deposits associated with mutations in the TGFBI gene. Exp. Eye Res. 2012, 96, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulsen, E.T.; Nielsen, N.S.; Jensen, M.M.; Nielsen, E.; Hjortdal, J.; Kim, E.K.; Enghild, J.J. LASIK surgery of granular corneal dystrophy type 2 patients leads to accumulation and differential pro-teolytic processing of transforming growth factor beta-induced protein (TGFBIp). Proteomics 2016, 16, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtney, D.G.; Poulsen, E.T.; Kennedy, S.; Moore, J.E.; Atkinson, S.D.; Maurizi, E.; Nesbit, M.A.; Moore, C.B.T.; Enghild, J.J. Protein Composition of TGFBI-R124C- and TGFBI-R555W- Associated Aggregates Suggests Multiple Mechanisms Leading to Lattice and Granular Corneal Dystrophy. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatraman, A.; Dutta, B.; Murugan, E.; Piliang, H.; Lakshminaryanan, R.; Yee, A.C.S.; Pervushin, K.V.; Sze, S.K.; Mehta, J.S. Proteomic Analysis of Amyloid Corneal Aggregates fromTGFBI-H626R Lattice Corneal Dystrophy Patient Implicates Serine-Protease HTRA1 in Mutation-Specific Pathogenesis of TGFBIp. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 2899–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulsen, E.T.; Runager, K.; Risør, M.W.; Dyrlund, T.F.; Scavenius, C.; Karring, H.; Praetorius, J.; Vorum, H.; Otzen, D.E.; Klintworth, G.K.; et al. Comparison of two phenotypically distinct lattice corneal dystrophies caused by mutations in the trans-forming growth factor beta induced (TGFBI) gene. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2014, 8, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karring, H.; Poulsen, E.T.; Runager, K.; Thøgersen, I.B.; Klintworth, G.K.; Højrup, P.; Enghild, J.J. Serine protease HtrA1 accumulates in corneal transforming growth factor beta induced protein (TGFBIp) amyloid deposits. Mol. Vis. 2013, 19, 861–876. [Google Scholar]
- Berggård, T.; Linse, S.; James, P. Methods for the detection and analysis of protein–protein interactions. Proteomics 2007, 7, 2833–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, V.S.; Srinivas, K.; Sujini, G.N.; Kumar, G.N.S. Protein-Protein Interaction Detection: Methods and Analysis. Int. J. Proteom. 2014, 2014, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caprioli, R.M.; Farmer, T.B.; Gile, J. Molecular Imaging of Biological Samples: Localization of Peptides and Proteins Using MALDI-TOF MS. Anal. Chem. 1997, 69, 4751–4760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwamborn, K. Imaging mass spectrometry in biomarker discovery and validation. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 4990–4998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwamborn, K.; Kriegsmann, M.; Weichert, W. MALDI imaging mass spectrometry—From bench to bedside. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2017, 1865, 776–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatraman, A.; Hochart, G.; Bonnel, D.; Stauber, J.; Shimmura, S.; Rajamani, L.; Pervushin, K.; Mehta, J.S.; Anandalakshmi, V.; Lakshminaryanan, R. Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization Mass Spectrometry Imaging of Key Proteins in Corneal Samples from Lattice Dystrophy Patients with TGFBI -H626R and TGFBI -R124C Mutations. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2019, 13, e1800053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazoe, K.; Yoshida, S.; Yasuda, M.; Hatou, S.; Inagaki, E.; Ogawa, Y.; Tsubota, K.; Shimmura, S. Development of a Transgenic Mouse with R124H Human TGFBI Mutation Associated with Granular Corneal Dystrophy Type 2. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gessel, M.M.; Spraggins, J.; Voziyan, P.; Hudson, B.; Caprioli, R.M. Decellularization of intact tissue enables MALDI imaging mass spectrometry analysis of the extracellular matrix. J. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 50, 1288–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulsen, E.T.; Runager, K.; Nielsen, N.S.; Lukassen, M.V.; Thomsen, K.; Snider, P.; Simmons, O.; Vorum, H.; Conway, S.J.; Enghild, J.J. Proteomic profiling of TGFBI-null mouse corneas reveals only minor changes in matrix composition sup-portive of TGFBI knockdown as therapy against TGFBI-linked corneal dystrophies. FEBS J. 2018, 285, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulsen, E.T.; Nielsen, N.S.; Scavenius, C.; Mogensen, E.H.; Risør, M.W.; Runager, K.; Lukassen, M.V.; Rasmussen, C.B.; Christiansen, G.; Richner, M.; et al. The serine protease HtrA1 cleaves misfolded transforming growth factor beta-induced protein (TGFBIp) and induces amyloid formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 11817–11828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandalakshmi, V.; Murugan, E.; Leng, E.G.T.; Ting, L.W.; Chaurasia, S.S.; Yamazaki, T.; Nagashima, T.; George, B.L.; Peh, G.S.L.; Pervushin, K.; et al. Effect of position-specific single-point mutations and biophysical characterization of amyloidogenic peptide fragments identified from lattice corneal dystrophy patients. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 1705–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, C.S.; Runager, K.; Scavenius, C.; Jensen, M.M.; Nielsen, N.S.; Christiansen, G.; Petersen, S.V.; Karring, H.; Sanggaard, K.W.; Enghild, J.J. Fibril Core of Transforming Growth Factor Beta-Induced Protein (TGFBIp) Facilitates Aggregation of Corneal TGFBIp. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 2943–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underhaug, J.; Koldsø, H.; Runager, K.; Nielsen, J.T.; Sørensen, C.S.; Kristensen, T.; Otzen, D.E.; Malmendal, A.; Schiøtt, B.; Enghild, J.J.; et al. Mutation in transforming growth factor beta induced protein associated with granular corneal dystrophy type 1 reduces the proteolytic susceptibility through local structural stabilization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013, 1834, 2812–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Køldso, H.; Andersen, O.J.; Nikolajsen, C.L.; Scavenius, C.; Sørensen, C.S.; Underhaug, J.; Runager, K.; Nielsen, N.C.; Enghild, J.J.; Schiøtt, B. Early Events in the Amyloid Formation of the A546T Mutant of Transforming Growth Factor β-Induced Protein in Corneal Dystrophies Compared to the Nonfibrillating R555W and R555Q Mutants. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 5546–5556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.C.; Hu, F.R.; Chen, M.S. An autosomal dominant granular corneal dystrophy family associated with R555W mutation in the BIGH3 gene. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2003, 102, 117–120. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Romero, P.; Moraga, M.; Herrera, L. Different phenotypes of lattice corneal dystrophy type I in patients with 417C > T (R124C) and 1762A > G (H572R) mutations in TGFBI (BIGH3). Mol. Vis. 2010, 16, 1601–1609. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Morishige, N.; Chikama, T.-I.; Ishimura, Y.; Nishida, T.; Takahashi, M.; Mashima, Y. Unusual Phenotype of an Individual with the R124C Mutation in the TGFBI Gene. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2004, 122, 1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anandalakshmi, V.; Hochart, G.; Bonnel, D.; Stauber, J.; Shimmura, S.; Lakshminarayanan, R.; Pervushin, K.; Mehta, J.S. Targeted Expression of TGFBIp Peptides in Mouse and Human Tissue by MALDI-Mass Spectrometry Imaging. Separations 2021, 8, 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8070097
Anandalakshmi V, Hochart G, Bonnel D, Stauber J, Shimmura S, Lakshminarayanan R, Pervushin K, Mehta JS. Targeted Expression of TGFBIp Peptides in Mouse and Human Tissue by MALDI-Mass Spectrometry Imaging. Separations. 2021; 8(7):97. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8070097
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnandalakshmi, Venkatraman, Guillaume Hochart, David Bonnel, Jonathan Stauber, Shigeto Shimmura, Rajamani Lakshminarayanan, Konstantin Pervushin, and Jodhbir S. Mehta. 2021. "Targeted Expression of TGFBIp Peptides in Mouse and Human Tissue by MALDI-Mass Spectrometry Imaging" Separations 8, no. 7: 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8070097
APA StyleAnandalakshmi, V., Hochart, G., Bonnel, D., Stauber, J., Shimmura, S., Lakshminarayanan, R., Pervushin, K., & Mehta, J. S. (2021). Targeted Expression of TGFBIp Peptides in Mouse and Human Tissue by MALDI-Mass Spectrometry Imaging. Separations, 8(7), 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations8070097