Abstract
Artemisia frigida Willd. (A. frigida), a traditional medicinal herb widely distributed in northern China, Mongolia, and Siberia, has garnered increasing scientific interest due to its diverse phytochemical profile and extensive pharmacological potential. Modern studies have identified a wide range of bioactive compounds in A. frigida, including flavonoids, sesquiterpene lactones and phenolic acids. These compounds exhibit various biological activities, such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, and antimicrobial effects. This review systematically summarizes the research progress on the chemical constituents of A. frigida and their extraction and separation methods, including solvent extraction, ultrasonic-assisted extraction, macroporous resin adsorption, and chromatography-based techniques. By integrating traditional knowledge with modern pharmacological evidence, this review provides a scientific foundation for the further development and utilization of A. frigida in functional food, pharmaceuticals, and ethnomedicine.
1. Introduction
Given the considerable toxic side effects associated with many synthetic pharmaceuticals [1], there is growing interest in developing plant-derived therapeutics that offer improved efficacy with reduced toxicity [2]. Traditional Mongolian Medicine (TMM), a vital component of China’s rich medical heritage, has played a pivotal role in disease prevention and treatment for thousands of years [3]. Globally, traditional remedies are increasingly adopted as alternative or complementary approaches to conventional medicine [4]. Recognizing their importance, the World Health Organization has emphasized the role of traditional medicine in addressing healthcare needs, particularly in developing regions [5].
Artemisia frigida Willd. (A. frigida) (Figure 1), commonly known as “Xiaobaihao” in Chinese and “Agei” in Mongolian, is a biennial to perennial herbaceous species belonging to the genus Artemisia within the family Asteraceae (Compositae). It is widely distributed throughout China and extends to other regions, including Mongolia, North America, Siberia, Kazakhstan, and adjacent areas [6,7]. As a traditional Mongolian medicinal herb, A. frigida has been used therapeutically for centuries. Both the whole plant and its aerial parts are commonly incorporated into traditional formulations [8], primarily for their hemostatic and anti-edematous properties [9]. A. frigida contains a diverse array of bioactive constituents, including flavonoids, sesquiterpenoids, and phenolic acids [10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17]. These compounds have been associated with notable anti-inflammatory [18,19], antioxidant [20,21,22,23], and antitumor activities [10,24], highlighting the considerable medicinal potential of A. frigida. As a traditional herbal medicine, A. frigida has attracted growing scientific interest. This review summarizes recent advances in the traditional uses, bioactive constituents, pharmacological activities, and extraction and isolation techniques of A. frigida.

Figure 1.
Artemisia frigida Willd. [21].
2. Traditional Ethnomedicinal Uses
As a prominent herb in Traditional Mongolian Medicine, A. frigida has a long-standing history of medicinal use and demonstrates considerable potential for further development as a traditional Chinese medicine resource [25]. Traditionally, the entire plant is used, valued for its characteristic bitter flavor and classified in ethnomedicine as possessing cooling, astringent, dull, and desiccating properties. A. frigida is believed to exert hemostatic effects, dispel pathogenic wind, promote meridian circulation, and reduce swelling [26,27,28,29,30]. Clinically, it is primarily employed in the treatment of joint swelling and pain, hyperactive kidney fire, menstrual disorders, abscesses, cholecystitis, dysuria, pruritus, eczema, and helminthic infections [8,19,31,32,33]. It is also frequently prescribed to alleviate systemic symptoms such as irritability, dizziness, cephalalgia, fatigue in the lower back and extremities, and localized swelling or pain in the breasts and limbs [31]. Among nomadic communities in regions such as Siberia and Mongolia, A. frigida holds cultural as well as medicinal significance. It is often consumed as sagaan aya, a traditional herbal infusion reputed for its antioxidant activity and general health-promoting effects. Beyond its medicinal roles, A. frigida is also incorporated into the diet; young shoots are commonly blanched, mixed with cornmeal, and steamed, serving as a seasonal food source with both nutritional and therapeutic value [21,25]. Taken together, A. frigida’s ethnomedical roles, dietary integration, and cultural significance position it for structured development as a traditional Chinese medicine resource.
3. Extraction and Separation Technologies of Active Compounds in AF
A. frigida is rich in phytochemicals and contains multiple classes of constituents. The rational design of extraction and separation workflows is critical for maximizing resource utilization and ensuring quality evaluation. At present, commonly used techniques (Figure 2) for A. frigida include solvent extraction (SE), ultrasonic-assisted extraction (UAE), supercritical fluid extraction (SFE), macroporous resin adsorption/enrichment (MAR), high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), preparative/semi-preparative HPLC (prep HPLC), column chromatography (CC), and high-performance capillary electrophoresis (HPCE) for rapid analytical separation. The strengths and limitations of these methods as applied are summarized in Table 1. Among them, SFE is regarded as particularly promising for industrial applications due to its scalability, efficiency, and environmentally friendly nature. For separation, MAR shows notable potential because of its reusability, cost-effectiveness, and feasibility for large-scale purification of bioactive compounds.
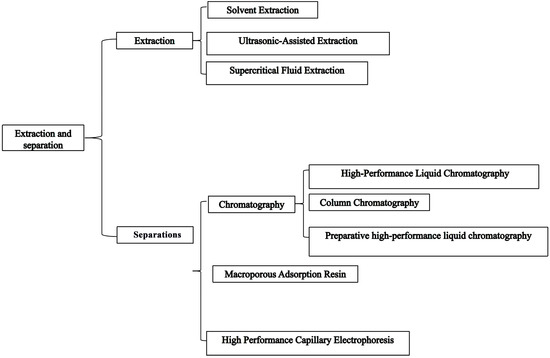
Figure 2.
Extraction and separation methods applied to A. frigida.

Table 1.
Summary of Key Features and Limitations of Extraction and Separation methods.
3.1. Solvent Extraction
Solvent extraction (SE) remains one of the most extensively employed methods for isolating bioactive compounds from plant materials due to its simplicity, adaptability, and broad applicability. The technique exploits the differential solubility of phytochemicals in various solvents, enabling selective extraction based on compound polarity and stability [34,52]. Liu et al. [53] applied ethanol reflux extraction to the aerial parts of A. frigida, followed by chromatographic separation using polyamide, Sephadex LH-20, silica gel, and C18 columns, ultimately isolating 16 compounds spanning flavonoids, terpenoids, and organic acids. Another study employed 70% ethanol extraction coupled with sequential liquid–liquid partitioning using petroleum ether, ethyl acetate, and saturated n-butanol to fractionate the crude extract. This workflow led to the successful isolation and structural elucidation of ten distinct monomeric constituents from AF [10]. Liu et al. [54] optimized the isolation of quercetin by introducing acidified ethanol (95% ethanol with 1.5 mol/L HCl) under reflux, enhancing extraction efficiency through targeted hydrolysis. Liu [12] used 95% ethanol reflux extraction followed by partitioning with petroleum ether, dichloromethane, and ethyl acetate to generate polarity-based fractions for downstream enrichment and separation. Despite its widespread application, conventional solvent extraction faces limitations such as low efficiency and solvent residue concerns, prompting a growing shift toward greener and more sustainable extraction alternatives.
3.2. Ultrasonic-Assisted Extraction
Ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) is an efficient and eco-friendly method that uses acoustic cavitation to enhance the release of bioactive compounds from plant tissues. Ultrasonic waves disrupt cell walls, improve solvent penetration, and accelerate mass transfer. Compared to traditional techniques, UAE offers higher yields in less time with lower solvent use, making it especially suitable for extracting thermolabile or structurally complex phytochemicals [55]. UAE has demonstrated high efficiency in recovering flavonoids from A. frigida, particularly when using methanol or ethanol-based solvents. By leveraging acoustic cavitation, UAE disrupts plant cell walls, thereby enhancing mass transfer and accelerating the release of target compounds [3]. Olennikov et al. [21] applied UAE to powdered A. frigida using 70% methanol at 50 °C for 60 min, under 100 W ultrasonic power and 35 kHz frequency. The process yielded a total extract of 22.14% after filtration and evaporation under reduced pressure. Zhang et al. [20] employed UAE to obtain total flavonoids from A. frigida, using 70% ethanol as the extraction solvent. Following a 24 h soak and ultrasonic treatment, the method achieved an extraction yield of 4.23%, with a recovery rate ranging from 92.0% to 99.6%, demonstrating the efficiency of UAE for isolating flavonoids from traditional Mongolian medicinal herbs. UAE presents significant advantages over traditional extraction techniques, including markedly shortened extraction times and reduced thermal degradation of heat-labile compounds. Moreover, UAE enhances extraction efficiency and minimizes the reliance on organic solvents, thereby offering a highly effective and environmentally sustainable method for the isolation of diverse bioactive constituents [35,56,57].
3.3. Supercritical Fluid Extraction
Supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) employs supercritical fluids—most commonly CO2, often with polar co-solvents—whose pressure- and temperature-tunable density enables rapid, selective, and low-residue extraction/fractionation of compounds from complex matrices [36,38]. Tang et al. [58,59] optimized supercritical CO2 extraction of A. frigida volatile oil by evaluating pressure, temperature, CO2 flow and time—identifying 30 MPa, 35–40 °C, 2 h, and 25 m3·h−1 as optimal—and subsequently profiled the SFE-CO2 oil by GC–MS to determine its constituents and relative abundances. SFE provides a scalable, contamination-free, and environmentally benign alternative widely used in food, nutraceutical, and pharmaceutical purification [60].
3.4. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography
High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is a foundational technique in chromatographic analysis, employing a high-pressure delivery system to propel a liquid mobile phase through a column packed with a stationary phase. The interaction between analytes and the stationary phase enables precise separation based on differences in polarity, molecular size, or affinity. As components elute from the column, they are detected for both qualitative identification and quantitative measurement [61]. HPLC has proven instrumental for the separation and quantification of flavonoids. Wang et al. [62] applied HPLC to analyze flavonoid-rich fractions obtained through ethanol extraction and subsequent partitioning. The samples were separated on a C18 reversed-phase column under gradient elution with acetonitrile and 0.2% phosphoric acid aqueous solution at a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min, with detection at 360 nm. This setup enabled efficient resolution of major flavonoid constituents, offering a robust analytical foundation for the pharmacological evaluation and quality control of AF-derived formulations. Tu et al. [63] isolated five major flavonoids from A. frigida using HPLC on an EZ0566 column, with a mobile phase of 30% acetonitrile in water, at a flow rate of 5.0 mL/min, and UV detection at 254 nm. The separated compounds were subsequently identified by NMR, confirming the presence of five distinct flavonoid compounds. Sakipova et al. [64] applied HPLC-UV for the quantification of santonin in A. frigida. The analysis was performed on a Thermo C18 column (250 mm × 4.6 mm, 5 μm), using a mobile phase composed of water (solvent A) and acetonitrile (solvent B) under a linear gradient from 35:65 to 65:45 (A:B) over 20 min. The flow rate was set at 1.0 mL/min, and detection was carried out at 236 nm. Zhi et al. [65] developed an HPLC method for quantifying chlorogenic acid in A. frigida, using a C18 column (250 × 4.6 mm, 5 μm) with a mobile phase of acetonitrile-0.4% phosphoric acid (12:88), a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min, column temperature at 30 °C, and UV detection at 327 nm. This method enabled the accurate determination of chlorogenic acid for quality control of A. frigida. HPLC, renowned for its high separation efficiency, enables the resolution of structurally similar compounds and is widely applied in the qualitative and quantitative analysis of active ingredients in traditional Chinese medicine, offering a rapid and reliable method for quality control and pharmacological evaluation.
3.5. Column Chromatography
Column chromatography (CC) is a classical and versatile separation technique that exploits differential interactions between sample components and stationary/mobile phases to achieve purification [66]. Borchuluun et al. [67] obtained the volatile oil of A. frigida by hydrodistillation and, via silica-gel column fractionation, isolated one new sesquiterpene together with four known sesquiterpenes. Wang et al. [68] isolated two new flavonoid glycosides from A. frigida by ethanol reflux extraction and solvent partitioning followed by silica gel/Sephadex LH-20 chromatography. Zhang et al. [69] first applied silica gel column chromatography to the dichloromethane-soluble fraction of A. frigida, achieving preliminary fractionation. After TLC-based pooling, they employed successive silica gel and Sephadex LH-20 column chromatography, along with preparative TLC and reversed-phase prep-HPLC, to isolate and purify a novel sesquiterpenolide. Column chromatography remains a classical technique in natural product separation workflows, particularly valued for its simplicity.
3.6. Preparative High-Performance Liquid Chromatography
Preparative high-performance liquid chromatography (prep-HPLC), built on classical HPLC principles and employing high-pressure delivery, high-efficiency stationary phases, and sensitive detection, is a robust, broadly applicable, and typically rapid method for large-scale purification of compounds from complex natural-product extracts—and has become a mainstay of natural-product isolation [70,71]. Liu et al. [12] applied ethanol reflux extraction, stepwise solvent partitioning, and successive silica gel/Sephadex/polyamide/macroporous-resin columns, using semi-prep HPLC on key fractions for final purification, and isolated 26 compounds from A. frigida. Wang et al. [72] employed silica gel and column chromatography in combination with prep-HPLC to separate the extracts, and isolated and identified 25 compounds. Li et al. [10] employed 70% EtOH reflux extraction, stepwise solvent partitioning and successive columns (silica gel, polyamide, Sephadex LH-20, macroporous resin) with semi-prep HPLC as the final step to obtain ten monomeric compounds from A. frigida. Collectively, these studies establish semi-prep/prep HPLC as the pivotal terminal step in A. frigida phytochemical workflows, enabling rapid, reproducible purification of numerous constituents for definitive structure elucidation [73,74].
3.7. Macroporous Adsorption Resin
Macroporous adsorption resin (MAR) technology is a recently developed method for the purification and enrichment of bioactive compounds. It utilizes the large specific surface area of the resin to physically adsorb target molecules through Van der Waals forces, and achieves effective separation and purification based on differences in adsorption affinity and molecular size, followed by selective elution with appropriate solvents. Hai et al. [75] extracted A. frigida using reflux with 95% ethanol, and after concentrating the combined filtrates, the crude total flavonoids were subjected to D101 macroporous resin column chromatography. Impurities were removed with 20% ethanol, followed by 75% ethanol elution, ultimately yielding 3.2 g of purified total flavonoids. Wang et al. [76] optimized the extraction and purification process of total flavonoids from A. frigida using D101 macroporous adsorption resin. Based on orthogonal test design, the optimal conditions were determined as follows: sample concentration of 0.6 mg/mL, sample volume of 4 bed volumes (BV) 20% ethanol for impurity removal, and 60% ethanol for elution. Under these conditions, the yield and purity of total flavonoids reached 85.46% and 65.54%, respectively. Macroporous resin chromatography exhibits excellent purification efficiency for active components from A. frigida, offering a rational, stable, and feasible approach.
3.8. High-Performance Capillary Electrophoresis
High-performance capillary electrophoresis (HPCE) is an electrophoretic technique that applies high voltage across narrow fused-silica capillaries to separate analytes by differences in effective mobility, delivering ultra-high efficiency [77,78]. Wang et al. and Hai et al. [15,79] both employed HPCE to quantify five flavonoids in AF; Wang et al. established a simultaneous assay and compared contents across different harvest times and plant parts, while Hai et al. evaluated processing conditions and identified 60 °C drying as the optimal procedure. HPCE is a rapid, sensitive, and solvent-sparing platform for quantitative profiling of A. frigida flavonoids, effectively supporting process optimization and routine quality control.
The above discussed the separation methods in A. frigida. And the separation mechanisms of chromatography and the components suitable for separation are summarized in Table 2. In summary, A. frigida extraction and separation technologies range from classical solvent and column-based methods to more advanced approaches such as UAE, SFE, MAR, and prep HPLC, each with distinct advantages and drawbacks. Integrating these complementary techniques offers a promising path toward efficient, scalable, and sustainable workflows that ensure both quality control and future application potential.

Table 2.
Summary of separation methods.
4. Active Components in AF
Numerous studies have investigated and identified the major constituents of A. frigida. Using the whole plant as a starting material, researchers have systematically isolated and purified its extracts through chromatographic methods, followed by structural elucidation using spectroscopic techniques via ultraviolet (UV) and mass spectrometry (MS). The main active compounds in A. frigida are shown in Table 3 and Figure 3.

Table 3.
The main compounds in A. frigida.
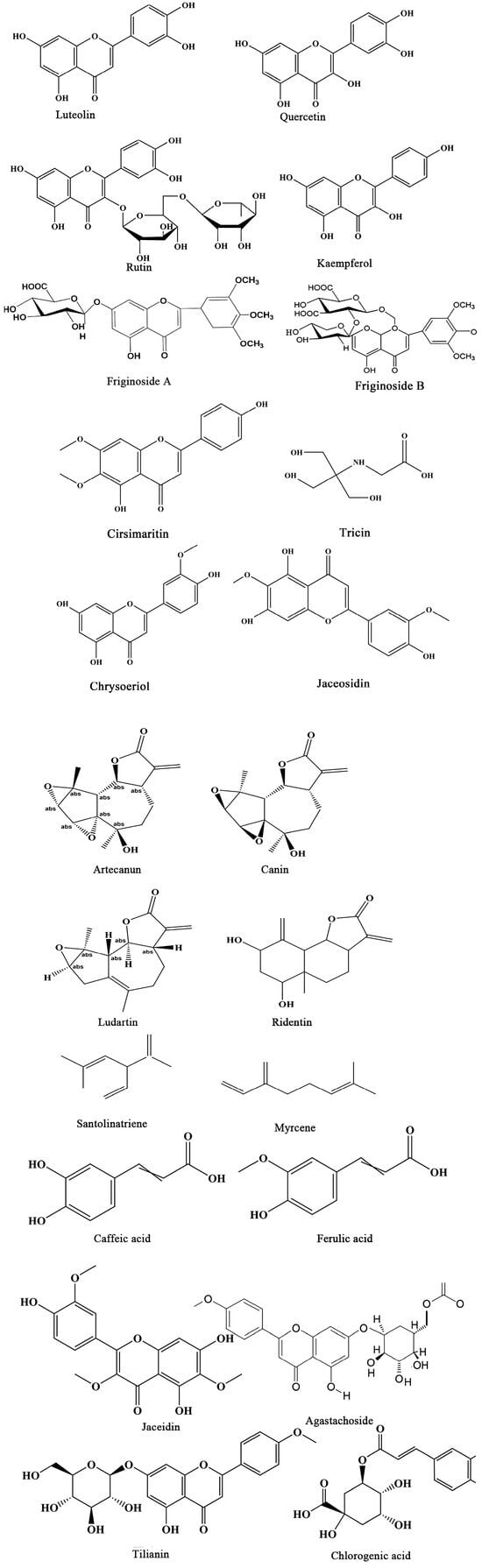
Figure 3.
The structures of Flavonoids, Sesquiterpenes and Polyphenols in A. frigida.
4.1. Flavonoids
Flavonoids, which are generally located in plant leaves, flowers, and stems [86], constitute a major class of bioactive compounds, accounting for approximately 10% of its total chemical composition [87,88]. Tu et al. [63] employed HPLC combined with natural bond orbital (NBR) analysis to isolate and identify the principal flavonoids from the aerial parts of A. frigida. The major components extracted included: 5,3′-Dihydroxy-3,6,7,4′-tetramethoxyflavone; 5,7,3′-Trihydroxy-6,4′-tetramethoxyflavone; 5,3′-Dihydroxy-6,7,4′-trimethoxyflavone; 5-Hydroxy-3′,4′-dimethoxyflavone-7-O-β-D-glucuronide; and 5-Hydroxy-3′,4″,5′-trimethoxyflavone-7-O-β-D-glucuronide. Further investigation by Liu et al. [12], who conducted a comprehensive chromatographic study on the whole herb of A. frigida, enabled systematic isolation, purification, and structural elucidation of its flavonoid constituents. The analysis revealed the efficient detection of several key bioactive flavonoids, including jaceosidin, luteolin, kaempferol, tricin, and eupatilin, among others. Two novel flavonoid glucuronides, friginoside A and friginoside B, were also isolated from the n-BuOH fraction of the aerial parts, further enriching the structural diversity of A. frigida flavonoids [68]. Olennikov et al. [11] isolated several new flavonoids from the aerial parts of A. frigida, including chrysoeriol-7-O-[2″-O-acetyl]-β-D-glucopyranoside and jaceosidin-4′-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (isojaceoside), alongside 13 previously known flavonoids. Overall, reported yields indicate that the total flavonoid content in A. frigida typically accounts for approximately 4–5% of the dry weight [20,82]. These results indicate that flavonoids are not only structurally diverse but also quantitatively significant constituents, reinforcing their central role in the phytochemical profile of A. frigida.
4.2. Sesquiterpenes
Sesquiterpenoids, a class of terpenes composed of three isoprene units and 15 carbon atoms, are widely distributed across the Asteraceae family [89]. Commonly found in essential oils of aromatic plants, these compounds are characterized by their strong fragrance and diverse biological activities. Zhan et al. [69] conducted a phytochemical investigation of A. frigida collected from Nanpi County and identified a novel sesquiterpenoid compound: 1α,3α-dihydroxy-7β,11αH-germacra-4Z,10 [14]-dien-12,6α-olide (1). In the same year, Li et al. [90] identified a novel sesquiterpenoid from A. frigida collected in Hebei Province, structurally characterized as 4α,5αH,6α,7β,10β,11α-1,15-dioxoeudesman-12,6-olide. Subsequently, Borchuluun et al. [67] isolated one new and four known sesquiterpenoids—including the newly reported compound Artefrigin—from the essential oil of A. frigida harvested in Tongliao, Inner Mongolia. In a separate study, Li et al. [10] reported, for the first time, the isolation and identification of the sesquiterpenoid Roxburghianin B from Altai-sourced A. frigida. Several sesquiterpene lactones, including canin, artecanin, ludartin, and 8-deoxycumambrin B, have been successfully isolated from the whole herb of AF [83,84]. Liu et al. [85] identified a total of 101 chemical constituents from the volatile oil of A. frigida via GC-MS analysis, among which sesquiterpenes were predominant. Characterized sesquiterpenoid compounds included santolinatriene, myrcene, and 3,3,6-trimethyl-1,5-heptadien-2-ol. Notably, compounds such as santolinatriene and 3,3,6-trimethyl-1,5-heptadien-2-ol were reported for the first time in A. frigida, expanding the known sesquiterpene profile of the species. Wang et al. [91] isolated and identified two novel guaianolide-type sesquiterpene lactone glycosides from A. frigida, named artemofriginoside A and B, thus enriching the sesquiterpene profile of the species.
4.3. Polyphenols
Phenolic compounds, a class of plant secondary metabolites [92], are commonly found in seeds, peels, leaves, and roots. Wang et al. [9,72] extracted A. frigida using organic solvents and further separated the constituents via elution chromatography. Structural elucidation of the isolated compounds using spectroscopic techniques led to the identification of 2 phenylpropanoids: caffeic acid and ferulic acid. In a more comprehensive study, Olennikov et al. [21] systematically investigated the phenolic profile of A. frigida and, for the first time, identified 12 caffeoylquinic acid derivatives. These included mono-, di-, and tri-ester forms such as 3-O-, 4-O-, and 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid, as well as 3,4-di-, 3,5-di-, and 3,4,5-tri-O-caffeoylquinic acid, among others. Liu et al. [12] identified jaceidin, agastachoside, and tilianin as polyphenolic compounds that were isolated for the first time from A. frigida.
Flavonoids, sesquiterpenes, and polyphenols are the main active components of A. frigida, reflecting both chemical diversity and pharmacological potential.
5. Pharmacological Properties
5.1. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
Pharmacological studies conducted both domestically and internationally have demonstrated that A. frigida exhibits potent anti-inflammatory activity, primarily due to its rich content of flavonoid compounds [93]. Wang et al. [62] using HPLC, identified five flavonoids with confirmed anti-inflammatory activity in the total flavonoid extract of A. frigida. In a subsequent investigation, Wang et al. [94] isolated and purified flavonoid and biflavonoid glycosides from the n-butanol fraction of A. frigida, which showed marked anti-inflammatory effects in a carrageenan-induced mouse paw edema model. Similarly, Tu et al. [63] demonstrated that total flavonoids from Artemisia leucophylla (50 mg/kg) significantly inhibited formalin-induced paw swelling in rats. Moreover, our previous work [95,96] revealed that aqueous extracts of A. frigida—prepared via ultrasonic extraction with distilled water—exhibited potent anti-inflammatory activity. Among several solvent fractions, the ethyl acetate extract displayed the most pronounced effect. Xue et al. [19] further reported that A. frigida extract effectively suppressed mouse paw edema, with mechanistic studies indicating that its anti-inflammatory action involves downregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and mitigation of inflammatory mediator overproduction in affected tissues. Total flavonoids from A. frigida exhibited dose-dependent anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting leukotriene B4 (LTB4) biosynthesis, reducing intracellular calcium mobilization, and enhancing cAMP levels in rat peritoneal leukocytes [97]. Collectively, the anti-inflammatory activity of A. frigida, particularly its flavonoid constituents, is mediated primarily through the suppression of pro-inflammatory cytokine expression, modulation of intracellular calcium signaling, and enhancement of cAMP-mediated anti-inflammatory pathways.
5.2. Antitumor Effects
Several studies have demonstrated the potential antitumor properties of A. frigida, particularly attributed to its sesquiterpene lactones and flavonoid constituents. Li et al. [10] isolated ten compounds from A. frigida, among which flavonoids were dominant. One compound, 3,5-dihydroxy-6,7,3′,4′-tetramethoxyflavone, showed significant cytotoxicity against HepG2 cells with an IC50 of 34.58 ± 2.42 μg/mL. Chen et al. [98] evaluated the effects of five sesquiterpene lactones isolated from A. frigida on the proliferation of human tumor cells using the MTT colorimetric assay. Dehydrocostuslactone (I) exhibited significant inhibitory activity against HeLa, T-98, HLE, and HMV-1 cells, while dihydrodehydrocostuslactone showed moderate antiproliferative effects. In summary, A. frigida contains sesquiterpene lactones with measurable in vitro antitumor activity, and these findings offer valuable references for the development of natural antitumor agents.
5.3. Antioxidant Activity
In recent years, increasing attention has been paid to the antioxidant potential of A. frigida due to its abundance of flavonoids and phenolic acids. Olennikov et al. [21] systematically investigated the antioxidant activity of A. frigida herbal tea, identifying 59 polyphenolic compounds, including caffeoylquinic acids and flavonoids. Using DPPH and ORAC assays, the extract exhibited high antioxidant capacity with an IC50 value of 12.63 μg/mL and an ORAC value of 2918.8 μmol TE/100 mL. Even after simulated gastrointestinal digestion, the antioxidant effect was only slightly reduced, indicating excellent bioavailability and stability. Further supporting these findings, Hai et al. [75] evaluated the total flavonoids extracted from A. frigida and demonstrated that they possess strong radical scavenging activities in vitro. Compared with standard antioxidants like vitamin C and rutin, A. frigida flavonoids showed superior capacity in neutralizing DPPH·, superoxide anion (O2−·), and hydroxyl radicals (·OH), with dose-dependent effects across a concentration range of 60–600 μg/mL. The study also identified 9 key flavonoid compounds by HPLC, including luteolin and methoxylated derivatives, contributing to the observed antioxidative effects. Zhang et al. [20] evaluated the hydroxyl radical scavenging ability of flavonoid extracts from A. frigida using the Fenton reaction and found that the scavenging capacity increased with the rising content of flavonoid compounds. In addition to polyphenols, alkaloids from A. frigida have also demonstrated potent antioxidant effects. Wu et al. [99] investigated the scavenging ability of A. frigida alkaloids using Fenton-induced hydroxyl radical systems, auto-oxidation of pyrogallol for superoxide radicals, and H2O2 reaction systems. The results indicated significant scavenging effects on ·OH, O2−·, and H2O2, with clear dose–response relationships. These results further underscore the potential of A. frigida flavonoids as natural antioxidants with strong activity and significant application prospects in functional foods and pharmaceuticals.
5.4. Other Biological Activities
In recent years, A. frigida has been found to possess various other biological activities in addition to its significant antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antitumor properties, highlighting its potential value for further development and application. Essential oil extracted from A. frigida was tested against a panel of bacterial and fungal strains, including Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, and Candida albicans, showing moderate to strong antimicrobial activity [100]. The antimicrobial effect was primarily attributed to major volatile constituents such as 1,8-cineole, and camphor, which are known to compromise microbial membrane integrity. In addition to antimicrobial properties, A. frigida essential oil also exhibits promising insecticidal activity. Liu et al. [101] analyzed the volatile composition of A. frigida essential oil and identified 1,8-cineole, camphor, and borneol as the predominant components. These compounds demonstrated significant fumigant toxicity against Sitophilus zeamais and Liposcelis bostrychophila, two common storage pests. These results suggest that A. frigida essential oil may serve as a potential botanical pesticide. Yan et al. [102] evaluated the hemostatic effects of A. frigida extracts obtained through different extraction methods and from various polarity-based fractions in mice. The results showed that the n-butanol and ethyl acetate fractions of A. frigida significantly shortened both bleeding time and coagulation time in mice. Moreover, the decoction extract demonstrated superior efficacy compared to the mixed plant decoction, suggesting that the hemostatic activity may be attributed to glycosidic compounds with relatively high polarity present in A. frigida. Zhao et al. [103] revealed that A. frigida extract modulates the immune response in loach by significantly altering the expression of multiple immune-related miRNAs, which in turn regulate key innate immune pathways including Toll-like receptor (TLR), NOD-like receptor (NLR), and RIG-I-like receptor (RLR) signaling, as well as pathways involved in apoptosis, endocytosis, and cytokine interactions. More recently, dehydrovomifoliol, an active constituent isolated from A. frigida, was shown to exhibit protective effects against nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) [95]. A. frigida has been shown to exert notable anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antitumor effects, mainly linked to its flavonoids and sesquiterpenes. It also displays antimicrobial, insecticidal, hemostatic, and immunomodulatory activities, highlighting its potential for further medicinal and practical applications (Table 4).

Table 4.
Active compounds of A. frigida with reported pharmacological activities and targets.
6. Conclusions
A. frigida exhibits considerable medicinal promise, attributable to its chemically diverse repertoire of bioactive constituents—including flavonoids, sesquiterpenoids, and phenolic acids. Supported by both its long-standing traditional use and emerging pharmacological evidence, A. frigida is increasingly recognized as a valuable candidate for the development of natural therapeutic agents. Nevertheless, several challenges remain before its broader application can be realized. Current pharmacological studies are largely limited to in vitro or preclinical models, with insufficient clinical validation to substantiate therapeutic claims. Systematic investigations into toxicity and safety are also scarce, leaving uncertainties regarding long-term use and dosage. In addition, the complexity of its phytochemical profile highlights the need for rigorous standardization of extraction, separation, and quality-control procedures to ensure reproducibility and efficacy. To fully harness its potential, future research should integrate multidisciplinary approaches: optimizing extraction and separation technologies, conducting comprehensive safety evaluations, and advancing clinical studies that can translate laboratory findings into evidence-based healthcare applications. Moreover, given its broad pharmacological spectrum and rich phytochemical profile, A. frigida holds substantial application potential not only in medicine but also in the fields of nutraceuticals, cosmeceuticals, and functional foods. These multidisciplinary intersections merit deeper exploration to support its translational development from traditional remedies to modern healthcare product.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.T. and X.L. (Xiumei Li); methodology, M.Z.; software, T.Z.; validation, M.Z., X.L. (Xianglong Li) and H.Z.; formal analysis, M.Z.; investigation, T.Z.; resources, X.L. (Xianglong Li); data curation, H.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, W.T.; writing—review and editing, W.T.; visualization, X.L. (Xianglong Li); supervision, T.Z.; project administration, X.L. (Xiumei Li); funding acquisition, X.L. (Xiumei Li). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by The Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program, grant number CAAS-ASTIP-2024-IFR-1.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Mengjie Zhang and Xianglong Li were employed by the company Micro-Ecological Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Changsha 410219, China. Author Haiying Zhang was employed by the company Shandong Lukang Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Shandong 272000, China. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- World Health Organization. WHO Guidelines on Safety Monitoring of Herbal Medicines in Pharmacovigilance Systems; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Salihu Shinkafi, T.; Bello, L.; Wara Hassan, S.; Ali, S. An Ethnobotanical Survey of Antidiabetic Plants Used by Hausa–Fulani Tribes in Sokoto, Northwest Nigeria. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 172, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.H.; Ao, W.L.J.; Tai, W.Q. Simultaneous Determination of Seven Flavonoids in Aerial Parts of Artemisia frigida by HPLC. Chin. Herb. Med. 2012, 4, 252–258. [Google Scholar]
- Winslow, L.C.; Kroll, D.J. Herbs as Medicines. Arch. Intern. Med. 1998, 158, 2192–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, R.; Sharma, N.; Oladeji, O.S.; Sourirajan, A.; Dev, K.; Zengin, G.; El-Shazly, M.; Kumar, V. Traditional Uses, Bioactive Composition, Pharmacology, and Toxicology of Phyllanthus emblica Fruits. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 282, 114570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu Ri, E.; Alatengbuya; Bao, J.Q.; Li, J.W. A Study on the Materia Medica of the Mongolian Medicinal Herb Agui. Chin. J. Ethnomed. Ethnopharm. 1998, 6, 2. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhanbula; Chen, S.H.; Zhang, H.; Cao, L.X.; Burenjiya. The characteristics, ecological and geographical distribution of Artemisia frigida. J. Inn. Mong. Agric. Univ. 1999, 1, 6–12. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hasibagen; Chen, S.; Mandula; Yinzhabu. Ethnobotanical Research on the Mongolian People’s Utilisation of Artemisia frigida Willd. J. Inn. Mong. Norm. Univ. 1994, 2, 59–65. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.H.; Wang, J.H.; Eerdengbagena; Na, T. Study on chemical constituents of Artemisia frigida Willd. In Proceedings of the Chinese Pharmaceutical Congress and the 10th China Pharmacist Week, Tianjin, China, 6–7 November 2010. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.J.; Zheng, L.H.; Liu, L. Research on the Chemical Constituents of Artemisia frigida Willd. in Altay. Chin. J. Ethnomed. Ethnopharm. 2022, 31, 38–44. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Olennikov, D.N. New Flavonoids from Artemisia frigida. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2020, 56, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Shi, N.N.; Wu, Y.H.; Li, W.H.; Zhang, M.L.; Shi, Q.W. Chemical constituents from plant of Artemisia frigida. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2017, 48, 5090–5098. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.H.; Si, Y.; Jiao, Y.F.; Zhang, Q.H.; Li, P.Y.; Liu, J.P.; Wang, Z. Research Advances on Constituents and Pharmacological Activities of Flavonoids in Artemisia Species. Spec. Prod. Res. 2020, 42, 80–94. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.H.; Ao, W.L.J.; Dai, N.Y.T. Structural Elucidation and HPLC Analysis of Six Flavone Glycosides from Artemisia frigida Willd. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2013, 29, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.H.; Ao, W.L.; Bao, J.H. Simultaneous Determination of Five Flavonoids in Artemisia frigida by HPCE. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2011, 17, 63–66. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kunert, O.; Alperth, F.; Pabi, E.; Bucar, F. Highly Oxidized Flavones in Artemisia Species—Structure Revisions and Improved UHPLC-MS(n) Analysis. Heliyon 2023, 9, e22309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepetkin, I.A.; Özek, G.; Özek, T.; Kirpotina, L.N.; Khlebnikov, A.I.; Klein, R.A.; Quinn, M.T. Neutrophil Immunomodulatory Activity of Farnesene, a Component of Artemisia dracunculus Essential Oils. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Liu, X.Y.; Gao, H.B.; Xue, Y.Z. Study on Anti-inflammatory Effects and Its Mechanism of Water Extract from Inner Mongolia Medicine Agi. China Pharm. 2020, 31, 1425–1429. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Q.; Ma, X.; Li, S.; Shi, M.; Song, T.; Cui, J. New Insights into the Interactions between the Gut Microbiota and the Inflammatory Response to Ulcerative Colitis in a Mouse Model of Dextran Sodium Sulfate and Possible Mechanisms of Action for Treatment with PE&AFWE. Anim. Model. Exp. Med. 2024, 7, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Bao, Y.M.; Wang, S.Y.; Huang, L.L.; Liu, Y.L. Determination of Flavonoids in the Artemisia frigida Willd of Mongolian Medicine and Study on lts Antioxidant Effect in vitro. Chin. J. Spectrosc. Lab. 2011, 28, 774–776. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Olennikov, D.N.; Kashchenko, N.I.; Chirikova, N.K.; Vasil’eva, A.G.; Gadimli, A.I.; Isaev, J.I.; Vennos, C. Caffeoylquinic Acids and Flavonoids of Artemisia frigida Willd. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 307. [Google Scholar]
- Zhigzhitzhapova, S.V.; Dylenova, E.P.; Goncharova, D.B.; Zhigzhitzhapov, B.V.; Emelyanova, E.A.; Polonova, A.V.; Tykheev, Z.A.; Bazarsadueva, S.V.; Taraskina, A.S.; Pintaeva, E.T. Functional Activity of the Antioxidant System of Artemisia Genus Plants in the Republic of Buryatia (Russia) and Its Significance in Plant Adaptation. Plants 2024, 13, 2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, W.; Yang, J.; Dou, J.H.; Li, X.M.; Dai, X.F.; Wang, X.M.; Sun, Y.H.; Li, Z.Y. Interbatch Quality Control of A. frigida Extract via Spectrum–Effect. Int. J. Food Prop. 2022, 25, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Thakur, R.K.; Khazir, J.; Ahmed, S.; Khan, M.I.; Rahi, P.; Peer, L.A.; Shanmugam, P.V.; Kaur, S.; Raina, S.N.; et al. The Genus Artemisia L.: A High-Value Medicinal Plant. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2024, 24, 301–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, B.H.; Yang, G.X.; Chen, B.R.; Xin, X.P.; Xiong, S.; Guo, Y.; Feng, J.; Huang, L. Investigation on Mongolian Medicine Plant Resources of Artemisia frigida Willd. in Inner Mongolia Region. China Agric. Sci. Bull. 2010, 38, 4077–4079. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.H.; Tegexibayaer; Sirigunqiqige; Wang, J.H. Study on Quality Standard of Mongolian Medicine Artemisia frigida. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 2010, 32, 616–619. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.H.; Wurensubude; Buhebateer; Wang, J.H. Review on Changes with History and Modern Research for Artemisia frigida Willd. Chin. Mod. Appl. Pharm. 2010, 27, 897–900+915. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cui, J.; Tang, L.; Lan, R.; Baoyindalai, B. Clinical Analysis of Cases on Curative Effect of Mongolian Medicinal Herb Agui in Treatment of Hemoptysis Caused by Bronchiectasis. J. Minzu Univ. China 2006, 15, 149–151+155. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhuna, Z.; Sarula, S.; Nasangsang, N. Processing Technology of Mongolian A. frigida and Pharmacological Study. Med. Plant 2017, 8, 32–34. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Xie, K.; Lou, C.X.; Liu, Y.; Cui, J. Contents and extraction rates of inorganic elements in raw versus processed Mongolian drug Agi (Artemisia frigida) Willd. Drugs Clin. 2008, 8, 852–854. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ao, W.L.; Bu Ri, E.; Wu, Q.S. Ethnobotanical Studies on Mongolian Medicinal Material Agi. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2001, 6, 394–396. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wulan; Temuqile; Yulan; Wulijibate’er; Narengaowa; Xurenqimuge. Analysis of the Efficacy of Mongolian Medicine in Treating Knee Osteoarthritis. Inn. Mong. Med. J. 2011, 43, 654–655. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Temuqile, T.; Dai, X.M.; Sarula; Yulan. Efficacy Evaluation of Mongolian Medicine in the Treatment of 132 Cases of Osteoarthritis. J. Chin. Ethn. Med. 2011, 17, 10–11. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Abedelmaksoud, T.G.; Younis, M.I.; Altemimi, A.B.; Tlay, R.H.; Ali Hassan, N. Bioactive Compounds of Plant-Based Food: Extraction, Isolation, Identification, Characteristics, and Emerging Applications. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 13, e70351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chan, S.W.; Singaram, N.; Teoh, M.L.; Mah, S.H.; Looi, C.Y. Essential oil from Aquilaria spp. (agarwood): A comprehensive review on the impact of extraction methods on yield, chemical composition, and biological activities. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2025, 37, 110–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dassoff, E.S.; Li, Y.O. Ultrasound-Assisted Supercritical CO2 Extraction. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 86, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marić, M.; Ninčević·Grassino, A.; Zhu, Z.; Barba, F.J.; Brnčić, M.; Rimac·Brnčić, S. An overview of the traditional and innovative approaches for pectin extraction from plant food wastes and by-products: Ultrasound-, microwaves-, and enzyme-assisted extraction. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 76, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjare, S.D.; Dhingra, K. Supercritical fluids in separation and purification: A review. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2019, 2, 463–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Lee, K. Process intensification for biodiesel production from Jatropha curcas L. seeds: Supercritical reactive extraction process parameters study. Appl. Energy 2013, 103, 712–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozzi, N.L.; Singh, R.K. Supercritical Fluids and the Food Industry. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2002, 1, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.R. Application of HPLC and ESI-MS techniques in the analysis of phenolic acids and flavonoids from green leafy vegetables (GLVs). J. Pharm. Anal. 2017, 7, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, F. Simultaneous determination of three curcuminoids in Curcuma longa L. by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with electrochemical detection. J. Pharm. Anal. 2014, 4, 325–330. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z. Separation, identification and quantification of active constituents in Fructus Psoraleae by high-performance liquid chromatography with UV, ion trap mass spectrometry and electrochemical detection. J. Pharm. Anal. 2012, 2, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- dos Santos, F.K.F.; de Rezende, C.M.; da Veiga Júnior, V.F. Macroporous polymeric resins as a tool to obtain bioactive compounds in food and food-waste: A review. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 114, 104703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che Zain, M.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Teo, C.Y.; Shaari, K. Adsorption/Desorption characteristics and simultaneous enrichment of orientin, isoorientin, vitexin and isovitexin from hydrolyzed oil palm leaf extract using macroporous resins. Processes 2021, 9, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Xiao, Y.; Guo, Z.; Yu, D.; Jin, Y.; Liang, X. 2D Prep Chromatography (Click OEG/C18) for Dalbergia odorifera. J. Sep. Sci. 2011, 34, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, A.; Chavan, S. Preparative HPLC and its applications: A review. Int. J. Res. Publ. Rev. 2024, 5, 1128–1132. [Google Scholar]
- Przybylska, A.; Gackowski, M.; Koba, M. Application of Capillary Electrophoresis to the Analysis of Bioactive Compounds in Herbal Raw Materials. Molecules 2021, 26, 2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Wan, X.; Tan, H.; Jiang, C. Separation and determination of isoflavonoids in several kudzu samples by high-performance capillary electrophoresis (HPCE). Ann. Chim. 2006, 96, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Wang, W.; Liu, Y. Research progress on extraction and separation of active components from loquat leaves. Separations 2023, 10, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dukre, T.P.; Sangale, S.S.; Shelke, A.K.; Chattar, N.M.; Narsale, D.D. A review on column chromatographic techniques as separation method. IRE J. 2023, 6, 116–120. [Google Scholar]
- Peron, G.; Ferrarese, I.; Dos Santos, N.C.; Rizzo, F.; Gargari, G.; Bertoli, N.; Gobbi, E.; Perosa, A.; Selva, M.; Dall’Acqua, S. Sustainable Extraction of Bioactive Compounds and Nutrients from Agri-Food Wastes: Potential Reutilization of Berry, Honey, and Chicory Byproducts. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 10785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, Z.J.; Li, W.L.; Tian, S.Y.; Bao, Y.L.; Sun, L.G.; Huang, Y.X.; Li, Y.X. Study on the chemical constituents of the aerial parts of Artemisia frigida. In Proceedings of the 10th National Symposium on Natural Organic Chemistry of the Chinese Chemical Society, Guangzhou, China, 21 November 2014. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.J.; Gao, Y.; Li, Y.J.; Ma, Y.Y.; Zhang, L.; Bao, Y.M. Determination of Quercetin in Artemisiafrigida by Catalytic Kinetic Spectrophotometry. J. Inn. Mong. Univ. Natl. 2010, 25, 266–267. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Rivera-Mondragón, A.; Broeckx, G.; Bijttebier, S.; Naessens, T.; Fransen, E.; Kiekens, F.; Caballero-George, C.; Vander Heyden, Y.; Apers, S.; Pieters, L.; et al. Ultrasound-assisted extraction optimization and validation of an HPLC-DAD method for the quantification of polyphenols in leaf extracts of Cecropia species. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.V.; Sengar, A.S.; Rawson, A. Ultrasonication—A green technology extraction technique for spices: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 116, 975–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marić, M.; Grassino, A.N.; Zhu, Z.; Barba, F.J.; Brnčić, M.; Rimac Brnčić, S. Pectin Extraction from Plant Wastes. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 76, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Yao, Q.Q.; Zhang, W.; Zeng, M.; Wang, D.X.; Cui, J. Studies on the Extraction of Arteisia frigida by Supercritical Fluid CO2. Liaoning J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2007, 7, 965–966. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.; Xie, K.; Zhang, W.; Yao, Q.Q.; Zeng, M.; Wang, D.X.; Cui, J. GC—MS Analysis of Volatile Oil in Mongolian Medicine Artemisia frigida. Acta Chin. Med. Pharmacol. 2007, 5, 36–37. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Díaz-Reinoso, B.; Moure, A.; Domínguez, H.; Parajó, J.C. Supercritical CO2: Antioxidant Compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 2441–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, E.; Wang, W.; Huang, Y.; Luo, Z.; Chen, B.; Xiao, S.; Li, D. Puerariae lobatae Radix: Progress in Extraction, Separation Methods and Pharmacological Activities Research. Separations 2024, 11, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.H.; Jin, J.M.; Dai, N.Y.T.; Han, N.R.C.K.T.; Han, J.J.; Bao, B.Y.M.Q.E. Anti-inflammatory effects, nuclear magnetic resonance identification, and high-performance liquid chromatography isolation of the total flavonoids from Artemisia frigida. J. Food Drug Anal. 2016, 24, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, B.X.; Wang, Q.H.; Baiyin Muker, B.; Dainaintai, D. Anti-inflammatory Effects, HPLC Isolation and NRM Identification of the Total Flavonoids from Artemisia frigida. Chin. J. Ethnomed. Ethnopharm. 2017, 26, 40–43. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sakipova, Z.; Wong, N.S.; Bekezhanova, T.; Sadykova; Shukirbekova, A.; Boylan, F. Quantification of santonin in eight species of Artemisia from Kazakhstan by means of HPLC-UV: Method development and validation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, H.; Ai, D.; Yang, X.H.; Liu, J.; Siqingerile; Zhang, L.L. A comparative study on the content of chlorogenic acid in wild and cultivated Artemisia frigida Willd. J. Chin. Ethn. Med. 2020, 26, 40–43. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Queiroz, E.F.; Guillarme, D.; Wolfender, J.-L. High-Resolution Chromatography for Natural Products Isolation. Phytochem. Rev. 2024, 23, 1415–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borchuluun, S.; Wang, Q.; Xu, Y.; He, X.; Bao, W.; Pa, B. New Sesquiterpene from A. frigida Volatile Oil. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 35, 2376–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.H.; Ao, W.L.; Wang, X.L.; Bao, X.H.; Wang, J.H. Two New Flavonoid Glycosides from Artemisia frigida Willd. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2010, 12, 950–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ni, Z.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Dong, M.; Sauriol, F.; Huo, C.; Shi, Q.; Yamada, T.; Kiyota, H.; et al. A new germacrane sesquiterpenolide isolated from Artemisia frigida. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2013, 49, 626–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhao, J.; Dai, X.; Li, X. Extraction and Analysis of Chemical Compositions of Natural Products and Plants. Separations 2023, 10, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latif, Z.; Sarker, S.D. Prep-HPLC for Natural Products. In Natural Products Isolation; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 255–274. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.H.; Wu, X.L.; Wang, J.H. Chemical constituents of Artemisia frigida (II). Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2011, 42, 1075–1078. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zeng, L.; Pham, C.; Xu, R. Preparative 2D LC/MS for Complex Pharmaceuticals. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1324, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Guo, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhong, Z.; Peng, X.; Dang, J.; Tao, Y.; Liang, X. Efficient purification of high-purity compounds from the stem of Lonicera japonica Thunb using two-dimensional preparative chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2013, 36, 2414–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hai, P.; Su, Y. Extraction Technology of Flavonoid in Mongolian Medicine Artemisia frigida and Its Antioxidative Activation. Chin. J. Exp. Tradit. Med. Formulae 2012, 18, 59–63. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.H.; Tong, Q.; Han, J.J.; Bao, B.Y.M.Q.E.; Wu, J.S.; Han, N.R.C.T.; Dai, N.Y.T.; Wu, R.J. Orthogonal test design for optimization of the isolation and purification of total favonoids from Artemisia frigida Willd using macroporous resin chromatography. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2016, 10, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Bai, Y.; Li, J.; Chang, Y.X. Screening Bioactives Using Capillary Electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2018, 39, 260–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laczkó Zöld, E.; Kis, C.; Nagy-György, E.; Domokos, E.; Ferencz, E.; Szabó, Z.I. Extraction and Characterization of Artichoke (Cynara cardunculus L.) Solid Waste from the Industrial Processing of Fresh-Cut Products for Nutraceutical Use. Foods 2025, 14, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Hai, P.; Su, Y.; Wang, Q.H. Determinaton of five flavonoids from different processing products of Artemisia frigida by HPCE. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2011, 42, 893–896. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.M.; Jia, L.; Cheng, L.Y.; Zhang, H.Q.; Zang, X.L.; Baoyin, T.; Zhang, R.; Gao, Y. Responses of phenolic acid and defensive enzyme activities to mechanical damage in Artemisia frigida. Chin. J. Plant Ecol. 2017, 41, 219–230. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tu, B.X.; Dainayintai; Hannarenchaoketu; Wang, Q.H. Progress of Modern Research on Mongolian Medicine Artemisia frigida. Chin. J. Ethnomed. Ethnopharm. 2017, 26, 63–68. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.; Pei, L.Y.; Cui, J. Pharmacy Research Progress on Mongolia Prescription Garidi-2. J. Minzu Univ. China (Nat. Sci.) 2013, 22, 63–68. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.L.; Mabry, T.J. Sesquiterpene Lactones from Artemisia frigida. J. Nat. Prod. 1981, 44, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohlmann, F.; Ang, W.; Trinks, C.; Jakupovic, J.; Huneck, S. Dimeric Guaianolides from Artemisia sieversiana. Phytochemistry 1985, 24, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.L.; Zhou, J.B.; Tao, Y.D.; Shao, Y. Analysis of chemical composition of volatile oil in Artemisia frigida willd. Chin. J. Spectrosc. Lab. 2008, 3, 25–29. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Harborne, J.B.; Williams, C.A. Advances in Flavonoid Research Since 1992. Phytochemistry 2000, 55, 481–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Sang, S.; Pan, M.H.; Lai, C.S.; Lo, C.Y.; Yang, C.S.; Ho, C.-T. Anti-Inflammatory Property of Urinary Metabolites of Nobiletin in Mouse. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 5177–5181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.H.; Lai, Y.S.; Lai, C.S.; Wang, Y.J.; Li, S.; Lo, C.Y.; Dushenkov, S.; Ho, C.-T. 5-Hydroxy-3,6,7,8,3′,4′-Hexamethoxyflavone Induces Apoptosis in Leukemia Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 5081–5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianca, I.; Anca, M.; Andreia, C. Sesquiterpene Lactones from Artemisia Genus: Biological activities and methods of analysis. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2015, 2015, 247685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.F.; Zhang, M.L.; Wang, Y.F.; Dong, M.; Sauriol, F.; Huo, C.H.; Shi, Q.-W.; Yamada, T.; Kiyota, H.; Gu, Y.-C.; et al. Arteminal, a New Eudesmane Sesquiterpenolide from Artemisia frigida. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2013, 49, 872–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.H.; Sha, Y.; Ao, W.L.J.; Wang, X.L.; Bao, X.H.; Li, W.; Wang, J.-H. Two New Sesquiterpene Lactone Glycosides from Artemisia frigida Willd. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2011, 13, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, G.; Vanz Borges, C.; Minatel, I.O.; Ferreira, M.I.; Gomez-Gomez, H.; Chen, C.-Y.O. Phenolic Compounds: Properties, Processing Impact and Bioavailability. In Phenolic Compounds—Biological Activity; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, W.; Wang, Y.D.; Zhang, T.C.; Li, X.M. Study on anti-inflammatory activity of 17 Chinese herbal medicines in vitro. China Feed 2024, 17, 98–103+128. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, J.; Wu, X.; Han, N.; Tai, W.; Dai, N.; Wu, R.; Ao, W. Flavonoid and Biflavonoid Glycosides from A. frigida. Monatshefte Chem. 2015, 146, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.M.; Yang, P.L.; Shi, D.D.; Wen, Z.G.; Wang, Y.D.; Yang, J. Extract of Artemisia frigida, Its Preparation Method and Application. CN111686143A, 22 September 2020. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.M.; Yang, P.L.; Shi, D.D.; Wen, Z.G.; Wang, Y.D.; Yang, J. Anti—Inflammatory Ethanol Extract of Artemisia frigida, and Its Preparation Method and Application. CN111840350A, 30 October 2020. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Hua, L.; Wang, Q.H.; Dai, N.Y.T.; Naren, Z.; Wu, R.J.; Wu, J.S. Effect of Artemisia frigida Total Flavonoids on the Levels of LTB4, 5-HETE, Ca2+ and Cyclic AMP in Rat Peritoneal Leukocytes. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2016, 28, 591–600. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.J.; Wang, S.M.; Li, C.F.; Zhang, M.L.; Dong, M.; Shi, Q.W. Studies of sesquiterpenoids from Artemisia frigida on the anti-growth activity of human tumor cell lines. Pharmacol. Clin. Chin. Mater. Med. 2011, 27, 24–26. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.L.; Fu, Z.; Jin, L. Study on In-vitro Antioxidant Activity of Alkaloids from Artemisia frigida. Acad. J. Educ. Res. 2012, 3, 64–65. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lopes-Lutz, D.; Alviano, D.S.; Alviano, C.S.; Kolodziejczyk, P.P. Screening of chemical composition, antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of Artemisia essential oils. Phytochemistry 2008, 69, 1732–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.C.; Li, Y.; Wang, T.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Z.L. Chemical Composition and Insecticidal Activity of Essential Oil of Artemisia frigida Willd (Compositae) against Two Grain Storage Insects. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2014, 13, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Wang, T.Z. Pharmaceutical screening of active fraction of haemostasis in Agi. Qingdao Med. Health Care 2012, 44, 3. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Dai, L.; Wang, H. Potential immunomodulatory effects of the extract from Artemisia frigida Willd on loaches infested with Aeromonas hydrophila revealed by microRNA analysis. Front. Genet. 2025, 16, 1584539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).