Prognostic Value of Immunohistochemical T-Cell Marker Loss in Early-Stage Mycosis Fungoides: A Single-Center Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
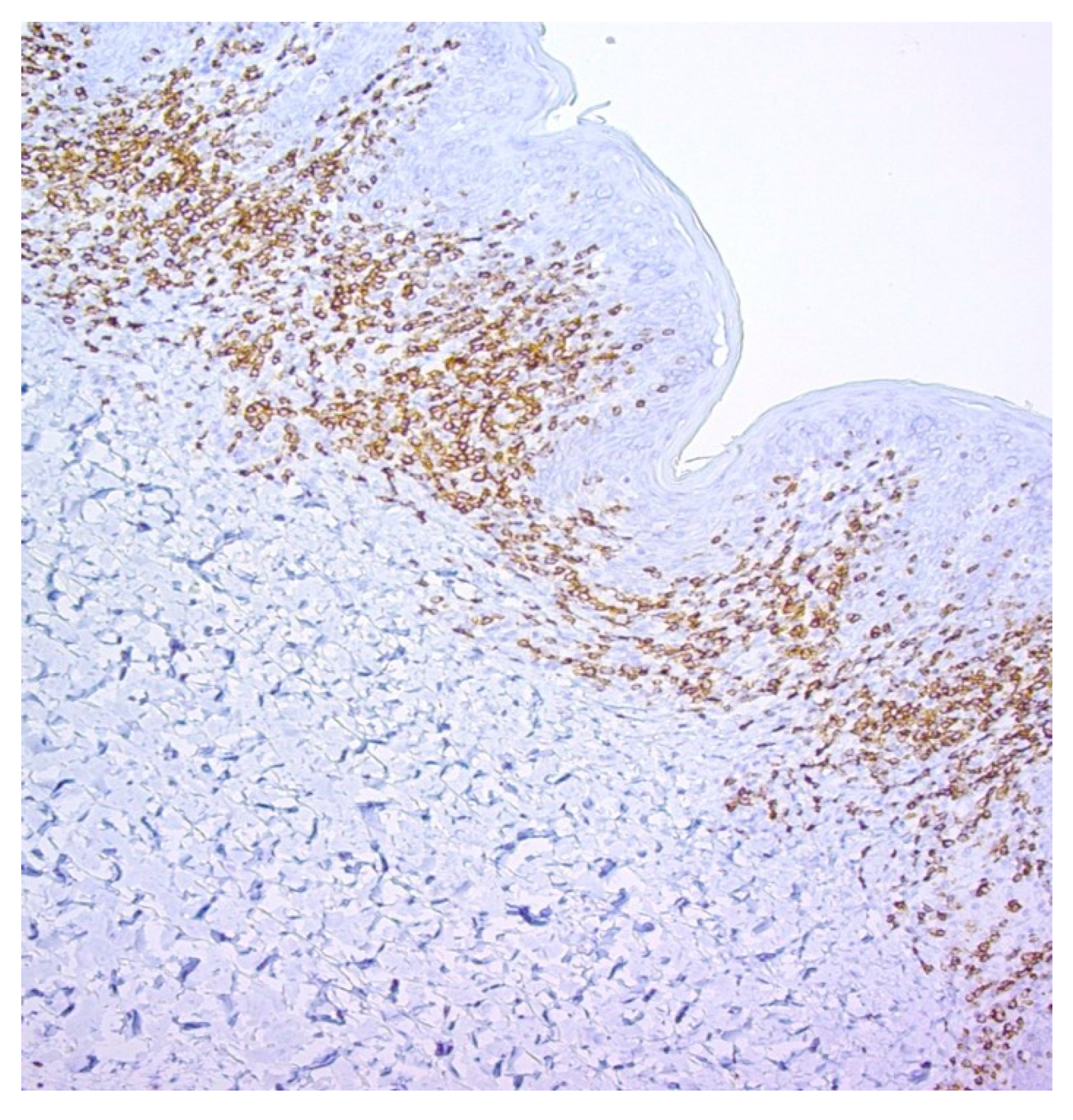
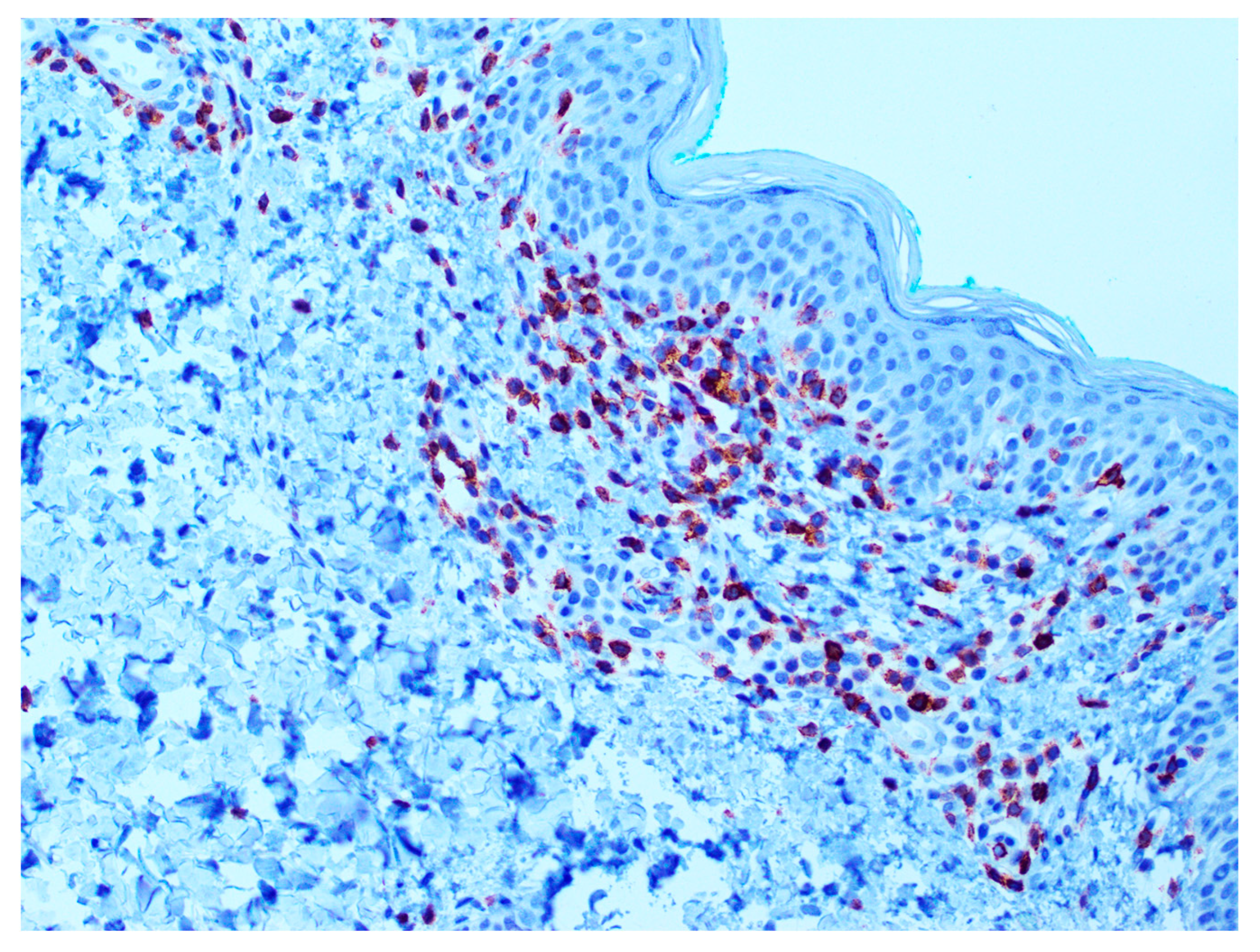
3. Results
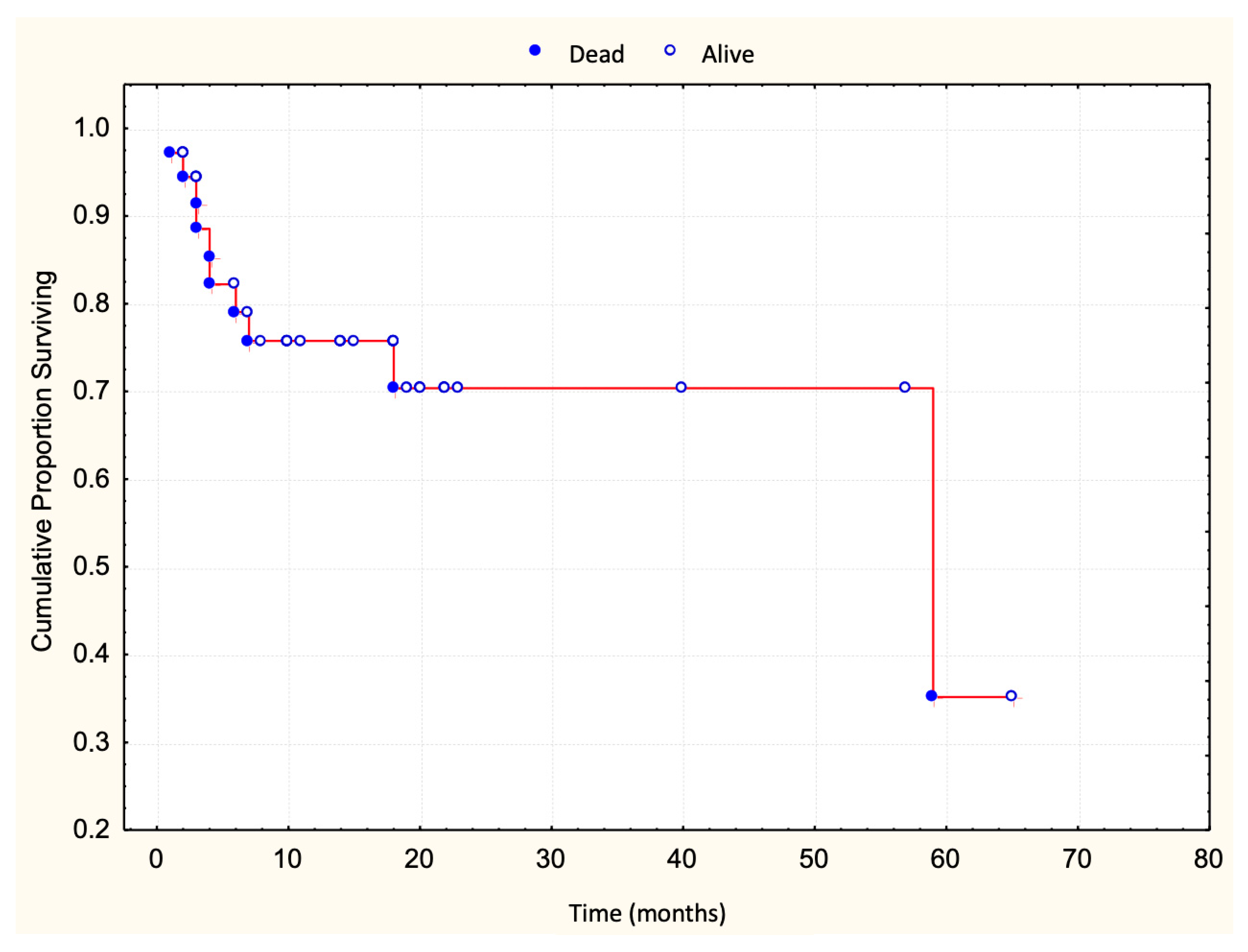
3.1. Prognostic Value of T-Cell Surface Marker Loss in Relation to Survival
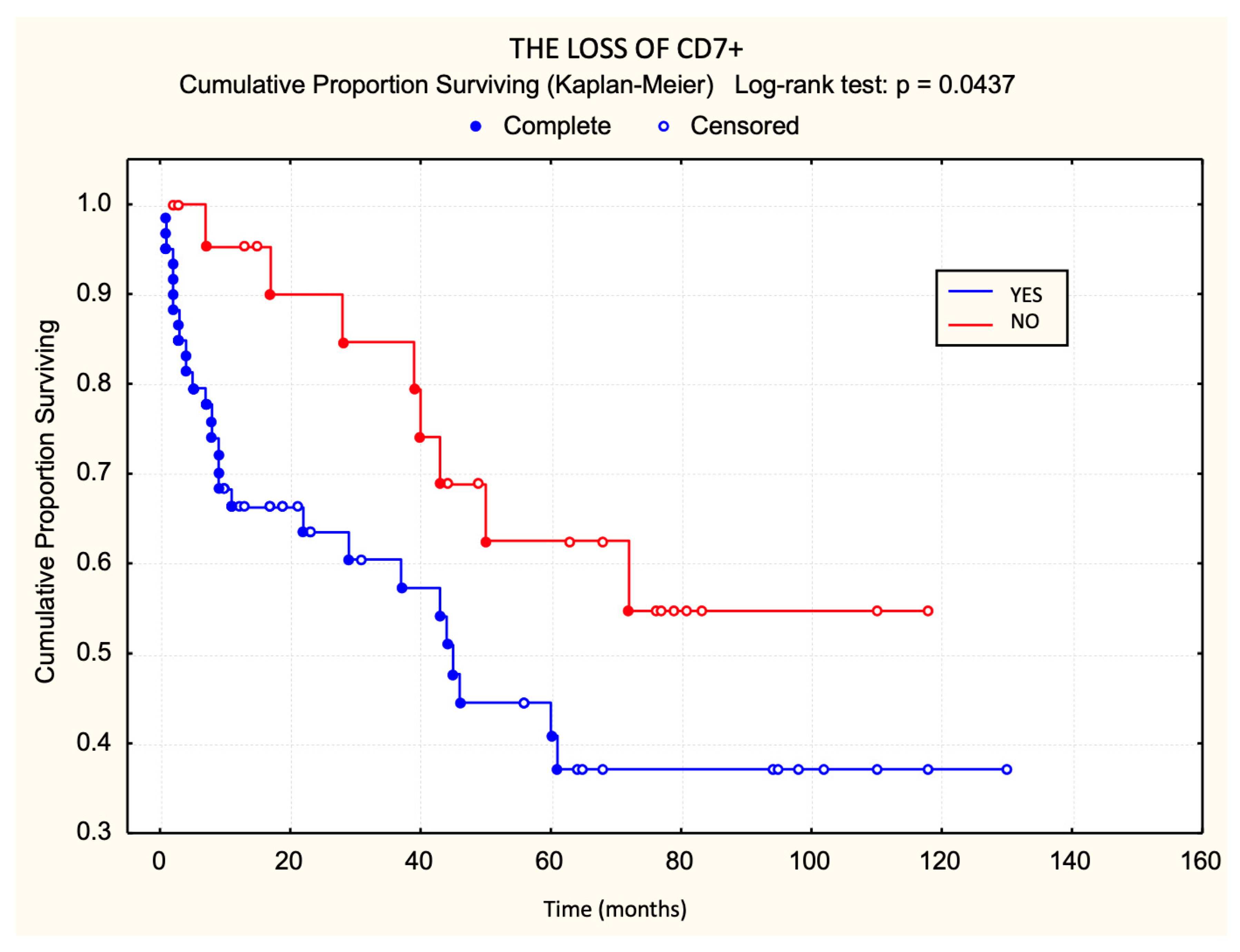
3.2. Prognostic Value of T-Cell Marker Loss in Relation to Progression-Free Survival
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- van Doorn, R.; Van Haselen, C.W.; van Voorst Vader, P.C.; Geerts, M.-L.; Heule, F.; de Rie, M.; Steijlen, P.M.; Dekker, S.K.; van Vloten, W.A.; Willemze, R. Mycosis fungoides: Disease evolution and prognosis of 309 Dutch patients. Arch. Dermatol. 2000, 136, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willemze, R.; Meijer, C.J. EORTC classification for primary cutaneous lymphomas: A comparison with the R.E.A.L. Classification and the proposed WHO Classification. Ann. Oncol. 2000, 11 (Suppl. S1), 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latzka, J.; Assaf, C.; Bagot, M.; Cozzio, A.; Dummer, R.; Guenova, E.; Gniadecki, R.; Hodak, E.; Jonak, C.; Klemke, C.-D.; et al. EORTC consensus recommendations for the treatment of mycosis fungoides/Sézary syndrome—Update 2023. Eur. J. Cancer. 2023, 195, 113343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempf, W.; Mitteldorf, C.; Cerroni, L.; Willemze, R.; Berti, E.; Guenova, E.; Scarisbrick, J.J.; Battistella, M. Classifications of cutaneous lymphomas and lymphoproliferative disorders: An update from the EORTC cutaneous lymphoma histopathology group. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2024, 38, 1491–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willemze, R.; Cerroni, L.; Kempf, W.; Berti, E.; Facchetti, F.; Swerdlow, S.H.; Jaffe, E.S. The 2018 update of the WHO-EORTC classification for primary cutaneous lymphomas. Blood 2019, 133, 1703–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santucci, M.; Biggeri, A.; Feller, A.C.; Massi, D.; Burg, G. Efficacy of histologic criteria for diagnosing early mycosis fungoides: An EORTC cutaneous lymphoma study group investigation. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2000, 24, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massone, C.; Kodama, K.; Kerl, H.; Cerroni, L. Histopathologic features of early (patch) lesions of mycosis fungoides: A morphologic study on 745 biopsy specimens from 427 patients. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2005, 29, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izban, K.F.; His, E.D.; Alkan, S. Immunohistochemical analysis of mycosis fungoides on paraffin-embedded tissue sections. Mod. Pathol. 1998, 11, 978–982. [Google Scholar]
- Kamarashev, J.; Burg, G.; Kempf, W.; Hess Schmid, M.; Dummer, R. Comparative analysis of histological and immunohistological features in mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome. J. Cutan. Pathol. 1998, 25, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodak, E.; David, M.; Maron, L.; Aviram, A.; Kaganovsky, E.; Feinmesser, M. CD4/CD8 double-negative epidermotropic cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: An immunohistochemical variant of mycosis fungoides. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2006, 55, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosca, A.D.; Varelzidis, A.G.; Economidou, J.; Stratigos, J.D. Mycosis fungoides: Evaluation of immunohistochemical criteria for the early diagnosis of the disease and differentiation between stages. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1986, 15, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimpinelli, N.; Olsen, E.A.; Santucci, M.; Vonderheid, E.; Haeffner, A.C.; Stevens, S.; Burg, G.; Cerroni, L.; Dreno, B.; Glusac, E.; et al. Defining early mycosis fungoides. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2005, 53, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quaglino, P.; Pimpinelli, N.; Berti, E.; Calzavara-Pinton, P.; Lombardo, G.A.; Rupoli, S.; Alaibac, M.; Bottoni, U.; Carbone, A.; Fava, C.; et al. Time course, clinical pathways, and long-term hazards risk trends of disease progression in patients with classic mycosis fungoides: A multicenter, retrospective follow-up study from the Italian Group of Cutaneous Lymphomas. Cancer 2012, 118, 5830–5839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benner, M.F.; Jansen, P.M.; Vermeer, M.H.; Willemze, R. Prognostic factors in transformed mycosis fungoides: A retrospective analysis of 100 cases. Blood 2012, 119, 1643–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerroni, L.; Rieger, E.; Hödl, S.; Kerl, H. Clinicopathologic and immunologic features associated with transformation of mycosis fungoides to large-cell lymphoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1992, 16, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamandidou, E.; Colome-Grimmer, M.; Fayad, L.; Duvic, M.; Kurzrock, R. Transformation of mycosis fungoides/Sezary syndrome: Clinical characteristics and prognosis. Blood 1998, 92, 1150–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willemze, R.; Jaffe, E.S.; Burg, G.; Cerroni, L.; Berti, E.; Swerdlow, S.H.; Ralfkiaer, E.; Chimenti, S.; Diaz-Perez, J.L.; Duncan, L.M.; et al. WHO-EORTC classification for cutaneous lymphomas. Blood 2005, 105, 3768–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham-Ledard, A.; Prochazkova-Carlotti, M.; Laharanne, E.; Vergier, B.; Jouary, T.; Beylot-Barry, M.; Merlio, J.-P. IRF4 gene rearrangements define a subgroup of CD30-positive cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: A study of 54 cases. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 816–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florell, S.R.; Cessna, M.; Lundell, R.B.; Boucher, K.M.; Bowen, G.M.; Harris, R.M.; Petersen, M.J.; Zone, J.J.; Tripp, S.; Perkins, S.L. Usefulness (or lack thereof) of immunophenotyping in atypical cutaneous T-cell infiltrates. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2006, 125, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, G.; Stefanato, C.M. Mycosis fungoides with reactive lymphoid follicles may represent an early histopathologic picture of granulomatous slack skin. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2013, 40, 611–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, G.; Chiarelli, C.; Simonetti, S. B-cell lymphofollicular infiltrates in mycosis fungoides. Tumori J. 2010, 96, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralfkiaer, E.; Lange Wantzin, G.; Mason, D.Y.; Stein, H.; Thomsen, K. Characterization of benign cutaneous lymphocytic infiltrates by monoclonal antibodies. Br. J. Dermatol. 1984, 111, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempf, W.; Kazakov, D.V.; Cipolat, C.; Kutzner, H.; Roncador, G.; Tomasini, D. CD4/CD8 double negative mycosis fungoides with PD-1 (CD279) expression—A disease of follicular helper T-cells? Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2012, 34, 757–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gammon, B.; Guitart, J. Intertriginous mycosis fungoides: A distinct presentation of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma that may be caused by malignant follicular helper T cells. Arch. Dermatol. 2012, 148, 1040–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guitart, J.; Gammon, B. The difficulties in defining follicular T helper phenotype in cutaneous lymphomas. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2013, 35, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerami, P.; Rosen, S.; Kuzel, T.; Boone, S.L.; Guitart, J. Folliculotropic mycosis fungoides: An aggressive variant of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Arch. Dermatol. 2008, 144, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallermann, C.; Niermann, C.; Schulze, H.-J. Regulatory T-cell phenotype in association with large cell transformation of mycosis fungoides. Eur. J. Haematol. 2007, 78, 260–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beljaards, R.C.; Meijer, C.J.; Van der Putte, S.C.; Hollema, H.; Geerts, M.L.; Bezemer, P.D.; Willemze, R. Primary cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: Clinicopathological features and prognostic parameters of 35 cases other than mycosis fungoides and CD30-positive large cell lymphoma. J. Pathol. 1994, 172, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aulasevich, N.; Haist, M.; Försch, S.; Weidenthaler-Barth, B.; Mailänder, V. The Role of the Immune Phenotype in Tumor Progression and Prognosis of Patients with Mycosis Fungoides: A Quantitative Immunohistology Whole Slide Approach. Cells 2022, 11, 3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, D.A.; Wilcox, R.A.; Weenig, R.H.; Gibson, L.E. Paucity of intraepidermal FoxP3-positive T cells in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma in contrast with spongiotic and lichenoid dermatitis. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2010, 37, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimura, T.; Okuyama, R.; Ito, Y.; Aiba, S. Profiles of Foxp3+ regulatory T cells in eczematous dermatitis, psoriasis vulgaris and mycosis fungoides. Br. J. Dermatol. 2008, 158, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gjerdrum, L.M.; Woetmann, A.; Odum, N.; Burton, C.M.; Rossen, K.; Skovgaard, G.L.; Ryder, L.P.; Ralfkiaer, E. FOXP3+ regulatory T cells in cutaneous T-cell lymphomas: Association with disease stage and survival. Leukemia 2007, 21, 2512–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermeer, M.H.; Geelen, F.A.; Kummer, J.A.; Meijer, C.J.; Willemze, R. Expression of cytotoxic proteins by neoplastic T cells in mycosis fungoides increases with progression from plaque stage to tumor stage disease. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 154, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horst, B.A.; Kasper, R.; LeBoit, P.E. CD4+, CD56+ mycosis fungoides: Case report and review of the literature. Am. J. Dermatopathol. 2009, 31, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiemessen, M.M.; Mitchell, T.J.; Hendry, L.; Whittaker, S.J.; Taams, L.S.; John, S. Lack of suppressive CD4+CD25+FOXP3+ T cells in advanced stages of primary cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2006, 126, 2217–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sen, F.; Kang, S.; Cangiarella, J.; Kamino, H.; Hymes, K. CD20 positive mycosis fungoides: A case report. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2008, 35, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borradori, L.; Lombardi, T.; Samson, J.; Girardet, C.; Saurat, J.H.; Hügli, A. Anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody (rituximab) for refractory erosive stomatitis secondary to CD20(+) follicular lymphoma-associated paraneoplastic pemphigus. Arch. Dermatol. 2001, 137, 269–272. [Google Scholar]
- Ishida, M.; Okabe, H. Reactive lymphoid follicles with germinal centers in granulomatous mycosis fungoides: A case report with review of the literature. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2013, 40, 284–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobisawa, S.; Honma, M.; Ishida-Yamamoto, A.; Saijo, Y.; Iizuka, H. Prognostic factors in 105 Japanese cases of mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome: Clusterin expression as a novel prognostic factor. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2013, 71, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Krieken, J.H.J.M.; Langerak, A.W.; Macintyre, E.A.; Kneba, M.; Hodges, E.; Sanz, R.G.; Morgan, G.J.; Parreira, A.; Molina, T.J.; Cabeçadas, J.; et al. Improved reliability of lymphoma diagnostics via PCR-based clonality testing: Report of the BIOMED-2 Concerted Action BHM4-CT98-3936. Leukemia 2007, 21, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, P.B.; McCook-Veal, A.A.; Switchenko, J.M.; Paulino, D.M.; Niyogusaba, T.; Baird, K.M.; Tarabadkar, E.S.; Lechowicz, M.J. Staging lymph nodes and blood at diagnosis in mycosis fungoides identifies patients at increased risk of progression to advanced stage: A retrospective cohort study. Cancer 2023, 129, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Coninck, E.C.; Kim, Y.H.; Varghese, A.; Hoppe, R.T. Clinical characteristics and outcome of patients with extracutaneous mycosis fungoides. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 19, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vonderheid, E.C.; Pavlov, I.; Delgado, J.C.; Martins, T.B.; Telang, G.H.; Hess, A.D.; Kadin, M.E. Prognostic factors and risk stratification in early mycosis fungoides. Leuk. Lymphoma 2014, 55, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grange, F.; Bagot, M. Prognosis of primary cutaneous lymphomas. Ann. Dermatol. Venereol. 2002, 129, 30–40. [Google Scholar]
- Ormsby, A.; Bergfeld, W.F.; Tubbs, R.R.; Hsi, E.D. Evaluation of a new paraffin-reactive CD7 T-cell deletion marker and a polymerase chain reaction-based T-cell receptor gene rearrangement assay: Implications for diagnosis of mycosis fungoides in community clinical practice. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2001, 45, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variable | Patients (N = 83) |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 60 (7–85) |
| Gender | |
| Male | 49 (59%) |
| Female | 34 (41%) |
| Disease Stage | |
| Ia | 27 (33%) |
| Ib | 35 (42%) |
| IIa | 21 (25%) |
| Disease Progression | 36 (43%) |
| Fatal Outcome | 10 (12%) |
| Loss of CD2 | 9 (11%) |
| Loss of CD3 | 0 |
| Loss of CD5 | 9 (11%) |
| Loss of CD7 | 60 (72%) |
| Marker | Survived N = 73 | Died N = 10 | Log-Rank Test p-Value |
| CD2 loss | 9 | 0 | p = 0.2349 |
| CD3 loss | 0 | 0 | |
| CD5 loss | 8 | 1 | p = 0.9050 |
| CD7 loss | 52 | 8 | p = 0.3369 |
| No Progression | Progression | Log-Rank Test | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Loss of CD2 | 9 | 0 | p = 0.2349 |
| Loss of CD3 | 0 | 0 | - |
| Loss of CD5 | 8 | 1 | p = 0.9050 |
| Loss of CD7 | 52 | 8 | p = 0.3369 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Published by MDPI on behalf of the European Society of Dermatopathology. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jerkovic Gulin, S.; Ilic, I.; Gulin, D.; Kravvas, G.; Ceovic, R. Prognostic Value of Immunohistochemical T-Cell Marker Loss in Early-Stage Mycosis Fungoides: A Single-Center Cohort Study. Dermatopathology 2025, 12, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology12030029
Jerkovic Gulin S, Ilic I, Gulin D, Kravvas G, Ceovic R. Prognostic Value of Immunohistochemical T-Cell Marker Loss in Early-Stage Mycosis Fungoides: A Single-Center Cohort Study. Dermatopathology. 2025; 12(3):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology12030029
Chicago/Turabian StyleJerkovic Gulin, Sandra, Ivana Ilic, Dario Gulin, Georgios Kravvas, and Romana Ceovic. 2025. "Prognostic Value of Immunohistochemical T-Cell Marker Loss in Early-Stage Mycosis Fungoides: A Single-Center Cohort Study" Dermatopathology 12, no. 3: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology12030029
APA StyleJerkovic Gulin, S., Ilic, I., Gulin, D., Kravvas, G., & Ceovic, R. (2025). Prognostic Value of Immunohistochemical T-Cell Marker Loss in Early-Stage Mycosis Fungoides: A Single-Center Cohort Study. Dermatopathology, 12(3), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/dermatopathology12030029






