Abstract
This study investigated the distribution and binding affinity of dissolved copper (Cu) and organic carbon (OC) in size-fractioned dissolved organic matter (DOM) in a constructed wetland (CW). Two sites were studied: one at the inflow (P-1) and one within the wetland (P-2). The DOMs (<0.45 μm) were separated into six size fractions using a cross-flow ultrafiltration system. In the wetland (P-2), the concentrations of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) increased while the concentrations of Cu decreased. The high molecular weight fraction (1 kDa–0.45 μm, HMW) contained most of the OC mass (57.4–71.2% averages). On the other hand, Cu was almost equally distributed in HMW and low molecular weight fractions (<1 kDa, LMW) with mean HMW percentages of 50.3–51.3%. The mean Cu binding affinity to DOM ratios (CuBADOM) was 74.9 ± 24.0 μmol/g-C at site P-1 and 17.3 ± 2.6 μmol/g-C at site P-2. The CuBADOM ratios were decreased in wetlands of bulk and size-fractioned DOM (p < 0.001 to p = 0.073). The SUVA254 values for bulk DOM solution were 2.54 ± 0.15 and 1.68 ± 0.18 L/mg-C/m, and humidification index (HIX) values were 1.74 ± 0.16 and 2.09 ± 0.19 for sites P-1 and P-2, respectively. Optical indicators suggested that the wetland process decreased aromaticity but increased the humification degree of DOM. Furthermore, the CuBADOM ratios positively correlated with SUVA254 and HIX within the constructed wetland DOM but not in the influent DOM. Understanding the Cu distribution and binding affinity to size-fractioned DOM makes it possible to develop strategies to mitigate the potential effects of copper pollution in wetlands.
1. Introduction
Constructed wetlands (CW) are effective in improving water quality by reducing organic pollutants, nutrients, and heavy metals (HMs) [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]. The water in CW contains different types of dissolved organic matter (DOM), originating from the inflow and also produced within the wetland itself [6,7,8,9]. DOM levels in the wetland can be reduced by natural processes like plant uptake, colloidal aggradation and deposition, biodegradation, and photodegradation, with biodegradation and photodegradation being the main processes [6,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17]. However, the growth of wetland plants, especially during spring and summer, can lead to an increase in the amount of DOM present [6,7], subsequently raising the concentration of dissolved organic carbon (DOC) in the wetland [6,7,8,9,10,11]. These transformations result in dynamic changes in the abundance, molecular size, and chemical composition of DOM in aquatic systems, leading to significant impacts on their environmental behavior and ecological function.
DOM is a complex mixture of organic substances including humic acid, proteins, and carbohydrates [11,12,18,19]. The composition, structure, and molecular weight distribution of DOM can vary across different water bodies due to distinct biogeochemical processes [12,20,21]. These variations in components and structures lead to different metal-binding properties of DOM, impacting the toxicity and transportation of metals in the environment [22].
HMs are significant environmental pollutants that are known for their biological toxicity and non-degradability [2,3,4,5]. HMs exist in various forms in the aquatic environment, with free ions being highly toxic. However, when heavy metals bind to organic colloids, their toxicity decreases [23,24]. Additionally, heavy metals that bind to different molecular weight organic matter can form complexes that may aggregate and deposit in sediment or promote the migration of heavy metals over longer distances [25,26,27].
The binding capacity of heavy metals to dissolved organic matter (DOM) is expressed as the binding affinity of heavy metals to DOM, which is known as the HMBA value [28,29,30,31,32]. This value represents the ratio of heavy metal concentration bound to a unit of organic carbon (μmol g-OC−1). A high HMBA value indicates a greater capacity of DOM to bind with heavy metals. The HMBA ratios determine the binding capacity and migration of river DOM, soil, and sediment-extracted DOM to bind with heavy metals [28,29,30,33]. In previous studies, the CuBA ratios in river water DOM have been observed to range from 7.5 to 29.8 μmol g-C−1 [9,29,31]. Furthermore, the CuBA ratios of water- and CaCl2-extracted soil organic matter were found to range from below the detection limit to 34.0 μmol g-C−1, and the CuBA ratios of NaOH-extracted soil and sediment organic matter varied from 13.2 to 56.2 μmol g-C−1 [28,33,34].
To assess the chemical composition and structure of DOM, optical indicators are used as they are rapid, cost-effective and sensitive tools [6,7,8,9,10,11,30,35,36,37,38]. One such indicator is SUVA254, which is the ratio of ultraviolet absorbance at 254 nm to DOC concentration [39]. This indicator provides information about the level of aromaticity of DOM, with higher values indicating a greater aromatic content [7,39]. The humification index (HIX) from the fluorescence spectrum can also be used to assess the degree of humification of DOM, with high HIX values indicating a great degree of humification [40,41]. Both SUVA254 and HIX are commonly used to examine the aromatic content and humification degree of DOM in water, soil, and sediment extraction solutions [11,37,38]. Previous studies have shown a significant positive link between CuBA values and SUVA254 in river water and soil extraction solutions [28,29,30,33].
There is limited research on the binding affinity of heavy metals to size-fractioned DOM in CWs, particularly regarding how plant-driven leaching DOM binds to heavy metals. Previous studies have mainly focused on heavy metal filtration in aqueous solutions and their binding affinity [28,29,30,33]. However, few studies have examined the ratios of different molecular weights of DOM in terms of their binding behavior with heavy metals, which could provide valuable insights into their behavior [31,34,42,43,44,45]. Understanding how heavy metals bind with DOM of different molecular weights is crucial in comprehending the migration, biotoxicity, and environmental fate of these metals [46,47,48].
The purpose of this study is to investigate how Cu binds to different sizes of DOM in a constructed wetland during the summer season. Copper was chosen for this study due to its toxicity to both humans and ecological organisms [11,21,49,50]. In the United States, regulations have been in place since 1991 to limit copper exposure through drinking water. The US Environmental Protection Agency has established a maximum contaminant level goal and a drinking water action level for copper at 1.3 mg Cu/L, guided by an oral reference dose of 0.04 mg Cu/kg/day to safeguard against acute or chronic toxicity in adults and children [49,50]. Moreover, the presence of various materials in DOM significantly influences copper behavior. The interaction of copper with DOM can be characterized by the spectral changes of Cu binding with DOM [38,51,52,53]. Water samples were collected from two points: the wetland influent (P-1) and within the wetland (P-2). These samples were filtered (<0.45 μm) and then separated into six size fractions using an ultrafiltration system based on their molecular weights. The concentrations of Cu and DOC, as well as the UV/Vis and fluorescence spectra of both bulk and size-fractioned DOM, were measured. To determine the Cu binding affinity of the DOM, the CuBADOM ratios and optical indicators (SUVA254 and HIX) were calculated for both the bulk and size-fractioned DOM. Linear correlation was used to examine the factors that affected CuBADOM, such as optical indicators and DOC and Cu concentrations.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Site and Sample Collection and Preparation
Water samples were collected from a constructed wetland located on the National Pingtung University of Science and Technology (NPUST) campus in Neipu Township, Pingtung County, Taiwan. The campus has geographical coordinates of 22°38′40″ N and 120°36′38″ E, with an altitude of approximately 70–100 m. The constructed wetland was previously an abandoned fish pond and grassland and is made up of a regulating area measuring 0.23 hectares and the main body of the wetland measuring 2.34 hectares, with an upstream catchment area of about 14.44 hectares (see Figure 1). The campus experiences a tropical climate with an average temperature of 25.5 °C and an annual rainfall of around 2600 mm. The composition of the constructed wetland sediment was reported as 30% sand, 36% clay, and 34% clay loam, with a soil organic matter content of 6.9% [54].
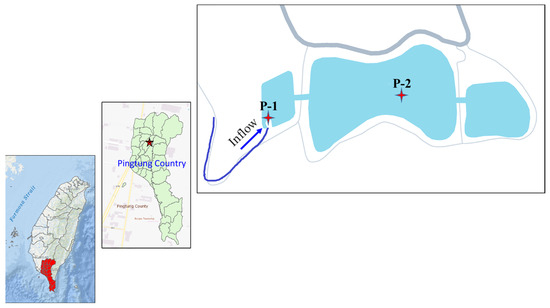
Figure 1.
The sampling location and sites.
The water sources of the constructed wetland include overflow water discharged from the aquaculture pond of the Department of Aquaculture at NPUST, rainfall, rainfall runoff collected from the upstream catchment area, and pumped groundwater used to maintain the water level of the wetland. The water losses of the constructed wetland include groundwater infiltration and evapotranspiration from the pool surface and plants. The average inflow volume was reported as 7372 m3 d−1, and the mean stored water volume was 9256 m3 in the constructed wetland [54]. As a result, the hydraulic retention time of the constructed wetland is estimated to be around 19.1 h.
Water samples were collected from two sites within the CW. The first water sampling site (P-1) is at the entrance of the CW and represents the influent. The second sampling site (P-2) is located central to the CW and represents wetland water samples. Water samples were collected three times in July 2015, with twenty-liter water collected at each sampling site. After the water samples were collected, they were taken back to the laboratory (<1 h) for water filtration (<0.45 um) and water quality analysis. The filtrate was named bulk DOM.
The measurement of basic water quality parameters includes pH, COD, dissolved oxygen (DO), suspended solids (SS), total suspended solids (TSS), and N-NH4+. These measurements are conducted according to the Taiwan EPA standard methods (NIEA W424.53A for pH, W515.55A for COD, W455.52C for DO, W210.58A for SS and TSS, and W448.52B for N-NH4+). At site P-1, the values were 7.02 ± 0.02 for pH, 60.3 ± 2.9 mg/L for COD, 2.23 ± 0.03 mg/L for DO, 4.0 ± 0.5 mg/L for SS, 147.7 ± 2.1 mg/L for TSS, and 4.27 ± 0.01 mg/L for N-NH4+, respectively. At site P-2, the values were 7.39 ± 0.02 for pH, 66.0 ± 0.2 mg/L for COD, 2.09 ± 0.01 mg/L for DO, 17.3 ± 0.3 mg/L for SS, 159.3 ± 3.1 mg/L for TSS, and 4.12 ± 0.01 mg/L for N-NH4+, respectively. The water parameters at site P-2 showed an increase in pH, COD, SS, and TSS (p = 0.001–0.08), but a decrease in DO and N-NH4+ values (p < 0.01).
2.2. DOM Separation
Ten liters of filtered DOM solutions (<0.45 μm) were separated into six size-fractioned DOM solutions. To accomplish this, a cross-flow ultrafiltration system equipped with ceramic membrane cartridges of nominal molecular weight cutoffs of 0.14 μm, 100 kDa, 10 kDa, 3 kDa, and 1 kDa (Filtanium, France) was employed. The six size-fractioned DOMs were designated as SF-A (0.14–0.45 μm), SF-B (100 kDa–0.14 μm), SF-C (10–100 kDa), SF-D (3–10 kDa), SF-E (1.0–3.0 kDa), and SF-F (<1.0 kDa).
The separation process was carried out with a feed flow rate of 1.7–2.0 L/min, and a total of five separation processes were performed. The duration of each separation process was about three hours, depending on the area and pore size of the filtrate membrane. During the concentration process, the volume ratio of retentate flow (Vr) and permeate flow (Vp) was kept at Vr:Vp = 1:9, which resulted in a concentration volume factor of 10. The permeate flow was collected in a separate container while the retentate flow was returned to the feed flow bottle. Once the designated volume ratio was achieved, the permeate flow was used for the next separation process. The mass balance rate (MassBR, %) for Cu and DOC was calculated using Equation (1), while the mass percentages (MassSFi %) of the size-fractioned DOM for DOC and Cu were calculated using Equation (2) [55]:
where Ci and Vi were the concentration and volume of DOC and Cu for each size-fractioned solution. Cb and Vb were the concentration and volume of DOC and Cu for bulk DOM. The volume ratios were 0.1, 0.09, 0.081, 0.0729, 0.0656, and 0.5905 for the size-fractioned solutions SF-A, SF-B, SF-C, SF-D, SF-E, and SF-F, respectively. In each separated process, the ultrafiltration membrane needed to be carefully cleaned; the cleaning process followed the sequence of reverse osmosis (RO) water, neutral detergent, RO water, 0.5 N sodium hydroxide (NaOH) solution, RO water, and DDW water. When the ultramembrane was not used for a long time, the cartridge was kept in 0.5 N NaOH solution.
2.3. Dissolved Organic Carbon and Metals Measurement
The concentrations of DOC in DOM solutions were determined using a total organic carbon (TOC)-V analyzer (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). The concentrations of Cu were measured using a graphite furnace atomic spectrometer (Hitachi, Z-3000, Tokyo, Japan).
2.4. UV/Vis Measurements
The absorbance measurement of bulk and size-fractioned DOM solutions were measured using a UV/Vis spectrophotometer (Hitachi, U-2900, Japan), on a scanning wavelength of 800–200 nm. Background was corrected according to the Helms et al. [56] method. An average absorbance value of 700–800 nm was adopted as the background value, which was subtracted from the sample value. Aromaticity plays a crucial role because the electron-withdrawing nature of aromatic moieties in DOM increases its molecular electronegativity, resulting in the improved complexation of positively charged metal ions [57]. The specific absorbance at 254 nm (SUVA254) is proportional to the percentage of aromatic carbon in the DOM [39]. The SUVA254 value calculation follows in Equation (3):
where UV254 (cm−1) is the UV/Vis absorbance at 254 nm of the sample, and [DOC] is the DOC concentration (mg-C/L) of the size-fractioned DOM solutions [39].
2.5. Fluorescence Measurements
In this study, three-dimensional fluorescence excitation/emission matrix spectroscopy (EEM) was recorded. The bulk and size-fractioned DOM solutions were measured by a fluorescence spectrophotometer (Hitachi, F-7000, Japan). Fluorescent scanning conditions were as follows: an excitation wavelength of 200–450 nm with 5 nm increases, an emission wavelength of 250–550 nm with 2 nm increases, a scan rate of 2400 nm/min, a slit width of 5 nm, and voltage amplifying of 700 V. The spectra were obtained by subtracting an ultrapure water blank spectrum, recorded in the same condition, to eliminate the Raman scatter peaks.
The HIX value was determined using Equation (4) as outlined by Birdwell and Engel [41] and Hansen et al. [58]. This involves dividing the sum of the fluorescence emission wavelengths (Em) between 435–480 nm by the sum of the emission wavelengths between 300–345 nm when excited (Ex) at a wavelength of 254 nm. When the excitation wavelength is 254 nm, an emission wavelength of 435–480 nm indicates the presence of humic acid-like and fulvic acid-like substances, while an emission wavelength of 300–345 nm indicates the presence of protein substances in the DOM. Therefore, the ratio of emission at 435–480 nm to emission at 300–345 nm represents the ratio of fulvic acid-like and humic acid-like substances to proteins. A high value indicates that the DOM contains a large proportion of humic acid-like substances [58,59,60].
2.6. Copper Binding Affinity to DOM
The copper binding affinity to DOM (CuBADOM ratios, μmol/g-C) is calculated by dividing the Cu concentration (μmol/L) by the concentration of dissolved organic carbon (g-C/L) [28,29,30,33].
2.7. Statistic and Data Analysis
This study utilized the S-Plus software version 6.2 to conduct linear regression and various tests, all at a significance level of p < 0.05. To perform two group difference tests between P-1 and P-2, including factors such as concentration, mass percentage, CuBA ratios, and indicators, the t-test method was employed. Additionally, the ANOVA test method was used for more than three group difference tests, including the test among size-fractioned DOM. Fluorescence indicators were calculated using the R script developed by Lapworth and Kinniburgh [61].
3. Results
3.1. DOC and Cu Concentrations in the DOM
Table 1 presents the concentrations of DOC and Cu in bulk and size-fractioned DOM at the P-1 and P-2 sampling sites. The concentrations of each fraction are actual measured values, not multiplied by their corresponding volume ratio. The average mass balance of DOC in the DOM is 93%, and that of Cu is 106%. Both Cu and organic carbon (OC) mass balances fall within the accepted range of 100 ± 25% [62].

Table 1.
The measured DOC and Cu concentrations of bulk and size-fractioned DOM.
In this study, the DOC concentration in bulk DOM was measured within a wetland and compared to the DOC concentration found in the influent of bulk DOM. The mean DOC concentration of bulk DOM in the wetland was 3.64 ± 0.63 mg/L, which was significantly higher than the mean DOC concentration of 1.51 ± 0.31 mg/L in the influent (p = 0.014). The DOC concentrations in the bulk DOM solutions were found to be lower than the DOC concentrations found in general river water and wetlands in other studies [6,7,8,10,11,29,30,37,45,63].
All size fractions of DOC concentrations were found to be increased at site P-2, with SF-B (100 kDa–0.14 μm) having the highest increased ratios (671%). This suggests that the wetland increased the concentration of DOC in HMW DOM, which implies that the leaching of plant-driven DOM in the wetland is a major possibility [6,7,10]. Similar results have been observed in CW water in other studies [6,7,10,38].
The average concentration of Cu in bulk DOM was found to be 3.93±0.16 μg/L in the wetland, which was significantly lower than the average concentration in the influent, which was 6.87 ± 0.65 μg/L (p = 0.012). These concentrations are comparable to those found in unpolluted river and wetland water [29,30,64,65,66] and lower than reported Cu concentrations in CW [3,4]. Furthermore, the Cu concentration of all size-fractioned DOM decreased with decreasing ratios ranging from 5.4% to 47.5%. The SF-B and SF-C had high decreasing ratios, while SF-D had a low decreasing ratio.
3.2. DOC and Cu Mass Percentages in Size-Fractioned DOM
The distribution of Cu and DOC in different sizes of fractionated DOM is crucial for understanding the migration and biotoxicity of Cu in the environment. In Figure 2, the OC and Cu mass percentages of the size-fractioned DOM are calculated by Equation (2). Two sites had a different order of OC mass distribution. In the influent (site P-1), the SF-F had the highest OC mass percentage of 42.6%, and OC mass percentages of the other fractions ranged from 8.3–15.5%. Within the wetland (site P-2), the OC mass percentage of SF-B was significantly increased (ratio of 186%) and had the highest OC mass percentage of 44.2%. The OC mass percentage of the other fractions was decreased with ratios of 25.6% to 52.6%. For site P-1 and site P-2, the OC mass percentages of colloids (1 kDa–0.45 μm, HMW) were 57.4% and 71.2%, respectively. The wetland increased the ratio of colloidal OC. In freshwater aquatic environments, HMW OC percentages ranged from 23% to 80% [11,13,67,68].
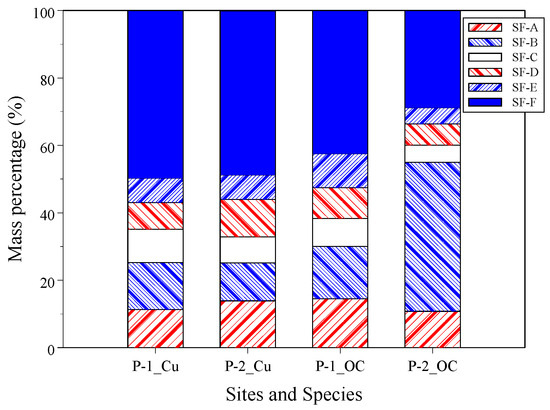
Figure 2.
Cu and OC mass percentage in size-fractioned DOM.
The distribution of Cu in size-fractioned DOM showed a consistent trend following size-fractioned DOM, although the Cu was significantly decreased in the CW. Cu mass was primarily distributed in the truly dissolved phase (<1 kDa, LMW) and was 49.7% and 48.7% for sites P-1 and P-2, respectively. The Cu mass percentages ranged from 7.3% to 13.9% for influent and from 7.2% to 13.9% within wetland for the other size fractions from SF-A to SF-E. Previous studies show that the Cu mass percentages in the HMW DOM varied in aquatic environments; for example, the Cu mass percentages of the HMW (1 kDa–0.22 μm) were 53% and 38% for lake and river water, respectively [69], and that Cu mass percentage of river water is comparable to the results of the present study. In four treatment processes of a municipal wastewater treatment plant, Hargreaves et al. [42] observed that HMW (1 kDa–0.45 μm) Cu mass percentages ranged from 69% to 77%, which were higher than the results of the present study.
During the current CW, the concentration of DOC increased while the concentration of Cu decreased. Specifically, the SF-B fraction exhibited the highest increase in both DOC concentration and mass percentage, while the SF-B and SF-C fractions showed the greatest decrease in Cu concentration. The SF-B fraction has the lowest aromaticity and humification degree, which will be further explained in Section 3.4. Properties of the SF-B fraction include low aromaticity and humification, resulting in low Cu binding affinity to SF-B DOM. The Cu in the SF-B fraction originally may have been redistributed to other molecular weight DOM. Additionally, there is a possibility that the high molecular weight fraction SF-B bound Cu and deposited it in the sediment. Therefore, the leaching of plant-derived DOM in the wetland significantly altered the DOC and Cu concentrations.
3.3. Cu Binding Affinity to DOM (CuBADOM)
The binding affinity of Cu to DOM, known as CuBADOM (μmol/g-C), is a measure of the ability of Cu to bind with DOM and its mobility [29,30,31]. The CuBADOM ratios varied with the size-fractioned DOM at sites P-1 and P-2, as shown in Figure 3. The CuBADOM ratios ranged from 58.9 to 101.3 μmol/g-C at site P-1 and from 5.1 to 36.3 μmol/g-C at site P-2, and they were found to vary between the sites. The bulk and size-fractioned CuBADOM ratios were lower at site P-2 (p = 0.001–0.073). The fraction SF-B had the highest decrease ratio of up to 93%, with Cu concentration decreasing by 46% and DOC concentration increasing by 671%. The leaching of plant-derived DOM in wetlands generated HMW DOM, which decreased the CuBADOM ratios. The CuBADOM ratio of bulk DOM decreased by 77%, and other size-fractioned DOMs increased from 46% to 65%.
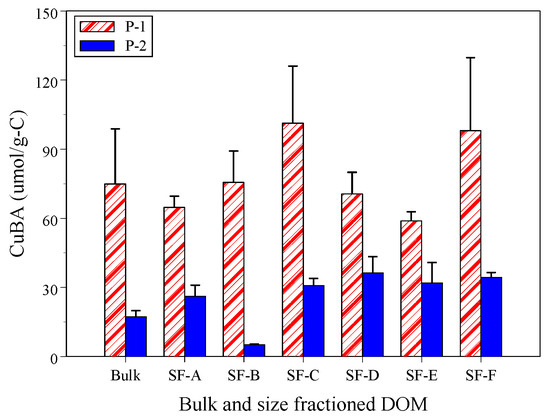
Figure 3.
Cu binding affinity to size-fractioned DOM at sites P-1 and P-2.
The main treatment processes in CW are biodegradation and photodegradation, which are responsible for consuming DOM in water [6,11,13]. Biodegradation results in the rapid loss of small labile aliphatic organic matter, carbohydrates, and proteins, converting HMW DOM to LMW fractions [6,11,13]. However, it can also release HMW aromatic carbon compounds, such as humic-like compounds, as byproducts of organic matter degradation [6].
In aquatic environments, photodegradation can shift HMW DOM to smaller photoproducts [6]. In this CW, plant-derived DOM is the dominant process significantly increasing DOC concentration at site P-2. The mass percentage of HMW OC increased, but the mass percentage of HMW Cu remained almost the same. Additionally, DOM with different molecular weights showed variations in metal binding efficiency [6,70,71]. Xu et al. [72] found that HMW DOM (>1 kDa) constituents had stronger complexing abilities with heavy metals. However, some studies have presented opposite views [73,74]. In this CW, the plant-derived leaching DOM fraction SF-B (100 kDa–0.14 μm) had the lowest copper binding affinity. This fraction exhibited low aromaticity and humification. Therefore, the source and process of wetlands affect the variation in DOM composition, structure, and molecular weight distribution, resulting in different metal-binding properties of DOM. This, in turn, impacts the toxicity and transportation of Cu in the environment [11,12,20,22].
The mean bulk CuBADOM ratio at site P-1 was 74.9 ± 24.0 μmol/g-C, which was higher than the CuBADOM ratios observed in river water (ranging from 7.5 to 29.8 μmol/g-C) [23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,64]. However, in the wetland, the CuBADOM ratio was 17.3 ± 2.6 μmol/g-C, which is comparable to the CuBADOM ratios observed in river water. It is worth noting that the LMW DOM (<100 kDa) had mean CuBADOM ratios ranging from 30.8 to 36.3 μmol/g-C. These DOM fractions may easily dissociate Cu from the Cu-DOM complex, which can increase Cu toxicity.
3.4. Optics Indicators of the DOM
Optical indicators are widely used to investigate the chemical composition and structure of DOM [15,28,30,33,75,76].
Figure 4a,b display the values of indicators for bulk and size-fractioned DOM, including SUVA254 and HIX. SUVA254 reflects the aromaticity of DOM, with high values indicating high aromaticity [35,39]. The SUVA254 values vary with both bulk and size-fractioned DOM at sites P-1 and P-2. At site P-1, the SUVA254 values of bulk DOM were significantly higher than those of site P-2 (p = 0.004). The mean total SUVA254 value of 2.25 ± 0.43 L/mg-C/m at site P-1 was also significantly higher than the SUVA254 value of 1.86 ± 0.64 L/mg-C/m at site P-2 (p = 0.036). Furthermore, the SUVA254 values of fraction SF-B at site P-2 were significantly lower (0.65 ± 0.14 L/mg-C/m) than those at site P-1 (1.57 ± 0.29 L/mg-C/m) (p = 0.02). All the SUVA254 values were less than 4.0, indicating that the DOM composition of the influent and wetland DOM primarily consisted of hydrophilic substances with poor aromaticity [59].
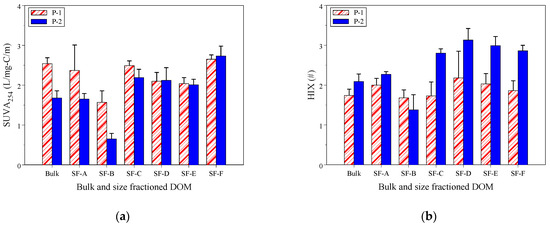
Figure 4.
(a,b) SUVA254 (a) and HIX (b) values of bulk and size-fractioned DOM at sites P-1 and P-2.
The HIX values are used to indicate the degree of humification of the DOM [41,58,77]. In Figure 4b, the HIX values varied with the bulk and size-fractioned DOM at sites P-1 and P-2. The HIX values of bulk DOM at site P-1 were lower than those of bulk DOM at site P-2 (p = 0.07). The mean total HIX values of 1.89 ± 0.33 at site P-1 were significantly lower than the HIX value of 2.50 ± 0.62 at site P-2 (p < 0.001). The HIX values at site P-1 were insignificantly different among size-fractioned DOM (p > 0.05). However, at site P-2, the HIX values (0.65 ± 0.14) of SF-B were significantly lower than those of SF-C to SF-F (2.01–2.73). This implies that the leaching of plant-derived DOM had a low humification degree. Furthermore, all HIX values at sites P-1 and P-2 were less than 4.0, suggesting that the DOM had a low degree of humification as the DOM composition predominantly comprised hydrophilic substances [41,58,77]. The DOM increased HIX, but decreased the SUVA254 value in the present CW. This could be because the plant DOM had low aromaticity and degree humification, but wetland biochemical processes slightly increased the humification degree of DOM.
The optical indicators of DOM may vary in river and wetland water, depending on the sources and biochemical processes of the aquatic environment. Previous research indicates that the SUVA254 values for DOM in wetlands ranged from 0.41 to 3.54 L/mg-C/m [6,7,9,11,21,37,38,78]. Similarly, the HIX values for river and wetland DOM ranged from 0.89 to 4.61 [11,21,38,78]. In the current study, the SUVA254 and HIX values of CW DOM are within the reported ranges of values in wetlands.
Figure 5 shows the correlation of SUVA254 and HIX at sites P-1 and P-2. In the influent (site P-1), the correlation of SUVA254 and HIX was insignificant (r = 0.01). However, within the wetland (site P-2), there was a significantly positive correlation between SUVA254 and HIX (r = 0.84, p < 0.001). Biochemical processes in the wetland stabilize and homogenize the DOM composition and structure for each size fraction of DOM, resulting in high aromatic DOM with a high degree of humification in size-fractioned DOM.
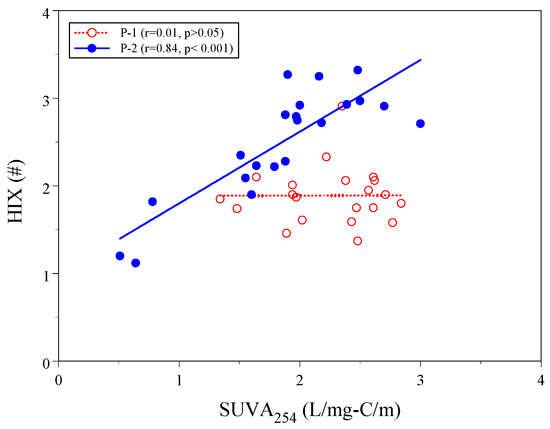
Figure 5.
Linear correlation between SUVA254 and HIX at sites P-1 and P-2.
3.5. Correlation between CuBADOM Ratios with Optical Indicators
Figure 6a,d demonstrate the linear correlation between CuBADOM ratios and various indicators such as SUVA254 and HIX, as well as the concentrations of Cu and DOC for the size-fractioned DOM at sites P-1 and P-2. At site P-1, the CuBADOM ratios showed a weak correlation with SUVA254, HIX, and Cu concentrations, but a significantly negative correlation with DOC concentrations. At site P-2, the CuBADOM ratios had a weak correlation with Cu concentrations and a significantly negative correlation with DOC concentrations. Moreover, the CuBADOM ratios exhibited significantly positive correlations with SUVA254 and HIX values. At site P-1, the incoming DOM had various sources, making it complex. However, the wetland processes helped to even out and stabilize the chemical composition and structure of DOM. This resulted in a higher degree of aromaticity, which is an indicator of humification. The high degree of humification facilitated the binding of Cu to the organic matter with high aromaticity and humification. Overall, the correlation indicated that CuBADOM ratios were more favorable when there was a significant degree of aromaticity and humification in the DOM.
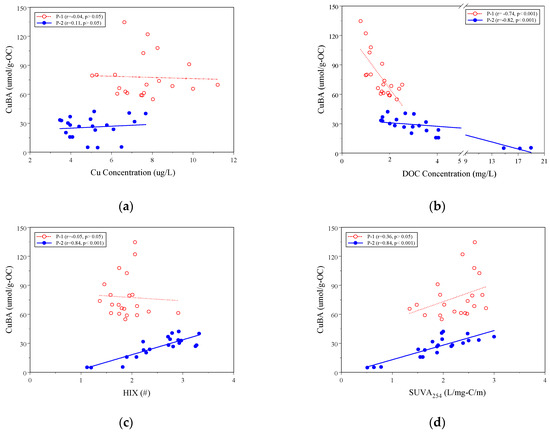
Figure 6.
(a–d) Linear correlation of CuBA ratios with Cu (a) and DOC (b) concentrations, as well as HIX (c) and SUVA254 (d) values at sites P-1 and P-2.
In the wetland (P-2), the CuBADOM ratios were significantly lower than in the influent water (site P-1). However, the solution’s DOC concentration increased (Table 1), while the Cu concentrations and CuBADOM ratios decreased (Table 1 and Figure 3). This is mainly due to the plant-derived DOM within the wetland, which led to a significant increase in the DOC concentration and the mass fraction of the molecular weight SF-B (0.14 μm–100 kDa) of P-2 (Table 1 and Figure 2). Furthermore, the SUVA254 and HIX fraction SF-B of P-2 are relatively lower compared to values of other molecular weights (Figure 4a,b), and these two indicators showed a significantly positive correlation (Figure 5). It suggests that the plant-derived DOM has a low aromaticity and low degree of humification. In comparison with the CuBADOM value of bulk DOM in P-2, the CuBADOM value of SF-B is also significantly reduced. These results indicate that the source and molecular weight of DOM have a significant impact on the binding affinity between Cu and DOM.
Previous studies have suggested that the CuBADOM ratios have a significantly positive correlation with the aromaticity of natural water DOM [29,30] and soil solution [28,33,34]. However, when the DOM has complex sources such as wastewater treatment plant effluent input [30] and anthropogenic ligand [29], the CuBADOM ratios have a poor correlation with SUVA254. Furthermore, several studies have observed a negative correlation between DOC concentrations and CuBADOM ratios [28,33,76].
4. Conclusions
The research revealed that the water passing through the CW resulted in an increase in DOC concentration and a decrease in Cu concentration. In the wetland, the Cu binding affinity to size-fractioned DOM decreased significantly compared to influent DOM. The HMW DOM increased DOC significantly, which suggests that the leaching of plant-derived DOM in the wetland contributed to the increased DOC concentration and decreased the CuBADOM ratios. Within the wetland (site P-2), the CuBADOM ratios positively correlated with indicators SUVA254 and HIX. The P-2 SUVA254 values decreased, while the HIX values increased. This change could be due to the low-aromatic nature of the DOC derived from wetland plants. However, wetland processes such as biodegradation and photodegradation still contribute to an increase in the HIX of low-molecular-weight DOM. The higher aromaticity and humification degree of DOM enhanced the Cu binding affinity to DOM.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.-Y.H. and T.-C.C.; methodology, M.-Y.H. and W.-H.H.; formal analysis, C.-Y.H. and T.-C.C.; investigation, M.-Y.H. and W.-H.H.; writing—original draft preparation, C.-Y.H., L.-F.H. and T.-C.C.; writing—review and editing, C.-Y.H., L.-F.H. and T.-C.C.; visualization, M.-Y.H., W.-H.H. and T.-C.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available upon request to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ali, M.; Rousseau, D.P.; Ahmed, S. A full-scale comparison of two hybrid constructed wetlands treating domestic wastewater in Pakistan. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 210, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J. Constructed wetlands for treatment of industrial wastewaters: A review. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 73, 724–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knox, A.S.; Paller, M.H.; Seaman, J.C.; Mayer, J.; Nicholson, C. Removal, distribution and retention of metals in a constructed wetland over 20 years. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 796, 149062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Ahmad, I.; Shah, M.T.; Rehman, S.; Khaliq, A. Use of constructed wetland for the removal of heavy metals from industrial wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 3451–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Luca, G.A.; Maine, M.A.; Mufarrege, M.; Hadad, H.R.; Sánchez, G.; Bonetto, C.A. Metal retention and distribution in the sediment of a constructed wetland for industrial wastewater treatment. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 1267–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurice, N.; Pochet, C.; Adouani, N.; Pons, M.-N. Role of seasons in the fate of dissolved organic carbon and nutrients in a large-scale surface flow constructed wetland. Water 2022, 14, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinney, M.L.; Westerhoff, P.K.; Baker, L. Transformations in dissolved organic carbon through constructed wetlands. Water Res. 2000, 34, 1897–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholz, C.; Jones, T.; West, M.; Ehbair, A.; Dunn, C.; Freeman, C. Constructed wetlands may lower inorganic nutrient inputs but enhance DOC loadings into a drinking water reservoir in North Wales. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 18192–18199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Choi, M.; Cho, J.; Chon, K. Transformation of dissolved organic matter in a constructed wetland: A molecular-level composition analysis using pyrolysis-gas chromatography mass spectrometry. Environ. Eng. Res. 2018, 23, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Johnston, S.E.; Bogard, M.J. Organic matter cycling in a model restored wetland receiving complex effluent. Biogeochemistry 2023, 162, 237–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Han, X.; Guo, L.; Ding, H.; Lang, Y. Effects of Cu (II)-DOM complexation on DOM degradation: Insights from spectroscopic evidence. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 921, 170928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Guo, L. Molecular size-dependent abundance and composition of dissolved organic matter in river, lake and sea waters. Water Res. 2017, 117, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Guo, L. Intriguing changes in molecular size and composition of dissolved organic matter induced by microbial degradation and self-assembly. Water Res. 2018, 135, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalán, N.; Marcé, R.; Kothawala, D.N.; Tranvik, L.J. Organic carbon decomposition rates controlled by water retention time across inland waters. Nat. Geosci. 2016, 9, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Chen, M.; Schlautman, M.A.; Hur, J. Dynamic exchanges between DOM and POM pools in coastal and inland aquatic ecosystems: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 551, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, A.G.; Bouchet, S.; Tolu, J.; Björn, E.; Mateos-Rivera, A.; Bertilsson, S. Molecular composition of organic matter controls methylmercury formation in boreal lakes. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeron, M.-A.; Radakovitch, O.; Charrière, B.; Vaultier, F.; Volkman, J.K.; Bianchi, T.S.; Ward, N.D.; Medeiros, P.M.; Sawakuchi, H.O.; Tank, S. Lipoxygenase-induced autoxidative degradation of terrestrial particulate organic matter in estuaries: A widespread process enhanced at high and low latitude. Org. Geochem. 2018, 115, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benner, R.; Amon, R.M. The size-reactivity continuum of major bioelements in the ocean. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2015, 7, 185–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellerman, A.M.; Dittmar, T.; Kothawala, D.N.; Tranvik, L.J. Chemodiversity of dissolved organic matter in lakes driven by climate and hydrology. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, M.L.; Meyer, J.S.; McKnight, D.M. Photooxidation of wetland and riverine dissolved organic matter: Altered copper complexation and organic composition. Hydrobiologia 2007, 579, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Han, X.; Guo, L.; Ding, H.; Hua, H.; Liu, C.-Q.; La, W.; Lang, Y. Role of molecular weight-dependent spectral properties in regulating Cu (II) binding by dissolved organic matter from different sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 873, 162246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Fang, X.; Wu, X.; Zhang, G.; Que, W.; Li, F. Alteration of bioaccumulation mechanisms of Cu by microalgae in the presence of natural fulvic acids. Chemosphere 2018, 211, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Jin, Z.; Hu, S.; Fang, X.; Li, F. Dissolved organic matter affects the bioaccumulation of copper and lead in Chlorella pyrenoidosa: A case of long-term exposure. Chemosphere 2017, 174, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palansooriya, K.N.; Shaheen, S.M.; Chen, S.S.; Tsang, D.C.; Hashimoto, Y.; Hou, D.; Bolan, N.S.; Rinklebe, J.; Ok, Y.S. Soil amendments for immobilization of potentially toxic elements in contaminated soils: A critical review. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, K.K.; Lofts, S.; Fortin, C.; Campbell, P.G. Trace metal speciation predictions in natural aquatic systems: Incorporation of dissolved organic matter (DOM) spectroscopic quality. Environ. Chem. 2012, 9, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Guéguen, C.l.; Smith, D.S.; Galceran, J.; Puy, J.; Companys, E. Metal (Pb, Cd, and Zn) binding to diverse organic matter samples and implications for speciation modeling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 4163–4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleinikova, O.V.; Shirokova, L.S.; Drozdova, O.Y.; Lapitskiy, S.A.; Pokrovsky, O.S. Low biodegradability of dissolved organic matter and trace metals from subarctic waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amery, F.; Degryse, F.; Cheyns, K.; De Troyer, I.; Mertens, J.; Merckx, R.; Smolders, E. The UV-absorbance of dissolved organic matter predicts the fivefold variation in its affinity for mobilizing Cu in an agricultural soil horizon. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2008, 59, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baken, S.; Degryse, F.; Verheyen, L.; Merckx, R.; Smolders, E. Metal complexation properties of freshwater dissolved organic matter are explained by its aromaticity and by anthropogenic ligands. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 2584–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, T.; Fujii, M.; Terao, K.; Jiwei, R.; Lee, Y.P.; Yoshimura, C. Correlations between aromaticity of dissolved organic matter and trace metal concentrations in natural and effluent waters: A case study in the Sagami River Basin, Japan. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 576, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chon, K.; Chon, K.; Cho, J. Characterization of size fractionated dissolved organic matter from river water and wastewater effluent using preparative high performance size exclusion chromatography. Org. Geochem. 2017, 103, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Xiao, M.; Mostofa, K.M.; Xu, S.; Wang, Z. Spatial Variations of Trace Metals and Their Complexation Behavior with DOM in the Water of Dianchi Lake, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amery, F.; Degryse, F.; Degeling, W.; Smolders, E.; Merckx, R. The copper-mobilizing-potential of dissolved organic matter in soils varies 10-fold depending on soil incubation and extraction procedures. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 2277–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.-H.; Lin, T.-C.; Huang, C.-M.; Chen, T.-C.; Yeh, Y.-L. Copper distribution and binding affinity of size-fractioned humic substances taken from paddy soil and correlation with optical characteristics. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Hur, J. Utilization of UV-Vis spectroscopy and related data analyses for dissolved organic matter (DOM) studies: A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 47, 131–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, T.-P.; Huang, W.-S.; Chen, T.-C.; Yeh, Y.-L. Fluorescence characteristics of dissolved organic matter (DOM) in percolation water and lateral seepage affected by soil solution (SS) in a lysimeter test. Sensors 2019, 19, 4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Wang, P.; Wang, C.; Qian, J.; Hou, J.; Cui, X.; Zhang, N. The effect of anthropogenic impoundment on dissolved organic matter characteristics and copper binding affinity: Insights from fluorescence spectroscopy. Chemosphere 2017, 188, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.; Yao, X.; Ren, H.; Ma, F.; Liu, L.; Huo, X.; Lin, T.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, Y. Multi-spectroscopic investigation of the molecular weight distribution and copper binding ability of dissolved organic matter in Dongping Lake, China. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 300, 118931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weishaar, J.L.; Aiken, G.R.; Bergamaschi, B.A.; Fram, M.S.; Fujii, R.; Mopper, K. Evaluation of specific ultraviolet absorbance as an indicator of the chemical composition and reactivity of dissolved organic carbon. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 4702–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huguet, A.; Vacher, L.; Relexans, S.; Saubusse, S.; Froidefond, J.-M.; Parlanti, E. Properties of fluorescent dissolved organic matter in the Gironde Estuary. Org. Geochem. 2009, 40, 706–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birdwell, J.E.; Engel, A.S. Characterization of dissolved organic matter in cave and spring waters using UV–Vis absorbance and fluorescence spectroscopy. Org. Geochem. 2010, 41, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, A.J.; Vale, P.; Whelan, J.; Constantino, C.; Dotro, G.; Campo, P.; Cartmell, E. Distribution of trace metals (Cu, Pb, Ni, Zn) between particulate, colloidal and truly dissolved fractions in wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 2017, 175, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-C.; Hseu, Z.-Y.; Jean, J.-S.; Chou, M.-L. Association between arsenic and different-sized dissolved organic matter in the groundwater of black-foot disease area, Taiwan. Chemosphere 2016, 159, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, S.-H.; Chiu, T.-P.; Huang, W.-S.; Chen, T.-C.; Yeh, Y.-L. Cadmium (Cd) and Nickel (Ni) Distribution on Size-Fractioned Soil Humic Substance (SHS). Int. J Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, C.-W.; Hsu, L.-F.; Tsai, H.-C.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Huang, W.-S.; Chen, T.-C. Nickel Binding Affinity with Size-Fractioned Sediment Dissolved and Particulate Organic Matter and Correlation with Optical Indicators. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiken, G.R.; Hsu-Kim, H.; Ryan, J.N. Influence of dissolved organic matter on the environmental fate of metals, nanoparticles, and colloids. ACS Publ. 2011, 45, 3196–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.A.; Hamilton-Taylor, J.; Lofts, S.; Meeussen, J.C.; Lin, C.; Zhang, H.; Davison, W. Testing copper-speciation predictions in freshwaters over a wide range of metal–organic matter ratios. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 1487–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ahmed, I.A.; Hamilton-Taylor, J.; Bieroza, M.; Zhang, H.; Davison, W. Improving and testing geochemical speciation predictions of metal ions in natural waters. Water Res. 2014, 67, 276–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.A.; Tsuji, J.S.; McArdle, M.E.; Adams, W.J.; Goodfellow, W.L., Jr. Recommended reference values for risk assessment of oral exposure to copper. Risk Anal. 2023, 43, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.A.; Tsuji, J.S.; Garry, M.R.; McArdle, M.E.; Goodfellow, W.L.; Adams, W.J.; Menzie, C.A. Critical review of exposure and effects: Implications for setting regulatory health criteria for ingested copper. Environ. Manag. 2020, 65, 131–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.-J.; He, X.-S.; Li, C.-W.; Li, N.-X. The binding properties of copper and lead onto compost-derived DOM using Fourier-transform infrared, UV-vis and fluorescence spectra combined with two-dimensional correlation analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 365, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Han, X.; Liu, C.-Q.; Guo, L.; Ding, H.; Lang, Y. Differences in the spectroscopic characteristics of wetland dissolved organic matter binding with Fe3+, Cu2+, Cd2+, Cr3+ and Zn2+. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 800, 149476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Ma, J.; Ji, G. Examination of effects of Cu(II) and Cr(III) on Al(III) binding by dissolved organic matter using absorbance spectroscopy. Water Res. 2016, 93, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.W. A study of wetland hydrology and water quality system at Jin-tsu Pond in National Pingtung University of Science and Technology. Master’s Thesis, National Pingtung University of Science and Technology, Pingtung, Taiwan, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Gao, X.; Song, J.; Chen, C.-T.A.; Chu, J. Colloidal toxic trace metals in urban riverine and estuarine waters of Yantai City, southern coast of North Yellow Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 135265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helms, J.R.; Stubbins, A.; Ritchie, J.D.; Minor, E.C.; Kieber, D.J.; Mopper, K. Absorption spectral slopes and slope ratios as indicators of molecular weight, source, and photobleaching of chromophoric dissolved organic matter. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2008, 53, 955–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leenheer, J.; Brown, G.; MacCarthy, P.; Cabaniss, S. Models of metal binding structures in fulvic acid from the Suwannee River, Georgia. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 2410–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, A.M.; Kraus, T.E.; Pellerin, B.A.; Fleck, J.A.; Downing, B.D.; Bergamaschi, B.A. Optical properties of dissolved organic matter (DOM): Effects of biological and photolytic degradation. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2016, 61, 1015–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matilainen, A.; Gjessing, E.T.; Lahtinen, T.; Hed, L.; Bhatnagar, A.; Sillanpää, M. An overview of the methods used in the characterisation of natural organic matter (NOM) in relation to drinking water treatment. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 1431–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, N.; Baker, A.; Reynolds, D. Fluorescence analysis of dissolved organic matter in natural, waste and polluted waters—A review. River Res. Appl. 2007, 23, 631–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapworth, D.J.; Kinniburgh, D. An R script for visualising and analysing fluorescence excitation-emission matrices (EEMs). Comput. Geosci. 2009, 35, 2160–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrin, A.; Roulier, J.-L.; Coquery, M. Colloidal and truly dissolved metal (oid) fractionation in sediment pore waters using tangential flow filtration. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 31, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Ma, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, F.; Han, X.; Li, M.; Ni, J. Optical property of dissolved organic matters (DOMs) and its link to the presence of metal ions in surface freshwaters in China. Chemosphere 2017, 188, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kang, S.Y.; Kim, S.Y. Hydroclimatic controls on dissolved organic matter (DOM) characteristics and implications for trace metal transport in Hwangryong River Watershed, Korea, during a summer monsoon period. Hydrol. Process. Int. J. 2007, 21, 3025–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duc, T.A.; Loi, V.D.; Thao, T.T. Partition of heavy metals in a tropical river system impacted by municipal waste. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 1907–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wan, Y.; Camara, A.Y.; Li, H. Effects of the addition and aging of humic acid-based amendments on the solubility of Cd in soil solution and its accumulation in rice. Chemosphere 2018, 196, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, J.R.; O’Driscoll, N.J.; Lean, D.R. Size distribution of methylmercury associated with particulate and dissolved organic matter in freshwaters. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 408, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvie, H.; Neal, C.; Rowland, A.; Neal, M.; Morris, P.; Lead, J.; Lawlor, A.; Woods, C.; Vincent, C.; Guyatt, H. Role of riverine colloids in macronutrient and metal partitioning and transport, along an upland–lowland land-use continuum, under low-flow conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 434, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilina, S.M.; Lapitskiy, S.A.; Alekhin, Y.V.; Viers, J.; Benedetti, M.; Pokrovsky, O.S. Speciation, size fractionation and transport of trace elements in the continuum soil water–mire–humic lake–river–large oligotrophic lake of a Subarctic watershed. Aquat. Geochem. 2016, 22, 65–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilina, S.M.; Drozdova, O.Y.; Lapitskiy, S.A.; Alekhin, Y.V.; Demin, V.V.; Zavgorodnyaya, Y.A.; Shirokova, L.S.; Viers, J.; Pokrovsky, O.S. Size fractionation and optical properties of dissolved organic matter in the continuum soil solution-bog-river and terminal lake of a boreal watershed. Org. Geochem. 2014, 66, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiikkilä, O.; Kitunen, V.; Smolander, A. Chemical and biological characterization of dissolved organic matter derived from Norway spruce litter divided into fractions according to molecular size. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2012, 50, 109–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zou, L.; Guan, D.; Li, W.; Jiang, H. Molecular weight-dependent spectral and metal binding properties of sediment dissolved organic matter from different origins. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 665, 828–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Li, D.; Li, W. Metal binding by dissolved organic matter in hypersaline water: A size fractionation study using different isolation methods. Limnologica 2021, 87, 125849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Zarruk, K.K.; Scholer, G.; Dudal, Y. Fluorescence fingerprints and Cu2+-complexing ability of individual molecular size fractions in soil-and waste-borne DOM. Chemosphere 2007, 69, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Lee, J.-H.; Hur, J. Anthropogenic signature of sediment organic matter probed by UV–Visible and fluorescence spectroscopy and the association with heavy metal enrichment. Chemosphere 2016, 150, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.-S.; Huang, W.-S.; Hsu, L.-F.; Yeh, Y.-L.; Chen, T.-C. Fluorescence of Size-Fractioned Humic Substance Extracted from Sediment and Its Effect on the Sorption of Phenanthrene. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrien, M.; Yang, L.; Hur, J. Lipid biomarkers and spectroscopic indices for identifying organic matter sources in aquatic environments: A review. Water Res. 2017, 112, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Guo, L. Variations in colloidal DOM composition with molecular weight within individual water samples as characterized by flow field-flow fractionation and EEM-PARAFAC analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 1657–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).