A Novel Protocol to Monitor Trace Levels of Selected Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Environmental Water Using Fabric Phase Sorptive Extraction Followed by High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Fluorescence Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Choice of Target PAHs
2.2. Chemicals and Materials
2.3. Instrumentation
2.4. Water Sample Collection
2.5. Preparation of Sol–Gel C18 Coated FPSE Media
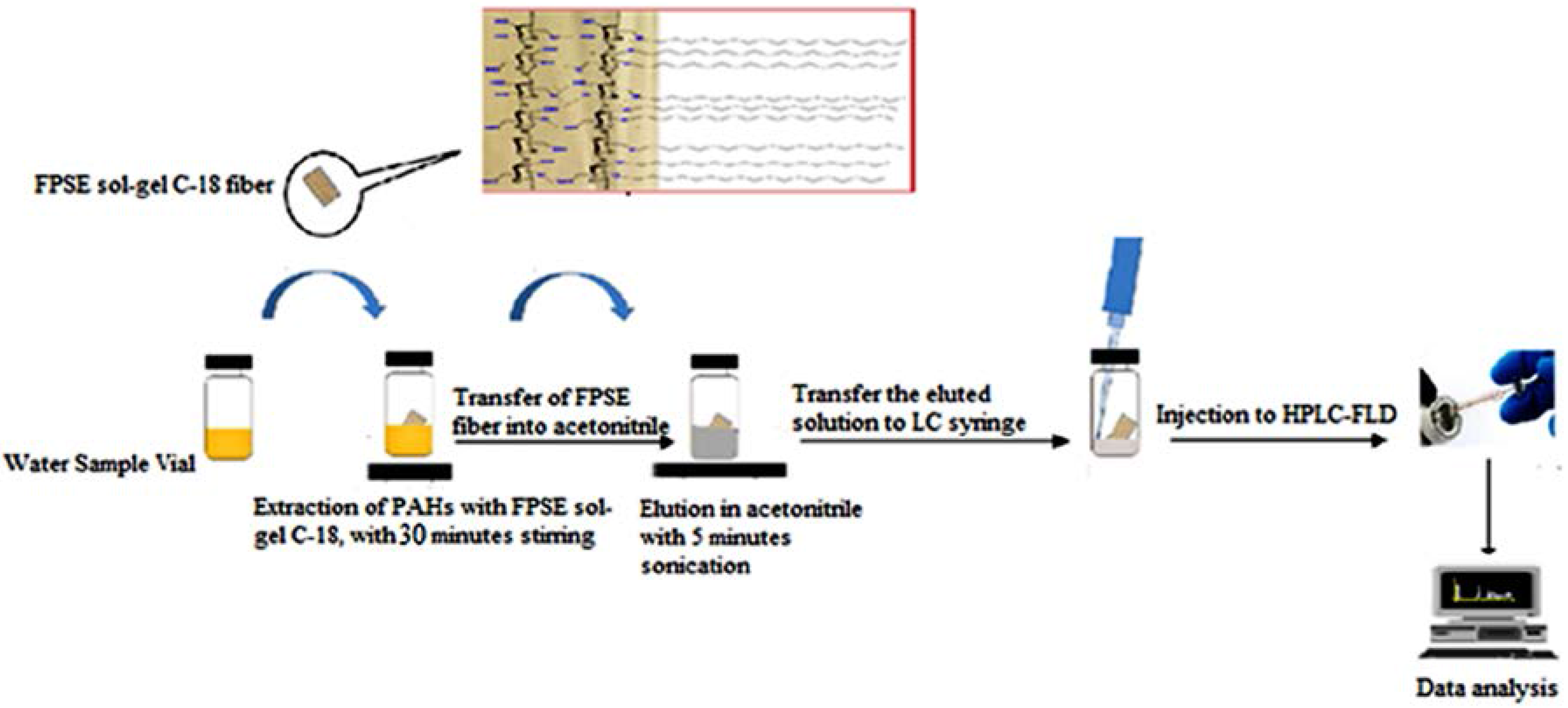
2.6. Fabric Phase Sorptive Extraction Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
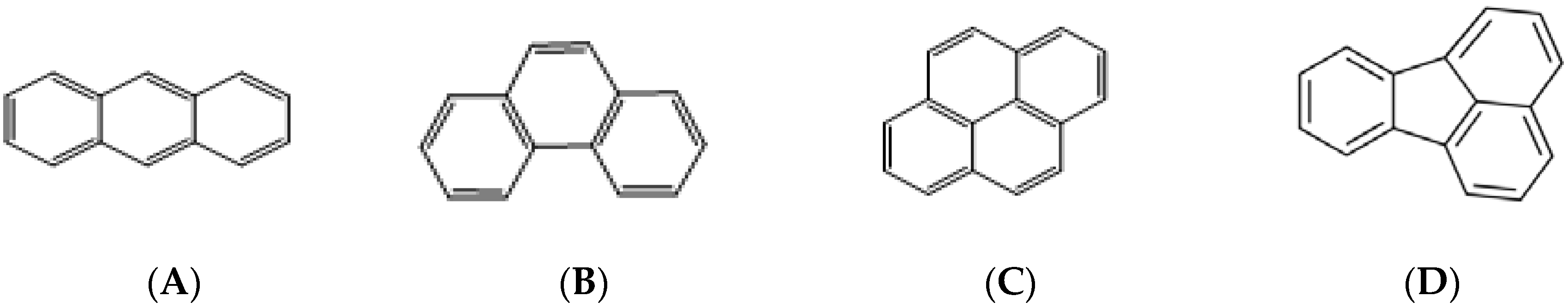
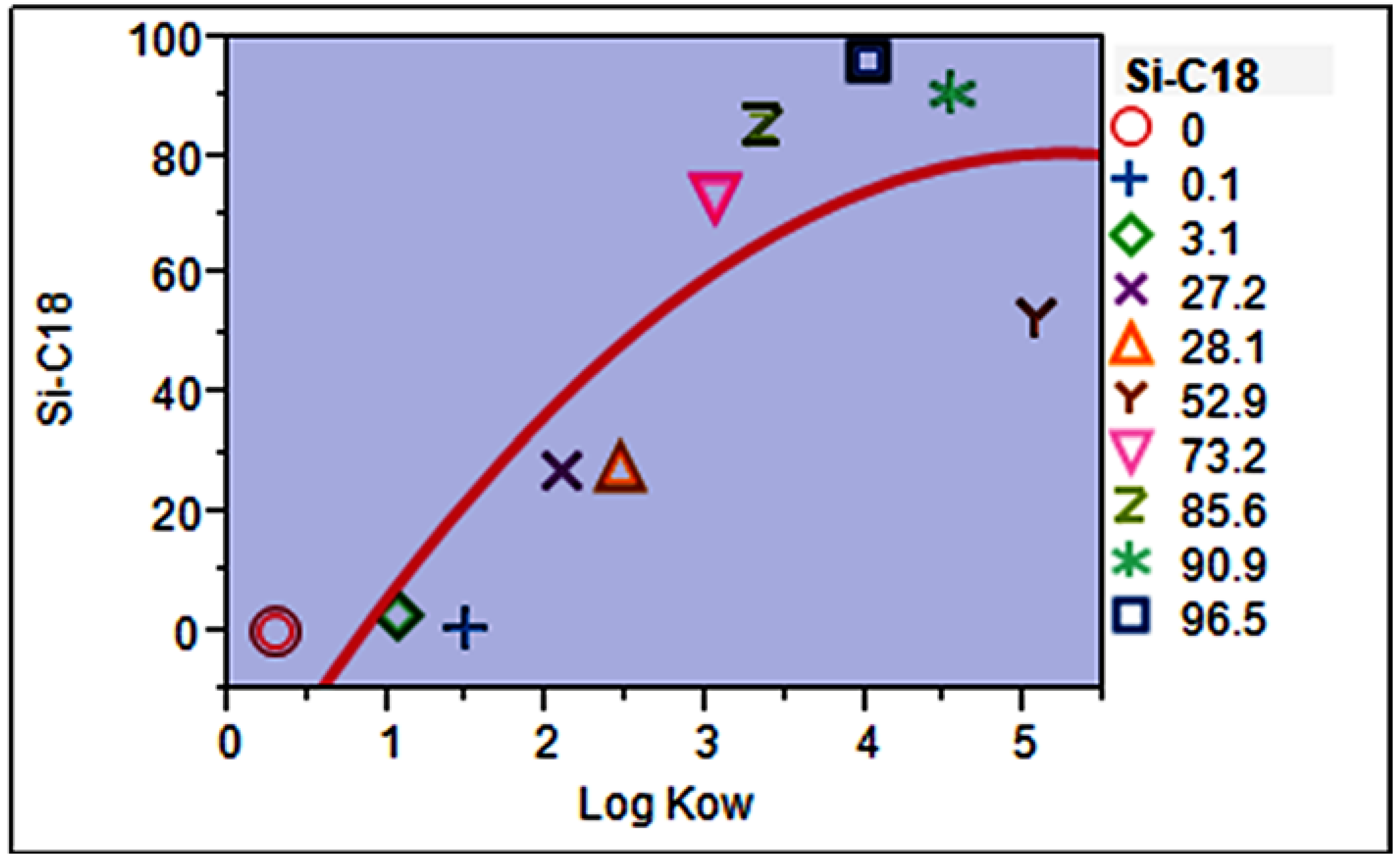
3.1. Selection of Fabric Phase Sorptive Extraction Sorbent Chemistry
3.2. Characterization of Sol–Gel C18 Coated FPSE Media
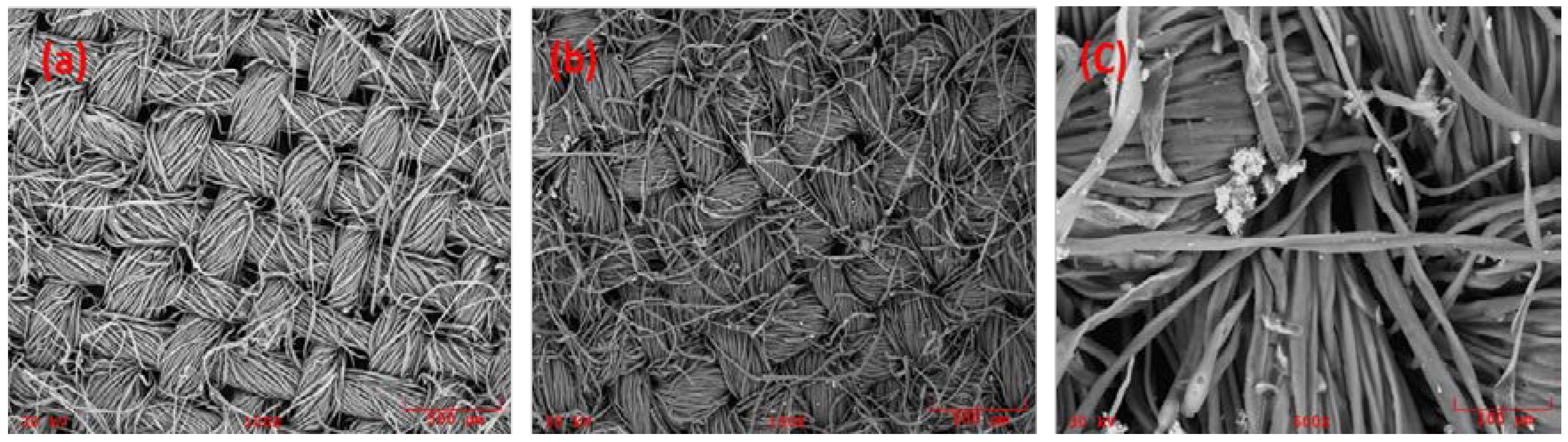
3.2.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy
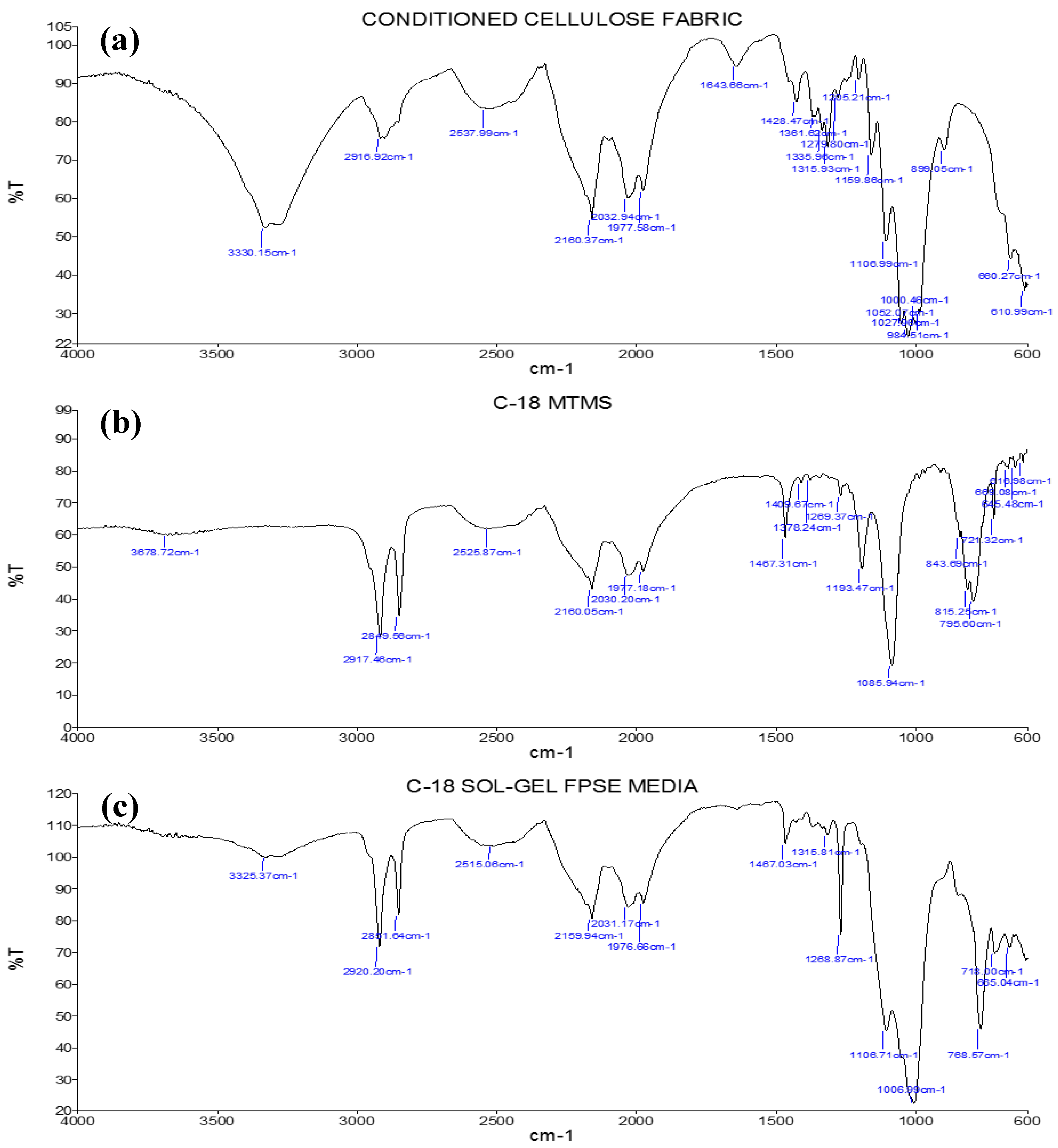
3.2.2. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
3.3. Optimization of the FPSE Procedure
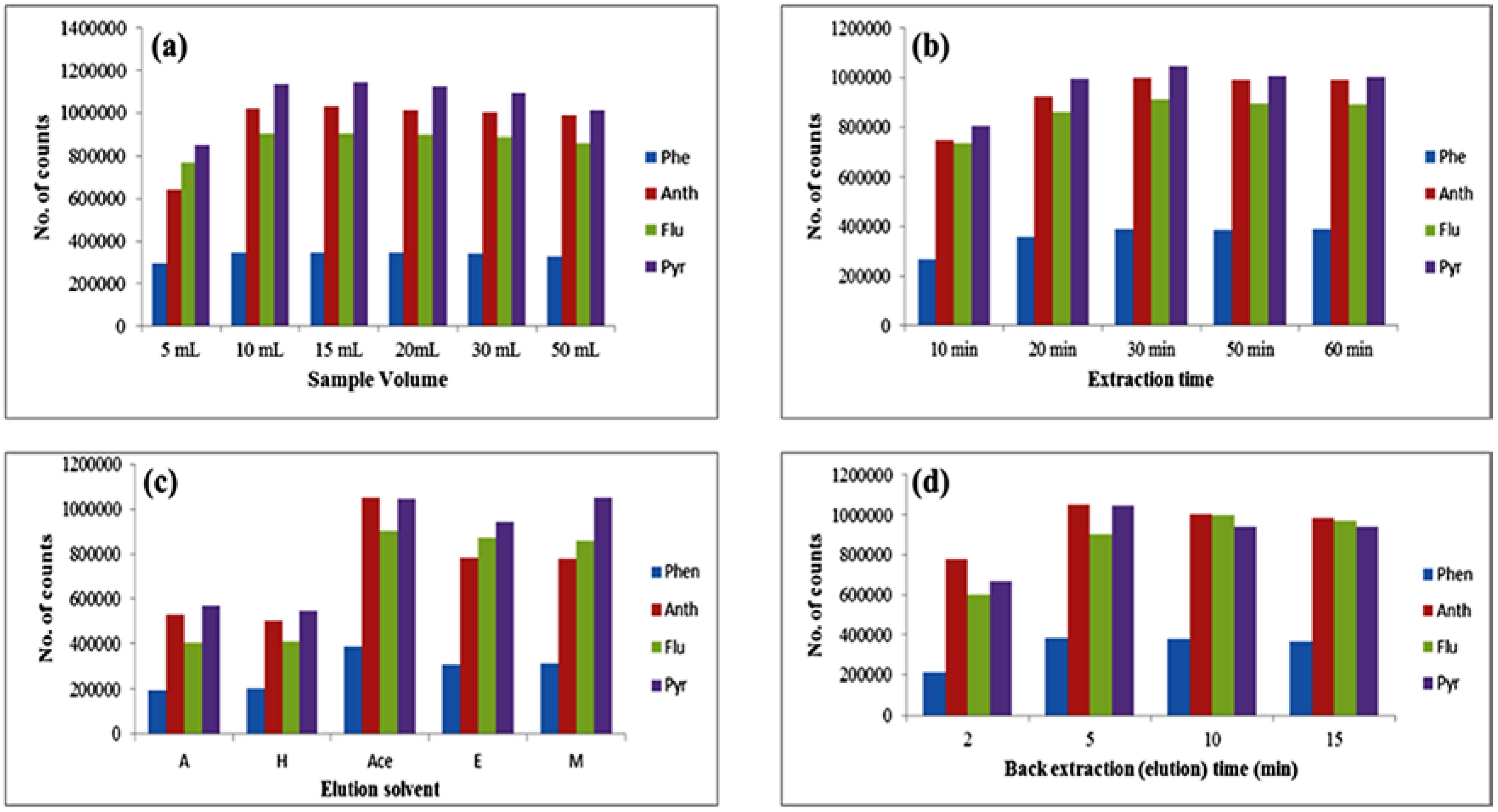
3.3.1. Optimization of Sample Volume
3.3.2. Optimization of Extraction Time
3.3.3. Optimization of Desorption Solvent and Time
3.3.4. Effect of Salt Concentration and Organic Modifiers
3.4. Regeneration and Reusability of Sol–Gel C18 Coated FPSE Media
3.5. Analytical Performance
3.6. Mathematical Model for Predicting Extraction Efficiency (Absolute Recovery, %)
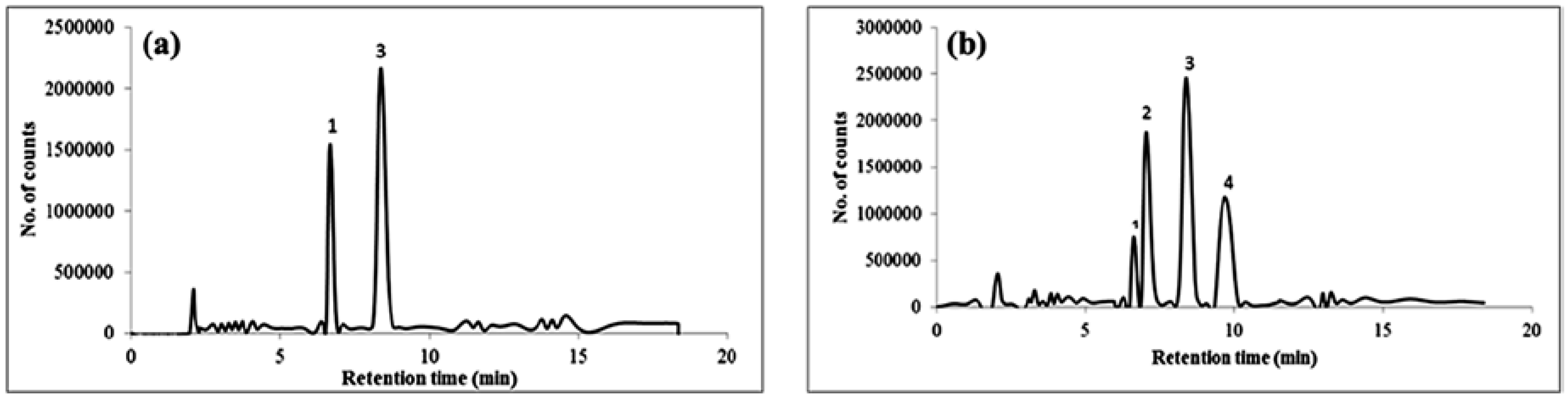
3.7. Application to Real Water Samples
3.8. Comparison of Sol–Gel C18 Coated FPSE Media with Other Sorbent Materials
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Drug Registry (ATSDR). Toxicological Profile for Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) Update; Agency for Toxic Substances and Drug Registry (ATSDR): Washington, DC, USA, 1995; Chapter 1; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Drug Registry (ATSDR). Toxicological Profile for Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) Update; Agency for Toxic Substances and Drug Registry (ATSDR): Washington, DC, USA, 1995; Chapter 2; pp. 11–207. [Google Scholar]
- Bostrom, C.E.; Gerde, P.; Hanberg, A.; Jernstrom, B.; Johansson, C.; Kyrklund, T.; Rannug, A.; Tornqvist, M.; Victorin, K.; Westerholm, R. Cancer risk assessment, indicators, and guidelines for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the ambient air. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 451–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, K.L. An overview of immunotoxicology and carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Environ. Carcinog. Rev. 1986, 4, 163–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srogi, K. Monitoring of environmental exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2007, 5, 169–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, J.; Jonsson, G.; Porte, C.; Krah, M.M.; Ariese, F. Analytical methods for determining metabolites of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) pollutants in fish bile: A review. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2010, 30, 224–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Oost, R.; Beyer, J.; Vermeulen, N.P.E. Fish bioaccumulation and biomarkers in environmental risk assessment: A review. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2003, 13, 57–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Y.; Wang, J.Z.; Wei, G.L.; Guan, Y.F.; Wong, C.S.; Zeng, E.Y. Sediment records of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the continental shelf of China: Implications for evolving anthropogenic impacts. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6497–6504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, S.O.; Field, R.A.; Goldstone, M.E.; Kirk, P.W.; Lester, J.N.; Perry, R. A review of atmospheric polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: Sources, fate and behavior. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1991, 60, 279–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Teng, Y.G.; Wang, J.S.; Song, L.T.; Zuo, R. Source apportionment of sediment PAHs in the Pearl River Delta region (China) using nonnegative matrix factorization analysis with effective weighted variance solution. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 444, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinstein, J.E.; Crawford, K.D.; Garner, T.R.; Flemming, A.J. Screening level ecological and human health risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in stormwater detention pond sediments of Coastal South Carolina, USA. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 178, 906–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.F.; Guo, Q.Z.; Yan, G.P. Determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water samples by hollow fiber extraction coupled with GC-MS. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 1071–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsipur, M.; Hashemi, B. Extraction and determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water samples using stir bar sorptive extraction (SBSE) combined with dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction based on the solidification of floating organic drop (DLLME-SFO) followed by HPLC-UV. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 20339–20345. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.; Gao, Y. Determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water samples by temperature-controlled ionic liquid dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction combined with high performance liquid chromatography. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 2553–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoli, E.; Samara, C. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in natural waters: Sources, occurrence and analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 1999, 18, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pánková, K. IACR Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenicity Risk of Chemical to Humans. Biol. Plant. 1986, 28, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahler, B.J.; Van Metre, P.C.; Bashara, T.J.; Wilson, J.T.; Johns, D.A. Parking lot sealcoat: An unrecognized source of urban polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 5560–5566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickhut, R.M.; Canuel, E.A.; Gustafson, K.E.; Liu, K.; Arzayus, K.M.; Walker, S.E.; Edgecombe, G.; Gaylor, M.O.; MacDonald, E.H. Automotive sources of carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons associated with particulate matter in the Chesapeake Bay region. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 4635–4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicre, M.A.; Marty, J.C.; Saliot, A.; Aparicio, X.; Grimalt, J.; Albaiges, J. Aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons in different sized aerosols over the Mediterranean Sea: Occurrence and origin. Atmos. Environ. 1967, 21, 2247–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fermin, L.; Valley, C.; Alonso, E.J.; Olmo, M.D.; Vilchez, J.L. Determination of ultra-traces of anthracene in water samples by solid-phase spectrofluorometry. Anal. Sci. 1993, 9, 117–120. [Google Scholar]
- Arbabi, M.; Nasseri, S.; Mesdaghinia, A.R.; Rezaie, S.; Naddafi, K.; Omrani, G.H.; Yunesian, M. Survey on physical, chemical and microbiological characteristics of PAH-contaminated soils in Iran. Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2004, 1, 26–33. [Google Scholar]
- Kanaly, R.; Harayama, S. Biodegradation of high-molecular-weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 2059–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kweon, O.; Kim, S.J.; Jones, R.C.; Freeman, J.P.; Adjei, M.D.; Edmondson, R.D.; Cerniglia, C.E. A polyomic approach to elucidate the fluoranthene-degradative pathway in Mycobacterium vanbaalenii PYR-1. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 4635–4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.J.; Shi, Z.; Lyv, J.X.; He, X.; Englert, N.A.; Zhang, S.Y. Pyrene is a novel constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) activator and causes hepatotoxicity by CAR. Toxicol. Sci. 2015, 147, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollosi, L.; Wenzl, T. Development and optimisation of a dopant assisted liquid chromatographic-atmospheric pressure photo ionisation-tandem mass spectrometric method for the determination of 15 + 1 EU priority PAHs in edible oils. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purcaro, G.; Moret, S.; Bucar-Miklavcic, M.; Conte, L.S. Ultra-high performance liquid chromatographic method for the determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in a passive environmental sampler. J. Sep. Sci. 2012, 35, 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, Y.; He, D.; Li, Y.; Ren, M.; Xu, Z.; Fang, J. Characterization and quantification of PAH atmospheric pollution from a large petrochemical complex in Guangzhou: GC–MS/MS analysis. Microchem. J. 2015, 119, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirivel, G.; Riffault, V.; Galloo, J.C. Simultaneous determination by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-atmospheric pressure chemical ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry of nitrated and oxygenated PAHs found in air and soot particles. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, F.; Guinez, M.; Cerutti, S.; Smichowski, P. UHPLC-(+)APCI-MS/MS determination of oxygenated and nitrated polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in airborne particulate matter and tree barks collected in Buenos Aires city. Microchem. J. 2014, 116, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Vera, M.; Lucena, R.; Ardenas, S.C.; Valcarcel, M. One-step in-syringe ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 6459–6465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.D.; Huang, Y.M.; Shu, W.Q.; Cao, J. Multiwalled carbon nanotubes as adsorbents of solid-phase extraction for determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in environmental waters coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1173, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Xiao, R.; Li, J.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, L. Determination of 16 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in environmental water samples by solid-phase extraction using multi-walled carbon nanotubes as adsorbent coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 5462–5469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brum, D.M.; Cassella, R.J.; Pereira Netto, A.D. Multivariate optimization of a liquid-liquid extraction of the EPA-PAHs from natural contaminated waters prior to determination by liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. Talanta 2008, 74, 1392–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamsipur, M.; Hassan, J. A novel miniaturized homogenous liquid-liquid solvent extraction-high performance liquid chromatographic-fluorescence method for determination of ultra traces of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediment samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 4877–4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elisabeth, R.; Rajasekhar, B. Optimization and validation of solid phase micro-extraction (SPME) method for analysis of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in rainwater and stormwater. Phys. Chem. Earth 2009, 34, 857–865. [Google Scholar]
- Bagheri, H.; Babanezhad, E.; Es-haghi, A. An aniline-based fiber coating for solid phase microextraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from water followed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1152, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.L.; Xia, L.B.; Chen, R.; Hu, B. Headspace single drop microextraction combined with HPLC for the determination of trace polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in environmental samples. Talanta 2008, 74, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, C.; Twu, P.; Anderson, J.L. Headspace single drop microextraction using micellar ionic liquid extraction solvents. Chromatographia 2010, 72, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djozan, D.J.; Assadi, Y. Modified pencil lead as a new fiber for solid-phase microextraction. Chromatographia 2004, 60, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djozan, D.; Assadi, Y.; Haddadi, S.H. Anodized aluminum wire as a solid-phase microextraction fiber. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 4054–4058. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, D.S.; Li, J.H.; Chen, S.B.; Chen, B.H. A novel cloud-point extraction process for preconcentrating selected polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in aqueous solution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 3936–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidari, H.; Razmi, H.; Jouyban, A. Preparation and characterization of ceramic/carbon coated Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticle nanocomposite as a solid-phase microextraction adsorbent. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1245, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Chen, C.; Yan, Z.; Cai, Q.; Yao, S. Evaluation of metal-organic framework 5 as a new SPE material for the determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in environmental waters. J. Sep. Sci. 2013, 36, 1283–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G. Fabric Phase Sorptive Extractors. U.S. Patent 9,283,544, 15 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Racamonde, I.; Rodit, R.; Quintana, J.B.; Sieira, J.B.; Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G.; Cela, R. Fabric phase sorptive extraction: A new sorptive microextraction technique for the determination of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs from environmental water samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 865, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Gomez, R.; Roldan-Pijuan, M.; Lucena, R.; Cárdenas, S.; Zafra-Gómez, A.; Ballesteros, O.; Valcárcel, M. Stir-membrane solid-liquid-liquid microextraction for the determination of parabens in human breast milk samples by ultra high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1354, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samanidou, V.; Kabir, A.; Galanopoulos, L.D.; Furton, K.G. Fast extraction of amphenicols residues from raw milk using novel fabric phase sorptive extraction followed by high-performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 855, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayillo, S.; Dennis, G.R.; Shalliker, R.A. An assessment of the retention behaviour of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on reversed phase stationary phases: Selectivity and retention on C18 and phenyl-type surfaces. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1126, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 2nd ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.; Heena, G.; Malik, A.K.; Kabir, A.; Furton, K.G. Efficient analysis of selected estrogens using fabric phase sorptive extraction and high performance liquid chromatography-fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1359, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brambilla, R.; Pires, G.P.; dos Santos, J.H.Z.; Miranda, M.S.L.; Chornik, B. Octadecylsilane-modified silicas prepared by grafting and sol–gel methods. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 2007, 156, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Wang, X.D.; Xiao, S.S.; Yu, L.G.; Zhang, Z.J. Preparation and characterization of TiO2 nanoparticles surface-modified by octadecyltrimethoxysilane. Indian J. Eng. Mater. Sci. 2013, 20, 561–567. [Google Scholar]
- Long, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, F.; Chen, C.; Pan, D.; Cai, Q.; Yao, S. Triphenylamine-functionalized magnetic microparticles as a new adsorbent coupled with high performance liquid chromatography for the analysis of trace polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in aqueous samples. Analyst 2012, 137, 2716–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Low, W.P.; Lee, H.K. Evaluation of sulfonated graphene sheets as sorbent for micro-solid-phase extraction combined with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1233, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Li, J.; Xu, S.; Ying, R.; Ma, J.; Liao, C.; Liu, D.; Yu, J.; Chen, L. Determination of 16 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in seawater using molecularly imprinted solid-phase extraction coupled with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Talanta 2012, 99, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, S.; Chen, C.; Zou, Y.; Hu, H.; Cai, Q.; Yao, S. Natural cotton fibers as adsorbent for solid phase extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water samples. Analyst 2014, 139, 3593–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Analyte | Linear Range (ng/mL) | Linearity Curve | R2 | LOD (pg/mL) | LOQ (pg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phen | 0.010–10 | y = 34,591x + 772 | 0.9997 | 1 | 3.33 |
| Anth | 0.010–10 | y = 104,873x + 2147 | 0.9997 | 0.1 | 0.33 |
| Flu | 0.010–10 | y = 90,258x + 247 | 0.9987 | 0.7 | 2.33 |
| Pyr | 0.010–10 | y = 114,921x + 497 | 0.9983 | 0.4 | 1.33 |
| Analyte | Phen | Anth | Flu | Pyr | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision (RSD%) | 0.01 | 0.5 | 5 | 0.01 | 0.5 | 5 | 0.01 | 0.5 | 5 | 0.01 | 0.5 | 5 |
| Intra-day | 5.6 | 4.7 | 3.6 | 1.9 | 2.8 | 2.2 | 2.1 | 2.8 | 1.8 | 1.9 | 2.1 | 1.1 |
| Inter-day | 4.9 | 5.01 | 4.1 | 2.2 | 2.3 | 2.5 | 1.8 | 2.9 | 1.9 | 3.1 | 2.7 | 2.0 |
| Accuracy (%) | ||||||||||||
| Intra-day | 88 | 87 | 90 | 90 | 92 | 91 | 91.1 | 90.1 | 92.1 | 90.8 | 91.6 | 92.8 |
| Inter-day | 86 | 89 | 89.4 | 91 | 90 | 89.3 | 91 | 90 | 92 | 90 | 89 | 91 |
| Recovery (%) (RSD%) | 88.1 (2.9) | 88 (4.1) | 88.4 (3.8) | 88.6 (3.1) | 88 (3.2) | 88.1 (2.4) | 92 (2.2) | 91 (2.8) | 90.5 (1.8) | 90.7 (3.2) | 91 (4.2) | 90.1 (1.4) |
| Compound | Log Kow | Expected Recovery (%) | Actual Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phen | 4.46 | 78.30 | 88.4 |
| Anth | 4.45 | 78.24 | 88.1 |
| Flu | 5.16 | 80.85 | 90.5 |
| Pyr | 4.88 | 80.32 | 90.1 |
| Sample | Phen (ng/mL) | Anth (ng/mL) | Flu (ng/mL) | Pyr (ng/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A a | n.d | n.d | n.d | n.d |
| B a | n.d | n.d | n.d | n.d |
| C b | 7.8 ± 2.6 | n.d | 5.6 ± 3.3 | n.d |
| D b | 8.8 ± 2.9 | n.d | 6.8 ± 3.4 | n.d |
| E c | n.d | n.d | n.d | n.d |
| F c | n.d | n.d | n.d | n.d |
| G d | 11 ± 3.1 | 7.8 ± 2.5 | 7.5 ± 3.8 | 5.8 ± 4.1 |
| H d | 4.1± 3.2 | 3.7 ± 3.1 | 7.7 ± 3.3 | 3.0 ± 2.8 |
| Method | Sorbent Material | Sorbent Preparation Time (Hours) | LOD (pg/mL) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSPE-HPLC-FLD | TPA-functionalized MNPs | 37.5 | 0.04–3.75 | [53] |
| µ-SPE-GC-MS | Functionalized graphene sheet | 29.5 | 0.8–3.9 | [54] |
| SPE-HPLC-FLD | Cotton fiber | 0.5 | 0.1–2 | [55] |
| MIPs-SPE-GC-MS | Imprinted sol-gel adsorbent | 38 | 5.2–12.6 | [56] |
| FPSE-HPLC-FLD | Sol-gel C18 (Cellulose) | 24 | 0.1–1 | Current work |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saini, S.S.; Kabir, A.; Rao, A.L.J.; Malik, A.K.; Furton, K.G. A Novel Protocol to Monitor Trace Levels of Selected Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Environmental Water Using Fabric Phase Sorptive Extraction Followed by High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Fluorescence Detection. Separations 2017, 4, 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations4020022
Saini SS, Kabir A, Rao ALJ, Malik AK, Furton KG. A Novel Protocol to Monitor Trace Levels of Selected Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Environmental Water Using Fabric Phase Sorptive Extraction Followed by High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Fluorescence Detection. Separations. 2017; 4(2):22. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations4020022
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaini, Shivender Singh, Abuzar Kabir, Avasarala Lakshmi Jagannadha Rao, Ashok Kumar Malik, and Kenneth G. Furton. 2017. "A Novel Protocol to Monitor Trace Levels of Selected Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Environmental Water Using Fabric Phase Sorptive Extraction Followed by High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Fluorescence Detection" Separations 4, no. 2: 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations4020022
APA StyleSaini, S. S., Kabir, A., Rao, A. L. J., Malik, A. K., & Furton, K. G. (2017). A Novel Protocol to Monitor Trace Levels of Selected Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Environmental Water Using Fabric Phase Sorptive Extraction Followed by High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Fluorescence Detection. Separations, 4(2), 22. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations4020022







