Abstract
Chondroitin sulphates belong to a group of naturally occurring glycosaminoglycans and play a role in many physiological processes including ageing and the effects of various diseases. Research into chondroitin sulphates has found that the most important analytes are 4- and 6-sulphated disaccharides. We developed an HPLC method for the separation and quantification of underivatized chondroitin/dermatan sulphates—unsaturated disaccharides (4- and 6-sulphated disaccharides). This method is based on the separation of disaccharides by amido as well as amino columns under acidic conditions. These columns enabled the successful separation of 4- and 6-sulphated disaccharides using 50 (amido column) and 25 mmol/L (amino column) phosphate buffer, pH 4.25 (detection at 230 nm), at retention times of less than 10 min. The limit of quantification was 0.5 μg/mL. The applicability of this method was demonstrated through analysis of unsaturated disaccharides produced from the enzymatic digestion of chondroitin/dermatan sulphates of the solubilized extracellular matrix produced from porcine urinary bladder and human umbilical cord.
1. Introduction
Chondroitin sulphates (CS) belong to a group of naturally occurring glycosaminoglycans and are characterized by repeating disaccharide units formed by glucuronic acid and N-acetyl-galactosamine residues linked by β-bonds [1]. CS, as a major component of the extracellular matrix of numerous tissues such as central and peripheral nerves or connective tissues (bone, cartilage, ligaments, skin, and tendons), is responsible for many important biomechanical properties such as elasticity, resistance, stiffness, and resilience [2,3]. CS plays a role in many physiological processes including tissue development, ageing or various diseases and pathologies [4], and it plays an important role inthe elasticity of cartilage [5]. Currently, CSs derived from animal cartilage tissues are used for osteoarthritis and osteoarthrosis therapeutics [6]. However, CSs obtained from animal tissue can differ in their proportions of 4- and 6-sulphated N-acetyl-β-D-galactosidase units (C4S or C6S) [7]. The sulphation position plays a crucial role in CS biological activity and applications. For example, the C4S/C6S disulphated motif can inhibit the activity of TNF-α, a proinflammatory cytokine involved in rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease, and psoriasis [8]. Critical variations in the sulphation patterns of CSs have been reported not only during embryonic development and maturation but also during ageing. The increasing C4S/C6S ratio in glycosaminoglycans extracted from perineuronal nets of rat brains induced by a large C6S reduction between 12 and 18 months of age and the simultaneous memory loss led to the conclusion that C4S is inhibitory and C6S is a stimulating element of neural plasticity [9]. As peptides binding C4S neutralize several inhibitory functions of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans, C4S-binding peptides may be beneficial in repairing mammalian nervous system injuries [10]. After neural injury, the upregulation of C6S makes the extracellular matrix even more permissive for axon regeneration [11].
C6S is the most abundantly found CS in normal adult articular cartilage. As cartilage degradation progresses in patients suffering from anterior cruciate ligament injury or osteoarthritis, C6S is replaced with C4S of the newly synthesized proteoglycan [12]. More than four decades ago, CSs supply was proposed as a therapeutic intervention to cartilage damage. CS supply could provide missing building blocks for the synthesis of new matrix component, since increasing CS concentration could act in favor of matrix regeneration and account for its beneficial effects [2]. CSs have been shown to have a favorable long-term safety profile when taken orally for up to six years [13]. On the one hand, C4S selectively promotes the tumor growth potential of BRAF V600E-expressing human melanoma cells in patient- and cell line-derived xenograft mice and confers resistance to BRAF inhibitors [14]; in contrast, clinical studies have shown that there is no association between chondroitin sulphate use and the risk of prostate cancer [15].
Thus, research into chondroitin sulphates has found that the most important analytes are 4- and 6-sulphated disaccharides. These compounds can be analyzed by using HPLC methods (propylamine bonded silica gel [16], strong anion exchange [5,7], or ion pair reversed-phase [17]) or capillary electromigration methods [1] (capillary zone electrophoresis, capillary isotachophoresis). We have to mention that, recently, Raman spectroscopy has been performed for the quantitative identification of isomeric chondroitin 4- and 6-sulphate [18]. However, all of these analytical methods are not only influenced by the matrix of the analyzed samples but also by the samples, that frequently cannot be analyzed, such as in capillary electromigration methods where salts in the sample can cause the results to deteriorate.
In this study, we wanted to develop a novel and simple method for separating 4-sulphated and 6-sulphated disaccharides using HPLC. We assume that this method can be applied for chondroitin analysis of biological tissues as well as of therapeutics.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. HPLC Analysis
Analysis was performed on an HPLC Agilent 1100 LC system (Agilent, Palo Alto, CA, USA) consisting of a degasser, binary pump, autosampler, thermostatted column compartment, and multi-wavelength detector. The amido column used here was a core-shell particle column with amide polyol and TMS end-capping (2.6 μm particles, 150 × 2.1 mm, bioZen Glycan, Phenomenex, Torrance, CA, USA). The amino column was a 3-aminopropyl silica SilaSpher Amine (5 μm, 12 nm pore, 100 × 3 mm, Silicycle, QC, Canada). The detection wavelength was 230 nm, and the separation temperature was 25 °C. The mobile phase was 50 (amino column) or 25 mmol/L (amido column) phosphate buffer, pH 4.25 (NaH2PO4·2H2O titrated by H3PO4), at a flow rate of 0.25 mL/min.
A phenylboronate-modified amino column (using the SilaSpher Amine) was prepared using a Ugi four-component reaction [19] based on a “one-pot” reaction of an equimolar mixture of primary amine (3-aminopropyl silica), aldehyde (benzaldehyde, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), isocyanide (tert-butyl isocyanide, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), and carboxylic acid (4-carboxyphenylboronic acid, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) in methanol (Penta, Praha, Czech Republic).
2.2. Standards
Standards (chondroitin disaccharides Δdi-4S and Δdi-6S) were obtained from Dextra Laboratories Ltd. (Reading, UK).
2.3. Sample Preparation
Porcine urinary bladder was obtained from a slaughterhouse (Cesky Brod, Czech Republic); the age of the animals was 6 months. Tissue decellularization was performed according to previously described protocols [20,21]. Tissues were frozen at −80 °C immediately after harvesting, thawed before use, and connective tissue was removed from the serosal surface of the bladder. The tunica serosa, tunica submucosa, and majority of the tunica muscularis mucosa were mechanically delaminated, which left the basement membrane and tunica propria intact. Luminal urothelial cells were dissociated from the basement membrane by soaking in deionized water. The extracellular matrix (ECM) was then agitated in 0.1% peracetic acid in 4.0% ethanol (v/v; 120 min; 300 rpm, 10 xG) followed by a series of phosphate buffered saline (PBS; IKEM, Praha, Czech Republic) rinses, deionized water rinses, lyophilization for 24 h (FreeZone® 2.5; Labconco Corporation, Kansas City, MO, USA), and milling (Mini-Mill Cutting Mills; Thomas Scientific, Swedesboro, NJ, USA).
Human umbilical cords were decellularized following previously described protocols [22]. The native tissue was obtained from healthy full-term neonates after spontaneous delivery. Informed consent of donors was obtained adhering to the guidelines approved by the Institutional Committee at University Hospital (Pilsen, Czech Republic). About 10–15 cm of umbilical tissues was frozen (>16 h at −20 °C), aseptically transported into the laboratory, and subsequently thawed and transversely cut into sections (<0.5 cm length). Tissue sections were agitated in a 0.1 mol/L phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) bath (48 h at 120 rpm, 1.6 xG, 4 °C). The PBS bath was exchanged three to five times before the tissue sections were soaked in 0.02% trypsin/0.05% EDTA (120 min at 120 rpm, 37 °C) followed by 0.1% peracetic acid in a 4.0% ethanol bath (120 min at 300 rpm; Penta, Czech Republic) and a series of PBS and deionized water soaks. Finally, tissue sections were lyophilized for 24 h (FreeZone® 2.5; Labconco Corporation, Kansas City, MO, USA) and milled (Mini-Mill Cutting Mills; Thomas Scientific, Swedesboro, NJ, USA). Finally, tissue sections were lyophilized for 24 h (FreeZone® 2.5; Labconco Corporation, Kansas City, MO, USA) and milled (Mini-Mill Cutting Mills; Thomas Scientific, Swedesboro, NJ, USA).
Powdered extracellular matrix (ECM) samples from porcine urinary bladder or human umbilical cord were solubilized with 1.0 mg/mL pepsin in 0.01 mol/L HCl (Merck) at an ECM concentration of 10 mg/mL and stirred at room temperature for 48 h (pH = 2).
The pepsin-HCl ECM solution was neutralized to pH 7.4 with 0.1 mol/L NaOH diluted with 1× Dulbecco’s Phosphate-Buffered Saline (DPBS) with Ca2+ to a final concentration of 8 mg/mL, which normally allows in vivo gelation. Next, the solubilized ECM was digested for 48 h in the presence of 0.2% collagenase from Clostridium histolyticum (125 U/mg, Merck), followed by digestion for 48 h in the presence of Chondroitinase ABC from Proteus vulgaris at a concentration of 0.15 U/mL (Merck) activated by 0.05 mol/L acetate.
3. Results and Discussion
Here, we developed an HPLC method for the separation and quantification of underivatized chondroitin/dermatan sulphates—unsaturated disaccharides (4- and 6-sulphated disaccharide). This method is based on the separation of disaccharides on both amido and amino columns under acidic conditions. We also tested an amino column modified with phenylboronate, which enables the separation of carbohydrates with vicinal diols at the cis position, but no significant improvement of separation was observed. The C18 reversed-phase columns could also separate the disaccharides investigated but only in the presence of an ion-pairing agent (25 mmol/L tetrabutyl ammonium bromide) and with a lower separation efficiency (data not shown).
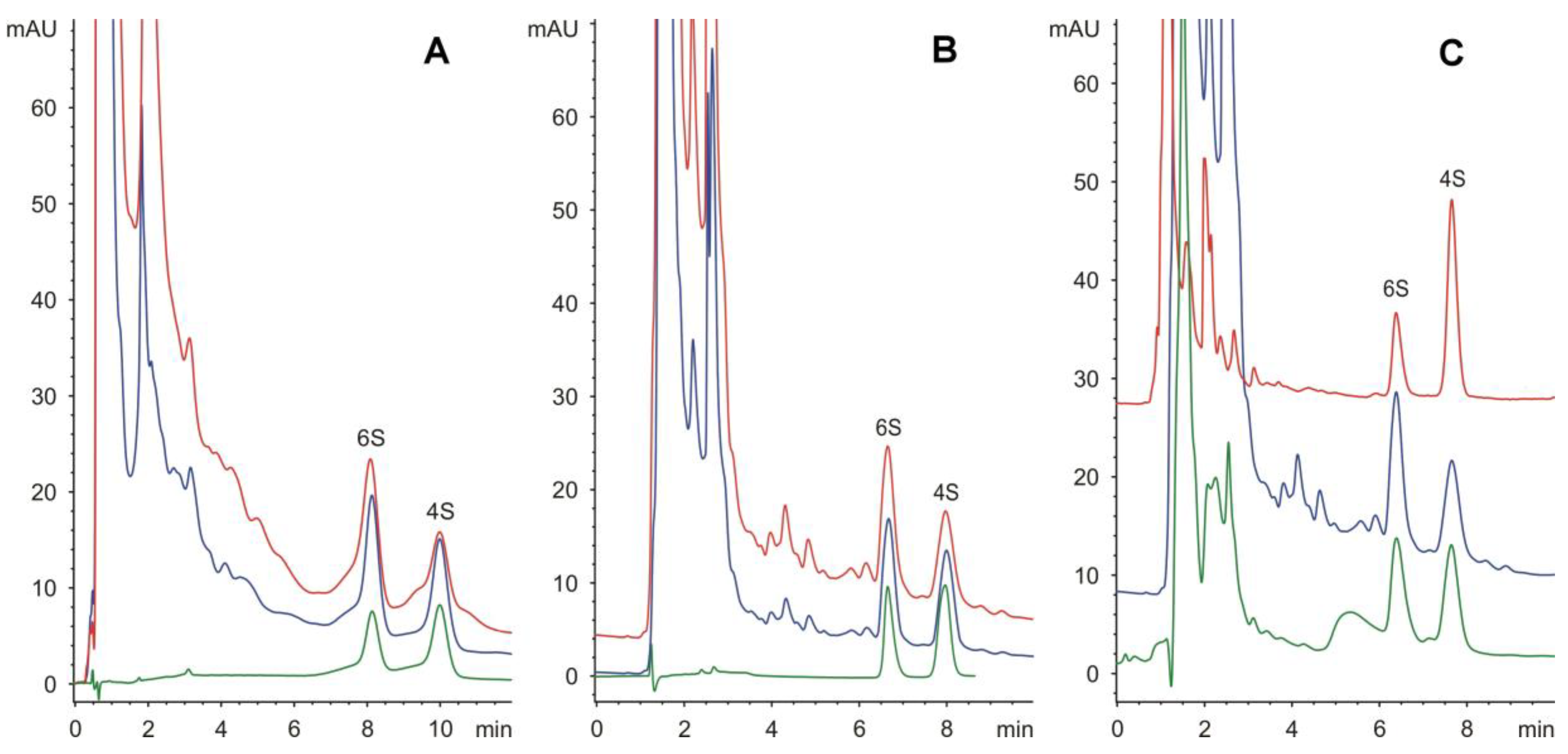
Both the amido as well as the amino columns enabled the successful separation of 4- and 6-sulphated disaccharides at 50 and 25 mmol/L phosphate buffer, pH 4.25, respectively, with a retention time of less than 10 min (Figure 1). Additionally, the separation on the amido column was selected for routine analysis regarding the better homogeneity of the peaks (see Figure 1).
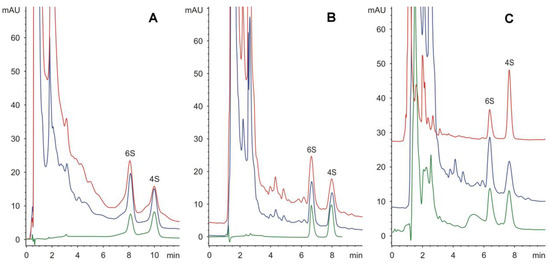
Figure 1.
Separation of 4-sulphated (4S) and 6-sulphated (6S) disaccharides on amino column (A), and on amido column (B): green line, standard (20 μg/mL); blue line, spiked real sample (40 μg/mL + standard, 1:1); red line, solubilized extracellular matrix from human umbilical cord (chondroitinase treatment only). Real samples analyzed on amido column (C): green line, solubilized extracellular matrix from human umbilical cord (collagenase/chondroitinase treatment) (48% 6S); blue line, solubilized extracellular matrix from human umbilical cord (chondroitinase treatment only) (56% 6S); red line, solubilized extracellular matrix from porcine urinary bladder (collagenase/chondroitinase treatment) (28% 6S).
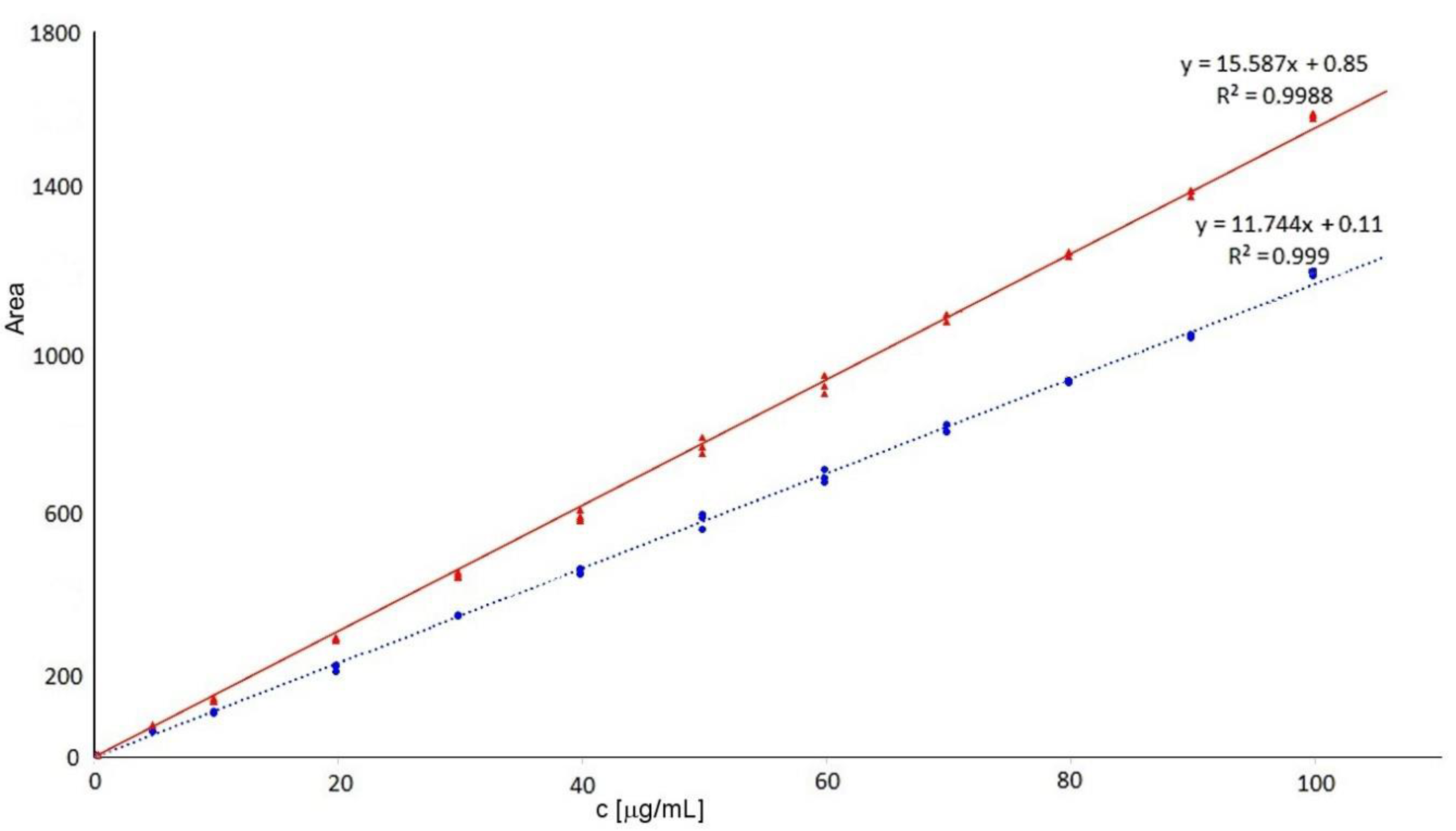
In this study, the limit of quantification was 0.5 μg/mL, the lowest point of the calibration curve. Calibrations were linear at the range 0.5–100 μg/mL when calibration curves (n = 3) were as follows: y = 15.587x + 0.85 R2 = 0.9988 for Δdi-4S, and y = 11.744x + 0.11 R2 = 0.9990 for Δdi-6S (see Figure 2). The limit of detection was 0.15 μg/mL (defined as S/N = 3).
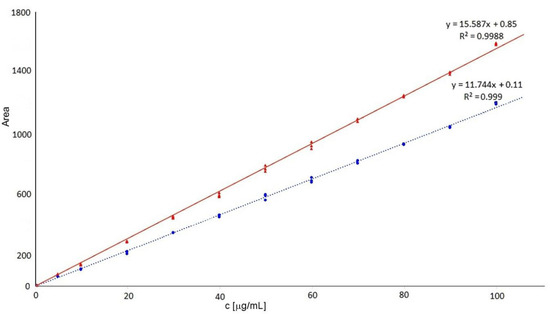
Figure 2.
Calibration curves of 4-sulphated (red solid line—triangles) and 6-sulphated (blue dotted line—spots) disaccharides.
The precision and accuracy within one day and between days (three days) were evaluated by analyses of samples at three concentration levels: low (10 μg/mL), medium (50 μg/mL), and high (100 μg/mL) concentration. In all cases, relative standard deviation (RSD) was below 5% in the intraday as well as interday analysis. These results are acceptable; however, the main topic of our analysis was the determination of the 4S/6S ratio.
The developed method was used to determine the ratio of 4S and 6S, but also allows the quantification of both disaccharides. For example, 18.3 μg/mL Δdi-6S and 14.4 μg/mL Δdi-4S were determined in a sample of solubilized ECM from human umbilical cord, and 9.7 μg/mL Δdi-6S and 24.9 μg/mL Δdi-4S were determined in a sample of solubilized ECM from porcine urinary bladder.
The method developed here demonstrated better results for analyzing biological samples compared to electromigration methods that are sensitive to the presence of ions in samples. This procedure is a simple and robust method for the analysis of relatively complex samples, which may be applied using instruments widely available in analytical laboratories.
Here, the applicability of this method was demonstrated through analysis of unsaturated disaccharides produced from the enzymatic digestion of chondroitin/dermatan sulphates of ECM produced from porcine urinary bladder or human umbilical cord (see Figure 1).
As it was mentioned in the Introduction, the main methods for the analysis of 4S and 6S are chromatographic methods. These methods are mainly used to determine disaccharide ratios, so accurate sensitivity information is poorly reported. The commonly used method is chromatography on strong anion exchangers [5,7]. For example, Sim et al. [5] determined disaccharides at the level of μg/mL. An LC-MS method based on separation by ion pair reversed-phase liquid chromatography and coupling to a turbo ionspray ionization triple quadrupole mass spectrometer has been described. In this case, a linear calibration curve was recorded at the range 0.43–18.15 pmol/injection [17]. Another LC-MS method for analysis of disaccharides was also mentioned by Wang et al. [23]. They also used a triple quadrupole mass spectrometer but coupled to reversed-phase HPLC. They described the determination of disaccharides at concentration ng/mL. Of course, these methods need an expensive instrumentation. The sensitivity of capillary isotachophoresis was worse when calibration was done for standards 0.1 to 1 mg/mL with different injections [1]. However, this method is more sensitive to various impurities in samples, i.e., ions.
4. Conclusions
A method for the separation of 4-sulphated and 6-sulphated disaccharides on amino and amido columns was developed and successfully applied for analyzing real samples and tissues—extracellular matrix from human umbilical cord and from porcine urinary bladder. We assume that this method can be applied for chondroitin analysis of biological tissues as well as of therapeutics.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.M., V.K. and Š.K.; methodology, I.M. and K.Z.; validation, I.M.; formal analysis, I.M. and M.M.; investigation, I.M., A.T. and M.M.; resources, Š.K. and K.V.; data curation, I.M.; writing—original draft preparation, I.M., K.Z., D.S.; writing—review and editing, I.M., Š.K., K.V., M.M., A.T., K.Z. and D.S.; visualization, I.M.; supervision, I.M.; project administration, I.M.; funding acquisition, I.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Czech Science Foundation, grant number 18-02597S, and SK and KV by Operational Programme Research, Development and Education in the framework of the project “Centre of Reconstructive Neuroscience” (registration number CZ.02.1.01/0.0./0.0/15_003/0000419).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Václavíková, E.; Kvasnička, F. Quality control of chondroitin sulphate used in dietary supplements. Czech. J. Food Sci. 2015, 33, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrotin, Y.; Mathy, M.; Sanchez, C.; Lambert, C. Chondroitin sulfate in the treatment of osteoarthritis: From in vitro studies to clinical recommendations. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2010, 2, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainreck, N.; Brézillon, S.; Sockalingum, G.D.; Maquart, F.-X.; Manfait, M.; Wegrowski, Y. Rapid characterization of glycosaminoglycans using a combined approach by infrared and Raman microspectroscopies. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collin, E.C.; Carroll, O.; Kilcoyne, M.; Peroglio, M.; See, E.; Hendig, D.; Alini, M.; Grad, S.; Pandit, A. Ageing affects chondroitin sulfates and their synthetic enzymes in the intervertebral disc. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 17049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, J.S.; Jun, G.; Toida, T.; Cho, S.Y.; Choi, D.W.; Chang, S.Y.; Linhardt, R.J.; Kim, Y.S. Quantitative analysis of chondroitin sulfate in raw materials, ophthalmic solutions, soft capsules and liquid preparations. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2005, 818, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishnoi, M.; Jain, A.; Hurkat, P.; Jain, S.K. Chondroitin sulphate: A focus on osteoarthritis. Glycoconj. J. 2016, 33, 693–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, G.R.C.; Piquet, A.A.; Glauser, B.F.; Tovar, A.M.F.; Pereira, M.S.; Vilanova, E.; Mourão, P.A.S. Systematic analysis of pharmaceutical preparations of chondroitin sulfate combined with glucosamine. Pharmaceuticals 2017, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tully, S.E.; Rawat, M.; Hsieh-Wilson, L.C. Discovery of a TNF-α Antagonist Using Chondroitin Sulfate Microarrays. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 7740–7741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foscarin, S.; Raha-Chowdhury, R.; Fawcett, J.W.; Kwok, J.C.F. Brain ageing changes proteoglycan sulfation, rendering perineuronal nets more inhibitory. Aging 2017, 9, 1607–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loers, G.; Liao, Y.; Hu, C.; Xue, W.; Shen, H.; Zhao, W.; Schachner, M. Identification and characterization of synthetic chondroitin-4-sulfate binding peptides in neuronal functions. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Rosahl, T.W.; Whiting, P.J.; Fawcett, J.W.; Kwok, J.C.F. 6-Sulphated Chondroitins Have a Positive Influence on Axonal Regeneration. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobue, Y.; Kojima, T.; Kurokouchi, K.; Takahashi, S.; Yoshida, H.; Poole, R.; Ishiguro, N. Prediction of progression of damage to articular cartilage 2 years after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: Use of aggrecan and type II collagen biomarkers in a retrospective observational study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017, 19, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hathcock, J.N.; Shao, A. Risk assessment for glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007, 47, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, R.; Xia, S.; Shan, C.; Chen, D.; Liu, Y.; Gao, X.; Wang, M.; Kang, H.-B.; Pan, Y.; Liu, S.; et al. The Dietary Supplement Chondroitin-4-Sulfate Exhibits Oncogene-Specific Pro-tumor Effects on BRAF V600E Melanoma Cells. Mol. Cell 2018, 69, 923–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brasky, T.M.; Kristal, A.R.; Navarro, S.L.; Lampe, J.W.; Peters, U.; Patterson, R.E.; White, E. Specialty Supplements and Prostate Cancer Risk in the VITamins And Lifestyle (VITAL) Cohort. Nutr. Cancer 2011, 63, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinmei, M.; Miyauchi, S.; Machida, A.; Miyazaki, K. Quantitation of chondroitin 4—sulfate and chondroitin 6—sulfate in pathologic joint fluid. Arthritis Rheum. 1992, 35, 1304–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguma, T.; Toyoda, H.; Toida, T.; Imanari, T. Analytical method of chondroitin/dermatan sulfates using high performance liquid chromatography/turbo ionspray ionization mass spectrometry: Application to analyses of the tumor tissue sections on glass slides. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2001, 15, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Álvarez, M.; López-Senra, E.; Valcárcel, J.; Vázquez, J.A.; Serra, J.; González, P. Quantitative evaluation of sulfation position prevalence in chondroitin sulphate by Raman spectroscopy. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2019, 50, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugi, I. The α-Addition of Immonium Ions and Anions to Isonitriles Accompanied by Secondary Reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1962, 1, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medberry, C.J.; Crapo, P.M.; Siu, B.F.; Carruthers, C.A.; Wolf, M.T.; Nagarkar, S.P.; Agrawal, V.; Jones, K.E.; Kelly, J.; Johnson, S.A.; et al. Hydrogels derived from central nervous system extracellular matrix. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crapo, P.M.; Medberry, C.J.; Reing, J.E.; Tottey, S.; Van der Merwe, Y.; Jones, K.E.; Badylak, S.F. Biologic scaffolds composed of central nervous system extracellular matrix. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 3539–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koci, Z.; Vyborny, K.; Dubisova, J.; Vackova, I.; Jager, A.; Lunov, O.; Jirakova, K.; Kubinova, S. Extracellular Matrix Hydrogel Derived from Human Umbilical Cord as a Scaffold for Neural Tissue Repair and Its Comparison with Extracellular Matrix from Porcine Tissues. Tissue Eng. Part. C Methods 2017, 23, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Lang, Y.; Li, Q.; Jin, X.; Li, G.; Yu, G. Glycosaminoglycanomic profiling of human milk in different stages of lactation by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2018, 258, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).