Carbon-Based Nanomaterials Functionalized with Ionic Liquids for Microextraction in Sample Preparation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Ionic Liquid-Coated Graphene-Based Nanomaterials
2.1. Solid-Phase Microextraction
2.2. Other Microextraction Technique
3. Ionic Liquid-Coated Carbon Nanotubes-Based Materials
3.1. Solid-Phase Microextraction
3.2. Dispersive Solid-Phase Microextraction
3.3. Other Microextraction Techniques
4. Ionic Liquid-Coated Magnetic Graphene-Based Nanomaterials
4.1. Magnetic Dispersive Solid-Phase Extraction
4.2. Other Microextraction Techniques
5. Ionic Liquid Coated Magnetic CNTs-Based Materials
5.1. Magnetic Solid-Phase Extraction MSPE
5.2. Other Microextraction Techniques
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CNTs | carbon nanotubes |
| DI | direct-immersion |
| DSPE | dispersive solid-phase microextraction |
| EDOT | 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene |
| EFs | enrichment factors |
| G | graphene |
| GO | graphene oxide |
| HS | headspace |
| IL | Ionic liquids |
| LODs | limits of detection |
| MSPE | magnetic solid-phase extraction |
| [NTf2] | bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl imide) |
| PAHs | polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons |
| PANI | polyaniline |
| PEDOT | poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) |
| PILs | polymeric ionic liquids |
| PT-SPE | pipette-tip solid-phase extraction |
| QuEChERS | Quick, Easy, Cheap, Effective, Rugged and Safe |
| SPE | solid-phase extraction |
| SPME | solid-phase microextraction |
| USA-IL-LDMME | ultrasound-assisted, ionic liquid-linked, dual-magnetic multi-walled carbon nanotube microextraction |
References
- Stalikas, C.D.; Fiamegos, Y.C. Microextraction combined with derivatization. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2008, 27, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.-T.; Zheng, X.; Li, H.-F.; Lin, J.-M. Application of carbon-based nanomaterials in sample preparation: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 784, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iijima, S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 1991, 354, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero Latorre, C.; Álvarez Méndez, J.; Barciela García, J.; García Martín, S.; Peña Crecente, R.M. Carbon nanotubes as solid-phase extraction sorbents prior to atomic spectrometric determination of metal species: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 749, 16–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speltini, A.; Merli, D.; Profumo, A. Analytical application of carbon nanotubes, fullerenes and nanodiamonds in nanomaterials-based chromatographic stationary phases: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 783, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Feng, H.; Li, J. Graphene oxide: Preparation, functionalization, and electrochemical applications. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 6027–6053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.; Row, K.H. Recent applications of ionic liquids in separation technology. Molecules 2010, 15, 2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasserscheid, P.; Welton, T. Ionic Liquids in Synthesis, 2nd ed.; Wiley-VCH: Berlin, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Vidal, L.; Riekkola, M.-L.; Canals, A. Ionic liquid-modified materials for solid-phase extraction and separation: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 715, 19–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Guo, Y.; Liang, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, X. Bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide-based ionic liquids grafted on graphene oxide-coated solid-phase microextraction fiber for extraction and enrichment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in potatoes and phthalate esters in food-wrap. Talanta 2016, 153, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Feng, J.; Bu, Y.; Duan, H.; Wang, X.; Luo, C. Development of a solid-phase microextraction fiber by the chemical binding of graphene oxide on a silver-coated stainless-steel wire with an ionic liquid as the crosslinking agent. J. Sep. Sci. 2014, 37, 3691–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Ai, Y.; Zeng, B.; Zhao, F. In situ solvothermal growth of metal-organic framework-ionic liquid functionalized graphene nanocomposite for highly efficient enrichment of chloramphenicol and thiamphenicol. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1427, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Bu, Y.; Feng, J.; Luo, C. Graphene oxide reinforced polymeric ionic liquid monolith solid-phase microextraction sorbent for high-performance liquid chromatography analysis of phenolic compounds in aqueous environmental samples. J. Sep. Sci. 2016, 39, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Wang, L.; Zeng, B.; Zhao, F. Fabrication of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-ionic liquid functionalized graphene nanosheets composite coating for headspace solid-phase microextraction of benzene derivatives. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1364, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, M.; Chatzimitakos, T.; Gallego, M.; Stalikas, C.D. 1-butyl-3-aminopropyl imidazolium-functionalized graphene oxide as a nanoadsorbent for the simultaneous extraction of steroids and β-blockers via dispersive solid-phase microextraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1436, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Wang, L.; Zhao, F.; Zeng, B. Ionic liquid polymer functionalized carbon nanotubes-coated polyaniline for the solid-phase microextraction of benzene derivatives. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 99483–99490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero-Vaca, M.; Trujillo-Rodríguez, M.J.; Zhang, C.; Pino, V.; Anderson, J.L.; Afonso, A.M. Automated direct-immersion solid-phase microextraction using crosslinked polymeric ionic liquid sorbent coatings for the determination of water pollutants by gas chromatography. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 4615–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Anderson, J.L. Polymeric ionic liquid bucky gels as sorbent coatings for solid-phase microextraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1344, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Sun, M.; Bu, Y.; Luo, C. Facile modification of multi-walled carbon nanotubes-polymeric ionic liquids-coated solid-phase microextraction fibers by on-fiber anion exchange. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1393, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Sun, M.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Duan, H.; Luo, C. Multiwalled carbon nanotubes-doped polymeric ionic liquids coating for multiple headspace solid-phase microextraction. Talanta 2014, 123, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narimani, O.; Dalali, N.; Rostamizadeh, K. Functionalized carbon nanotube/ionic liquid-coated wire as a new fiber assembly for determination of methamphetamine and ephedrine by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 8645–8653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Wang, L.; Zeng, B.; Zhao, F. Ionic liquid polymer functionalized carbon nanotubes-doped poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) for highly-efficient solid-phase microextraction of carbamate pesticides. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1444, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, Y.; Wu, M.; Li, L.; Zhao, F.; Zeng, B. Highly selective and effective solid phase microextraction of benzoic acid esters using ionic liquid functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes-doped polyaniline coating. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1437, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, L.; Zhang, S.; Liu, M.; Long, N.; Qi, X.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, L. Determination of rhodamine b in food using ionic liquid–coated multiwalled carbon nanotube-based ultrasound-assisted dispersive solid-phase microextraction followed by high-performance liquid chromatography. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 1696–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grijalba, A.C.; Escudero, L.B.; Wuilloud, R.G. Ionic liquid-assisted multiwalled carbon nanotube-dispersive micro-solid phase extraction for sensitive determination of inorganic as species in garlic samples by electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Spectrochim. Acta Part B 2015, 110, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alguacil, F.J.; García-Díaz, I.; López, F.A.; Rodríguez, O. Liquid-liquid extraction of cadmium(ii) by tioacl (tri-iso-octylammonium chloride) ionic liquid and its application to a tioacl impregnated carbon nanotubes system. Rev. Met. 2015, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazhenov, A.V.; Fursova, T.N.; Turanov, A.N.; Aronin, A.S.; Karandashev, V.K. Properties of a composite material based on multi-walled carbon nanotubes and an ionic liquid. Phys. Solid State 2014, 56, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polo-Luque, M.L.; Simonet, B.M.; Valcárcel, M. Ionic liquid combined with carbon nanotubes: A soft material for the preconcentration of pahs. Talanta 2013, 104, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polo-Luque, M.L.; Simonet, B.M.; Valcárcel, M. Solid-phase extraction of nitrophenols in water by using a combination of carbon nanotubes with an ionic liquid coupled in-line to ce. Electrophoresis 2013, 34, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Yuan, Y.; Xiang, C.; Yan, H.; Han, Y.; Qiao, F. Graphene/multi-walled carbon nanotubes functionalized with an amine-terminated ionic liquid for determination of (z)-3-(chloromethylene)-6-fluorothiochroman-4-one in urine. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1474, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunckol, M.; Fantini, S.; Malbosc, F.; Durand, J.; Serp, P. Effect of the synthetic strategy on the non-covalent functionalization of multi-walled carbon nanotubes with polymerized ionic liquids. Carbon 2013, 57, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankovich, S.; Dikin, D.A.; Piner, R.D.; Kohlhaas, K.A.; Kleinhammes, A.; Jia, Y.; Wu, Y.; Nguyen, S.T.; Ruoff, R.S. Synthesis of graphene-based nanosheets via chemical reduction of exfoliated graphite oxide. Carbon 2007, 45, 1558–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maidatsi, K.V.; Chatzimitakos, T.G.; Sakkas, V.A.; Stalikas, C.D. Octyl-modified magnetic graphene as a sorbent for the extraction and simultaneous determination of fragrance allergens, musks, and phthalates in aqueous samples by gas chromatography with mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 38, 3758–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, M.-Q.; Su, J.; Hu, J.-Q.; Wang, Q.; Dong, C.-Y.; Pan, S.-D.; Jin, M.-C. Planar graphene oxide-based magnetic ionic liquid nanomaterial for extraction of chlorophenols from environmental water samples coupled with liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1459, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Pan, Q.; Ding, X.; Xu, K.; Li, N.; Wen, Q. Ionic liquid-coated fe3o4/aptes/graphene oxide nanocomposites: Synthesis, characterization and evaluation in protein extraction processes. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 5718–5728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Pan, Q.; Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Xu, K. Preparation of magnetic chitosan and graphene oxide-functional guanidinium ionic liquid composite for the solid-phase extraction of protein. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 861, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Li, L.; Luo, C.; Fan, L. Synthesis of magnetic graphene nanocomposites decorated with ionic liquids for fast lead ion removal. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 85, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xu, K.; Li, N.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Q.; Zhou, Y. Magnetic solid-phase extraction of protein by ionic liquid-coated fe@graphene oxide. Talanta 2016, 160, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotfi, Z.; Mousavi, H.Z.; Sajjadi, S.M. Covalently bonded double-charged ionic liquid on magnetic graphene oxide as a novel, efficient, magnetically separable and reusable sorbent for extraction of heavy metals from medicine capsules. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 90360–90370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhao, H.; Xiao, D.; Chuong, P.-H.; He, J.; He, H. Mixed hemimicelles solid-phase extraction of cephalosporins in biological samples with ionic liquid-coated magnetic graphene oxide nanoparticles coupled with high-performance liquid chromatographic analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1454, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazemi, E.; Haji Shabani, A.M.; Dadfarnia, S.; Abbasi, A.; Rashidian Vaziri, M.R.; Behjat, A. Development of a novel mixed hemimicelles dispersive micro solid phase extraction using 1-hexadecyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide coated magnetic graphene for the separation and preconcentration of fluoxetine in different matrices before its determination by fiber optic linear array spectrophotometry and mode-mismatched thermal lens spectroscopy. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 905, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Shen, L.; Ye, X.; Zhang, F.; Chen, J.; Mo, W. Ultrasound-assisted magnetic solid-phase extraction based ionic liquid-coated fe3o4@graphene for the determination of nitrobenzene compounds in environmental water samples. Analyst 2014, 139, 1938–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliyari, E.; Alvand, M.; Shemirani, F. Modified surface-active ionic liquid-coated magnetic graphene oxide as a new magnetic solid phase extraction sorbent for preconcentration of trace nickel. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 64193–64202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzin, L.; Shamsipur, M.; Sheibani, S. Solid phase extraction of hemin from serum of breast cancer patients using an ionic liquid coated fe3o4/graphene oxide nanocomposite, and its quantitation by using faas. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 2623–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cao, S.; Zhang, L.; Xi, C.; Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, G. Preparation of size-controlled magnetite nanoparticles with a graphene and polymeric ionic liquid coating for the quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged and safe extraction of preservatives from vegetables. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1448, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvand, M.; Shemirani, F. Fabrication of fe3o4@graphene oxide core-shell nanospheres for ferrofluid-based dispersive solid phase extraction as exemplified for cd(ii) as a model analyte. Microchim. Acta 2016, 183, 1749–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Song, Z.; Nie, J.; Yu, G.; Li, Z.; Lee, M. Ionic liquid-based carbon nanotube coated magnetic nanoparticles as adsorbent for the magnetic solid phase extraction of triazole fungicides from environmental water. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 81877–81885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Liu, D.; Zhao, L.; Han, J.; Liang, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhou, Z. A novel magnetic ionic liquid modified carbon nanotube for the simultaneous determination of aryloxyphenoxy-propionate herbicides and their metabolites in water. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 852, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xu, K.; Li, N.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Q. A novel polymeric ionic liquid-coated magnetic multiwalled carbon nanotubes for the solid-phase extraction of cu, zn-superoxide dismutase. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 939, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Xu, K.; Li, N.; Wen, Q.; Zhou, Y. Magnetic multiwall carbon nanotubes modified with dual hydroxy functional ionic liquid for the solid-phase extraction of protein. Analyst 2015, 140, 3474–3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, D.; Yuan, D.; He, H.; Pham-Huy, C.; Dai, H.; Wang, C.; Zhang, C. Mixed hemimicelle solid-phase extraction based on magnetic carbon nanotubes and ionic liquids for the determination of flavonoids. Carbon 2014, 72, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirani, M.; Semnani, A.; Habibollahi, S.; Haddadi, H. Ultrasound-assisted, ionic liquid-linked, dual-magnetic multiwall carbon nanotube microextraction combined with electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry for simultaneous determination of cadmium and arsenic in food samples. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2015, 30, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
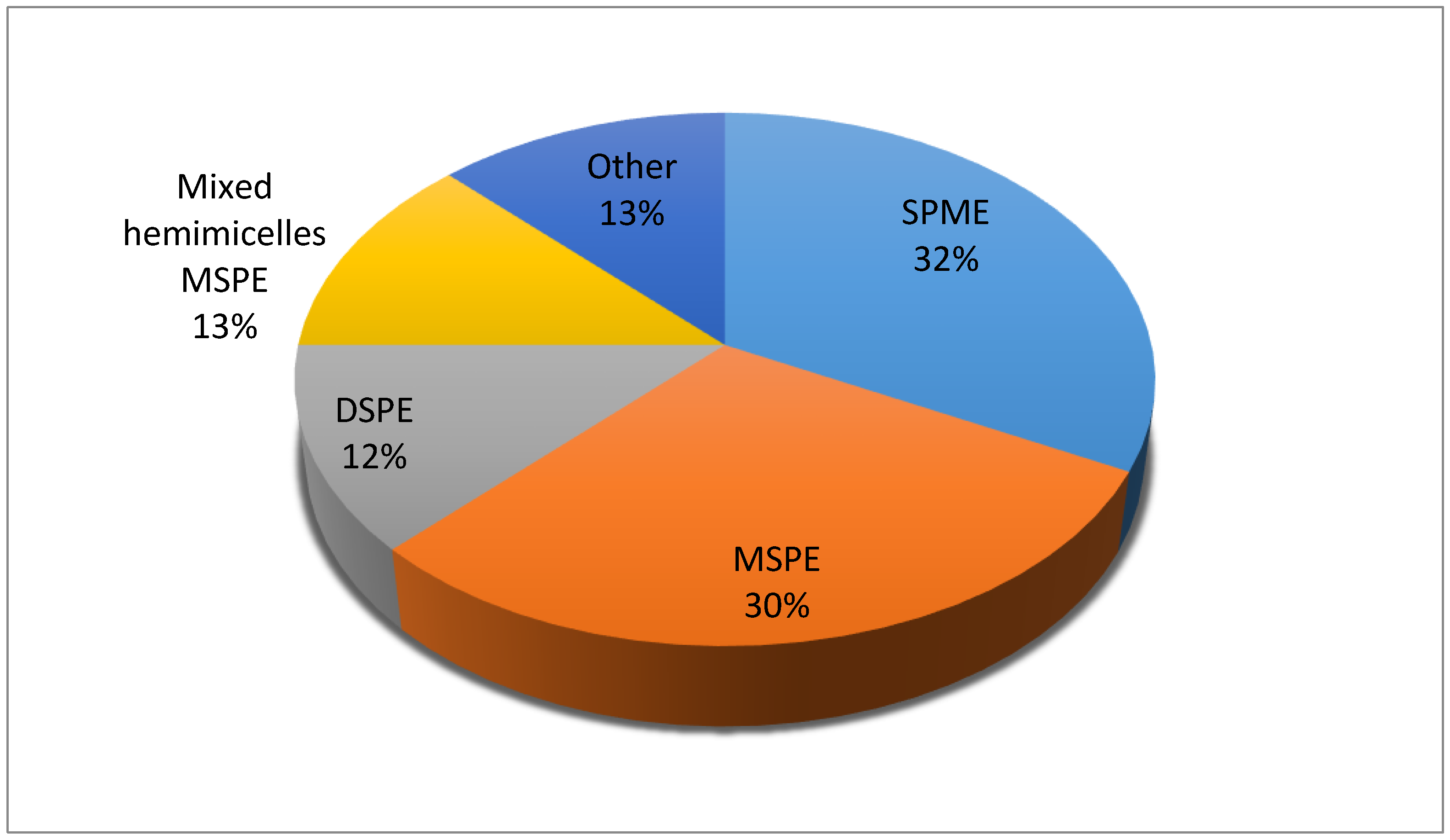
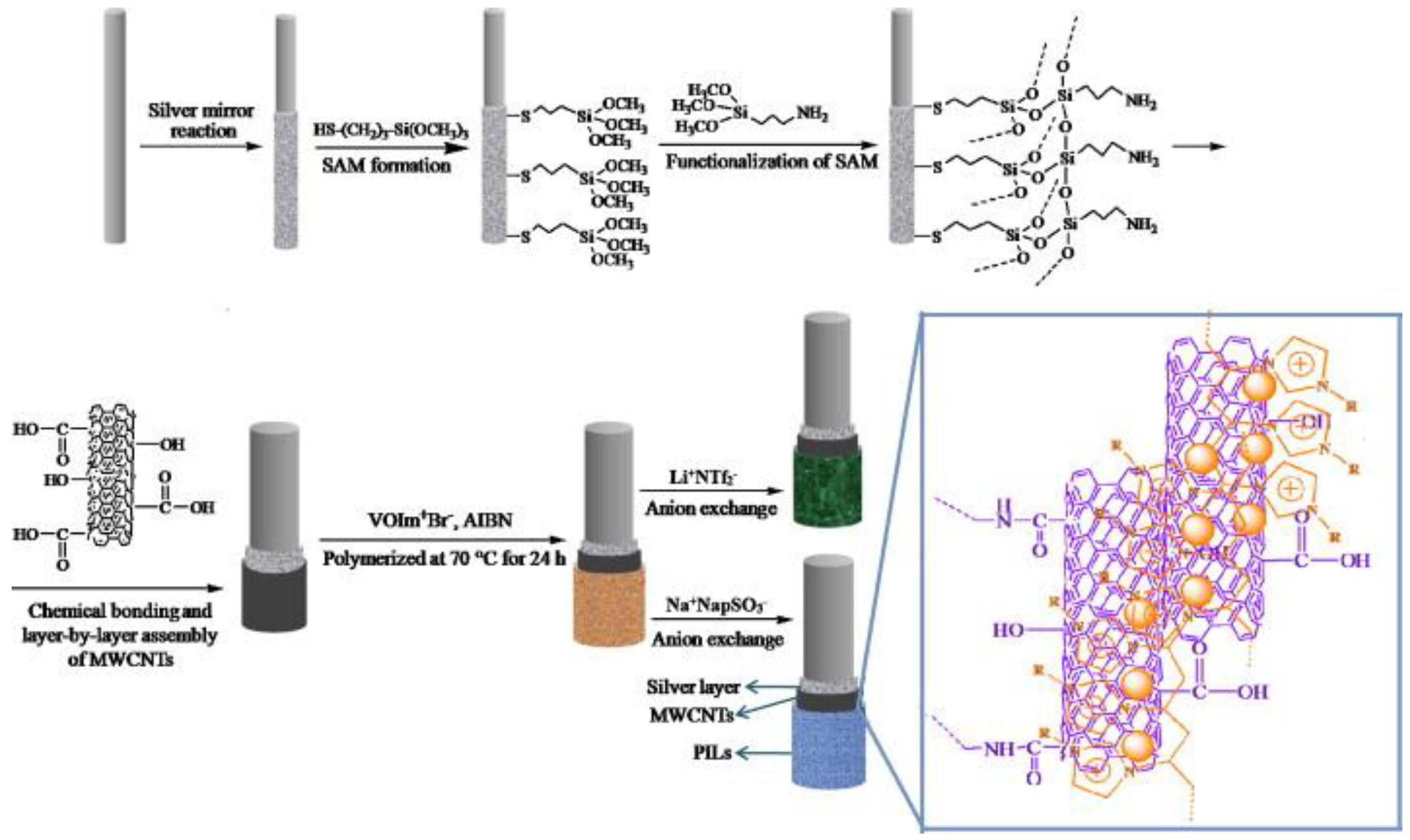

| Ionic Liquid | Microextraction Technique | Matrix | Target Analytes | LOD (μg/L) | Recoveries (%) | Instrumental Analytical System | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| poly(1-vinyl-3-hexylimidazolium-[NTf2]) | (HS)SPME | food-wrap, potato | PAHs and phthalate esters | 0.015–0.025 | 78.3–101.7 | GC-FID | [10] |
| 1-methyl-3-[3-(trimethoxysilyl)propyl]imidazolium chloride | (DI)SPME | rain and river water | PAHs | 0.05–0.10 | 92.3–120 | GC-FID | [11] |
| 1-(3-aminopropyl)-3-methylimidazolium bromide | (HS)SPME | milk, honey, urine and serum | antibiotics | 0.014–0.019 | 82.3–103.2 | GC-FID | [12] |
| 1-(3-aminopropyl)-3-(4-vinylbenzyl)imidazolium 4-styrenesulfonate | (DI)SPME | groundwater of industrial park and river water | phenols | 0.2–0.5 | 75.5–113 | HPLC-DAD | [13] |
| 1-hydroxyethyl-3-methyl imidazolium-[NTf2] | (HS)SPME | petrochemical, printing, dyeing wastewater and lake water | benzene derivatives | 0.010–0.019 | 82.3–108.3 | GC-FID | [14] |
| 1-butyl-3-aminopropyl imidazolium chloride | DSPE | effluent municipal wastewater treatment plant water, river and lake water | steroids, β-blockers | 0.007–0.023 | 87–98 | HPLC-DAD | [15] |
| Ionic Liquid | Microextraction Technique | Matrix | Target Analytes | LOD (μg/L) | Recoveries (%) | Instrumental Analytical System | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| poly(1-vinyl-3-hexyl-imidazolium [NTf2]) | (HS)SPME | Petrochemical waste water, lake and tap water | benzene derivatives | 0.0177–0.0326 | 84.0–106.9 | GC-FID | [16] |
| monomer: (1-vinyl-3-butylimidazolium [NTf2]), crosslinker: (1, 12-di(3-vinylimidazolium)dodecane [NTf2]) | (DI)SPME | - | phenols and PAHs | 0.75–121.0 | - | GC-FID | [17] |
| poly(1-vinyl-3-octylimidazolium bromide) | (HS)SPME | - | alcohols | 0.015–0.05 | - | GC-FID | [19] |
| - | n-alkanes | 0.02–1 | - | ||||
| poly(1-vinyl-3-octylimidazolium [NTf2]) | - | n-alkanes | 0.01–0.2 | - | |||
| poly(1-vinyl-3-octylimidazolium 2-naphthalene-sulfonate) | - | phthalate esters | 0.005–0.02 | - | |||
| industrial park groundwater | halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons | 0.05–2 | 75–113 | ||||
| monomer: (1-vinyl-3-ethylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate), crosslinker: 1,1′-(1,6-hexanediyl)bis(1-vinylimidazolium) bis(hexafluoro-phosphate) | (HS)SPME | citrus fruits | 2-naphthol | - | 81.9–110 | GC-FID | [20] |
| 1-methyl 3-[(3-octylamino)propyl] imidazolium [NTf2] | (HS)SPME | urine | methamphetamine, ephedrine | 0.07–0.1 | 94.0–104.0 | GC-MS | [21] |
| poly(1-vinyl-3-ethylimidazole bromide) | (DI)SPME | apple, lettuce | carbamate pesticides | 0.0152–0.0272 | 87.5–106.5 | GC-FID | [22] |
| 1-(3-aminopropyl)-3-methylimidazolium bromide | (HS)SPME | perfume | benzoic acid esters | 0.0015–0.0061 | 87.8–110.8 | GC-FID | [23] |
| monomer: (1-vinyl-3-butylimidazolium [NTf2], crosslinker: 1,12-di(3-vinylimidazolium) dodecane [NTf2] | (HS)SPME | river and tap water | PAHs | 0.001–0.0025 | 60.0–122.3 | GC-MS | [18] |
| 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate | ultrasound-assisted DSPE | wine, grape juice, blueberry juice and chili oil | rhodamine B | 0.28 | 85.1–96.0 | HPLC-DAD | [24] |
| trihexyl (tetradecyl)phosphonium chloride | DSPE | garlic | As(V) | 0.0071 | 98.0–106.0 | Electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometer | [25] |
| tri-iso-octylammonium chloride | DSPE | acidic aqueous solutions | Cd(II) | - | - | Atomic absorption spectrometer | [26] |
| 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate | DSPE | Nitric acid solutions | lanthanide ions | - | - | Inductively-coupled plasma -mass spectrometer | [27] |
| 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate | fabric-sorptive phase extraction | river water | PAHs | - | 87.0–105.0 | Spectrofluorometer | [28] |
| 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate | in-line micro-SPE | river water | nitrophenols | 0.22–0.28 | 90.0–112.0 | Capillary electrophoresis | [29] |
| 1-(3-aminopropyl)-3-methylimidazolium chloride | PT-SPE | urine | (Z)-3-(chloromethylene)-6-fluorothiochroman-4-one | 0.009 | 73.9–93.9 | HPLC-UV | [30] |
| Ionic Liquid | Microextraction Technique | Matrix | Target Analytes | LOD (μg/L) | Recoveries (%) | Instrumental Analytical System | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-carboxymethyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride | MSPE | tap, river and well water | chlorophenols | 0.0002–0.0026 | 85.3–99.3 | LC–MS/MS | [34] |
| N,N,N-trimethylglycine butanoate | MSPE | bovine calf whole blood | bovine serum albumin | - | - | UV-Vis spectrophotometer | [35] |
| di(6-hydroxyhexyl) tetramethyl guanidinium chloride | MSPE | - | trypsin, lysozyme, ovalbumin and bovine serum albumin | - | - | UV-Vis spectrophotometer | [36] |
| tetraoctylammonium bromide | MSPE | - | Pb | - | - | Atomic absorption spectrometer | [37] |
| N,N′-bis(2-aminoethyl)-N,N,N′,N′-tetramethyl-chloride | MSPE | porcine and bovine blood | hemoglobin | 11,870 | - | UV-Vis spectrophotometer | [38] |
| 1,4-diazabicyclo[2.2.2]octane | Ultrasound assisted-MSPE | medicine capsules | Pb(II), Cd(II), Ni(II), Cu(II) and Cr(III) | 0.2–1.811 | 95.4–102.4 | Flame atomic absorption spectrometer | [39] |
| 1-dodecyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate | mixed hemimicelles MSPE | urine | cephalosporins | 0.0006–0.0019 | 84.3–101.7 | HPLC-UV | [40] |
| 1-hexadecyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide | mixed hemimicelles MSPE | human urine, environmental water and pharmaceutical formulation | fluoxetine | 0.21 | 95.3–100.6 | Angled mode-mismatched thermal lens spectrometer | [41] |
| 1-heptyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate | ultrasound-assisted mixed hemimicelles MSPE | river, lake and rain water | nitrobenzenes | 1.35–4.57 | 80.35–102.77 | HPLC-UV | [42] |
| 1-hexadecyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride | MSPE | sea and river water, tea, spinach, cacao powder and cigarette | nickel | 0.16 | 96.8–99.2 | Flame atomic absorption spectrometer | [43] |
| 1,3-didecyl-2-methylimidazolium chloride | MSPE | blood serum | hemin | 3.0 | 97.3–105.6 | Flame atomic absorption spectrometer | [44] |
| 1-vinyl-3-octylimidazolium bromide | QuEChERS | purple cabbage, bitter gourd, sponge gourd, tomatoes and cabbage | preservatives residues | 0.82–6.64 μg/kg | 81.7–118.3 | GC–MS | [45] |
| 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate | ferrofluid-based DSPE | river and sea water, carrot, lettuce and tobacco | Cd | 0.12 | 98.2–101.5 | Flame atomic absorption spectrometer | [46] |
| Ionic Liquid | Microextraction Technique | Matrix | Target Analytes | LOD (μg/L) | Recoveries (%) | Instrumental Analytical System | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1-butyl-3-aminopropyl imidazolium chloride | MSPE | canal water | triazole fungicides | 0.05–0.22 | 84.7–105.3 | GC-MS | [47] |
| 1-butyl-3-aminopropyl imidazolium bromide | MSPE | ground and reservoir water | aryloxyphenoxy-propionate herbicides | 2.8–14.3 | 66.1–89.6 | HPLC-DAD | [48] |
| 0.002–3.4 | HPLC-MS/MS | ||||||
| 1-(4-vinylbenzyl)-(3-aminopropyl)-imidazolium chloride | MSPE | porcine whole blood | Cu, Zn-superoxide | - | 82.7–102.3 | UV-Vis spectrophotometer | [49] |
| 6-hydroxy-N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-N,N-dimethylhexan-1-aminium chloride | MSPE | - | lysozyme | - | - | UV-Vis Spectrophotometer | [50] |
| 1-hexadecyl-3-methyl-imidazolium bromide | mixed hemimicelles MSPE | human urine | flavonoids | 0.20–0.75 | 90.1–97.6 | HPLC-UV | [51] |
| 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluorophosphate | USA-IL-LDMME | tap and well water, cow milk, fish liver | Cd, As | 0.003–0.005 | 94.6–98.0 | Atomic absorption spectrometer | [52] |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chatzimitakos, T.; Stalikas, C. Carbon-Based Nanomaterials Functionalized with Ionic Liquids for Microextraction in Sample Preparation. Separations 2017, 4, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations4020014
Chatzimitakos T, Stalikas C. Carbon-Based Nanomaterials Functionalized with Ionic Liquids for Microextraction in Sample Preparation. Separations. 2017; 4(2):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations4020014
Chicago/Turabian StyleChatzimitakos, Theodoros, and Constantine Stalikas. 2017. "Carbon-Based Nanomaterials Functionalized with Ionic Liquids for Microextraction in Sample Preparation" Separations 4, no. 2: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations4020014
APA StyleChatzimitakos, T., & Stalikas, C. (2017). Carbon-Based Nanomaterials Functionalized with Ionic Liquids for Microextraction in Sample Preparation. Separations, 4(2), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations4020014







