Determination of Topiramate and Carbamazepine in Plasma by Combined Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction and Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Plasma Samples
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.4. Study of DLLME Parameters
2.5. Instrumentation
2.6. Identification of Compounds
2.7. Method of Validation
3. Results
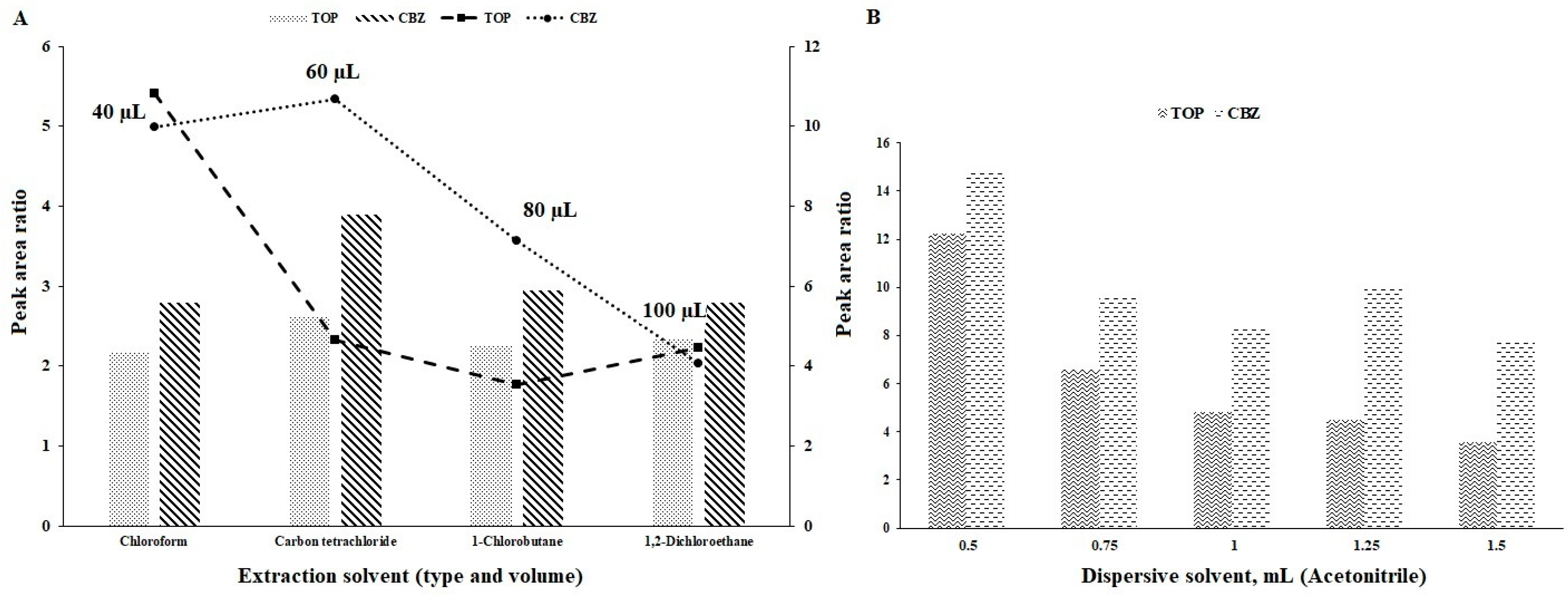
3.1. Type of Extraction and Dispersive Solvents
3.2. Volume of Extraction Solvent
3.3. Volume of Dispersive Solvent
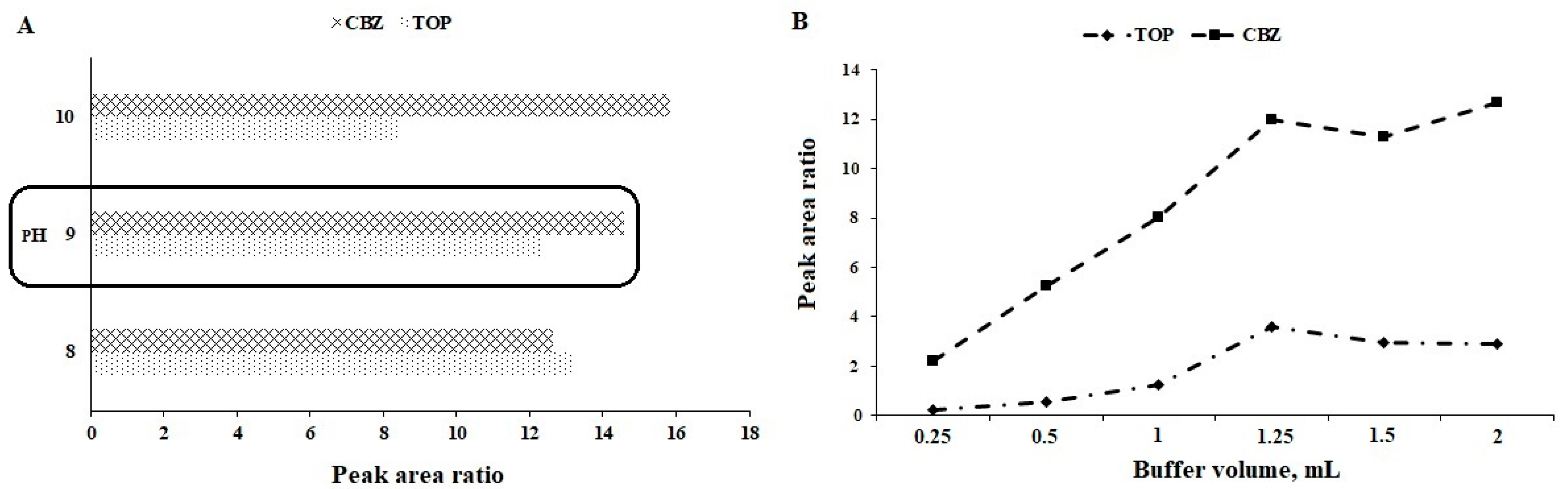
3.4. pH of the Sample Solution
3.5. Volume of Buffer Solution
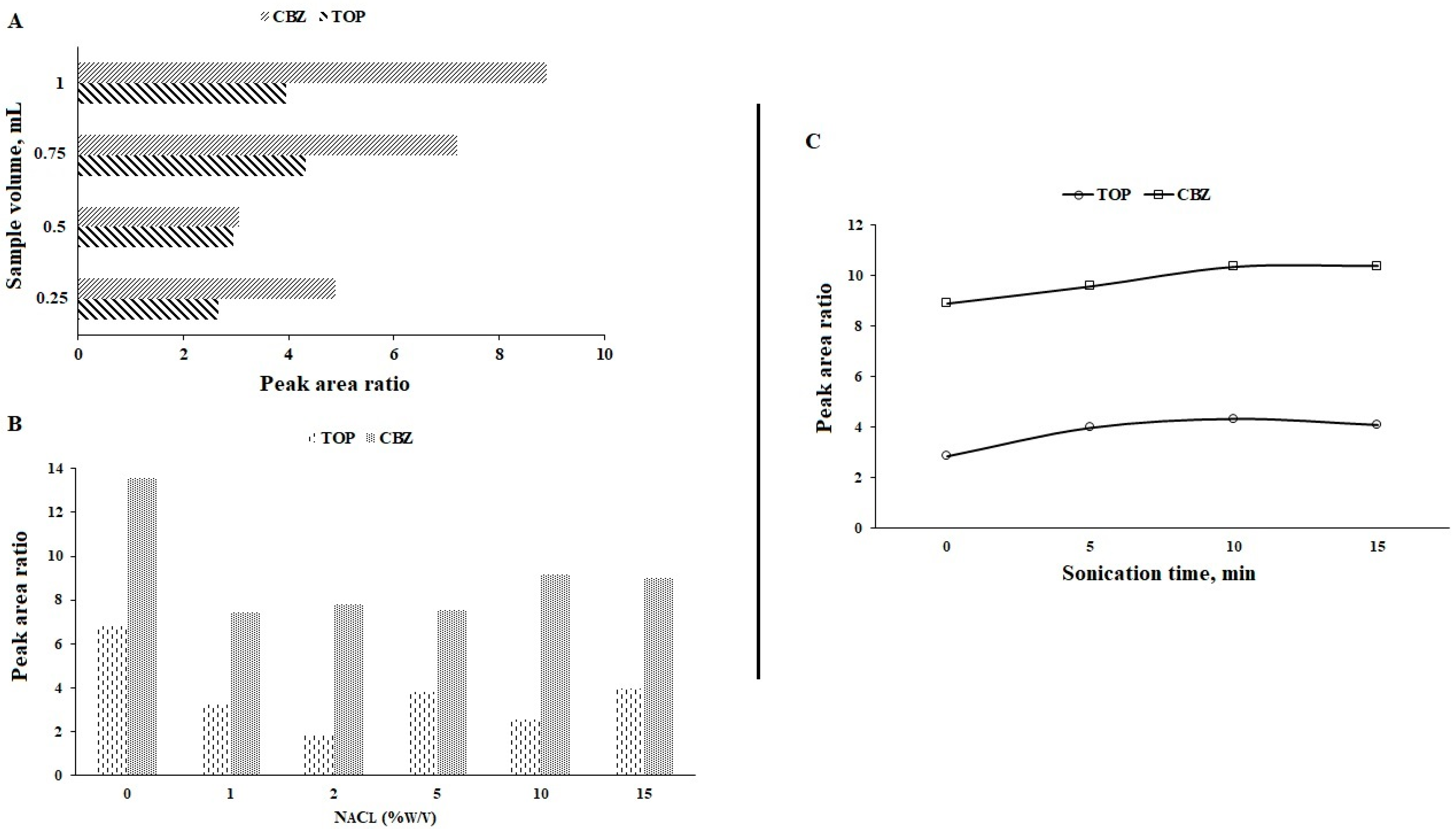
3.6. Volume of Sample
3.7. Ionic Strength
3.8. Sonication Time
3.9. Validation of the Optimized Method
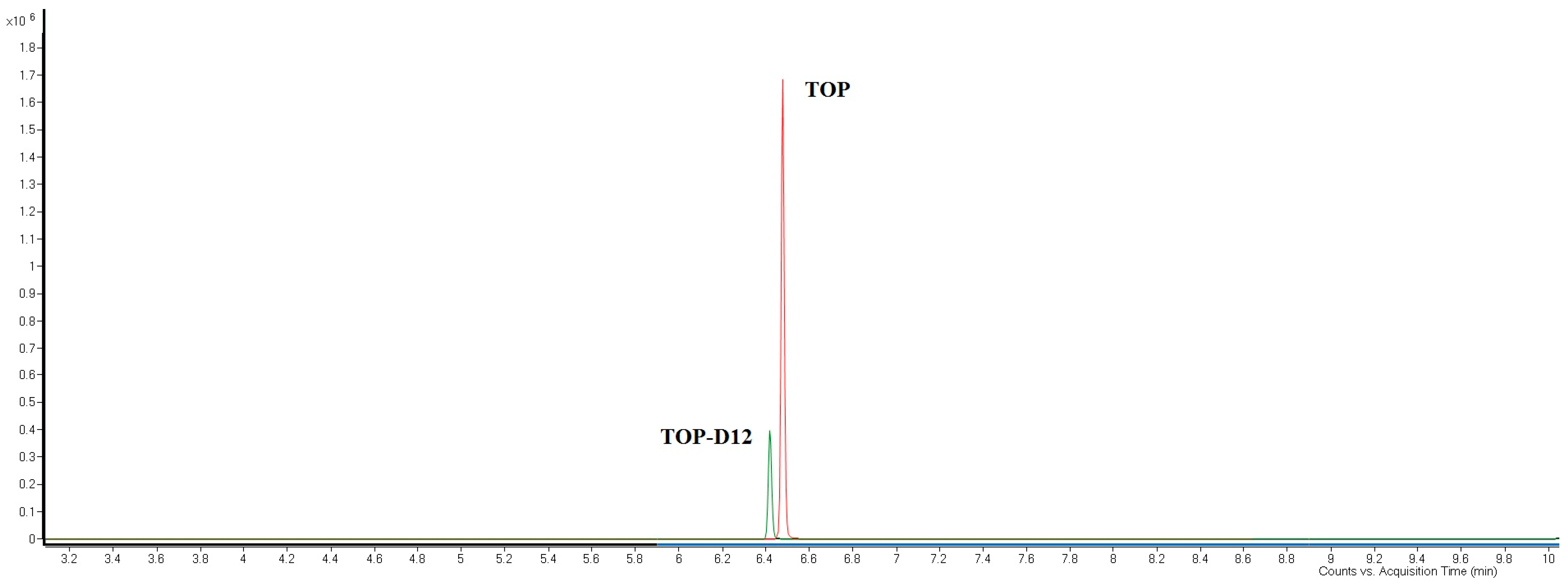
3.9.1. Selectivity
3.9.2. Linearity
3.9.3. Precision and Accuracy
3.9.4. Recovery
3.9.5. Applicability of the Proposed Method
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prevalencia e Incidencia de la Epilepsia. 2023. Available online: https://www.apiceepilepsia.org/prevalencia-e-incidencia-de-la-epilepsia/ (accessed on 17 July 2023).
- Qiu, E.; Yu, L.; Liang, Q.; Wen, C. Simultaneous determination of Lamotrigine, Oxcarbazepine, Lacosamide and Topiramate in rat plasma by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Int. J. Anal. Chem. 2022, 2022, 1838645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, A.; Rodriguez, M.; Oliveira, P.; Francisco, J.; Fortuna, A.; Rosado, L.; Rosado, P.; Falcao, A.; Alves, G. Liquid chromatography assay based on microextraction by packed sorbent for therapeutic drug monitoring of Carbamazepine, Lamotrigine, Oxcarbazepine, Fenobarbital, Phentoin and the active metabolites Carbamazepine-10,11-epoxide and Licarbazepine. J. Chromatogr. B 2014, 971, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zilles, R.; Venzon, M.A.; Costa, P.A.; Bordin, N.A.; Gasparin, S.V.; Linden, R. Determination of Topiramate in dried blood spots using single-quadropole gas chromatography-mass spectrometry after flash methylation with Trimethylanilinium hydroxide. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1046, 131–137. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, S.; Tao, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Zhu, P.; Wang, Q.; Wu, H.; Sawan, M. On-site biolayer interferometry-based biosensing of Carbamazepine in whole blood of epileptic patients. Biosensors 2021, 11, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serralheiro, A.; Alvez, G.; Fortuna, A.; Rocha, M.; Falcao, A. First HPLC-UV method for rapid and simultaneous quantification of Phenobarbital, Primidone, Phenytoin, Carbamazepine, Carbamazepine-10,11-epoxide, 10,11-trans-dihydroxy-10,11-dihydrocarbamazepine, Lamotrigine, Oxcarbazepine and Licarbazepine in human plasma. J. Chromatogr. B 2013, 925, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Conway, J.M.; Birnbaum, A.K.; Marino, S.E.; Cloyd, J.C.; Remmel, R.P. A sensitive capillary GC-MS method for analysis of Topiramate from plasma obtained from single-dose studies. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2012, 26, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beer, B.; Libiseller, K.; Oberacher, H.; Pavlic, M. A fatal intoxication case involving Topiramate. For. Sci. Int. 2010, 202, e9–e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeij, T.A.C.; Edelbroek, P.M. Robust isocratic high performance liquid chromatographic method for simultaneous determination of seven antiepileptic drugs including Lamotrigine, Oxcarbazepine and Zonisamide in serum after solid-phase extraction. J. Chromatogr. B 2007, 857, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speed, D.J.; Dickson, S.J.; Cairns, E.R.; Kim, N.D. Analysis of six anticonvulsant drugs using solid-phase extraction, deuterated internal standards, and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2000, 24, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.T.; Lim, S.H.; Lee, W.B.; Kumar, P.K.; Wang, H.Y.S.; Ng, Y.L.; Wong, P.S.; Ho, P.C. Clinical validation and implications of dried blood spot sampling of Carbamazepine, Valproic acid and Phenytoin in patients with epilepsy. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, S.; Malik, A.K. A novel microextraction by packed sorbent-gas chromatography procedure for the simultaneous analysis of antiepileptic drugs in human plasma and urine. J. Sep. Sci. 2012, 35, 2970–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feriduni, B.; Farajzadeh, M.A.; Jouyban, A. Determination of two antiepileptic drugs in urine by homogenous liquid-liquid extraction performed in a narrow tube combined with dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction followed by gas chromatography-flame ionization detection. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2019, 18, 620–630. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cabarcos-Fernández, P.; Álvarez-Freire, I.; Tabernero-Duque, M.J.; Bermejo-Barrera, A.M. Quantitative determination of Clozapine in plasma using an environmentally friendly technique. Microchem. J. 2022, 180, 107612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabarcos, P.; Cocho, J.A.; Moreda, A.; Míguez, M.; Tabernero, M.J.; Fernández, P.; Bermejo, A.M. Application of dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for the determination of Phoshatidylethanol in blood by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Talanta 2013, 11, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Rooyen, G.F.; Badenhorst, D.; Swart, K.J.; Hundt, H.K.L.; Scanes, T.; Hundt, A.F. Determination of Carbamazepine and Carbamazepine 10,11-epoxide in human plasma by tandem liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry with electrospray ionization. J. Chromatogr. B 2002, 769, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, A.A.; da Silva, R.M.; Ferreira, S.M.; da Costa, E.R.; Sakamoto, A.C.; Carrilho, E.; de Gaitani, C.M.; Garcia, C.D. Determination of Topiramate by capillary electrophoresis with capacitively-coupled contactless conductivity detection: A powerful tool for therapeutic monitoring in epileptic patients. Electrophoresis 2018, 39, 2598–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandrioli, R.; Musenga, A.; Kenndler, E.; de Donno, M.; Amore, M.; Raggi, M.A. Determination of Topiramate in human plasma by capillary electrophoresis with indirect UV detection. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 53, 1319–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services; Food and Drug Administration. Bioanalytical Method Validation. Guidance for Industry. May 2018. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/files/drugs/published/Bioanalytical-Method-Validation-Guidance-for-Industry.pdf (accessed on 5 December 2023).
- Álvarez-Freire, I.; Marqués-Rodríguez, T.; Bermejo-Barrera, A.M.; Cabarcos-Fernández, P.; Tabernero-Duque, M.J. Determination of Levetirazetam in plasma: Comparison of gas chromatography-mass spectrometry technique and Abbot® Architect system. Microchem. J. 2021, 160, 105715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, F.R.; Khairy, M.A. Pharmaceutical and biomedical applications of dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1061–1062, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouibari, T.A.; Fattahi, N.; Shamsipur, M. Rapid extraction and determination of Amphetamines in human urine samples using dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and solidification of floating organic drop followed by high performance liquid chromatography. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 94, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repetto, M.R.; Repetto, M. Tabla de Concentraciones de Xenobióticos en Fluidos Biológicos Humanos Como Referencia Para el Diagnóstico Toxicológico (Versión 2015), Ampliación de Toxicología de Postgrado; Depósito Legal: SE-182-07; Ilustre Colegio Oficial de Químicos: Sevilla, Spain, 2015; ISBN 13, 978-84-695-3142-6. [Google Scholar]
- Launiainen, T.; Ojanperä, I. Drug concentration in post-mortem femoral blood compared with therapeutic concentrations in plasma. Drug Test. Anal. 2014, 6, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musshoff, F.; Padosch, S.; Steinborn, S.; MadeaB. Fatal blood and tissue concentrations of more than 200 drugs. For. Sci. Int. 2004, 142, 161–210. [Google Scholar]
- Schulz, M.; Iwersen-Bergmann, S.; Andresen, H.; Schmoldt, A. Therapeutic and toxic blood concentrations of nearly 1000 drugs and other xenobiotics. Critical Care 2012, 16, R136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.Y.; Lü, C.X.; Shi, Y.H.; Yuan, N.; Liang, J.H.; An, Q.; Guo, Z.Y.; Yun, K.M. Detection of Carbamazepine and its metabolites in blood samples by LC-MS/MS. Fa Yi Xue Za Zhi 2023, 39, 34–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, M.; He, X.; Li, H.; Haseeb, S.; Chen, H.; Li, W. Simultaneous determination of Phentermine and Topiramate in human plasma by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry with positive-negative ion-switching electrospray ionization and its application in pharmacokinetic study. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 107, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popov, T.V.; Maricic, L.C.; Prosen, H.; Voncina, D.B. Development and validation of dried blood spots technique for quantitative determination of Topiramate using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2013, 27, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- la Marca, G.; Malvagia, S.; Filippi, L.; Fiorini, P.; Innocenti, M.; Luceri, F.; Pieraccini, G.; Moneti, G.; Francese, S.; Dani, F.R.; et al. Rapid assay of Topiramate in dried blood spots by a new liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometric method. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 48, 1392–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, G.; Mirzaeei, S.; Kiani, A. Sensitive analytical method for Topiramate in human serum by HPLC with pre-column fluorescent derivatization and its application in human pharmacokinetic studies. J. Chromatogr. B 2004, 813, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinc, B.; Roskar, R.; Grabnar, I.; Vovk, T. Simultaneous determination of Gabapentin, Pregabalin, Vigabatrin and Topiramate in plasma by HPLC with fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. B 2014, 962, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, G.; Mirzaeei, S.; Mohammadi, B.; Kiani, A. High performance liquid chromatographic determination of Topiramate in human serum using UV detection. J. Chromatogr. B 2005, 822, 322–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, S.; Daryasari, A.P.; Soleimani, M. Ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction for the simultaneous determination of Carbamazepine and Lamotrigine in biological samples. Acta Chim. Slov. 2020, 67, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karinen, R.; Vindenes, V.; Hasvold, I.; Olsen, K.M.; Christophersen, A.S.; Oiestad, E. Determination of a selection of anti-epileptic drugs and two active metabolites in whole blood by reversed phase UPLC-MS/MS and some examples of application of the method in forensic toxicology cases. Drug Test. Anal. 2015, 7, 634–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Yazbi, A.F.; Wagih, M.M.; Ibrahim, F.; Barary, M.A. Spectrofluorimetric determination of Topiramate and Levetirazetam as single components in tablet formulations and in human plasma and simultaneous fourth derivative synchronous fluorescence determination of their co-adminstered mixture in human plasma. J. Fluoresc. 2016, 26, 1225–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Fleming, D.H.; Mathew, B.S.; Winston, B.; Prabhakar, A.R.; Alexander, M. Determination of serum Carbamazepine concentration using dried blood spot specimens for resource-limited settings. Hosp. Pract. 2017, 45, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Carbamazepine | Topiramate | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentrations (µg mL−1) | Concentrations (µg mL−1) | ||||||||
| 0.05 | 2 | 3 | 0.025 | 5 | 8 | ||||
| Intraday assay | %RSD | 15.5 | 14.4 | 12.4 | Intraday assay | %RSD | 15.4 | 6.4 | 6.3 |
| %RE | 18.2 | 8.3 | 7.9 | %RE | 16.2 | 6.8 | 6.9 | ||
| %R | 90.3 | 91.7 | 107.9 | %R | 91.5 | 93.2 | 113.9 | ||
| Inter-day assay | %RSD | 12.8 | 11.0 | 9.6 | Inter-day assay | %RSD | 13.4 | 9.4 | 10.6 |
| %RE | 16.5 | 14.7 | 2.6 | %RE | 18.5 | 3.4 | 5.4 | ||
| %R | 90.5 | 116.7 | 102.6 | %R | 92.4 | 96.6 | 105.4 | ||
| Case N° | Age (Sex) | Etiology of Death | [CBZ] (µg/mL) | [TOP] (µg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 31 (F) | Accidental | - | 1.34 |
| 2 | 45 (M) | Suicide death | - | 2.05 |
| 3 | 24 (M) | Suicide death | - | 1.81 |
| 4 | 35 (F) | Accidental | - | 2.62 |
| 5 | 48 (M) | Suicide death | - | 1.62 |
| 6 | 62 (M) | Natural | - | 1.09 |
| 7 | 52 (F) | Overdose | 0.10 | - |
| 8 | 42 (M) | Suicide death | 0.31 | - |
| 9 | 48 (M) | Overdose | 0.20 | - |
| 10 | 59 (F) | Natural | 0.25 | - |
| 11 | 37 (F) | Accidental | 0.21 | - |
| 12 | 44 (M) | Accidental | 0.44 | - |
| 13 | 60 (M) | Accidental | 0.26 | - |
| 14 | 37 (M) | Natural | 0.34 | - |
| 15 | 44 (F) | Suicide death | 0.12 | - |
| 16 | 62 (M) | Accidental | 0.4 | - |
| 17 | 41 (F) | Sexual assault | 0.64 | - |
| 18 | 52 (M) | Natural | 0.41 | 0.06 |
| References | Biological Matrix | Extraction Technique | Detection Technique | Drugs | Data of Interest |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D.J.S. et al., 2000 [10] | Whole blood | SPE | GC-MS | CBZ | LR: 0.5–60 LOD: - %R: 158 Total run: 15 min Derivatization step |
| G.F.V.R. et al., 2002 [16] | Plasma | LLE | LC-MS/MS | CBZ | LR: 0.0008–6.6 LOD: - %R: 95.1 Total run: 4 min |
| G.B. et al., 2004 [31] | Plasma | LLE | HPLC- FD | TOP | LR: 0.02–5.1 LOD: 0.001 %R: 98 Total run: 5 min Derivatization step |
| G.B. et al., 2005 [33] | Plasma | LLE | LC-UV | TOP | LR: 0.04–40 LOD: 0.005 %R: - Total run: 7 min Derivatization step |
| T.A.C.V. et al., 2007 [9] | Plasma | SPE | HPLC-DAD | CBZ | LR: 0.37–14.8 LOD: 0.018 %R: 100 Total run: 20 min |
| G.M. et al., 2008 [30] | Blood | DBS | LC-MS/MS | TOP | LR: 0.5–50 LOD: - %R: - Total run: 3 min |
| R.M. et al., 2010 [18] | Plasma | SPE | CE | TOP | LR: 2–60 LOD: 0.8 %R: >92 Total run: 5 min |
| J.M.C. et al., 2012 [7] | Plasma | SPE | GC-MS | TOP | LR: 0.1–40 LOD: - %R: 56.1 Total run: 6.5 min |
| * S.R. et al., 2012 [12] | Plasma and urine | MEPS | GC-MS | CBZ | LR: 0.0088–0.5 LOD: 0.0029 %R: 85.2 Total run: 16 min |
| A.S. et al., 2013 [6] | Plasma | SPE | HPLC-UV | CBZ | LR: 0.1–50 LOD: 0.01 %R: 87.9 Total run: 16 min |
| T.V.P. et al., 2013 [29] | Whole blood | DBS | LC-MS/MS | TOP | LR: 0.01–2 LOD: - %R: 93 Total run: 2 min |
| S.T.K. et al., 2014 [11] | Whole blood | DBS | GC-MS | CBZ | LR: 0.5–120 LOD: 0.07 %R: 75–97 Total run: 14 min |
| A.F. et al., 2014 [3] | Plasma | MEPS | HPLC-DAD | CBZ | LR: 0.1–15 LOD: - %R: 88.1 Total run: 16 min |
| R.K. et al., 2015 [35] | Whole blood | PP | UPLC-MS/MS | CBZ | LR: 0.6–24 LOD: 0.12 LLOQ: 0.3 %R: 98 Total run: 6 min |
| TOP | LR: 1.7–68 LOD: 0.11 LLOQ: 0.34 %R: 105 Total run: 6 min | ||||
| B.M. et al., 2014 [32] | Plasma | SPE | HPLC- FD | TOP | LR: 0.5–20 LOD: - %R: 95 Total run: 21 min Derivatization step |
| Y.N. et al., 2015 [28] | Plasma | PP | LC-MS/MS | TOP | LR: 0.001–1 LOD: - %R: 90 Total run: 8 min |
| A.F.E-Y. et al., 2016 [36] | Plasma | PP | HPLC-UV | TOP | LR: 0.15–1.2 LOD: 0.038 R (%): 98 Derivatization step |
| R.Z.H. et al., 2017 [4] | Plasma | DBS | GC-MS | TOP | LR: 0.05–30 LOD: - LLOQ: 0.5 Total run: 10 min Derivatization step |
| S.D. et al., 2017 [37] | Serum | DBS | HPLC | CBZ | LR: 2–20 %R: >90 |
| A.A.I. et al., 2018 [17] | Plasma | LLE | CE | TOP | LR: 1–30 LOD: - Total run: 2.5 min |
| B.F. et al., 2019 [13] | Urine | HLLE-DLLME | GC-FID | CBZ | LR: 0.04–100 LOD: 0.010 LLOQ: 0.033 Total run: 16 min |
| S.R. et al., 2020 [34] | Plasma | IL-DLLME | HPLC-UV | CBZ | LR: 0.1–20 LOD: 0.04 |
| S.B. et al., 2021 [5] | Whole blood | - | FO-BLI | CBZ | LR: 0.1–10 LOD: 0.01 Total run: 8 min |
| E.Q. et al., 2022 [2] | Plasma rat | PP | UPLC-MS/MS | TOP | LR: 0.005–5 LOD: - %R: 90.9 Total run: 6.5 min |
| H-Y.C. et al., 2023 [27] | Plasma | UAE | LC-MS/MS | CBZ | LLOQ: 0.008 LOD: 0.003 |
| Proposed method | Plasma | DLLME | GC-MS | CBZ | LR: 0.05–3 LOD: 0.025 %R: 90.3–116.7 |
| TOP | LR: 0.025–8 LOD: 0.01 %R: 91.5–113.9 Total run: 10 min |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cabarcos-Fernández, P.; Tabernero-Duque, M.J.; Álvarez-Freire, I.; Bermejo-Barrera, A.M. Determination of Topiramate and Carbamazepine in Plasma by Combined Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction and Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Separations 2024, 11, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11020051
Cabarcos-Fernández P, Tabernero-Duque MJ, Álvarez-Freire I, Bermejo-Barrera AM. Determination of Topiramate and Carbamazepine in Plasma by Combined Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction and Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Separations. 2024; 11(2):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11020051
Chicago/Turabian StyleCabarcos-Fernández, Pamela, María Jesús Tabernero-Duque, Iván Álvarez-Freire, and Ana María Bermejo-Barrera. 2024. "Determination of Topiramate and Carbamazepine in Plasma by Combined Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction and Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry" Separations 11, no. 2: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11020051
APA StyleCabarcos-Fernández, P., Tabernero-Duque, M. J., Álvarez-Freire, I., & Bermejo-Barrera, A. M. (2024). Determination of Topiramate and Carbamazepine in Plasma by Combined Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction and Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry. Separations, 11(2), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations11020051






