Sustainable and Rapid Determination of Two Halogenated Pesticides in a Commercial Formulation by Solid Phase Microextraction and Liquid Phase Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Supplies
2.2. Standard Solution Preparation
2.3. Instruments and Equipment
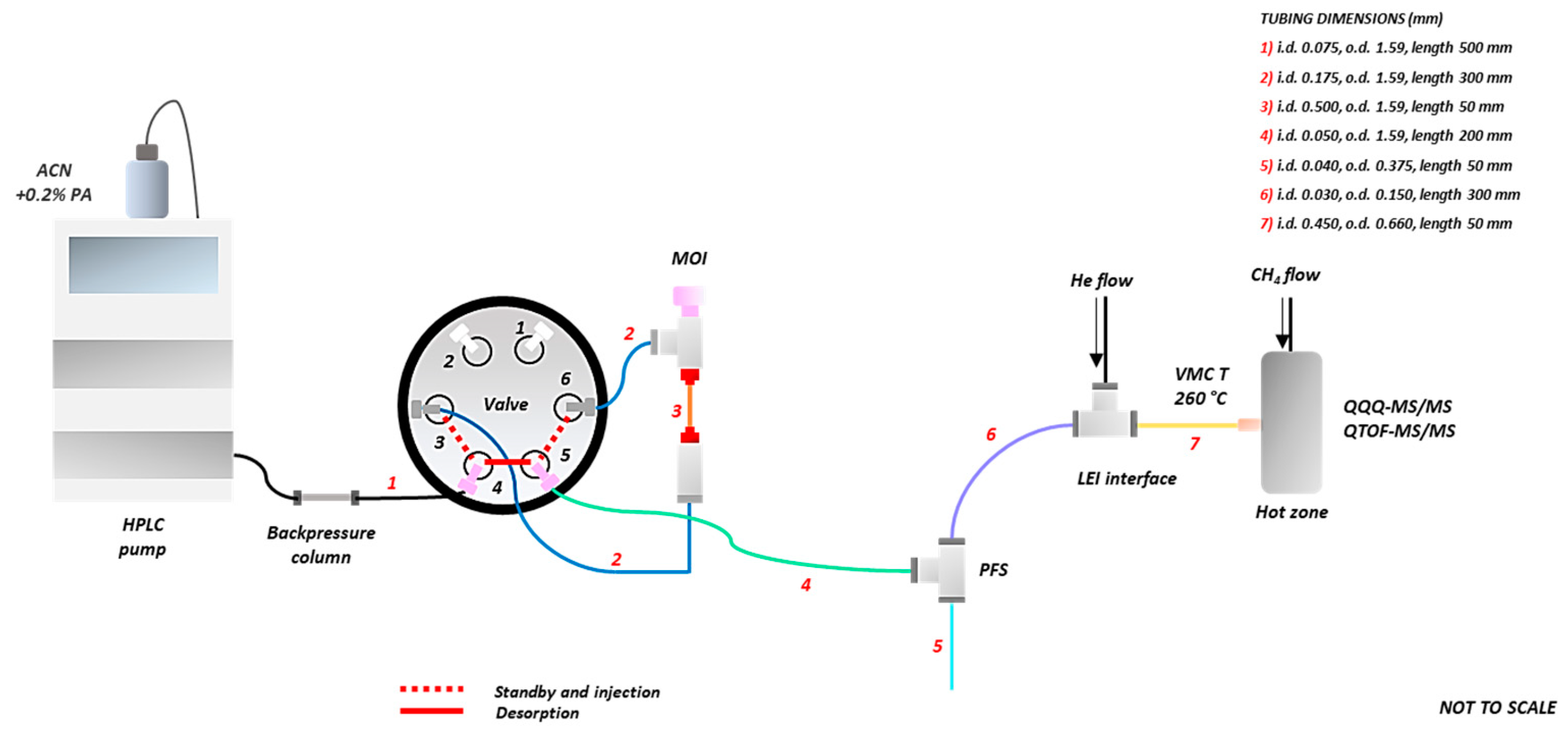
2.3.1. Microfluidic Open Interface (MOI) and Passive Flow Splitter (PFS)
2.3.2. MOI-PFS-LEI-QQQ and MOI-PFS-LEI-QTOF Systems
2.4. Direct Immersion-SPME Method Optimization
3. Results and Discussion
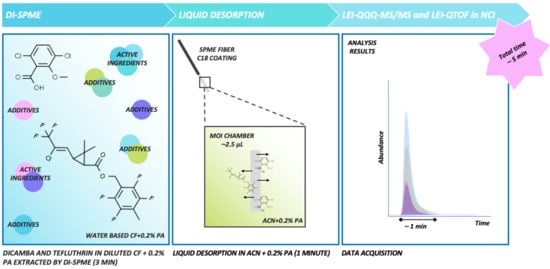
3.1. Sampling and Desorption Steps
3.2. Low-Resolution Experiments: MOI-PFS-LEI-QQQ
Matrix Effects (ME) Evaluation
3.3. High-Resolution Experiments: MOI-PFS-LEI-QTOF
3.4. Greenness Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anastas, P.; Eghbali, N. Green Chemistry: Principles and Practice. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byliński, H.; Gębicki, J.; Dymerski, T.; Namieśnik, J. Direct Analysis of Samples of Various Origin and Composition Using Specific Types of Mass Spectrometry. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2017, 47, 340–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthur, C.L.; Pawliszyn, J. Solid Phase Microextraction with Thermal Desorption Using Fused Silica Optical Fibers. Anal. Chem. 1990, 62, 2145–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissoudi, M.; Samanidou, V. Recent Advances in Applications of Ionic Liquids in Miniaturized Microextraction Techniques. Molecules 2018, 23, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tascon, M.; Alam, M.N.; Gómez-Ríos, G.A.; Pawliszyn, J. Development of a Microfluidic Open Interface with Flow Isolated Desorption Volume for the Direct Coupling of SPME Devices to Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 2631–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marittimo, N.; Famiglini, G.; Palma, P.; Arigò, A.; Cappiello, A. Enhanced Microfluidic Open Interface for the Direct Coupling of Solid Phase Microextraction with Liquid Electron Ionization-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1681, 463479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervera, M.I.; Medina, C.; Portolés, T.; Pitarch, E.; Beltrán, J.; Serrahima, E.; Pineda, L.; Muñoz, G.; Centrich, F.; Hernández, F. Multi-Residue Determination of 130 Multiclass Pesticides in Fruits and Vegetables by Gas Chromatography Coupled to Triple Quadrupole Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 2873–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paíga, P.; Sousa, S.; Vera, J.; Bitencourt, L.; Vieira, J.; Jorge, S.; Silva, J.G.; Correia, M.; Domingues, V.F.; Delerue-Matos, C. Multi-Residue Analysis of Fifty Pesticides in River Waters and in Wastewaters. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 66787–66803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. EU Policy for a Sustainable Use of Pesticides. The Story Behind the Strategy; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2007; ISBN 92-79-03221-6. [Google Scholar]
- Parra-Arroyo, L.; González-González, R.B.; Castillo-Zacarías, C.; Melchor Martínez, E.M.; Sosa-Hernández, J.E.; Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Barceló, D.; Parra-Saldívar, R. Highly Hazardous Pesticides and Related Pollutants: Toxicological, Regulatory, and Analytical Aspects. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation (EC) No 396/2005 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 23 February 2005 on Maximum Residue Levels of Pesticides in or on Food and Feed of Plant and Animal Origin and Amending Council Directive 91/414/EEC Text with EEA Relevance. OJ L 70, 16.3.2005, p. 1–16. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg/2005/396/oj (accessed on 18 May 2023).
- Li, C.; Begum, A.; Xue, J. Analytical Methods to Analyze Pesticides and Herbicides. Water Environ. Res. 2020, 92, 1770–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maragou, N.C.; Balayiannis, G.; Karanasios, E.; Markellou, E.; Liapis, K. Targeted Multiresidue Method for the Analysis of Different Classes of Pesticides in Agro-Food Industrial Sludge by Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2021, 26, 6888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nasir, F.M.; Jiries, A.G.; Al-Rabadi, G.J.; Alu’datt, M.H.; Tranchant, C.C.; Al-Dalain, S.A.; Alrabadi, N.; Madanat, O.Y.; Rasha, S.; Al-Dmour, R.S. Determination of pesticide residues in selected citrus fruits and vegetables cultivated in the Jordan Valley. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 123, 109005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, J.H. Mass Spectrometry. A Text Book, 3rd ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 978-3-319-54397-0. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trufelli, H.; Palma, P.; Famiglini, G.; Cappiello, A. An Overview of Matrix Effects in Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2011, 30, 491–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Termopoli, V.; Famiglini, G.; Palma, P.; Piergiovanni, M.; Cappiello, A. Atmospheric Pressure Vaporization Mechanism for Coupling a Liquid Phase with Electron Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 2049–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Famiglini, G.; Palma, P.; Termopoli, V.; Cappiello, A. The History of Electron Ionization in LC-MS, from the Early Days to Modern Technologies: A Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1167, 338350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Termopoli, V.; Famiglini, G.; Palma, P.; Piergiovanni, M.; Rocio-Bautista, P.; Ottaviani, M.F.; Cappiello, A.; Saeed, M.; Perry, S. Evaluation of a liquid electron ionization liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry interface. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1591, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Termopoli, V.; Torrisi, E.; Famiglini, G.; Palma, P.; Zappia, G.; Cappiello, A.; Vandergrift, G.W.; Zvekic, M.; Krogh, E.T.; Gill, C.G. Mass Spectrometry Based Approach for Organic Synthesis Monitoring. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 11916–11922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Termopoli, V.; Famiglini, G.; Vocale, P.; Morini, G.L.; Palma, P.; Rocío-Bautista, P.; Saeed, M.; Perry, S.; Cappiello, A. Microfluidic water-assisted trap focusing method for ultra-large volume injection in reversed-phase nano-liquid chromatography coupled to electron ionization tandem-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1627, 461421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Termopoli, V.; Piergiovanni, M.; Cappiello, A.; Palma, P.; Famiglini, G. Tyrosol and Hydroxytyrosol Determination in Extra Virgin Olive Oil with Direct Liquid Electron Ionization–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Separations 2021, 8, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappiello, A.; Termopoli, V.; Palma, P.; Famiglini, G.; Saeed, M.; Perry, S.; Navarro, P. Liquid Chromatography–Electron Capture Negative Ionization–Tandem Mass Spectrometry Detection of Pesticides in a Commercial Formulation. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2022, 33, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, E.H.; Choi, J.H.; Abd El-Aty, A.M.; Khay, S.; Kim, S.J.; Im, M.H.; Kwon, C.H.; Shim, J.H. Simultaneous Determination of Three Acidic Herbicide Residues in Food Crops Using HPLC and Confirmation via LC-MS/MS. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2011, 25, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougherty, R.C. Negative Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 1981, 53, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsol-Vall, A.; Ainsa, S.; Lopez, R.; Ferreira, V. Development and Validation of a Method for the Analysis of Halophenols and Haloanisoles in Cork Bark Macerates by Stir Bar Sorptive Extraction Heart-Cutting Two-Dimensional Gas Chromatography Negative Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1673, 463186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocío-Bautista, P.; Famiglini, G.; Termopoli, V.; Palma, P.; Nazdrajić, E.; Pawliszyn, J.; Cappiello, A. Direct Coupling of Bio-SPME to Liquid Electron Ionization-MS/MS via a Modified Microfluidic Open Interface. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2021, 32, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gionfriddo, E.; Gruszecka, D.; Li, X.; Pawliszyn, J. Direct-Immersion SPME in Soy Milk for Pesticide Analysis at Trace Levels by Means of a Matrix-Compatible Coating. Talanta 2020, 211, 120746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, M.J.; Pawliszyn, J. Solid-Phase Microextraction. A Solvent-Free Alternative for Sample Preparation. Anal. Chem. 1994, 66, 844A–853A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuckovic, D.; Shirey, R.; Chen, Y.; Sidisky, L.; Aurand, C.; Stenerson, K.; Pawliszyn, J. In Vitro Evaluation of New Biocompatible Coatings for Solid-Phase Microextraction: Implications for Drug Analysis and in Vivo Sampling Applications. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 638, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawliszyn, J. Handbook of Solid Phase Microextraction; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; ISBN 9780124160170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górecki, T.; Yu, X.; Pawliszyn, J. Theory of Analyte Extraction by Selected Porous Polymer SPME Fibres. Analyst 1999, 124, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisert, R.; Pawliszyn, J. Design of Automated Solid-Phase Microextraction for Trace Analysis of Organic Compounds in Aqueous Samples. J. Chromatogr. A 1997, 776, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Riter, L.S.; Wujcik, C.E.; Armstrong, D.W. Talanta Quantitative Analysis of Dicamba Residues in Raw Agricultural Commodities with the Use of Ion-Pairing Reagents in LC–ESI–MS/MS. Talanta 2016, 149, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ccanccapa-Cartagena, A.; Masiá, A.; Picó, Y. Simultaneous Determination of Pyrethroids and Pyrethrins by Dispersive Liquid-Liquid Microextraction and Liquid Chromatography Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry in Environmental Samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 4787–4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koesukwiwat, U.; Sanguankaew, K.; Leepipatpiboon, N. Rapid Determination of Phenoxy Acid Residues in Rice by Modified QuEChERS Extraction and Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 626, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McManus, S.L.; Moloney, M.; Richards, K.G.; Coxon, C.E.; Danaher, M. Determination and Occurrence of Phenoxyacetic Acid Herbicides and Their Transformation Products in Groundwater Using Ultra High Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2014, 19, 20627–20649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, W.; Tao, X.; Pang, S.; Yang, X.; Tang, G.L.; Bian, Z. Separation and Quantitation of Three Acidic Herbicide Residues in Tobacco and Soil by Dispersive Solid-Phase Extraction and UPLC-MS/MS. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2014, 52, 1326–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.Y.; Cao, X.W.; Shen, W.J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Wu, B.; Yu, K.Y.; Liu, H.; Lian, H.Z. Determination of 17 Pyrethroid Residues in Troublesome Matrices by Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry with Negative Chemical Ionization. Talanta 2011, 84, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besil, N.; Uclés, S.; Mezcúa, M.; Heinzen, H.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. Negative Chemical Ionization Gas Chromatography Coupled to Hybrid Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry and Automated Accurate Mass Data Processing for Determination of Pesticides in Fruit and Vegetables. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 6327–6343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmonte Valles, N.; Retamal, M.; Mezcua, M.; Fernández-Alba, A.R. A Sensitive and Selective Method for the Determination of Selected Pesticides in Fruit by Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry with Negative Chemical Ionization. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1264, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosetti, F.; Mazzucco, E.; Zampieri, D.; Gennaro, M.C. Signal Suppression/Enhancement in High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 3929–3937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Yang, S.; Wang, P.G. Matrix Effects and Application of Matrix Effect Factor. Bioanalysis 2017, 9, 1839–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruce-Vanderpuije, P.; Megson, D.; Ryu, S.H.; Choi, G.H.; Park, S.W.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, H.S. A Comparison of the Effectiveness of QuEChERS, FaPEx and a Modified QuEChERS Method on the Determination of Organochlorine Pesticides in Ginseng. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, M.; Płotka-Wasylka, J. Green Analytical Chemistry Metrics: A Review. Talanta 2022, 238, 123046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, J.V.D.; Tosta, C.L.; da Cunha Neto, Á.; Fagg, C.W.; Silva, C.A.G.; Gomes-Copeland, K.K.P.; Magalhães, P.O.; Fonseca-Bazzo, Y.M.; Jamal, C.M.; Silveira, D. Chemical Profile and Biological Activity of Crinum americanum L. (Amaryllidaceae). S. Afr. J. Bot. 2022, 146, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Płotka-Wasylka, J. A New Tool for the Evaluation of the Analytical Procedure: Green Analytical Procedure Index. Talanta 2018, 181, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gałuszka, A.; Migaszewski, Z.M.; Konieczka, P.; Namieśnik, J. Analytical Eco-Scale for Assessing the Greenness of Analytical Procedures. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 37, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Compound | Matrix | Linearity Range (ng/mL) | Levels | R2 | LOD (ng/mL) | LOQ (ng/mL) | RSD% Intraday | RSD% Interday |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dicamba | CF | 0.5–100 | 6 | 0.9925 | 0.05 | 0.5 | 20% | 21% |
| Tefluthrin | CF | 0.5–100 | 6 | 0.9958 | 0.05 | 0.5 | 8% | 12% |
| Compound | Matrix | Linearity Range (ng/mL) | Levels | R2 | LOD (ng/mL) | LOQ (ng/mL) | RSD% Intraday |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dicamba | CF | 0.5–100 | 6 | 0.9752 | 0.05 | 0.5 | 26% |
| Tefluthrin | CF | 0.5–100 | 6 | 0.9397 | 0.05 | 0.5 | 24% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marittimo, N.; Grasselli, G.; Arigò, A.; Famiglini, G.; Palma, P.; Saeed, M.; Perry, S.; Navarro, P.; Clarke, P.; Brittin, M.; et al. Sustainable and Rapid Determination of Two Halogenated Pesticides in a Commercial Formulation by Solid Phase Microextraction and Liquid Phase Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Separations 2023, 10, 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10060325
Marittimo N, Grasselli G, Arigò A, Famiglini G, Palma P, Saeed M, Perry S, Navarro P, Clarke P, Brittin M, et al. Sustainable and Rapid Determination of Two Halogenated Pesticides in a Commercial Formulation by Solid Phase Microextraction and Liquid Phase Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Separations. 2023; 10(6):325. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10060325
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarittimo, Nicole, Genny Grasselli, Adriana Arigò, Giorgio Famiglini, Pierangela Palma, Mansoor Saeed, Simon Perry, Pablo Navarro, Phil Clarke, Mark Brittin, and et al. 2023. "Sustainable and Rapid Determination of Two Halogenated Pesticides in a Commercial Formulation by Solid Phase Microextraction and Liquid Phase Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry" Separations 10, no. 6: 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10060325
APA StyleMarittimo, N., Grasselli, G., Arigò, A., Famiglini, G., Palma, P., Saeed, M., Perry, S., Navarro, P., Clarke, P., Brittin, M., & Cappiello, A. (2023). Sustainable and Rapid Determination of Two Halogenated Pesticides in a Commercial Formulation by Solid Phase Microextraction and Liquid Phase Chemical Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Separations, 10(6), 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations10060325