Separation Process for Methanol–Methylal–Methyl Formate Multicomponent System in Polyformaldehyde Production Waste Liquid: Modeling and Techno-Economic Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Analytical Method
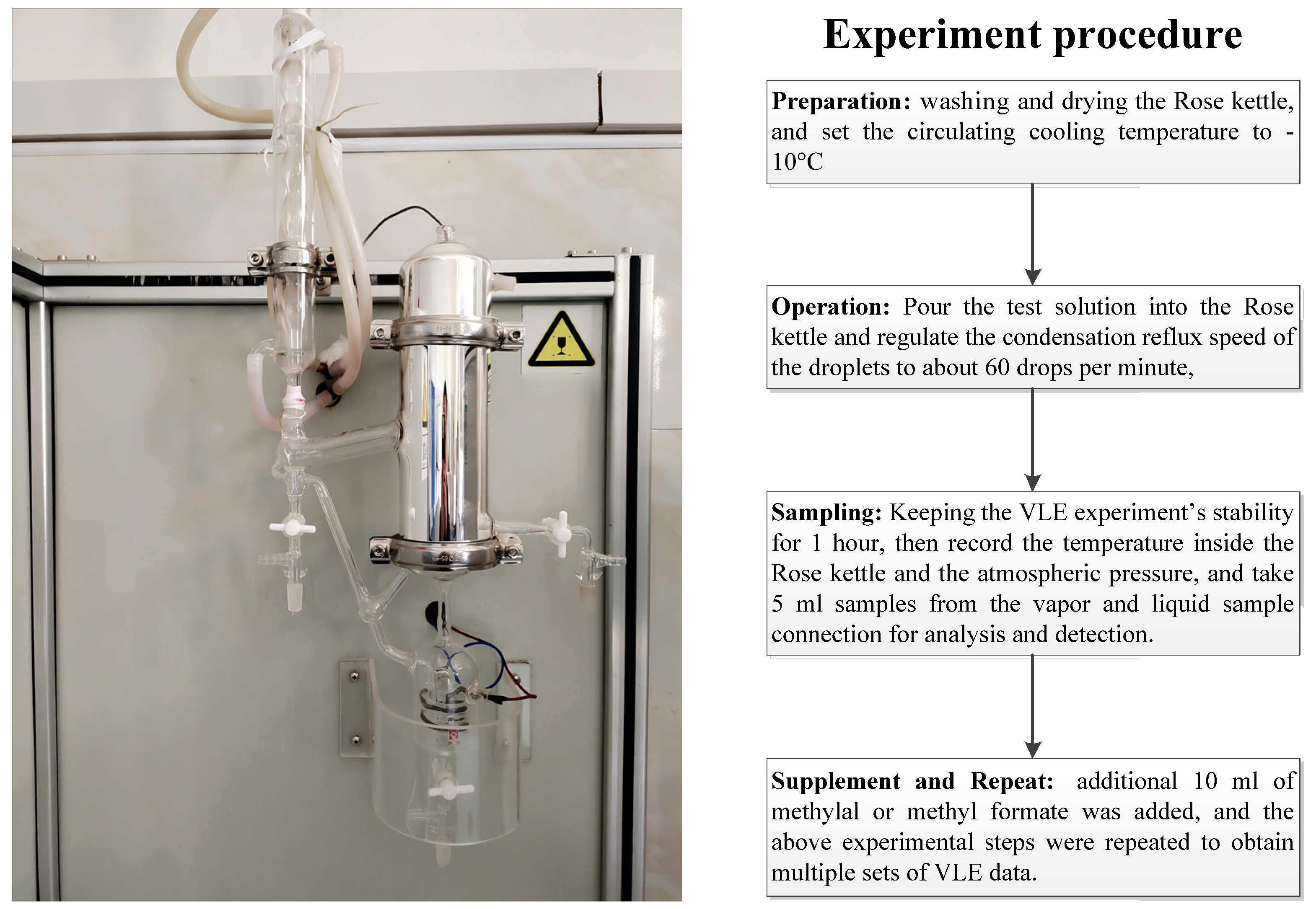
2.2. Procedure
3. Modeling
3.1. Wilson Model
3.2. NRTL Model
3.3. UNIQUAC Model
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Measurement and Correlation of VLE Data for the Ternary System
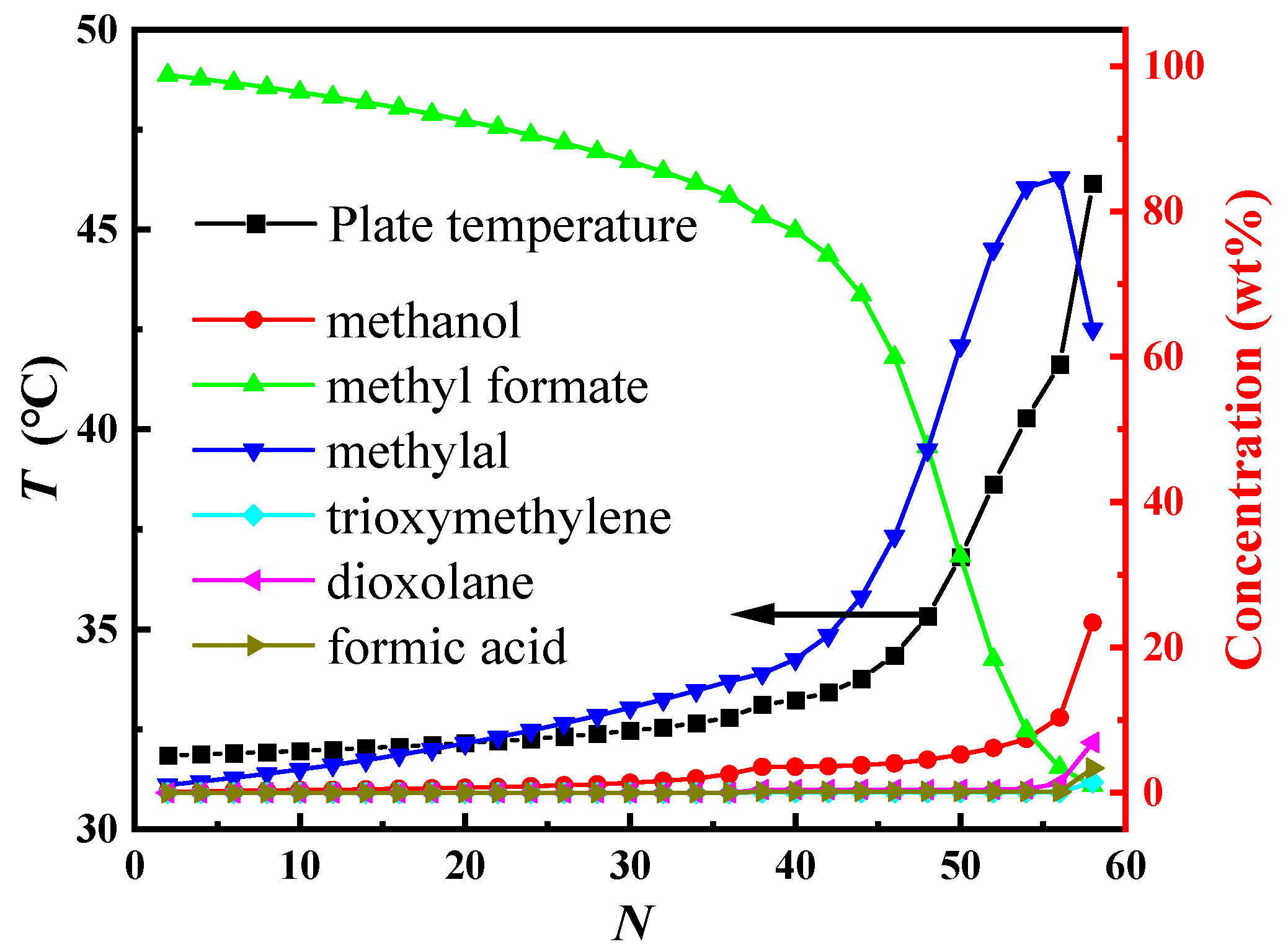
4.2. The Analysis of the Residual Curve Phase Diagram for POM Organic Waste Liquid
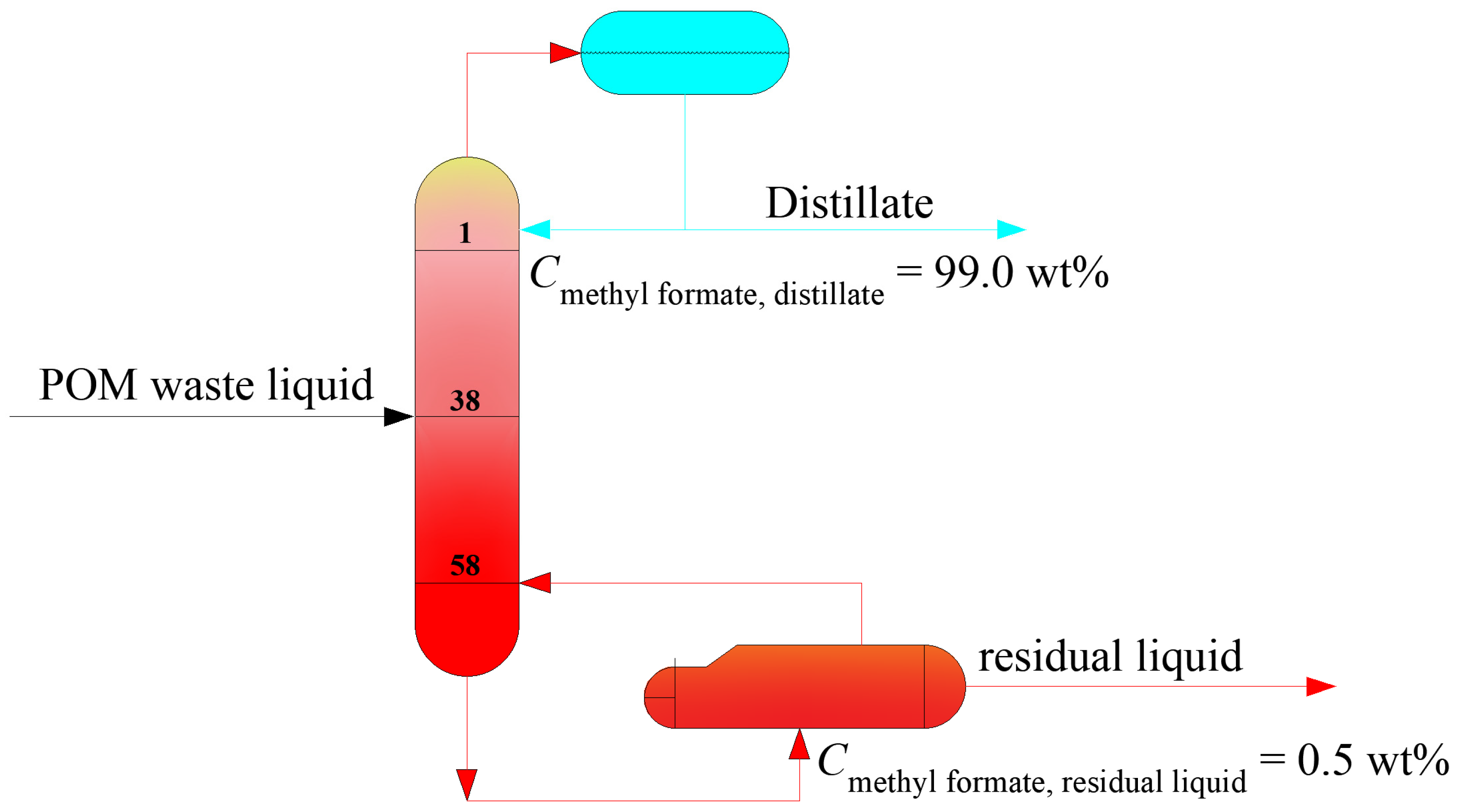
4.3. The Optimization for Methyl Formate Separation Process
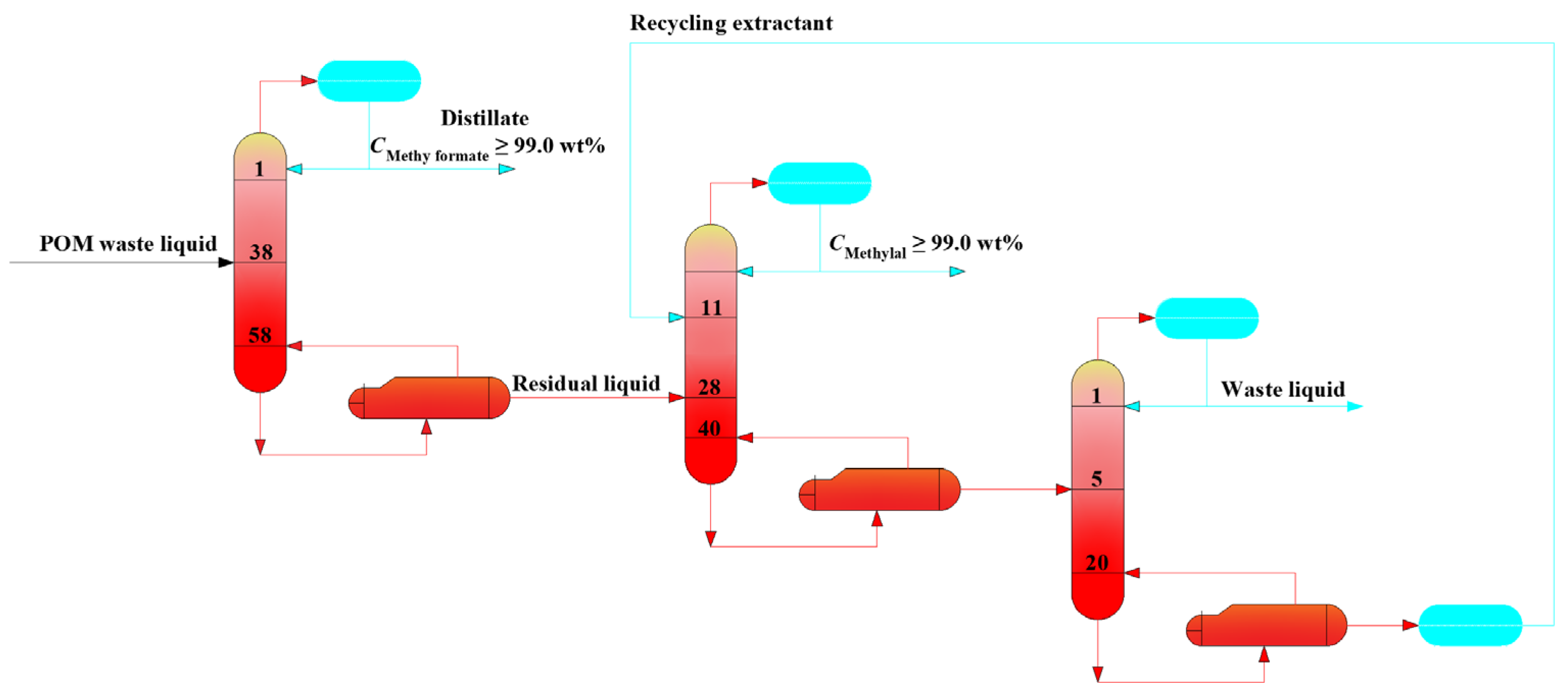
4.4. The Techno-Economic Comparison of Various Design Flowsheet for POM Waste Liquid
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| VLE | Vapor–liquid equilibrium |
| RMSD | Root mean square deviation |
| POM | Polyformaldehyde |
| TOX | Trioxane |
| RR | Reflux ratio |
| DF | Distillate to feed ratio |
| γ | Activity coefficient |
| T | Temperature |
| C | Concentration |
| Y | Yield |
| Q | The energy consumption of reboiler |
| η | Energy efficiency |
| Ns | The total number of theoretical numbers |
| Nf | The number of feed plates |
| G | Gibbs free energy |
| θ | Average area fraction |
| φ | Volume fraction |
| R | Volume parameter |
| q | Surface parameter |
| Z | Lattice coordination number |
| u | Interaction energy |
References
- Zhang, H.; Yang, X.; Gao, G.; Yan, J.; Zhao, M.; Su, H. An efficient catalyst of CuPt/TiO2 for photocatalytic direct dehydrogenation of methanol to methyl formate at ambient temperature. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2022, 12, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikzad, A.; Iranshahi, D. Analysis of integrated system for ammonia synthesis and methyl formate production in the thermally coupled reactor. Chem. Eng. Process. 2021, 166, 108418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Quan, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, H.; Ren, J. Highly active CuZn/SBA-15 catalyst for methanol dehydrogenation to methyl formate: Influence of ZnO promoter. Mol. Catal. 2021, 505, 111514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, L.; Xu, Z.; Sun, J.; Guo, G. New methyl formate synthesis method: Coal to methyl formate. J. Energy Chem. 2018, 27, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, Y.; Li, X.; Gao, X. Process intensification for energy efficient reactive distillation of trioxane production from aqueous formaldehyde. Chem. Eng. Process. 2022, 175, 108914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Ren, Y.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Gao, X. Simultaneous Extractive and Azeotropic Distillation Separation Process for Production of PODEn from Formaldehyde and Methylal. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 5252–5260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Hu, Y.; Ma, W.; Wang, H.; Jiang, S.; Yin, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Y. The reactions that determine the yield and selectivity of 1,3,5-trioxane. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 331, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grützner, T.; Hasse, H.; Lang, N.; Siegert, M.; Ströfer, E. Development of a new industrial process for trioxane production. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2007, 62, 5613–5620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J. Formaldehyde, 2nd ed.; Reinhold Publishing Corporation: New York, NY, USA, 1953; pp. 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, H.; Li, L.; He, W.; Chen, P.; Yu, X. Solid–Liquid Phase Equilibria of the Aqueous Quaternary System Rb+, Cs+, Mg2+//SO42−—H2O at T = 323.2 K. Separations 2024, 11, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Lin, X.F.; Zhang, J.F.; Chen, H.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, H.; Cheng, L.; Ouyang, X. Measurement and correlation of liquid-liquid equilibrium data for n-hexane isopropanol azeotropic system. CIESC J. 2020, 71, 3009–3017. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.C.; Yang, B.; Abdeltawab, A.A.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Yu, G.; Yong, X. Isobaric Vapor-Liquid Equilibrium for Acetone + Methanol + Phosphate Ionic Liquids. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2015, 60, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, G. Vapor-liquid equilibrium of formaldehyde and water containing multicomponent mixtures. AIChE J. 1986, 32, 932–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hasse, H.; Maurer, G. Enthalpy change on vaporization of aqueous and methanolic formaldehyde solutions. AIChE J. 1992, 38, 1693–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandani, S.; Brandani, V.; Flammini, D. Isothermal vapor-liquid equilibria for the water—1,3,5-trioxane system. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1994, 39, 184–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandani, S.; Brandani, V. Isothermal vapor-liquid equilibria and solubility in the system methanol + 1,3,5-trioxane. J. Chem. Eng. Data 1994, 39, 203–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandani, V.; Brandani, S.; Giacomo, G. The system formaldehyde-water-methanol thermodynamics of solvated and associated solutions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1992, 7, 1792–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohorecki, R.; Moniuk, W.; Machniewski, P. Calculations of the vapour-liquid phase equilibrium for the formaldehyde-water-trioxane system. Chem. Process Eng. 2008, 29, 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Grutzner, T.; Hasse, H. Solubility of formaldehyde and trioxane in aqueous solutions. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2004, 49, 642–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasse, H.; Hahnenstein, I.; Maurer, G. Revised vapor-liquid equilibrium model for multi-component formaldehyde mixtures. AIChE J. 1990, 36, 1807–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasse, H.; Maurer, G. Vapor-liquid equilibrium of formaldehyde containing mixtures at temperatures below 320 K. Fluid Phase Equilibria 1991, 64, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berje, J.; Baldamus, J.; Burger, J.; Hasse, H. Vapor-liquid equilibrium of mixtures containing formaldehyde, water, and butynediol. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2019, 490, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilsak, R.; Campbell, S.; Thodos, G. Vapor-liquid equilibrium measurements for the methanol-acetone system at 372.8, 397.7 and 422.6 K. Fluid Phase Equilibria 1986, 28, 13–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, K.; Wang, Z.; Gao, J.; Zhang, L.; Xu, D.; Wang, Y. Vapour-liquid equilibrium and extractive distillation for separation of azeotrope isopropyl alcohol and diisopropyl ether. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2019, 131, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soujanya, J.; Satyavathi, B.; Sankarshana, T. Isobaric ternary vapour-liquid equilibrium of methanol(1) + diisopropyl ether(2) + isopropyl alcohol(3) along with methanol + isopropyl alcohol binary data at atmospheric and sub-atmospheric pressures. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2015, 405, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Hála, E.; Pick, J.; Fried, V. Vapour-Liquid Equilibrium, 2nd ed.; Pergamon Oxford: Oxford, UK, 1967; pp. 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Zafarani-Moattar, M.; Majdan-Cegincara, R. New local composition model for modeling of thermodynamic and transport properties of binary aqueous electrolyte solutions. Calphad 2011, 35, 109–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, R. New local composition model for polymer solutions. Polymer 2005, 46, 11517–11526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, G. Vapor-Liquid Equilibrium. XI. A New Expression for the Excess Free Energy of Mixing. Am. Chem. Soc. 1964, 86, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renon, H.; Prausnitz, J. Local compositions in thermodynamic excess functions for liquid mixtures. AIChE J. 1968, 14, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrams, D.; Prausnitz, J. Statistical Thermodynamics of Liquid Mixtures:A New Expression for the Excess Gibbs Energy of Partly or Completely Miscible Systems. AIChE J. 1975, 21, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Dai, C.; Lei, Z. Extractive distillation of methylal/methanol mixture using ethylene glycol as entrainer. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2018, 462, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Property Method | Component I | Component J | aij | aji | bij | bji | c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NRTL | methanol | methylal | 3.384 | −6.675 | −797.871 | 2255.810 | 0.3 |
| methylal | methyl formate | 1.854 | −1.806 | −408.250 | 460.696 | 0.3 | |
| methyl formate | methanol | −6.631 | 14.887 | 2472.880 | −4596.970 | 0.3 | |
| UNIQUAC | methanol | methylal | −0.498 | 3.355 | 169.514 | −1360.960 | |
| methylal | methyl formate | 0.184 | 0.331 | −224.381 | 6.789 | ||
| methyl formate | methanol | 4.137 | −7.087 | −1661.870 | 2256.160 | ||
| Wilson | methanol | methylal | 1.895 | 3.059 | −763.567 | −1265.430 | |
| methylal | methyl formate | 0.535 | 0.709 | −62.422 | −406.588 | ||
| methyl formate | methanol | −6.749 | −4.802 | 1926.970 | 1196.420 |
| Components | CAS Number | MW | Melting Point/°C | Boiling Point/°C | Content /wt% | Price a CNY/t |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| methanol | 67-56-1 | 32.04 | −97.8 | 65.4 | 5.49 | 3400 |
| trioxymethylene | 110-88-3 | 90.08 | 59–62 | 114.5 | 0.34 | 12,000 |
| dioxolane | 646-06-0 | 74.08 | −95 | 74–75 | 1.59 | 23,000 |
| formic acid | 64-18-6 | 46.03 | 8.2–8.4 | 100.8 | 0.78 | 9500 |
| methylal | 109-87-5 | 76.09 | −105 | 42.3 | 15.34 | 3950 |
| methyl formate | 107-31-3 | 60.05 | −99.8 | 32 | 76.46 | 15,000 |
| Items | Production and Consumption | Economic Interest/CNY | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 1 | Case 2 | |
| Methyl formate/99 wt% | 771.2 | 771.2 | 6940.8 | 6940.8 |
| Methylal/99 wt% | — | 147.8 | — | 516.6 |
| Reboiler/Gcal·h−1 | 0.499 | 0.617 | −190.1 | −235.0 |
| Cooling/Gcal·h−1 | 0.486 | 0.574 | −19.4 | −22.9 |
| Residual liquid/kg·h−1 | 228.8 | 81.0 | 228.8 | 81.0 |
| Total/CNY | — | — | 6960.1 | 7281.2 |
| Property Method | RMSD (y1) a | RMSD (y2) a | RMSD (y3) a | RMSD (T) b | RMSD (P) c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NRTL | 0.0087 | 0.0069 | 0.0066 | 0.4435 | 0.0011 |
| UNIQUAC | 0.0085 | 0.0069 | 0.0068 | 0.4375 | 0.0011 |
| Wilson | 0.0090 | 0.0070 | 0.0075 | 0.4863 | 0.0012 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Fan, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Ai, Q.; Li, Y. Separation Process for Methanol–Methylal–Methyl Formate Multicomponent System in Polyformaldehyde Production Waste Liquid: Modeling and Techno-Economic Analysis. Separations 2025, 12, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12010012
Liu H, Fan J, Liu W, Wang Y, Ai Q, Li Y. Separation Process for Methanol–Methylal–Methyl Formate Multicomponent System in Polyformaldehyde Production Waste Liquid: Modeling and Techno-Economic Analysis. Separations. 2025; 12(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Huajie, Jun Fan, Weiping Liu, Yong Wang, Qiuhong Ai, and Yonglin Li. 2025. "Separation Process for Methanol–Methylal–Methyl Formate Multicomponent System in Polyformaldehyde Production Waste Liquid: Modeling and Techno-Economic Analysis" Separations 12, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12010012
APA StyleLiu, H., Fan, J., Liu, W., Wang, Y., Ai, Q., & Li, Y. (2025). Separation Process for Methanol–Methylal–Methyl Formate Multicomponent System in Polyformaldehyde Production Waste Liquid: Modeling and Techno-Economic Analysis. Separations, 12(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations12010012





