Abstract
Sulfides should be removed before the recovery of cassiterite from tin-rich minerals due to their similarity in flotation properties. However, the traditional methods used have low selectivity. Therefore, moderately thermophilic microorganisms were used to desulfurize tin ore in this study, and the success of the microbial community was investigated. The bio-desulfurization rate reached 90% on the 10th day using the mixed culture of Leptospirillum ferriphilum (L. ferriphilum), Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans (S. thermosulfidooxidans), and Acidithiobacillus caldus (A. caldus), while the pure culture needs at least 14 days. The results of X-ray Diffraction (XRD) and Inductively Coupled Plasma show that the sulfides were nearly fully solubilized. XRD results showed no pyrite in the residue, indicating that pyrite was almost fully removed while cassiterite was enriched compared with the original minerals. The high-throughput sequencing analysis showed that S. thermosulfidooxidans were the predominant species during the early bioleaching period, and L. ferriphilum were the predominant species in the following period. A. caldus is consistently detected and accounts for 30–50% of the different growth stages. This study supplied a potentially practical application for the desulfurization in tin ore.
1. Introduction
With the rapid development of industry and urbanization, the demand for tin has greatly increased, leading to its significant consumption. However, it is reported that global tin deposits—defined as known reserves that are economically mineable under current conditions—have a static lifetime of 22 years [1]. This is relatively short compared to other metals. On the other hand, the high content of sulfide minerals in most tin ores significantly decreases the metal recovery during the flotation process [2]. The close specific gravity of iron sulfides (e.g., pyrite with a density of 4.9–5.2 and pyrrhotite with a density of 4.6–4.7) to cassiterite severely interferes with the gravity separation process, resulting in poor separation performance. Therefore, effectively removing sulfides before cassiterite gravity separation to mitigate their adverse effects and comprehensively recover valuable sulfides is a key challenge and focus for the efficient development of these primary tin ores [3]. Consequently, removing sulfide ores before the recovery of tin ores is considered an essential pretreatment method. The most effective traditional method to remove sulfide ores is through flotation. Researchers used different flotation reagents to separate tin ore from other iron sulfides [4]. However, these methods have low or insufficient selectivity which causes cassiterite to decrease or become low-grade [4]. The presence of iron sulfides, especially pyrrhotite, makes it more difficult to separate and recover copper and zinc sulfides. This is due to their varying properties, tendency to oxidize, and ability to form slimes, which disrupt the flotation process. Addressing these challenges is essential to improving sulfide removal and achieving selective recovery [5].
Bio-desulfurization has attracted widespread attention because of its environmental friendliness, low costs, and high efficiency. Xu et al. reported that the cost of bio-desulfurization from coal is about CNY 40–50 (Chinese Yuan)/ton [6]. It is more market-competitive than the traditional ways of desulfurization, such as pre-combustion desulfurization. The bio-desulfurization of chemically treated coal using the bacterial strain IQMJ-5 coated with iron oxide (Fe3O4) can remove approximately 61% of organic sulfur and 86.57% of total sulfur from coal [7]. The main sulfides found in cassiterite ores include pyrite [8], chalcopyrite [9], etc. However, there are almost no studies related to removing pyrite from tin-rich ores. The organisms used for bio-desulfurization are the bio-hydrometallurgical microorganisms from coal or other minerals such as A. ferrooxidans, A.thiooxidans, and L. ferriphilum [10]. Therefore, the bio-desulfurization of tin ores is promising. Nevertheless, there is almost no research related to the bio-desulfurization of tin-rich ores.
Based on their growth temperature range, bacteria used in bioleaching are classified into three types. These include extreme thermophilic bacteria [11,12] (optimal growth temperature > 60 °C), moderately thermophilic bacteria (optimal growth temperature between 40 and 60 °C), and mesophilic bacteria (optimal growth temperature between 20 and 40 °C) [13]. Moderate thermophiles have certain advantages compared with the other temperature bacteria. They can tolerate higher pulp density and metal ion concentration compared to extreme thermophiles [14]. Compared with mesophiles, they have higher enzyme activity and leaching rates [15]. Therefore, moderately thermophilic bacteria were selected to remove sulfide minerals from tin-rich ores. Liu et al. used moderate thermophiles to bioleach pyrite and achieved pyrite leaching rates of up to 91.14 % [16]. Vardanyan et al., using Leptospirillum ferriphilum CC to bioleach pyrite, extracted 91.4% of iron [17]. The mixed culture shows a higher bioleaching rate than pure culture, showing different dominant strains during diverse cultures [17]. Thus, to improve the bioleaching rate, it is necessary to determine the success of the microbial community.
In this study, tin ore was desulfurized by a defined consortium that consisted of typical moderate thermophiles. The success of microbial communities during the process was analyzed by high-throughput sequencing. The pyrite removal rate was determined by Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP). After bioleaching, the mineral residue was analyzed by a Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) and X-ray Diffraction (XRD). This study aims to demonstrate the potential of bio-desulfurization of tin ore in industrial applications through laboratory-scale investigations.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Minerals
The cassiterite–polymetallic sulfide minerals used in this study were from Myanmar. The material was crushed and sieved to obtain a size fraction < 1 mm. The analysis of minerals was conducted using X-ray Diffraction (XRD). The procedures were as follows: The wavelength and step size were 0.15406 nm, and the operating conditions were 45 kV and 25 °C. The step time was 0.004 s and 28.5 s. The samples were scanned at 5–80 °C. The elemental analysis and semi-quantitative determination of minerals were carried out using the semi-quantitative method of X-ray Fluorescence (XRF).
2.2. Bacterial Strains and Cultivation Conditions
S. thermosulfidooxidans, A. caldus, and L. ferriphilum were selected from an acid mine drainage and were stored in the Key Laboratory of Biohydrometallurgy of Ministry of Education, Central South University. This medium was modified by an iron-free 9 K medium and consisted of the following compounds: (NH4)2SO4 3.0 g/L, Na2SO4 2.1 g/L, MgSO4·7H2O 0.5 g/L, K2HPO4 0.05 g/L, KCl 0.1 g/L, and Ca (NO3)2 0.01 g/L [18]. Also, 10 % tin-rich minerals were added into a 150 mL medium, and the pH was adjusted to 2.0.
2.3. Bioleaching Experiments
Bioleaching experiments were performed with a 10% pulp density, inoculated with L. ferriphilum, S. thermosulfidooxidans, and A. caldus by a mixed culture and pure culture suspension at 10% v/v. The percentage of the three strains in diverse cultures was 1:1:1. The cells at the mid-logarithmic phase were obtained by centrifuging at 10,000× g for 10 min. Then, they were washed twice with sterilized acidified water (pH 2.0) and resuspended in the medium. The initial bacterial population in the inoculation was 2 × 107 cells/mL. The tin ore was autoclaved at 115 °C for 30 min. Flasks (5 L) were incubated at 45 °C and shaken at 170 rpm. All experiments were carried out in triplicate.
The total iron concentrations were determined every two days by Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) [18]. The percentage of bio-desulfurization was defined as the concentration of the total iron divided by the value of the total concentration of iron in tin ore (tin ore was digested with aqua regia). The pH and reduction–oxidation potential (ORP) were determined every two days [12]. The pH value was measured with a PHS-3E acid meter (LEICI, Shanghai, China), and the ORP (vs. Ag/AgCl) value was measured with a platinum electrode as a reference. Bacterial populations in the liquid phase were counted with a blood cell counting chamber under a CX31 optical microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan).
2.4. EPS Extraction and Measurement
The cells were collected after 4-, 8-, 12-, and 20-day incubation. Each 200 mL culture was collected by centrifuging at 10,000× g, 4 °C for 20 min, and resuspended the cell pellets with 15 mL Milli-Q water and 1 g of glass beads. Next, the mixture was vortexed for 15 min at 3000 rpm, the solution was centrifuged at 10,000× g, 4 °C for 15 min, and the supernatant was collected.
The concentration of EPS was detected following our previous work [19,20]. The concentration of extracellular polysaccharides was measured using the phenol sulfuric acid method. Protein contents were detected with a BCA kit (Elabsience, Shanghai, China). eDNA was quantified by a NanoDrop ND-1000 spectrophotometer (NanoDrop Technologies, Wilmington, DC, USA). The activity of glucose-6-phosphate-dehydrogenase (G6PDH) was measured, following the product instructions for calculating cell lysis rate.
2.5. Community Structure Analysis of the Mixed Culture
2.5.1. DNA Extraction
The DNA was extracted from a 100 mL sample of the stirred tank reactor by centrifugation at 10,000× g for 15 min. Genomic DNA was prepared using the EZ-10 spin column genomic DNA isolation kit from Bio Basic Inc. (Changsha, China), according to the manufacturer’s instructions for bacterial DNA extraction [21].
2.5.2. Primers and PCR Amplification for High-Throughput Sequencing and Calculation of Cell Number of Three Strains
16S rRNA gene V4 variable-region were amplified using universal primers 27F and 1492R [22]. PCR amplification was performed using Taq DNA polymerase, and samples were subjected to 30 cycles of 45 s of denaturation at 95 °C, 45 s of annealing at 55 °C, and 2 min of elongation at 72 °C in a Mastercycler Personal of Eppendorf Model (Hamburg, Germany). Amplification products were analyzed by electrophoresis on a 0.9% agarose gel and stained with ethidium bromide (EB). The DNA was sequenced by Illumina HiSeq2000 (Major, China). The cell density was calculated after high-throughput sequencing. The total cell density was calculated by hemocytometer under the microscope.
3. Results
S. thermosulfidooxidans, L. ferriphilum, and A. caldus are the typical moderately thermophilic bacteria. They were used for the bio-desulfurization of tin ore in this study. This indicates that a mixed culture of S. thermosulfidooxidans, L. ferriphilum, and A. caldus can enhance the sulfide mineral removal compared with the pure culture.
3.1. The Bio-Desulfurization of Tin Ore by the Moderately Thermophilic Bacteria
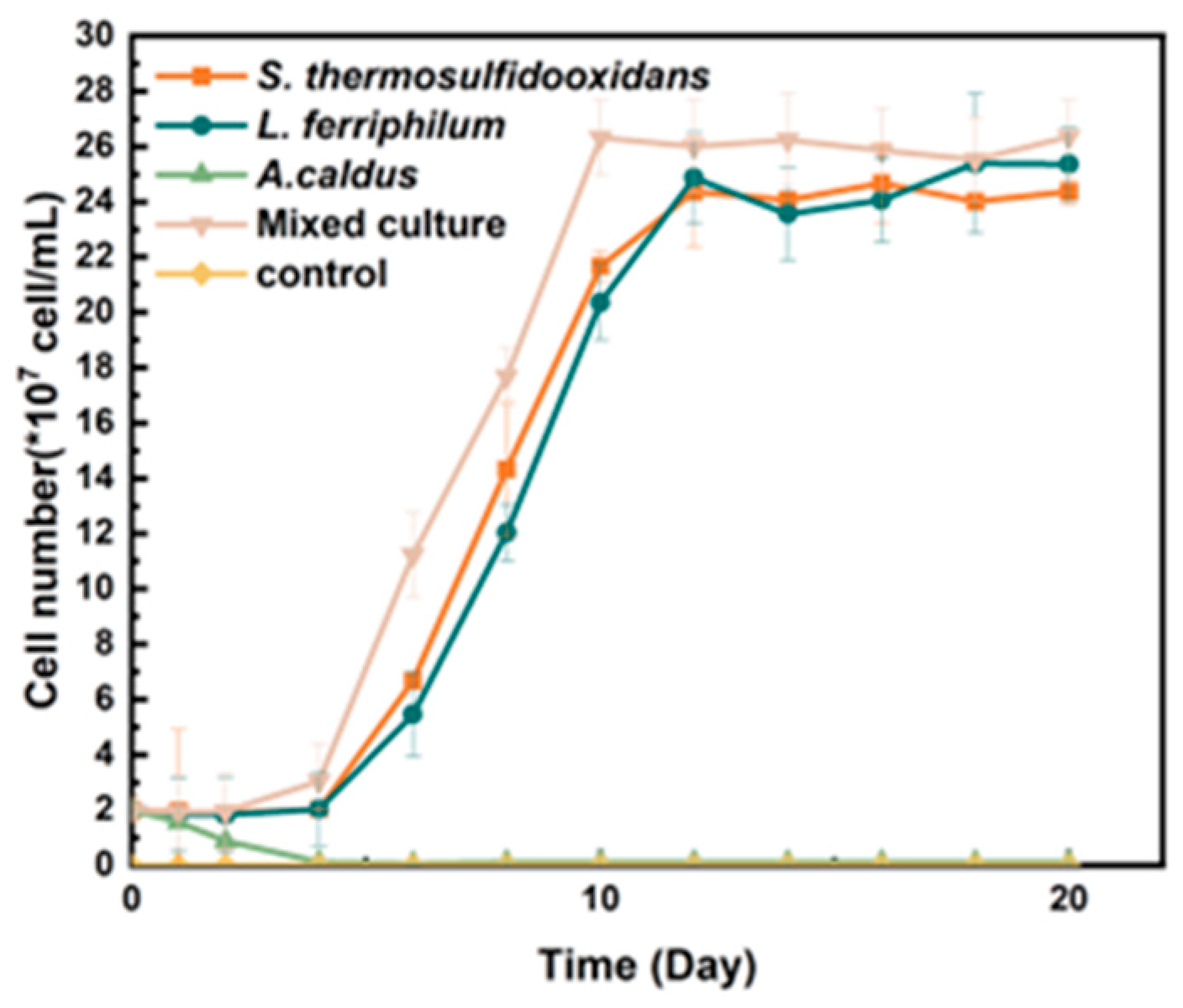
Mixed and pure cultures were used for the bio-desulfurization of tin ore, respectively. It was shown in Figure 1 that the diverse culture could achieve the maximum cell density on the 8th day, which was 2.6 × 108 cells/mL. In the pure culture, the cell density of S. thermosulfidooxidans and L. ferriphilum could reach 2.38 × 108 cells/mL and 2.41 × 108 cells/mL on the 12th day, respectively. However, A. caldus showed minimal growth in the bio-desulfurization system.
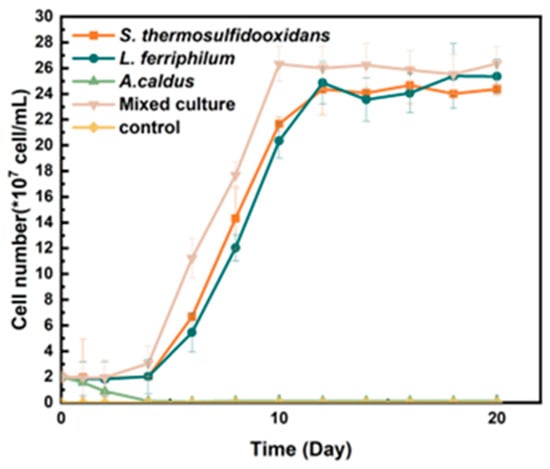
Figure 1.
Growth curve of moderately thermophilic bacteria used for bio-desulfurezation of tin ore.
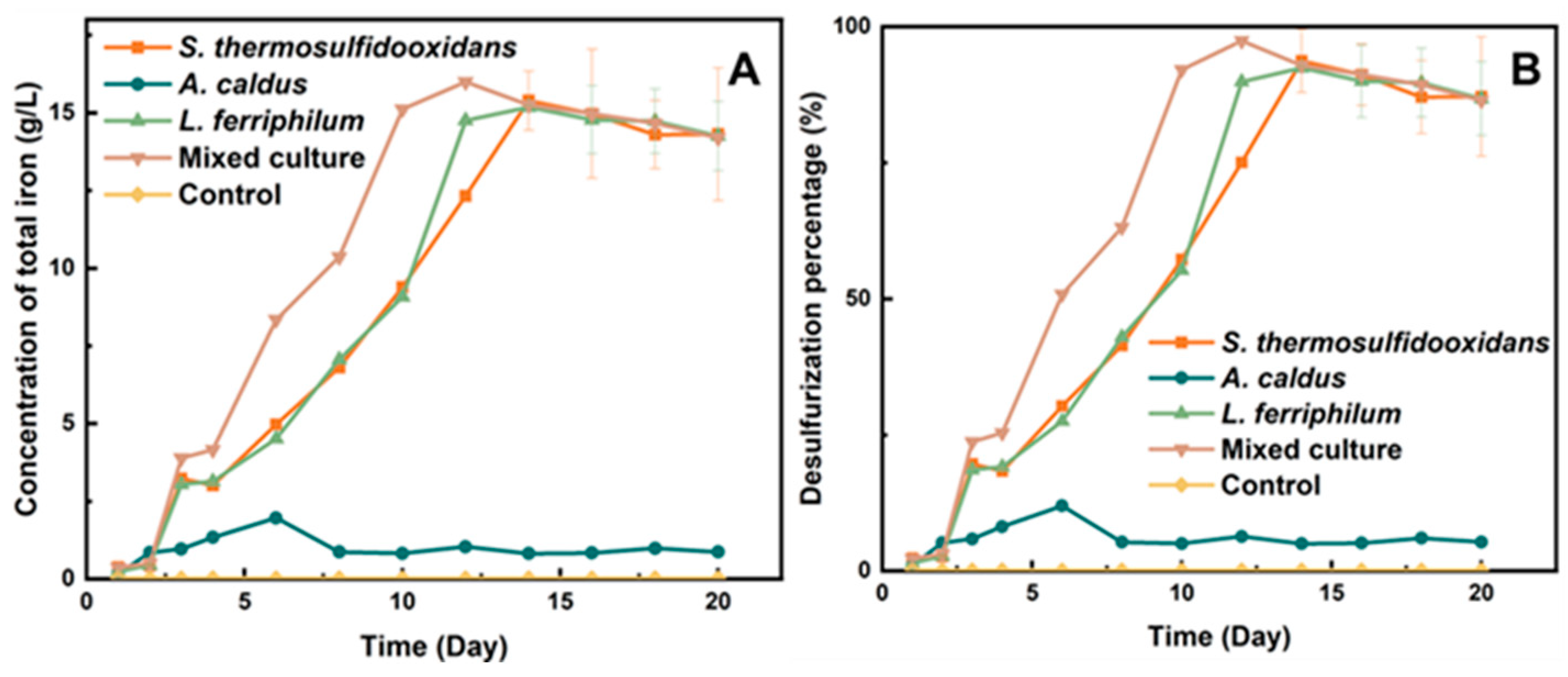
As shown in Figure 2A, the concentration of the total iron ions (both Fe3+ and Fe2+) in the system by the mixed culture reached the maximum value (15.98 g/L) on the 12th day (the percentage of desulfurization achieved over 90%). However, the pure culture of L. ferriphilum and S. thermosulfidooxidans took 14 days to achieve the same percent of desulfurization.
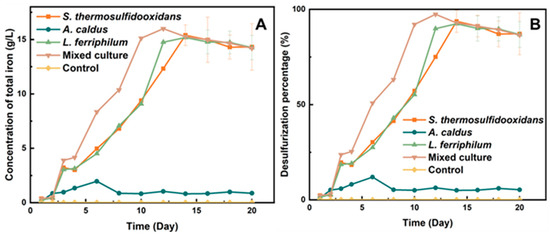
Figure 2.
Total concentration of iron (A) and percentage of desulfurization of tin ore (B) by moderately thermophilic bacteria.
3.2. Changes in pH and Oxidation–Reduction Potential During Bio-Desulfurization of Tin-Rich Ore
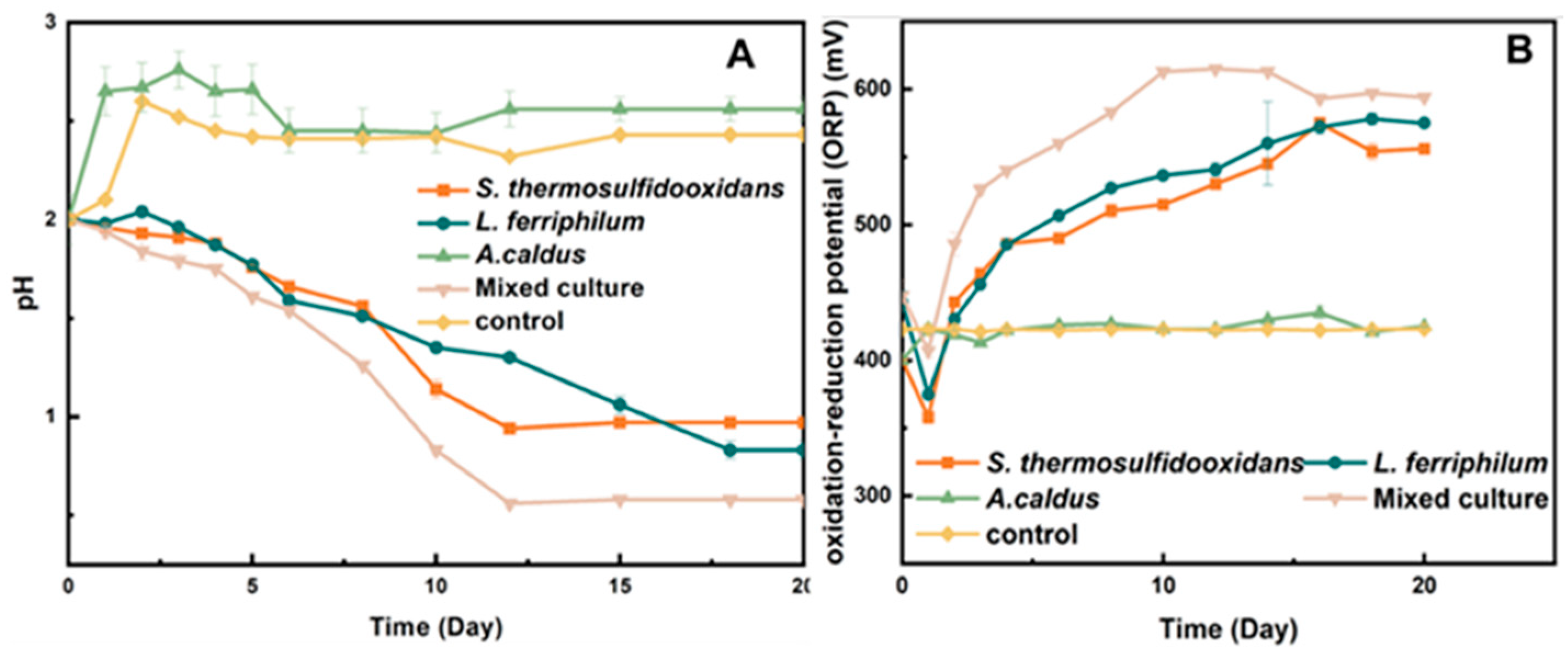
The bio-oxidation of pyrite was a process of sulfuric acid production. During the bio-desulfurization process, the pH values decreased on a large scale. It can be seen in Figure 3A that the pH value achieved the minimum value on the 16th day by the mixed culture, and it was consistently lower than that of the pure culture (Figure 3A). The pH values of S. thermosulfidooxidans and L. ferriphilum reached 0.93 and 0.83 on the 18th day, respectively. As shown in Figure 3B, the oxidation–reduction potential (ORP) of the mixed culture reached 615 mV on the 10th day, while the pure culture reached the maximum value (575 mV) at least 16 days. When the ions in the bioleaching system achieved balance, the ORP remained stable.
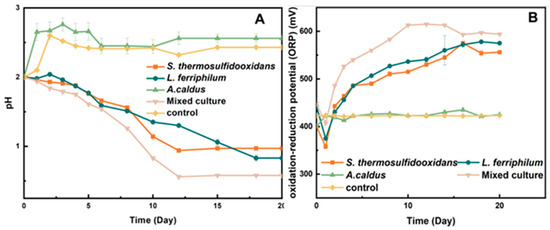
Figure 3.
pH (A) and ORP (B) during bio-desulfurization of tin ore by pure culture and mixed culture.
3.3. SEM and XRD Analysis of Residues After Desulfurization of Tin Ore
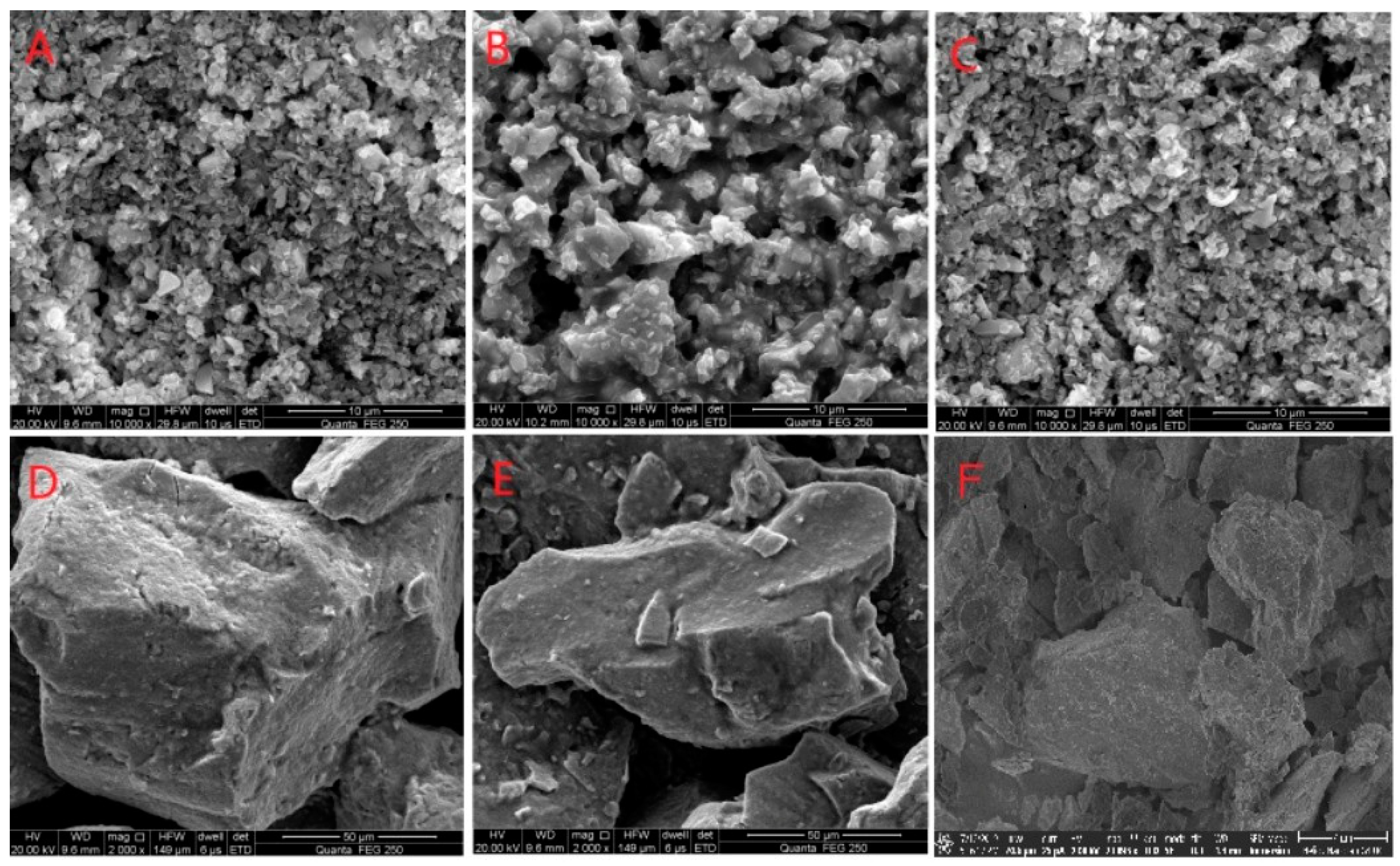
SEM was used to observe the tin ore after bio-desulfurization. It is shown in Figure 4 that during bio-desulfurization by the mixed culture, the pure culture of S. thermosulfidooxidans, or L. ferriphilum, the mineral body and lattice were severely damaged, and the mineral particle size decreased on a large scale. The residues were crushed and porous. However, the incubation of tin-rich ore with A. caldus did not significantly alter the mineral’s shape or particle size.
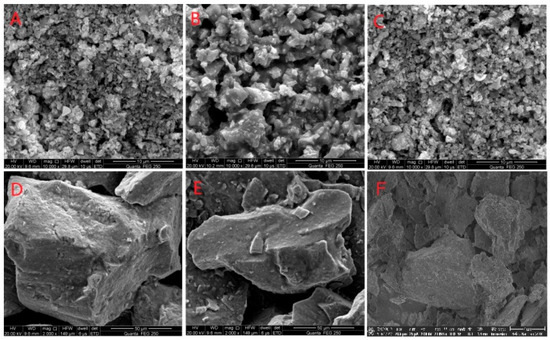
Figure 4.
SEM Analysis of desulfurization of tin ore by pure culture and mixed culture. ((A): Mixed culture; (B): L. ferriphilum; (C): S. thermosulfidooxidans; (D): A. caldus; (E): abiotic control; (F): the original ore).
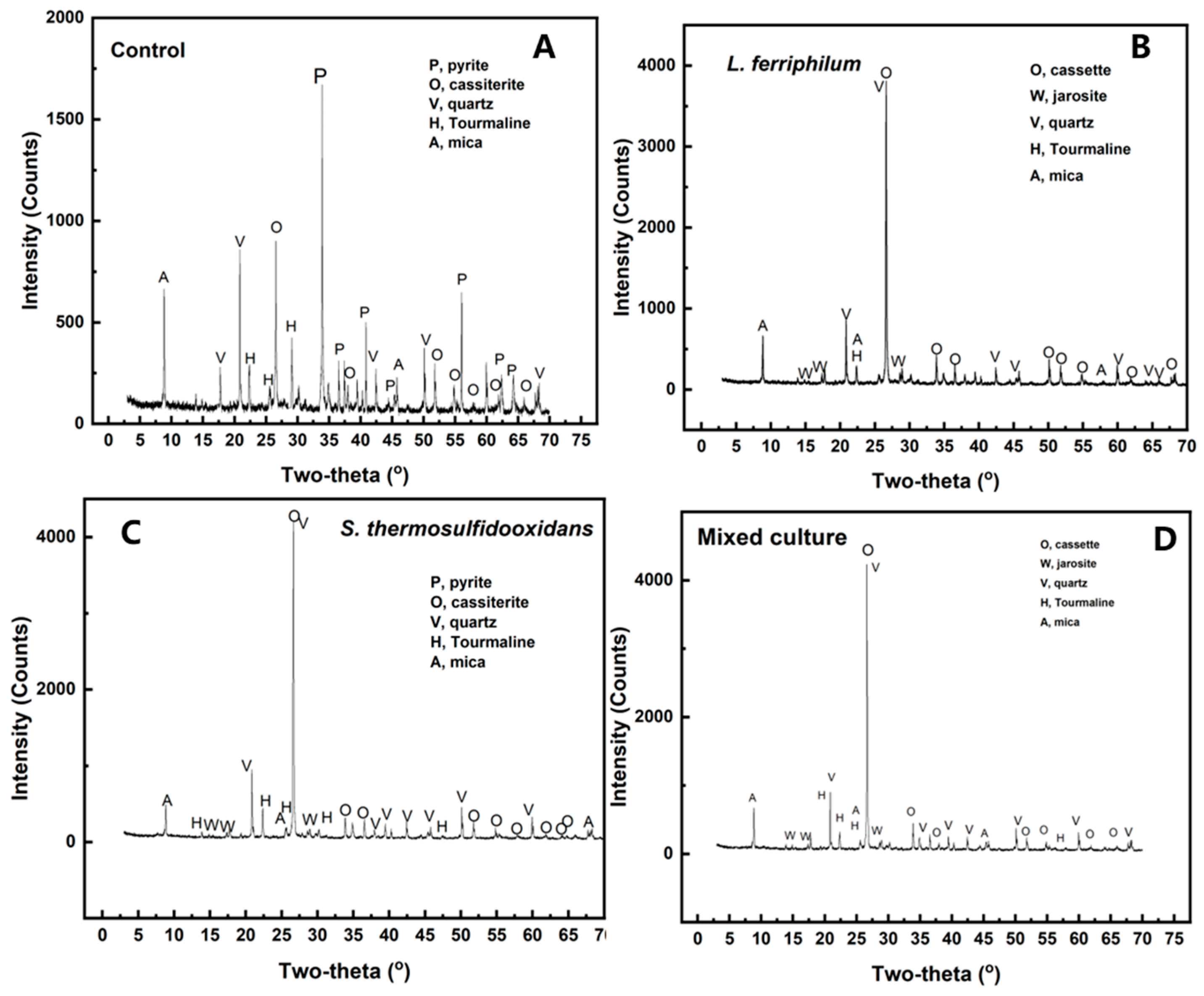
The residues after desulfurization and the original tin ores were analyzed by XRD. As shown in Figure 5 and Table 1, there was 44.76% pyrite in the original tin ores, while it cannot be detected after bioleaching. However, residues showed that the jarosite (KFe3(SO4)2(OH)6) formed on the surface of minerals was mainly sulfide. Pyrite was almost completely leached out by the mixed culture, and jarosite (5.74%) produced lower than that in the pure culture (over 6.43%). As pyrite bioleached, the percentage of the other phases increased. This showed an increase in cassiterite concentration during the desulfurization of tin ore. The main composition of cassiterite was SnO2, which cannot be dissolved in diluted sulfuric acid.
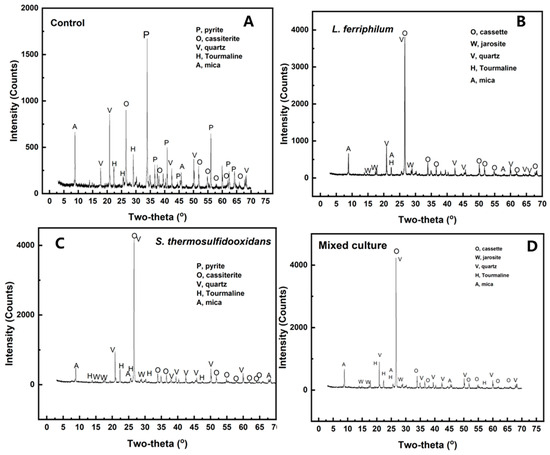
Figure 5.
XRD analysis of tin ore after bioleaching by control (A), L. ferriphilum (B), S. thermosulfidooxidans (C), and mixed culture (D).

Table 1.
Phase analysis from XRD of control, S. thermosulfidooxidans, L. ferriphilum, and mixed culture.
To analyze the elemental composition of the residues, XRF analysis was conducted, with the results presented in Table 2. After incubation with bacteria, the concentrations of sulfur (S) and iron (Fe) decreased to approximately 2% and 0.005–3.269%, respectively. Meanwhile, the concentration of tin (Sn) increased from 3.66% to 4.781% in the mixed culture system. Compared to the pure cultures of S. thermosulfidooxidans and L. ferriphilum, the mixed culture achieved a nearly complete leaching of iron. As mentioned before, the iron originated from pyrite. Therefore, the mixed culture demonstrated higher efficiency in desulfurization than the pure cultures.

Table 2.
Elements analysis from XRF of control, S. thermosulfidooxidans, L. ferriphilum, and mixed culture.
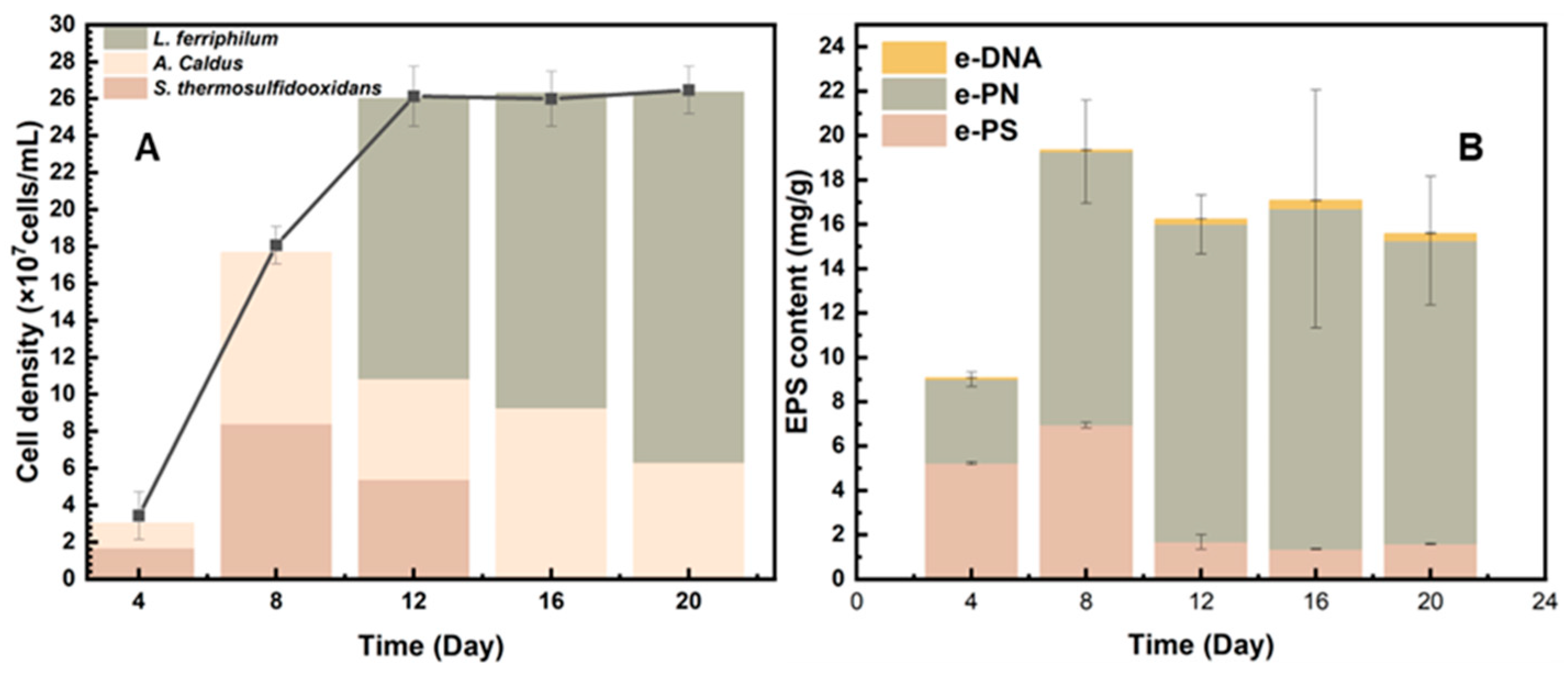
3.4. Community Success and EPS Changes in Mixed Culture During Bio-Desulfurization of Tin Ore
The community structure was analyzed to demonstrate why the mixed culture behaved better than the pure culture during the bio-desulfurization of tin ore. As shown in Figure 6A, the community success of mixed culture during the bio-desulfurization of tin ore at the fourth, eighth, twelfth, sixteenth, and twentieth days was characterized by high-throughput sequencing. As shown in Figure 6A, during the early period of desulfurization, S. thermosulfidooxidans and A. caldus are the dominant species. They account for 55.75% and 42.94%, respectively, while almost no L. ferriphilum existed in the system. The reason for S.thermosulfidooxidans and A.caldus being the dominant species during the early phase might be attributed to the high pH values (Figure 2A). In the early phase, S. thermosulfidooxidans could grow with Fe2+ and sulfides. A. caldus was the main contributor in consuming sulfides. In addition, S. thermosulfidooxidans and A.caldus thrive better within this range (1.6 to 2.0). The pH range between 1.4 and 1.8 is optimal for L. ferriphilum, which explains why L. ferriphilum was hardly detected [10].
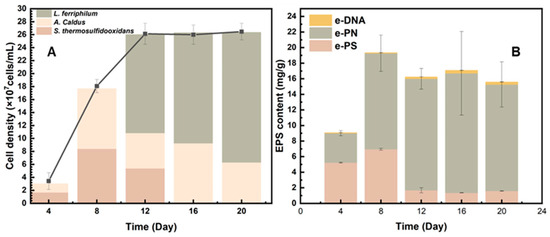
Figure 6.
Community success (A) and EPS contents (B) of the mixed culture during the bio-desulfurization of tin ore on the fourth, eighth, twelfth, sixteenth, and twentieth day.
EPS was also measured as shown in Figure 6B. Extracellular proteins (e-PN) were the major components of EPS during the whole bioleaching process. Extracellular polysaccharides (e-PS) produce a large ratio during the early bioleaching period, but it decreased after 12 days. The low concentration of e-DNA indicates that the result of EPS extraction is significant.
4. Discussion
S. thermosulfidooxidans, L. ferriphilum, and A. caldus are the typical moderately thermophilic bacteria. They are commonly used for bioleaching. However, the knowledge gap is caused by a lack of exploration of the bio-desulfurization of tin ore using moderately thermophilic bacteria. Thus, the results obtained in our study provide an alternative approach to the desulfurization of tin ore.
4.1. Mixed Culture of the Moderately Thermophilic Bacteria Enhanced the Bio-Desulfuriztion of Tin Ore
As shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2, the mixed culture of S. thermosulfidooxidans, L. ferriphilum and A. caldus can improve the bio-desulfurization rate of tin ore. Dana et al. reported that S. thermosulfidooxidans and L. ferriphilum are iron oxidation bacteria and pyrite was bioleached [23]. However, A. caldus is a sulfur-oxidizing bacterium and cannot directly biodegrade pyrite [24]. It indicated that pyrite was initially bioleached by iron-oxidizers, and when the sulfur of pyrite is soluble or becomes S0 on the surface of the minerals, A. caldus can biodegrade them [24]. It indicated that the mixed culture was more easily adapted to the bio-desulfurization environment than the pure culture. In addition, irons dissolved in a medium by L. ferriphilum and S. thermosulfidooxidans can promote the growth of A.caldus [25]. It also demonstrated that bio-desulfurization of the tin-rich ore is a promising method for removing pyrite.
4.2. Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of the Desulfurization System
A higher concentration of H⁺ ions was produced by the mixed culture compared to the pure culture. This indicates that A. caldus in the mixed culture metabolized the soluble thiosulfate and sulfur to sulfuric acid, which leads to a drop in pH value [26]. During the bioleaching of tin ores with the pure culture, the pH values of S. thermosulfidooxidans were lower than that of L. ferriphilum because it could metabolize both iron and sulfides, resulting in the production of more H⁺ ions [27]. ORP is associated with the concentration of iron and H+. Higher concentrations of iron ions and H+ in the system increase the ORP value. The concentration of iron ions in the mixed culture was higher than in the pure culture and the pH value was lower than that of the pure culture. Therefore, the ORP value of the mixed culture is higher than that of the pure culture.
Compared to the pure culture, there was less jarosite produced in the mixed culture system. It is reported that the low pH values are beneficial to decrease the content of jarosite in residues [28]. But a higher concentration of Fe3+ and loss of Fe2+ enhanced the formation of jarosite [29]. During pyrite bioleaching, the percentage of other phases increased, showing concentrated cassiterite during the desulfurization of tin ore. The main composition of cassiterite was SnO2, which cannot be dissolved in diluted sulfuric acid [30]. The formation of jarosite on the surface of the residue may affect the flotation of tin ore; therefore, whether jarosite affects the subsequent flotation needs to be verified by flotation, which will also be a test conducted in the future. It is reported that many collectors are efficient in recovering the particle size 6~38 μm. The flotation efficiency decreases the particle sizes by >38 μm and <6 μm [8]. However, the characteristics of tin ores are lower tin-grade, finer grain size, and more complicated mineralogy [8]. The residues after the bio-desufurization of tin ores also showed that cassiterite became finer grain size. Thus, to improve the flotation efficiency and tin-grade, using the traditional flotation method to remove most of the sulfide minerals to obtain cassiterite, bio-desulfurizing the cassiterite in the next step may be a good choice. The solution after bioleaching may be used for recovering lithium from the cathode material of waste lithium iron phosphate batteries, bioleached minerals like chalcopyrite, or other precious metals [31,32,33].
4.3. Mechanism of Mixed Culture Enhancing Bio-Desulfurization of Tin-Rich Ore
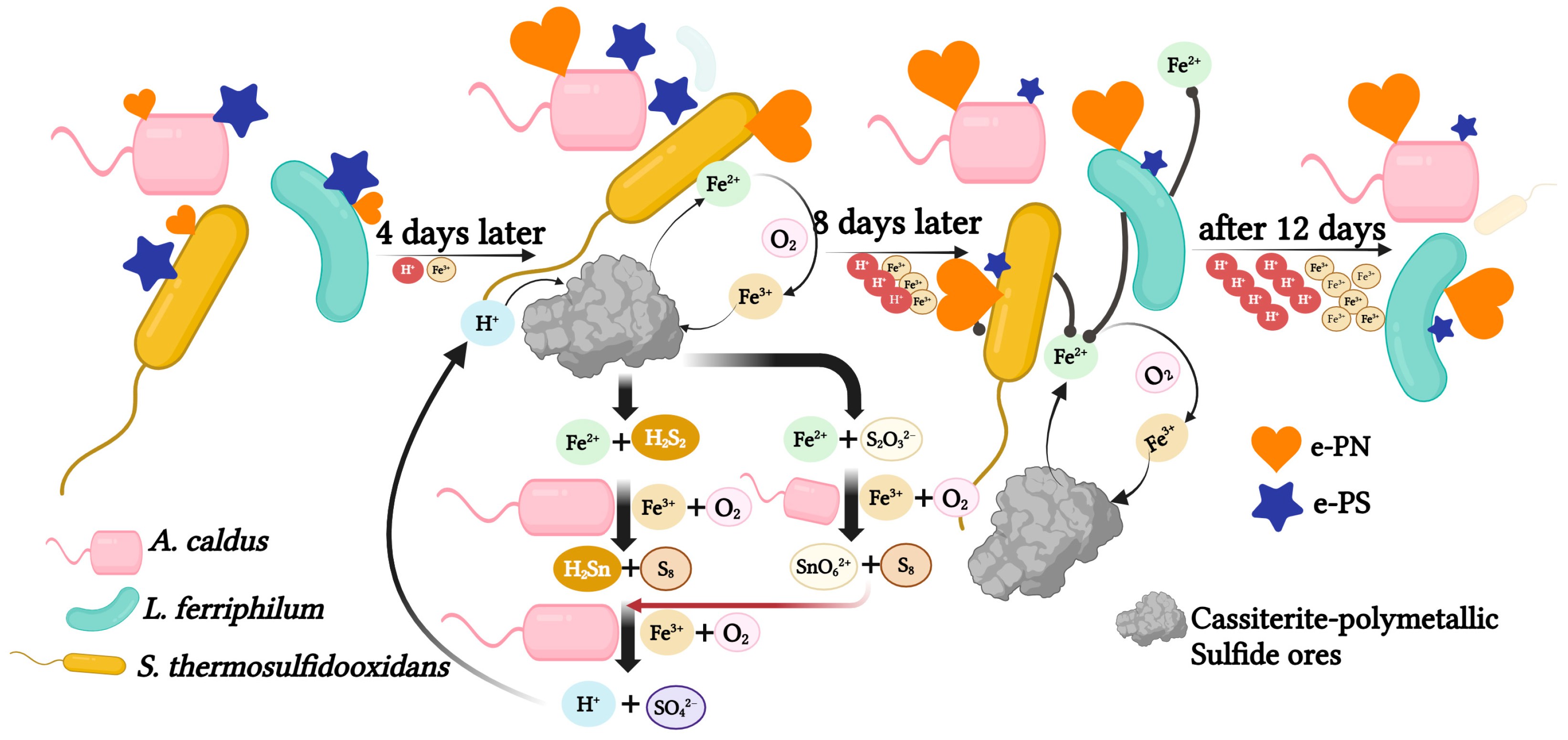
A mixed culture can enhance the bio-desulfurization of tin-rich ore due to the cooperation of three strains. S. thermosulfidooxidans could grow with Fe2+ and sulfides. As shown in Figure 7 A. caldus was the main contributor in consuming sulfides. In addition, S. thermosulfidooxidans and A. caldus thrive better within this range (1.6 to 2.0). While the pH range between 1.4 and 1.8 is optimal for L. ferriphilum. It was proven that a higher concentration of ferrous ions in the solution is conducive to the growth of L. ferriphilum [30]. In addition, the previous studies suggested that the cell numbers of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria often exceed iron-oxidizing strains [34], which may explain the lower biomass of L. ferriphilum. As the bioleaching went on, L. ferriphilum eventually became the dominant species (76.08%). It suggested that the tolerance of L. ferriphilum to low pH and high concentrations of Fe3+ is much better compared with S. thermosulfidooxidans, which is consistent with previous reports [30]. In addition, the accumulation of organic compounds in the later stage is beneficial to L. ferriphilum [33]. Moreover, A. caldus was consistently detected in the system as A. caldus is a sulfur-oxidizing bacterium with acid-producing solid ability. The low pH environment generated inhibits the formation of jarosite [35]. In addition, S. thermosulfidooxidans and L. ferriphilum could grow in a co-culture with A. caldus, which researchers have confirmed [36,37]. This defined consortium can strengthen strain communication and cooperation, which results in more practical applications in bio-desulfurization processes. It indicated that increasing the biomass of S. thermosulfidooxidans and A. caldus during the early bioleaching process would be beneficial to the bio-desulfurization of tin ore. Increasing the biomass of L. ferriphilum during the stable period could improve the desulfurization efficiency.
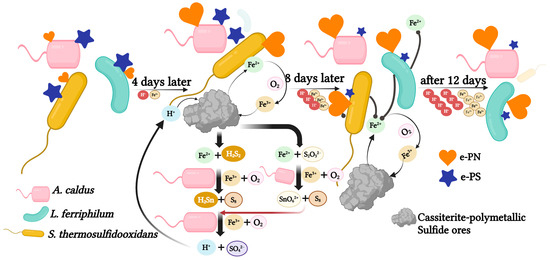
Figure 7.
The mechanism of the mixed culture during the desulfurization of tin ore. The ratio of hearts and stars indicates the content of extracellular proteins (e-PN) and extracellular polysaccharides (e-PS), respectively. The pyrite from tin-polymetallic sulfide ores was leached with the H+, resulting in the formation of Fe2+, H2S2 and S2O32−. After 4 days of incubation, pH and Fe2+ concentrations are favorable for the growth of S. thermosulfidooxidans and A. caldus growth. As the concentration of H+ and Fe3+ increases, the cell density of L. ferriphilum increases, eventually becoming dominant. A. caldus removes elemental sulfur S0 and other sulfides enhancing the bioleaching of pyrite, therefore it persists throughout the bioleaching system. In addition, the content of e-PN increased as the concentration of H+ and Fe3+ increased while the content of e-PS decreased.
In addition, cells produced more e-PNs to detoxify Fe3+ and extremely acidic conditions [20,38]. Moreover, e-PNs involved in the quorum-sensing system could enhance the bioleaching efficiency and facilitate bacteria-to-bacteria movement [37,38,39]. In addition, e-PNs were also found to participate in defending against reactive oxygen species (ROS) [40]. ROS is generated by surface reactions in metal sulfides due to molecular oxygen in the solution reacting with lattice-bound iron, which harms cellular metabolic activity [40]. It is reported that e-PS and e-PNs and biofilm formation are defense ROS strategies for L. ferriphilum [10], which can explain the ratio of L. ferriphilum increased in the later bioleaching period. Furthermore, as we all know, the iron oxidation pathway in L. ferriphilum involves the electron from Fe2+ transferring from outer membrane cytochrome c (Cyt572) to periplasmic cytochrome c (Cyt579). The electrons then pass through a cbb3-type terminal oxidase, generating water using oxygen as the electron acceptor. Alternatively, the electrons can be transferred to the bc1 complex and then to NADH dehydrogenase via the quinone pool [41]. Altogether, this led to the increased production of e-PNs.
5. Conclusions
Typical moderately thermophilic bacteria were used for the bio-desulfurization for tin ore. The desulfurization efficiency of tin ore was achieved at 90% within ten days by the mixed culture, while six extra days were required to reach the same efficiency with the pure culture. The XRD analysis of residues showed that pyrite was completely leached out by the mixed culture, and the quantity of jarosite was lower than in the pure culture. Furthermore, the mixed culture-reduced jarosite led to high-efficiency bioleaching in desulfurization. Moreover, S. thermosulfidooxidans was the dominant species in the early period while the L. ferriphilum was the dominant species in the later stage instead. A. caldus was the main contributor during the whole bioleaching process. Thus, to achieve the industrial application, the flotation of cassiterite will be explored in the future, and combining traditional methods with biological desulfurization of cassiterite will be another viable option. Additionally, investigating whether the bioleaching solution can be used to leach other metals from waste or ores will be an important research direction.
Author Contributions
All the authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by M.W. Supervision, funding acquisition, and writing—review and editing were performed by Y.L. and W.Z. The first draft of the manuscript was written by M.W., and all the authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Changsha Municipal Natural Science Foundation (No. kq2402202), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51274268, 50904080, 51934009, 52274289, 52074353), National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2019YFC1803600), Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (2021JJ30855), China Scholarship Council (No. 202006370228).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| XRD | X-ray Diffraction |
| XRF | X-ray Fluorescence |
| ICP | Inductively Coupled Plasma |
| ORP | Oxide Redox Potential |
| EPS | Extracellular Polymeric Substance |
| e-PN | Extracellular Proteins |
References
- Li, H.; Qin, W.; Li, J.; Tian, Z.; Jiao, F.; Yang, C. Tracing the global tin flow network: Highly concentrated production and consumption. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 169, 105495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, B. Extraction and Separation of Tin from Tin-Bearing Secondary Resources: A Review. JOM J. Miner. Met. Mater. Soc. 2017, 69, 2364–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassine, A.-K.; Mostafa, B.; Isabelle, D. Environmental desulfurization of mine wastes using various mineral processing techniques: Recent advances and opportunities. Miner. Eng. 2021, 174, 107225. [Google Scholar]
- Matveeva, T.N.; Chanturiya, V.A.; Getman, V.V.; Gromova, N.K.; Minaev, V.A. The Effect of Complexing Reagents on Flotation of Sulfide Minerals and Cassiterite from Tin-Sulfide Tailings. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. Rev. 2020, 43, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunin, I.Z.; Khabarova, I.A.; Ryazantseva, M.V. The Effect of Low-Temperature Atmospheric Discharge Plasma on the Physical–Chemical and Technological Properties of Iron Sulfide Minerals; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Koyunoğlu, C.; Karaca, H. Microbial desulphurisation of coal: A review. Int. J. Sustain. Energy 2023, 42, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, J.; Ali, M.I.; Khan Achakzai, J.; Jamal, A.; Ahmed, I.; Manan Kakar, A.; Uddin, S. Sequential Chemical and Biological Desulphurization of High Sulfur Containing Pakistani Coal. Geomicrobiol. J. 2024, 41, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angadi, S.I.; Sreenivas, T.; Jeon, H.S.; Baek, S.H.; Mishra, B.K. A review of cassiterite beneficiation fundamentals and plant practices. Miner. Eng. 2015, 70, 178–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levie, M.; Chitalu, C.; Jeanne, P.M.; Govinda, P.K.; Subramanian, S.; Hyunjung, K.; Lev, F. Experimental, benchmarks and theoretical investigations into the complexation of chalcopyrite and silica with guar gum and beneficiation of a siliceous copper ore using polyethylene oxide as a silica depressant. Miner. Eng. 2024, 216, 108874. [Google Scholar]
- Vera, M.; Schippers, A.; Sand, W. Progress in bioleaching: Fundamentals and mechanisms of microbial metal sulfide oxidation–part A. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 6933–6952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenbing, A.; Yuting, L.; Bo, M.; Chen, M.; Zeng, W.; Guanzhou, Q. Identification and Analysis of a Novel Gene Cluster Involves in Fe(2+) Oxidation in Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans ATCC 23270, a Typical Biomining Acidophile. Curr. Microbiol. 2018, 75, 818–826. [Google Scholar]
- Chenbing, A.; Zhang, Y.; Hongsheng, C.; Tianyuan, G.; Junjun, W.; Liyuan, C. Increased chalcopyrite bioleaching capabilities of extremely thermoacidophilic Metallosphaera sedula inocula by mixotrophic propagation. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 46, 1113–1127. [Google Scholar]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Huntley, J.; Fierer, N. Ultra-high-throughput microbial community analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1621–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pina, P.S.; Oliveira, V.A.; Flávio, L.S.; Cruz Leeo, V.A. Kinetics of ferrous iron oxidation by Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans. Biochem. Eng. J. 2010, 51, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leahy, M.J.; Davidson, M.R.; Schwarz, M.P. A model for heap bioleaching of chalcocite with heat balance: Mesophiles and moderate thermophiles. Hydrometallurgy 2007, 85, 24–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, X.T.; Han, Y.; Li, W.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, C.; Yu, L.; Zheng, Y. Enhanced pyrite bioleaching through the synergistic interactions between Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans and Alicyclobacillus ferrooxydans. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2025, 37, 104005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardanyan, A.; Khachatryan, A.; Castro, L.; Willscher, S.; Gaydardzhiev, S.; Zhang, R.; Vardanyan, N. Bioleaching of Sulfide Minerals by Leptospirillum ferriphilum CC from Polymetallic Mine (Armenia). Minerals 2023, 13, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rito, B.; Almeida, D.; Coimbra, C.; Diogo, V.; Romeu, F.; Rita, B.; Harald, W.; Paula, V.M. Post-measurement compressed calibration for ICP-MS-based metal quantification in mine residues bioleaching. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 16007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingwei, W.; Christel, V.; Bente, S.; Huang, Y.; Xueling, W.; Li, S.; Jiaokun, L.; Yuandong, L.; Runlan, Y.; Wolfgang, R.S.; et al. Extracellular proteins enhance Cupriavidus pauculus nickel tolerance and cell aggregate formation. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 393, 130133. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, A.; Yu, R.; Qiu, G.; Zeng, W. Insights into the EPS production and distribution of planktonic and attached Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans cells during bioleaching. Miner. Eng. 2014, 205, 108494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, C.; Yan, Z.; Hou, C.; Zeng, W. Metagenomic Insights into the Effects of Seasonal Temperature Variation on the Activities of Activated Sludge. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Saini, H.S.; Engr, S.; Sani, R.K.; Kumar, S. Bioleaching of metals from waste printed circuit boards using bacterial isolates native to abandoned gold mine. Biometals 2021, 34, 1043–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouchalová, D.; Rouchalová, K.; Čablík, V. Bioleaching of mine tailings by mesophilic: Acidithiobacillus spp., Leptospirillum ferrooxidans, and Thermophilic: Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans cultures with the addition of Ag+ additive. Minerals 2024, 14, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Li, L.L.; Zhao, S.; Chen, Y.; Yu, A.F. Bioleaching of metals from spent fluid catalytic cracking catalyst using adapted Acidithiobacillus caldus. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 125689–125701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.L.; Liao, W.Q.; Peng, T.J.; Shen, L.; Qiu, G.; Zeng, W. Biodissolution of pyrite and bornite by moderate thermophiles. J. Cent. South Univ. 2022, 29, 3630–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, X.; Gao, C.; Guan, Y.; Lin, J.; Liu, X.; Pang, X. The essential role of OmpR in Acidithiobacillus caldus adapting to the high osmolarity and its regulation on the tetrathionate-metabolic pathway. Microorganisms 2022, 11, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Shi, H.; Ding, H.; Zhang, X.; Gu, T.; Zhu, M.; Tan, W. Multi-scale analysis of nickel ion tolerance mechanism for thermophilic Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans in bioleaching. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443, 130245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vladimir, A.; Daniel, L.; José, J.G.; Fanny, B.; Ismael, M. Analysis of the Oxidation-Reduction Potential and Bacterial Population of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans during the Bioleaching Study of Sulfide Ores; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hee, S.; Dae-Weon, K.; Byung, M.; Sang, W. A Study on the Leaching and Recovery of Lithium by Reaction between Ferric Chloride Etching Solution and Waste Lithium Iron Phosphate Cathode Powder. Resour. Recycl. 2023, 32, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Zhou, H. Growth in ever-increasing acidity condition enhanced the adaptation and bioleaching ability of Leptospirillum ferriphilum. Int. Microbiol. 2022, 25, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- René, H.L.; Jorge, V.A.; Guadalupe, R.; Marcelo, G.; Luis, L. Experimental and Theoretical Analysis Accounting for Differences of Pyrite and Chalcopyrite Oxidative Behaviors for Prospective Environmental and Bioleaching Applications. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 18364–18379. [Google Scholar]
- Falco, L.; Pogliani, C.; Curutchet, G.; Donati, E. A comparison of bioleaching of covellite using pure cultures of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans or a mixed culture of Leptospirillum ferrooxidans and Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans. Hydrometallurgy 2003, 71, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panyushkina, A.E.; Tsaplina, I.A.; Kondrat’eva, T.F.; Bely, A.V.; Bulaev, A.G. Physiological and Morphological Characteristics of Acidophilic Bacteria Leptospirillum ferriphilum and Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans, Members of a Chemolithotrophic Microbial Consortium. Microbiology 2018, 87, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.X.; Lu TA, N.G.; Xia, J.L.; Chu YI, N.; Cai, L.Y.; Zhao, X.J.; Nie, Z.Y.; Liu, J.S.; Qiu, G.Z. Relationships among bioleaching performance, additional elemental sulfur, microbial population dynamics and its energy metabolism in bioleaching of chalcopyrite. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2012, 22, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladipo, B.; Ojumu, T.V. Influence of solution pH on the properties of biogenic jarosite produced from ferrous ion bio-oxidation in a bioreactor. Hydrometallurgy 2023, 221, 106144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellenberg, S.; Salas, B.; Ganji, S.; Jorquera-Román, C.; Valenzuela, M.L.; Buetti-Dinh, A.; Unelius, C.R.; Dopson, M.; Vera, M. Diffusible signal factor signaling controls bioleaching activity and niche protection in the acidophilic, mineral-oxidizing leptospirilli. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Liu, Z.; Liao, W.; Cheng, J.; Wu, X.; Qiu, G.; Shen, L. Distribution and content changes of extracellular polymeric substance and iron ions on the pyrite surface during bioleaching. J. Cent. South Univ. 2023, 30, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, L.; Zhang, R.; Muñoz, J.A.; González, F.; Blázquez, M.L.; Sand, W.; Ballester, A. Characterization of exopolymeric substances (EPS) produced by Aeromonas hydrophila under reducing conditions. Biofouling 2014, 30, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.-Y.; Liu, X.-J.; Fu, C.-A.; Gu, X.-F.; Lin, J.-Q.; Liu, X.-M.; Pang, X.; Lin, J.-Q.; Chen, L.-X. Novel Strategy for Improvement of the Bioleaching Efficiency of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans Based on the AfeIR Quorum Sensing System. Minerals 2022, 10, 236–246. [Google Scholar]
- Bellenberg, S.; Huynh, D.; Poetsch, A.; Sand, W.; Vera, M. Proteomics Reveal Enhanced Oxidative Stress Responses and Metabolic Adaptation in Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans Biofilm Cells on Pyrite. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Bingyang, T.; Yihui, B.; Can, Q.; Yiran, Y.; Tianqi, N.; Baoping, X. Functional exploration of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) in the bioleaching of obsolete electric vehicle LiNixCoyMn1-x−yO2 Li-ion batteries. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 354, 250–257. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).