Enhanced Degradation of Different Tetracyclines by Nonthermal Plasma and Activated Persulfate: Insights into Synergistic Effects and Degradation Mechanism
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
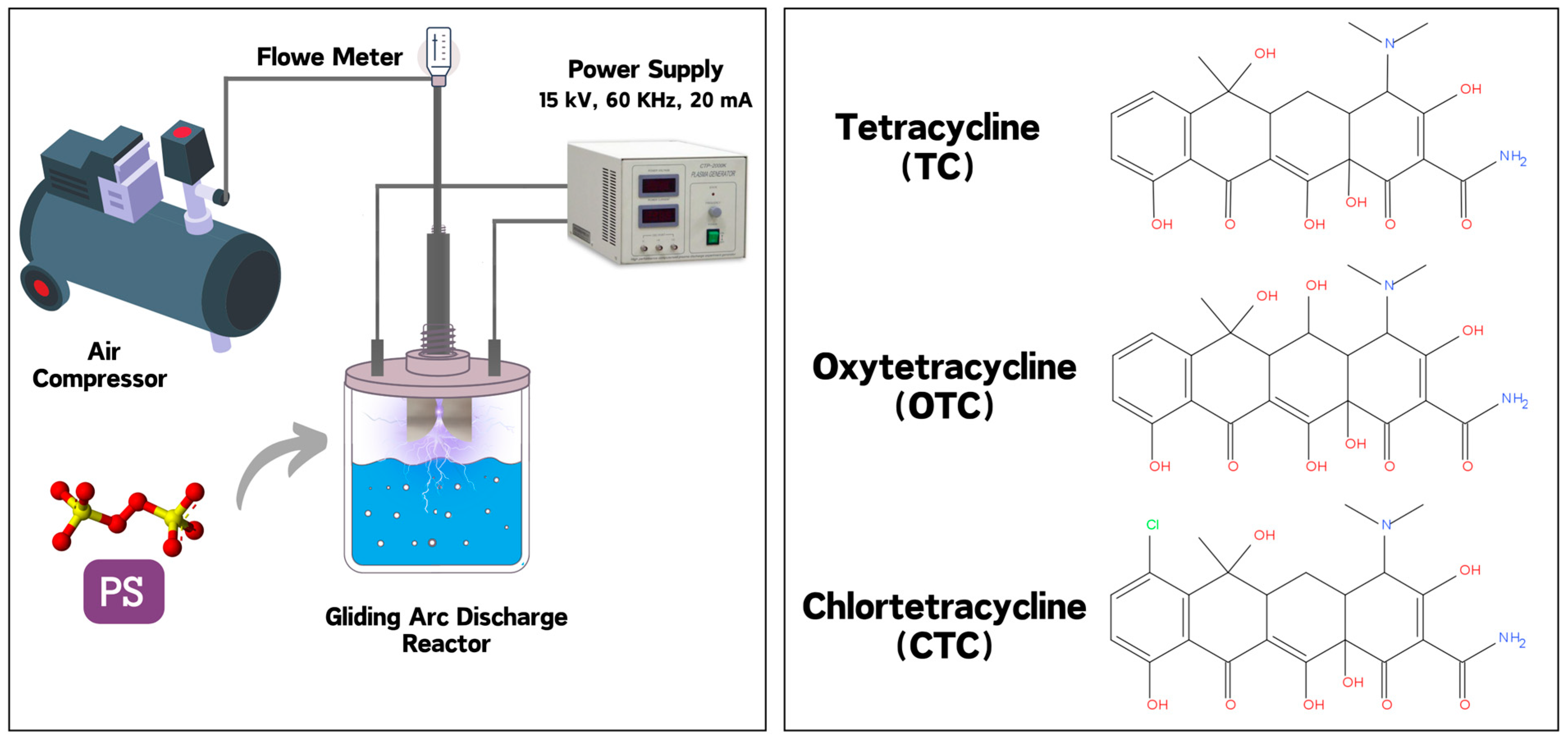
2.1. Plasma Discharge Setup and Treatment Procedure
2.2. Plasma Persulfate Activation Process
2.3. Analytical Methods
3. Results
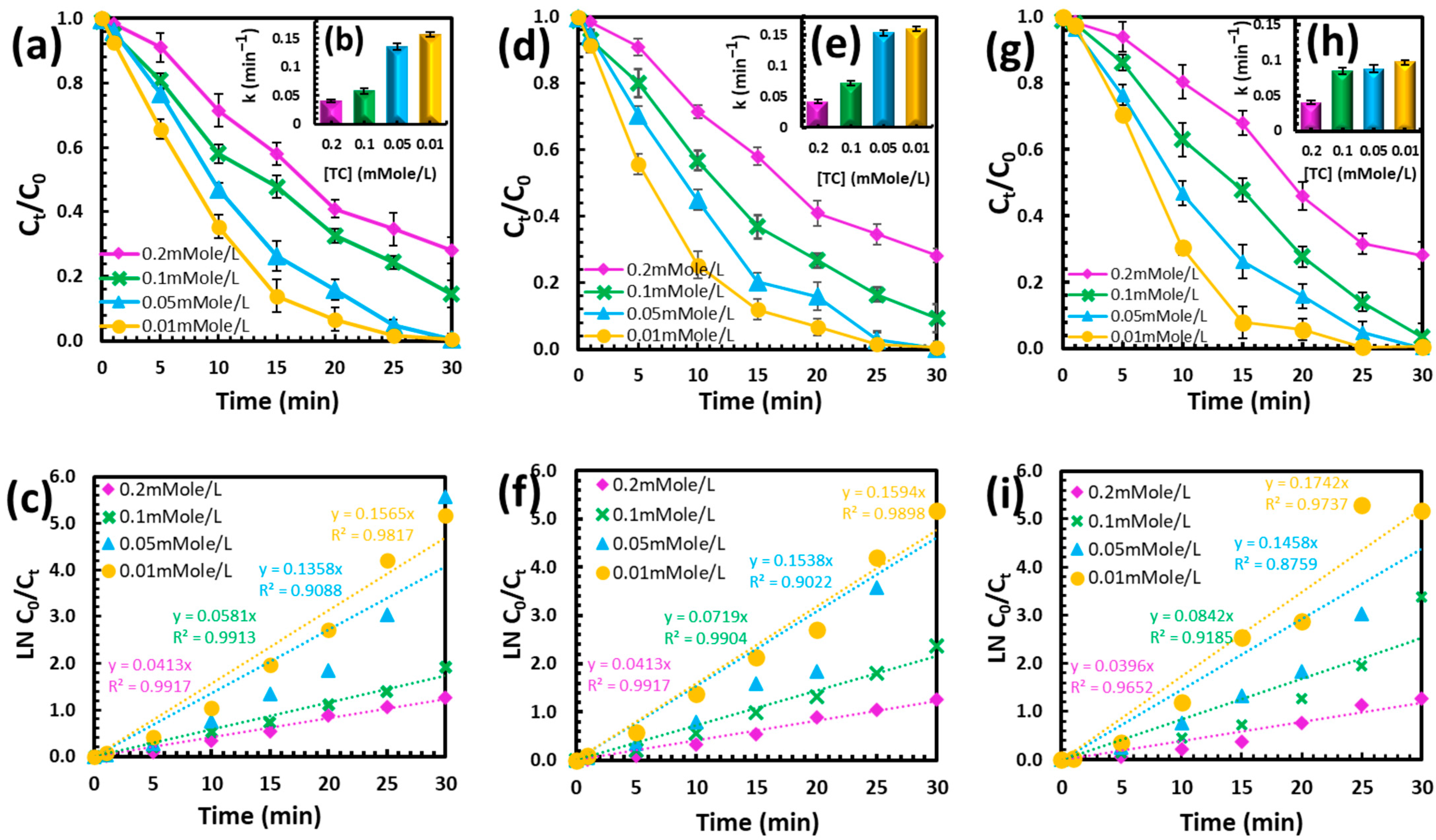
3.1. Degradation Efficiency and Kinetic Study
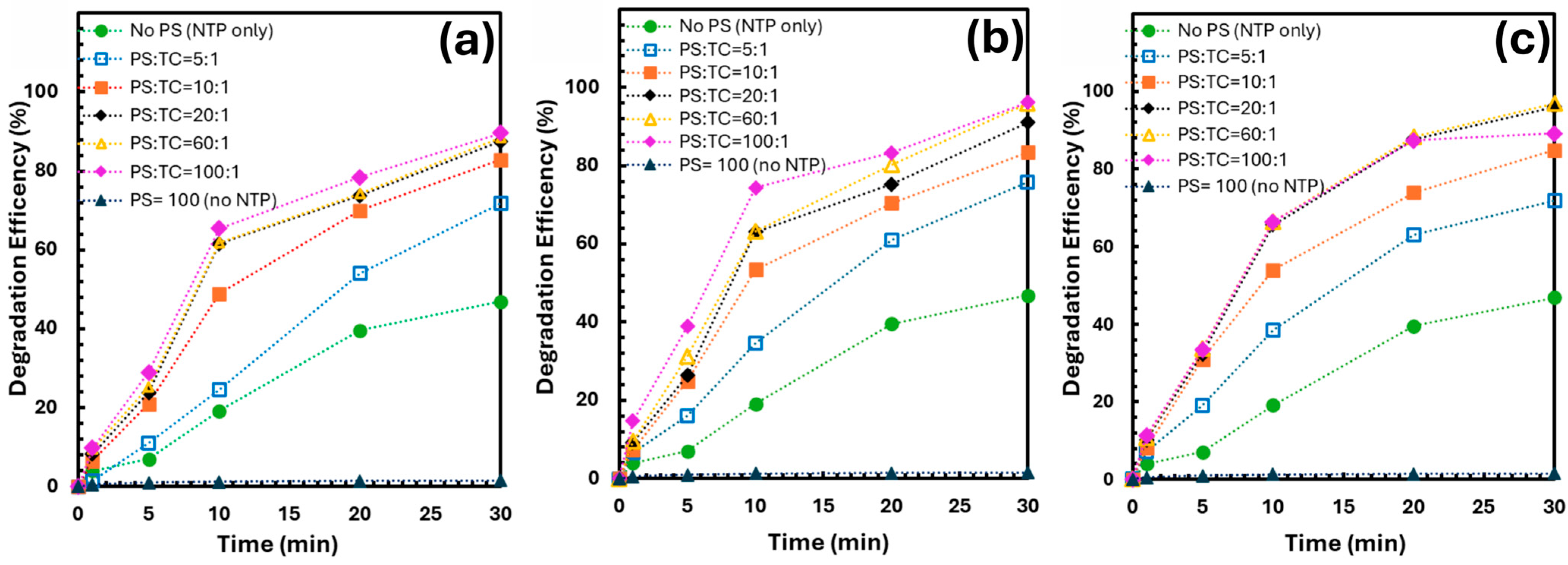
3.2. Effect of PS: TCs Molar Ratio
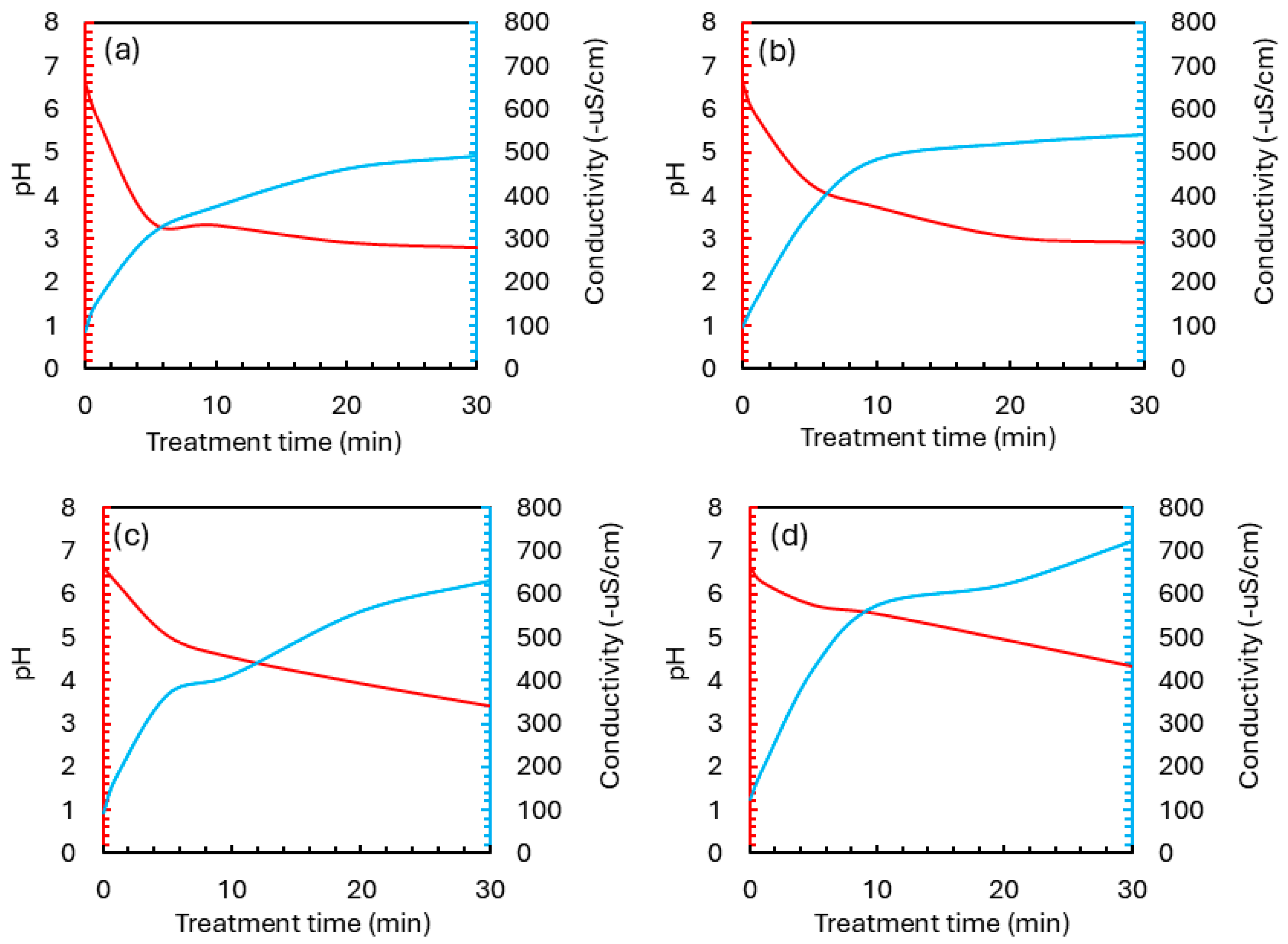
3.3. Initial pH and Conductivity
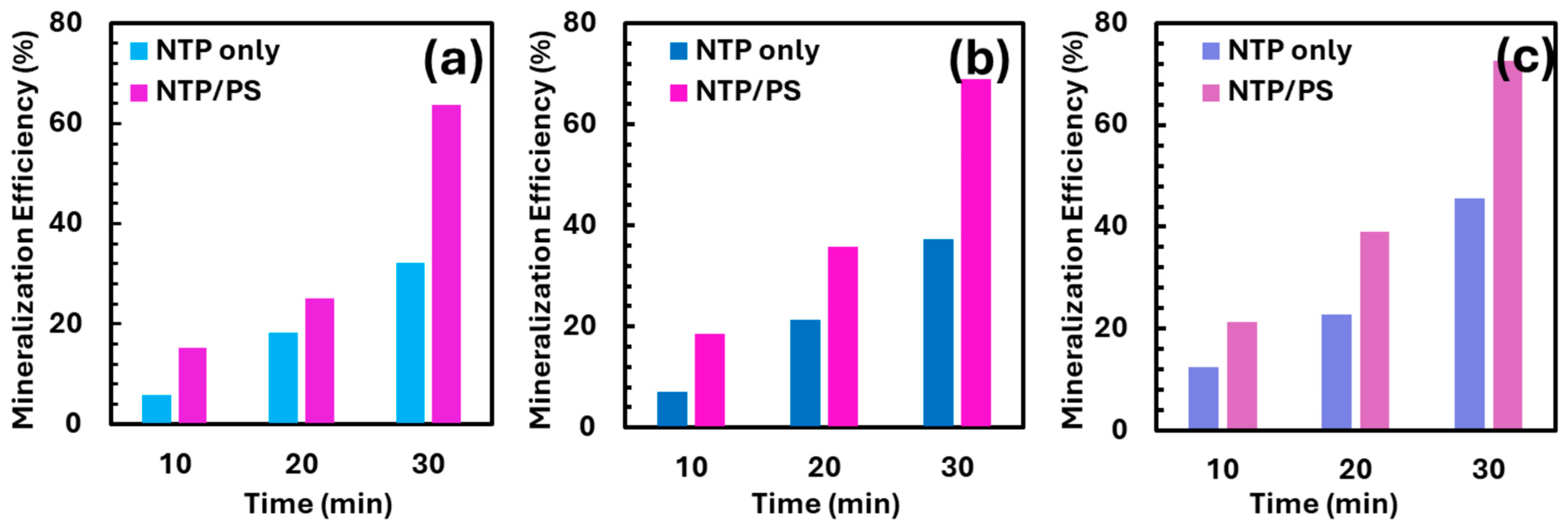
3.4. Evaluation of Mineralization Efficiency
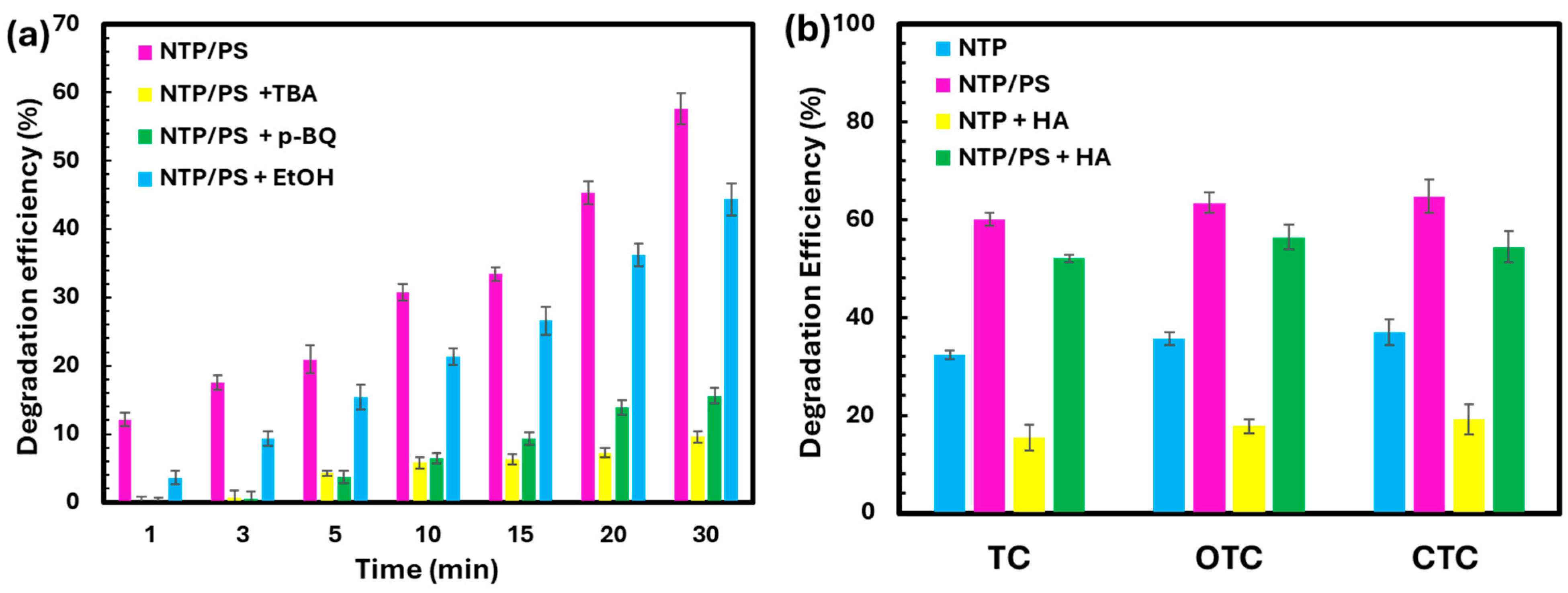
3.5. Role of Reactive Species
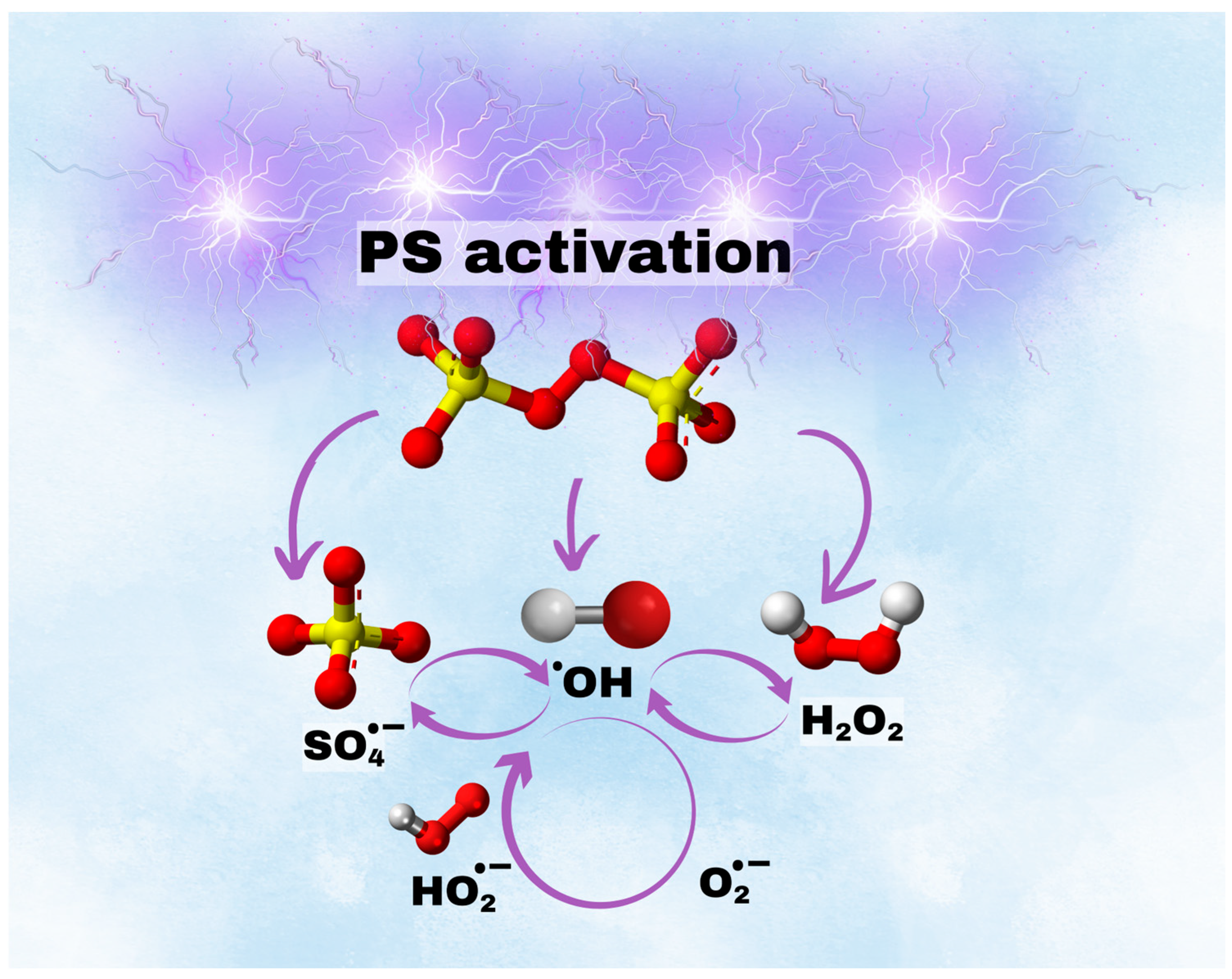
3.6. The Mechanism of Plasma-Activated Persulfate (PS)
3.7. Degradation Pathway of TC, OTC, and CTC by NTP/PS
3.8. Toxicity Assessment
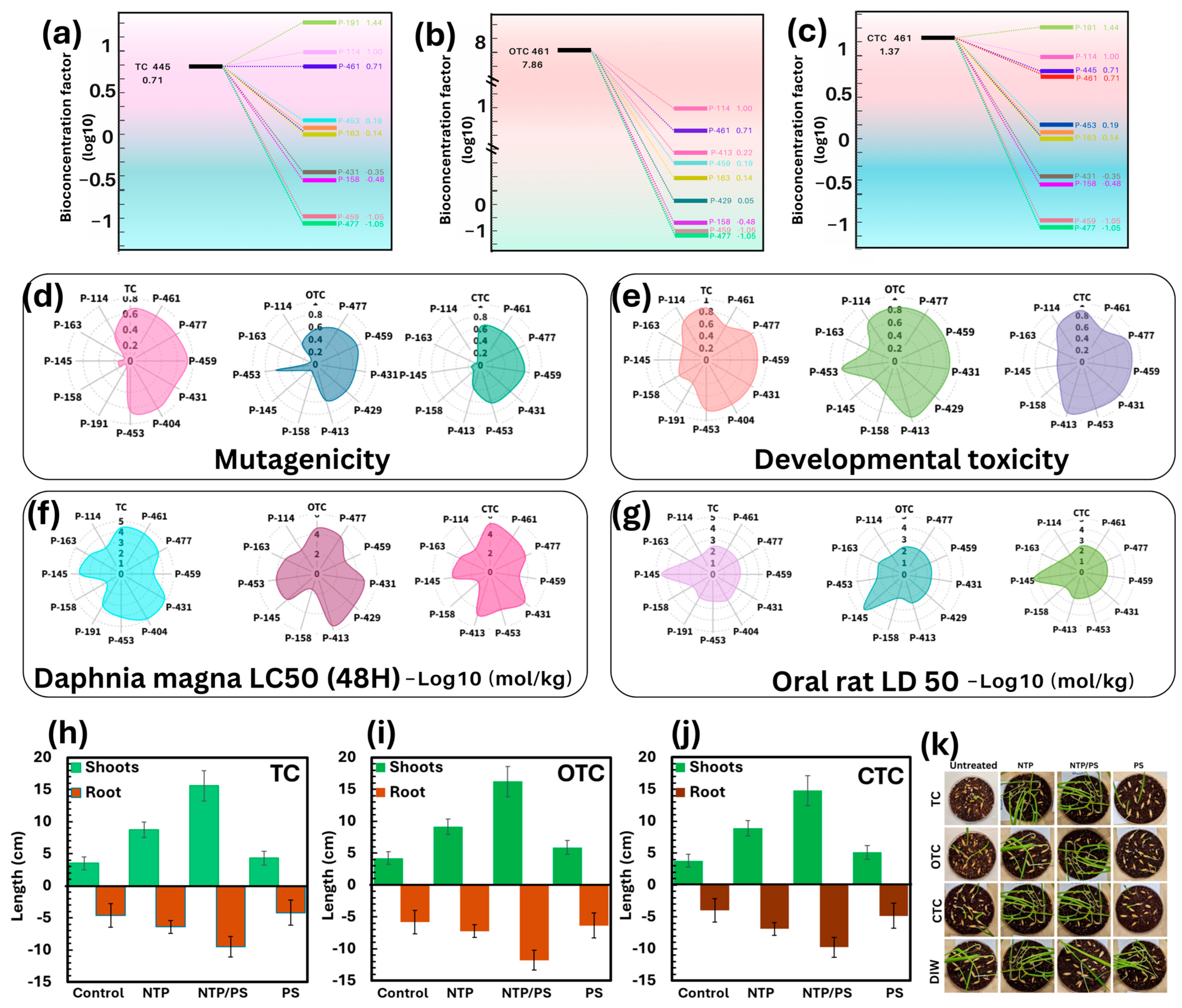
3.8.1. Bioconcentration Factor (BCF)
3.8.2. Mutagenicity and Developmental Toxicity
3.8.3. Aquatic Toxicity (Daphnia magna LC50)
3.8.4. Mammalian Toxicity (Oral Rat LD50)
3.8.5. Phytotoxicity Assays
3.9. Advantages and Practical Considerations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grossman, T.H. Tetracycline antibiotics and resistance. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a025387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Hong, Y.; Park, J.E.; Sharma, V.K.; Cho, S.I. Sulfonamides and tetracyclines in livestock wastewater. Chemosphere 2013, 91, 888–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Shaer, M.; Eldaly, M.; Heikal, G.; Sharaf, Y.; Diab, H.; Mobasher, M.; Rousseau, A. Antibiotics Degradation and Bacteria Inactivation in Water by Cold Atmospheric Plasma Discharges Above and Below Water Surface. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2020, 40, 971–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.; Mao, Y.; Qiu, W.; Wu, Y.; Cai, B. The Source and Distribution of Tetracycline Antibiotics in China: A Review. Toxics 2023, 11, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amangelsin, Y.; Semenova, Y.; Dadar, M.; Aljofan, M.; Bjørklund, G. The Impact of Tetracycline Pollution on the Aquatic Environment and Removal Strategies. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Xiao, Y.; Pan, H.; Mei, Y. Toxic effects of tetracycline and its degradation products on freshwater green algae. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 147, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daghrir, R.; Drogui, P. Tetracycline antibiotics in the environment: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2013, 11, 209–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chohra, H.; Lee, K.A.; Choe, H.; Cho, J.Y.; Kantharaj, V.; Cheong, M.S.; Kim, Y.-N.; Lee, Y.B. Dose-Dependent Physiological Response to Transient Bioaccumulation of Tetracycline in Kimchi Cabbage (Brassica campestris L.). Antibiotics 2025, 14, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, J.; An, J.; Wang, X.; Cheng, M.; Cui, Y. A novel DBD/VUV/PMS process for efficient sulfadiazine degradation in wastewater: Singlet oxygen-dominated nonradical oxidation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 461, 132650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillanpää, M.; Ncibi, M.C.; Matilainen, A. Advanced oxidation processes for the removal of natural organic matter from drinking water sources: A comprehensive review. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 208, 56–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.H.; Bui, H.M.; Bui, T.X. Advanced Oxidation Processes for the Removal of Pesticides; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Ma, C.; Yang, Y.; Yang, X.; Demeestere, K.; Nikiforov, A.; Van Hulle, S. Degradation of micropollutants in secondary wastewater effluent using nonthermal plasma-based AOPs: The roles of free radicals and molecular oxidants. Water Res. 2023, 235, 119881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Pan, S.; Hu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, W.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Han, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, T. Persulfate activated by non-thermal plasma for organic pollutants degradation: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 470, 144094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Wang, H.; Huang, Y.; Ma, Y. Analysis of influencing parameters and reactive substance for enrofloxacin degradation in a dielectric barrier discharge plasma/peroxydisulfate system. Environ. Eng. Res. 2024, 29, 230717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Xu, Y.; Shi, H.; Yang, X. Enhanced activation of persulfate by magnetic NiFe2O4@CuO coupled with ultrasonic for degradation of oxytetracycline: Activation mechanism and degradation pathway. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 652, 159373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Köpke, J.; Akay, C.; Kümmel, S.; Imfeld, G. Sulfamethoxazole Transformation by Heat-Activated Persulfate: Linking Transformation Products Patterns with Carbon and Nitrogen Isotope Fractionation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 5704–5714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabizadeh, A.; Abdipour, H.; Mansoorian, H.J. A new approach for the elimination of Rhodamine B dye using a combination of activated persulfate and dithionite in the presence of magnetic fields. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2025, 209, 110160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlad, I.E.; Anghel, S.D. Time stability of water activated by different on-liquid atmospheric pressure plasmas. J. Electrostat. 2017, 87, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Guo, H.; Puyang, C.; Han, J.; Li, Y.; Ruan, Y. Mechanism and process of sulfamethoxazole decomposition with persulfate activated by pulse dielectric barrier discharge plasma. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 287, 120540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzar, A.; Goutomo, B.T.; Nam, K.; Kim, I.K. Efficient removal of tetracycline antibiotic by nonthermal plasma-catalysis combination process. Environ. Eng. Res. 2025, 30, 240254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzar, A.; Goutomo, B.T.; Nam, K.; Kim, I.K. Enhanced removal of malachite green from wastewater using nonthermal plasma gliding arc discharge combined with ferrate oxidation. Desalin. Water Treat. 2024, 320, 100743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Huang, Q. Dielectric barrier discharge plasma activates persulfate to degrade norfloxacin: Mechanism and degradation pathways. Plasma Med. 2018, 8, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Chi, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Tan, M.; Li, C.; Du, H.; Hao, D.; Zhu, H.; Wang, Q.; et al. Synergistic electric fields induced by unilateral doping modulation for enhanced organic pollutant degradation and sterilization. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2025, 692, 162711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wu, H.; Fan, J.; Fang, Z.; Lin, S. Activated persulfate by DBD plasma and activated carbon for the degradation of acid orange II. Plasma Sci. Technol. 2020, 22, 034009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Wang, S.; Xu, H.; Huang, Q. Degradation of tetracycline by atmospheric-pressure non-thermal plasma: Enhanced performance, degradation mechanism, and toxicity evaluation. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 812, 152455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Yuan, D.; Rao, Y.; Li, N.; Qi, J.; Cheng, T.; Sun, Z.; Gu, J.; Huang, H. Persulfate activation in gas phase surface discharge plasma for synergetic removal of antibiotic in water. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 337, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KyereYeboah, K.; Qiao, X.C. Non-thermal plasma activated peroxide and percarbonate for tetracycline and oxytetracycline degradation: Synergistic performance, degradation pathways, and toxicity evaluation. Chemosphere 2023, 336, 139246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Qu, G.; Wang, T.; Deng, F.; Liang, D. Removal of tetracycline antibiotics from wastewater by pulsed corona discharge plasma coupled with natural soil particles. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 346, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Cai, W. Coupling of heterogeneous advanced oxidation processes and photocatalysis in efficient degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride by Fe-based MOFs: Synergistic effect and degradation pathway. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 369, 745–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrocas, B.T.; Fernandes, S.M.; Alcobia, T.; Lourenço, M.C.; Oliveira, M.C.; Marques, A.C. Optimization of TiO2 loaded sol-gel derived MICROSCAFS® for enhanced minocycline removal from water and real wastewater. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2025, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ouzar, A.; Goutomo, B.T.; Lee, K.-M.; Kim, I.-K. Enhanced Degradation of Different Tetracyclines by Nonthermal Plasma and Activated Persulfate: Insights into Synergistic Effects and Degradation Mechanism. Separations 2025, 12, 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12080222
Ouzar A, Goutomo BT, Lee K-M, Kim I-K. Enhanced Degradation of Different Tetracyclines by Nonthermal Plasma and Activated Persulfate: Insights into Synergistic Effects and Degradation Mechanism. Separations. 2025; 12(8):222. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12080222
Chicago/Turabian StyleOuzar, Amina, Bimo Tri Goutomo, Kyung-Min Lee, and Il-Kyu Kim. 2025. "Enhanced Degradation of Different Tetracyclines by Nonthermal Plasma and Activated Persulfate: Insights into Synergistic Effects and Degradation Mechanism" Separations 12, no. 8: 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12080222
APA StyleOuzar, A., Goutomo, B. T., Lee, K.-M., & Kim, I.-K. (2025). Enhanced Degradation of Different Tetracyclines by Nonthermal Plasma and Activated Persulfate: Insights into Synergistic Effects and Degradation Mechanism. Separations, 12(8), 222. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12080222







