Abstract
Countercurrent distribution based on liquid–liquid partition is a powerful separation method with minimal incurrence of loss of solutes, but its industrial application has been limited by cumbersome shifting of immiscible solvents. Although centrifugation has been employed to facilitate equilibration between phases, process scaling-up remains difficult. In this study, a dispersed mobile-phase countercurrent chromatography (DMCC) method has been developed to adapt the countercurrent distribution principle to a continuous column chromatography format. Continuous solute exchange between two immiscible phases within a series of separation columns is achieved by mechanical dispersion of an influx of mobile phase into an upward stream of small droplets travelling through the columns filled with stationary phase. The diameter, length, and number of columns, and the number of stationary phases employed in the different columns can be varied to match the requisite scale and resolution of operation. Illustrations of DMCC were provided by examples of solute separations where the fractionated solutes could be collected either from the eluate of the series of columns, or from drainage of the stationary phases in the individual columns at the end of a chromatographic run.
1. Introduction
Countercurrent distribution provides high-resolution separation for various classes of compounds [1,2,3], including the breakthrough purification of tRNA for sequencing [4,5]. While its avoidance of irreversible adsorptive losses represents an important advantage, its requirement of shifting and reequilibration of upper and lower phases from multiple tubes is mechanically complicated. In droplet countercurrent chromatography (DCCC), the passage of single droplets of mobile phase through a column of stationary phase of comparable diameter facilitates solute distribution [6], but the small diameter of the column renders scaling-up difficult. A range of modifications incorporating centrifugation, such as centrifugal partition chromatography (CPC) and high speed countercurrent chromatography (HSCCC) can speed up separation [3,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17], but the use of centrifugation increases the cost of equipment, especially on an industrial scale. In controlled-cycle pulsed liquid-liquid chromatography (CPLC), mixing of upper and lower phases is conducted in columns segmented into a cascade of chambers by horizontal perforated plates, yet equilibration of solutes between the phases still has to be achieved on a discontinuous basis with intervening pauses for phase separation in each transfer cycle [18,19,20].
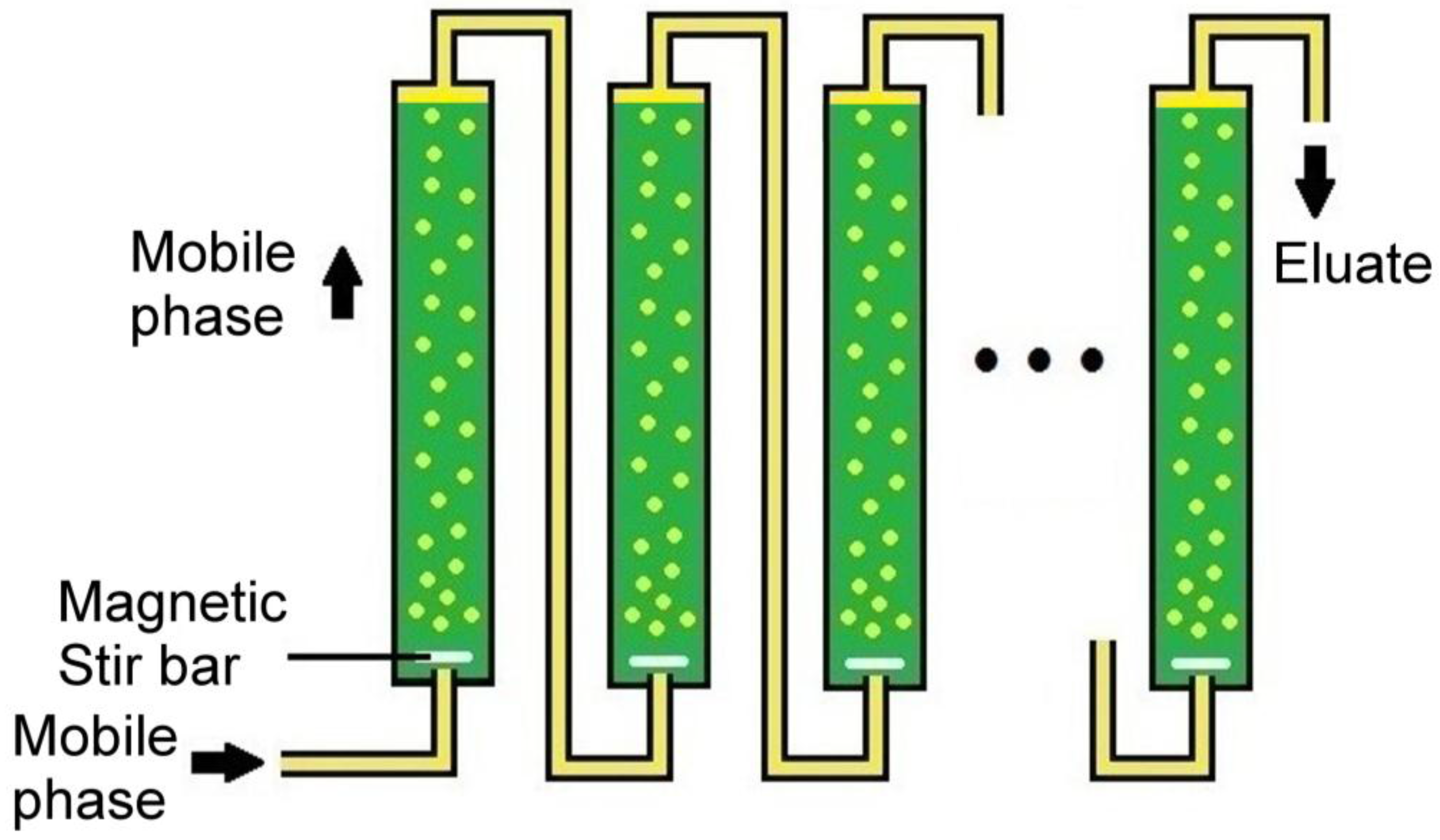
In order to combine the advantages of countercurrent distribution with those of column chromatography, in this study, we have developed a dispersed mobile-phase countercurrent chromatography (DMCC) method that enables continuous chromatography based on the dispersal of mobile phase into a stream of fine droplets travelling through a column of stationary phase (Figure 1). Dispersion of the mobile phase can be brought about by devices such as magnetic stirring or ultrasound. Since DMCC employs columns of much larger diameters relative to the dispersed droplets, it can be readily scaled up to provide preparative and industrial separations. As illustrated in the present study, the fractionated solutes can be collected from different fractions of eluate emerging from a series of separation columns, or from the solutes left in the stationary phases in the individual columns at the end of a run. The placement of different stationary phases in different columns, and the effects of column dead-volume, flow rate of mobile phase, and the number of columns employed were also investigated.
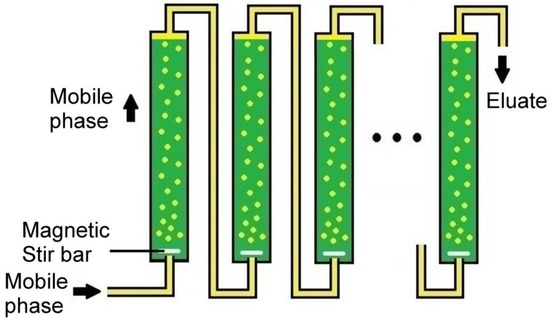
Figure 1.
Setup of dispersed mobile-phase countercurrent chromatography (DMCC): A stream of dispersed lighter mobile-phase (yellow) is shown ascending through a series of separation columns, each containing a denser stationary phase (green).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagent and Materials
Distilled water was employed throughout. Equilibrated phenol (pH 8.0, Ultrapure MB grade) was obtained from USB Corp. (Cleveland, OH, USA), o-cresol from Riedel-de Haën (Seelze, Germany), tripotassium phosphate from Nacalai Tesque (Kyoto, Japan), benzyl alcohol, benzoic acid, sodium hydroxide, and sodium hydrogencarbonate from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA), n-butanol from VWR Chemical (Radnor, PA, USA), baicalein from Indofine Chemical Co., Inc. (Hillsborough, CA, USA), and wogonin from Wako Pure Chemical Industries (Osaka, Japan).
2.2. Selection of Two-Phase System
A quantity of each of the key compounds to be separated by DMCC was dissolved in a two-phase system such that their concentrations in the two phases could be determined accurately by absorbance measurement. After mixing and phase-settling, the concentration of the compound in the upper phase (A1) and in the lower phase (A2) were determined by absorbance at 254 nm to yield the distribution coefficient KD = A1/A2. The selected upper and lower phases provided KD values within the range of 0.5–12 (Table 1) for the different compounds to be separated.

Table 1.
KD of each solute in different solvent systems.
2.3. DMCC Setup
The DMCC system consisted of ten Econo-Column® chromatography columns (except where specified otherwise), each with 25 mm i.d., length of 20 cm, and volume of 117 mL (BioRad, Hercules, CA, USA). They were connected in series with 35 cm lengths of MasterFlex silicone tubing with 1.6 mm i.d. (except in the high dead-volume runs in where 3.1 mm i.d. tubing and 46 cm tubing lengths were employed instead). All of the columns were filled with approximately 116 mL of the denser of a selected pair of immiscible solvents serving as stationary phase, and all connecting tubings were subsequently filled with the lighter solvent serving as mobile phase by pumping the mobile phase through all of the columns of stationary phase. Prior to the start of a DMCC run, the lighter solvent—serving as the mobile phase—was pumped into the columns at 4 mL/min (except where specified otherwise) through an influx port at the bottom of column-1 by an easy-load™ MasterFlex® model 7518-00 (Cole-Parmer, Vernon Hills, IL, USA). Upon entry into column-1, as well as each successive column, this inflow of mobile phase was broken up by a magnetic stir bar rotating at 350 rpm, driven by a Thermolyne Mirak stirrer from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA) into a stream of dispersed droplets ascending through the column of stationary phase (Figure 1). Insofar that a stirring device can be positioned more readily at the bottom of the column compared to the top of the column, transit of mobile phase through the stationary phase in DMCC is more easily implemented in the ascending mode than in the descending mode.
An hour later, the inflow of mobile phase was halted, and a sample solution containing a mixture of solutes was injected into the bottom of column-1, followed by the resumption of inflow of mobile-phase. The absorbance of the eluate emerging from the last column was monitored at 254 nm using a Biologic™ LP (BioRad, Hercules, CA, USA). At the end of the DMCC run, the stationary phases remaining in all the different columns were individually drained and analyzed at 254 nm with a UV-1201 spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan).
3. Rusults
3.1. Separation of o-Cresol and Benzyl Alcohol Using an n-Butanol–NaOH(aq) Two-Solvent System
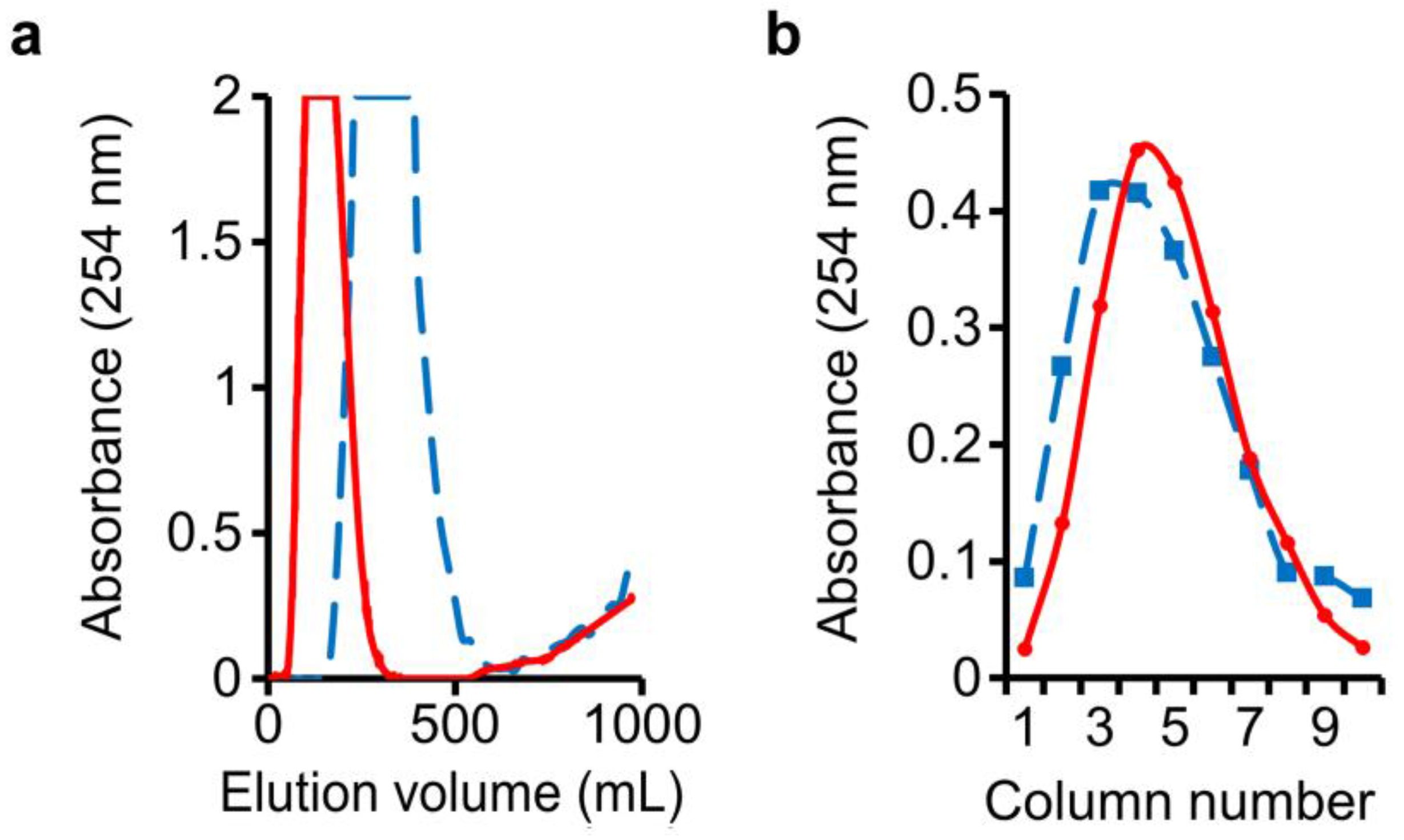
In this DMCC run, water-saturated n-butanol was employed as the mobile phase. An n-butanol–1% NaOH (1:1, v/v) mixture was shaken and allowed to settle, and its lower phase was employed as the stationary phase in the columns. Following the passage of mobile phase through the columns to pre-equilibrate the phases, a 4 mL sample mixture consisting of 2 g of o-cresol and 2 g of benzyl alcohol was injected into column-1 at the start of DMCC run, followed by resumption of influx of mobile phase. Monitoring of the eluate from the last column showed that passage of 320 mL of mobile phase through the column system was required to elute all the benzyl alcohol, and o-cresol began to appear after passage of 580 mL mobile phase (Figure 2a, solid line).
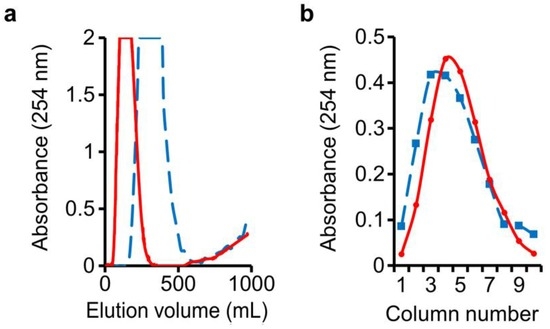
Figure 2.
Separation of benzyl alcohol and o-cresol: (a) Benzyl alcohol peak in mobile-phase eluate was followed by beginning elution of o-cresol; (b) o-Cresol distribution in the stationary phases drained from individual separation columns. Solid line: regular setup; dashed line: high dead-volume setup.
At the end of the run, drainage of the stationary phases in the individual separation columns enabled the recovery of o-cresol in columns 1–10, peaking at column-5 (Figure 2b, solid line). Importance of increased dead-volume in the columns was examined by repeating the run, filling at the start 80% (v/v) of each column (around 95 mL) with the denser stationary phase and 20% (v/v) with the lighter mobile phase, and connecting the columns with longer and wider-bore tubings (see Methods). Total volume in the ten columns plus connecting tubings was around 1170 mL in the regular runs, and around 1190 mL in the high dead-volume runs. In this instance, the benzyl alcohol peak was widened substantially, and the spread of o-cresol in the stationary phases in the columns widened to a smaller extent (Figure 2a,b, dashed line), showing the need to limit excessive dead-volume of mobile phase over and above that which is present inside the connecting tubings between columns, in order to restrict peak widening—especially for the eluted solutes.
3.2. Separation of Benzoic Acid, Phenol, and Benzyl Alcohol Using n-Butanol–NaHCO3(aq) and n-Butanol–NaOH(aq) Two-Solvent Systems
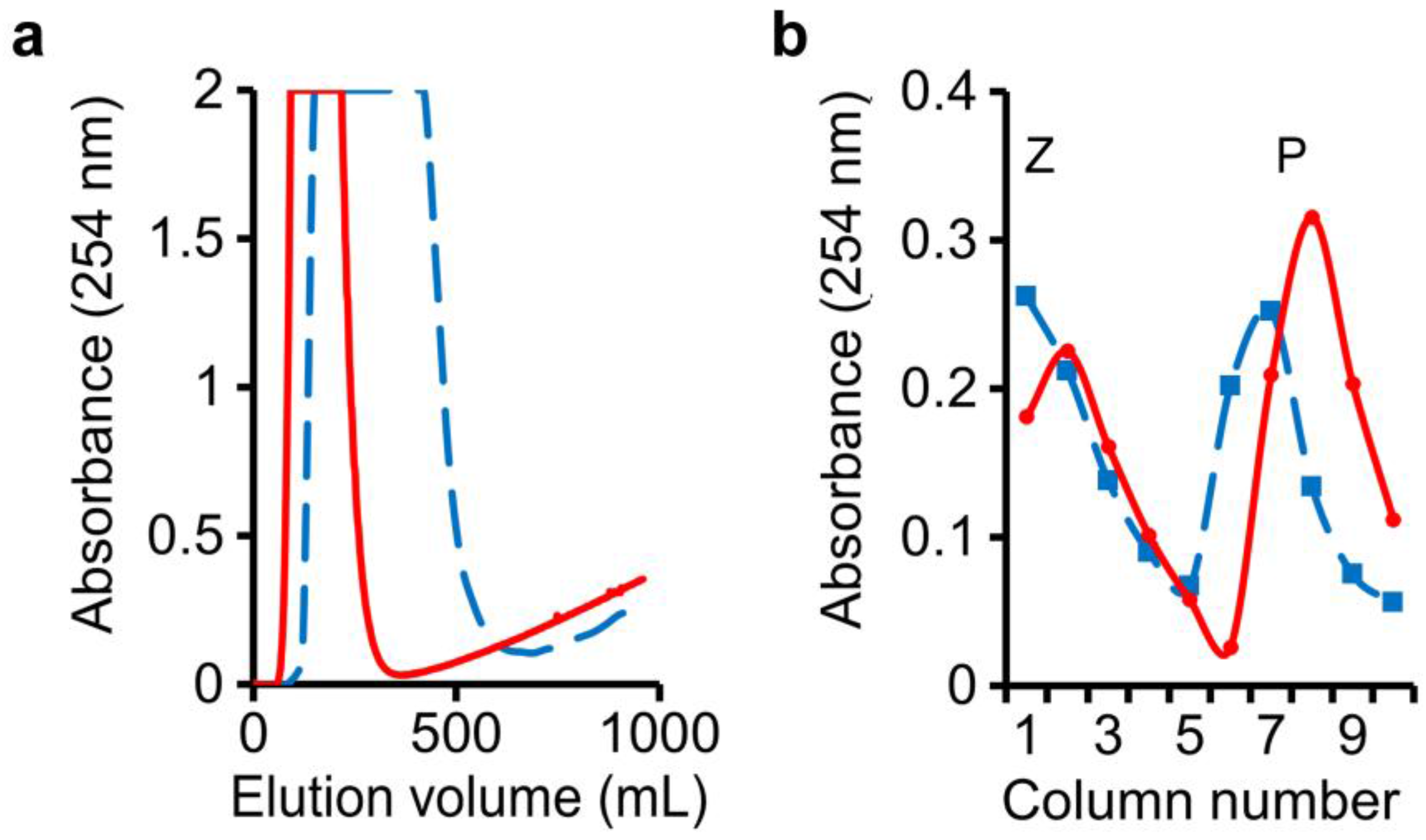
In this run, water-saturated n-butanol was employed as the mobile phase. An n-butanol–0.1 M NaHCO3 (1:1, v/v) mixture was shaken and allowed to settle, and its lower phase employed as the stationary phase in columns 1–5. An n-butanol–0.1 M NaOH (1:1, v/v) mixture was shaken and allowed to settle, and its lower phase was employed as the stationary phase in columns 6–10. The sample mixture consisting of 1 g of benzoic acid, 1 g of phenol, and 3 g of benzyl alcohol was injected into column-1 to begin the run. Monitoring of the eluate from the last column showed that the passage of 340 mL of mobile phase into the column system was required to elute all the benzyl alcohol (Figure 3a, solid line). At the end of the run, drainage of the stationary phases in the individual separation columns enabled the recovery of benzoic acid in columns 1–5, peaking at column-2, and phenol in columns 7–10, peaking at column-8 (Figure 3b, solid line).
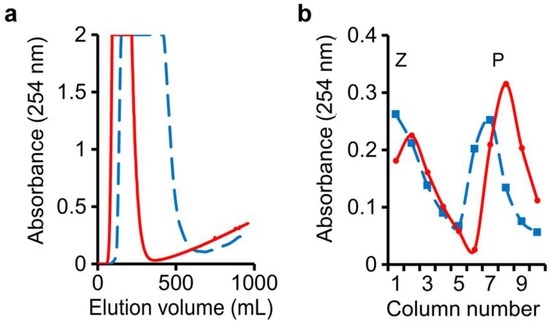
Figure 3.
Separation of benzyl alcohol, phenol, and benzoic acid: (a) Benzyl alcohol peak was followed by initial appearance of phenol in mobile-phase eluate; (b) Benzoic acid (Z) and phenol (P) in stationary phases drained from individual separation columns. Solid line: regular setup; dashed line: high dead-volume setup.
Thus the use of two different stationary phases—one in columns 1–5 and the other in columns 6–10—made possible the separate retention of benzoic acid in columns 1–5, and phenol in columns 7–10. The importance of dead-volume in the columns was tested again by filling at the start 80% (v/v) of each column with the denser stationary phase and 20% (v/v) with the lighter mobile phase, and the use of longer and wider-bore connecting tubing between columns. In agreement with the results of Figure 2, the eluted peak of benzyl alcohol was widened substantially, whereas the spreads of benzoic acid and phenol in the stationary phases were only somewhat widened, possibly owing to a compression effect by the stationary phase (Figure 3a,b, dashed line).
3.3. Separation of Baicalein and Wogonin Using a n-Butanol–K3PO4(aq) Two-Solvent System
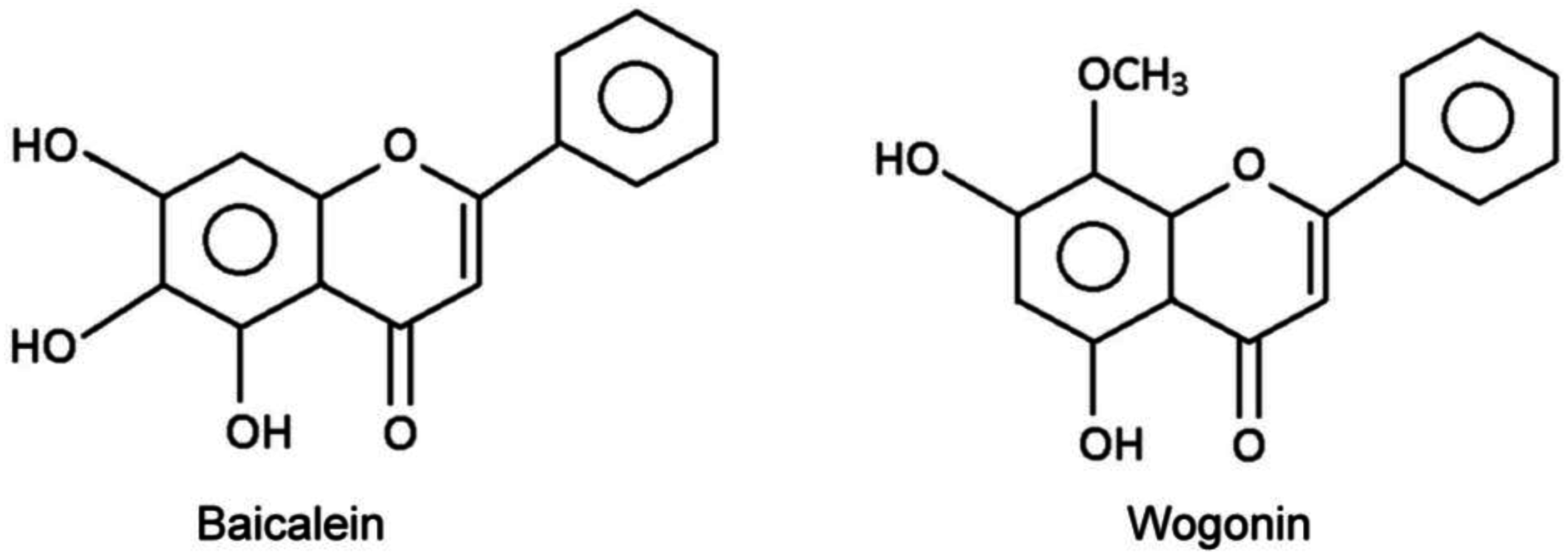
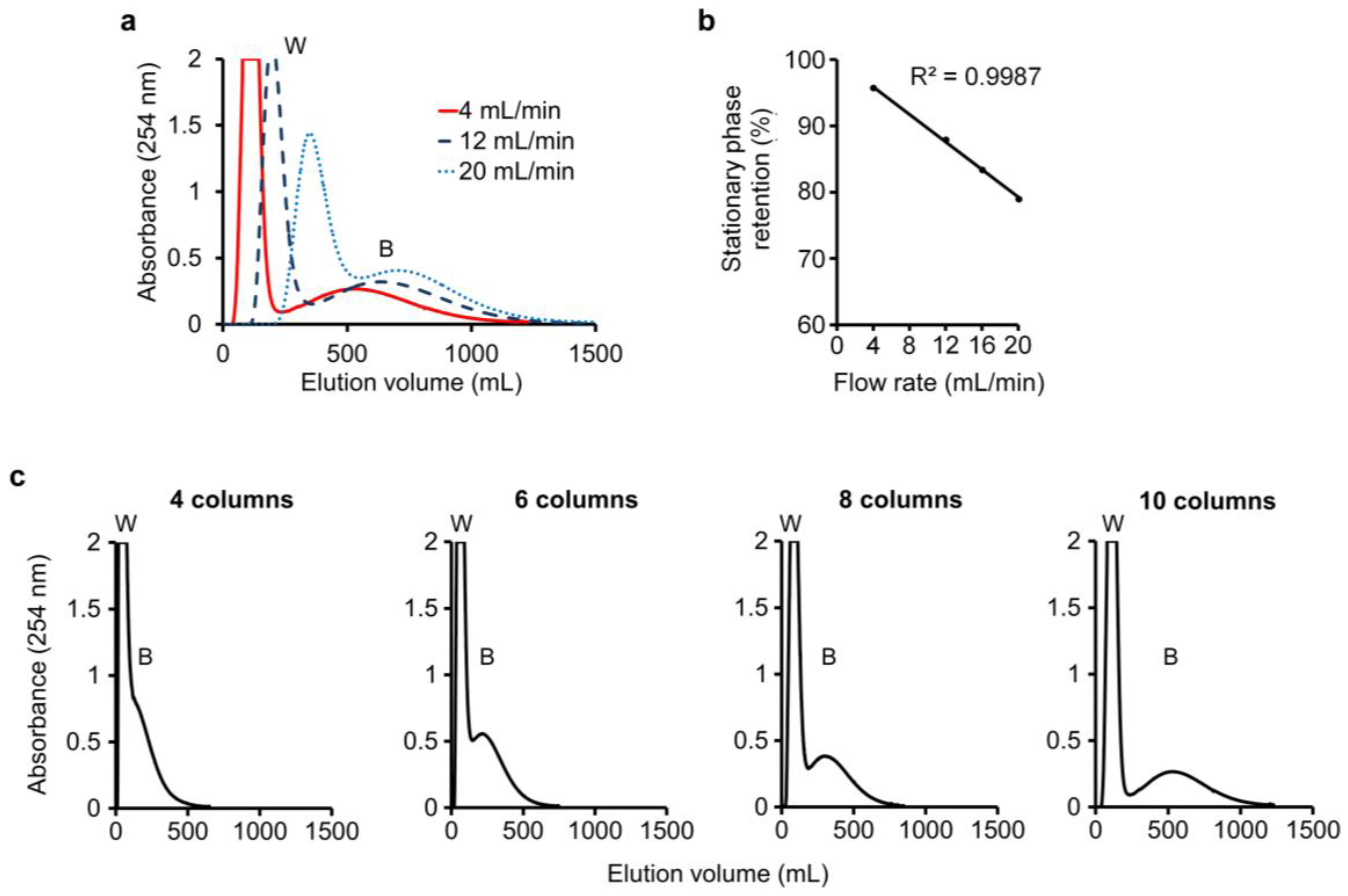
In this run, water-saturated n-butanol was employed as the mobile phase. An n-butanol–0.1 M K3PO4 (1:1, v/v) mixture was shaken and allowed to settle, and its lower phase was employed as the stationary phase in the columns. A sample mixture consisting of 20 mg baicalein and 20 mg wogonin (Figure 4) dispersed in 8 mL n-butanol–0.1 M K3PO4 (1:1, v/v) mixture was injected into column-1 to begin the run. Monitoring of the eluate from the last column showed flow-rate dependence of the DMCC chromatogram. At a flow rate of 4, 12, or 20 mL/min, the passage of 240 mL, 360 mL, or 540 mL of mobile phase through the column system was required to elute all the wogonin from the columns, and the passage of 1200 mL, 1400 mL, or 1600 mL of mobile phase was required to elute all the baicalein, respectively (Figure 5a).
Figure 4.
Structures of Baicalein and Wogonin.
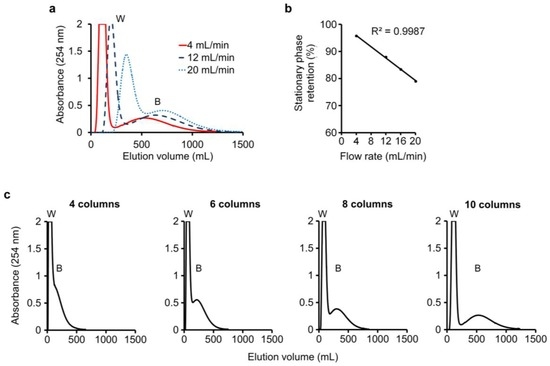
Figure 5.
Separation of wogonin and baicalein: (a) Separation of wogonin (W) and baicalein (B) in eluate at a flow rate of 4, 12, or 20 mL/min using ten columns; (b) Effect of flow rate on stationary phase retention; (c) Effect of number of columns on separation.
Notably, the flow rate of the mobile phase was a significant factor in stationary phase retention, which was found to be 95.8%, 87.9%, 83.4%, and 79.0% for flow rates of 4, 12, 16, and 20 mL/min, respectively. The correlation between flow rate (x) and stationary phase retention (y) conformed to the linear relationship y = −1.0409x + 100, with R2 = 0.9987 (Figure 5b). Thus, a fast flow rate brought about increased loss of stationary phase, replaced by increased mobile phase within the columns and tubings, thereby possibly delaying the migration of the solutes and adversely affecting separation. The importance of employing an adequate number of columns was illustrated in Figure 5c, where ten columns were required to separate the wogonin (W) and baicalein (B) peaks.
4. Discussion
The DMCC method adapts the powerful countercurrent distribution principle [21] to a continuous column chromatographic format for solute separations, which makes continuous countercurrent equilibration between two immiscible phases possible without the use of centrifugation. Scaling up to large scale operations can therefore be readily achieved through the use of large columns, avoiding the high costs of centrifugal equipment. As illustrated in Figure 2 and Figure 3, fractionated solutes can be collected from either the mobile-phase eluate from a series of columns or from the stationary phases in the individual columns at the end of a chromatographic run. Collection from stationary phases eliminates the need to elute all the solutes from the separation columns. By shortening the chromatographic run and reducing the solvent requirement, it is particularly well-suited for the fractionation of slow-eluting solutes.
Furthermore, in column chromatography, gradient elution can be introduced to improve separation. The use of multiple solid stationary phases in stationary phase-optimized selectivity liquid chromatography (SOSLC) furnishes another approach to enhance separation [22,23,24,25]. In DMCC, separation can be enhanced by the use of multiple liquid stationary phases. In separating benzyl alcohol, phenol, and benzoic acid, for example, the distribution coefficients were notably very close for benzyl alcohol (KD = 4.77) and phenol (KD = 4.68) in an n-butanol–0.1 M NaHCO3 two-solvent system, and they were very close for phenol (KD = 0.49) and benzoic acid (KD = 0.50) in an n-butanol–0.1 M NaOH solvent system. Therefore, the separation of benzyl alcohol, phenol, and benzoic acid is difficult to achieve using DMCC with either one of these two-solvent systems. However, when DMCC was carried out in Figure 3, placing the lower phases from these two-solvent systems separately in columns 1–5 and columns 6–10 as stationary phases, separation of these three solutes was obtained using only ten columns with a combined column volume of ~1200 mL. Likewise, either a succession of multiple mobile phases—or a stream of mobile phase incorporating a concentration gradient in one or more of its chemical components—may also be employed during a DMCC rum.
Complex solute mixtures are commonly encountered in plant extracts, and numerous medicinal herbs are known to contain a wide range of pharmacologically-active ingredients, many of which being present in small amounts that have not been fully investigated. For such potentially important medicinal ingredients from plants, mixtures of cellular RNAs and complex products of organic synthesis, etc., DMCC provides a convenient and useful method for both laboratory investigation and industrial production, with only minimal obstacles posed by extraneous factors such as inconvenience of operation [18], adsorptive losses [20], and high equipment cost.
In conclusion, the DMCC method combines the outstanding advantages of countercurrent distribution and continuous column chromatography. Both the number of columns employed and the dimensions of the columns can be varied to suit the scale of operation. As in any countercurrent distribution system, the separation attainable between any pair of solutes is predicted almost exclusively by the difference between their distribution coefficients in the immiscible mobile and stationary phases. Accordingly, provided that the solutes are not chemically affected by the two solvents, and that there is a sufficient difference between their distribution coefficients, DMCC may be expected to provide a basis for their separation.
Acknowledgments
We thank J. Tze-Fei Wong for valuable discussion and Peggy Lee for expert support. We would like to indicate that a Provisional US Patent on the method has been filed by the HKUST R & D Corp of the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology of which Timothy Yiu-Cheong Ho and Hong Xue are inventors.
Author Contributions
The article was written and approved by both authors. Timothy Yiu-Cheong Ho and Hong Xue participated in DMCC design and data analysis; Timothy Yiu-Cheong Ho performed the experiments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| CPC | Centrifugal Partition Chromatography |
| CPLC | Controlled-cycle Pulsed Liquid-liquid Chromatography |
| DCCC | Droplet Countercurrent Chromatography |
| DMCC | Dispersed Mobile-phase Countercurrent Chromatography |
| HSCCC | High Speed Countercurrent Chromatography |
| KD | Distribution coefficient |
| RNA | Ribonucleic acid |
| SOSLC | Stationary-phase Optimized Selectivity Liquid Chromatography |
References
- Craig, L. Identification of smalll amounts of organic compounds by distribution studies: II. Separation by counter-current distribution. J. Biol. Chem. 1944, 155, 535–546. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, Y.; Kitamura, H.; Hayashi, K. A method for separating commercial colistin complex into new components: Colistins pro-A, pro-B and pro-C. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 1982, 35, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.B.; Chen, F. Isolation and purification of baicalein, wogonin and oroxylin a from the medicinal plant scutellaria baicalensis by high-speed counter-current chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1074, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apgar, J.; Holley, R.W.; Merrill, S.H. Purification of the alanine-, valine-, histidine-, and tyrosine-acceptor ribonucleic acids from yeast. J. Biol. Chem. 1962, 237, 796–802. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Holley, R.W.; Apgar, J.; Everett, G.A.; Madison, J.T.; Marquisee, M.; Merrill, S.H.; Penswick, J.R.; Zamir, A. Structure of a ribonucleic acid. Science 1965, 147, 1462–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanimura, T.; Pisano, J.J.; Ito, Y.; Bowman, R.L. Droplet countercurrent chromatography. Science 1970, 169, 54–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthod, A. Countercurrent Chromatography: The Support-Free Liquid Stationary Phase; Elsevier Science Ltd.: Boston, MA, USA, 2002; Volume 38, p. 397. [Google Scholar]
- Berthod, A.; Maryutina, T.; Spivakov, B.; Shpigun, O.; Sutherland, I.A. Countercurrent chromatography in analytical chemistry (IUPAC Technical report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2009, 81, 355–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, W.D. Countercurrent Chromatography: Apparatus, Theory and Applications; VCH Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Q.; Wu, P.; Ito, Y. Low-speed rotary countercurrent chromatography using a convoluted multilayer helical tube for industrial separation. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 3363–3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, Y.; Conway, W.D. High-Speed Countercurrent Chromatography; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, Y.; Sandlin, J.; Bowers, W.G. High-speed preparative counter-current chromatography with a coil planet centrifuge. J. Chromatogr. A 1982, 244, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, I.A. Recent progress on the industrial scale-up of counter-current chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1151, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Sun, A.; Liu, R. Separation and purification of baicalin and wogonoside from the Chinese medicinal plant Scutellaria baicalensis georgi by high-speed counter-current chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1066, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foucault, A.P. Centrifugal partition chromatography. In Chromatographic Science Series; Foucault, A.P., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1995; Volume 68, pp. 25–49. [Google Scholar]
- Marchal, L.; Legrand, J.; Foucault, A. Centrifugal partition chromatography: A survey of its history, and our recent advances in the field. Chem. Rec. 2003, 3, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murayama, W.; Kobayashi, T.; Kosuge, Y.; Yano, H.; Nunogaki, Y.; Nunogaki, K. A new centrifugal counter-current chromatograph and its application. J. Chromatogr. A 1982, 239, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostanyan, A.E.; Voshkin, A.A.; Kodin, N.V. Controlled-cycle pulsed liquid–liquid chromatography. A modified version of Craig’s counter-current distribution. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 6135–6143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belter, P.A.; Speaker, S.M. Controlled-cycle operations applied to extraction processes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Process Des. Dev. 1967, 6, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Bowman, R.L. Countercurrent chromatography. Anal. Chem. 1971, 43, 69A–75A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, L.; Otto, P. Apparatus for countercurrent distribution. Anal. Chem. 1949, 21, 500–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyiredy, S.; Szucs, Z.; Szepesy, L. Stationary phase optimized selectivity liquid chromatography: Basic possibilities of serially connected columns using the “prisma” principle. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1157, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Beer, M.; Lynen, F.; Chen, K.; Ferguson, P.; Hanna-Brown, M.; Sandra, P. Stationary-phase optimized selectivity liquid chromatography: Development of a linear gradient prediction algorithm. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 1733–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Lynen, F.; Szucs, R.; Hanna-Brown, M.; Sandra, P. Gradient stationary phase optimized selectivity liquid chromatography with conventional columns. Analyst 2013, 138, 2914–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Lynen, F.; De Beer, M.; Hitzel, L.; Ferguson, P.; Hanna-Brown, M.; Sandra, P. Selectivity optimization in green chromatography by gradient stationary phase optimized selectivity liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 7222–7230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).