Type I Interferon Signature in Chilblain-Like Lesions Associated with the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Immunohistochemistry
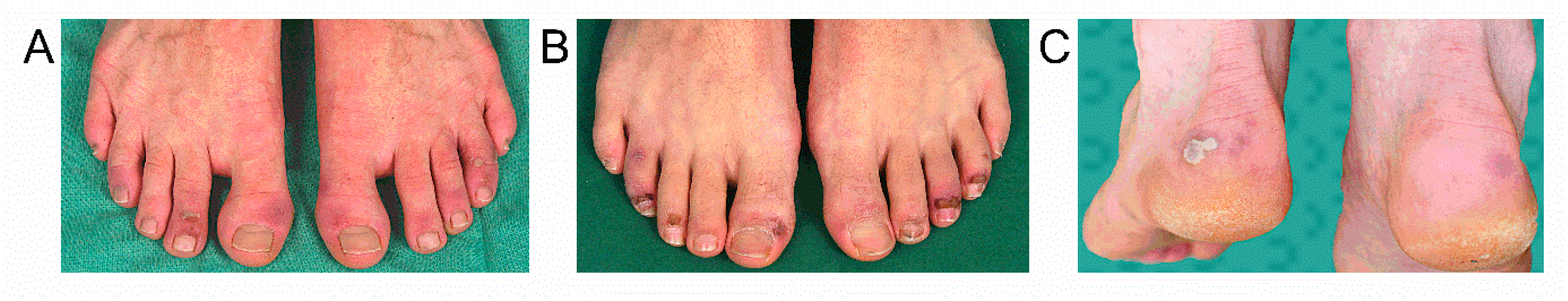
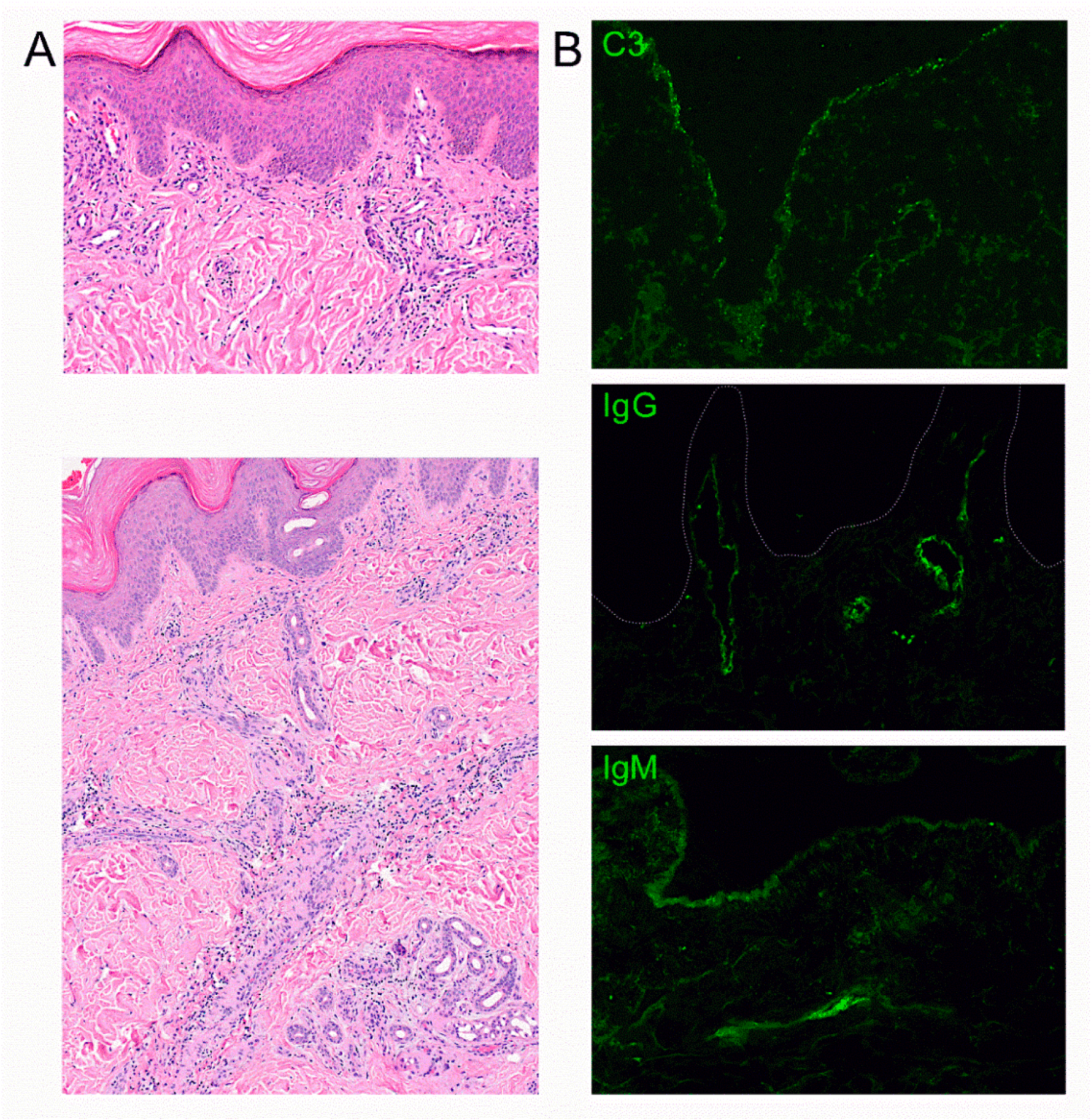
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mehra, M.R.; Desai, S.S.; Kuy, S.; Henry, T.D.; Patel, A.N. Cardiovascular Disease, Drug Therapy, and Mortality in Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, e102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunther, C.; Aschoff, R.; Beissert, S. Cutaneous autoimmune diseases during COVID-19 pandemic. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Nieto, D.; Jimenez-Cauhe, J.; Suarez-Valle, A.; Moreno-Arrones, O.M.; Saceda-Corralo, D.; Arana-Raja, A.; Ortega-Quijano, D. Characterization of acute acral skin lesions in nonhospitalized patients: A case series of 132 patients during the COVID-19 outbreak. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 83, e61–e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landa, N.; Mendieta-Eckert, M.; Fonda-Pascual, P.; Aguirre, T. Chilblain-like lesions on feet and hands during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Dermatol. 2020, 59, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccolo, V.; Neri, I.; Filippeschi, C.; Oranges, T.; Argenziano, G.; Battarra, V.C.; Berti, S.; Manunza, F.; Fortina, A.B.; Di Lernia, V.; et al. Chilblain-like lesions during COVID-19 epidemic: A preliminary study on 63 patients. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, e291–e293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolivras, A.; Dehavay, F.; Delplace, D.; Feoli, F.; Meiers, I.; Milone, L.; Olemans, C.; Sass, U.; Theunis, A.; Thompson, C.T.; et al. Coronavirus (COVID-19) infection-induced chilblains: A case report with histopathologic findings. JAAD Case Rep. 2020, 6, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recalcati, S.; Barbagallo, T.; Frasin, L.A.; Prestinari, F.; Cogliardi, A.; Provero, M.C.; Dainese, E.; Vanzati, A.; Fantini, F. Acral cutaneous lesions in the time of COVID-19. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, e346–e347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recalcati, S. Cutaneous manifestations in COVID-19: A first perspective. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, e212–e213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, D.M.; Kanno, Y.; Villarino, A.; Ward, M.; Gadina, M.; O’Shea, J.J. JAK inhibition as a therapeutic strategy for immune and inflammatory diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 843–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, Z.; Flammer, A.J.; Steiger, P.; Haberecker, M.; Andermatt, R.; Zinkernagel, A.S.; Mehra, M.R.; Schuepbach, R.A.; Ruschitzka, F.; Moch, H. Endothelial cell infection and endotheliitis in COVID-19. Lancet 2020, 395, 1417–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colmenero, I.; Santonja, C.; Alonso-Riano, M.; Noguera-Morel, L.; Hernandez-Martin, A.; Andina, D.; Wiesner, T.; Rodríguez-Peralto, J.L.; Requena, L.; Torrelo, A. SARS-CoV-2 endothelial infection causes COVID-19 chilblains: Histopathological, immunohistochemical and ultrastructural study of seven paediatric cases. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 183, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santonja, C.; Heras, F.; Nunez, L.; Requena, L. COVID-19 chilblain-like lesion: Immunohistochemical demonstration of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in blood vessel endothelium and sweat gland epithelium in a polymerase chain reaction-negative patient. Br. J. Dermatol. 2020, 183, 778–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, A.; Peeters, C.; Verroken, A.; Tromme, I.; Tennstedt, D.; Marot, L.; Dachelet, C.; Gruson, D.; Hermans, C.; Baeck, M. Evaluation of Chilblains as a Manifestation of the COVID-19 Pandemic. JAMA Dermatol. 2020, 156, 998–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, N.; Wolf, C.; Schwenke, R.; Luth, A.; Schmidt, F.; Engel, K.; Lee-Kirsch, M.A.; Günther, C. Assessment of Clinical Response to Janus Kinase Inhibition in Patients with Familial Chilblain Lupus and TREX1 Mutation. JAMA Dermatol. 2019, 155, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunther, C.; Berndt, N.; Wolf, C.; Lee-Kirsch, M.A. Familial chilblain lupus due to a novel mutation in the exonuclease III domain of 3′ repair exonuclease 1 (TREX1). JAMA Dermatol. 2015, 151, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee-Kirsch, M.A. The Type I Interferonopathies. Annu. Rev. Med. 2017, 68, 297–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battesti, G.; El Khalifa, J.; Abdelhedi, N.; Ferre, V.; Bouscarat, F.; Picard-Dahan, C.; Brunet-Possenti, F.; Collin, G.; Lavaud, J.; Le Bozec, P.; et al. New insights in COVID-19-associated chilblains: A comparative study with chilblain lupus erythematosus. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 83, 1219–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damsky, W.; Peterson, D.; King, B. When interferon tiptoes throuugh COVID-19: Pernio-like lesions and their prognostic implications during SARS-CoV-2 infection. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 83, e269–e270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjadj, J.; Yatim, N.; Barnabei, L.; Corneau, A.; Boussier, J.; Smith, N.; Péré, H.; Charbit, B.; Bondet, V.; Chenevier-Gobeaux, C.; et al. Impaired type I interferon activity and inflammatory responses in severe COVID-19 patients. Science 2020, 369, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallet, B.; Narr, K.; Ertuna, Y.I.; Remy, M.; Sommerstein, R.; Cornille, K.; Kreutzfeldt, M.; Page, N.; Zimmer, G.; Geier, F.; et al. Interferon-driven deletion of antiviral B cells at the onset of chronic infection. Sci. Immunol. 2016, 1, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Roca-Gines, J.; Torres-Navarro, I.; Sanchez-Arraez, J.; Abril-Perez, C.; Sabalza-Baztan, O.; Pardo-Granell, S.; Cózar, V.M.; Botella-Estrada, R.; Évole-Buselli, M. Assessment of Acute Acral Lesions in a Case Series of Children and Adolescents During the COVID-19 Pandemic. JAMA Dermatol. 2020, 156, 992–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, C.; Bruckner, A.L. Focus on “COVID Toes”. JAMA Dermatol. 2020, 156, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aschoff, R.; Zimmermann, N.; Beissert, S.; Günther, C. Type I Interferon Signature in Chilblain-Like Lesions Associated with the COVID-19 Pandemic. Dermatopathology 2020, 7, 57-63. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology7030010
Aschoff R, Zimmermann N, Beissert S, Günther C. Type I Interferon Signature in Chilblain-Like Lesions Associated with the COVID-19 Pandemic. Dermatopathology. 2020; 7(3):57-63. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology7030010
Chicago/Turabian StyleAschoff, Roland, Nick Zimmermann, Stefan Beissert, and Claudia Günther. 2020. "Type I Interferon Signature in Chilblain-Like Lesions Associated with the COVID-19 Pandemic" Dermatopathology 7, no. 3: 57-63. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology7030010
APA StyleAschoff, R., Zimmermann, N., Beissert, S., & Günther, C. (2020). Type I Interferon Signature in Chilblain-Like Lesions Associated with the COVID-19 Pandemic. Dermatopathology, 7(3), 57-63. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology7030010