Optimizing Vertical Zone Refining for Ultra-High-Purity Tin: Numerical Simulations and Experimental Analyses
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Numerical Simulations and Experimental Procedure
3. Result and Discussion
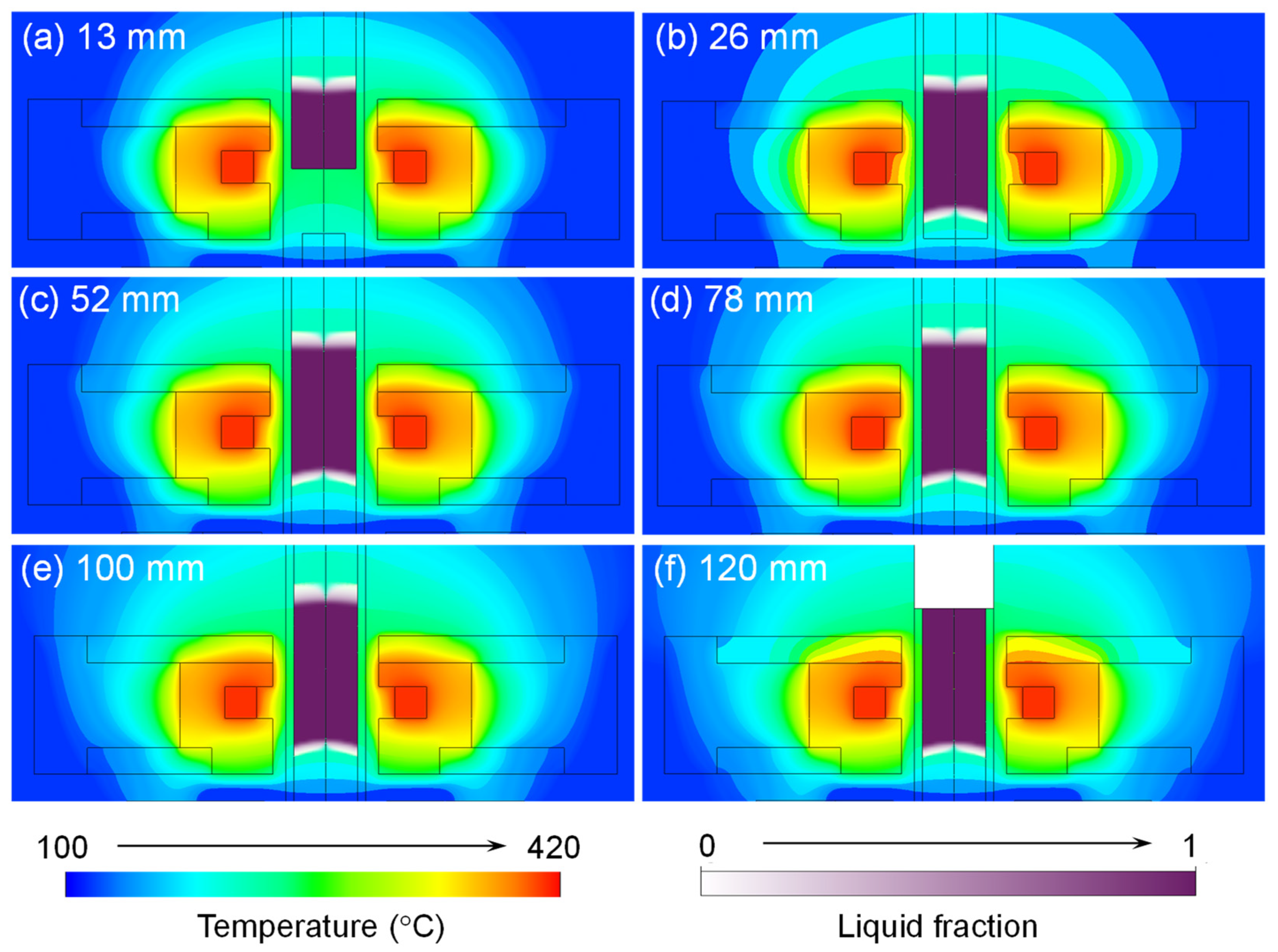
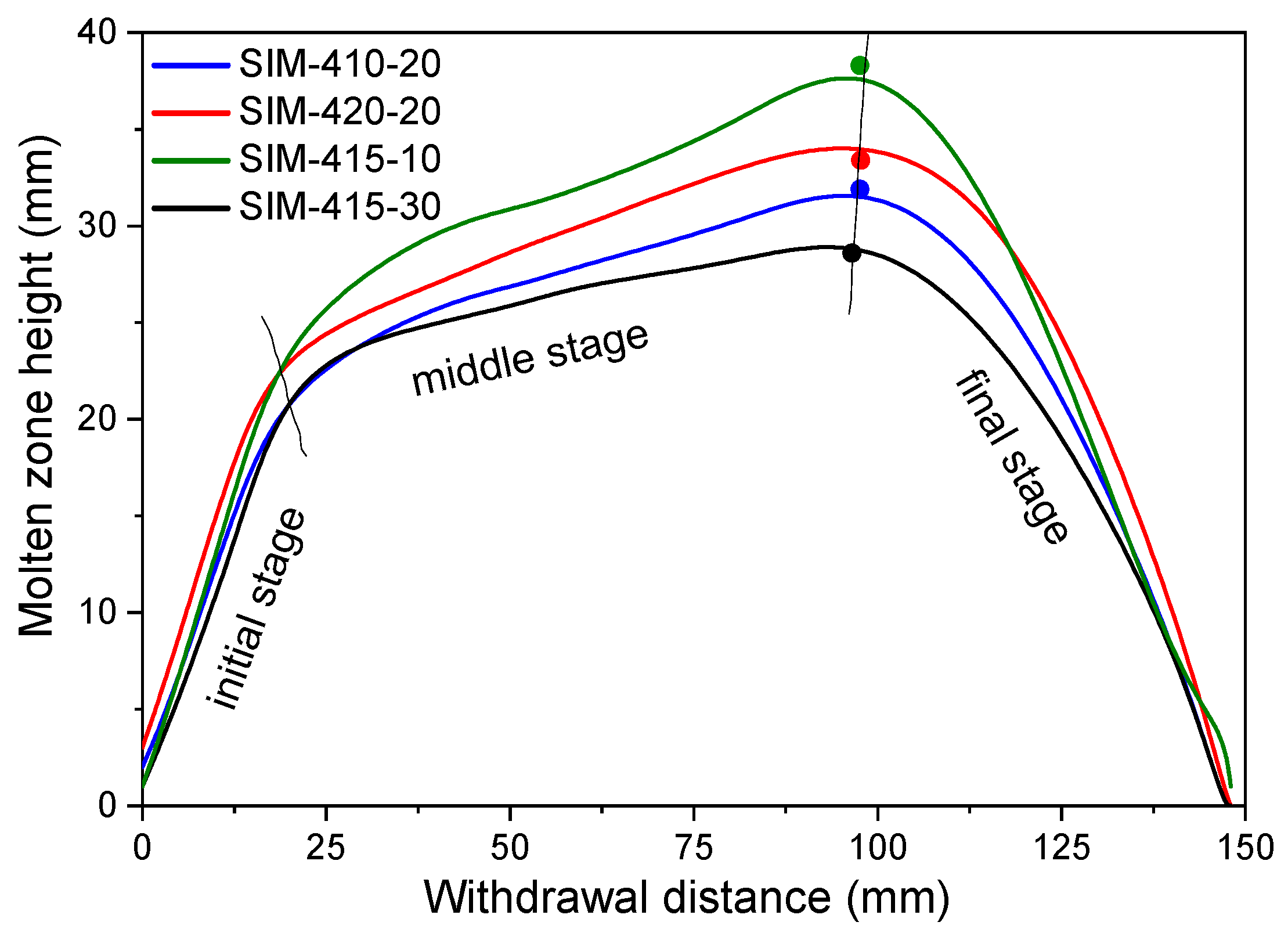
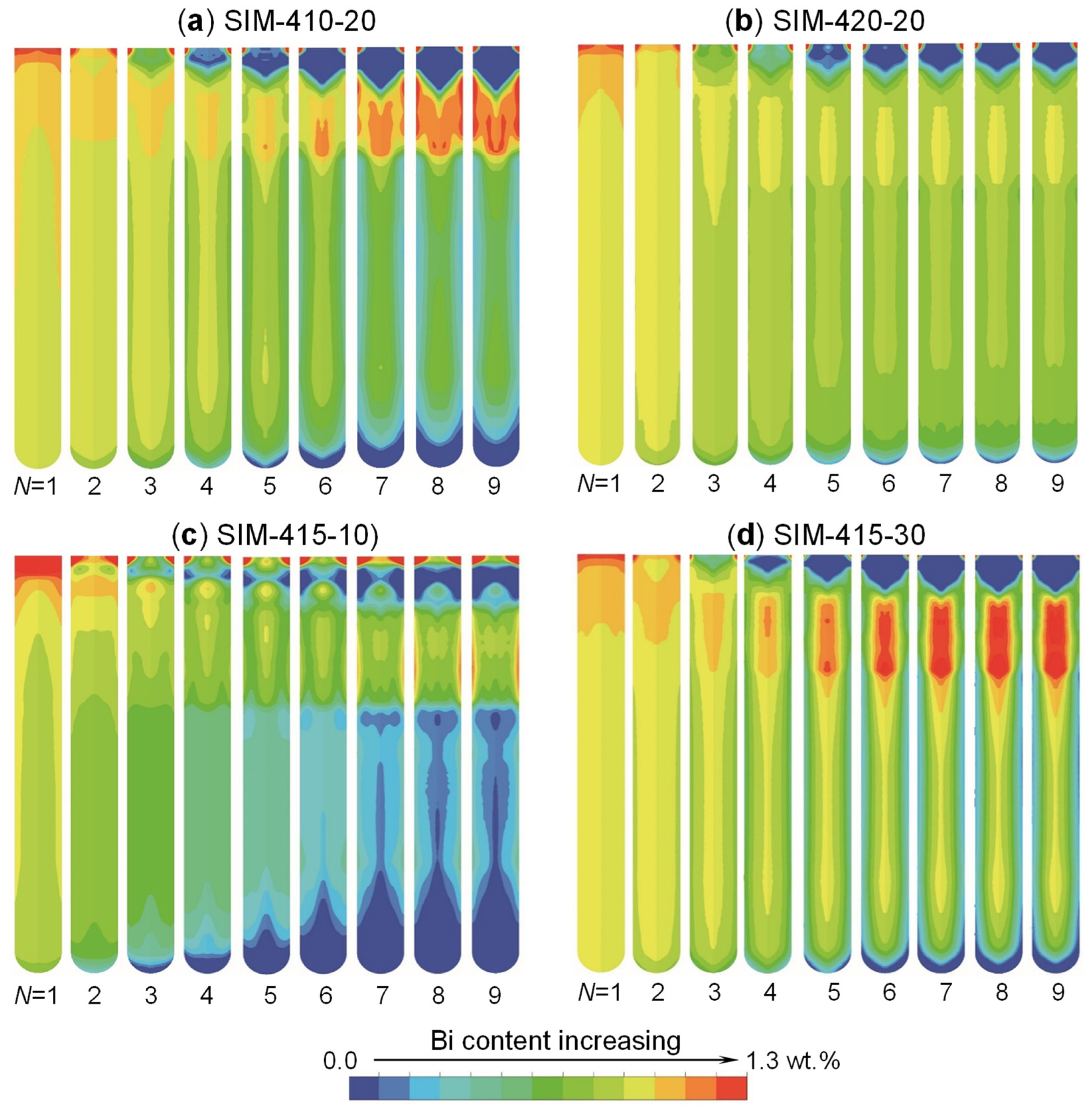
3.1. Numerical Simulation of Processing Parameters’ Impact
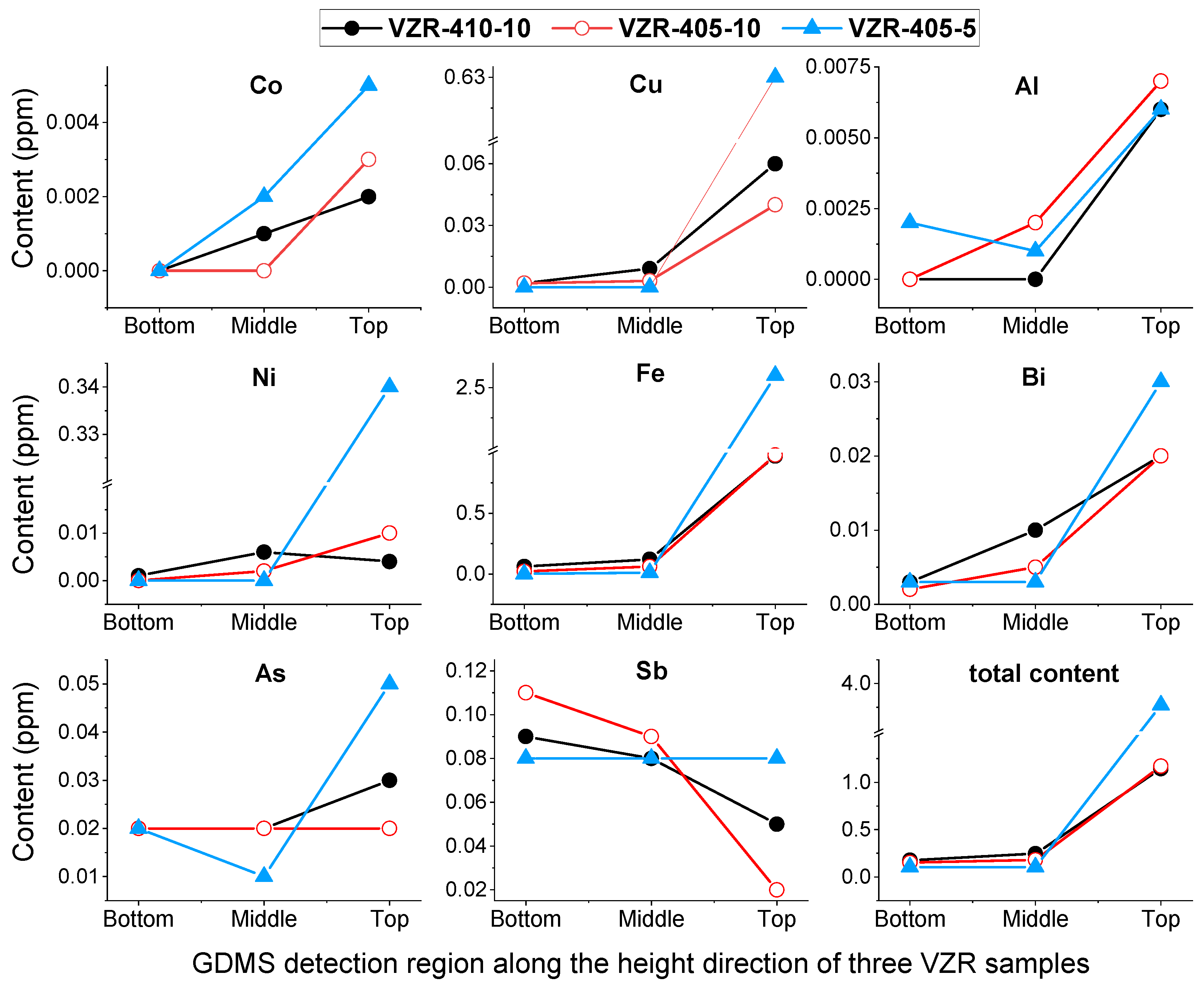
3.2. Vertical Zone Refining Experiments for 7N-Grade Ultra-High-Purity Tin
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Versolato, O.O. Physics of laser-driven tin plasma sources of EUV radiation for nanolithography. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2019, 28, 083001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flosdorf, E.W.; Palmer, A.E. Purification of materials by vacuum distillation. J. Rheol. 1932, 3, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J. Removal of impurities from tin by vacuum distillation. Nature 1952, 169, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.B.; Yang, B.; Liu, D.C. Deeply removing lead from Pb-Sn alloy with vacuum distillation. Trans. Nonferr. Metal. Soc. 2013, 23, 1822–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, C.B.; Yang, H.W.; Yang, B.; Liu, D.C.; Xiong, H. Experimental and modeling vapor-liquid equilibria: Separation of Bi from Sn by vacuum distillation. Vacuum 2017, 135, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Z.H.; Han, J.B.; Li, Y.F.; Dai, Y.N.; Yang, B.; Wang, A.X. Removal of arsenic from crude tin by vacuum distillation. Mater. Trans. 2018, 59, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.J.; Pu, Z.H.; Li, Y.F.; Yang, B.; Xu, J.J. Study on separation of Sn-Sb alloy by vacuum distillation. In 10th International Symposium on High-Temperature Metallurgical Processing, The Minerals, Metals & Materials Series; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 361–370. [Google Scholar]
- Filzwieser, A.; Filzwieser, I.; Konetschnik, S. New technology for electrorefining of copper. JOM 2012, 64, 1290–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gana, R.E.; Figueroa, M.G.; Kattan, L.; Orpinas, J.M. The anode-support system: An alternative for the electrorefining of tin in sulphuric acid medium. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1993, 23, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulcsar, T.; Toth, G.B.; Kekesi, T. Complex evaluation and development of electrolytic tin refining in acidic chloride media for processing tin-based scrap from lead-free soldering. Miner. Process. Extr. Metall. 2016, 125, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimaszeki, G.; Kulcsar, T.; Kekesi, T. Investigation and optimization of tin electrorefining in hydrochloric acid solutions. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2012, 42, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.X.; Friedrich, S.; Friedrich, B. Production of high purity metals: A review on zone refining process. J. Cryst. Process Technol. 2018, 8, 33–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, J.Y.; Xu, J.J.; Li, Y.F.; Pu, Z.H.; Xu, B.Q.; Yang, B. Preparation of high-purity tin by zone melting. Russ. J. Non-Ferr. Met. 2020, 61, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.Y.; Oh, J.K.; Lee, D.H. Purification of tin by zone refining with development of a new model. Metall. Trans. B 1990, 21, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, T.; Cheung, N.; Tobar, C.M.T.; Mei, P.R.; Garcia, A. Zone refining of tin: Optimization of zone length by a genetic algorithm. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2013, 28, 746–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Z.W.; Lian, Z.H.; Li, M.J.; Han, K.; Zheng, H.X. Machine-learning-assisted multi-objective optimization in vertical zone refining of ultra-high purity indium. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 305, 122430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.X.; Tian, Q.L.; Wu, M.Z.; Peng, J.B.; Zhang, J.T.; Chen, L.S.; Lu, X.W.; Xu, Z.S.; Zheng, H.X. Numerical simulation analysis on solute redistribution of In–1 wt%Sn alloy during multipass vertical zone refining process. J. Cryst. Growth 2021, 565, 126156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.J.; Wu, M.Z.; Peng, J.B.; Zheng, H.X. Purification of high-purity tin via vertical zone refining. Separations 2023, 10, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massalski, T.; Murray, J.; Bennett, L.; Baker, H. Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams; American Society for Metals: Detroit, MI, USA, 1986; Volume 3, p. 2874. [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino, Y.; Utsunomiya, T. Purification of tin by a new method of zone refining. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1980, 15, 1521–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, C.H.; Kang, K.; Park, U.J.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, H.S.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, S.H. Numerical investigation on the evolution of thin liquid layer and dynamic behavior of an electro-thermal drilling probe during close-contact heat transfer. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voller, V.R.; Beckerman, C. Approximate models of microsegregation with coarsening. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 1999, 30, 3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voller, V.R. On a general back-diffusion parameter. J. Cryst. Growth 2001, 226, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, Y.; Saitou, Y.; Sugimoto, Y.; Kumagawa, M. Analysis of impurity concentration distributions in pulled semiconductor crystals. J. Electron. Mater. 1990, 19, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watauchi, S.; Tanaka, I.; Hayashi, K.; Hirano, M.; Hosono, H. Crystal growth of Ca12Al14O33 by the floating zone method. J. Cryst. Growth 2002, 237, 801–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
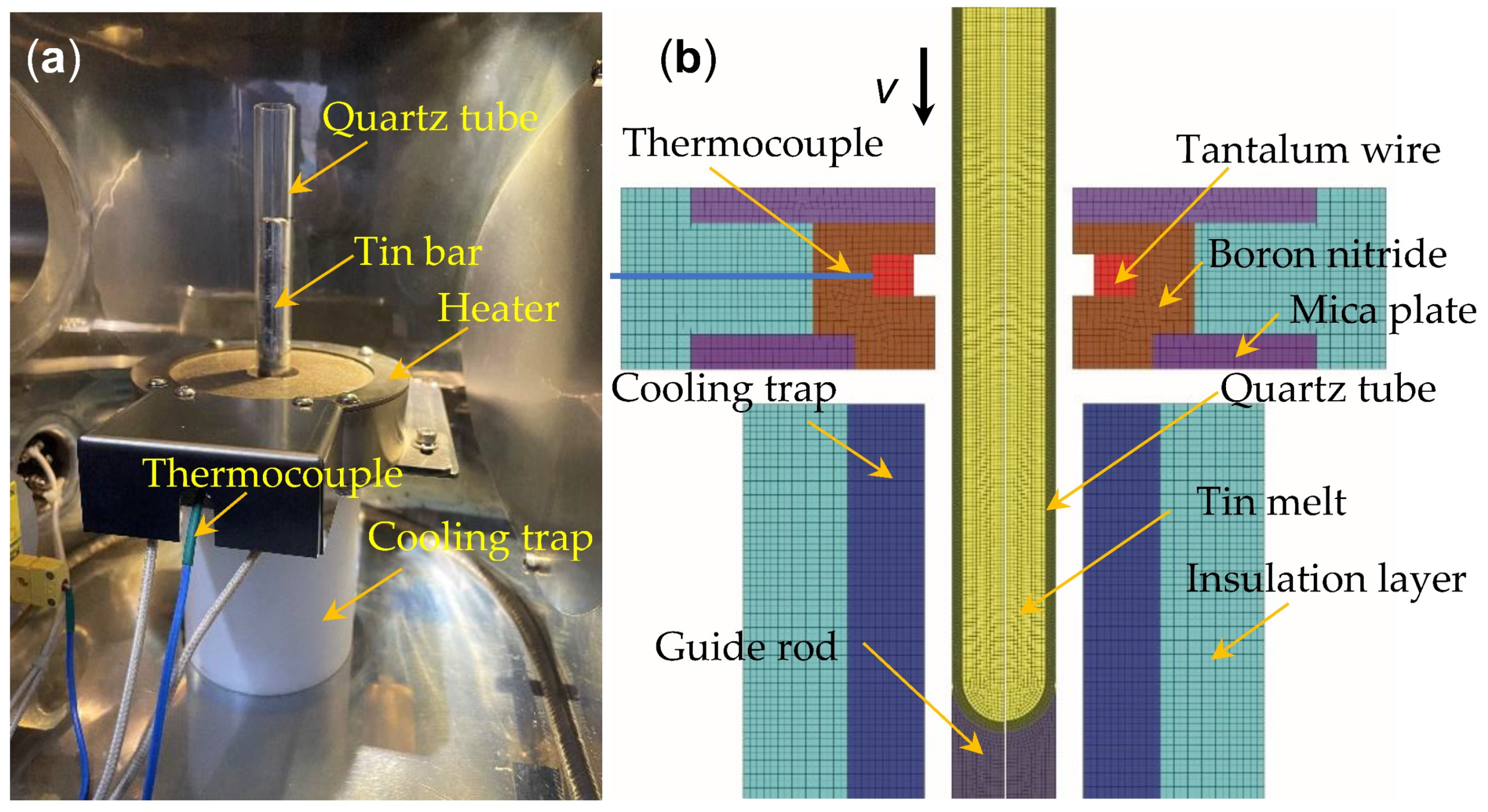



| Parameter | Symbol | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solid density | ρ0 | 7.298 × 103 | kg/m3 |
| Specific heat | CP | 2.26 × 102 | J/(kg·K) |
| Thermal conductivity | k | 67 | W/(m·K) |
| Viscosity | μ | 1.593 × 10−3 | kg/(m·s) |
| Solute diffusivity in liquid phase | Dl | 3 × 10−9 | m2/s |
| Solute diffusivity in solid phase | Ds | 1 × 10−12 | m2/s |
| Thermal expansion coefficient | βT | 9.5 × 10−5 | /K |
| latent heat of melting | ΔHf | 2.88 × 104 | J/kg |
| Solute expansion coefficient | βc | 3.8 × 10−3 | /(wt.%) |
| Solidus temperature | Ts | 227.5 | °C |
| Liquidus temperature | TL | 231.5 | °C |
| Equilibrium partition coefficient | k0 | 0.30 | - |
| Heater Temperature (°C) | Pulling Rate (µm/s) | |
|---|---|---|
| SIM-410-20 | 410 | 20 |
| SIM-420-20 | 420 | 20 |
| SIM-415-10 | 415 | 10 |
| SIM-415-30 | 415 | 30 |
| Heater Temperature (°C) | Pulling Rate (µm/s) | |
|---|---|---|
| VZR-410-10 | 410 | 10 |
| VZR-405-10 | 405 | 10 |
| VZR-405-5 | 405 | 5 |
| 6N-Grade Sn Starting Material | VZR-410-10 | VZR-405-10 | VZR-405-5 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bottom | Middle | Top | Bottom | Middle | Top | Bottom | Middle | Top | ||
| Co | 0.001 | — | 0.001 | 0.002 | — | — | 0.003 | — | 0.002 | 0.005 |
| Zn | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Ag | 0.001 | — | — | 0.002 | — | — | 0.003 | — | — | 0.02 |
| Cu | 0.01 | 0.002 | 0.009 | 0.06 | 0.002 | 0.003 | 0.04 | — | — | 0.63 |
| Ca | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Al | 0.005 | — | — | 0.006 | — | 0.002 | 0.007 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.006 |
| Mg | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Ni | 0.007 | 0.001 | 0.006 | 0.004 | — | 0.002 | 0.01 | — | — | 0.34 |
| Pb | 0.005 | — | — | 0.004 | — | — | 0.008 | — | — | 0.01 |
| Au | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Fe | 0.13 | 0.06 | 0.12 | 0.97 | 0.02 | 0.06 | 0.98 | — | 0.01 | 2.6 |
| In | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Bi | 0.005 | 0.003 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.002 | 0.005 | 0.02 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.03 |
| Sb | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| As | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.05 |
| Total | 0.264 | 0.176 | 0.246 | 1.146 | 0.154 | 0.182 | 1.171 | 0.105 | 0.106 | 3.771 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, Y.; Wen, J.; He, Q.; Wu, M.; Chen, L.; Bao, Y.; Zheng, H. Optimizing Vertical Zone Refining for Ultra-High-Purity Tin: Numerical Simulations and Experimental Analyses. Separations 2024, 11, 273. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11090273
Yao Y, Wen J, He Q, Wu M, Chen L, Bao Y, Zheng H. Optimizing Vertical Zone Refining for Ultra-High-Purity Tin: Numerical Simulations and Experimental Analyses. Separations. 2024; 11(9):273. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11090273
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Yu, Jiajun Wen, Qi He, Meizhen Wu, Lishi Chen, Yuxu Bao, and Hongxing Zheng. 2024. "Optimizing Vertical Zone Refining for Ultra-High-Purity Tin: Numerical Simulations and Experimental Analyses" Separations 11, no. 9: 273. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11090273
APA StyleYao, Y., Wen, J., He, Q., Wu, M., Chen, L., Bao, Y., & Zheng, H. (2024). Optimizing Vertical Zone Refining for Ultra-High-Purity Tin: Numerical Simulations and Experimental Analyses. Separations, 11(9), 273. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11090273






